Etonogestrel Administration Reduces the Expression of PHOX2B and Its Target Genes in the Solitary Tract Nucleus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Etonogestrel Serum Levels in Nexplanon®-Instrumented Rats
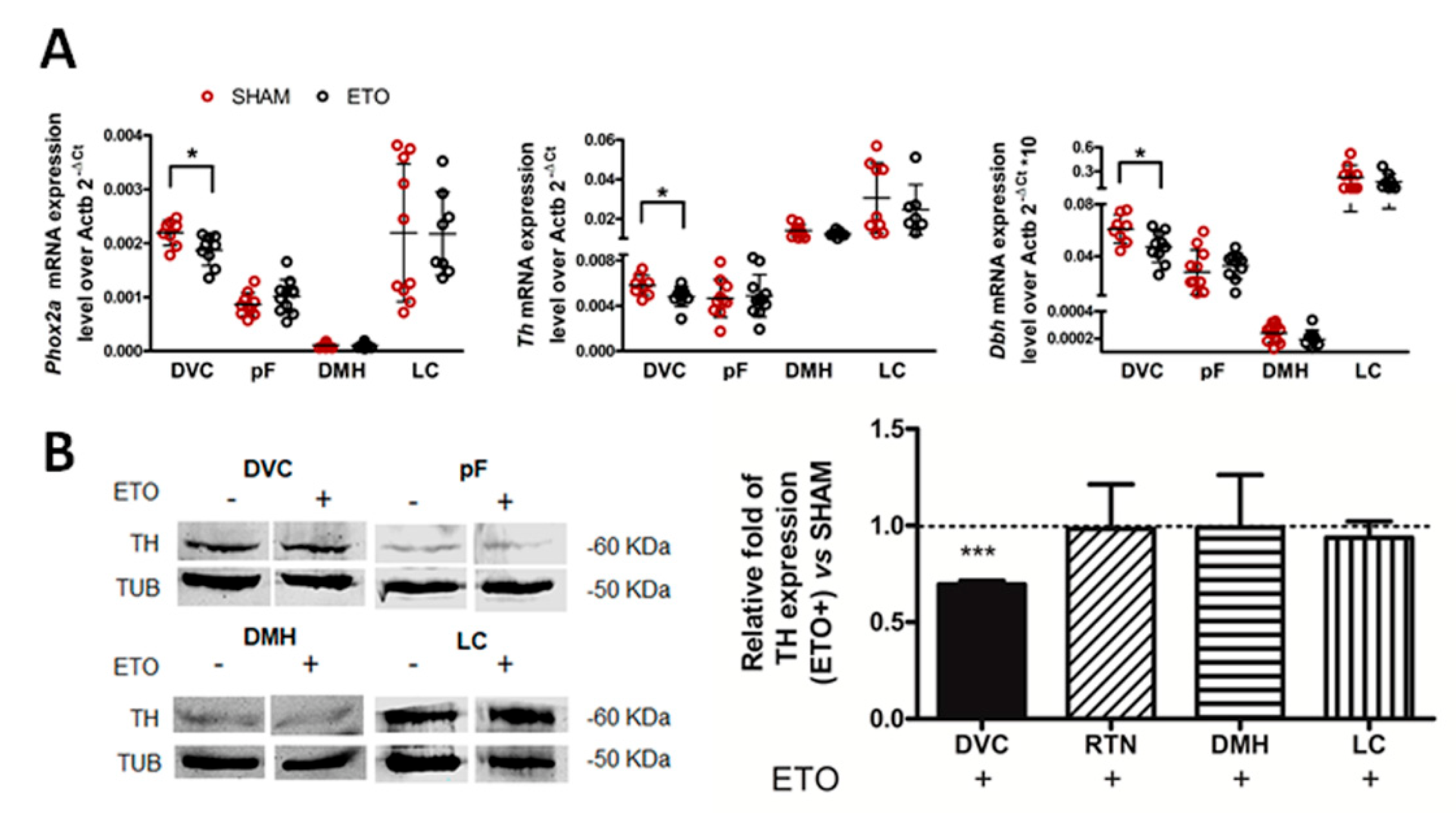
2.2. Etonogestrel Treatment Down-Regulates Phox2b Gene and Protein Expression in the Dorsal Vagal Complex
2.3. ETO Treatment Does Not Affect PHOX2B Expression in RTN CO2-Sensing Neurons
2.4. ETO-Mediated PHOX2B Down-Regulation in the NTS Results in Decreased Expression of PHOX2B Target Genes
2.5. ETO Treatment Does Not Alter Baseline Breathing or Respiratory Response to Chemoreflex Activation
2.6. ETO Enhances Alveolar Hyperventilation during High CO2
2.7. ETO Increases Inter-Breath Variability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Determination of Oestrous Cycle
4.3. Surgical Implantation of Nexplanon®
4.4. Data Acquisition and Analysis of Respiratory Measurements
4.5. Tissue Collection and Thionine Staining
4.6. Total RNA and Protein Extraction
4.7. Reverse Transcription and qPCR
4.8. Western Blot Analyses
4.9. In Situ Hybridization (RNAScope) and Immunofluorescence
4.10. Histological Analysis and Quantification
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amiel, J.; Laudier, B.; Attie-Bitach, T.; Trang, H.; de Pontual, L.; Gener, B.; Trochet, D.; Etchevers, H.; Ray, P.; Simonneau, M.; et al. Polyalanine expansion and frameshift mutations of the paired-like homeobox gene PHOX2B in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lascio, S.; Benfante, R.; Cardani, S.; Fornasari, D. Research Advances on Therapeutic Approaches to Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome (CCHS). Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 615666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weese-Mayer, D.E.; Rand, C.M.; Zhou, A.; Carroll, M.S.; Hunt, C.E. Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome: A bedside-to-bench success story for advancing early diagnosis and treatment and improved survival and quality of life. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang, H.; Samuels, M.; Ceccherini, I.; Frerick, M.; Garcia-Teresa, M.A.; Peters, J.; Schoeber, J.; Migdal, M.; Markstrom, A.; Ottonello, G.; et al. Guidelines for diagnosis and management of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, A.; Morin, X.; Cremer, H.; Goridis, C.; Brunet, J.F. Expression and interactions of the two closely related homeobox genes Phox2a and Phox2b during neurogenesis. Development 1997, 124, 4065–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, A.; Morin, X.; Cremer, H.; Goridis, C.; Brunet, J.F. The homeobox gene Phox2b is essential for the development of autonomic neural crest derivatives. Nature 1999, 399, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, A.; Hirsch, M.; Goridis, C.; Brunet, J.F. Control of hindbrain motor neuron differentiation by the homeobox gene Phox2b. Development 2000, 127, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, J.F.; Pattyn, A. Phox2 genes—From patterning to connectivity. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.J.; Chang, D.A.; Mackay, D.D.; West, G.H.; Moreira, T.S.; Takakura, A.C.; Gwilt, J.M.; Guyenet, P.G.; Stornetta, R.L. Central nervous system distribution of the transcription factor Phox2b in the adult rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 503, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyenet, P.G.; Stornetta, R.L.; Souza, G.; Abbott, S.B.G.; Shi, Y.; Bayliss, D.A. The Retrotrapezoid Nucleus: Central Chemoreceptor and Regulator of Breathing Automaticity. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 11, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccal, D.B.; Furuya, W.I.; Bassi, M.; Colombari, D.S.A.; Colombari, E. The nucleus of the solitary tract and the coordination of respiratory and sympathetic activities. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutsforth-Gregory, J.K.; Benarroch, E.E. Nucleus of the solitary tract, medullary reflexes, and clinical implications. Neurology 2017, 88, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubreuil, V.; Ramanantsoa, N.; Trochet, D.; Vaubourg, V.; Amiel, J.; Gallego, J.; Brunet, J.F.; Goridis, C. A human mutation in Phox2b causes lack of CO2 chemosensitivity, fatal central apnea, and specific loss of parafacial neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanantsoa, N.; Hirsch, M.R.; Thoby-Brisson, M.; Dubreuil, V.; Bouvier, J.; Ruffault, P.L.; Matrot, B.; Fortin, G.; Brunet, J.F.; Gallego, J.; et al. Breathing without CO(2) chemosensitivity in conditional Phox2b mutants. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 12880–12888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, R.M.; Kumar, R.; Macey, P.M.; Harper, R.K.; Ogren, J.A. Impaired neural structure and function contributing to autonomic symptoms in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobuta, H.; Cilio, M.R.; Danhaive, O.; Tsai, H.-H.; Tupal, S.; Chang, S.M.; Murnen, A.; Kreitzer, F.; Bravo, V.; Czeisler, C.; et al. Dysregulation of locus coeruleus development in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 130, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böing, S.; Randerath, W.J. Chronic hypoventilation syndromes and sleep-related hypoventilation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonds, A.K. Chronic hypoventilation and its management. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2013, 22, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, F.; Perrin-Terrin, A.S.; Verkaeren, E.; Cardot, P.; Fiamma, M.N.; Frugiere, A.; Rivals, I.; Similowski, T.; Straus, C.; Bodineau, L. Desogestrel enhances ventilation in ondine patients: Animal data involving serotoninergic systems. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, C.; Trang, H.; Becquemin, M.H.; Touraine, P.; Similowski, T. Chemosensitivity recovery in Ondine’s curse syndrome under treatment with desogestrel. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010, 171, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behan, M.; Zabka, A.G.; Thomas, C.F.; Mitchell, G.S. Sex steroid hormones and the neural control of breathing. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2003, 136, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behan, M.; Wenninger, J.M. Sex steroidal hormones and respiratory control. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2008, 164, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohl, K.P.; Hensley, M.J.; Saunders, N.A.; Scharf, S.M.; Brown, R.; Ingram, R.H., Jr. Progesterone administration and progressive sleep apneas. JAMA 1981, 245, 1230–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, W.R.; Benich, J.J.; Wooten, S.A. Indices of severity of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome do not change during medroxyprogesterone acetate therapy. Chest 1989, 96, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, C.K.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Woodard, W.D.; Hagerman, D.D.; Weil, J.V.; Moore, L.G. Progestin and estrogen reduce sleep-disordered breathing in postmenopausal women. J. Appl. Physiol. 1989, 66, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cistulli, P.A.; Barnes, D.J.; Grunstein, R.R.; Sullivan, C.E. Effect of short-term hormone replacement in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea in postmenopausal women. Thorax 1994, 49, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saaresranta, T.; Polo, O. Hormones and breathing. Chest 2002, 122, 2165–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collop, N.A. Medroxyprogesterone acetate and ethanol-induced exacerbation of obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 1994, 106, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, H.S.; McLean, H.; Kumar, D.V.; Farr, N.; Day, A.G.; Fitzpatrick, M.F. The influence of the menstrual cycle on upper airway resistance and breathing during sleep. Sleep 2005, 28, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.L.; Bittencourt, L.R.; Antunes, I.B.; Tufik, S. Effects of progesterone on sleep: A possible pharmacological treatment for sleep-breathing disorders? Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 3575–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, C.; Cayetanot, F.; Joubert, F.; Perrin-Terrin, A.S.; Cardot, P.; Fiamma, M.N.; Frugiere, A.; Straus, C.; Bodineau, L. Current Perspectives for the use of Gonane Progesteronergic Drugs in the Treatment of Central Hypoventilation Syndromes. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1433–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinton, R.D.; Thompson, R.F.; Foy, M.R.; Baudry, M.; Wang, J.; Finch, C.E.; Morgan, T.E.; Pike, C.J.; Mack, W.J.