WGS Revealed Novel BBS5 Pathogenic Variants, Missed by WES, Causing Ciliary Structure and Function Defects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Index Patient Case History
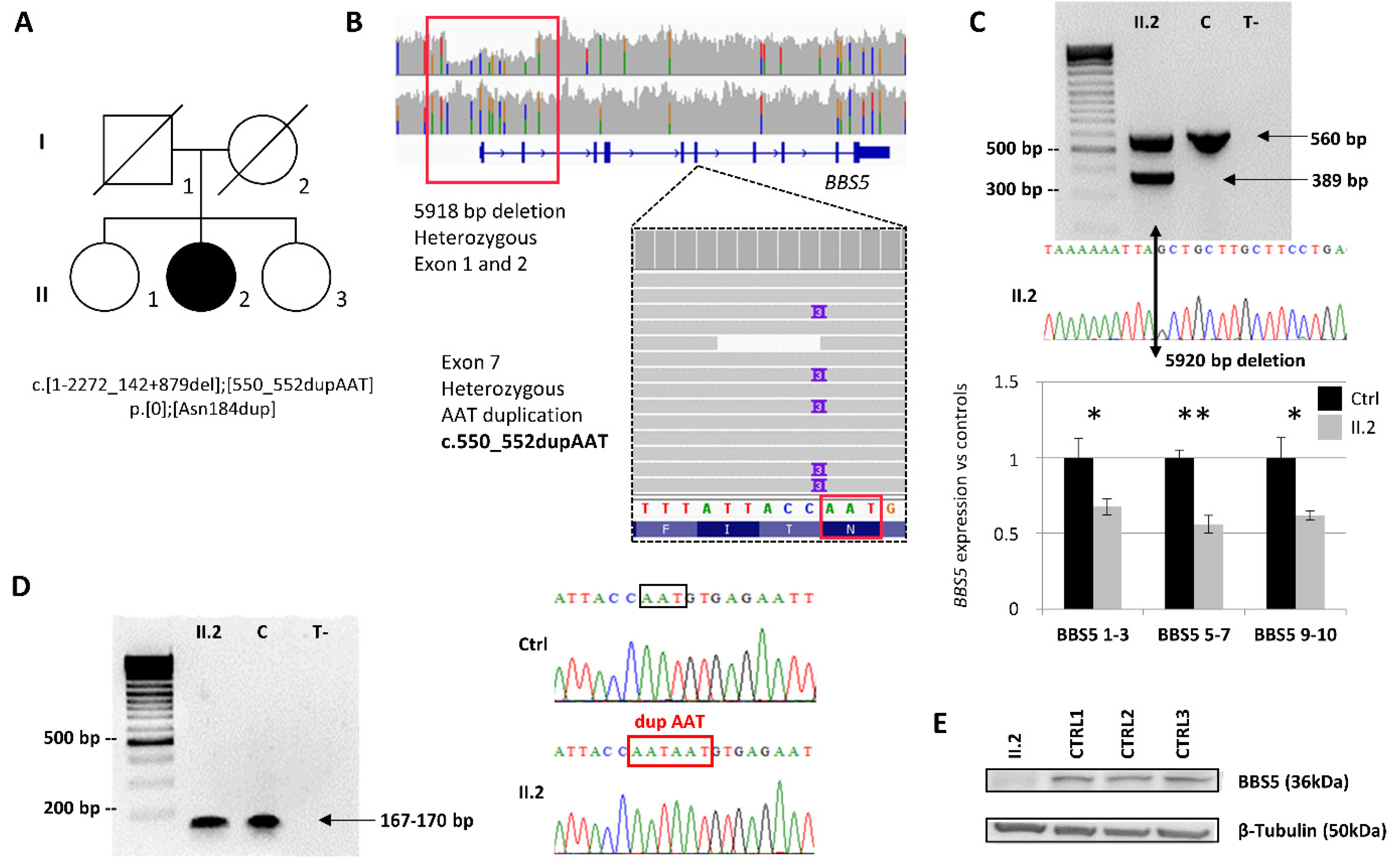
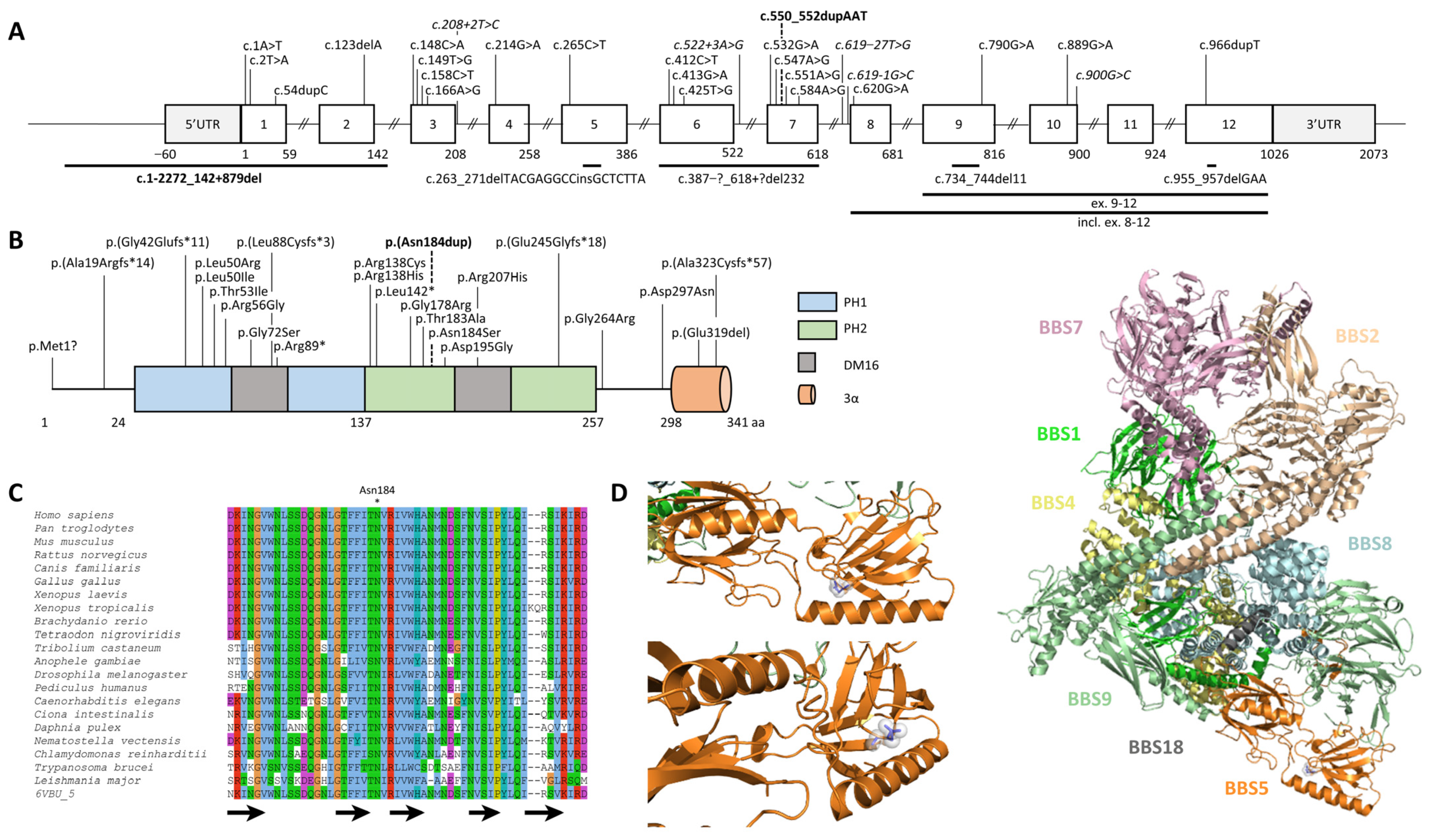
2.2. Identification and Characterization of Biallelic Variants in BBS5
2.3. BBS5 Exons 1 and 2 Deletion Screening in a Large Cohort
2.4. Non-functional BBS5 Affects Primary Ciliogenesis and Ciliary Length
2.5. Alteration of Canonical Hh Signalling in Patient’s Cells Lacking BBS5
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Genetics Investigation
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Genomic DNA Extraction, PCRs
4.4. Sanger Sequencing and Segregation
4.5. Cohort Screening
4.6. RNA Extraction, Reverse-Transcription, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.7. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
4.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waters, A.M.; Beales, P.L. Ciliopathies: An Expanding Disease Spectrum. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 1039–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, E.; Beales, P.L. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 21, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouronc, A.; Zilliox, V.; Jacquemont, M.-L.; Darcel, F.; Leuvrey, A.-S.; Nourisson, E.; Antin, M.; Alessandri, J.-L.; Doray, B.; Gueguen, P.; et al. High Prevalence of Bardet-Biedl Syndrome in La Réunion Island Is Due to a Founder Variant in ARL6/BBS3. Clin. Genet. 2020, 98, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, L.; Caba, L.; Gorduza, E.V. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome-Multiple Kaleidoscope Images: Insight into Mechanisms of Genotype-Phenotype Correlations. Genes 2021, 12, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvarian, Z.; Mykytyn, K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Pedersen, L.B.; Christensen, S.T. Cellular Signalling by Primary Cilia in Development, Organ Function and Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseldin, H.E.; Shaheen, R.; Ewida, N.; Bubshait, D.K.; Alkuraya, H.; Almardawi, E.; Howaidi, A.; Sabr, Y.; Abdalla, E.M.; Alfaifi, A.Y.; et al. The Morbid Genome of Ciliopathies: An Update. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2020, 22, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, G.; Raleigh, D.R.; Reiter, J.F. How the Ciliary Membrane Is Organized Inside-out to Communicate Outside-in. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R421–R434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosengren, T.; Larsen, L.J.; Pedersen, L.B.; Christensen, S.T.; Møller, L.B. TSC1 and TSC2 Regulate Cilia Length and Canonical Hedgehog Signaling via Different Mechanisms. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2663–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimkus, T.K.; Carpenter, R.L.; Qasem, S.; Chan, M.; Lo, H.-W. Targeting the Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway: Review of Smoothened and GLI Inhibitors. Cancers 2016, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denef, N.; Neubüser, D.; Perez, L.; Cohen, S.M. Hedgehog Induces Opposite Changes in Turnover and Subcellular Localization of Patched and Smoothened. Cell 2000, 102, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachury, M.V.; Loktev, A.V.; Zhang, Q.; Westlake, C.J.; Peränen, J.; Merdes, A.; Slusarski, D.C.; Scheller, R.H.; Bazan, J.F.; Sheffield, V.C.; et al. A Core Complex of BBS Proteins Cooperates with the GTPase Rab8 to Promote Ciliary Membrane Biogenesis. Cell 2007, 129, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loktev, A.V.; Zhang, Q.; Beck, J.S.; Searby, C.C.; Scheetz, T.E.; Bazan, J.F.; Slusarski, D.C.; Sheffield, V.C.; Jackson, P.K.; Nachury, M.V. A BBSome Subunit Links Ciliogenesis, Microtubule Stability, and Acetylation. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingfield, J.L.; Lechtreck, K.-F.; Lorentzen, E. Trafficking of Ciliary Membrane Proteins by the Intraflagellar Transport/BBSome Machinery. Essays Biochem. 2018, 62, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachury, M.V.; Mick, D.U. Establishing and Regulating the Composition of Cilia for Signal Transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.B.; Gerdes, J.M.; Haycraft, C.J.; Fan, Y.; Teslovich, T.M.; May-Simera, H.; Li, H.; Blacque, O.E.; Li, L.; Leitch, C.C.; et al. Comparative Genomics Identifies a Flagellar and Basal Body Proteome That Includes the BBS5 Human Disease Gene. Cell 2004, 117, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, S.; Cheng, J.; Fu, J.; Mobasher-Jannat, A.; Wei, C.; Mohazzab-Torabi, S.; Jadidi, K.; Khosravi, M.H.; Shasaltaneh, M.D.; Yang, L.; et al. Novel Splicing Variant c. 208+2T>C in BBS5 Segregates with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome in an Iranian Family by Targeted Exome Sequencing. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Seo, S.; Bugge, K.; Stone, E.M.; Sheffield, V.C. BBS Proteins Interact Genetically with the IFT Pathway to Influence SHH-Related Phenotypes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, J.; Stoetzel, C.; Vincent, M.C.; Leitch, C.C.; Laurier, V.; Danse, J.M.; Hellé, S.; Marion, V.; Bennouna-Greene, V.; Vicaire, S.; et al. Identification of 28 Novel Mutations in the Bardet–Biedl Syndrome Genes: The Burden of Private Mutations in an Extensively Heterogeneous Disease. Hum. Genet. 2010, 127, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redin, C.; Le Gras, S.; Mhamdi, O.; Geoffroy, V.; Stoetzel, C.; Vincent, M.