Light-Up Split Broccoli Aptamer as a Versatile Tool for RNA Assembly Monitoring in Cell-Free TX-TL Systems, Hybrid RNA/DNA Origami Tagging and DNA Biosensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Expression and Self-Assembly in an E. Coli Cell-Free TX-TL System
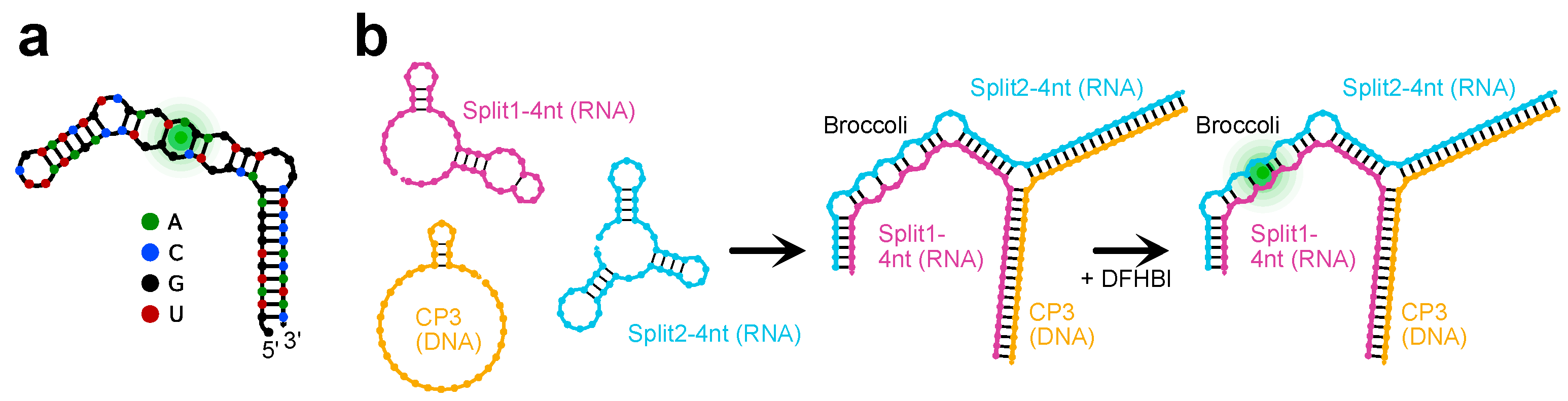
2.2. Activation of the Split Broccoli Aptamer through Hybrid RNA/DNA Origami
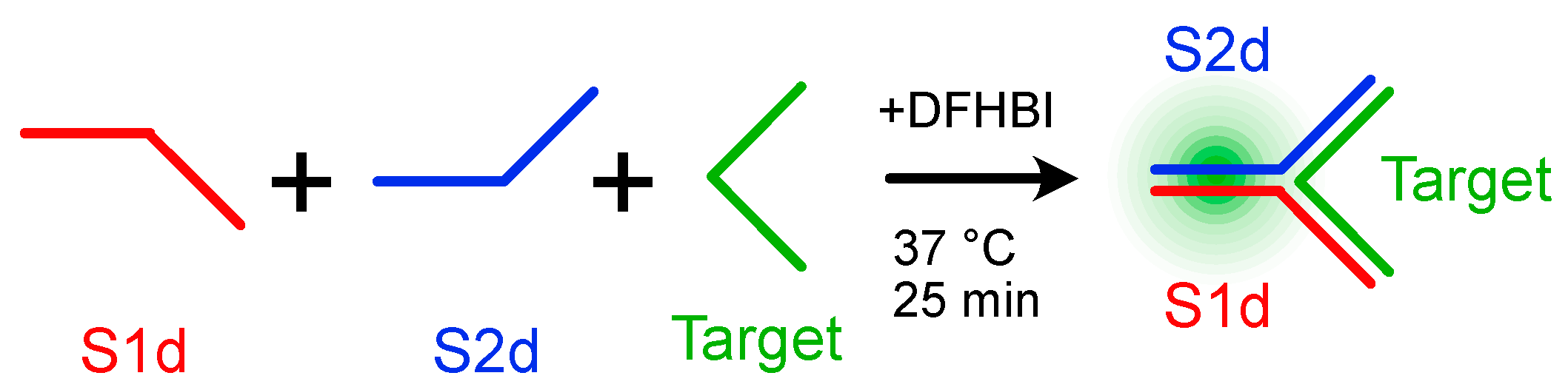
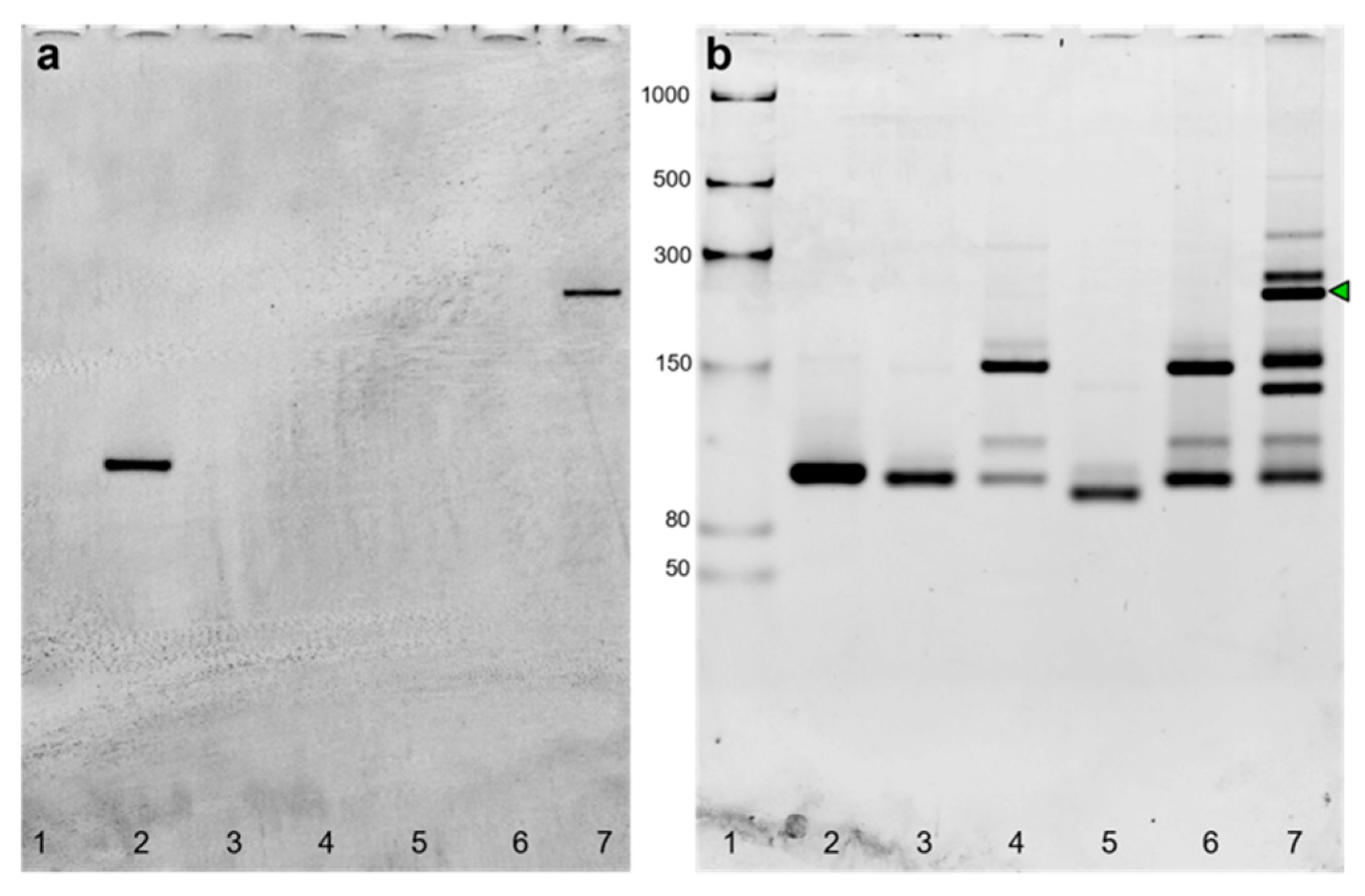
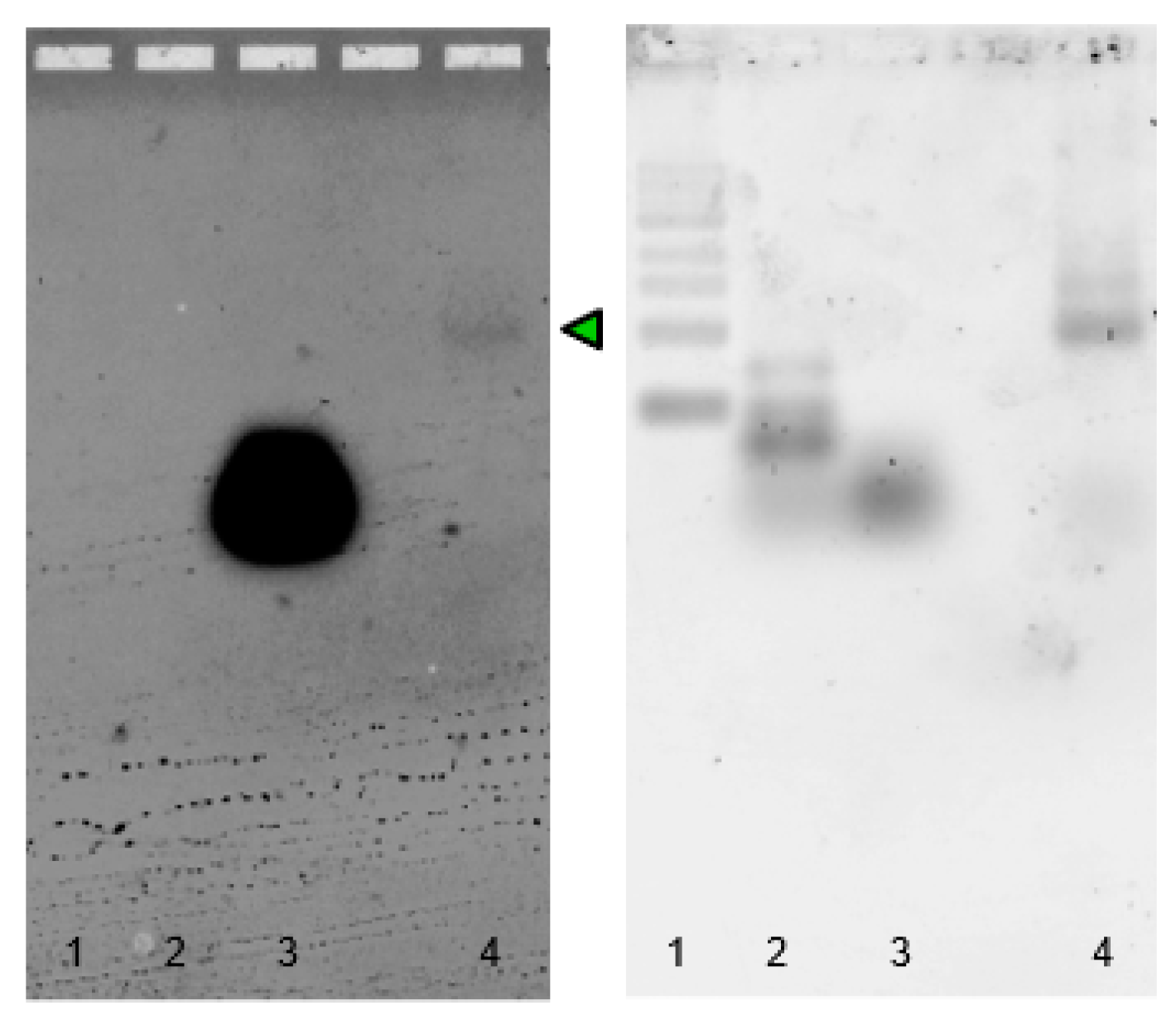
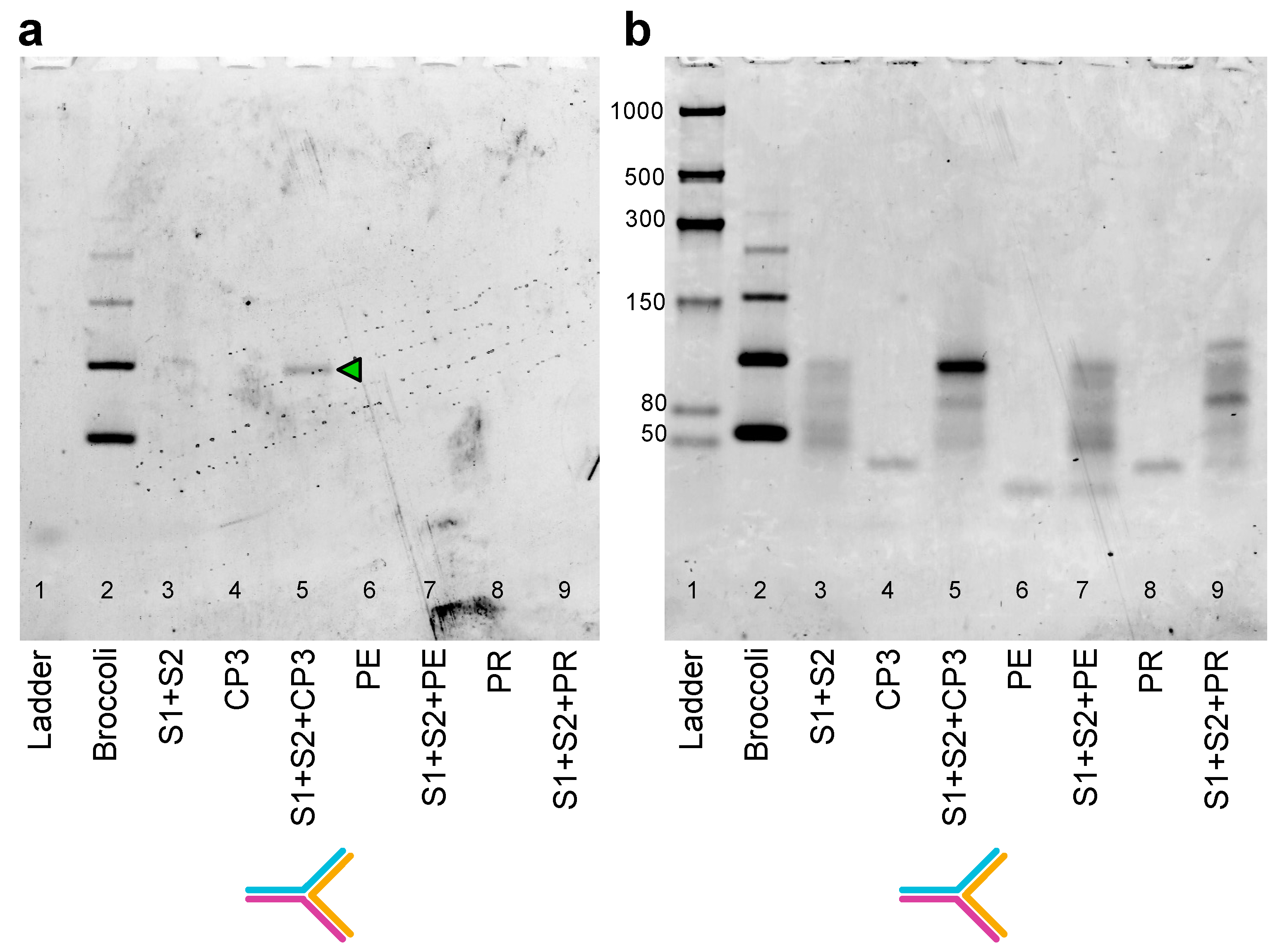
2.3. Sequence Design, Dot Blot Assay on Target CP3 and Denaturing PAGE Analysis of DNA/RNA Oligonucleotides
2.4. Split Broccoli Aptamer System: PAGE Analysis and in-Gel Imaging
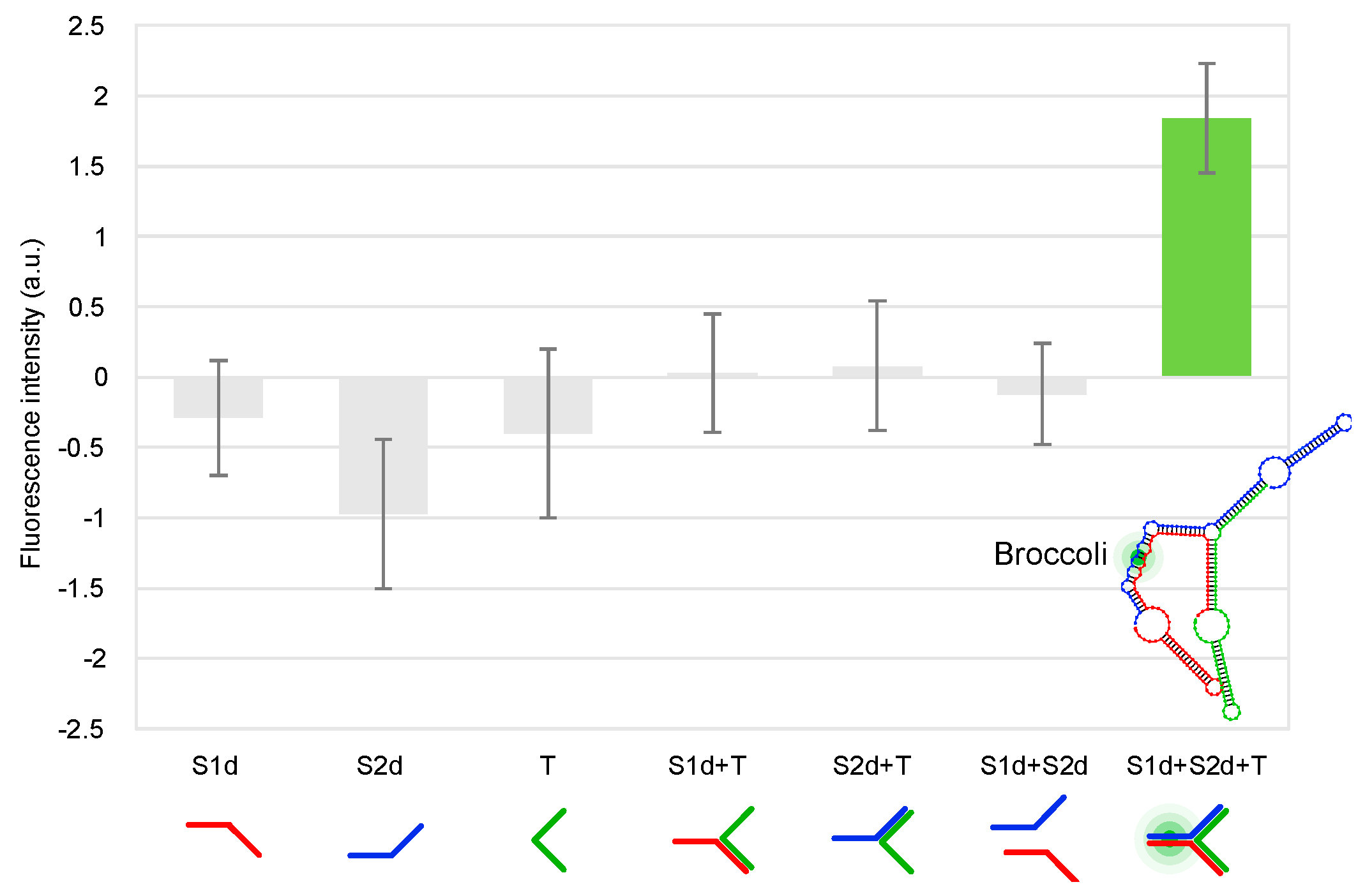
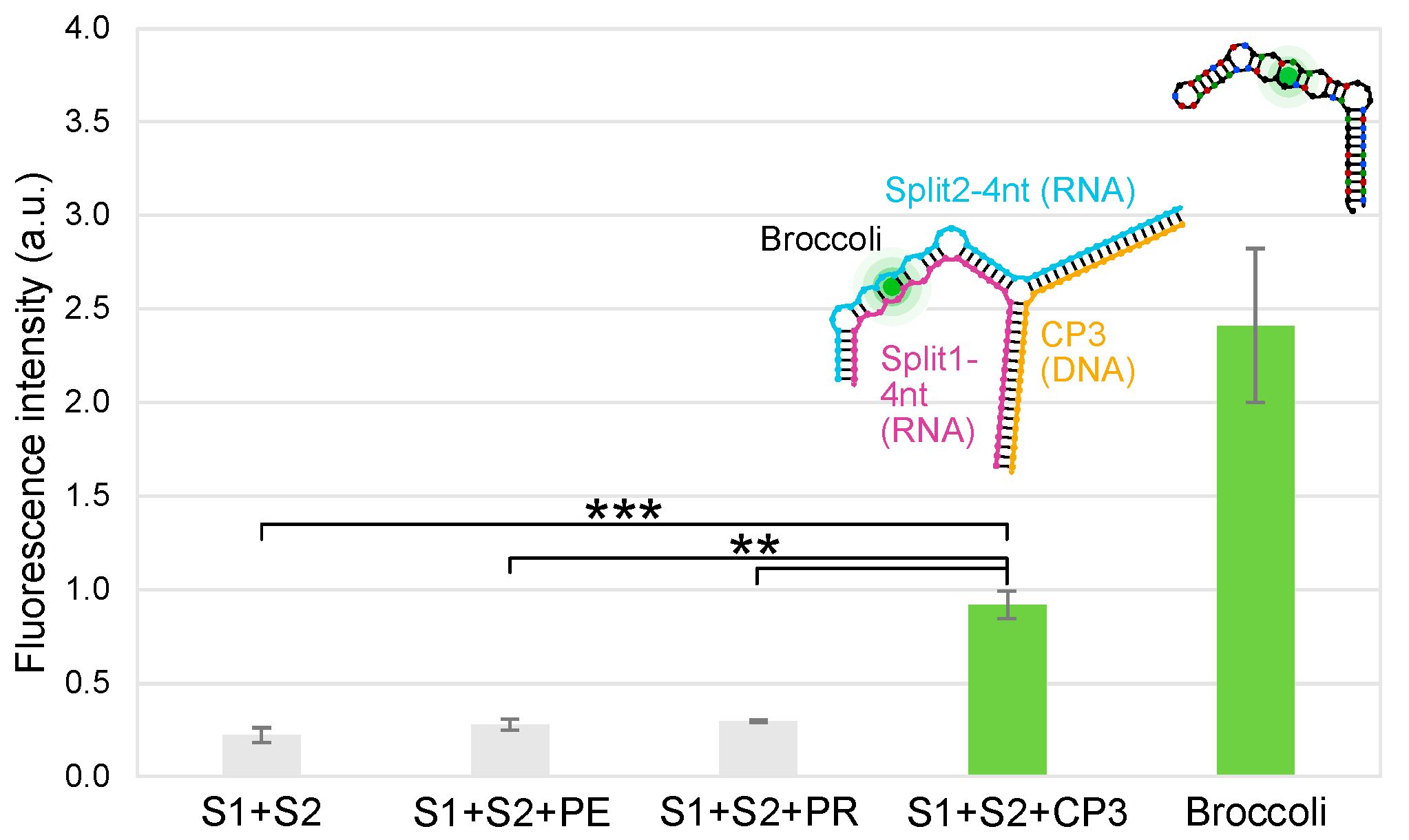
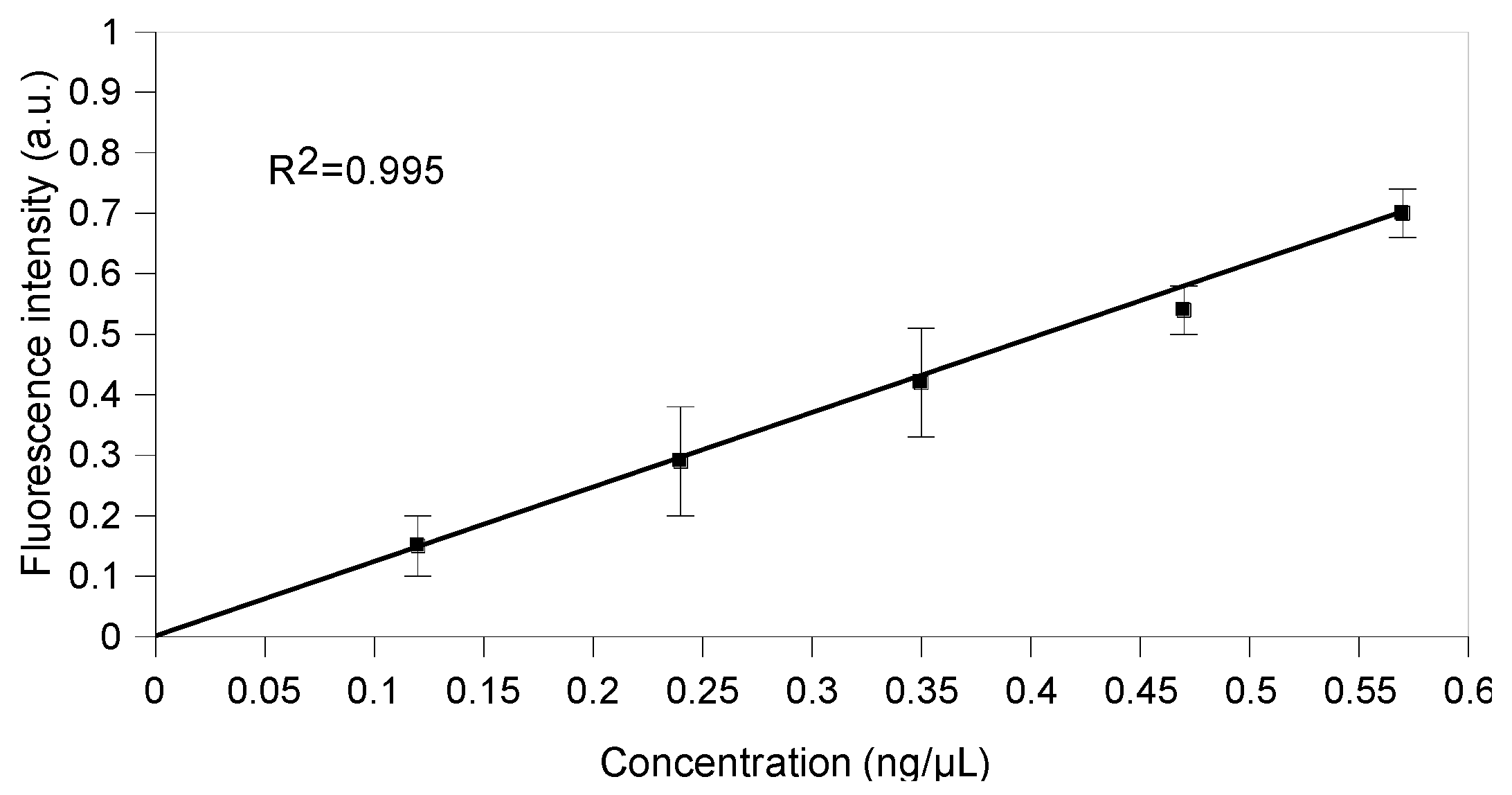
2.5. Split Broccoli Aptamer System: Fluorescence Measurements In Vitro
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Sequence Design and Prediction of Complex Folding
3.3. Expression, Assembly and Fluorescence Measurements in PURExpress Cell-Free TX-TL System
3.4. Hybrid RNA/DNA Origami Synthesis and Purification
3.5. Hybrid DNA/RNA Origami Characterization: Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) Imaging
3.6. Hybrid RNA/DNA Origami and In-Gel Imaging
3.7. Dot Blot Assay
3.8. Synthesis of Broccoli Aptamer and Purity Control of the Split Aptamer Sequences (Split1,2-8nt, Split1,2-4nt and Split1,2-0nt) by Denaturing PAGE
3.9. Assembly of RNA Split Sequences with Complementary CP3 and Non-Complementary Sequences PE and PR: PAGE and In-Gel Imaging
3.10. Assembly of RNA Split Sequences with Complementary CP3 and Non-Complementary Sequences PE and PR: PAGE and Fluorescence Measurements by qPCR Equipment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolpashchikov, D.M.; Spelkov, A. Binary (Split) light-up aptameric sensors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4988–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grate, D.; Wilson, C. Laser-mediated, site-specific inactivation of RNA