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; et al. Progesterone receptors: Form and function in brain. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 313–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giatti, S.; Melcangi, R.C.; Pesaresi, M. The other side of progestins: Effects in the brain. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 57, R109–R126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Su, C.; Ng, S. Non-genomic mechanisms of progesterone action in the brain. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannhart, B.; Pickett, C.K.; Moore, L.G. Effects of estrogen and progesterone on carotid body neural output responsiveness to hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 68, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeppky, J.A.; Scotto, P.; Charlton, G.C.; Gates, L.; Icenogle, M.; Roach, R.C. Ventilation is greater in women than men, but the increase during acute altitude hypoxia is the same. Respir. Physiol. 2001, 125, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran-Rauhut, M.A.; Petersen, S.L. The distribution of progestin receptor mRNA in rat brainstem. Brain Res. Gene Expr. Patterns 2002, 1, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, C.; Osinski, D.; Joubert, F.; Straus, C.; Similowski, T.; Bodineau, L. The progestin etonogestrel enhances the respiratory response to metabolic acidosis in newborn rats. Evidence for a mechanism involving supramedullary structures. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 567, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardani, S.; Di Lascio, S.; Belperio, D.; Di Biase, E.; Ceccherini, I.; Benfante, R.; Fornasari, D. Desogestrel down-regulates PHOX2B and its target genes in progesterone responsive neuroblastoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 370, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennink, H.J. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Implanon, a single-rod etonogestrel contraceptive implant. Eur. J. Contracept. Reprod. Health Care Off. J. Eur. Soc. Contracept. 2000, 5 (Suppl. 2), 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Palomba, S.; Falbo, A.; Di Cello, A.; Materazzo, C.; Zullo, F. Nexplanon: The new implant for long-term contraception. A comprehensive descriptive review. Gynecol. Endocrinol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2012, 28, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quadros, P.S.; Pfau, J.L.; Wagner, C.K. Distribution of progesterone receptor immunoreactivity in the fetal and neonatal rat forebrain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 504, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quadros, P.S.; Schlueter, L.J.; Wagner, C.K. Distribution of progesterone receptor immunoreactivity in the midbrain and hindbrain of postnatal rats. Dev. Neurobiol. 2008, 68, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flora, A.; Lucchetti, H.; Benfante, R.; Goridis, C.; Clementi, F.; Fornasari, D. Sp proteins and Phox2b regulate the expression of the human Phox2a gene. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7037–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, L.; Morin, X.; Brunet, J.F.; Anderson, D.J. Specification of neurotransmitter identity by Phox2 proteins in neural crest stem cells. Neuron 1999, 22, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Lewis, E.J. The paired-like homeodomain protein, Arix, mediates protein kinase A-stimulated dopamine beta-hydroxylase gene transcription through its phosphorylation status. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22915–22924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Huang, J.; Duffourc, M.; Kao, R.L.; Ordway, G.A.; Huang, R.; Zhu, M.Y. Transcription factor Phox2 upregulates expression of norepinephrine transporter and dopamine β-hydroxylase in adult rat brains. Neuroscience 2011, 192, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grueso, E.; Rocha, M.; Puerta, M. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid leptin levels are maintained despite enhanced food intake in progesterone-treated rats. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 144, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khoo, M.C.; Kronauer, R.E.; Strohl, K.P.; Slutsky, A.S. Factors inducing periodic breathing in humans: A general model. J. Appl. Physiol. 