The Role of Pulmonary Surfactant Phospholipids in Fibrotic Lung Diseases
Abstract
1. Pulmonary Surfactant (PS)
1.1. Pulmonary Surfactant Lipids
1.1.1. Lipid Biosynthesis Pathways
1.1.2. Pulmonary Surfactant Metabolism: The Role of Lipids
1.1.3. The Role of Phospholipids in Lung Surfactant Biophysics
2. Interstitial Lung Diseases
2.1. ILD of Know Cause: Occupational Exposure
2.1.1. Asbestosis
2.1.2. Silicosis
2.2. ILD of Know Cause: Related to Treatment
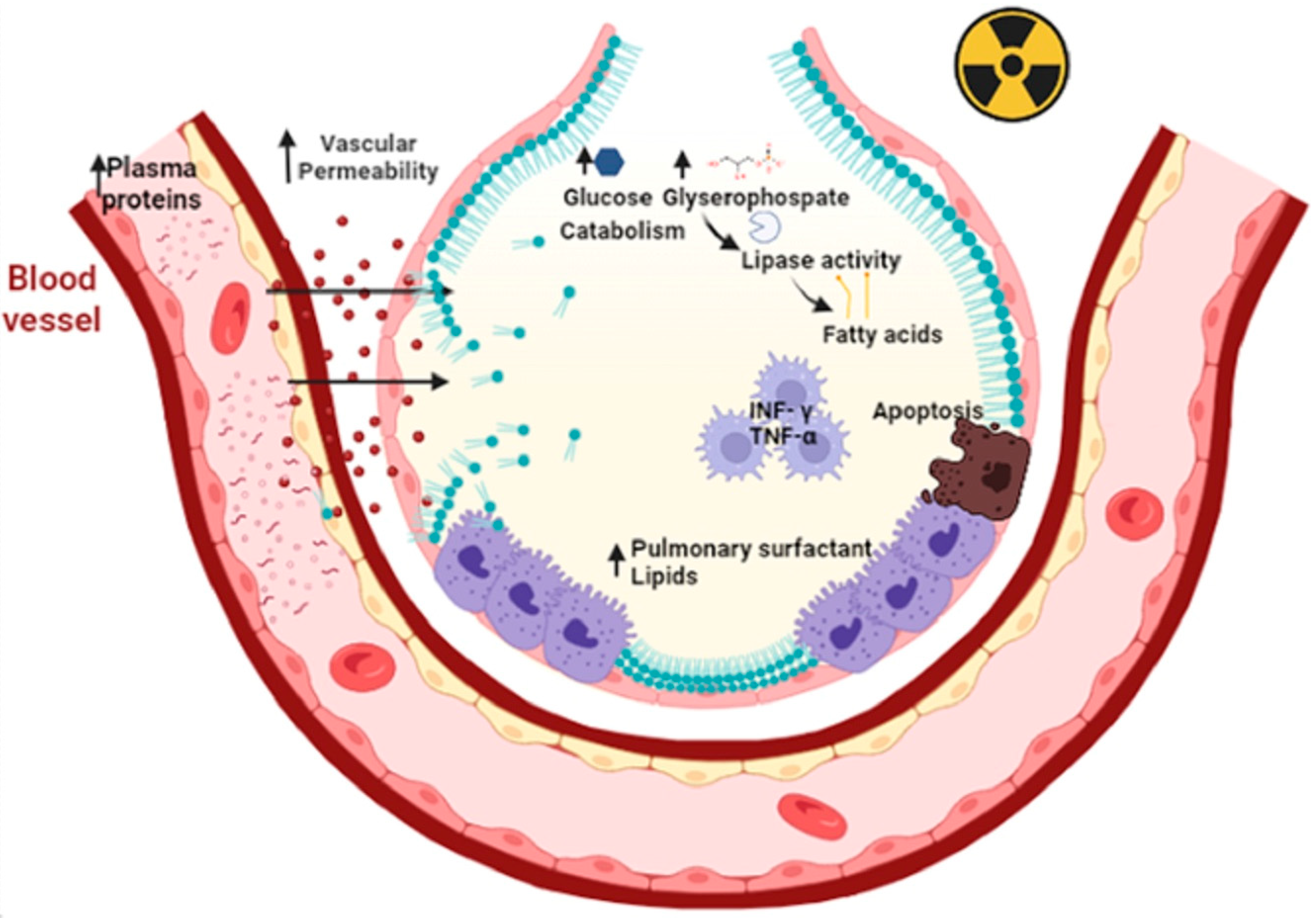
2.2.1. Radiation
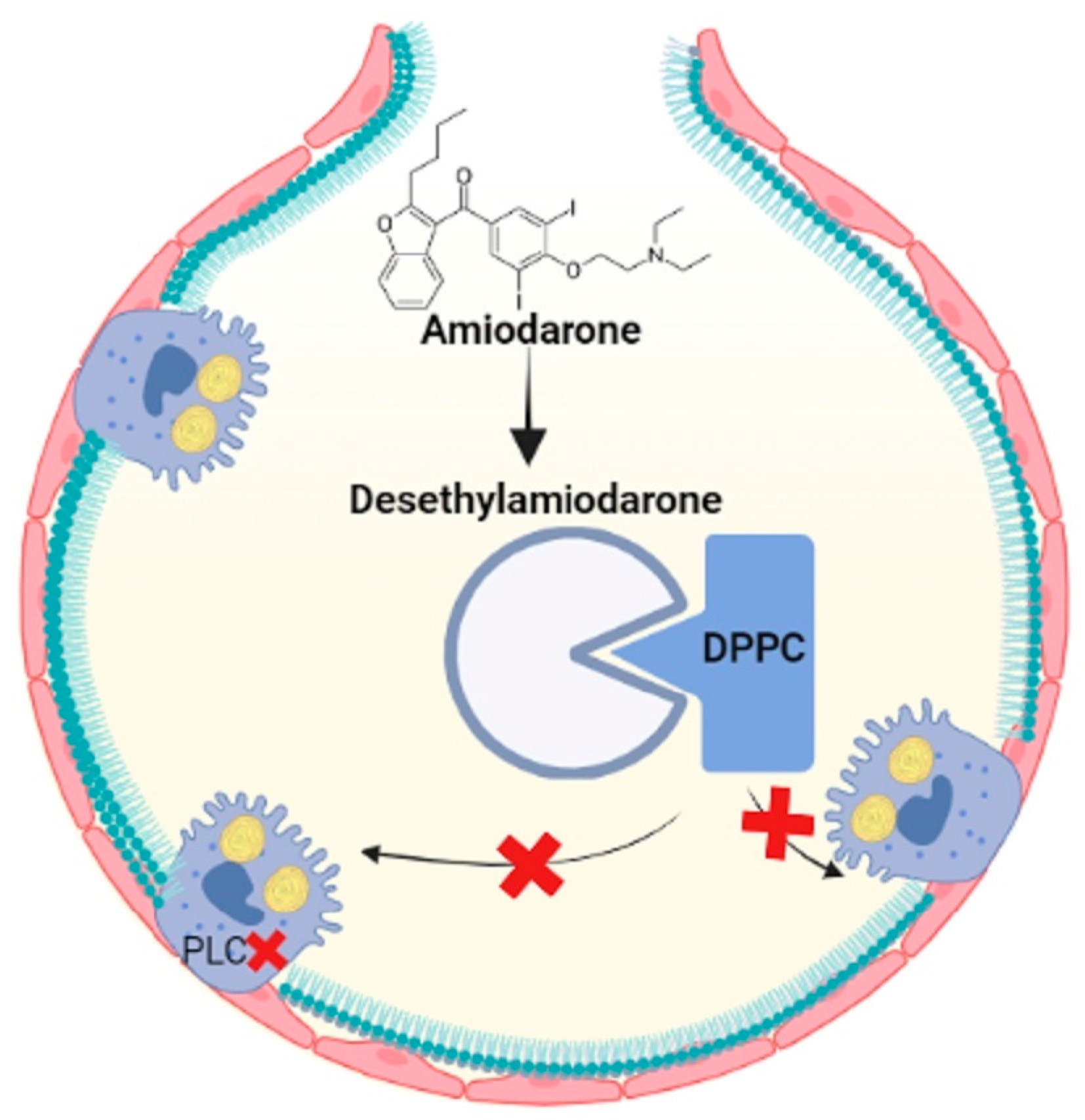
2.2.2. Amiodarone
3. Granulomatous Diseases
3.1. Sarcoidosis
3.2. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
4. ILD of Unknow Cause: Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
5. Pulmonary Fibrosis Secondary to COVID-19 and ARDS
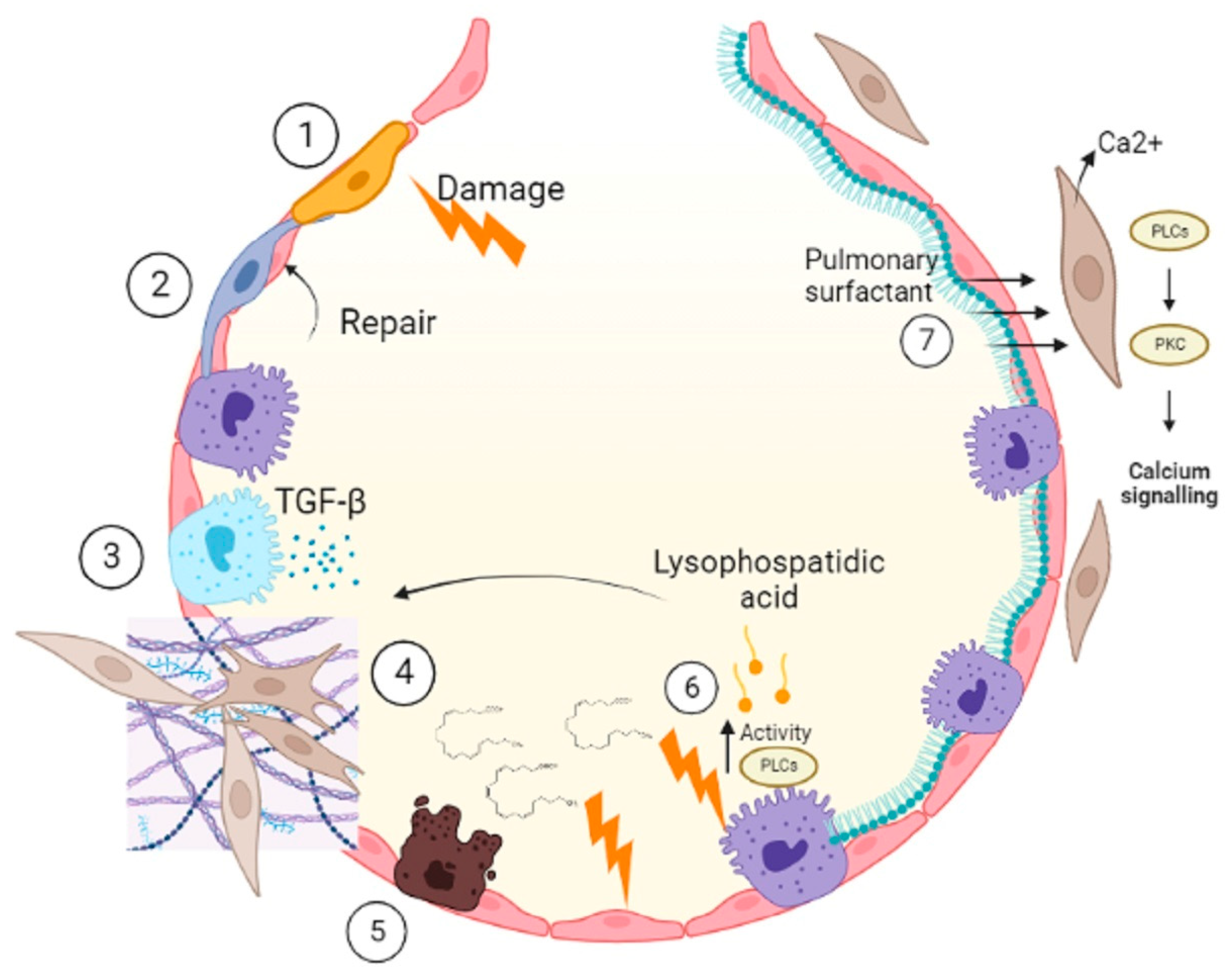
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guagliardo, R.; Pérez-Gil, J.; De Smedt, S.; Raemdonck, K. Pulmonary Surfactant and Drug Delivery: Focusing on the Role of Surfactant Proteins. J. Control. Release 2018, 291, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.H.; Zou, X.; Abed, S.M.; Korma, S.A.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X. Natural Phospholipids: Occurrence, Biosynthesis, Separation, Identification, and Beneficial Health Aspects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañadas, O.; Olmeda, B.; Alonso, A.; Pérez-Gil, J. Lipid–Protein and Protein–Protein Interactions in the Pulmonary Surfactant System and Their Role in Lung Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudelo, C.W.; Samaha, G.; Garcia-Arcos, I. Alveolar Lipids in Pulmonary Disease. A Review. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallner, S.; Orsó, E.; Grandl, M.; Konovalova, T.; Liebisch, G.; Schmitz, G. Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphatidylethanolamine Plasmalogens in Lipid Loaded Human Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autilio, C.; Pérez-Gil, J. Understanding the Principle Biophysics Concepts of Pulmonary Surfactant in Health and Disease. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018, 104, F443–F451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, M.; Voelker, D.R. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Viral Actions of Anionic Pulmonary Surfactant Phospholipids. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2022, 1867, 159139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollag, W.B.; Gonzales, J.N. Phosphatidylglycerol and Surfactant: A Potential Treatment for COVID-19? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, W. Lung Surfactant: Function and Composition in the Context of Development and Respiratory Physiology. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2016, 208, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, P.; Zarini, S.; Chan, E.D.; Leslie, C.C.; Murphy, R.C.; Voelker, D.R. Pulmonary Surfactant Phosphatidylglycerol Inhibits Mycoplasma Pneumoniae-Stimulated Eicosanoid Production from Human and Mouse Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7841–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelker, D.R.; Numata, M. Phospholipid Regulation of Innate Immunity and Respiratory Viral Infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 4282–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-Z.; Cui, B.; Liu, H.