transcripts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6131–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babendure, J.R.; Adams, S.R.; Tsien, R.Y. Aptamers Switch on Fluorescence of Triphenylmethane Dyes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14716–14717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strack, R.L.; Disney, M.D.; Jaffrey, S.R. A super folding Spinach2 reveals the dynamic nature of trinucleotide repeat—Containing RNA. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, K.D.; Chen, M.C.; Song, W.; Strack, R.L.; Thorn, A.; Jaffrey, S.R.; Ferre-D’Amare, A.R. Structural basis for activity of highly efficient RNA mimics of green fluorescent protein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autour, A.; Westhof, E.; Ryckelynck, M. iSpinach: A fluorogenic RNA aptamer optimized for in vitro applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2491–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonov, G.S.; Moon, J.D.; Svensen, N.; Jaffrey, S.R. Broccoli: Rapid Selection of an RNA Mimic of Green Fluorescent Protein by Fluorescence-Based Selection and Directed Evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16299–16308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonov, G.S.; Kam, C.W.; Song, W.; Jaffrey, S.R. In-gel imaging of RNA processing using Broccoli reveals optimal aptamer expression strategies. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, E.; Kozyra, J.W.; Gu, J.Y.; Stimming, U.; Piantanida, L.; Voïtchovsky, K.; Krasnogor, N. Isothermal folding of a light-up bio-orthogonal RNA origami nanoribbon. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.K.; Tawiah, K.D.; Lichte, M.F.; Porciani, D.; Burke, D.H. A fluorescent split aptamer for visualizing RNA-RNA assembly in vivo. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanayake Mudiyanselage, A.P.K.K.; Yu, Q.; Leon-Duque, M.A.; Zhao, B.; Wu, R.; You, M. Genetically Encoded Catalytic Hairpin Assembly for Sensitive RNA Imaging in Live Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 8739–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xie, X.; Hu, X.; Song, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Glinsky, G.; Chen, N.; et al. In Situ Spatial Complementation of Aptamer-Mediated Recognition Enables Live-Cell Imaging of Native RNA Transcripts in Real Time. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Wu, R.; Karunanayake Mudiyanselage, A.P.K.K.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, B.; Xie, Y.; Bagheri, Y.; Tian, Q.; You, M. In Situ Genetically Cascaded Amplification for Imaging RNA Subcellular Locations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2968–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocabey, S.; Chiarelli, G.; Acuna, P.G.; Ruegg, C. Ultrasensitive and multiplexed miRNA detection system with DNA-PAINT. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 224, 115053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothoulakis, G.; Nguyen, M.T.A.; Andersen, E.S. Utilizing RNA origami scaffolds in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for dCas9-mediated transcriptional control. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 7176–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, M.D.E.; Sparvath, S.M.; Nielsen, T.B.; Langvad, A.H.; Grossi, G.; Gothelf, K.V.; Andersen, E.S. Development of a genetically encodable FRET system using fluorescent RNA aptamers. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro Vallina, N.; McRae, E.K.S.; Hansen, B.K.; Boussebayle, A.; Andersen, E.S. RNA origami scaffolds facilitate cryo-EM characterization of a Broccoli–Pepper aptamer FRET pair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 1, gkad224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, E.; Kozyra, J.W.; Shirt-Ediss, B.; Piantanida, L.; Voïtchovsky, K.; Krasnogor, N. Co-transcriptional folding of a bio-orthogonal fluorescent scaffolded RNA origami. ACS Synth. Biol. 2020, 9, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopiccolo, A.; Shirt-Ediss, B.; Torelli, E.; Olulana, A.F.A.; Castronovo, M.; Fellermann, H.; Krasnogor, N. A last-in first-out stack data structure implemented in DNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, K.; Grubmuller, H.; Igaev, M.; Göpfrich, K. Choice