BRCA2 C-Terminal RAD51-Binding Domain Confers Resistance to DNA-Damaging Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
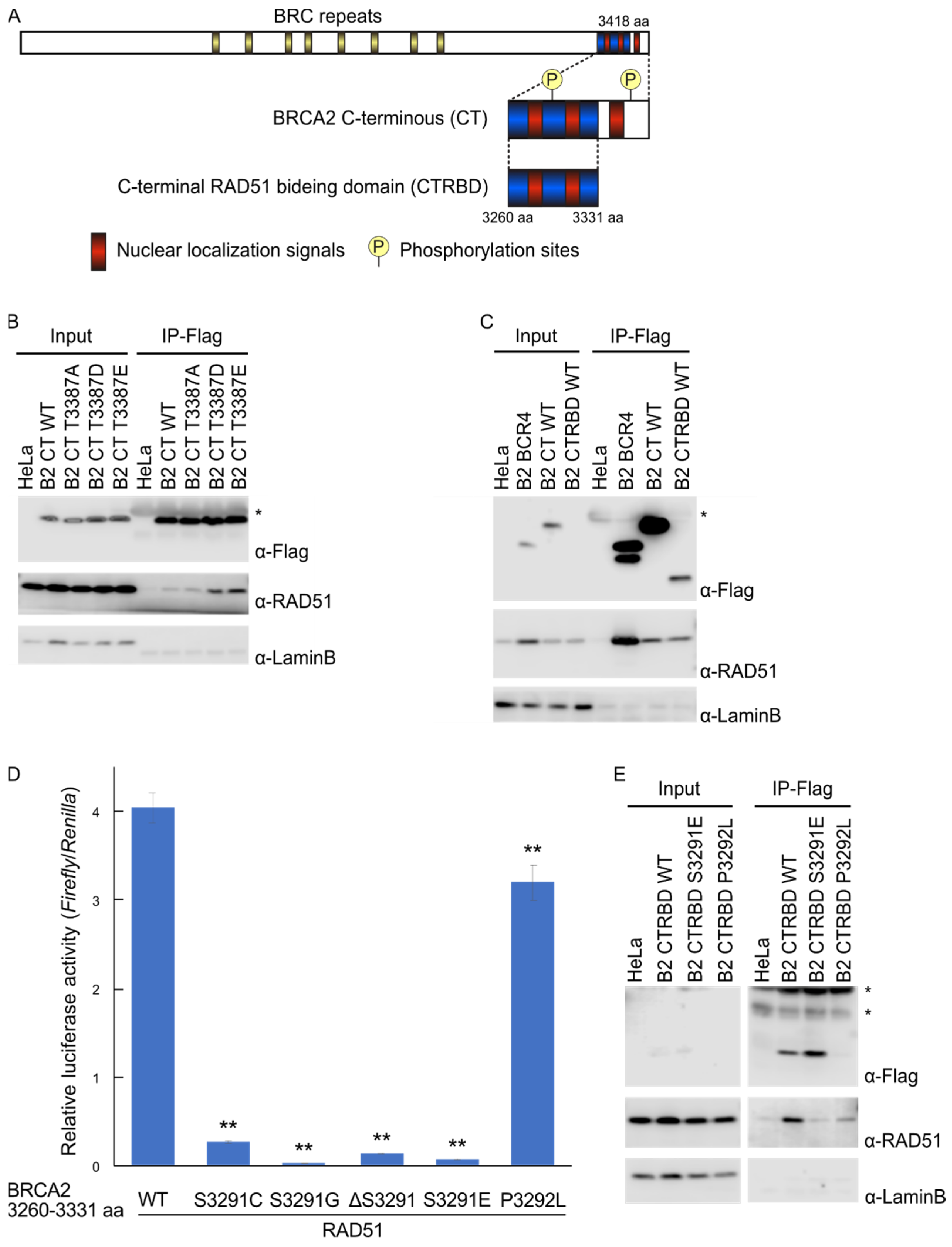
2.1. Phosphorylation Sites and the C-Terminal Flanking Region of CTRBD Affect RAD51 Interaction
2.2. CTRBD but Not BRCA2 C-Terminus Confers Resistance to X-ray Irradiation and MMC Treatment
2.3. Resistance to X-ray Irradiation Conferred by CTRBD Depends on Endogenous BRCA2
2.4. Exogenous Expression of BRCA2 CTRBD Affects HR Efficiency but Not NHEJ Efficiency
2.5. CTRBD Expression Does Not Affect Cell Cycle Kinetics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture, Antibodies, and Generated Cell Lines
4.2. Immunoprecipitation
4.3. Mammalian Two-Hybrid Assay
4.4. Clonogenic Assay
4.5. HR and NHEJ Assay
4.6. Immunostaining and Microscopy
4.7. Cell Cycle Analysis Using Flow Cytometry
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van de Kamp, G.; Heemskerk, T.; Kanaar, R.; Essers, J. DNA double strand break repair pathways in response to different types of ionizing radiation. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 738230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, S.; Tsuda, M.; Bunch, H.; Sasanuma, H.; Austin, C.; Takeda, S. Type II DNA topoisomerases cause spontaneous double-strand breaks in genomic DNA. Genes 2019, 10, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, N.; Seo, E.-J.; Efferth, T. Prevention from Radiation Damage by Natural Products. Phytomedicine 2018, 47, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, P.; Hartmann, L.; Wenz, F.; Herskind, C. Cellular Pathways in Response to Ionizing Radiation and Their Targetability for Tumor Radiosensitization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Citrin, D.E. Radiation Modifiers. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.H. Recognition, Signaling, and Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks Produced by Ionizing Radiation in Mammalian Cells: The Molecular Choreography. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2012, 751, 158–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michl, J.; Zimmer, J.; Tarsounas, M. Interplay between Fanconi Anemia and Homologous Recombination Pathways in Genome Integrity. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-X.; Zhou, P.-K. DNA Damage Response Signaling Pathways and Targets for Radiotherapy Sensitization in Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, K.; Mayer, C.; Wanner, G.; Kehlbach, R.; Rodemann, H.P. The Radioprotector O-Phospho-Tyrosine Stimulates DNA-Repair via Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor- and DNA-Dependent Kinase Phosphorylation. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 84, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, R.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, W.; Jasin, M. Homologous Recombination and Human Health: The Roles of BRCA1, BRCA2, and Associated Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a016600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.T.; Kim, T.; Wagner, J.E.; Conti, B.A.; Lach, F.P.; Huang, A.L.; Molina, H.; Sanborn, E.M.; Zierhut, H.; Cornes, B.K.; et al. A Dominant Mutation in Human RAD51 Reveals Its Function in DNA Interstrand Crosslink Repair Independent of Homologous Recombination. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakai, W.; Swisher, E.M.; Karlan, B.Y.; Agarwal, M.K.; Higgins, J.; Friedman, C.; Villegas, E.; Jacquemont, C.; Farrugia, D.J.; Couch, F.J.; et al. Secondary Mutations as a Mechanism of Cisplatin Resistance in BRCA2-Mutated Cancers. Nature 2008, 451, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Heyer, W.-D. Homologous Recombination in DNA Repair and DNA Damage Tolerance. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carreira, A.; Kowalczykowski, S.C. Two Classes of BRC Repeats in BRCA2 Promote RAD51 Nucleoprotein Filament Function by Distinct Mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10448–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esashi, F.; Christ, N.; Gannon, J.; Liu, Y.; Hunt, T.; Jasin, M.; West, S.C. CDK-Dependent Phosphorylation of BRCA2 as a Regulatory Mechanism for Recombinational Repair. Nature 2005, 434, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esashi, F.; Galkin, V.E.; Yu, X.; Egelman, E.H.; West, S.C. Stabilization of RAD51 Nucleoprotein Filaments by the C-Terminal Region of BRCA2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, O.R.; Pellegrini, L. Interaction with the BRCA2 C Terminus Protects RAD51–DNA Filaments from Disassembly by BRC Repeats. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, P.R.; Seo, J.; Wiek, C.; Hanenberg, H. Understanding BRCA2 function as a tumor suppressor based on domain-specific activities in DNA damage responses. Genes 2021, 12, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahassi, E.M.; Ovesen, J.L.; Riesenberg, A.L.; Bernstein, W.Z.; Hasty, P.E.; Stambrook, P.J. The Checkpoint Kinases Chk1 and Chk2 Regulate the Functional Associations between HBRCA2 and Rad51 in Response to DNA Damage. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3977–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y.; Mi, K.; Li, M.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Z.; Huang, J. Association of somatic mutations in BRCA2 BRC domain with chemotherapy sensitivity and survival in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 406, 112742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomme, J.; Renodon-Cornière, A.; Asanomi, Y.; Sakaguchi, K.; Stasiak, A.Z.; Stasiak, A.; Norden, B.; Tran, V.; Takahashi, M. Design of Potent Inhibitors of Human RAD51 Recombinase Based on BRC Motifs of BRCA2 Protein: Modeling and Experimental Validation of a Chimera Peptide. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5782–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trenner, A.; Godau, J.; Sartori, A.A. A Short BRCA2-Derived Cell-Penetrating Peptide Targets RAD51 Function and Confers Hypersensitivity towards PARP Inhibition. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, D.E.; Francis-Newton, N.J.; Marsh, M.E.; Coyne, A.G.; Fischer, G.; Moschetti, T.; Bayly, A.R.; Sharpe, T.D.; Haas, K.T.; Barber, L.; et al. A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the BRCA2-RAD51 Interaction Modulates RAD51 Assembly and Potentiates DNA Damage-Induced Cell Death. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 835–847.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Morimatsu, M.; Ochiai, K.; Ishiguro-Oonuma, T.; Morioka, R.; Okuda, K.; Orino, K. Identification of the Core Motif of the BRCA2 C-Terminal RAD51-Binding Domain by Comparing Canine and Human BRCA2. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennardo, N.; Cheng, A.; Huang, N.; Stark, J.M. Alternative-NHEJ Is a Mechanistically Distinct Pathway of Mammalian Chromosome Break Repair. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pierce, A.J.; Johnson, R.D.; Thompson, L.H.; Jasin, M. XRCC3 Promotes Homology-Directed Repair of DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2633–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, C.; Moynahan, M.E.; Jasin, M. Double-Strand Break Repair by Interchromosomal Recombination: Suppression of Chromosomal Translocations. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3831–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, C.C.; Zhan, B.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Haas, W.; Gygi, S.P.; Cohn, M.A. UHRF1 Is a Sensor for DNA Interstrand Crosslinks and Recruits FANCD2 to Initiate the Fanconi Anemia Pathway. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moffat, J.; Grueneberg, D.A.; Yang, X.; Kim, S.Y.; Kloepfer, A.M.; Hinkle, G.; Piqani, B.; Eisenhaure, T.M.; Luo, B.; Grenier, J.K.; et al. A Lentiviral RNAi Library for Human and Mouse Genes Applied to an Arrayed Viral High-Content Screen. Cell 2006, 124, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Guertin, D.A.; Ali, S.M.; Sabatini, D.M. Phosphorylation and Regulation of Akt/PKB by the Rictor-MTOR Complex. Science 2005, 307, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Ochiai, K.; Morimatsu, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Wada, S.; Taoda, T.; Iwai, S.; Chikazawa, S.; Orino, K.; Watanabe, K. Effects of the Missense Mutations in Canine BRCA2 on BRC Repeat 3 Functions and Comparative Analyses between Canine and Human BRC Repeat 3. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ochiai, K.; Morimatsu, M.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Syuto, B.; Hashizume, K. Brca2 C-Terminus Interacts with Rad51 and Contributes to Nuclear Focus Formation in Double-Strand Break Repair of DNA. Biomed. Res. 2004, 25, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Kitano, T.; Morimatsu, M.; Tanaka, A.; Morioka, R.; Lin, X.; Orino, K.; Yoshikawa, Y. BRCA2 C-Terminal RAD51-Binding Domain Confers Resistance to DNA-Damaging Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23074060
Zhu Z, Kitano T, Morimatsu M, Tanaka A, Morioka R, Lin X, Orino K, Yoshikawa Y. BRCA2 C-Terminal RAD51-Binding Domain Confers Resistance to DNA-Damaging Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(7):4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23074060
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zida, Taisuke Kitano, Masami Morimatsu, Arisa Tanaka, Ryo Morioka, Xianghui Lin, Koichi Orino, and Yasunaga Yoshikawa. 2022. "BRCA2 C-Terminal RAD51-Binding Domain Confers Resistance to DNA-Damaging Agents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 7: 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23074060
APA StyleZhu, Z., Kitano, T., Morimatsu, M., Tanaka, A., Morioka, R., Lin, X., Orino, K., & Yoshikawa, Y. (2022). BRCA2 C-Terminal RAD51-Binding Domain Confers Resistance to DNA-Damaging Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(7), 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23074060