1982, 53, 644–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, C.; Casciato, A.; Barka, B.; Cayetanot, F.; Bodineau, L. Orexin Neurons Contribute to Central Modulation of Respiratory Drive by Progestins on ex vivo Newborn Rodent Preparations. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukari, R.; Marcouiller, F.; Joseph, V. Relative Contribution of Nuclear and Membrane Progesterone Receptors in Respiratory Control. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 860, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcouiller, F.; Boukari, R.; Laouafa, S.; Lavoie, R.; Joseph, V. The Nuclear Progesterone Receptor Reduces Post-Sigh Apneas during Sleep and Increases the Ventilatory Response to Hypercapnia in Adult Female Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Hong, S.J.; Guo, S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, C.H.; Hwang, D.Y.; Isacson, O.; Rosenthal, A.; Kim, K.S. A direct role of the homeodomain proteins Phox2a/2b in noradrenaline neurotransmitter identity determination. J. Neurochem. 2002, 80, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosenpud, J.D.; Hart, M.V.; Morton, M.J.; Hohimer, A.R.; Resko, J.A. Progesterone-induced hyperventilation in the guinea pig. Respir. Physiol. 1983, 52, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodeur, P.; Mockus, M.; McCullough, R.; Moore, L.G. Progesterone receptors and ventilatory stimulation by progestin. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 60, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliss, D.A.; Millhorn, D.E.; Gallman, E.A.; Cidlowski, J.A. Progesterone stimulates respiration through a central nervous system steroid receptor-mediated mechanism in cat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7788–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, O.; Morin-Surun, M.P.; Barna, B.; Denavit-Saubie, M.; Pequignot, J.M.; Champagnat, J. Progesterone reverses the neuronal responses to hypoxia in rat nucleus tractus solitarius in vitro. J. Physiol. 2002, 544, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliss, D.A.; Millhorn, D.E. Central neural mechanisms of progesterone action: Application to the respiratory system. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 73, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairam, A.; Boukari, R.; Joseph, V. Targeting progesterone receptors in newborn males and females: From the animal model to a new perspective for the treatment of apnea of prematurity? Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2019, 263, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, V.; Uppari, N.; Kouchi, H.; De Bruyn, C.; Boukari, R.; Bairam, A. Respiratory regulation by steroids in newborn rats: A sex-specific balance between allopregnanolone and progesterone receptors. Exp. Physiol. 2018, 103, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, H.S.; Behan, M.; Wenninger, J.M. Age and sex differences in the ventilatory response to hypoxia and hypercapnia in awake neonatal, pre-pubertal and young adult rats. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2012, 180, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhler, K.D.; Wuttke, W. Changes with age in levels of serum gonadotropins, prolactin and gonadal steroids in prepubertal male and female rats. Endocrinology 1975, 97, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quadros, P.S.; Wagner, C.K. Regulation of progesterone receptor expression by estradiol is dependent on age, sex and region in the rat brain. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, T.R.; Gore, A.C. Aging-related changes in ovarian hormones, their receptors, and neuroendocrine function. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-Araiza, C.; Villamar-Cruz, O.; González-Arenas, A.; Chavira, R.; Camacho-Arroyo, I. Changes in Progesterone Receptor Isoforms Content in the Rat Brain During the Oestrous Cycle and After Oestradiol and Progesterone Treatments. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2003, 15, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Greer, J.J. Neurosteroid modulation of respiratory rhythm in rats during the perinatal period. J. Physiol. 2006, 574, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortola, J.P.; Matsuoka, T.; Saiki, C.; Naso, L. Metabolism and ventilation in hypoxic rats: Effect of body mass. Respir. Physiol. 