of fluorophore affects dynamic DNA nanostructures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 4186–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzini, P.; Manzano, M.; Farre, C.; Meylheuc, T.; Chaix, C.; Ramarao, N.; Vidic, J. Highly sensitive detection of Campylobacter spp. in chicken meat using a silica nanoparticle enhanced dot blot DNA biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, L. Flow-homogeneous electrochemical sensing system based on 2D metal-organic framework nanozyme for successive microRNA assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 206, 114120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossettini, A.; Vidic, J.; Maifreni, M.; Marino, M.; Pinamonti, D.; Manzano, M. Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, Campylobacter spp., and Escherichia coli in food using biosensors. Food Control 2022, 137, 108962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, D.; Wang, R. DNA-Based Biosensors for the Biochemical Analysis: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.K.; Archuleta, C.M.; Alam, K.K.; Lucks, J.B. Programming cell-free biosensors with DNA strand displacement circuits. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.A.; Pothoulakis, G.; Andersen, E.S. Synthetic Translational Regulation by Protein-Binding RNA Origami Scaffolds. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laohakunakorn, N.; Grasemann, L.; Lavickova, B.; Michielin, G.; Shahein, A.; Swank, Z.; Maerkl, S.J. Bottom-up Construction of Complex Biomolecular Systems with Cell-Free Synthetic Biology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, R.; Noireaux, V. Synthetic Biology with an All E. coli TXTL System: Quantitative Characterization of Regulatory Elements and Gene Circuits. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1772, 61–93. [Google Scholar]
