Peptidomic Analysis on Mouse Lung Tissue Reveals AGDP as a Potential Bioactive Peptide against Pseudorabies Virus Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
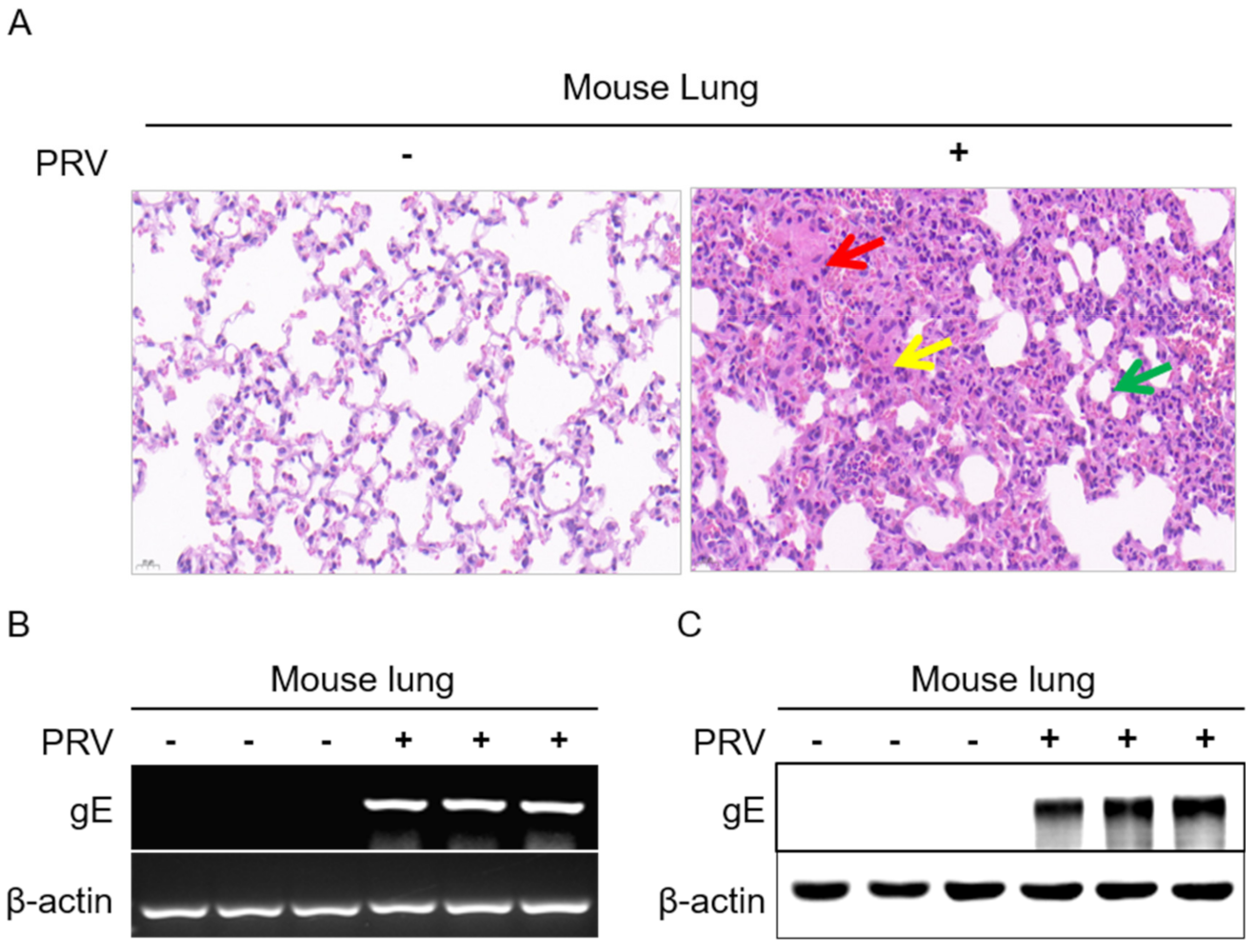
2.1. Establishment of PRV Infection Models in Mice
2.2. Identification of Bioactive Peptides and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Down-Regulated Expression of RAGE mRNA in the Response to PRV Infection
2.4. AGDP Exhibited Anti-PRV Infection and Inhibited the Inflammatory Response In Vitro
2.5. AGDP Suppressed the Extracellular Release of HMGB1 from the PRV-Infected MLE-12 Cells
2.6. AGDP Regulated the Degradation of IκBα Protein and the Phosphorylation Levels of P65 Protein in PRV-Infected Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells, Virus, and Infection
4.2. Animals, Virus Infection, and Samples Collection
4.3. Histopathological Observation
4.4. Peptidomic Analysis
4.5. Peptide Synthesis
4.6. Effects of AGDP in Responding to PRV Infection In Vitro
4.7. PCR/RT-PCR and qPCR/qRT-PCR
4.8. Western Blotting (WB)
4.9. IFC and Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy
4.10. Plaque Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Müller, T.; Hahn, E.C.; Tottewitz, F.; Kramer, M.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Freuling, C. Pseudorabies virus in wild swine: A global perspective. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomeranz: L., E.; Reynolds, A.E.; Hengartner, C.J. Molecular biology of pseudorabies virus: Impact on neurovirology and veterinary medicine. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 462–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Auclert, L.Z.; Zhai, X.; Wong, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H.; Xing, G.; Wang, S.; He, W.; Li, K.; et al. Interspecies Transmission, Genetic Diversity, and Evolutionary Dynamics of Pseudorabies Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettenleiter, T.C. Aujeszky’s Disease and the Development of the Marker/DIVA Vaccination Concept. Pathogens 2020, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laval, K.; Enquist, L.W. The Neuropathic Itch Caused by Pseudorabies Virus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Peng, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W. Isolation and Characterization of a Variant Psedorabies Virus HNXY and Construction of rHNXY-TK/gE. Animals 2020, 10, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehl, J.; Teifke, J.P. Comparative Pathology of Pseudorabies in Different Naturally and Experimentally Infected Species—A Review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yan, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, L.; Yan, H.; et al. Construction of a gE-Deleted Pseudorabies Virus and Its Efficacy to the New-Emerging Variant PRV Challenge in the Form of Killed Vaccine. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 684945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhuang, D.; Li, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, E.; Xie, B.; Chen, J.; Zhao, M. Recombinant pseudorabies virus with gI/gE deletion generated by overlapping polymerase chain reaction and homologous recombination technology induces protection against the PRV variant PRV-GD2013. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Yao, J.; Yang, Y.; Luo, W.; Yuan, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, A. Current Status and Challenge of Pseudorabies Virus Infection in China. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 588–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Coban, C.; Akira, S. Innate immune response to viral infection. Cytokine 2008, 43, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.D.; Lin, P.Y.; Liao, M.H.; Chang, C.I.; Hsu, J.L.; Yu, F.L.; Wu, H.Y.; Shih, W.L. Suppression of apoptosis by pseudorabies virus Us3 protein kinase through the activation of PI3-K/Akt and NF-kappaB pathways. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Chi, X.; Yan, R.