Comparative Genomic Analysis of Vibrio cincinnatiensis Provides Insights into Genetic Diversity, Evolutionary Dynamics, and Pathogenic Traits of the Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Genomic Information for V. cincinnatiensis
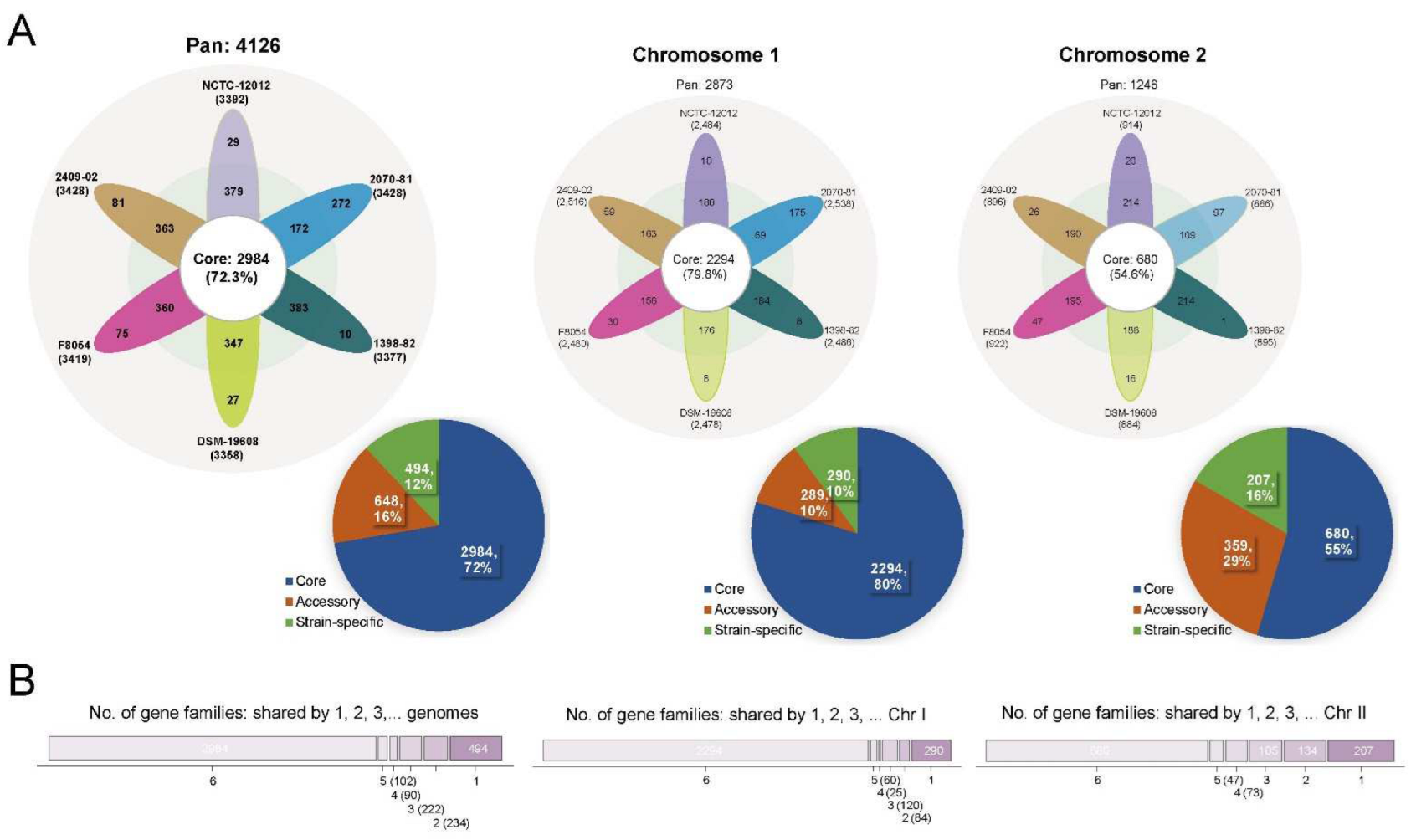
2.2. Pan-Genome Analyses Revealed That a High Degree of Genetic Variability on Chr II Promoted the Genetic Diversity of V. cincinnatiensis
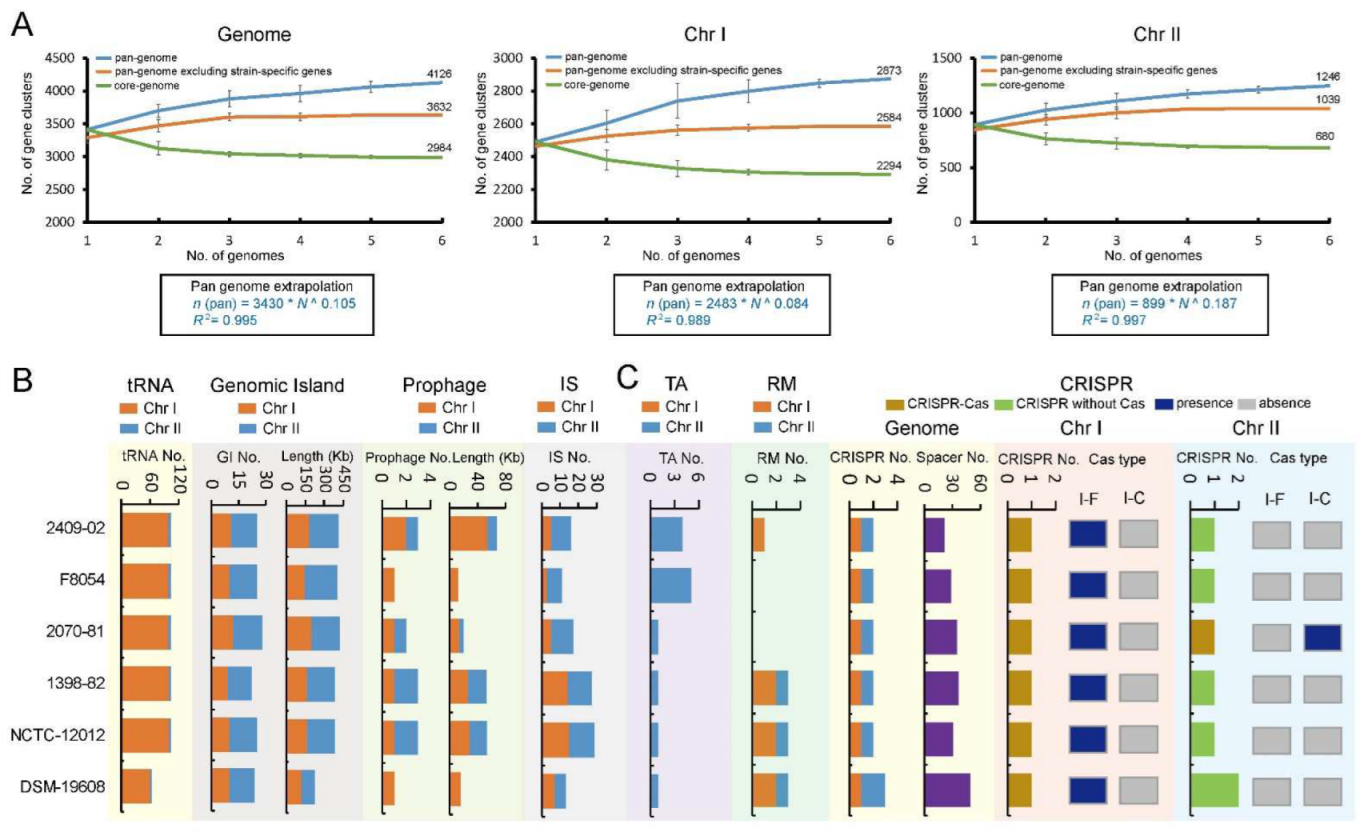
2.3. An Open Pan-Genome of V. cincinnatiensis Exhibited the Potential for Genetic Innovation, Especially for Chr II
2.4. Distribution of tRNAs, Mobile Genetic Elements, and Multiple Barriers in the V. cincinnatiensis Genomes
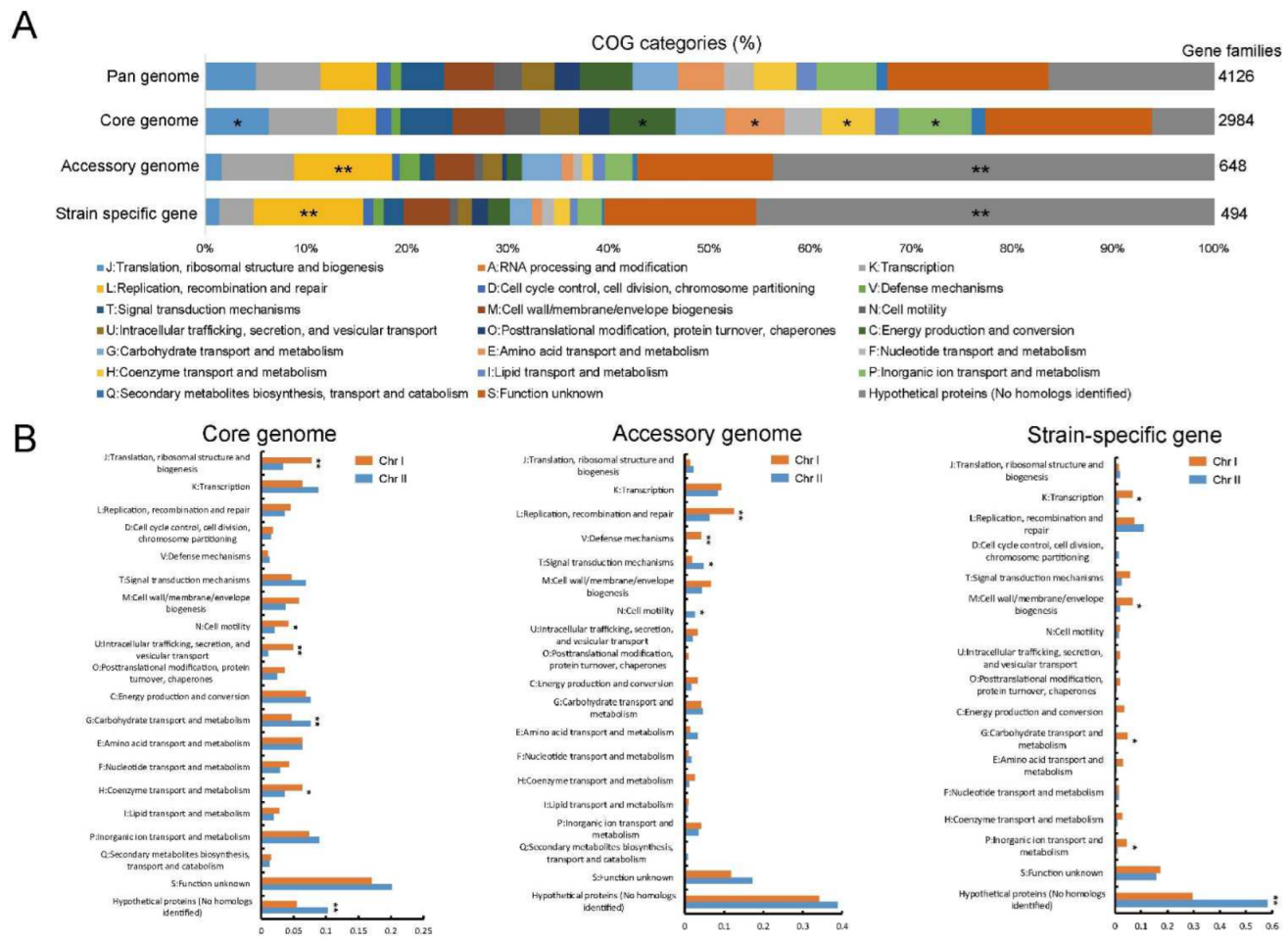
2.5. Comparison of Functional Characteristics for Pan-Genome Revealed the Evolutionary Divergence
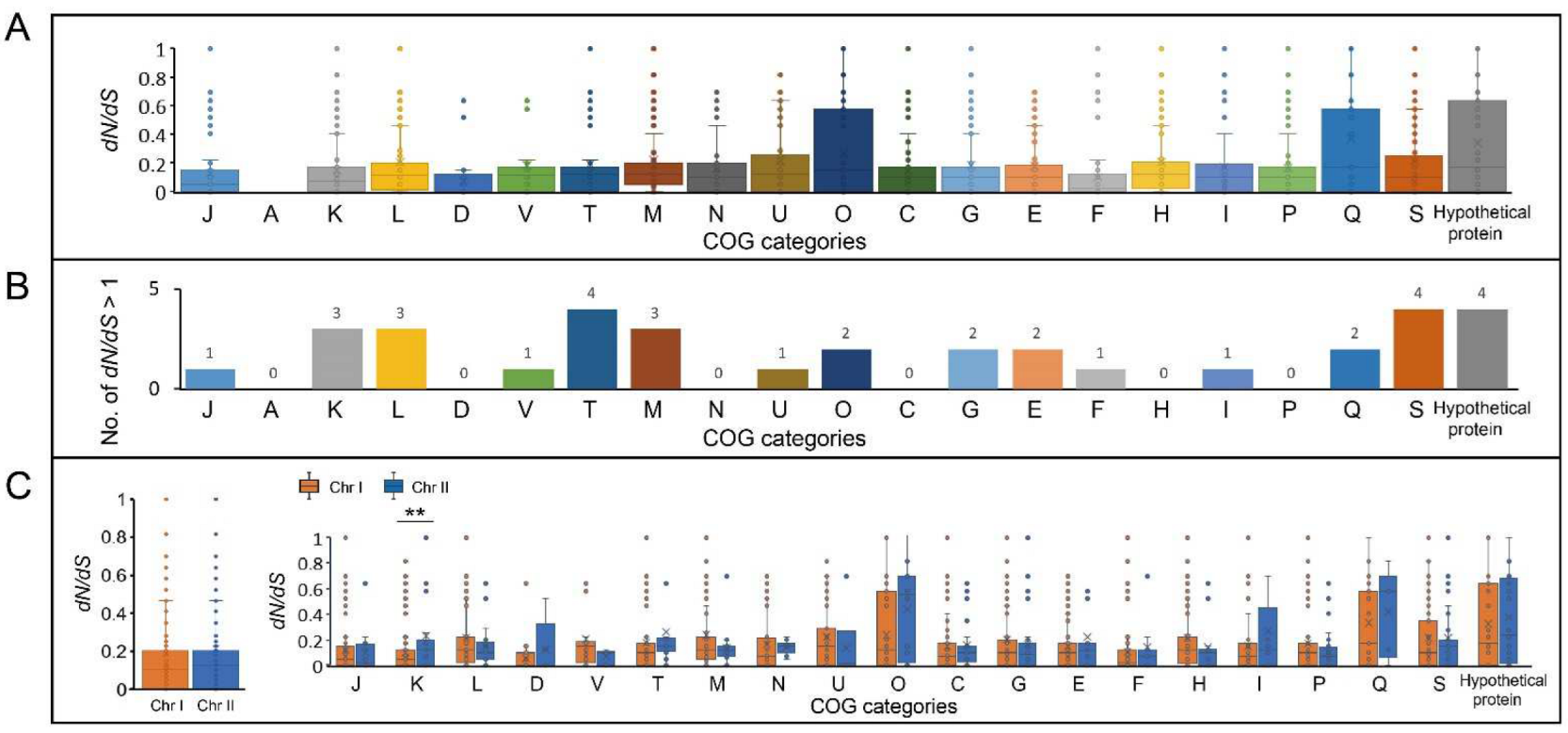
2.6. Selective Pressure Analysis Exhibited the Dynamics of Natural Selection in Core Genome
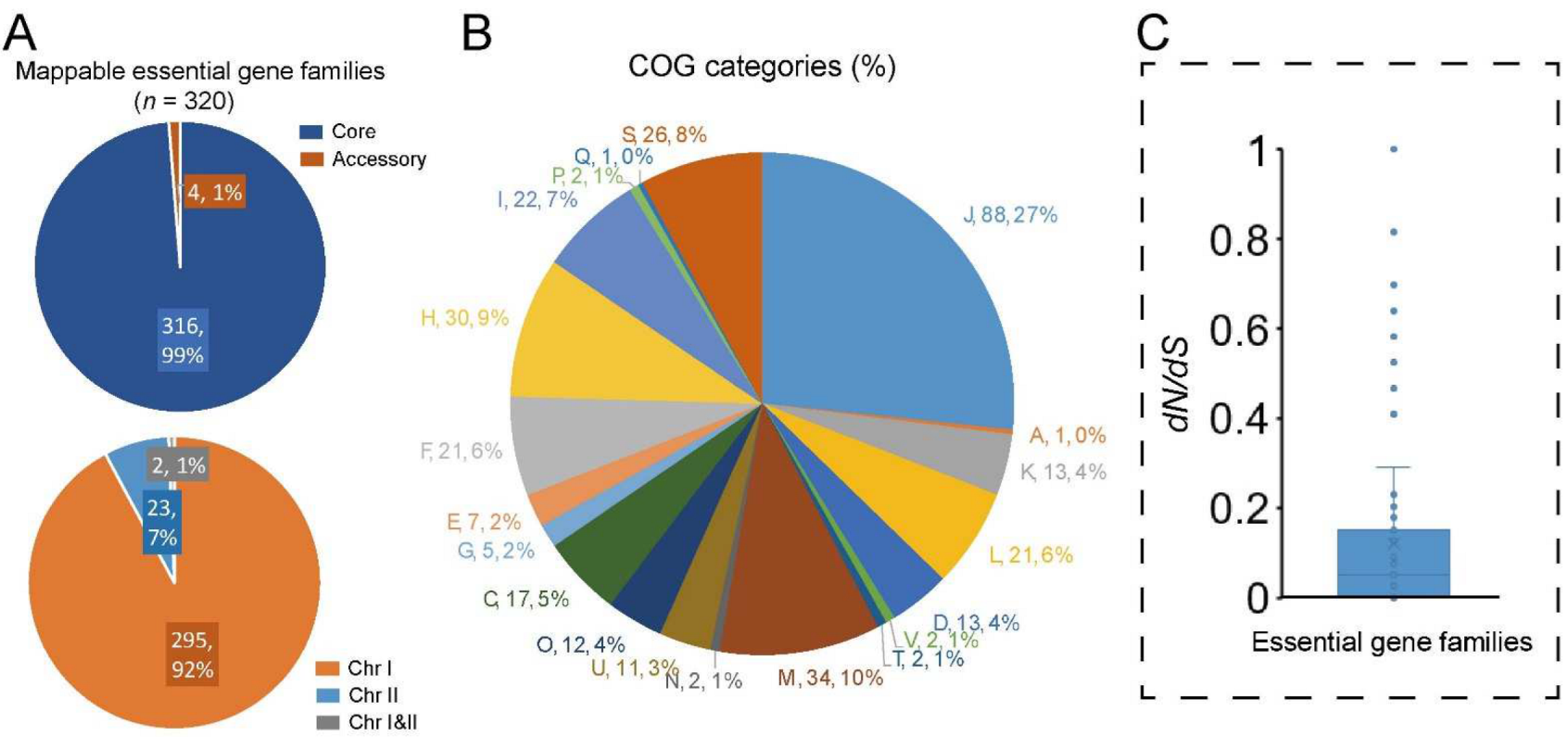
2.7. Evaluation of Potential Essential Genes in V. cincinnatiensis
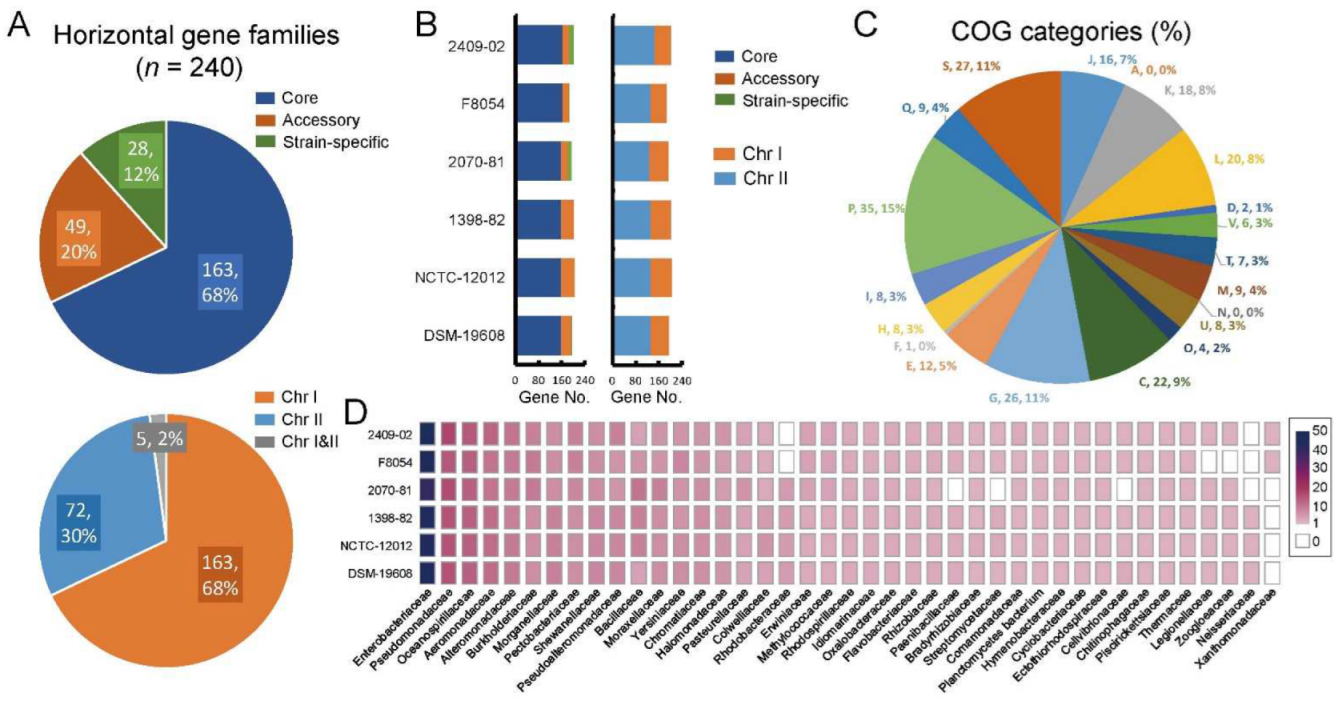
2.8. Identification of Potential Horizontal Gene Families in V. cincinnatiensis
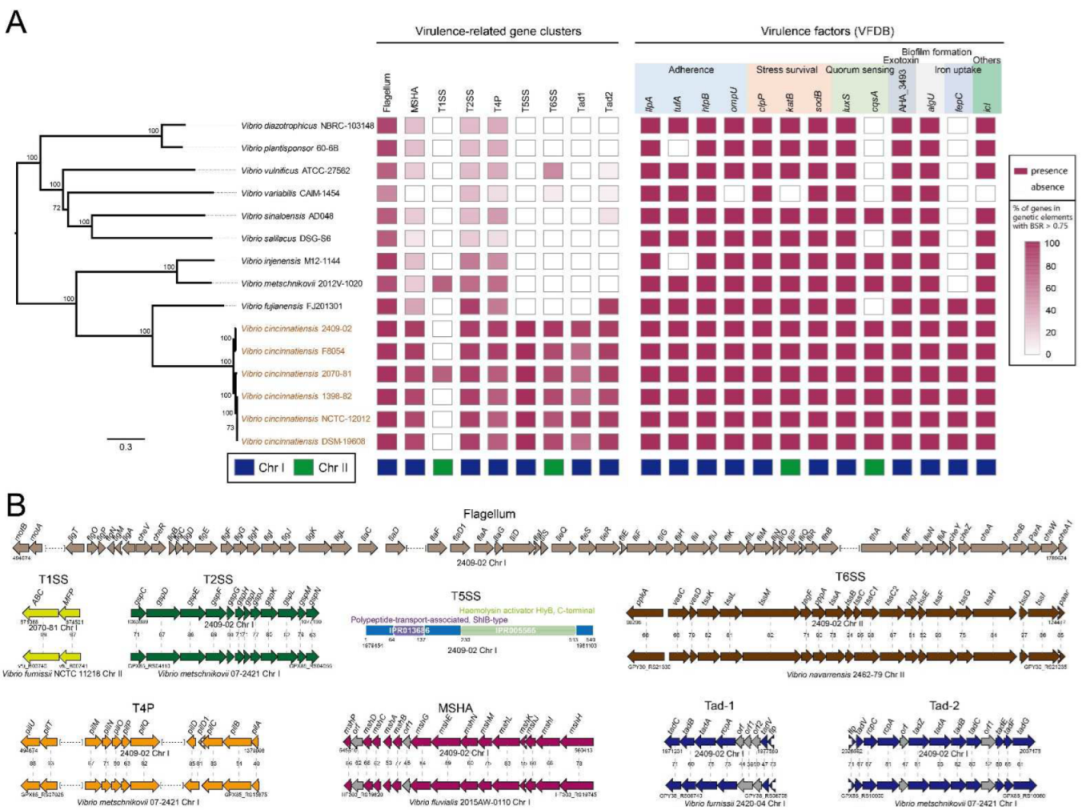
2.9. Phylogenetic Position of V. Cincinnatiensis in the Genus Vibrio
2.10. HGT Promoted Genotypic Profile of Virulence in V. cincinnatiensis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Genome Collection and Annotation
3.2. Pan-Genome Analysis
3.3. Identification of MGEs and Barriers to HGT
3.4. Selective Pressure Analysis
3.5. Identification of Potential Horizontal Genes
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.7. Genomic Characteristic Analysis
3.8. Identification of Virulence-Related Genetic Elements and Resistance Genes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker-Austin, C.; Trinanes, J.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Non-Cholera Vibrios: The Microbial Barometer of Climate Change. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Oliver, J.D.; Alam, M.; Ali, A.; Waldor, M.K.; Qadri, F.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Vibrio spp. infections. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roux, F.; Blokesch, M. Eco-evolutionary Dynamics Linked to Horizontal Gene Transfer in Vibrios. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 72, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazen, T.H.; Pan, L.; Gu, J.