Coronary Artery Ectasia: Review of the Non-Atherosclerotic Molecular and Pathophysiologic Concepts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Acute Myocardial Infarction in CAE
3. Clinical Sequelae
4. Risk Factors
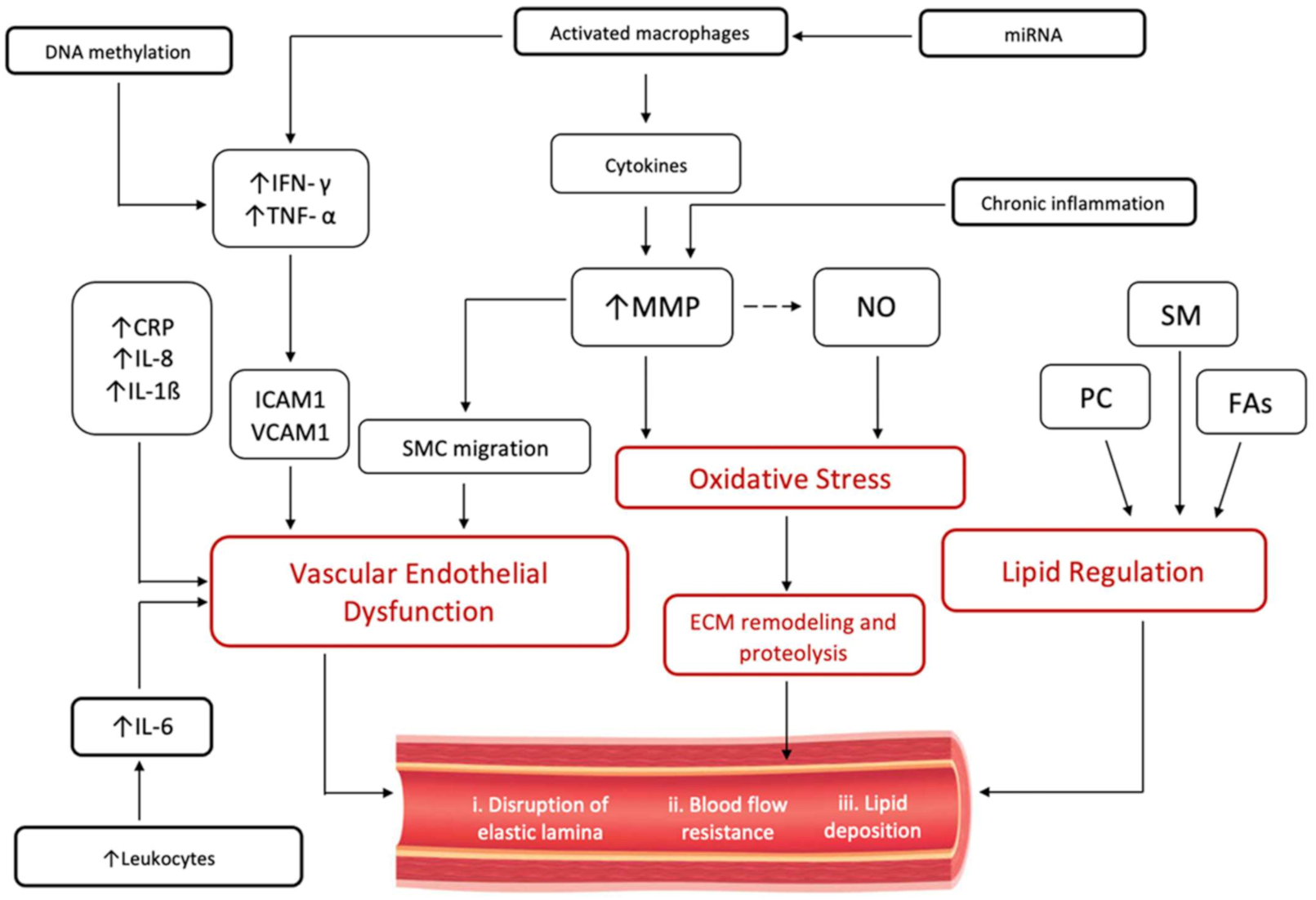
5. Atherosclerotic vs. Non-Atherosclerotic Inflammatory Response in CAE
6. Immuno-Inflammatory Response in CAE
7. Lipid Profiling in CAE
8. Treatment Options of CAE
9. Epigenetics in CAE Pathogenesis
10. Gut Microbial Metabolites in CAE
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanner, R.; David, S.; Conlon, R.; Boles, R. Coronary Artery Ectasia; Clinical Updates and Management Options in Acute Presentation. Med. Res. Arch. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawsara, A.; Gil, I.J.N.; Alqahtani, F.; Moreland, J.; Rihal, C.S.; Alkhouli, M. Management of Coronary Artery Aneurysms. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boles, U.; Eriksson, P.; Zhao, Y.; Henein, M.Y. Coronary artery ectasia: Remains a clinical dilemma. Coron. Artery Dis. 2010, 21, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitan, A.; Roguin, A. Coronary artery ectasia: New insights into pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Coron. Artery Dis. 2016, 27, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanile, A.; Sozzi, F.B.; Consonni, D.; Piscione, F.; Sganzerla, P.; Indolfi, C.; Stabile, A.; Migliorini, A.; Antoniucci, D.; Ferraresi, R.; et al. Primary PCI for the treatment of ectatic infarct-related coronary artery. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2014, 62, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Bogana Shanmugam, V.; Psaltis, P.J.; Wong, D.T.L.; Meredith, I.T.; Malaiapan, Y.; Ahmar, W. Outcomes after Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Caused by Ectatic Infarct Related Arteries. Heart Lung Circ. 2017, 26, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, T.; Kataoka, Y.; Noguchi, T.; Shibata, T.; Nakashima, T.; Kawakami, S.; Nakao, K.; Fujino, M.; Nagai, T.; Kanaya, T.; et al. Coronary Artery Ectasia Predicts Future Cardiac Events in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 2350–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Yin, D.; Song, W.; Dou, K. Diffuse coronary artery dilation predicted worse long-term outcomes in patients with coronary artery Ectasia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 319, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-J.; Nie, S.-P.; Qian, X.-W.; Zeng, H.-S.; Zhang, C.-Y. Chronic inflammatory status in patients with coronary artery ectasia. Cytokine 2009, 46, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghetti, G.; Taglieri, N.; Donati, F.; Minnucci, M.; Bruno, A.G.; Palmerini, T.; Saia, F.; Marrozzini, C.; Galié, N. Correlation between aortic root dimension and coronary ectasia. Coron. Artery Dis. 2020, 32, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, A.S.; Siasos, G.; Oikonomou, E.; Mourouzis, K.; Mavroudeas, S.E.; Papageorgiou, N.; Papaioannou, S.; Tsiamis, E.; Toutouzas, K.; Tousoulis, D. Characterization of vascular phenotype in patients with coronary artery ectasia: The role of endothelial dysfunction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 215, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Chen, L.; Wu, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S. Neutrophil serine proteases and their endogenous inhibitors in coronary artery ectasia patients. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2015, 16, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Peláez, J.A.; Martín-Reyes, R.; Pello-Lázaro, A.M.; Aceña, Á.; Lorenzo, Ó.; Martín-Ventura, J.L.; Blanco-Colio, L.; González-Casaus, M.L.; Hernández-González, I.; Carda, R.; et al. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Is an Independent Predictor of Coronary Artery Ectasia in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogeni, S. Coronary Artery Ectasia: Diagnosis and Treatment. E-J. Cardiol. Pract. Hellenic J. Cardiol 2010, 51, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Şen, F.; Yılmaz, S.; Kuyumcu, M.S.; Ozeke, O.; Balcı, M.M.; Aydogdu, S. The Presence of Fragmented QRS on 12-Lead Electrocardiography in Patients with Coronary Artery Ectasia. Korean Circ. J. 2014, 44, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conlon, R.; Tanner, R.; David, S.; Szeplaki, G.; Galvin, J.; Keaney, J.; Keelan, E.; Boles, U. Evaluation of the Tp-Te Interval, QTc and P-Wave Dispersion in Patients with Coronary Artery Ectasia. Cardiol. Res. 2017, 8, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunasekaran, P.; Stanojevic, D.; Drees, T.; Fritzlen, J.; Haghnegahdar, M.; McCullough, M.; Barua, R.; Mehta, A.; Hockstad, E.; Wiley, M.; et al. Prognostic significance, angiographic characteristics and impact of antithrombotic and anticoagulant therapy on outcomes in high versus low grade coronary artery ectasia: A long-term follow-up study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 93, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, U.; Wiklund, U.; David, S.; Ahmed, K.; Henein, M.Y. Coronary artery ectasia carries worse prognosis: A long-term follow-up study. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2019, 129, 833–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Tang, C.; Ma, C.; Yan, G. Risk factors for coronary artery ectasia and the relationship between hyperlipidemia and coronary artery ectasia. Coron. Artery Dis. 2019, 30, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwańczyk, S.; Borger, M.; Kamiński, M.; Chmara, E.; Cieślewicz, A.; Tykarski, A.; Radziemski, A.; Krasiński, Z.; Lesiak, M.; Araszkiewicz, A. Inflammatory response in patients with coronary artery ectasia and CAD. Kardiol. Pol. 2021, 79, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boles, U.; Zhao, Y.; David, S.; Eriksson, P.; Henein, M.Y. Pure coronary ectasia differs from atherosclerosis: Morphological and risk factors analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 155, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.-H.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.-H.; Li, X.-L.; Huang, Z.-H.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.-L. Anti-inflammatory effects of rosuvastatin treatment on coronary artery ectasia patients of different age groups. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniadis, A.P.; Chatzizisis, Y.S.; Giannoglou, G.D. Pathogenetic mechanisms of coronary ectasia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 130, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, S.A.; Tok, O.O.; Taşköylü, Ö.; Goktekin, O.; Kilic, I.D. Coronary Artery Aneurysms: A Review of the Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vrachatis, D.A.; Papathanasiou, K.A.; Kazantzis, D.; Sanz-Sánchez, J.; Giotaki, S.G.; Raisakis, K.; Kaoukis, A.; Kossyvakis, C.; Deftereos, G.; Reimers, B.; et al. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Ectasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, U.; Johansson, A.; Wiklund, U.; Sharif, Z.; David, S.; McGrory, S.; Henein, M.Y. Cytokine Disturbances in Coronary Artery Ectasia Do Not Support Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dereli, S.; Cerik, I.B.; Kaya, A.; Bektaş, O. Assessment of the Relationship between C-Reactive Protein-to-Albumin Ratio and the Presence and Severity of Isolated Coronary Artery Ectasia. Angiology 2020, 71, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bakry, S.A.; Fayez, D.; Morad, C.S.; Abdel-Salam, A.M.; Abdel-Salam, Z.; ElKabarity, R.H.; El Dakrony, A.H.M. Ischemic heart disease and rheumatoid arthritis: Do inflammatory cytokines have a role? Cytokine 2017, 96, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllis, A.S.; Kalogeropoulos, A.S.; Rigopoulos, A.G.; Sakadakis, E.A.; Toumpoulis, I.K.; Tsikrikas, S.; Kremastinos, D.T.; Rizos, I. Coronary artery ectasia and inflammatory cytokines: Link with a predominant Th-2 immune response? Cytokine 2013, 64, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Oufella, H.; Taleb, S.; Mallat, Z.; Tedgui, A. Recent Advances on the Role of Cytokines in Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohno, S.; Keenan, A.L.; Ntambi, J.M.; Miyazaki, M. Lipidomic insight into cardiovascular diseases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, P.J.; Wong, G.; Tsorotes, D.; Barlow, C.K.; Weir, J.M.; Christopher, M.J.; MacIntosh, G.L.; Goudey, B.; Stern, L.; Kowalczyk, A.; et al. Plasma Lipidomic Analysis of Stable and Unstable Coronary Artery Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2723–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jafari, J.; Daum, A.; Abu Hamed, J.; Osherov, A.; Orlov, Y.; Yosefy, C.; Gallego-Colon, E. Low High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Predisposes to Coronary Artery Ectasia. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boles, U.; Pinto, R.C.; David, S.; Abdullah, A.S.; Henein, M.Y. Dysregulated fatty acid metabolism in coronary ectasia: An extended lipidomic analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 228, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Xiao, N.; Wang, X.; Song, L.; Bai, C.; Wen, H.; Ge, J.; et al. Metabolomic Characterization of Fatty Acids in Patients With Coronary Artery Ectasias. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 770223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, A.; Neupane, B.; Proskuriakova, E.; Jada, K.; Kakieu Djossi, S.; Mostafa, J.A. Pharmacologic Management of Coronary Artery Ectasia. Cureus 2021, 13, e17832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogeni, S. Coronary artery ectasia: From diagnosis to treatment. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2010, 51, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hartnell, G.G.; Parnell, B.M.; Pridie, R.B. Coronary artery ectasia, its prevalence and clinical significance in 4993 patients. Br. Heart J. 1985, 54, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoporis, J.N.; Triantafyllis, A.; Gupta, S.; Izhar, S.; Sakadakis, E.; Rigopoulos, A.G.; Parker, T.G.; Rizos, I. Differential Regulation of Circulating Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Patients With Coronary Artery Ectasia. Circulation 2021, 144, A12511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzacasa, B.; Amati, F.; Romeo, F.; Novelli, G.; Mehta, J.L. Epigenetic Modification in Coronary Atherosclerosis: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1352–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.M.; Dear, A.; Craig, J.M.; Norman, P.E.; Golledge, J. The potential role of homocysteine mediated DNA methylation and associated epigenetic changes in abdominal aortic aneurysm formation. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.P.; Guo, Y.Y.; Che, L.; Wu, X.Z. Hypomethylation of interleukin-6 promoter is associated with the risk of coronary heart disease. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2016, 107, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, M.W.; Moore, K.J. MicroRNA regulation of atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 703–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouimet, M.; Ediriweera, H.N.; Gundra, U.M.; Sheedy, F.J.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Hutchison, S.B.; Rinehold, K.; van Solingen, C.; Fullerton, M.D.; Cecchini, K.; et al. MicroRNA-33-dependent regulation of macrophage metabolism directs immune cell polarization in atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 4334–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanika, N.K.; Lydia, A.B.; Nadim, J.A.; He, H.; Zhao, J.; Joseph, F.P.; Adolfo, C.; He, J. Gut Microbiome Associates With Lifetime Cardiovascular Disease Risk Profile Among Bogalusa Heart Study Participants. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 956–964. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, Z.; Xia, H.; Zhong, S.-L.; Feng, Q.; Li, S.; Liang, S.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Lin, S.L.; Kwok, M.K.; Leung, G.M.; Schooling, C.M.; Schooling, C.M. The Roles of 27 Genera of Human Gut Microbiota in Ischemic Heart Disease, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Their Risk Factors: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, A.; Miyamoto, J.; Inaba, Y.; Sutou, A.; Saito, T.; Sato, T.; Tachibana, N.; Inoue, H.; Kimura, I. Dietary soybean protein ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity by modifying the gut microbiota-dependent biotransformation of bile acids. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202083. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Xia, R.; Li, C. Gut microbiota in coronary artery disease: A friend or foe? Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.J.; de Aguiar Vallim, T.Q.; Wang, Z.; Shih, D.M.; Meng, Y.; Gregory, J.; Allayee, H.; Lee, R.; Graham, M.; Crooke, R.; et al. Trimethylamine-N-oxide, a metabolite associated with atherosclerosis, exhibits complex genetic and dietary regulation. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roncal, C.; Martínez-Aguilar, E.; Orbe, J.; Ravassa, S.; Fernandez-Montero, A.; Saenz-Pipaon, G.; Ugarte, A.; de Mendoza, A.E.-H.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Fernández-Alonso, S.; et al. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) Predicts Cardio-vascular Mortality in Peripheral Artery Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amrein, M.; Li, X.S.; Walter, J.; Wang, Z.; Zimmermann, T.; Strebel, I.; Honegger, U.; Leu, K.; Schäfer, I.; Twerenbold, R.; et al. Gut microbiota-dependent metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) and cardiovascular risk in patients with suspected functionally relevant coronary artery disease (fCAD). Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacón, M.R.; Lozano-Bartolomé, J.; Portero-Otín, M.; Rodríguez, M.M.; Xifra, G.; Puig, J.; Blasco, G.; Ricart, W.; Chaves, F.J.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; et al. The gut mycobiome composition is linked to carotid atherosclerosis. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type I | Diffuse ectasia of two or three vessels |
| Type II | Diffuse disease in one vessel only and localised in another vessel |
| Type III | Diffuse disease in one vessel |
| Type IV | Localised or segmental ectasia |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Richards, G.H.C.; Hong, K.L.; Henein, M.Y.; Hanratty, C.; Boles, U. Coronary Artery Ectasia: Review of the Non-Atherosclerotic Molecular and Pathophysiologic Concepts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23095195
Richards GHC, Hong KL, Henein MY, Hanratty C, Boles U. Coronary Artery Ectasia: Review of the Non-Atherosclerotic Molecular and Pathophysiologic Concepts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):5195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23095195
Chicago/Turabian StyleRichards, Gavin H. C., Kathryn L. Hong, Michael Y. Henein, Colm Hanratty, and Usama Boles. 2022. "Coronary Artery Ectasia: Review of the Non-Atherosclerotic Molecular and Pathophysiologic Concepts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 5195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23095195
APA StyleRichards, G. H. C., Hong, K. L., Henein, M. Y., Hanratty, C., & Boles, U. (2022). Coronary Artery Ectasia: Review of the Non-Atherosclerotic Molecular and Pathophysiologic Concepts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 5195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23095195






