Lysophosphatidylserine Induces MUC5AC Production via the Feedforward Regulation of the TACE-EGFR-ERK Pathway in Airway Epithelial Cells in a Receptor-Independent Manner
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
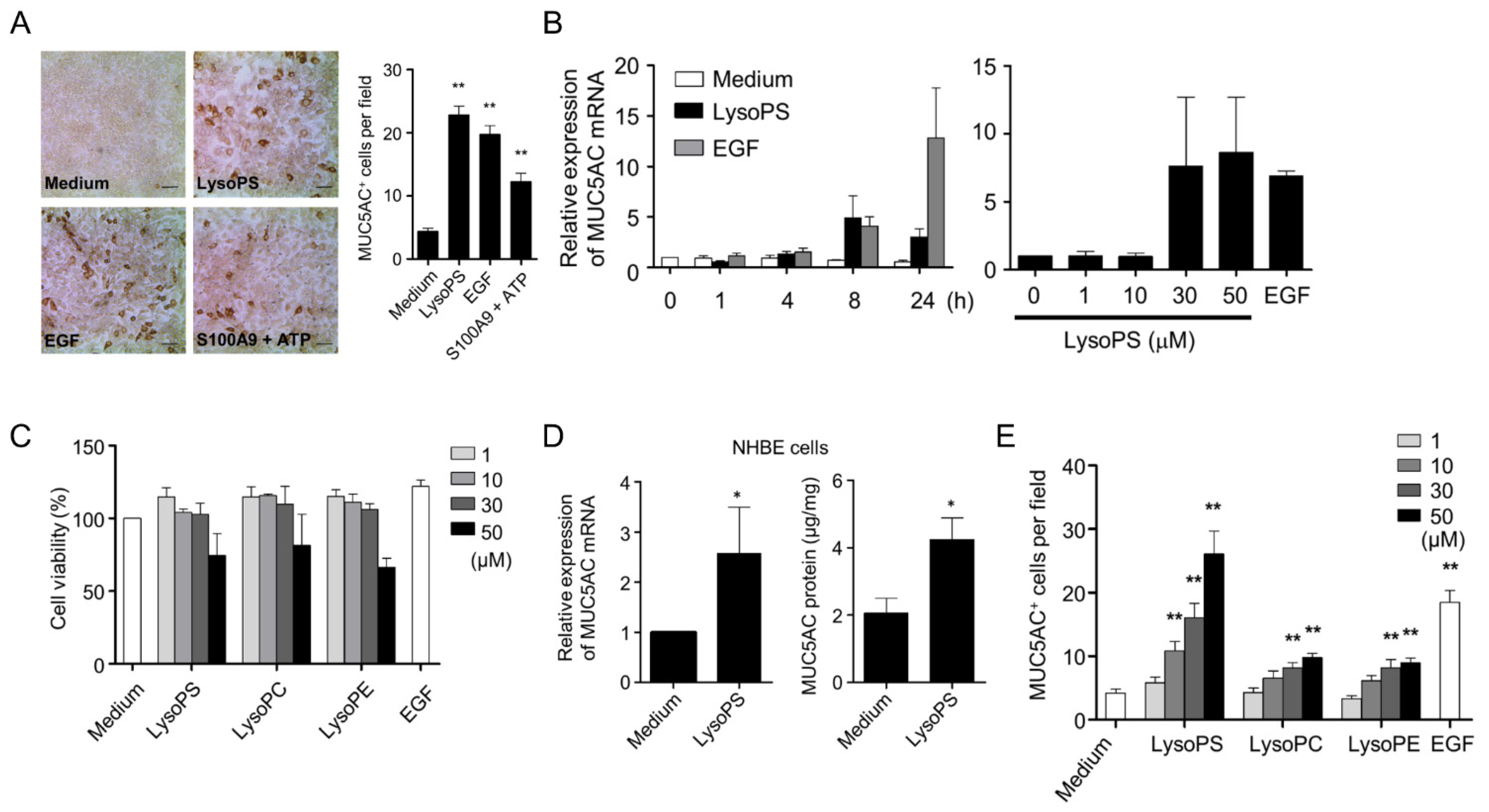
2.1. LysoPS Induces MUC5AC Production in Airway Epithelial Cells
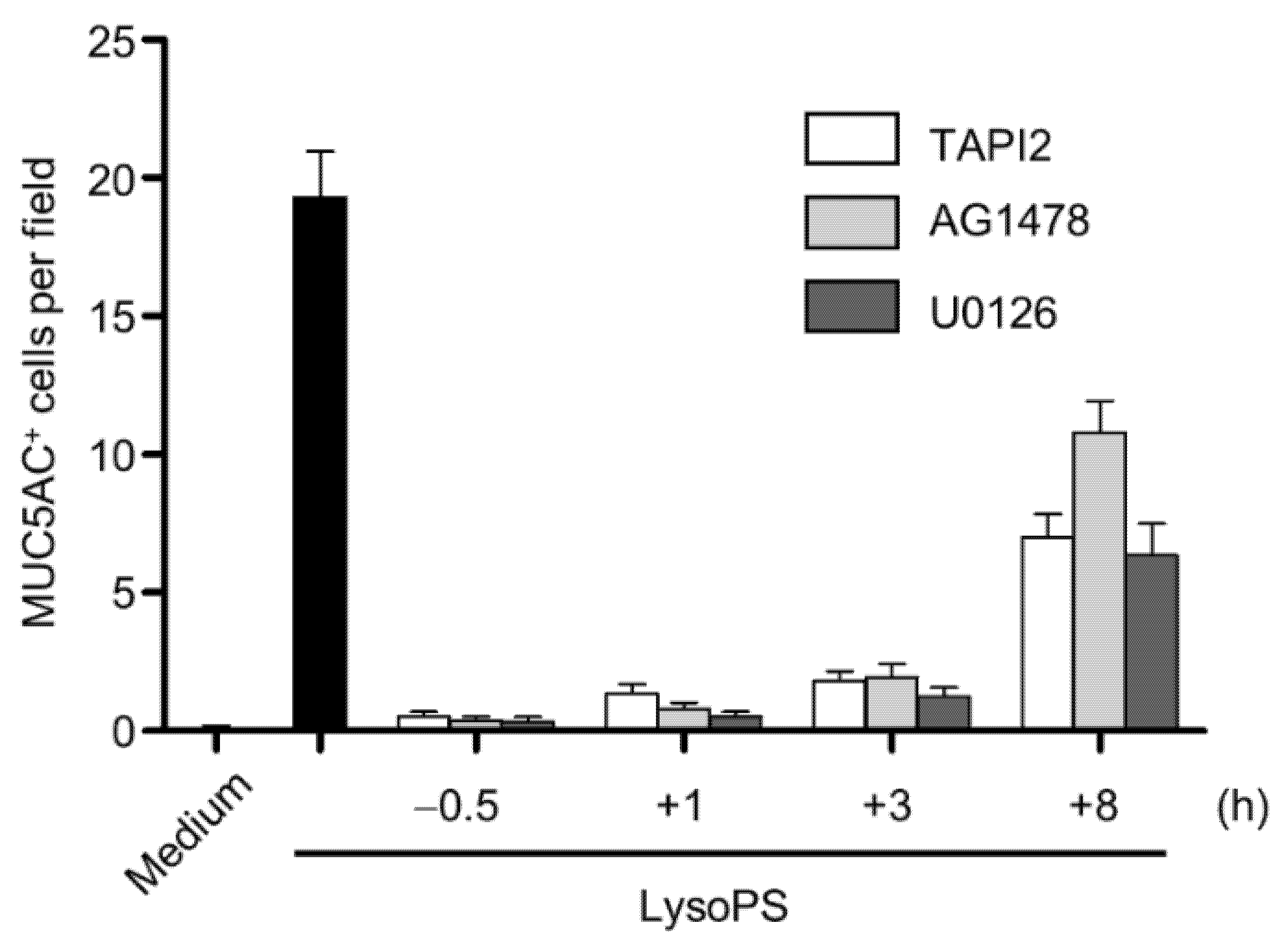
2.2. LysoPS-Induced MUC5AC Production Is Blocked by Inhibitors of TACE, EGFR, and MEK1/2 but Not by Inhibitors of Caspase-1 or NF-κB
2.3. LysoPS Induces ERK Phosphorylation in a Biphasic Manner with Robust Activation of EGFR in the Late Phase
2.4. Early-Phase ERK Phosphorylation Is at Least in Part the Result of Activation of EGFR
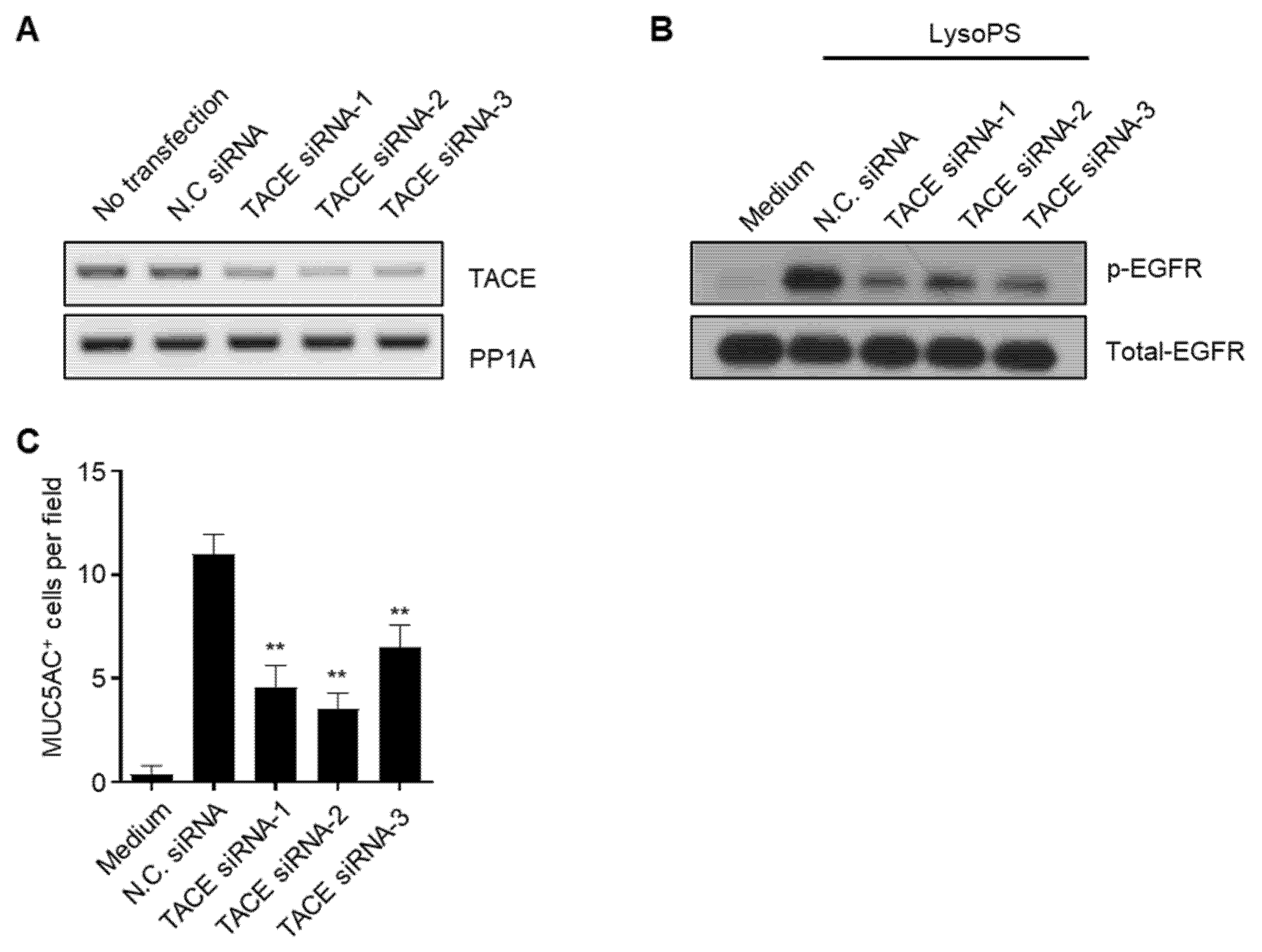
2.5. The TACE-EGFR-ERK Pathway Is Required for MUC5AC Production during the Late Phase
2.6. LysoPS Induces TGF-α Production in a TACE-Dependent Manner
2.7. Neither GPCRs nor TLR2 Is Responsible for LysoPS-Induced ERK Phosphorylation and MUC5AC Production
2.8. ROS Production Tends to Be Weakly Induced by LysoPS, but Is Not Involved in MUC5AC Production
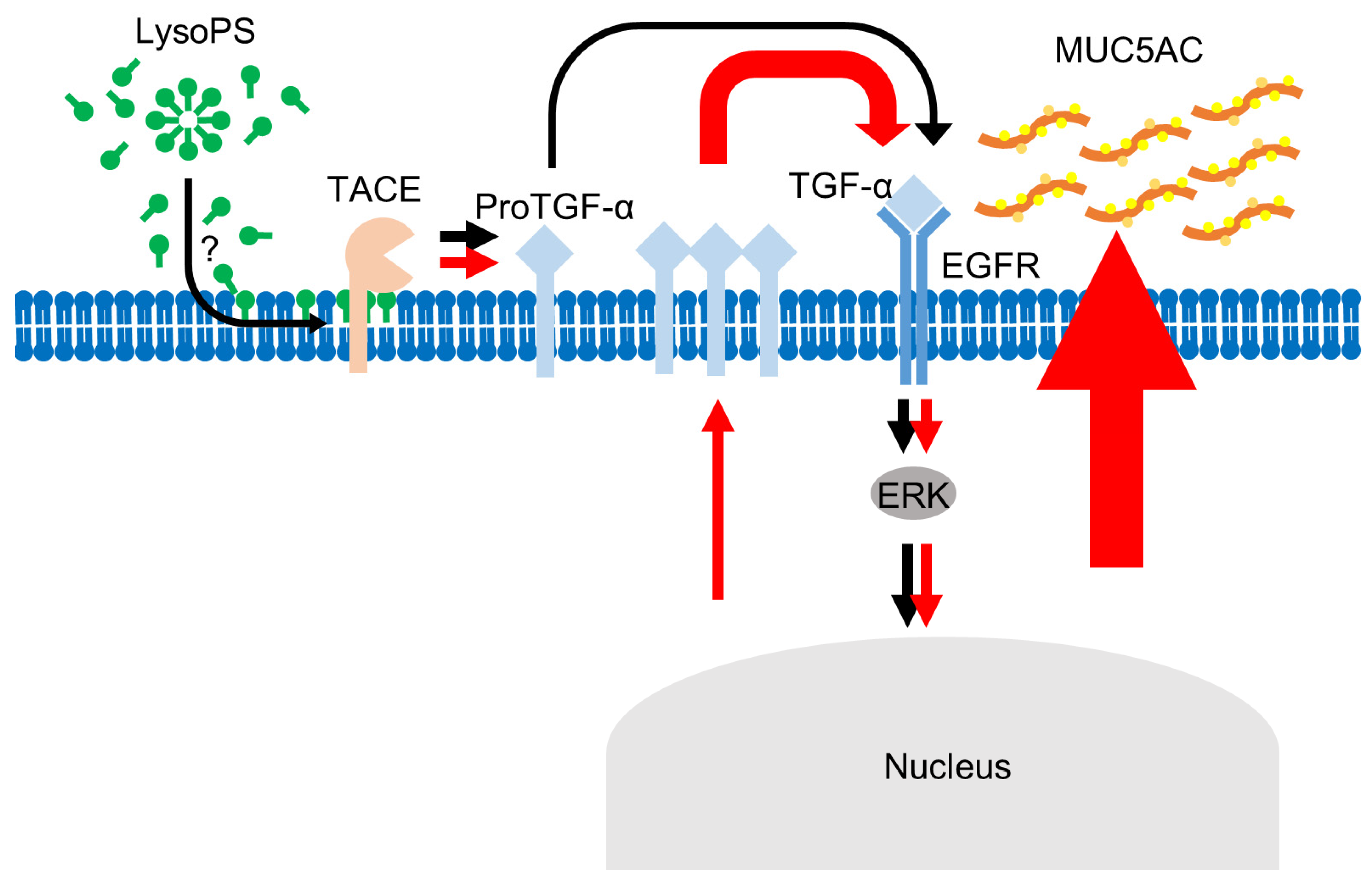
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Cultures for NCI-H292 and Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells
4.3. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription-PCR, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.4. TACE siRNA Transfection
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Cell Viability Assays
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Immunocytochemistry
4.9. ELISA of Secreted TGF-α and MUC5AC
4.10. Analysis of Cellular ROS Levels
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, J.; Rubin, B.K.; Voynow, J.A. Mucins, Mucus, and Goblet Cells. Chest 2018, 154, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesimer, M.; Ford, A.A.; Ceppe, A.; Radicioni, G.; Cao, R.; Davis, C.W.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Alexis, N.E.; Anderson, W.H.; Henderson, A.G.; et al. Airway Mucin Concentration as a Marker of Chronic Bronchitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdicombe, J.H.; Wine, J.J. Airway Gland Structure and Function. