Identification and Characterization of a Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Influencing RNAi Efficiency in the Rice Leaf Folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
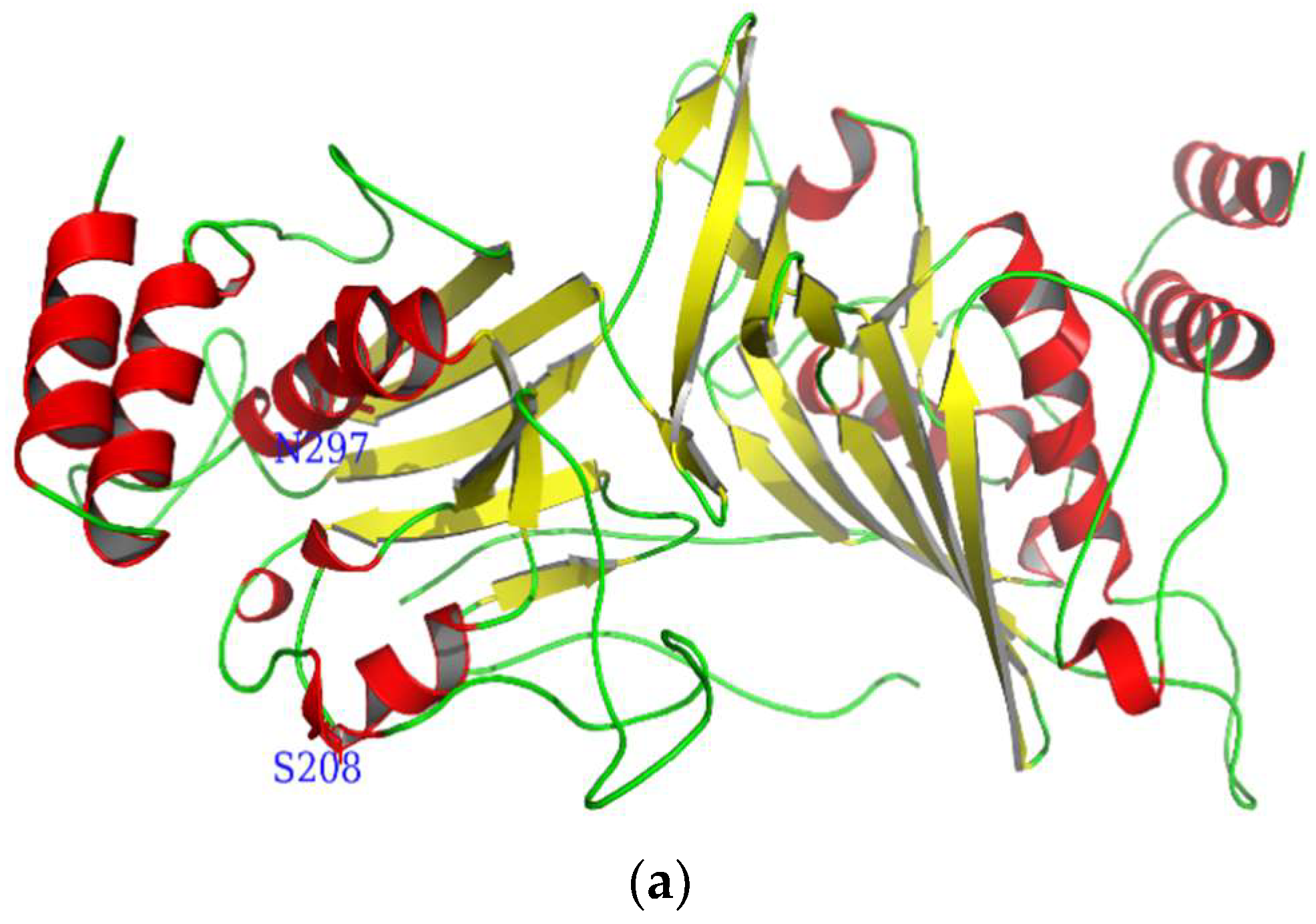
2.1. Characteristics of CmdsRNase
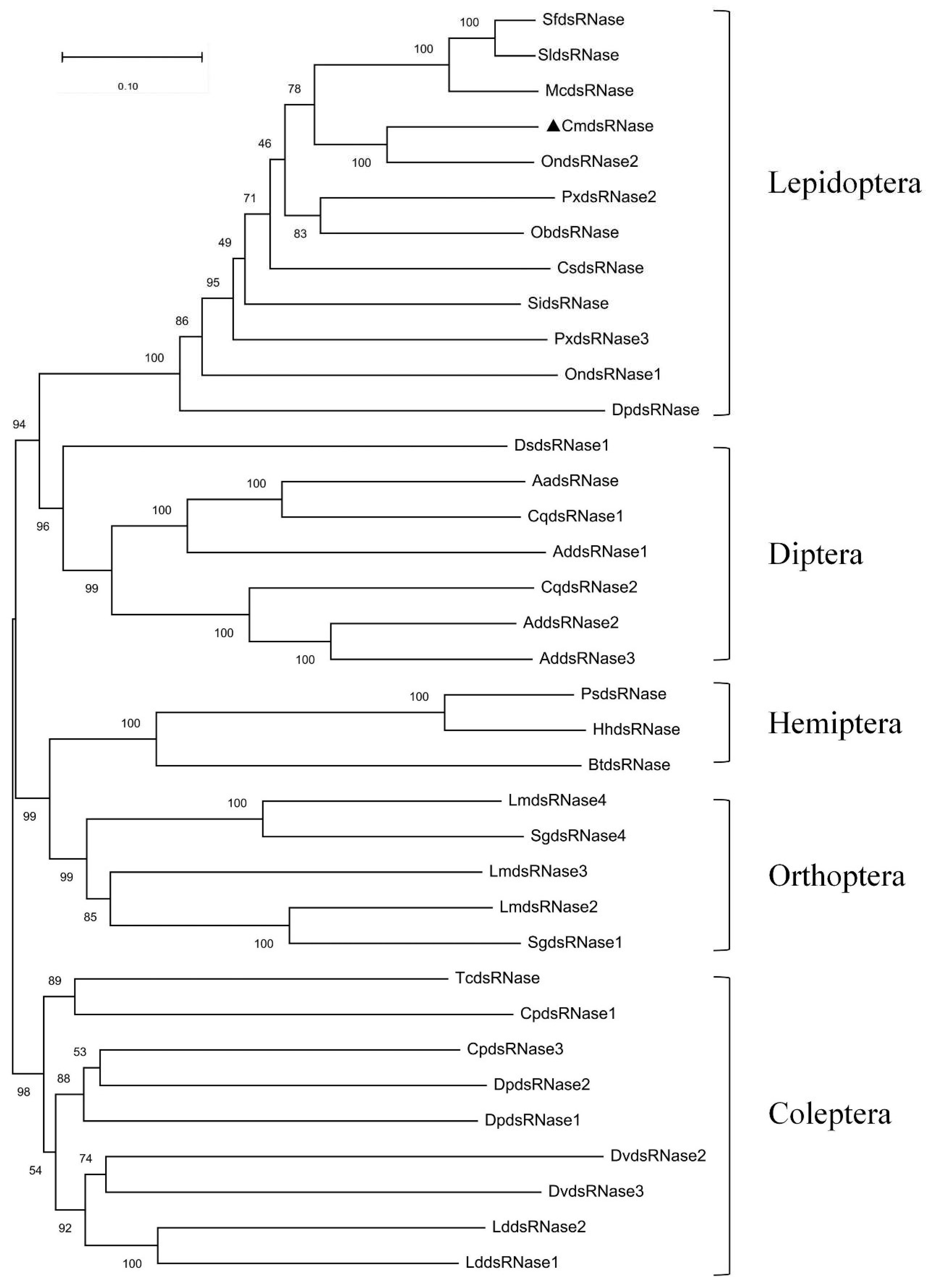
2.2. Homology Comparison and Cluster Dendrogram
2.3. Gene Expression Profiles
2.4. Degradation of dsRNA by Crude CmdsRNase
2.5. Effect of dsCmdsRNase Injection on RNAi Efficiency
2.6. Effect of RNAi on Phenotypes of C. medinalis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect-Rearing and Sample Preparation
4.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. Cloning CmdsRNase
4.4. Bioinformatic Analyses of CmdsRNase
4.5. Gene Expression Analyses Using ddPCR
4.6. Crude CmdsRNase Extraction and dsRNA Degrading Assay
4.7. RNA Interference
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hammond, S.M.; Caudy, A.A.; Hannon, G.J. Post-transcriptional gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, A.; Qun, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.; Gatehouse, J. RNAi-mediated crop protection against insects. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belles, X. Beyond Drosophila: RNAi in vivo and functional genomics in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huvenne, H.; Smagghe, G. Mechanisms of dsRNA uptake in insects and potential of RNAi for pest control: A review. J. Insect Physiol. 2010, 56, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.A.; Bogaert, T.; Clinton, W.; Heck, G.R.; Feldmann, P.; Ilagan, O.; Johnson, S.; Plaetinck, G.; Munyikwa, T.; Pleau, M.; et al. Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoyasu, Y.; Miller, S.C.; Tomita, S.; Schoppmeier, M.; Grossmann, D.; Bucher, G. Exploring systemic RNA interference in insects: A genome-wide survey for RNAi genes in Tribolium. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, F.; Xu, J.; Palli, R.; Ferguson, J.; Palli, S.R. Ingested RNA interference for managing the populations of the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Peng, Y.; Pu, J.; Fu, W.; Wang, J.; Han, Z. Variation in RNAi efficacy among insect species is attributable to dsRNA degradation in vivo. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 77, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyard, S.; Singh, A.D.; Wong, S. Ingested double-stranded RNAs can act as species-specific insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenius, O.; Papanicolaou, A.; Garbutt, J.S.; Eleftherianos, I.; Huvenne, H.; Kanginakudru, S.; Albrechtsen, M.; An, C.; Aymeric, J.-L.; Barthel, A.; et al. RNA interference in Lepidoptera: An overview of successful and unsuccessful studies and implications for experimental design. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joga, M.R.; Zotti, M.J.; Smagghe, G.; Christiaens, O. RNAi efficiency, systemic properties, and novel delivery methods for pest insect control: What we know so far. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, H.