Multivariate Genetic Structure of Externalizing Behavior and Structural Brain Development in a Longitudinal Adolescent Twin Sample
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenotypic Development of Externalizing Behavior
2.2. Heritability of Externalizing Behavior
2.3. Phenotypic Development and Heritability of Brain Structures
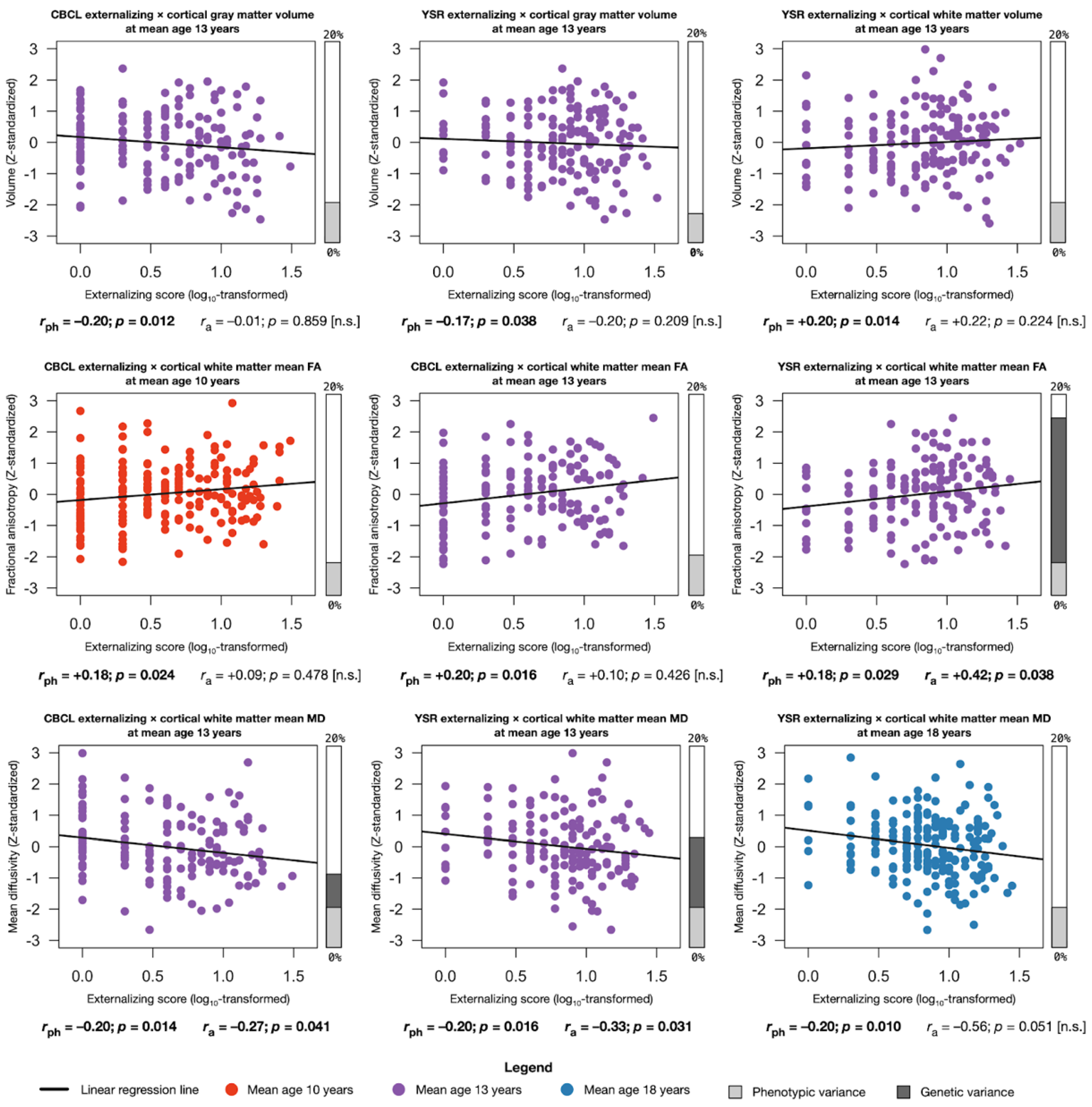
2.4. Assocations between Externalizing Behavior and Global Brain Structures
2.4.1. Phenotypic Associations
2.4.2. Genetic Associations
2.4.3. Environmental Associations
2.5. Assocations between Externalizing Behavior and Regional Brain Measures
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Externalizing Behavior
4.3. Brain Imaging
4.3.1. MRI Protocol
4.3.2. Volumetric Brain Measures
4.3.3. White Matter Microstructural Integrity Brain Measures
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.4.1. Main Analysis
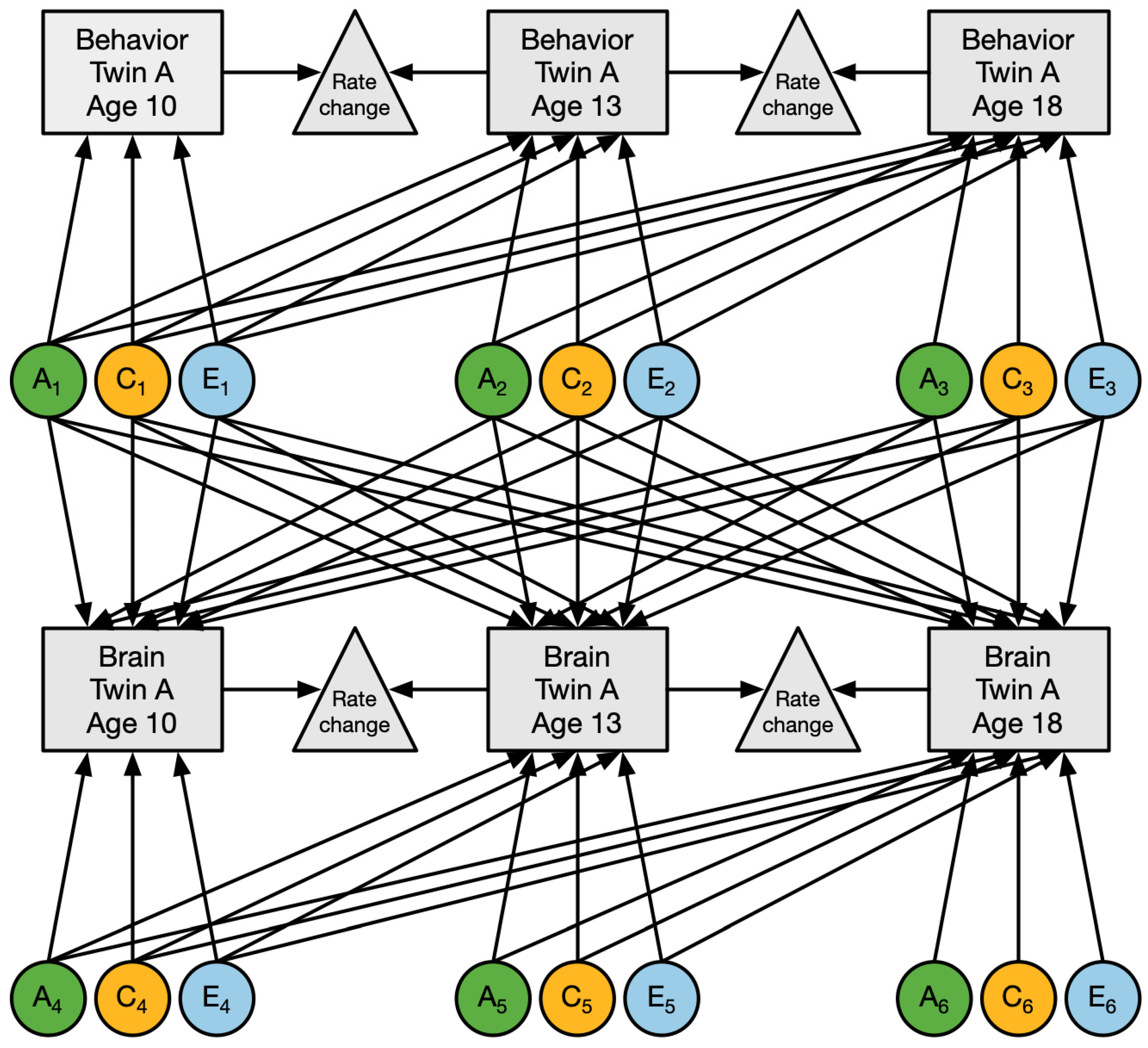
4.4.2. Genetic Modeling
4.4.3. Structural Equation Modeling
4.4.4. Genetic and Environmental Influences on Longitudinal Externalizing Behavior and Brain Measures
4.4.5. Statistical Testing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christenson, J.D.; Crane, D.R.; Malloy, J.; Parker, S. The Cost of Oppositional Defiant Disorder and Disruptive Behavior: A Review of the Literature. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2016, 25, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, T.M.; Reschorla, L.A. Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms and Profiles; Achenbach: Burlington, VT, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bongers, I.L.; Koot, H.M.; van der Ende, J.; Verhulst, F.C. Developmental Trajectories of Externalizing Behaviors in Childhood and Adolescence. Child Dev. 2004, 75, 1523–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Lier, P.A.; Verhulst, F.C.; Van Der Ende, J.; Crijnen, A.A. Classes of disruptive behaviour in a sample of young elementary school children. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2003, 44, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hazebroek, B.C.M.; Blokland, A.A.J.; Wermink, H.T.; De Keijser, J.W.; Popma, A.; Van Domburgh, L. Delinquent Development Among Early-Onset Offenders: Identifying and Characterizing Trajectories Based on Frequency Across Types of Offending. Crim. Justice Behav. 2019, 46, 1542–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eme, R.F. Sex differences in child-onset, life-course-persistent conduct disorder. A review of biological influences. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2007, 27, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmer, D.H.; Hooley, M.; Sheen, J.; McGillivray, J.A.; Lum, J.A.G. Sex Differences in the Prevalence of Oppositional Defiant Disorder During Middle Childhood: A Meta-Analysis. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2016, 45, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormel, J.; Raven, D.; van Oort, F.; Hartman, C.A.; Reijneveld, S.A.; Veenstra, R.; Vollebergh, W.A.M.; Buitelaar, J.; Verhulst, F.C.; Oldehinkel, A.J. Mental health in Dutch adolescents: A TRAILS report on prevalence, severity, age of onset, continuity and co-morbidity of DSM disorders. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zwirs, B.W.C.; Burger, H.; Schulpen, T.W.J.; Wiznitzer, M.; Fedder, H.; Buitelaar, J.K. Prevalence of Psychiatric Disorders among Children of Different Ethnic Origin. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2007, 35, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fairchild, G.; Hawes, D.J.; Frick, P.J.; Copeland, W.E.; Odgers, C.; Franke, B.; Freitag, C.M.; De Brito, S.A. Conduct disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Hale, D.; Das, S.; Goddings, A.-L.; Blakemore, S.-J.; Viner, R.M. Effectiveness of Universal Self-regulation–Based Interventions in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masi, G.; Milone, A.; Brovedani, P.; Pisano, S.; Muratori, P. Psychiatric evaluation of youths with Disruptive Behavior Disorders and psychopathic traits: A critical review of assessment measures. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 91, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, R.J.R.; Leibenluft, E.; Pine, D.S. Conduct Disorder and Callous–Unemotional Traits in Youth. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frick, P.J.; Viding, E. Antisocial behavior from a developmental psychopathology perspective. Dev. Psychopathol. 2009, 21, 1111–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, R.R.; McCuish, E.C.; Hart, S.D.; DeLisi, M. The role of psychopathic traits and developmental risk factors on offending trajectories from early adolescence to adulthood: A prospective study of incarcerated youth. J. Crim. Justice 2015, 43, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Valk, J.C.; van der Oord, E.J.C.G.; van der Verhulst, F.C.; Boomsma, D.I. Using shared and unique parental views to study the etiology of 7-year-old twins’ internalizing and externalizing problems. Behav. Genet. 2003, 33, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spatola, C.A.M.; Rende, R.; Battaglia, M. Genetic and environmental influences upon the CBCL/6-18 DSM-oriented scales: Similarities and differences across three different computational approaches and two age ranges. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 19, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hicks, B.M.; Foster, K.T.; Iacono, W.G.; McGue, M. Genetic and Environmental Influences on the Familial Transmission of Externalizing Disorders in Adoptive and Twin Offspring. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerekes, N.; Lundström, S.; Chang, Z.; Tajnia, A.; Jern, P.; Lichtenstein, P.; Nilsson, T.; Anckarsäter, H. Oppositional defiant- and conduct disorder-like problems: Neurodevelopmental predictors and genetic background in boys and girls, in a nationwide twin study. PeerJ 2014, 2, e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porsch, R.M.; Middeldorp, C.M.; Cherny, S.S.; Krapohl, E.; van Beijsterveldt, C.E.M.; Loukola, A.; Korhonen, T.; Pulkkinen, L.; Corley, R.; Rhee, S.; et al. Longitudinal heritability of childhood aggression. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2016, 171, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wesseldijk, L.W.; Bartels, M.; Vink, J.M.; van Beijsterveldt, C.E.M.; Ligthart, L.; Boomsma, D.I.; Middeldorp, C.M. Genetic and environmental influences on conduct and antisocial personality problems in childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2018, 27, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luningham, J.M.; Hendriks, A.; Krapohl, E.; Ip, H.F.; van Beijsterveldt, T.; Lundström, S.; Vuoksimaa, E.; Korhonen, T.; Lichtenstein, P.; Plomin, R.; et al. Harmonizing behavioral outcomes across studies, raters, and countries: Application to the genetic analysis of aggression in the ACTION Consortium. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2020, 61, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polderman, T.J.C.; Benyamin, B.; de Leeuw, C.A.; Sullivan, P.F.; Van Bochoven, A.; Visscher, P.M.; Posthuma, D. Meta-analysis of the heritability of human traits based on fifty years of twin studies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gard, A.M.; Dotterer, H.L.; Hyde, L.W. Genetic influences on antisocial behavior: Recent advances and future directions. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2019, 27, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odintsova, V.V.; Roetman, P.J.; Ip, H.F.; Pool, R.; van der Laan, C.M.; Tona, K.-D.; Vermeiren, R.R.J.M.; Boomsma, D.I. Genomics of human aggression: Current state of genome-wide studies and an automated systematic review tool. Psychiatr. Genet. 2019, 29, 170–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Valk, J.C.; van den Oord, E.J.C.G.; Verhulst, F.C.; I Boomsma, D. Genetic and Environmental Contributions to Stability and Change in Children’s Internalizing and Externalizing Problems. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2003, 42, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haberstick, B.C.; Schmitz, S.; Young, S.E.; Hewitt, J.K. Contributions of Genes and Environments to Stability and Change in Externalizing and Internalizing Problems During Elementary and Middle School. Behav. Genet. 2005, 35, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubke, G.H.; McArtor, D.B.; Boomsma, D.I.; Bartels, M. Genetic and environmental contributions to the development of childhood aggression. Dev. Psychol. 2018, 54, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, S.L.; Clark, D.A.; Hyde, L.W.; Klump, K.L.; Burt, S.A. Continuity and Change in the Genetic and Environmental Etiology of Youth Antisocial Behavior. Behav. Genet. 2021, 51, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatoum, A.S.; Rhee, S.H.; Corley, R.P.; Hewitt, J.K.; Friedman, N. Etiology of Stability and Growth of Internalizing and Externalizing Behavior Problems across Childhood and Adolescence. Behav. Genet. 2018, 48, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Onnink, M.; van Donkelaar, M.; Wolfers, T.; Harich, B.; Shi, Y.; Dammers, J.; Arias-Vásquez, A.; Hoogman, M.; Franke, B. Brain imaging genetics in ADHD and beyond–Mapping pathways from gene to disorder at different levels of complexity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 80, 115–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giedd, J.N.; Blumenthal, J.; Jeffries, N.O.; Castellanos, F.X.; Liu, H.; Zijdenbos, A.; Paus, T.; Evans, A.C.; Rapoport, J.L. Brain development during childhood and adolescence: A longitudinal MRI study. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakemore, S.-J. Imaging brain development: The adolescent brain. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, A.M.; Van Haren, N.E.M.; Schnack, H.G.; Kahn, R.S.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Human brain changes across the life span: A review of 56 longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 1987–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenroot, R.K.; Giedd, J.N. Brain development in children and adolescents: Insights from anatomical magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2006, 30, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.; Kabani, N.J.; Lerch, J.P.; Eckstrand, K.; Lenroot, R.; Gogtay, N.; Greenstein, D.; Clasen, L.; Evans, A.; Rapoport, J.L.; et al. Neurodevelopmental Trajectories of the Human Cerebral Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3586–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeuw, J.; Brouwer, R.M.; Koenis, M.M.G.; Swagerman, S.C.; I Boomsma, D.