1994, 97, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.A.; Smith, C.A.; Blain, G.M.; Xie, A.; Gong, Y.; Teodorescu, M. Role of central/peripheral chemoreceptors and their interdependence in the pathophysiology of sleep apnea. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 758, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, P.G.; Kanbar, R.; Basting, T.M.; Hodges, W.M.; Viar, K.E.; Stornetta, R.L.; Guyenet, P.G. State-dependent control of breathing by the retrotrapezoid nucleus. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 2909–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese-Mayer, D.E.; Berry-Kravis, E.M.; Ceccherini, I.; Keens, T.G.; Loghmanee, D.A.; Trang, H.; Subcommittee, A.T.S.C.C.H.S. An official ATS clinical policy statement: Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome: Genetic basis, diagnosis, and management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 626–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Xue, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Chemosensitive Phox2b-expressing neurons are crucial for hypercapnic ventilatory response in the nucleus tractus solitarius. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4973–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Shi, L.; Wei, Z.; Yu, H.; Hao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, F.; et al. Activation of Phox2b-Expressing Neurons in the Nucleus Tractus Solitarii Drives Breathing in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 2837–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lascio, S.; Bachetti, T.; Saba, E.; Ceccherini, I.; Benfante, R.; Fornasari, D. Transcriptional dysregulation and impairment of PHOX2B auto-regulatory mechanism induced by polyalanine expansion mutations associated with congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 50, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lascio, S.; Belperio, D.; Benfante, R.; Fornasari, D. Alanine Expansions Associated with Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome Impair PHOX2B Homeodomain-mediated Dimerization and Nuclear Import. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13375–13393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirone, L.; Caldinelli, L.; Di Lascio, S.; Di Girolamo, R.; Di Gaetano, S.; Fornasari, D.; Pollegioni, L.; Benfante, R.; Pedone, E. Molecular insights into the role of the polyalanine region in mediating PHOX2B aggregation. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 2505–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, S.; Di Zanni, E.; Di Lascio, S.; Bocca, P.; Prigione, I.; Fornasari, D.; Pennuto, M.; Bachetti, T.; Ceccherini, I. The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM11 mediates the degradation of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome-associated polyalanine-expanded PHOX2B. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lascio, S.; Benfante, R.; Cardani, S.; Fornasari, D. Advances in the molecular biology and pathogenesis of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome—implications for new therapeutic targets. Expert Opin. Orphan Drugs 2018, 6, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lascio, S.; Benfante, R.; Di Zanni, E.; Cardani, S.; Adamo, A.; Fornasari, D.; Ceccherini, I.; Bachetti, T. Structural and functional differences in PHOX2B frameshift mutations underlie isolated or syndromic congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Su, Y.N.; Hung, C.C.; Hsieh, W.S.; Wu, K.J. Interaction between PHOX2B and CREBBP mediates synergistic activation: Mechanistic implications of PHOX2B mutants. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.M.; Murr, A.S.; Cooper, R.L. The rodent estrous cycle: Characterization of vaginal cytology and its utility in toxicological studies. Birth Defects Res. Part B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 80, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortola, J.P.; Frappell, P.B. On the barometric method for measurements of ventilation, and its use in small animals. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1998, 76, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, E.L.; Knowles, J.; Mortola, J.P. Continuous circadian measurements of ventilation in behaving adult rats. Respir. Physiol. 