Integrative Analysis of Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Molecular Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Metabolism in the Zikui Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis cv. Zikui)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
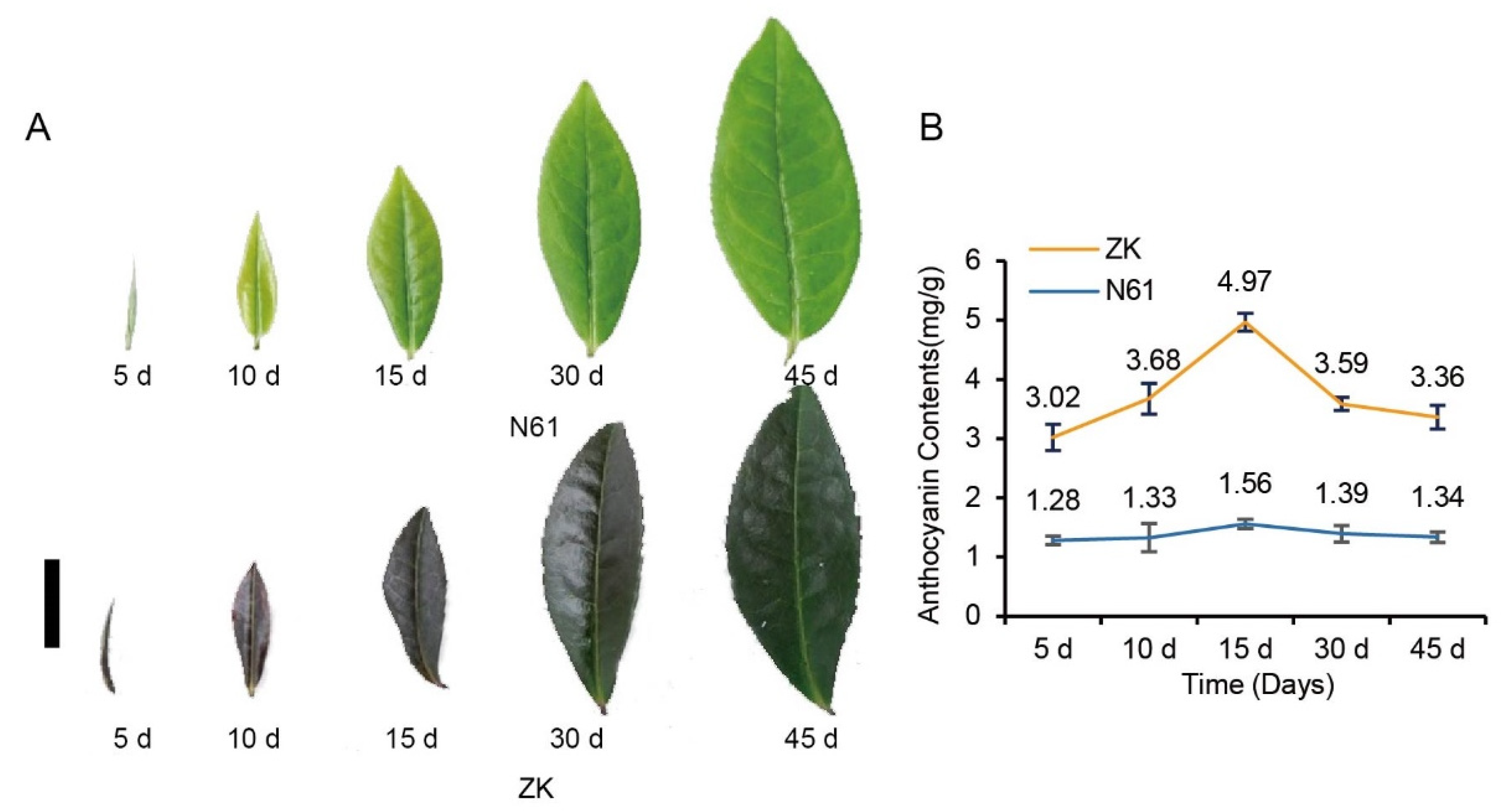
2.1. Phenotypic Observation and Anthocyanin Content in ZK and N61 in Different Periods
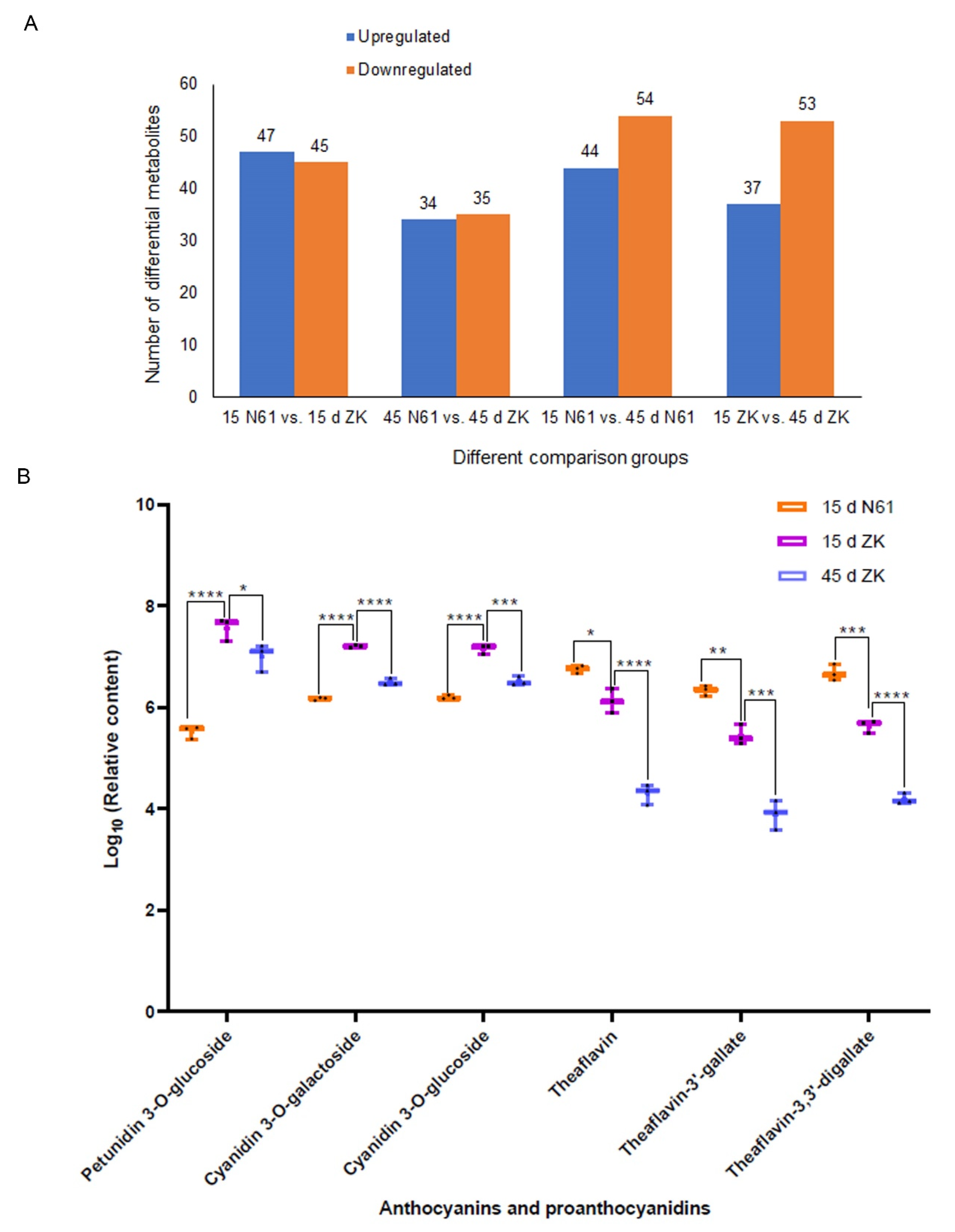
2.2. Analysis of Differential Metabolite Components and Relative Contents in ZK and N61
2.3. Analysis of Transcriptome Sequencing Quality
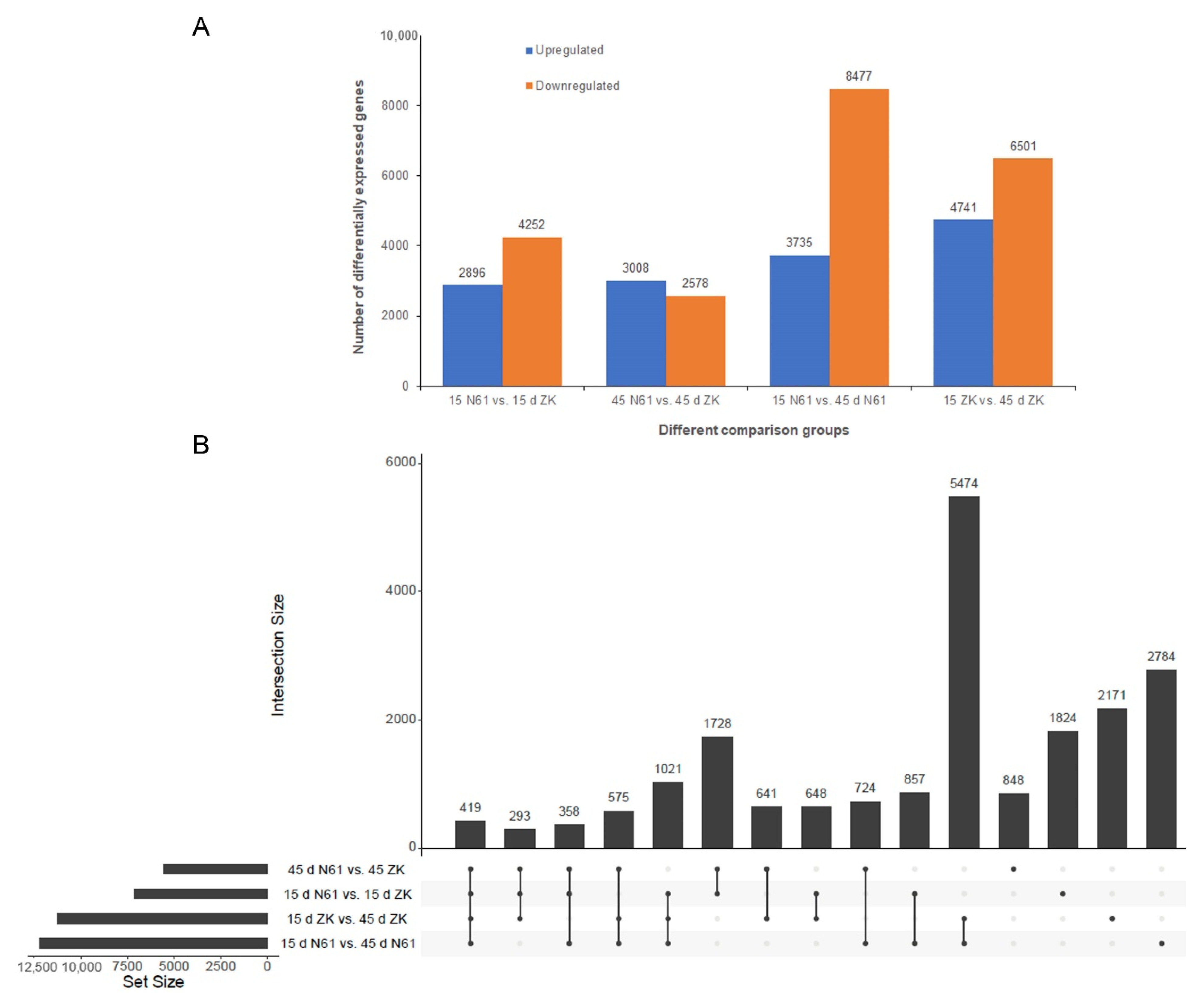
2.4. Analysis of DEGs in ZK and N61
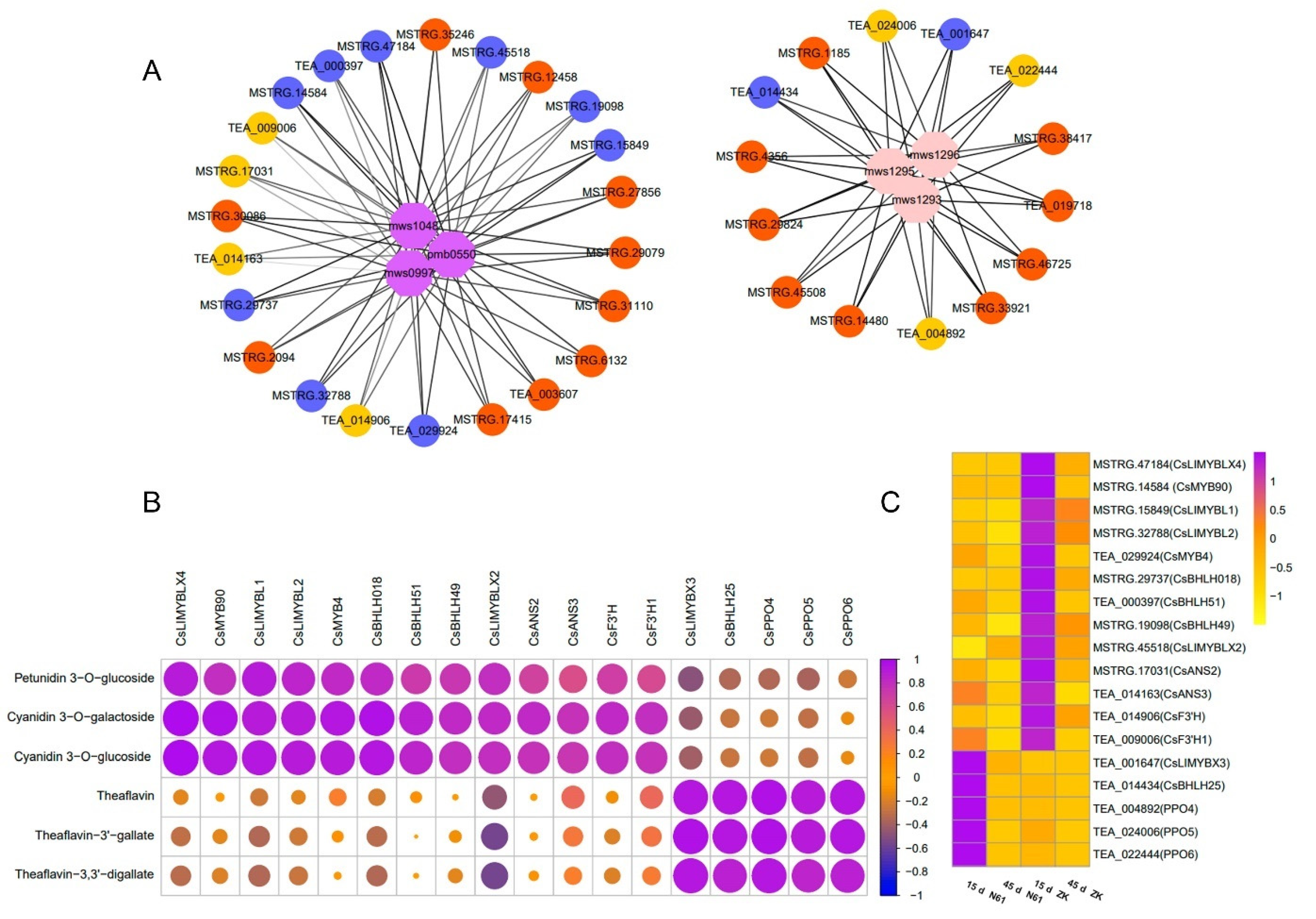
2.5. Candidate Genes for Purple Coloration Obtained by Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis
2.6. Regulation of Anthocyanidin Biosynthesis and Accumulation
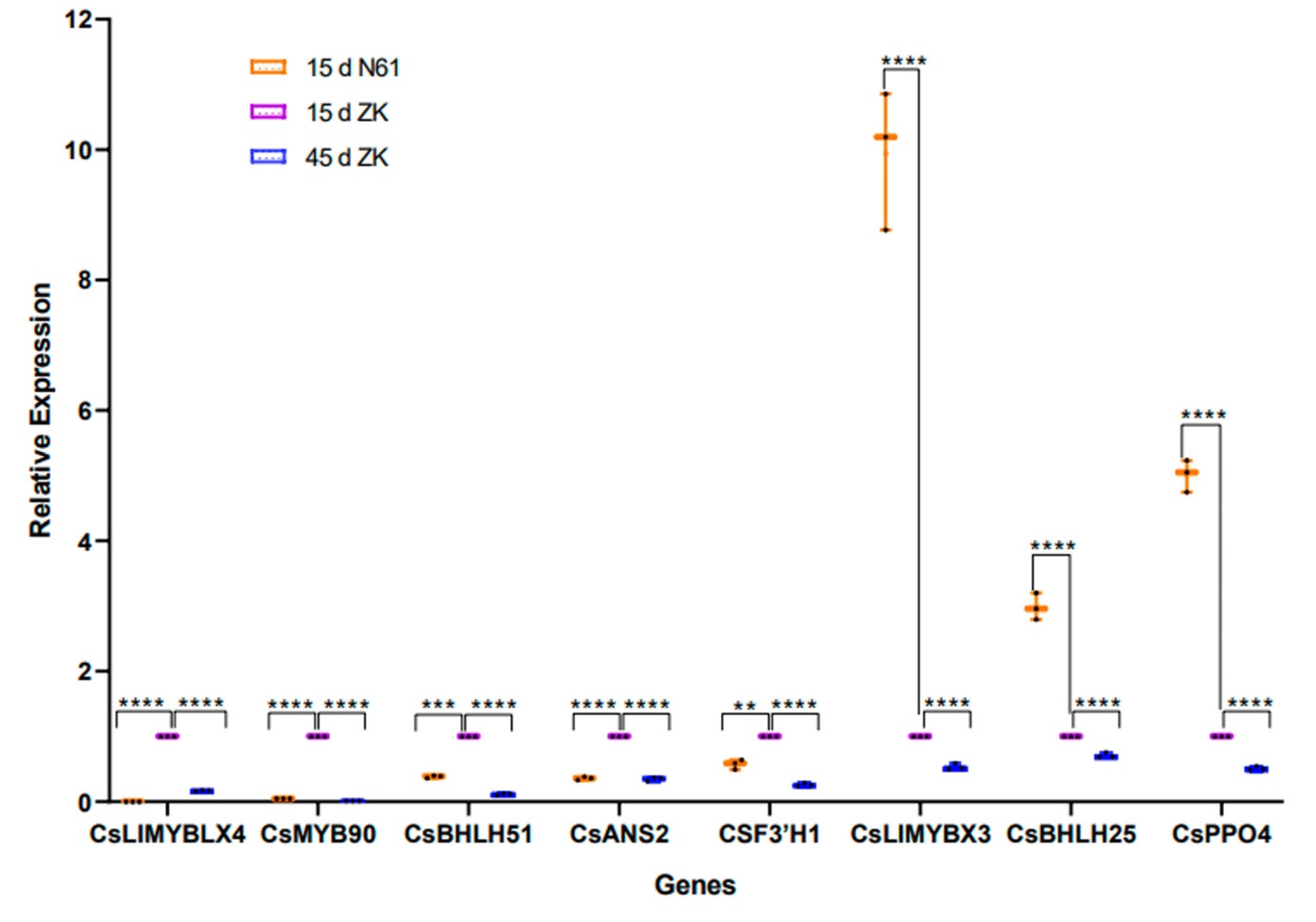
2.7. Quantitative RT-PCR Validation of the Transcriptomic Data
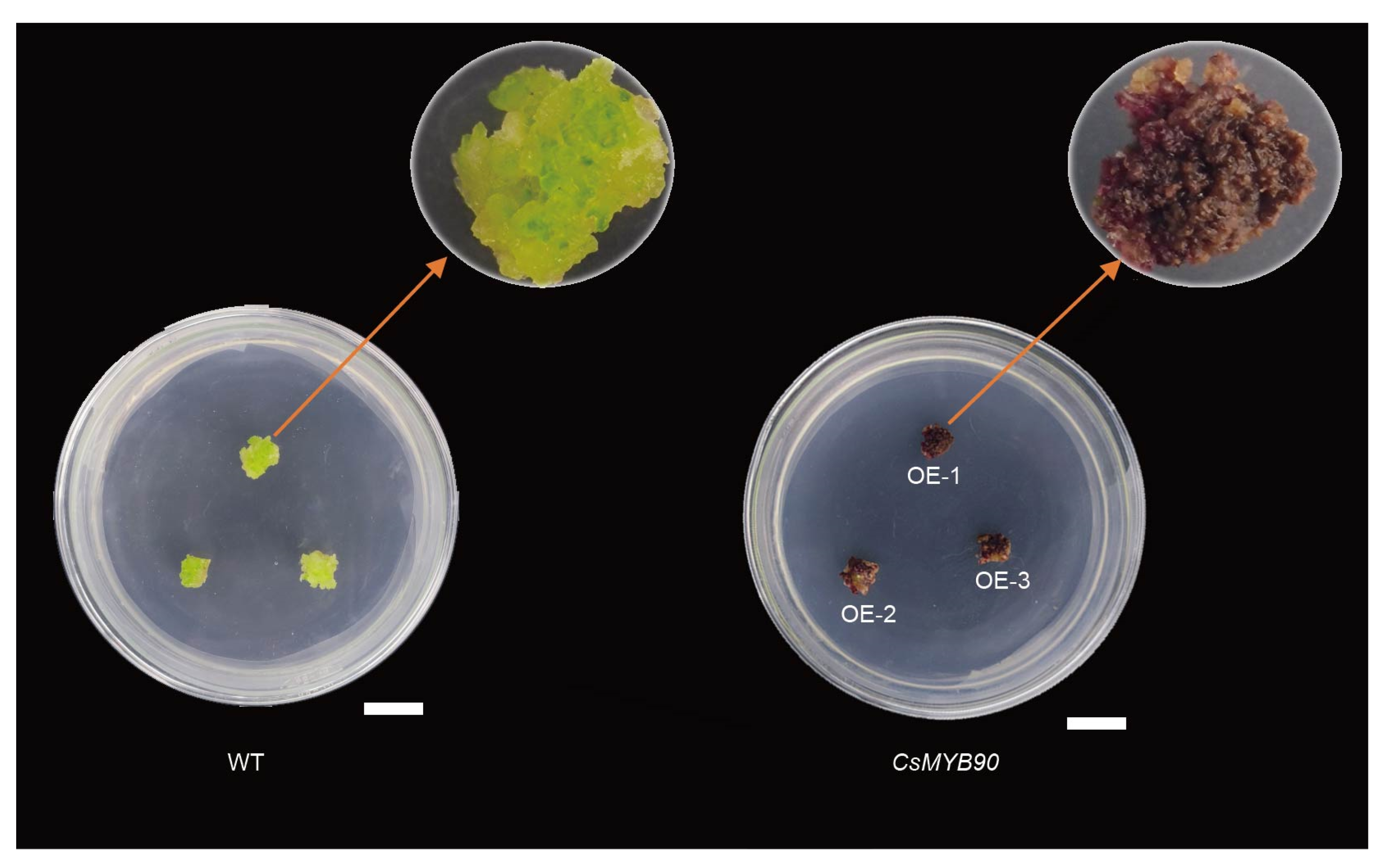
2.8. Functional Analysis of the CsMYB90 Gene in Nicotiana Tabacum
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Determination of Anthocyanin Content in the Leaves at Different Stages
4.3. Metabolite Extraction
4.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Conditions
4.5. ESI-QTRAP-MS/MS
4.6. Identification and Quantitative Analysis of Metabolites
4.7. RNA Extraction and Illumina Sequencing
4.8. RNA Sequencing Data Analysis and Annotation
4.9. Integrated Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis
4.10. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.11. Transformation of Tobacco Plants with CsMYB90