-Z.; Chen, Z.-R.; Yan, H.-M.; Hua, F.; Hu, Z.-W. Targeting TLR2 Attenuates Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis by Reversion of Suppressive Immune Microenvironment. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Go, H.; Akira, S.; Chung, D.H. TLR2-Mediated Production of IL-27 and Chemokines by Respiratory Epithelial Cells Promotes Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4007–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, H.; Koh, J.; Kim, H.S.; Jeon, Y.K.; Chung, D.H. Expression of Toll-like Receptor 2 and 4 Is Increased in the Respiratory Epithelial Cells of Chronic Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia Patients. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Agassandian, M.; Mallampalli, R.K. Surfactant Phospholipid Metabolism. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2013, 1831, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabré, E.J.; Loura, L.M.S.; Fedorov, A.; Perez-Gil, J.; Prieto, M. Topology and Lipid Selectivity of Pulmonary Surfactant Protein SP-B in Membranes: Answers from Fluorescence. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, E.; Pérez-Gil, J. Composition, Structure and Mechanical Properties Define Performance of Pulmonary Surfactant Membranes and Films. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 185, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.Y.; Veldhuizen, R.A.W.; Neumann, A.W.; Petersen, N.O.; Possmayer, F. Current Perspectives in Pulmonary Surfactant—Inhibition, Enhancement and Evaluation. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 1947–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzada, E.; Onguka, O.; Claypool, S.M. Phosphatidylethanolamine Metabolism in Health and Disease. In International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 321, pp. 29–88. ISBN 978-0-12-804707-1. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-de-Lara, L.G.; Tlatelpa-Romero, B.; Romero, Y.; Fernández-Tamayo, N.; Vazquez-de-Lara, F.; Justo-Janeiro, M.J.; Garcia-Carrasco, M.; De-la-Rosa Paredes, R.; Cisneros-Lira, J.G.; Mendoza-Milla, C.; et al. Phosphatidylethanolamine Induces an Antifibrotic Phenotype in Normal Human Lung Fibroblasts and Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Wallace, A.M.; Schneider, D.A.; Burg, E.; Kim, J.; Alekseeva, E.; Ubags, N.D.J.; Cool, C.D.; Fang, L.; Suratt, B.T.; et al. AIBP Augments Cholesterol Efflux from Alveolar Macrophages to Surfactant and Reduces Acute Lung Inflammation. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e120519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras-Gómez, M.; Shoaib, T.; Steer, D.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Leal, C. Pathological Cardiolipin-Promoted Membrane Hemifusion Stiffens Pulmonary Surfactant Membranes. Biophys. J. 2022, 121, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markin, C.J.; Hall, S.B. The Anionic Phospholipids of Bovine Pulmonary Surfactant. Lipids 2021, 56, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harayama, T.; Shimizu, T. Roles of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, from Mediators to Membranes. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dial, C.F.; Tune, M.K.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Mock, J.R. Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cell Expression of Keratinocyte Growth Factor Enhances Lung Epithelial Proliferation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R.J. Biology of Alveolar Type II Cells. Respirology 2006, 11, S12–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsma, J.; Postle, A.D. Analysis of the Regulation of Surfactant Phosphatidylcholine Metabolism Using Stable Isotopes. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2017, 211, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakane, F.; Hoshino, F.; Murakami, C. New Era of Diacylglycerol Kinase, Phosphatidic Acid and Phosphatidic Acid-Binding Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonsson, B. Phosphatidylinositol Synthase from Mammalian Tissues. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Lipids Lipid Metab. 1997, 1348, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, D.E. A Stimulating Factor for Fatty Acid Biosynthesis—Research with Konrad Bloch: Mentor and Friend. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 292, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, G.S.; Templer, R.H.; Smith, W.S.; Hunt, A.N.; Jackowski, S. Modulation of CTP:Phosphocholine Cytidylyltransferase by Membrane Curvature Elastic Stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9032–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agassandian, M.; Chen, B.B.; Pulijala, R.; Kaercher, L.; Glasser, J.R.; Mallampalli, R.K. Calcium-Calmodulin Kinase I Cooperatively Regulates Nucleocytoplasmic Shuttling of CCTα by Accessing a Nuclear Export Signal. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2755–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Magdaleno, S.; Tabas, I.; Jackowski, S. Early Embryonic Lethality in Mice with Targeted Deletion of the CTP:Phosphocholine Cytidylyltransferase α Gene (Pcyt1a). Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Tontonoz, P. Phospholipid Remodeling in Physiology and Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautel, S.E.; Kyle, J.E.; Clair, G.; Sontag, R.L.; Weitz, K.K.; Shukla, A.K.; Nguyen, S.N.; Kim, Y.-M.; Zink, E.M.; Luders, T.; et al. Lipidomics Reveals Dramatic Lipid Compositional Changes in the Maturing Postnatal Lung. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster, C.R. From Yeast to Humans—Roles of the Kennedy Pathway for Phosphatidylcholine Synthesis. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hyatt, B.A.; Mucenski, M.L.; Mason, R.J.; Shannon, J.M. Identification and Characterization of a Lysophosphatidylcholine Acyltransferase in Alveolar Type II Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11724–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, V.; Hunt, A.N.; Postle, A.D. Regulation of Lung Surfactant Phospholipid Synthesis and Metabolism. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2013, 1831, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, W.; Bilal, M.; McClory, J.; Dourado, D.; Quinn, D.; Moody, T.S.; Sutcliffe, I.; Huang, M. Mechanism of Phosphatidylglycerol Activation Catalyzed by Prolipoprotein Diacylglyceryl Transferase. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 7092–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunsom, N.J.; Cockcroft, S. CDP-Diacylglycerol Synthases (CDS): Gateway to Phosphatidylinositol and Cardiolipin Synthesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, J.N.; Kennelly, J.P.; Wan, S.; Vance, J.E.; Vance, D.E.; Jacobs, R.L. The Critical Role of Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphatidylethanolamine Metabolism in Health and Disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansson, M.; Hokynar, K.; Somerharju, P. Mechanisms of Glycerophospholipid Homeostasis in Mammalian Cells. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunsom, N.J.; Gomez-Espinosa, E.; Ashlin, T.G.; Cockcroft, S. Mitochondrial CDP-Diacylglycerol Synthase Activity Is Due to the Peripheral Protein, TAMM41 and Not Due to the Integral Membrane Protein, CDP-Diacylglycerol Synthase 1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1863, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradies, G.; Paradies, V.; Ruggiero, F.M.; Petrosillo, G. Role of Cardiolipin in Mitochondrial Function and Dynamics in Health and Disease: Molecular and Pharmacological Aspects. Cells 2019, 8, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzuto, M.; Pelegrin, P. Cardiolipin in Immune Signaling and Cell Death. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.-C.; Chiang, Y. Sphingomyelin Synthase Family and Phospholipase Cs. In Sphingolipid Metabolism and Metabolic Disease; Jiang, X.-C., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; Volume 1372, pp. 77–86. ISBN 978-981-19039-3-9. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, M.; Okazaki, T. Role of Ceramide/Sphingomyelin (SM) Balance Regulated through “SM Cycle” in Cancer. Cell. Signal. 2021, 87, 110119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmeda, B.; Martínez-Calle, M.; Pérez-Gil, J. Pulmonary Surfactant Metabolism in the Alveolar Airspace: Biogenesis, Extracellular Conversions, Recycling. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2017, 209, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobi, N.; Siber, G.; Bouzas, V.; Ravasio, A.; Pérez-Gil, J.; Haller, T. Physiological Variables Affecting Surface Film Formation by Native Lamellar Body-like Pulmonary Surfactant Particles. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, N.; Miličić, G.; Bodnar, N.O.; Wu, X.; Rapoport, T.A. Mechanism of Lamellar Body Formation by Lung Surfactant Protein B. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 49–66.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindlbeck, U.; Wittmann, T.; Höppner, S.; Kinting, S.; Liebisch, G.; Hegermann, J.; Griese, M. ABCA3 Missense Mutations Causing Surfactant Dysfunction Disorders Have Distinct Cellular Phenotypes. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, R.; Kaltenborn, E.; Frixel, S.; Wittmann, T.; Liebisch, G.; Schmitz, G.; Griese, M. ABCA3 Protects Alveolar Epithelial Cells against Free Cholesterol Induced Cell Death. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Trapnell, B.C. Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Syndrome. Clin. Chest Med. 2016, 37, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazawa, R.; Ueda, T.; Abe, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Eda, R.; Kondoh, S.; Morimoto, K.; Tanaka, T.; Yamaguchi, E.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Inhaled GM-CSF for Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, J.; Thada, P.K.; Sedhai, Y.R. Asbestosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- La Maestra, S.; Micale, R.T.; Ferretti, M.; Izzotti, A.; Gaggero, L. Attenuation of Oxidative Stress and Chromosomal Aberrations in Cultured Macrophages and Pulmonary Cells Following Self-Sustained High Temperature Synthesis of Asbestos. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, A.J.; Holian, A.; Scheule, R.K. Lung Lining Fluid Modification of Asbestos Bioactivity for the Alveolar Macrophage. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1991, 110, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesur, O.; Bernard, A.M.; Bégin, R.O. Clara Cell Protein (CC-16) and Surfactant-Associated Protein A (SP-A) in Asbestos-Exposed Workers. Chest 1996, 109, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, L.; Betsholtz, C.; Andrae, J. PDGF-A Signaling Is Required for Secondary Alveolar Septation and Controls Epithelial Proliferation in the Developing Lung. Development 2018, 145, dev161976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrington, J.M.; Hershberger, D.M. Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Beri, R.; Mueller, A.; Kamp, D.W. Molecular Mechanisms of Asbestos-Induced Lung Epithelial Cell Apoptosis. Chem. -Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krefft, S.; Wolff, J.; Rose, C. Silicosis: An Update and Guide for Clinicians. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, M.I.; Waksman, J.; Curtis, J. Silicosis: A Review. Dis. Mon. 2007, 53, 394–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.O.; Lamberty, J.; Pizzolato, P.; Coover, J. The ultrastructure of acute silicosis. Arch. Pathol. 1973, 96, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wei, W.; Liu, Z.; Song, E.; Lou, J.; Feng, L.; Huang, R.; Chen, C.; Ke, P.C.; Song, Y. Serum Apolipoprotein A-I Depletion Is Causative to Silica Nanoparticles–Induced Cardiovascular Damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2108131118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.E.; Bakewell, W.E.; Katyal, S.L.; Singh, G.; Hook, G.E.R. Induction of Surfactant Protein (SP-A) Biosynthesis and SP-A MRNA in Activated Type II Cells during Acute Silicosis in Rats. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1990, 3, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesur, O.; Bouhadiba, T.; Melloni, B.; Cantin, A.; Whitsett, J.A.; Bégin, R. Alterations of Surfactant Lipid Turnover in Silicosis: Evidence of a Role for Surfactant-Associated Protein A (SP-A). Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1995, 76, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Niedermann, G.; Burnet, N.G.; Siva, S.; Lee, A.W.M.; Hegi-Johnson, F. Radiotherapy Toxicity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, M.; Cortesi, M.; Zamagni, A.; Tesei, A. The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Radiation-Induced Lung Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubags, N.D.J.; Marsland, B.J. Mechanistic Insight into the Function of the Microbiome in Lung Diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1602467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, R.; Mora, A.L. Lipid Metabolism: A New Player in the Conundrum of Lung Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 61, 669–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Clark, J.C.; Shaw-White, J.R.; Stahlman, M.T.; Boutell, C.J.; Whitsett, J.A. Gene Structure and Expression of Human Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 in Respiratory Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 8108–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, C.; Guo, J.; Sun, W.; Xian, L.; Bai, D.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, B.; Cui, J.; et al. Radiation-Driven Lipid Accumulation and Dendritic Cell Dysfunction in Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.; Nandkeolyar, S.; Lan, H.; Desai, P.; Evans, J.; Hauschild, C.; Choksi, D.; Abudayyeh, I.; Contractor, T.; Hilliard, A. Amiodarone: A Comprehensive Guide for Clinicians. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2020, 20, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baritussio, A.; Marzini, S.; Agostini, M.; Alberti, A.; Cimenti, C.; Bruttomesso, D.; Manzato, E.; Quaglino, D.; Pettenazzo, A. Amiodarone Inhibits Lung Degradation of SP-A and Perturbs the Distribution of Lysosomal Enzymes. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 281, L1189–L1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaki, S.; Suezawa, T.; Moriguchi, K.; Nakao, K.; Toyomoto, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Murakami, K.; Hagiwara, M.; Gotoh, S. Hydroxypropyl Cyclodextrin Improves Amiodarone-Induced Aberrant Lipid Homeostasis of Alveolar Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beketov, V.D.; Lebedeva, M.V.; Mukhin, N.A.; Serova, A.G.; Ponomarev, A.B.; Popova, E.N.; Yanakaeva, A.S.; Solomka, V.A.; Kondrashov, A.V.; Konovalov, D.V. Clinical Significance of the Determination of Surfactant Proteins A and D in Assessing the Activity of Lung Sarcoidosis. Ter. Arkhiv 2018, 90, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesur, O.; Mancini, N.M.; Janot, C.; Chabot, F.; Boitout, A.; Polu, J.M.; Gérard, H. Loss of lymphocyte modulatory control by surfactant lipid extracts from acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Comparison with sarcoidosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 1994, 7, 1944–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnula, V.L. Cell Specific Expression of Peroxiredoxins in Human Lung and Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Thorax 2002, 57, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peroxiredoxin Systems: Structures and Functions; Flohé, L., Harris, J.R., Eds.; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-1-4020-6050-2. [Google Scholar]