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, R.; Wang, Z.; Fei, J. Knockdown of ecdysis-triggering hormone gene with a binary UAS/GAL4 RNA interference system leads to lethal ecdysis deficiency in silkworm. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, M.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Chai, C.L.; Zhang, C.D.; Lu, C.; Xiang, Z.H. Identification and function of Abdominal-A in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajuria, C.; Buschman, L.L.; Chen, M.-S.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Zhu, K.Y. A gut-specific chitinase gene essential for regulation of chitin content of peritrophic matrix and growth of Ostrinia nubilalis larvae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, R.; Ramaseshadri, P.; Anderson, J.; Bachman, P.; Clinton, W.; Flannagan, R.; Ilagan, O.; Lawrence, C.; Levine, S.; Moar, W.; et al. Characterizing the mechanism of action of double-stranded RNA activity against western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhe, A.S.; John, S.H.; Nagaraju, J. Noduler, a novel immune up-regulated protein mediates nodulation response in insects. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 6943–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, Y.-B.; Cai, W.-J.; Wang, J.-W.; Hong, G.-J.; Tao, X.-Y.; Wang, L.-J.; Huang, Y.-P.; Chen, X.-Y. Silencing a cotton bollworm P450 monooxygenase gene by plant-mediated RNAi impairs larval tolerance of gossypol. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Swevers, L.; Iatrou, K.; Huvenne, H.; Smagghe, G. Bombyx mori DNA/RNA non-specific nuclease: Expression of isoforms in insect culture cells, subcellular localization and functional assays. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Fitches, E.C. A systematic study of RNAi effects and dsRNA stability in Tribolium castaneum and Acyrthosiphon pisum, following injection and ingestion of analogous dsRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loll, B.; Gebhardt, M.; Wahle, E.; Meinhart, A. Crystal structure of the EndoG/EndoGI complex: Mechanism of EndoG inhibition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 7312–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arimatsu, Y.; Kotani, E.; Sugimura, Y.; Furusawa, T. Molecular characterization of a cDNA encoding extracellular dsRNase and its expression in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Carrillo, A.; Renaud, J. Endonuclease G: A (dG)n X (dC)n-specific DNase from higher eukaryotes. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiranti, V.; Rossi, E.; Ruiz-Carrillo, A.; Rossi, G.; Rocchi, M.; DiDonato, S.; Zuffardi, O.; Zeviani, M. Chromosomal localization of mitochondrial transcription factor A (TCF6), single-stranded DNA-binding protein (SSBP), and endonuclease G (ENDOG), three human housekeeping genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis. Genomics 1995, 25, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimatsu, Y.; Furuno, T.; Sugimura, Y.; Togoh, M.; Ishihara, R.; Tokizane, M.; Kotani, E.; Hayashi, Y.; Furusawa, T. Purification and properties of double-stranded RNA-degrading nuclease, dsRNase, from the digestive juice of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Biotechnol. Seicol. 