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mondal, T.K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Laxmikumaran, M.; Ahuja, P.S. Recent advances of tea (Camellia sinensis) biotechnology. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2004, 76, 195–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shen, Y.; Ling, T.; Ho, C.T.; Li, D.; Guo, H.; Xie, Z. Analysis of differentiated chemical components between Zijuan purple tea and Yunkang green tea by UHPLC-Orbitrap-MS/MS Combined with Chemometrics. Foods 2021, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zuo, T.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, W. Improving albino tea quality by foliar application of glycinebetaine as a green regulator under lower temperature conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Li, H.; Ruan, L.; Bai, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Wang, L. Gene expression analysis of bud and leaf color in tea. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 107, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, P.; He, W.; Du, X.; Chen, C.; Suo, L.; Liang, M.; Zhang, N.; Na, A.; Zhang, Y. The prevention and inhibition effect of anthocyanins on colorectal cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 4919–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, J.F.; Monteiro, V.V.S.; de Souza Gomes, R.; do Carmo, M.M.; da Costa, G.V.; Ribera, P.C.; Monteiro, M.C. Action mechanism and cardiovascular effect of anthocyanins: A systematic review of animal and human studies. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Shen, X.; Shoji, T.; Kanda, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, L. Characterization and activity of anthocyanins in Zijuan tea (Camellia sinensis var. kitamura). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3306–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tan, L.; Zou, Y.; Tan, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, W.; Tang, Q. The effects of ultraviolet A/B treatments on anthocyanin accumulation and gene expression in dark-purple tea cultivar ‘Ziyan’ (Camellia sinensis). Molecules 2020, 25, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochanda, S.O.; Wanyoko, J.K.; Ruto, H.K. Effect of spices on consumer acceptability of purple tea (Camellia sinensis). Food Nutr. Sci. 2015, 6, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pervaiz, T.; Songtao, J.; Faghihi, F.; Haider, M.S.; Fang, J. Naturally occurring anthocyanin, structure, functions and biosynthetic pathway in fruit plants. J. Plant Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.; Faria, A.; Calhau, C.; de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N. Bioavailability of anthocyanins and derivatives. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Gao, G.; Yu, C.; Zhu, A.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Abubakar, A.S.; Chen, P. Transcriptome and metabolome analysis reveals anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway associated with ramie (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.) leaf color formation. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.J.; Guo, H.M.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, H.M. Chalcone synthase EaCHS1 from Eupatorium adenophorum functions in salt stress tolerance in tobacco. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.C.; Hou, J.M.; Tian, S.K.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y. Overexpressing chalcone synthase (CHS) gene enhanced flavonoids accumulation in Glycyrrhiza uralensis hairy roots. Bot. Lett. 2019, 167, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.H.; Sun, Q.G.; Chen, M.; Wang, N.; Xu, H.F.; Fang, H.