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Genetic Influences on the Development of Cerebral Cortical Thickness During Childhood and Adolescence in a Dutch Longitudinal Twin Sample: The Brainscale Study. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 29, 978–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogtay, N.; Giedd, J.N.; Lusk, L.; Hayashi, K.M.; Greenstein, D.; Vaituzis, A.C.; Nugent, T.F.; Herman, D.H.; Clasen, L.S.; Toga, A.W.; et al. Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8174–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brouwer, R.M.; Mandl, R.C.W.; Schnack, H.G.; Van Soelen, I.L.C.; Van Baal, G.C.; Peper, J.S.; Kahn, R.S.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. White Matter Development in Early Puberty: A Longitudinal Volumetric and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Twin Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebel, C.; Treit, S.; Beaulieu, C. A review of diffusion MRI of typical white matter development from early childhood to young adulthood. NMR Biomed. 2017, 32, e3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blokland, G.A.M.; de Zubicaray, G.I.; McMahon, K.L.; Wright, M.J. Genetic and Environmental Influences on Neuroimaging Phenotypes: A Meta-Analytical Perspective on Twin Imaging Studies. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2012, 15, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Douet, V.; Chang, L.; Cloak, C.; Ernst, T. Genetic influences on brain developmental trajectories on neuroimaging studies: From infancy to young adulthood. Brain Imaging Behav. 2014, 8, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, A.G.; Mous, S.E.; White, T.; Posthuma, D.; Polderman, T.J.C. What Twin Studies Tell Us About the Heritability of Brain Development, Morphology, and Function: A Review. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2015, 25, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strike, L.T.; Couvy-Duchesne, B.; Hansell, N.K.; Cuellar-Partida, G.; Medland, S.E.; Wright, M.J. Genetics and Brain Morphology. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2015, 25, 63–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Soelen, I.; Brouwer, R.; van Baal, G.; Schnack, H.; Peper, J.; Collins, D.; Evans, A.; Kahn, R.; Boomsma, D.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Genetic influences on thinning of the cerebral cortex during development. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 3871–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Soelen, I.L.; Brouwer, R.M.; van Baal, G.C.M.; Schnack, H.G.; Peper, J.S.; Chen, L.; Kahn, R.S.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Heritability of volumetric brain changes and height in children entering puberty. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, R.M.; Panizzon, M.S.; Glahn, D.C.; Hibar, D.P.; Hua, X.; Jahanshad, N.; Abramovic, L.; de Zubicaray, G.I.; Franz, C.E.; Hansell, N.K.; et al. Genetic influences on individual differences in longitudinal changes in global and subcortical brain volumes: Results of the ENIGMA plasticity working group. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 4444–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brans, R.G.H.; Van Haren, N.E.M.; Van Baal, G.C.M.; Schnack, H.G.; Kahn, R.S.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Heritability of Changes in Brain Volume Over Time in Twin Pairs Discordant for Schizophrenia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2008, 65, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brans, R.G.H.; Kahn, R.S.; Schnack, H.G.; Van Baal, G.C.M.; Posthuma, D.; Van Haren, N.E.M.; Lepage, C.; Lerch, J.P.; Collins, D.L.; Evans, A.C.; et al. Brain Plasticity and Intellectual Ability Are Influenced by Shared Genes. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5519–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, R.M.; Hedman, A.M.; van Haren, N.E.; Schnack, H.G.; Brans, R.G.; Smit, D.J.; Kahn, R.S.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Heritability of brain volume change and its relation to intelligence. NeuroImage 2014, 100, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, A.M.; Van Haren, N.E.M.; Van Baal, G.C.M.; Brouwer, R.M.; Brans, R.G.H.; Schnack, H.G.; Kahn, R.S.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Heritability of cortical thickness changes over time in twin pairs discordant for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2016, 173, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johanson, M.; Vaurio, O.; Tiihonen, J.; Lähteenvuo, M. A Systematic Literature Review of Neuroimaging of Psychopathic Traits. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blair, R.J.R.; Zhang, R. Recent neuro-imaging findings with respect to conduct disorder, callous-unemotional traits and psychopathy. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2020, 33, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, R.; Dotterer, H.L.; Murray, L.; Maxwell, A.M.; Hyde, L.W. White-matter tract abnormalities and antisocial behavior: A systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies across development. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 14, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordermeer, S.D.S.; Luman, M.; Oosterlaan, J. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Neuroimaging in Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) and Conduct Disorder (CD) Taking Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Into Account. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2016, 26, 44–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, R.H.; Clanton, R.L.; Rogers, J.C.; De Brito, S.A. Neuroimaging findings in disruptive behavior disorders. CNS Spectr. 2015, 20, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raine, A.; Lencz, T.; Bihrle, S.; Lacasse, L.; Colletti, P. Reduced Prefrontal Gray Matter Volume and Reduced Autonomic Activity in Antisocial Personality Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohn, M.D.; Viding, E.; McCrory, E.; Pape, L.; Brink, W.V.D.; Doreleijers, T.A.; Veltman, D.J.; Popma, A. Regional grey matter volume and concentration in at-risk adolescents: Untangling associations with callous-unemotional traits and conduct disorder symptoms. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2016, 254, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayard, F.; The IMAGEN Consortium; Thunell, C.N.; Abé, C.; Almeida, R.; Banaschewski, T.; Barker, G.; Bokde, A.L.W.; Bromberg, U.; Büchel, C.; et al. Distinct brain structure and behavior related to ADHD and conduct disorder traits. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 3020–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, R.; Hawes, S.W.; Byrd, A.L.; Dick, A.S.; Sutherland, M.T.; Riedel, M.C.; Tobia, M.J.; Bottenhorn, K.L.; Laird, A.R.; Gonzalez, R. Disruptive Behavior Problems, Callous-Unemotional Traits, and Regional Gray Matter Volume in the Adolescent Brain and Cognitive Development Study. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2020, 5, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, E.L.; Jeong, H.J.; Moore, T.M.; Dupont, R.M.; Cardenas-Iniguez, C.; Cui, Z.; Stone, F.E.; Berman, M.G.; Lahey, B.B.; Kaczkurkin, A.N. Association of gray matter volumes with general and specific dimensions of psychopathology in children. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, A.; Lencz, T.; Taylor, K.; Hellige, J.B.; Bihrle, S.; Lacasse, L.; Lee, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Colletti, P. Corpus Callosum Abnormalities in Psychopathic Antisocial Individuals. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2003, 60, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pape, L.E.; Cohn, M.D.; Caan, M.W.A.; van Wingen, G.; Brink, W.V.D.; Veltman, D.J.; Popma, A. Psychopathic traits in adolescents are associated with higher structural connectivity. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2015, 233, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolhuis, K.; Muetzel, R.L.; Stringaris, A.; Hudziak, J.J.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Hillegers, M.H.; White, T.; Kushner, S.A.; Tiemeier, H. Structural Brain Connectivity in Childhood Disruptive Behavior Problems: A Multidimensional Approach. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 85, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolhuis, K.; Viding, E.; Muetzel, R.L.; El Marroun, H.; Kocevska, D.; White, T.; Tiemeier, H.; Cecil, C.A.M. Neural Profile of Callous Traits in Children: A Population-Based Neuroimaging Study. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neumann, A.; Muetzel, R.L.; Lahey, B.B.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J.; Van Ijzendoorn, M.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hillegers, M.H.J.; White, T.; Tiemeier, H. White Matter Microstructure and the General Psychopathology Factor in Children. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 59, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, Q.R.; Geeraert, B.L.; Lebel, C. Brain structure and internalizing and externalizing behavior in typically developing children and adolescents. Brain Struct. Funct. 2020, 225, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenlocher, P.R. Synaptic density in human frontal cortex—Developmental changes and effects of aging. Brain Res. 1979, 163, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paus, T. Growth of white matter in the adolescent brain: Myelin or axon? Brain Cogn. 2010, 72, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deoni, S.C.L.; Dean, D.C.; Remer, J.; Dirks, H.; O’Muircheartaigh, J. Cortical maturation and myelination in healthy toddlers and young children. NeuroImage 2015, 115, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ameis, S.H.; Ducharme, S.; Albaugh, M.D.; Hudziak, J.J.; Botteron, K.N.; Lepage, C.; Zhao, L.; Khundrakpam, B.; Collins, D.L.; Lerch, J.P.; et al. Cortical Thickness, Cortico-Amygdalar Networks, and Externalizing Behaviors in Healthy Children. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, J.Z.K.; Armstrong, J.M.; Hanson, J.L.; Sutterer, M.J.; Stodola, D.E.; Koenigs, M.; Kalin, N.H.; Essex, M.J.; Davidson, R.J. Preschool Externalizing Behavior Predicts Gender-Specific Variation in Adolescent Neural Structure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostermeijer, S.; Whittle, S.; Suo, C.; Allen, N.B.; Simmons, J.G.; Vijayakumar, N.; Van De Ven, P.M.; Jansen, L.M.C.; Yücel, M.; Popma, A. Trajectories of adolescent conduct problems in relation to cortical thickness development: A longitudinal MRI study. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, M.G.N.; Wierenga, L.M.; Blankenstein, N.E.; Schreuders, E.; Tamnes, C.K.; Crone, E.A. Longitudinal structural brain development and externalizing behavior in adolescence. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2018, 59, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whittle, S.; Vijayakumar, N.; Simmons, J.G.; Allen, N.B. Internalizing and Externalizing Symptoms Are Associated with Different Trajectories of Cortical Development During Late Childhood. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 59, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, H.; Pozzi, E.; Vijayakumar, N.; Richmond, S.; Bray, K.; Deane, C.; Whittle, S. Structural Brain Development and Aggression: A Longitudinal Study in Late Childhood. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 21, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzer, M.; Derome, M.; Morosan, L.; Salaminios, G.; Debbané, M. Cortical thickness of the insula and prefrontal cortex relates to externalizing behavior: Cross-sectional and prospective findings. Dev. Psychopathol. 2020, 33, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muetzel, R.L.; Blanken, L.M.; Van Der Ende, J.; El Marroun, H.; Shaw, P.; Sudre, G.; Van Der Lugt, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Verhulst, F.C.; Tiemeier, H.; et al. Tracking Brain Development and Dimensional Psychiatric Symptoms in Children: A Longitudinal Population-Based Neuroimaging Study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Morales, A.M.; Nagel, B.J. Resilience to Risk for Psychopathology: The Role of White Matter Microstructural Development in Adolescence. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2019, 4, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garic, D.; Broce, I.; Graziano, P.; Mattfeld, A.; Dick, A.S. Laterality of the frontal aslant tract (FAT) explains externalizing behaviors through its association with executive function. Dev. Sci. 2019, 22, e12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telzer, E.H.; McCormick, E.M.; Peters, S.; Cosme, D.; Pfeifer, J.H.; van Duijvenvoorde, A.C.K. Methodological considerations for developmental longitudinal fMRI research. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 33, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peper, J.S.; Schnack, H.G.; Brouwer, R.M.; Van Baal, G.C.M.V.; Pjetri, E.; Székely, E.; van Leeuwen, M.; Van Den Berg, S.M.; Collins, D.L.; Evans, A.C.; et al. Heritability of regional and global brain structure at the onset of puberty: A magnetic resonance imaging study in 9-year-old twin pairs. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 2184–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, R.M.; Mandl, R.C.; Peper, J.S.; van Baal, G.C.M.; Kahn, R.S.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Heritability of DTI and MTR in nine-year-old children. NeuroImage 2010, 53, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swagerman, S.C.; Brouwer, R.M.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E.; Boomsma, D.I. Development and heritability of subcortical brain volumes at ages 9 and 12. Genes Brain Behav. 2014, 13, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teeuw, J.; Brouwer, R.M.; Guimarães, J.P.O.F.T.; Brandner, P.; Koenis, M.M.G.; Swagerman, S.C.; Verwoert, M.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Genetic and environmental influences on functional connectivity within and between canonical cortical resting-state networks throughout adolescent development in boys and girls. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenis, M.M.G.; Brouwer, R.M.; Heuvel, M.P.V.D.; Mandl, R.C.W.; Van Soelen, I.L.; Kahn, R.S.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Development of the brain’s structural network efficiency in early adolescence: A longitudinal DTI twin study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 4938–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenis, M.M.G.; Brouwer, R.M.; Swagerman, S.C.; van Soelen, I.L.C.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Association between structural brain network efficiency and intelligence increases during adolescence. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartels, M.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hudziak, J.J.; Rietveld, M.J.H.; van Beijsterveldt, T.C.E.M.; van den Oord, E.J.C.G. Disentangling Genetic, Environmental, and Rater Effects on Internalizing and Externalizing Problem Behavior in 10-year-old Twins. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2004, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichers, M.; Gardner, C.; Maes, H.H.; Lichtenstein, P.; Larsson, H.; Kendler, K.S. Genetic Innovation and Stability in Externalizing Problem Behavior Across Development: A Multi-Informant Twin Study. Behav. Genet. 2013, 43, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niv, S.; Tuvblad, C.; Raine, A.; Baker, L.A. Aggression and rule-breaking: Heritability and stability of antisocial behavior problems in childhood and adolescence. J. Crim. Justice 2013, 41, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Achterberg, M.; Peper, J.S.; Van Duijvenvoorde, A.C.K.; Mandl, R.C.W.; Crone, E. Frontostriatal White Matter Integrity Predicts Development of Delay of Gratification: A Longitudinal Study. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Shi, H.; Huang, B.; Situ, W.; Yi, J.; Zhu, X.; Yao, S. Increased Structural Connectivity in Corpus Callosum in Adolescent Males with Conduct Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2014, 53, 466–475.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Shi, H.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Situ, W.; Cai, W.; Yi, J.; Zhu, X.; Yao, S. Sex Differences of Uncinate Fasciculus Structural Connectivity in Individuals with Conduct Disorder. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 673165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passamonti, L.; Fairchild, G.; Fornito, A.; Goodyer, I.M.; Nimmo-Smith, I.; Hagan, C.C.; Calder, A.J. Abnormal Anatomical Connectivity between the Amygdala and Orbitofrontal Cortex in Conduct Disorder. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Craig, M.C.; Catani, M.; Dell’Acqua, F.; Fahy, T.; Deeley, Q.; Murphy, D.G.M. Frontotemporal white-matter microstructural abnormalities in adolescents with conduct disorder: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Psychol. Med. 2013, 43, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Dell’Acqua, F.; Walsh, S.F.; Blackwood, N.; Scott, S.; Craig, M.C.; Deeley, Q.; Murphy, D. A Whole-Brain Investigation of White Matter Microstructure in Adolescents with Conduct Disorder. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menks, W.M.; Furger, R.; Lenz, C.; Fehlbaum, L.V.; Stadler, C.; Raschle, N.M. Microstructural White Matter Alterations in the Corpus Callosum of Girls With Conduct Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 56, 258–265.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeij, A.; Kempes, M.M.; Cima, M.J.; Mars, R.B.; Brazil, I.A. Affective traits of psychopathy are linked to white-matter abnormalities in impulsive male offenders. Neuropsychology 2018, 32, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, P.; Budhiraja, M.; Westerman, J.; Savic, I.; Jokinen, J.; Tiihonen, J.; Hodgins, S. White matter correlates of psychopathic traits in a female community sample. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2017, 12, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Shi, F.; Liu, H.; Li, G.; Ding, Z.; Shen, H.; Shen, C.; Lee, S.-W.; Hu, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Reduced White Matter Integrity in Antisocial Personality Disorder: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, R.C.; Pujara, M.S.; Motzkin, J.C.; Newman, J.P.; Kiehl, K.A.; Decety, J.; Kosson, D.S.; Koenigs, M. Interpersonal traits of psychopathy linked to reduced integrity of the uncinate fasciculus. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 4202–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haney-Caron, E.; Caprihan, A.; Stevens, M.C. DTI-measured white matter abnormalities in adolescents with Conduct Disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 48, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundram, F.; Deeley, Q.; Sarkar, S.; Daly, E.; Latham, R.; Craig, M.; Raczek, M.; Fahy, T.; Picchioni, M.; Barker, G.J.; et al. White matter microstructural abnormalities in the frontal lobe of adults with antisocial personality disorder. Cortex 2012, 48, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, J.; Harrison, B.J.; Contreras-Rodriguez, O.; Cardoner, N. The contribution of brain imaging to the understanding of psychopathy. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viding, E.; Fontaine, N.M.G.; McCrory, E.J. Antisocial behaviour in children with and without callous-unemotional traits. J. R. Soc. Med. 2012, 105, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dotterer, H.L.; Waller, R.; Shaw, D.S.; Plass, J.; Brang, D.; Forbes, E.E.; Hyde, L.W. Antisocial behavior with callous-unemotional traits is associated with widespread disruptions to white matter structural connectivity among low-income, urban males. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 23, 101836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puzzo, I.; Seunarine, K.; Sully, K.; Darekar, A.; Clark, C.; Sonuga-Barke, E.J.S.; Fairchild, G. Altered White-Matter Microstructure in Conduct Disorder Is Specifically Associated with Elevated Callous-Unemotional Traits. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2018, 46, 1451–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breeden, A.L.; Cardinale, E.M.; Lozier, L.M.; VanMeter, J.W.; Marsh, A.A. Callous-unemotional traits drive reduced white-matter integrity in youths with conduct problems. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 3033–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pappa, I.; Pourcain, B.S.; Benke, K.; Cavadino, A.; Hakulinen, C.; Nivard, M.G.; Nolte, I.M.; Tiesler, C.M.T.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J.; Davies, G.E.; et al. A genome-wide approach to children’s aggressive behavior:The EAGLE consortium. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2016, 171, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tielbeek, J.J.; Johansson, A.; Polderman, T.; Rautiainen, M.-R.; Jansen, P.; Taylor, M.; Tong, X.; Lu, Q.; Burt, A.S.; Tiemeier, H.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies of a Broad Spectrum of Antisocial Behavior. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demontis, D.; ADHD Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (PGC); Walters, R.K.; Rajagopal, V.M.; Waldman, I.D.; Grove, J.; Als, T.D.; Dalsgaard, S.; Ribasés, M.; Bybjerg-Grauholm, J.; et al. Risk variants and polygenic architecture of disruptive behavior disorders in the context of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, H.F.; van der Laan, C.M.; Krapohl, E.M.L.; Brikell, I.; Sánchez-Mora, C.; Nolte, I.M.; Pourcain, B.S.; Bolhuis, K.; Palviainen, T.; Zafarmand, H.; et al. Genetic association study of childhood aggression across raters, instruments, and age. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satizabal, C.L.; Adams, H.H.H.; Hibar, D.P.; White, C.C.; Knol, M.J.; Stein, J.L.; Scholz, M.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Jahanshad, N.; Roshchupkin, G.V.; et al. Genetic architecture of subcortical brain structures in 38,851 individuals. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1624–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grasby, K.L.; Jahanshad, N.; Painter, J.N.; Colodro-Conde, L.; Bralten, J.; Hibar, D.P.; Lind, P.A.; Pizzagalli, F.; Ching, C.R.K.; McMahon, M.A.B.; et al. The genetic architecture of the human cerebral cortex. Science 2020, 367, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, P.M.; Jahanshad, N.; Ching, C.R.K.; Salminen, L.E.; Thomopoulos, S.I.; Bright, J.; Baune, B.T.; Bertolín, S.; Bralten, J.; Bruin, W.B.; et al. ENIGMA and global neuroscience: A decade of large-scale studies of the brain in health and disease across more than 40 countries. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brouwer, R.M.; Klein, M.; Grasby, K.L.; Schnack, H.G.; Jahanshad, N.; Teeuw, J.; Thomopoulos, S.I.; Sprooten, E.; Franz, C.E.; Gogtay, N.; et al. Dynamics of Brain Structure and its Genetic Architecture over the Lifespan. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, C.C.A.; Su, Z.; Donnelly, P.; Marchini, J. Designing Genome-Wide Association Studies: Sample Size, Power, Imputation, and the Choice of Genotyping Chip. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van der Ende, J.; Verhulst, F.C.; Tiemeier, H. Multitrait-multimethod analyses of change of internalizing and externalizing problems in adolescence: Predicting internalizing and externalizing DSM disorders in adulthood. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2020, 129, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soelen, I.L.C.; Brouwer, R.M.; Peper, J.S.; Van Leeuwen, M.; Koenis, M.M.G.; van Beijsterveldt, T.; Swagerman, S.C.; Kahn, R.S.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E.; Boomsma, D.I. Brain SCALE: Brain Structure and Cognition: An Adolescent Longitudinal Twin Study into the Genetic Etiology of Individual Differences. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2012, 15, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomsma, D.I.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Vink, J.M.; Stubbe, J.H.; Distel, M.A.; Hottenga, J.-J.; Posthuma, D.; van Beijsterveldt, T.C.E.M.; Hudziak, J.J.; Bartels, M.; et al. Netherlands Twin Register: From Twins to Twin Families. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2006, 9, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beijsterveldt, C.E.M.; Groen-Blokhuis, M.; Hottenga, J.J.; Franić, S.; Hudziak, J.; Lamb, D.; Huppertz, C.; de Zeeuw, E.; Nivard, M.; Schutte, N.; et al. The Young Netherlands Twin Register (YNTR): Longitudinal Twin and Family Studies in Over 70,000 Children. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2013, 16, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ligthart, L.; van Beijsterveldt, C.E.; Kevenaar, S.T.; de Zeeuw, E.; van Bergen, E.; Bruins, S.; Pool, R.; Helmer, Q.; van Dongen, J.; Hottenga, J.-J.; et al. The Netherlands Twin Register: Longitudinal Research Based on Twin and Twin-Family Designs. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2019, 22, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Achenbach, T.M. DSM-Oriented Guide for the Achenbach System of Empirically Based Assessment (ASEBA); University of Vermont Research Center for Children, Youth, and Families: Burlington, VT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogers, J.C.; De Brito, S.A. Cortical and Subcortical Gray Matter Volume in Youths with Conduct Problems: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Inokuchi, R.; Nakao, T.; Yamasue, H. Neural bases of antisocial behavior: A voxel-based meta-analysis. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2014, 9, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Skare, S. A Model-Based Method for Retrospective Correction of Geometric Distortions in Diffusion-Weighted EPI. NeuroImage 2002, 16, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, A.; Jones, D.K. TheB-matrix must be rotated when correcting for subject motion in DTI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 61, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basser, P.J.; Pierpaolib, C. Microstructural and Physiological Features of Tissues Elucidated by Quantitative-Diffusion-Tensor MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. B 1996, 111, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- I Boomsma, D.; Busjahn, A.; Peltonen, L. Classical twin studies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthuma, D.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Neale, M.C.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E.; Baaré, W.E.C.; Kahn, R.S.; Boomsma, D. Multivariate Genetic Analysis of Brain Structure in an Extended Twin Design. Behav. Genet. 2000, 30, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falconer, D.S.; MacKay, T.F.C. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics; Pearson, Prentice Hall: Harlow, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Neale, M.C.; Hunter, M.D.; Pritikin, J.N.; Zahery, M.; Brick, T.R.; Kirkpatrick, R.M.; Estabrook, R.; Bates, T.C.; Maes, H.H.; Boker, S.M. OpenMx 2.0: Extended Structural Equation and Statistical Modeling. Psychometrika 2016, 81, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Version 4.0.3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dominicus, A.; Skrondal, A.; Gjessing, H.K.; Pedersen, N.L.; Palmgren, J.; Dominicus, A.; Skrondal, A.; Gjessing, H.K.; Pedersen, N.L.; Palmgren, J.; et al. Likelihood Ratio Tests in Behavioral Genetics: Problems and Solutions. Behav. Genet. 2016, 36, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, C.R.; Lazar, N.A.; Nichols, T. Thresholding of Statistical Maps in Functional Neuroimaging Using the False Discovery Rate. NeuroImage 2002, 15, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Instrument | Age 10 Years | Age 13 Years | Age 18 Years |
| CBCL | Score = 5.31 ± 6.1 [0; 30] h2 = 80% [57%; 92%] c2 = 9% [0%; 29%] e2 = 12% [7%; 21%] | Score = 4.35 ± 5.1 [0; 30] h2 = 88% [70%; 96%] c2 = 7% [0%; 25%] e2 = 5% [3%; 8%] | Score = 3.46 ± 4.9 [0; 27] h2 = 82% [63%; 91%] c2 = 5% [0%; 22%] e2 = 13% [9%; 22%] |
| YSR | N/A | Score = 7.57 ± 6.0 [0; 32] h2 = 76% [58%; 86%] c2 = 0% [0%; 10%] e2 = 24% [14%; 40%] | Score = 7.64 ± 5.3 [0; 27] h2 = 42% [15%; 59%] c2 = 0% [0%;18%] e2 = 58% [41% ;80%] |
| Instrument | Age 10 to 13 years | Age 13 to 18 years | Age 10 to 18 years |
| CBCL | = 86% [70%; 92%] = 0% [0%; 7%] = 14% [7%; 29%] | = 84% [69%; 90%] = 0% [0%; 13%] = 16% [10%; 26%] | = 78% [55%; 88%] = 1% [0%; 12%] = 22% [12%; 38%] |
| YSR | N/A | = 26% [0%; 47%] = 0% [0%; 17%] = 74% [53%; 94%] | N/A |
| Trait | Assessment #1: Age 10 Years | Assessment #1: Age 13 Years | Assessment #1: Age 18 Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| Families | 112 | 102 | 93 |
| Participants | 311 214 twins and 97 siblings | 283 203 twins and 80 siblings | 253 182 twins and 71 siblings |
| Sex | 149 M and 162 F | 133 M and 150 F | 109 M and 144 F |
| Age 1 | 10.0 ± 1.4 [9.0; 15.0] | 13.0 ± 1.5 [11.7; 18.0] | 18.0 ± 1.4 [16.8; 22.9] |
| MRI scans | 283 | 178 | 232 |
| CBCL data | 247 | 264 | 241 |
| YSR data | N/A | 253 | 243 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teeuw, J.; Klein, M.; Mota, N.R.; Brouwer, R.M.; van ‘t Ent, D.; Al-Hassaan, Z.; Franke, B.; Boomsma, D.I.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Multivariate Genetic Structure of Externalizing Behavior and Structural Brain Development in a Longitudinal Adolescent Twin Sample. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063176
Teeuw J, Klein M, Mota NR, Brouwer RM, van ‘t Ent D, Al-Hassaan Z, Franke B, Boomsma DI, Hulshoff Pol HE. Multivariate Genetic Structure of Externalizing Behavior and Structural Brain Development in a Longitudinal Adolescent Twin Sample. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(6):3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063176
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeeuw, Jalmar, Marieke Klein, Nina Roth Mota, Rachel M. Brouwer, Dennis van ‘t Ent, Zyneb Al-Hassaan, Barbara Franke, Dorret I. Boomsma, and Hilleke E. Hulshoff Pol. 2022. "Multivariate Genetic Structure of Externalizing Behavior and Structural Brain Development in a Longitudinal Adolescent Twin Sample" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 6: 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063176
APA StyleTeeuw, J., Klein, M., Mota, N. R., Brouwer, R. M., van ‘t Ent, D., Al-Hassaan, Z., Franke, B., Boomsma, D. I., & Hulshoff Pol, H. E. (2022). Multivariate Genetic Structure of Externalizing Behavior and Structural Brain Development in a Longitudinal Adolescent Twin Sample. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(6), 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063176