- Garenne, D.; Haines, M.C.; Romantseva, E.F.; Freemont, P.; Strychalski, E.A.; Noireaux, V. Cell-free gene expression. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Morales, O.; Gueye, M.; Lacombe, L.; Nowak, C.; Schmachtenberg, R.; Hörner, M.; Jerez-Longres, C.; Mohsenin, H.; Wagner, H.I.; Weber, W. Synthetic biology as driver for the biologization of material sciences. Materials Today Bio. 2021, 11, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Inoue, A.; Tomari, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Yokogawa, T.; Nishikawa, K.; Ueda, T. Cell-free translation reconstituted with purified components. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Fan, C.; Gothelf, K.V.; Li, J.; Lin, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, N.; Nijenhuis, M.A.D.; Saccà, B.; Simmel, F.C.; et al. DNA origami. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers. 2021, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, P.W. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns. Nature 2006, 440, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Ko, S.H.; Tian, C.; Hao, C.; Mao, C. RNA-DNA hybrid origami: Folding of a long RNA single strand into complex nanostructures using short DNA helper strands. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Tatsumi, K.; Emura, T.; Hidaka, K.; Sugiyama, H. RNA-templated DNA origami structures. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozyra, J.; Ceccarelli, A.; Torelli, E.; Lopiccolo, A.; Gu, J.Y.; Fellermann, H.; Stimming, U.; Krasnogor, N. Designing Uniquely Addressable Bio-orthogonal Synthetic Scaffolds for DNA and RNA Origami. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 11401149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chandrasekaran, A.R.; Yan, M.; Valsangkar, V.A.; Feldblyum, J.I.; Sheng, J.; Halvorsen, K. A mini DNA-RNA hybrid origami nanobrick. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, F.; Wu, T.; Shang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ding, B. An RNA/DNA hybrid origami-based nanoplatform for efficient gene therapy. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.M.; Marblestone, A.H.; Teerapittayanon, S.; Vazquez, A.; Church, G.M.; Shih, W.M. Rapid prototyping of 3D DNA-origami shapes with caDNAno. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 5001–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liber, M.; Tomov, T.E.; Tsukanov, R.; Berger, Y.; Popov, M.; Khara, D.C.; Nir, E. Study of DNA Origami Dimerization and Dimer Dissociation Dynamics and of the Factors that Limit Dimerization. Small 2018, 14, 1800218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonin, K.A.; Bindewald, E.; Yaghoubian, A.J.; Voss, N.; Jacovetty, E.; Shapiro, B.A.; Jaeger, L. In vitro assembly of cubic RNA-based scaffolds designed in silico. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Hao, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Bustamante, C.; Fan, C. Programming PAM antennae for efficient CRISPR-Cas9 DNA Editing. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay9948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, A.; Sagredo, S.; Grossi, G.; Andersen, E.S.; Simmel, F.C. Out-of-Plane Aptamer Functionalization of RNA Three-Helix Tiles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debias, M.; Lelievre, A.; Smietana, M.; Müller, S. Splitting aptamers and nucleic acid enzymes for the development of advanced biosensors. Nucleic Acid. Res. 2020, 48, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, M.; Lyalina, T.; Halman, J.; Rackley, L.; Lee, L.; Dang, D.; Ke, W.; Sajja, S.; Woods, S.; Acharya, S.; et al. Broccoli Fluorets: Split Aptamers as a User-Friendly Fluorescent Toolkit for Dynamic RNA Nanotechnology. Molecules. 2018, 23, 3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzini, P.; Manzano, M.; Vidic, J.; Ramarao, N. DNA Probe for Detection of Pathogens. Patent Number IT 102020000012496, 27 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vidic, J.; Ramarao, N.; Chaix, C.; Farre, C.; Manzano, M.; Vizzini, P. Biosensor for the Determination of Pathogens in a Sample. Patent Number FR 2005578, 27 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- WHO, World Health Organization. Campylobacter. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/campylobacter (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Kanavarioti, A. HPLC method for purity evaluation of man-made single-stranded RNAs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajja, S.; Chandler, M.; Striplin, C.D.; Afonin, K.A. Activation of Split RNA Aptamers: Experiments Demonstrating the Enzymatic Synthesis of Short RNAs and Their Assembly As Observed by Fluorescent Response. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 95, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Suslov, N.; Li, N.S.; Shelke, S.A.; Evans, M.E.; Koldobskaya, Y.; Rice, P.A.; Piccirilli, J.A. A G-quadruplex–containing RNA activates fluorescence in a GFP-like fluorophore. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, N. On Using Magnesium and Potassium Ions in RNA Experiments. In Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs; Carmichael, G.G., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1206, pp. 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, J.N.; Steenberg, C.D.; Bois, J.S.; Wolfe, B.R.; Pierce, M.B.; Khan, A.R.; Dirks, R.M.; Pierce, N.A. NUPACK: Analysis and design of nucleic acid systems. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Honer zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, D.; Lee, B.L.; Stérin, T. Scadnano: A browser-based, scriptable tool for designing DNA nanostructures, DNA 2020. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on DNA Computing and Molecular Programming, Oxford, UK, 14–17 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Corpet, F. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 10881–10890. Available online: http://multalin.toulouse.inra.fr/multalin/ (accessed on 1 March 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jullien, N. AmplifX 1.7.0; Aix-Marseille University, CNRS, INP, Inst. Neurophysiopathol: Marseille, France.
- IDT OligoAnalyzer3.1. Available online: https://eu.idtdna.com/calc/analyzer (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Kalendar, R.; Khassenov, B.; Ramanculov, E.; Samuilova, O.; Ivanov, K.I. FastPCR: An in silico tool for fast primer and probe design and advanced sequence analysis. Genomics 2017, 109, 312–319. Available online: https://primerdigital.com/fastpcr.html (accessed on 1 March 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nečas, D.; Klapetek, P. Gwyddion: An open-source software for SPM data analysis. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 2012, 10, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.; Hirooka, E.Y.; de Oliveira, T.C.R.M. Development of a multiplex real-time PCR assay with an internal amplification control for the detection of Campylobacter spp. and Salmonella spp. in chicken meat. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Chon, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Hyeon, J.Y.; Seo, K.H. New colorimetric aptasensor for rapid on-site detection of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in chicken carcass samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1029, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torelli, E.; Shirt-Ediss, B.; Navarro, S.A.; Manzano, M.; Vizzini, P.; Krasnogor, N. Light-Up Split Broccoli Aptamer as a Versatile Tool for RNA Assembly Monitoring in Cell-Free TX-TL Systems, Hybrid RNA/DNA Origami Tagging and DNA Biosensing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108483
Torelli E, Shirt-Ediss B, Navarro SA, Manzano M, Vizzini P, Krasnogor N. Light-Up Split Broccoli Aptamer as a Versatile Tool for RNA Assembly Monitoring in Cell-Free TX-TL Systems, Hybrid RNA/DNA Origami Tagging and DNA Biosensing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108483
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorelli, Emanuela, Ben Shirt-Ediss, Silvia A. Navarro, Marisa Manzano, Priya Vizzini, and Natalio Krasnogor. 2023. "Light-Up Split Broccoli Aptamer as a Versatile Tool for RNA Assembly Monitoring in Cell-Free TX-TL Systems, Hybrid RNA/DNA Origami Tagging and DNA Biosensing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108483
APA StyleTorelli, E., Shirt-Ediss, B., Navarro, S. A., Manzano, M., Vizzini, P., & Krasnogor, N. (2023). Light-Up Split Broccoli Aptamer as a Versatile Tool for RNA Assembly Monitoring in Cell-Free TX-TL Systems, Hybrid RNA/DNA Origami Tagging and DNA Biosensing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108483