2000, 120, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drorbaugh, J.E.; Fenn, W.O. A barometric method for measuring ventilation in newborn infants. Pediatrics 1955, 16, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depocas, F.; Hart, J.S. Use of the Pauling oxygen analyzer for measurement of oxygen consumption of animals in open-circuit systems and in a short-lag, closed-circuit apparatus. J. Appl. Physiol. 1957, 10, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighton, J.R.B. Measuring Metabolic Rates: A Manual for Scientists; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, M.; Palaniswami, M.; Kamen, P. Poincaré plot interpretation using a physiological model of HRV based on a network of oscillators. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 283, H1873–H1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.; Jensen, E.W.; Gambús, P.L.; Vallverdú, M. Poincaré plot analysis of cerebral blood flow signals: Feature extraction and classification methods for apnea detection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfante, R.; Antonini, R.A.; Kuster, N.; Schuderer, J.; Maercker, C.; Adlkofer, F.; Clementi, F.; Fornasari, D. The expression of PHOX2A, PHOX2B and of their target gene dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (DbetaH) is not modified by exposure to extremely-low-frequency electromagnetic field (ELF-EMF) in a human neuronal model. Toxicol. In Vitro 2008, 22, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancardi, V.; Saini, J.; Pageni, A.; Prashaad, M.H.; Funk, G.D.; Pagliardini, S. Mapping of the excitatory, inhibitory, and modulatory afferent projections to the anatomically defined active expiratory oscillator in adult male rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2021, 529, 853–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 5th ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Stornetta, R.L.; Stornetta, D.S.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Farber, E.A.; Turner, S.D.; Guyenet, P.G.; Bayliss, D.A. Neuromedin B Expression Defines the Mouse Retrotrapezoid Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11744–11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCloy, R.A.; Rogers, S.; Caldon, C.E.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A.; Burgess, A. Partial inhibition of Cdk1 in G2 phase overrides the SAC and decouples mitotic events. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| SHAM | ETO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poincaré Analysis | Pre-Surgery | 4 Weeks | Pre-Surgery | 4 Weeks | p-Value |
| SD1 | 0.085 ± 0.022 | 0.086 ± 0.019 | 0.086 ± 0.016 | 0.101 ± 0.019 | Pre-post p = 0.129 Interaction p = 0.178 Treatment p = 0.305 |
| SD2 | 0.149 ± 0.026 | 0.152 ± 0.034 | 0.151 ± 0.024 | 0.196 ± 0.043 | Pre-post p = 0.022 * Interaction p = 0.038 * Treatment p = 0.080 |
| SD1/SD2 | 0.569 ± 0.098 | 0.579 ± 0.132 | 0.579 ± 0.109 | 0.531 ± 0.113 | Pre-post p = 0.547 Interaction p = 0.359 Treatment p = 0.671 |
| Area | 0.041 ± 0.017 | 0.042 ± 0.016 | 0.041 ± 0.012 | 0.063 ± 0.019 | Pre-post p = 0.019 * Interaction p = 0.028 * Treatment p = 0.110 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardani, S.; Janes, T.A.; Saini, J.K.; Di Lascio, S.; Benfante, R.; Fornasari, D.; Pagliardini, S. Etonogestrel Administration Reduces the Expression of PHOX2B and Its Target Genes in the Solitary Tract Nucleus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094816
Cardani S, Janes TA, Saini JK, Di Lascio S, Benfante R, Fornasari D, Pagliardini S. Etonogestrel Administration Reduces the Expression of PHOX2B and Its Target Genes in the Solitary Tract Nucleus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094816
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardani, Silvia, Tara A. Janes, Jasmeen K. Saini, Simona Di Lascio, Roberta Benfante, Diego Fornasari, and Silvia Pagliardini. 2022. "Etonogestrel Administration Reduces the Expression of PHOX2B and Its Target Genes in the Solitary Tract Nucleus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094816
APA StyleCardani, S., Janes, T. A., Saini, J. K., Di Lascio, S., Benfante, R., Fornasari, D., & Pagliardini, S. (2022). Etonogestrel Administration Reduces the Expression of PHOX2B and Its Target Genes in the Solitary Tract Nucleus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094816