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, X.S. Methylome and transcriptome analyses of apple fruit somatic mutations reveal the difference of red phenotype. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nan, Y.; Zhao, K.; Li, X.; Rong, Z.; Am, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, L. Comprehensive analysis of wintersweet flower reveals key structural genes involved in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Gene 2018, 676, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Ning, G.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Jin, H.; Li, P.; Huang, S.; Jian, Z.; Bao, M. Disequilibrium of flavonol synthase and dihydroflavonol-4-reductase expression associated tightly to white vs. red color flower formation in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Pei, T.; Bai, Z.; Han, R.; Liang, Z. Overexpression of SmANS enhances anthocyanin accumulation and alters phenolic acids content in Salvia miltiorrhiza and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge F. alba plantlets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, M.; Wen, C.; Xie, X.; Tian, W.; Wen, S.; Lu, R.; Liu, L. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of the anthocyanin regulatory networks in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. flowers. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, B.; Qin, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhao, J. Advance of the negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by MYB transcription factors. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Pei, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Chiang, V.L.; Sederoff, R.R.; Zhao, X. MYB-mediated regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W.; Wang, N.; Chen, X. MdMYB114 regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis and functions downstream of MdbZIP4-like in apple fruit. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 257, 153353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H. CBFs function in anthocyanin biosynthesis by interacting with MYB113 in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, N.; Wang, J.-J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Sun, J.; Yan, P.; Sun, Y.; Wan, P.; Ye, W.; Fan, B. DcTT8, a bHLH transcription factor, regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in Dendrobium candidum. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.P.; Zhao, S.J. Development and research status offunctional (special tea) tea products. China Tea 2014, 36, 10–13. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=CAYA201411006&DbName=CJFQ2014 (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Tian, Y.; Yin, Z.Q.; Tang, Q. Water extraction process of anthocyanins from “Ziyan” tea and the antitumor activity of its extracts. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2019, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongkowijoyo, P.; Luna-Vital, D.A.; de Mejia, E.G. Extraction techniques and analysis of anthocyanins from food sources by mass spectrometry: An update. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.; Song, W.; Tian, Y.; Xia, L.; Chen, L. Anthocyanin accumulation and expression of synthesis-related genes in leaves of different developmental stages in Camellia sinensis cv. Zijuan. J. Tea Sci. 2018, 38, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, M.; Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Jin, S.; Ye, N. Comparison of metabolome and transcriptome of flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in a purple-leaf tea germplasm Jinmingzao and a green-leaf tea germplasm Huangdan reveals their relationship with genetic mechanisms of color formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takino, Y.; Imagawa, H.; Horikawa, H.; Tanaka, A. Studies on the mechanism of the oxidation of tea leaf catechins: Part III. Formation of a reddish orange pigment and its spectral relationship to some benzotropolone derivatives. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1964, 28, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tian, S.; Chen, G. Anthocyanin accumulation and molecular analysis of correlated genes in purple kohlrabi (Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4160–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, S.; Wei, C. Metabolites and transcriptional profiling analysis reveal the molecular mechanisms of the anthocyanin metabolism in the “Zijuan” tea plant (Camellia sinensis var. assamica). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 69, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Z.; Zhou, F.; Ran, L.S.; Li, Y.L.; Tan, B.; Wang, K.-B.; Huang, J.-A.; Liu, Z.-H. Metabolic profiling and gene expression analyses of purple-leaf formation in tea cultivars (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis and var. assamica). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 606962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Xin, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, L.A. Overexpression of the GbF3’H1 gene enhanced the epigallocatechin, gallocatechin, and catechin contents in transgenic populus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Shi, Q.; Niu, L.; Zhang, Y. Transcriptomic analysis of leaf in tree peony reveals differentially expressed pigments genes. Molecules 2017, 22, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Pozo-Insfran, D.; Balaban, M.O.; Talcott, S.T. Inactivation of polyphenol oxidase in muscadine grape juice by dense phase-CO2 processing. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhao, X.; Gao, L.; Shi, X.; Dai, X.; Liu, Y.; Xia, T.; Wang, Y. Isolation and characterization of key genes that promote flavonoid accumulation in purple-leaf tea (Camellia sinensis L.). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, B.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X.; Mao, Y.; Lei, J.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, W. Purple foliage coloration in tea (Camellia sinensis L.) arises from activation of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor CsAN1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhou, L.; Han, L.; Zou, H.; Miao, K.; Wang, Y. PsbHLH1, a novel transcription factor involved in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 154, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E. HMDB 3.0—The human metabolome database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Schultz, A.W.; Wang, J.; Johnson, C.H.; Yannone, S.M.; Patti, G.J.; Siuzdak, G. Liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry characterization of metabolites guided by the METLIN database. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccenti, E.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Hendriks, M.M. Reflections on univariate and multivariate analysis of metabolomics data. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, J.; Lv, L.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Tian, W.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Integrative Analysis of Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Molecular Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Metabolism in the Zikui Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis cv. Zikui). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094780
Cai J, Lv L, Zeng X, Zhang F, Chen Y, Tian W, Li J, Li X, Li Y. Integrative Analysis of Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Molecular Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Metabolism in the Zikui Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis cv. Zikui). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094780
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Ju, Litang Lv, Xiaofang Zeng, Fen Zhang, Yulu Chen, Weili Tian, Jianrong Li, Xiangyang Li, and Yan Li. 2022. "Integrative Analysis of Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Molecular Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Metabolism in the Zikui Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis cv. Zikui)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094780
APA StyleCai, J., Lv, L., Zeng, X., Zhang, F., Chen, Y., Tian, W., Li, J., Li, X., & Li, Y. (2022). Integrative Analysis of Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Reveals Molecular Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Metabolism in the Zikui Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis cv. Zikui). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094780