-D.; Sobecky, P.A. The contribution of mobile genetic elements to the evolution and ecology of Vibrios. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 74, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y. Entry of Vibrio cincinnatiensis into viable but nonculturable state and its resuscitation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, R.B.; Brayton, P.R.; Colwell, R.R.; Russo, F.M.; Bullock, W.E. A new Vibrio species, Vibrio cincinnatiensis, causing meningitis: Successful treatment in an adult. Ann. Intern. Med. 1986, 104, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuthe, H.H.; Aleksić, S.; Hein, W. Contribution to some phenotypical characteristics of Vibrio cincinnatiensis. Studies in one strain of a diarrhoeic human patient and in two isolates from aborted bovine fetuses. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. 1993, 279, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Heidemann Olsen, R.; Ye, L.; Yan, H.; Nie, Q.; Meng, H.; Shi, L. Antimicrobial Resistance and Resistance Genes in Aerobic Bacteria Isolated from Pork at Slaughter. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Pang, Q. Complement-mediated killing of Vibrio species by the humoral fluids of amphioxus Branchiostoma belcheri: Implications for a dual role of O-antigens in the resistance to bactericidal activity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qian, D.; Yan, X.J. Studies on pathogenicity and prevalence of white spot syndrome virus in mud crab, Scylla serrata (Forskal), in Zhejiang Province, China. J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäckel, C.; Hammerl, J.A.; Arslan, H.-H.-T.; Göllner, C.; Vom Ort, N.; Taureck, K.; Strauch, E. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Veterinary Vibrio cincinnatiensis Isolates. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Pang, L.; Qi, Z.; Chen, J.; Austin, B.; Zhang, X.-H. Distribution of five vibrio virulence-related genes among Vibrio harveyi isolates. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heidelberg, J.F.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Colwell, R.R. Seasonality of Chesapeake Bay bacterioplankton species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5488–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ripabelli, G.; Sammarco, M.L.; Grasso, G.M.; Fanelli, I.; Caprioli, A.; Luzzi, I. Occurrence of Vibrio and other pathogenic bacteria in Mytilus galloprovincialis (mussels) harvested from Adriatic Sea, Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 49, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, K.; Kiiyukia, C.; Takaki, M.; Nakano, H.; Matsuda, H.; Kawakami, H.; Hashimoto, H. Characterization of toxigenic vibrios isolated from the freshwater environment of Hiroshima, Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 2613–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sulca, M.A.; Orozco, R.; Alvarado, D.E. Antimicrobial resistance not related to 1,2,3 integrons and Superintegron in Vibrio spp. isolated from seawater sample of Lima (Peru). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, J.; Du, B.; Ruan, H.H.; Huo, Y.X.; Du, Y.; Qiao, J. Whole-Genome-Based Survey for Polyphyletic Serovars of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Provides New Insights into Public Health Surveillance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 21, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Yuan, C.; Du, Y.; Yang, P.; Qian, C.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.; Liu, B. Comparative genomic analysis of the Hafnia genus reveals an explicit evolutionary relationship between the species alvei and paralvei and provides insights into pathogenicity. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, D.; Dong, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; et al. Metabacillus dongyingensis sp. nov. Is Represented by the Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium BY2G20 Isolated from Saline-Alkaline Soil and Enhances the Growth of Zea mays L. under Salt Stress. mSystems 2022, 8, e0142621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, J.; Cheng, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Chen, H. Comparative Genomic Analysis Reveals Genetic Mechanisms of the Variety of Pathogenicity, Antibiotic Resistance, and Environmental Adaptation of Providencia Genus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 572642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibani, C.M.; Roth, O.; Liesegang, H.; Wendling, C.C. Genomic variation among closely related Vibrio alginolyticus strains is located on mobile genetic elements. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathamuni, S.; Jangam, A.K.; Katneni, V.K.; Selvaraj, A.; Krishnan, K.; Kumar, S.; Avunje, S.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Grover, M.; Alavandi, S.V.; et al. Insights on genomic diversity of Vibrio spp. through Pan-genome analysis. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettelin, H.; Riley, D.; Cattuto, C.M.D. Comparative genomics: The bacterial pan-genome. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Han, M.; Yang, P.; Chen, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Ning, K. Comprehensive Analysis Reveals the Evolution and Pathogenicity of Aeromonas, Viewed from Both Single Isolated Species and Microbial Communities. mSystems 2019, 4, e00252-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Yuan, C.; Jiang, L.; Du, Y. Horizontal Gene Transfer Clarifies Taxonomic Confusion and Promotes the Genetic Diversity and Pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides. mSystems 2020, 5, e00448-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochman, H.; Lawrence, J.G.; Groisman, E. A Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature 2000, 405, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fan, Y.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Qian, C.; et al. Genomic insights into evolution of pathogenicity and resistance of multidrug-resistant Raoultella ornithinolytica WM1. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1497, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Qian, C.; Sun, L.; Pang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Huang, W.; Cui, S.; Zhang, C.; et al. Pan-Genome Analysis of Delftia tsuruhatensis Reveals Important Traits Concerning the Genetic Diversity, Pathogenicity, and Biotechnological Properties of the Species. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 11, e0207221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Matelska, D.; Ginalski, K.; Riegel, P.; Hansmann, Y.; Bloom, J.; Pestel-Caron, M.; Dahyot, S.; Lebeurre, J.; Prévost, G. Comparative genomic analysis of Staphylococcus lugdunensis shows a closed pan-genome and multiple barriers to horizontal gene transfer. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, N.; Dudley, E.G. CRISPRs: Molecular Signatures Used for Pathogen Subtyping. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordan, I.K.; Rogozin, I.B.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E. V Essential genes are more evolutionarily conserved than are nonessential genes in bacteria. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bekaert, M.; Goffin, N.; McMillan, S.; Desbois, A.P. Essential Genes of Vibrio anguillarum and Other Vibrio spp. Guide the Development of New Drugs and Vaccines. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 755801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, T.P.; Chao, M.C.; Abel, S.; Blondel, C.J.; Abel Zur Wiesch, P.; Zhou, X.; Davis, B.M.; Waldor, M.K. Genetic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus intestinal colonization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6283–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chao, M.C.; Pritchard, J.R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Rubin, E.J.; Livny, J.; Davis, B.M.; Waldor, M.K. High-resolution definition of the Vibrio cholerae essential gene set with hidden Markov model-based analyses of transposon-insertion sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 9033–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sriskanda, V.; Shuman, S. A second NAD(+)-dependent DNA ligase (LigB) in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4930–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watnick, P.I.; Lauriano, C.M.; Klose, K.E.; Croal, L.; Kolter, R. The absence of a flagellum leads to altered colony morphology, biofilm development and virulence in Vibrio cholerae O139. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utada, A.S.; Bennett, R.R.; Fong, J.C.N.; Gibiansky, M.L.; Yildiz, F.H.; Golestanian, R.; Wong, G.C.L. Vibrio cholerae use pili and flagella synergistically to effect motility switching and conditional surface attachment. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shime-Hattori, A.; Iida, T.; Arita, M.; Park, K.-S.; Kodama, T.; Honda, T. Two type IV pili of Vibrio parahaemolyticus play different roles in biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 264, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, T.L.; Fong, J.C.; Rule, C.; Rogers, A.; Yildiz, F.H.; Sandkvist, M. The Type II secretion system delivers matrix proteins for biofilm formation by Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 4245–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duong-Nu, T.-M.; Jeong, K.; Hong, S.H.; Puth, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Tan, W.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, S.E.; Rhee, J.H. A stealth adhesion factor contributes to Vibrio vulnificus pathogenicity: Flp pili play roles in host invasion, survival in the blood stream and resistance to complement activation. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sikora, A.E. Proteins Secreted via the Type II Secretion System: Smart Strategies of Vibrio cholerae to Maintain Fitness in Different Ecological Niches. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanonenberg, K.; Schwarz, C.K.W.; Schmitt, L. Type I secretion systems—A story of appendices. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntyre, D.L.; Miyata, S.T.; Kitaoka, M.; Pukatzki, S. The Vibrio cholerae type VI secretion system displays antimicrobial properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19520–19524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, T.; Sabharwal, D.; Bröms, J.; Milton, D.L.; Sjöstedt, A.; Uhlin, B.E.; Wai, S.N. Pathoadaptive conditional regulation of the type VI secretion system in Vibrio cholerae O1 strains. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.C.E.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Solving fundamental biases in whole genome comparisons dramatically improves orthogroup inference accuracy. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaps, H.S. Information Retrieval-Computational and Theoretical Aspects; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Expanded Microbial genome coverage and improved protein family annotation in the COG database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D261–D269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Forslund, K.; Coelho, L.P.; Szklarczyk, D.; Jensen, L.J.; Von Mering, C.; Bork, P. Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arndt, D.; Grant, J.R.; Marcu, A.; Sajed, T.; Pon, A.; Liang, Y.; Wishart, D.S. PHASTER: A better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W16–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertelli, C.; Laird, M.R.; Williams, K.P.; Lau, B.Y.; Hoad, G.; Winsor, G.L.; Brinkman, F.S.L. IslandViewer 4: Expanded prediction of genomic islands for larger-scale datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W30–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waack, S.; Keller, O.; Asper, R.; Brodag, T.; Damm, C.; Fricke, W.F.; Surovcik, K.; Meinicke, P.; Merkl, R. Score-based prediction of genomic islands in prokaryotic genomes using hidden Markov models. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsiao, W.; Wan, I.; Jones, S.J.; Brinkman, F.S.L. IslandPath: Aiding detection of genomic islands in prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Hsiao, W.W.L.; Brinkman, F.S.L. Evaluation of genomic island predictors using a comparative genomics approach. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siguier, P.; Perochon, J.; Lestrade, L.; Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. ISfinder: The reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Wei, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Tai, C.; Deng, Z.; Ou, H.-Y. TADB 2.0: An updated database of bacterial type II toxin-antitoxin loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D749–D753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roer, L.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Lukjancenko, O.; Kaas, S.; Hasman, H. Is the Evolution of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Linked to Restriction-Modification Systems? mSystems 2016, 1, e00009–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Couvin, D.; Bernheim, A.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Touchon, M.; Michalik, J.; Néron, B.; Rocha, E.P.C.; Vergnaud, G.; Gautheret, D.; Pourcel, C. CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W246–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Dai, L. ParaAT: A parallel tool for constructing multiple protein-coding DNA alignments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 419, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, B.; Moola, S.; Mabona, A.; Weighill, T.; Sheward, D.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Scheffler, K. FUBAR: A fast, unconstrained bayesian AppRoximation for inferring selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Kosoy, M.; Dittmar, K. HGTector: An automated method facilitating genome-wide discovery of putative horizontal gene transfers. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability Article Fast Track. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Didelot, X.; Wilson, D.J. ClonalFrameML: Efficient Inference of Recombination in Whole Bacterial Genomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurtz, S.; Phillippy, A.; Delcher, A.L.; Smoot, M.; Shumway, M.; Antonescu, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touchon, M.; Rocha, E.P.C.; Abby, S.S.; Ne, B. MacSyFinder: A Program to Mine Genomes for Molecular Systems with an Application to CRISPR-Cas Systems. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abby, S.S.; Rocha, E.P.C. Identification of protein secretion systems in bacterial genomes using MacSyFinder. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1615, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Blum, M.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Brown, S.D.; Chang, H.-Y.; El-Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.I.; et al. InterPro in 2019: Improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D351–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; Cattoir, V.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strain | Assembly | Genome | Chromosome I | Chromosome II | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (bp) | GC Content (%) | Gene No. | Length (bp) | GC Content (%) | Gene No. | Length (bp) | GC Content (%) | Gene No. | ||
| 2409-02 | Complete | 3,799,536 | 43.8 | 3533 | 2,796,027 | 44.2 | 2575 | 1,003,509 | 42.6 | 958 |
| F8054 | Complete | 3,802,622 | 43.7 | 3533 | 2,768,337 | 44.2 | 2539 | 1,034,285 | 42.5 | 994 |
| 2070-81 | Complete | 3,807,910 | 43.8 | 3519 | 2,805,763 | 44.2 | 2591 | 1,002,147 | 42.6 | 928 |
| 1398-82 | Complete | 3,781,792 | 43.8 | 3496 | 2,771,467 | 44.2 | 2548 | 1,010,325 | 42.7 | 948 |
| NCTC-12012 | Scaffold | 3,800,816 | 43.8 | 3541 | 2,772,819 | 44.2 | 2546 | 1,027,997 | 42.7 | 995 |
| DSM-19608 | Contig | 3,665,830 | 43.7 | 3434 | 2,698,098 | 44.04 | 2525 | 966,360 | 42.8 | 908 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, B.; Yue, J.; Yin, Z. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Vibrio cincinnatiensis Provides Insights into Genetic Diversity, Evolutionary Dynamics, and Pathogenic Traits of the Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094520
Du Y, Jin Y, Li B, Yue J, Yin Z. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Vibrio cincinnatiensis Provides Insights into Genetic Diversity, Evolutionary Dynamics, and Pathogenic Traits of the Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094520
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yuhui, Yuan Jin, Beiping Li, Junjie Yue, and Zhiqiu Yin. 2022. "Comparative Genomic Analysis of Vibrio cincinnatiensis Provides Insights into Genetic Diversity, Evolutionary Dynamics, and Pathogenic Traits of the Species" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094520
APA StyleDu, Y., Jin, Y., Li, B., Yue, J., & Yin, Z. (2022). Comparative Genomic Analysis of Vibrio cincinnatiensis Provides Insights into Genetic Diversity, Evolutionary Dynamics, and Pathogenic Traits of the Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094520