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1241–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostedgaard, L.S.; Moninger, T.O.; McMenimen, J.D.; Sawin, N.M.; Parker, C.P.; Thornell, I.M.; Powers, L.S.; Gansemer, N.D.; Bouzek, D.C.; Cook, D.P.; et al. Gel-forming mucins form distinct morphologic structures in airways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6842–6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, H.W.J.; Williams, O.W.; Chandra, D.; Bellinghausen, L.K.; Perez, G.; Suarez, A.; Tuvim, M.J.; Roy, M.G.; Alexander, S.N.; Moghaddam, S.J.; et al. Central role of muc5ac expression in mucous metaplasia and its regulation by conserved 5′ elements. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, C.M.; Kim, K.; Tuvim, M.J.; Dickey, B.F. Mucus hypersecretion in asthma: Causes and effects. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2009, 15, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, C.M.; Raclawska, D.S.; Ttofali, F.; Liptzin, D.R.; Fletcher, A.A.; Harper, D.N.; McGing, M.A.; McElwee, M.M.; Williams, O.W.; Sanchez, E.; et al. The polymeric mucin Muc5ac is required for allergic airway hyperreactivity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lachowicz-Scroggins, M.E.; Finkbeiner, W.E.; Gordon, E.D.; Yuan, S.; Zlock, L.; Bhakta, N.R.; Woodruff, P.G.; Fahy, J.V.; Boushey, H.A. Corticosteroid and long-acting beta-agonist therapy reduces epithelial goblet cell metaplasia. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.G.; Livraghi-Butrico, A.; Fletcher, A.A.; McElwee, M.M.; Evans, S.E.; Boerner, R.M.; Alexander, S.N.; Bellinghausen, L.K.; Song, A.S.; Petrova, Y.M.; et al. Muc5b is required for airway defence. Nature 2014, 505, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, T.; Liu, F.; Zhu, A.R.; Lin, Y.P.; Luo, J.P.; Ye, F.; He, J.X.; Zhao, J.C.; et al. Elevated MUC1 and MUC5AC mucin protein levels in airway mucus of critical ill COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonser, L.R.; Erle, D.J. Airway Mucus and Asthma: The Role of MUC5AC and MUC5B. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thai, P.; Loukoianov, A.; Wachi, S.; Wu, R. Regulation of airway mucin gene expression. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 405–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, H.Y.; Rogers, D.F. Mucus hypersecretion in asthma: Intracellular signalling pathways as targets for pharmacotherapy. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 10, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrais, M.; Pigny, P.; Copin, M.C.; Aubert, J.P.; Van Seuningen, I. Induction of MUC2 and MUC5AC mucins by factors of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family is mediated by EGF receptor/Ras/Raf/Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase cascade and Sp1. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32258–32267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lora, J.M.; Zhang, D.M.; Liao, S.M.; Burwell, T.; King, A.M.; Barker, P.A.; Singh, L.; Keaveney, M.; Morgenstern, J.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha triggers mucus production in airway epithelium through an I kappa B kinase beta-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36510–36517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koff, J.L.; Shao, M.X.G.; Ueki, I.F.; Nadel, J.A. Multiple TLRs activate EGFR via a signaling cascade to produce innate immune responses in airway epithelium. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L1068–L1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Lewis, C.; Nadel, J.A. CCL20/CCR6 Feedback Exaggerates Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Dependent MUC5AC Mucin Production in Human Airway Epithelial (NCI-H292) Cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3392–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.H.; Hwang, S.M.; Chung, I.Y. S100A8, S100A9 and S100A12 activate airway epithelial cells to produce MUC5AC via extracellular signal-regulated kinase and nuclear factor-kappa B pathways. Immunology 2015, 144, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeyama, K.; Dabbagh, K.; Shim, J.J.; Dao-Pick, T.; Ueki, I.F.; Nadel, J.A. Oxidative stress causes mucin synthesis via transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor: Role of neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, M.X.G.; Nadel, J.A. Dual oxidase 1-dependent MUC5AC mucin expression in cultured human airway epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chokki, M.; Eguchi, H.; Hamamura, I.; Mitsuhashi, H.; Kamimura, T. Human airway trypsin-like protease induces amphiregulin release through a mechanism involving protease-activated receptor-2-mediated ERK activation and TNF alpha-converting enzyme activity in airway epithelial cells. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 6387–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.M.; Pu, J.D.; He, F.; Liao, B.L.; Hao, B.W.; Hong, W.; Ye, X.Q.; Chen, J.L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; et al. Positive feedback of the amphiregulin-EGFR-ERK pathway mediates PM2.5 from wood smoke-induced MUC5AC expression in epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Bak, S.M.; Suh, I.B.; Lee, S.Y.; Shin, C.; Shim, J.J.; In, K.H.; Kang, K.H.; Yoo, S.H. Effects of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor on LPS-induced goblet cell metaplasia. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, L127–L133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Ishiguro, J.; Kitamura, H.; Arima, N.; Okutani, M.; Shuto, A.; Higashiyama, S.; Ohwada, T.; Arai, H.; Makide, K.; et al. TGF alpha shedding assay: An accurate and versatile method for detecting GPCR activation. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasch, S.C.; Bratton, D.L. Emerging roles for lysophosphatidylserine in resolution of inflammation. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2012, 51, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Kleij, D.; Latz, E.; Brouwers, J.F.H.M.; Kruize, Y.C.M.; Schmitz, M.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Espevik, T.; de Jong, E.C.; Kapsenberg, M.L.; Golenbock, D.T.; et al. A novel host-parasite lipid cross-talk—Schistosomal lyso-phosphatidylserine activates Toll-like receptor 2 and affects immune polarization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48122–48129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanbhag, K.; Mhetre, A.; Khandelwal, N.; Kamat, S.S. The Lysophosphatidylserines-An Emerging Class of Signalling Lysophospholipids. J. Membr. Biol. 2020, 253, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.T.; Ramesh, T.; Toh, X.R.; Nguyen, L.N. Emerging roles of lysophospholipids in health and disease. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2020, 80, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurano, M.; Dohi, T.; Nojiri, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Hirowatari, Y.; Inoue, A.; Kano, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Igarashi, K.; Nishikawa, M.; et al. Blood levels of serotonin are specifically correlated with plasma lysophosphatidylserine among the glycero-lysophospholipids. BBA Clin. 2015, 4, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.H.; Lee, E.H.; Park, S.W.; Chung, I.Y. MUC5AC Expression through Bidirectional Communication of Notch and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Pathways. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeyama, K.; Dabbagh, K.; Lee, H.M.; Agusti, C.; Lausier, J.A.; Ueki, I.F.; Grattan, K.M.; Nadel, J.A. Epidermal growth factor system regulates mucin production in airways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3081–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Kim, H.J.; Binas, B.; Kang, J.H.; Chung, I.Y. Inflammatory mediators ATP and S100A12 activate the NLRP3 inflammasome to induce MUC5AC production in airway epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makide, K.; Uwamizu, A.; Shinjo, Y.; Ishiguro, J.; Okutani, M.; Inoue, A.; Aoki, J. Novel lysophosphoplipid receptors: Their structure and function. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Nanayakkara, G.; Cheng, J.L.; Cueto, R.; Yang, W.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.F. Lysophospholipids and Their Receptors Serve as Conditional DAMPs and DAMP Receptors in Tissue Oxidative and Inflammatory Injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsuzzaman, M.; Uddin, M.S.; Shah, M.A.; Mathew, B. Natural inhibitors on airway mucin: Molecular insight into the therapeutic potential targeting MUC5AC expression and production. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Weskamp, G.; Kelly, K.; Zhou, H.M.; Higashiyama, S.; Peschon, J.; Hartmann, D.; Saftig, P.; Blobel, C.P. Distinct roles for ADAM10 and ADAM17 in ectodomain shedding of six EGFR ligands. J. Cell. Biol. 2004, 164, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smyth, L.A.; Collins, I. Measuring and interpreting the selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors. J. Chem. Biol. 2009, 2, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugo, T.; Tachimoto, H.; Chikatsu, T.; Murakami, Y.; Kikukawa, Y.; Sato, S.; Kikuchi, K.; Nagi, T.; Harada, M.; Ogi, K.; et al. Identification of a lysophosphatidylserine receptor on mast cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwind, A.; Hart, S.; Fischer, O.M.; Ullrich, A. TACE cleavage of proamphiregulin regulates GPCR-induced proliferation and motility of cancer cells. Embo. J. 2003, 22, 2411–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idzko, M.; Laut, M.; Panther, E.; Sorichter, S.; Durk, T.; Fluhr, J.W.; Herouy, Y.