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Shao, W.; Chen, J.L. Alpha/beta interferon receptor deficiency in mice significantly enhances susceptibility of the animals to pseudorabies virus infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 203, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 Years of NF-kappaB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, N.; Van Waesberghe, C.; Favoreel, H.W. Pseudorabies Virus Infection of Epithelial Cells Leads to Persistent but Aberrant Activation of the NF-kappaB Pathway, Inhibiting Hallmark NF-kappaB-Induced Proinflammatory Gene Expression. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00196-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, N.; Favoreel, H.W. Pseudorabies Virus Infection Triggers NF-kappaB Activation via the DNA Damage Response but Actively Inhibits NF-kappaB-Dependent Gene Expression. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0166621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.L.; Schneider, T.; Peoples, A.J.; Spoering, A.L.; Engels, I.; Conlon, B.P.; Mueller, A.; Schaberle, T.F.; Hughes, D.E.; Epstein, S.; et al. A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance. Nature 2015, 517, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.B.; Zhang, X.; Paul, D.; Kays, L.M.; Gough, W.; Stewart, J.; Uhlik, M.T.; Chen, Q.; Hui, Y.H.; Zamek-Gliszczynski, M.J.; et al. Identification of LY2510924, a novel cyclic peptide CXCR4 antagonist that exhibits antitumor activities in solid tumor and breast cancer metastatic models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radek, K.; Gallo, R. Antimicrobial peptides: Natural effectors of the innate immune system. Semin. Immunopathol. 2007, 29, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.L.; Dunn, M.K. Therapeutic peptides: Historical perspectives, current development trends, and future directions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavari, B.; Mahjub, R.; Saidijam, M.; Raigani, M.; Soleimani, M. The Potential Use of Peptides in Cancer Treatment. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilas Boas, L.C.P.; Campos, M.L.; Berlanda, R.L.A.; de Carvalho Neves, N.; Franco, O.L. Antiviral peptides as promising therapeutic drugs. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3525–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Sunderland, K.; Mao, C. Virus-Derived Peptides for Clinical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10377–10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Ding, J.; Liao, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, W. Defensins: The natural peptide antibiotic. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 114008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, N.; Popel, A.S. Peptides that immunoactivate the tumor microenvironment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1875, 188486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.K.; Sung, J.J.; To, K.F.; Yu, L.; Li, H.T.; Li, Z.J.; Chu, K.M.; Yu, J.; Cho, C.H. The host defense peptide LL-37 activates the tumor-suppressing bone morphogenetic protein signaling via inhibition of proteasome in gastric cancer cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2010, 223, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Huang, H.; Tang, M.; Cai, Z.; Huang, C.; Qi, B.; Chen, J.L. Role of neuromedin B and its receptor in the innate immune responses against influenza A virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Tao, X.; Fei, M.; Chen, J.; Guo, W.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Human encephalitis caused by pseudorabies virus infection: A case report. J. Neurovirol. 2020, 26, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaby, D.M.; Mornon, J.P. The immunoglobulin superfamily: An insight on its tissular, species, and functional diversity. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 46, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Yan, S.D.; Yan, S.F.; Stern, D.M. The multiligand receptor RAGE as a progression factor amplifying immune and inflammatory responses. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, C.; Bierhaus, A.; Hofer, S.; Bouchon, A.; Nawroth, P.P.; Martin, E.; Weigand, M.A. Bench-to-bedside review: The inflammation-perpetuating pattern-recognition receptor RAGE as a therapeutic target in sepsis. Crit. Care 2008, 12, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jules, J.; Maiguel, D.; Hudson, B.I. Alternative splicing of the RAGE cytoplasmic domain regulates cell signaling and function. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Kinoshita, R.; Putranto, E.W.; Ruma, I.; Sumardika, I.W.; Youyi, C.; Tomonobu, N.; Yamamoto, K.I.; Murata, H. Signal Diversity of Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products. Acta Med. Okayama 2017, 71, 459–465. [Google Scholar]
- Egawa, K.; Shimojima, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Nagata, N.; Tani, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurosu, T.; Watanabe, S.; Fukushi, S.; Saijo, M. Virulence, pathology, and pathogenesis of Pteropine orthoreovirus (PRV) in BALB/c mice: Development of an animal infection model for PRV. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, C.Z.; Hu, W.Y.; Zhang, J.W.; Wei, Y.Y.; Yu, M.L.; Hu, T.J. Establishment of inflammatory model induced by Pseudorabies virus infection in mice. J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 22, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Far, A.H.; Sroga, G.; Jaouni, S.K.A.; Mousa, S.A. Role and Mechanisms of RAGE-Ligand Complexes and RAGE-Inhibitors in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Gao, Y.; Dai, X.; Fu, W.; Cai, S.; Fang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Z. SIRT1-mediated HMGB1 deacetylation suppresses sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, F20–F31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moisy, D.; Avilov, S.V.; Jacob, Y.; Laoide, B.M.; Ge, X.; Baudin, F.; Naffakh, N.; Jestin, J.L. HMGB1 protein binds to influenza virus nucleoprotein and promotes viral replication. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9122–9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Lotze, M.T.; Tang, D. HMGB1 in cancer: Good, bad, or both? Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4046–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Luo, X.; Yan, R.; Wang, Q.; Qi, Q.; Chi, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Cai, B.; Chen, J.L.; et al. 3-Anhydro-6-hydroxy-ophiobolin A displays high in vitro and in vivo efficacy against influenza A virus infection. Protein Cell 2016, 7, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Names of Primers | Sequences of Primers (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| PRV gE Forward | CCACTCGCAGCTCTTCTCG |
| PRV gE Reverse | CAGTCCAGCGTGGCAGTAAA |
| Mouse HMGB1 Forward | GCTGACAAGGCTCGTTATGAA |
| Mouse HMGB1 Reverse | CCTTTGATTTTGGGGCGGTA |
| Mouse IL-8 Forward | CAAGGCTGGTCCATGCTCC |
| Mouse IL-8 Reverse | TGCTATCACTTCCTTTCTGTTGC |
| Mouse TNF-α Forward | ACGGCATGGATCTCAAAGAC |
| Mouse TNF-α Reverse | CGGCAGAGAGGAGGTTGACT |
| Mouse β-actin Forward | AATGGGTCAGAAGGACTCCT |
| Mouse β-actin Reverse | ACGGTTGGCCTTAGGGTTCAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Tian, S.; Wan, Q.; Kong, Y.; Liu, C.; Tian, K.; Ning, H.; Xu, X.; Qi, B.; Yang, G. Peptidomic Analysis on Mouse Lung Tissue Reveals AGDP as a Potential Bioactive Peptide against Pseudorabies Virus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063306
Ma Y, Tian S, Wan Q, Kong Y, Liu C, Tian K, Ning H, Xu X, Qi B, Yang G. Peptidomic Analysis on Mouse Lung Tissue Reveals AGDP as a Potential Bioactive Peptide against Pseudorabies Virus Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(6):3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063306
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yijie, Shimao Tian, Qianhui Wan, Yingying Kong, Chang Liu, Ke Tian, Hongya Ning, Xiaodong Xu, Baomin Qi, and Guihong Yang. 2022. "Peptidomic Analysis on Mouse Lung Tissue Reveals AGDP as a Potential Bioactive Peptide against Pseudorabies Virus Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 6: 3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063306