- Letsiou, E.; Htwe, Y.M.; Dudek, S.M. Secretory Phospholipase A2 Enzymes in Acute Lung Injury. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, B.; Gomez-Manjarres, D.; Cosgrove, G.; Patel, D.C. What Is Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, P7–P8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churg, A. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: New Concepts and Classifications. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekananda, J.; Smith, D.; King, R.J. Sphingomyelin Metabolites Inhibit Sphingomyelin Synthase and CTP:Phosphocholine Cytidylyltransferase. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 281, L98–L107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guan, L.; Wang, E.; Schuchman, E.H.; He, X.; Zeng, M. SiO 2 Stimulates Macrophage Stress to Induce the Transformation of Lung Fibroblasts into Myofibroblasts and Its Relationship with the Sphingomyelin Metabolic Pathway. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 1584–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. The Leading Role of Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis—PubMed. Cell. Signal. 2019, 66, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremayne, P.; John Clark, S. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A More Common Condition than You May Think. Br. J. Nurs. 2021, 30, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somogyi, V.; Chaudhuri, N.; Torrisi, S.E.; Kahn, N.; Müller, V.; Kreuter, M. The Therapy of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: What Is Next? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Tan, C.; Zhang, J. Alveolar Epithelial Type 2 Cell Dysfunction in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lung 2022, 200, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lara, L.V.; Becerril, C.; Montaño, M.; Ramos, C.; Maldonado, V.; Meléndez, J.; Phelps, D.S.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M. Surfactant Components Modulate Fibroblast Apoptosis and Type I Collagen and Collagenase-1 Expression. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L950–L957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsinde, J.; Pérez, R.; Balboa, M.A. Calcium-Independent Phospholipase A2 and Apoptosis. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2006, 1761, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; He, A.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Xie, H.; Luo, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guan, J.; He, Q.; et al. TSSK4 Upregulation in Alveolar Epithelial Type-II Cells Facilitates Pulmonary Fibrosis through HSP90-AKT Signaling Restriction and AT-II Apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M.; Van der Aar, E.M.; Van de Steen, O.; Allamassey, L.; Desrivot, J.; Dupont, S.; Fagard, L.; Ford, P.; Fieuw, A.; Wuyts, W. Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of GLPG1690, a Novel Autotaxin Inhibitor, to Treat Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (FLORA): A Phase 2a Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafadi, H.N.; Staab-Weijnitz, C.A.; Lehmann, M.; Lindner, M.; Peschel, B.; Königshoff, M.; Wagner, D.E. An Ex Vivo Model to Induce Early Fibrosis-like Changes in Human Precision-Cut Lung Slices. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L896–L902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Chun, J.; Duffield, J.S.; Lagares, D.; Wada, T.; Luster, A.D.; Tager, A.M. Lysophosphatidic Acid Signaling through Its Receptor Initiates Pro-Fibrotic Epithelial Cell Fibroblast Communication Mediated by Epithelial Cell Derived Connective Tissue Growth Factor. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Xie, Y.; Abel, P.W.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, L.; Hao, J.; Wolff, D.W.; Wei, T.; Tu, Y. Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-Β1-Induced MiR-133a Inhibits Myofibroblast Differentiation and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Morgani, S.M.; David, C.J.; Wang, Q.; Er, E.E.; Huang, Y.-H.; Basnet, H.; Zou, Y.; Shu, W.; Soni, R.K.; et al. TGF-β Orchestrates Fibrogenic and Developmental EMTs via RAS Effector RREB1. Nature 2020, 577, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Kalaycioglu, O.; Schoenfeld, B.; Hamm, H.; Bartsch, W.; Costabel, U. Increased surfactant protein A content in human alveolar macrophages in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Acta Cytol. 1992, 36, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaku, S.; Nguyen, C.D.; Htet, N.N.; Tutera, D.; Barr, J.; Paintal, H.S.; Kuschner, W.G. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Etiology, Pathogenesis, and Summary on Management. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumende, C.M. Pulmonary Fibrosis Caused by Severe COVID-19 Infection: Discharge May Not Be The End of Treatment. Acta Med. Indones. 2021, 53, 141–142. [Google Scholar]
- Michalski, J.E.; Kurche, J.S.; Schwartz, D.A. From ARDS to Pulmonary Fibrosis: The next Phase of the COVID-19 Pandemic? Transl. Res. 2022, 241, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xiao, K.; Xie, L. Progress in Preclinical Studies of Macrophage Autophagy in the Regulation of ALI/ARDS. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 922702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, L.T. Healing after COVID-19: Are Survivors at Risk for Pulmonary Fibrosis? Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L257–L265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, K.; Hu, J.; Cheng, M.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, T.; et al. Autotaxin Levels in Serum and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Are Associated with Inflammatory and Fibrotic Biomarkers and the Clinical Outcome in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. J. Intensive Care 2021, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tlatelpa-Romero, B.; Cázares-Ordoñez, V.; Oyarzábal, L.F.; Vázquez-de-Lara, L.G. The Role of Pulmonary Surfactant Phospholipids in Fibrotic Lung Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010326
Tlatelpa-Romero B, Cázares-Ordoñez V, Oyarzábal LF, Vázquez-de-Lara LG. The Role of Pulmonary Surfactant Phospholipids in Fibrotic Lung Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010326
Chicago/Turabian StyleTlatelpa-Romero, Beatriz, Verna Cázares-Ordoñez, Luis F. Oyarzábal, and Luis G. Vázquez-de-Lara. 2023. "The Role of Pulmonary Surfactant Phospholipids in Fibrotic Lung Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010326
APA StyleTlatelpa-Romero, B., Cázares-Ordoñez, V., Oyarzábal, L. F., & Vázquez-de-Lara, L. G. (2023). The Role of Pulmonary Surfactant Phospholipids in Fibrotic Lung Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010326