2007, 76, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynant, N.; Santos, D.; Verdonck, R.; Spit, J.; Van Wielendaele, P.; Vanden Broeck, J. Identification, functional characterization and phylogenetic analysis of double stranded RNA degrading enzymes present in the gut of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Q.; Luan, J.; Chung, S.H.; Van Eck, J.; Turgeon, R.; Douglas, A.E. Towards an understanding of the molecular basis of effective RNAi against a global insect pest, the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 88, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhu, G.; Han, Q.; Chen, J.; Elzaki, M.E.A.; Sheng, C.; Zhao, C.; Palli, S.R.; Han, Z. Identification and characterization of multiple dsRNases from a lepidopteran insect, the tobacco cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 162, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, O.; Swevers, L.; Smagghe, G. DsRNA degradation in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) associated with lack of response in RNAi feeding and injection assay. Peptides 2014, 53, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, K.; Fu, W.; Sheng, C.; Han, Z. Biochemical comparison of dsRNA degrading nucleases in four different insects. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Cooper, A.M.W.; Silver, K.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Ma, E.; Zhu, K.Y.; Zhang, J. A double-stranded RNA degrading enzyme reduces the efficiency of oral RNA interference in migratory locust. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 86, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spit, J.; Philips, A.; Wynant, N.; Santos, D.; Plaetinck, G.; Broeck, J.V. Knockdown of nuclease activity in the gut enhances RNAi efficiency in the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata, but not in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 81, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, K.; Smagghe, G.; Gheysen, G.; Christians, O. Nuclease activity decreases the RNAi response in the sweetpotato weevil Cylas puncticollis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 110, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.N. Research summary of rice leaf roller in foreign countries. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 1985, 31, 287–289. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.X.; Lu, Z.Q.; Geng, J.G.; Li, G.Z.; Chen, X.L.; Wu, X.W. Studies on the migration of rice leaf roller Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Guenee. Acta Entomol. Sin. 1980, 23, 130–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.C.; Zhang, G.F.; Xue, J.J.; Zhao, B.B.; Guo, S.Q.; Zhou, H. Prediction system model of rice leaf roller. Sci. Agric. Sin. 1988, 21, 58–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vatanparast, M.; Kim, Y. Optimization of recombinant bacteria expressing dsRNA to enhance insecticidal activity against a lepidopteran insect, Spodoptera exigua. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garbutt, J.S.; Belles, X.; Richards, E.H.; Reynolds, S.E. Persistence of double-stranded RNA in insect hemolymph as a potential determiner of RNA interference success: Evidence from Manduca sexta and Blattella germanica. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Component | Volume per Reaction, μL | Final Concentration | Cycling Step | Temperature, °C | Time | Ramp Rate | Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2× QX200 ddPCR EvaGreen Supermix | 10 | 1× | Enzyme activation | 95 | 5 min | 2 °C/s | 1 |
| Forward primer (2 μM) | 1 | 100 nM | Denaturation | 95 | 30 s | 40 | |
| Reverse primer (2 μM) | 1 | 100 nM | Annealing and extension | 60 | 1 min | ||
| Diluted cDNA template | 1 | 200 ng/μL | Signal stabilization | 4 | 5 min | 1 | |
| DNase-free water | 7 | - | 90 | 5 min | 1 | ||
| Total volume | 20 | - | Hold | 4 | Infinite | 1 |
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | Primer Usage |
|---|---|---|
| CmdsRNase-F | ATGCATTCGCTGGTGCTTC | RT-PCR |
| CmdsRNase-R | TTAGGACAGAAGACCAACAAC | |
| CmdsRNase-dF | GACGCCAAGTGCCAGTTCCT | ddPCR |
| CmdsRNase-dR | GTGCTTCAGCCGCCGTATAGT | |
| CmCHS-dF | TGGAATACCTTCGCCAGTCATC | |
| CmCHS-dR | CCAGGAACACCAGGAGGCATT | |
| CmdsRNase-iF | CGACAGGAATCGTCTTGAAG | dsRNA synthesis |
| CmdsRNase-iR | AGGCTATACGAGCACGGAGGT | |
| CmdsRNase-dsF | taatacgactcactatagggCGACAGGAATCGTCTTGAAG | |
| CmdsRNase-dsR | taatacgactcactatagggAGGCTATACGAGCACGGAGGT | |
| CmCHS-iF | ACGAGGTTACACGAGAGG | |
| CmCHS-iR | CATCCAATGTTCCAATGTTCCT | |
| CmCHS-dsF | taatacgactcactatagggACGAGGTTACACGAGAGG | |
| CmCHS-dsR | taatacgactcactatagggCATCCAATGTTCCAATGTTCCT | |
| GFP-iF | GCCAACACTTGTCACTACTT | |
| GFP-iR | GGAGTATTTTGTTGATAATGGTCTG | |
| GFP-dsF | taatacgactcactatagggGCCAACACTTGTCACTACTT | |
| GFP-dsR | taatacgactcactatagggGGAGTATTTTGTTGATAATGGTCTG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Du, J.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Identification and Characterization of a Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Influencing RNAi Efficiency in the Rice Leaf Folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073961
Li J, Du J, Li S, Wang X. Identification and Characterization of a Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Influencing RNAi Efficiency in the Rice Leaf Folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(7):3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073961
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiajing, Juan Du, Shangwei Li, and Xin Wang. 2022. "Identification and Characterization of a Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Influencing RNAi Efficiency in the Rice Leaf Folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 7: 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073961
APA StyleLi, J., Du, J., Li, S., & Wang, X. (2022). Identification and Characterization of a Double-Stranded RNA Degrading Nuclease Influencing RNAi Efficiency in the Rice Leaf Folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(7), 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073961