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Myrtek, D.; Elsner, P.; et al. Lysophosphatidic acid induces chemotaxis, oxygen radical production, CD11b up-regulation, Ca2+ mobilization, and actin reorganization in human eosinophils via pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4480–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gon, Y.; Asai, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Mizumura, K.; Jibiki, I.; Machino, T.; Ra, C.; Horie, T. A20 inhibits toll-like receptor 2-and 4-mediated interleukin-8 synthesis in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.X.G.; Nade, J.A. Neutrophil elastase induces MUC5AC mucin production in human airway epithelial cells via a cascade involving protein kinase C, reactive oxygen species, and TNF-alpha-converting enzyme. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, M.X.G.; Nakanaga, T.; Nadel, J.A. Cigarette smoke induces MUC5AC mucin overproduction via tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme in human airway epithelial (NCI-H292) cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, L420–L427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, Y.D.; Moon, U.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Leon, J.H.; Lee, J.G.; Bae, Y.S.; Yoon, J.H. The Role of Nox4 in Oxidative Stress-Induced MUC5AC Overexpression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sommer, A.; Kordowski, F.; Buch, J.; Maretzky, T.; Evers, A.; Andra, J.; Dusterhoft, S.; Michalek, M.; Lorenzen, I.; Somasundaram, P.; et al. Phosphatidylserine exposure is required for ADAM17 sheddase function. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, F.G.; Li, W.; Jono, H.; Li, Q.M.; Zhang, S.M.; Li, J.D.; Shen, H.H. Reactive oxygen species regulate Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide-induced MUC5AC mucin expression via PKC-NADPH oxidase-ROS-TGF-alpha signaling pathways in human airway epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.X.; Lee, B.; Zhu, L.X.; Ding, Z.; Chen, Y. Exposure to mold proteases stimulates mucin production in airway epithelial cells through Ras/Raf1/ERK signal pathway. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frasch, S.C.; Berry, K.Z.; Fernandez-Boyanapalli, R.; Jin, H.S.; Leslie, C.; Henson, P.M.; Murphy, R.C.; Bratton, D.L. NADPH oxidase-dependent generation of lysophosphatidylserine enhances clearance of activated and dying neutrophils via G2A. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33736–33749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uwamizu, A.; Inoue, A.; Suzuki, K.; Okudaira, M.; Shuto, A.; Shinjo, Y.; Ishiguro, J.; Makide, K.; Ikubo, M.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Lysophosphatidylserine analogues differentially activate three LysoPS receptors. J. Biochem. 2015, 157, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omi, J.; Kano, K.; Aoki, J. Current Knowledge on the Biology of Lysophosphatidylserine as an Emerging Bioactive Lipid. Cell. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, N.; Shaikh, M.; Mhetre, A.; Singh, S.; Sajeevan, T.; Joshi, A.; Balaji, K.N.; Chakrapani, H.; Kamat, S.S. Fatty acid chain length drives lysophosphatidylserine-dependent immunological outputs. Cell. Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, K.; Cornelsen, I.; Husmann, M.; Gimpl, G.; Bhakdi, S. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Drive Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase (ADAM)-dependent Cell Adhesion, Proliferation, and Migration by Modulating Membrane Fluidity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26931–26942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sommer, A.; Fries, A.; Cornelsen, I.; Speck, N.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Gimpl, G.; Andra, J.; Bhakdi, S.; Reiss, K. Melittin Modulates Keratinocyte Function through P2 Receptor-dependent ADAM Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 23678–23689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, G.A.; Hesketh, T.R.; Plumb, R.W.; Metcalfe, J.C. The exogenous lipid requirement for histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells stimulated by concanavalin A. FEBS Lett. 1979, 105, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruni, A.; Palatini, P. Biological and pharmacological properties of phospholipids. Prog. Med. Chem. 1982, 19, 111–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Rodriguez, E.; Montero, J.C.; Esparis-Ogando, A.; Yuste, L.; Pandiella, A. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylates tumor necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme at threonine 735: A potential role in regulated shedding. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 2031–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y. A neuroinflammation emerging target. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Aoki, J.; Nagai, Y.; Dohmae, N.; Takio, K.; Doi, T.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Serine phospholipid-specific phospholipase A that is secreted from activated platelets—A new member of the lipase family. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2192–2198. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, T.; Kurano, M.; Shirai, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Tahara, K.; Hayashi, H.; Igarashi, K.; Fujio, K.; Aoki, J.; Yatomi, Y. Serum phosphatidylserine-specific phospholipase A1 as a novel biomarker for monitoring systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sim, M.S.; Kim, H.J.; Jo, S.H.; Kim, C.; Chung, I.Y. Lysophosphatidylserine Induces MUC5AC Production via the Feedforward Regulation of the TACE-EGFR-ERK Pathway in Airway Epithelial Cells in a Receptor-Independent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073866
Sim MS, Kim HJ, Jo SH, Kim C, Chung IY. Lysophosphatidylserine Induces MUC5AC Production via the Feedforward Regulation of the TACE-EGFR-ERK Pathway in Airway Epithelial Cells in a Receptor-Independent Manner. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(7):3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073866
Chicago/Turabian StyleSim, Myeong Seong, Hye Jeong Kim, Sang Hee Jo, Chun Kim, and Il Yup Chung. 2022. "Lysophosphatidylserine Induces MUC5AC Production via the Feedforward Regulation of the TACE-EGFR-ERK Pathway in Airway Epithelial Cells in a Receptor-Independent Manner" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 7: 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073866
APA StyleSim, M. S., Kim, H. J., Jo, S. H., Kim, C., & Chung, I. Y. (2022). Lysophosphatidylserine Induces MUC5AC Production via the Feedforward Regulation of the TACE-EGFR-ERK Pathway in Airway Epithelial Cells in a Receptor-Independent Manner. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(7), 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073866