-C.; Chiurazzi, P.; Lacombe, D.; Ouertani, I.; Petit, F.; et al. Targeted High-Throughput Sequencing for Diagnosis of Genetically Heterogeneous Diseases: Efficient Mutation Detection in Bardet-Biedl and Alström Syndromes. J Med Genet 2012, 49, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, D.W.A.; Jones, D.T. The PSIPRED Protein Analysis Workbench: 20 Years On. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W402–W407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, R.; Szymanska, K.; Basu, B.; Patel, N.; Ewida, N.; Faqeih, E.; Al Hashem, A.; Derar, N.; Alsharif, H.; Aldahmesh, M.A.; et al. Characterizing the Morbid Genome of Ciliopathies. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delvallée, C.; Nicaise, S.; Antin, M.; Leuvrey, A.-S.; Nourisson, E.; Leitch, C.C.; Kellaris, G.; Stoetzel, C.; Geoffroy, V.; Scheidecker, S.; et al. A BBS1 SVA F Retrotransposon Insertion Is a Frequent Cause of Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. Clin. Genet. 2021, 99, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadaie, Z.; Whelan, L.; Dockery, A.; Li, C.H.Z.; van den Born, L.I.; Hoyng, C.B.; Gilissen, C.; Corominas, J.; Rowlands, C.; Megaw, R.; et al. BBS1 Branchpoint Variant Is Associated with Non-Syndromic Retinitis Pigmentosa. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 59, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.C.; Martin, H.C.; Lise, S.; Broxholme, J.; Cazier, J.-B.; Rimmer, A.; Kanapin, A.; Lunter, G.; Fiddy, S.; Allan, C.; et al. Factors Influencing Success of Clinical Genome Sequencing across a Broad Spectrum of Disorders. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilissen, C.; Hehir-Kwa, J.Y.; Thung, D.T.; van de Vorst, M.; van Bon, B.W.M.; Willemsen, M.H.; Kwint, M.; Janssen, I.M.; Hoischen, A.; Schenck, A.; et al. Genome Sequencing Identifies Major Causes of Severe Intellectual Disability. Nature 2014, 511, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin-Tse, C.A.; Jobanputra, V.; Perry, D.L.; Bick, D.; Taft, R.J.; Venner, E.; Gibbs, R.A.; Young, T.; Barnett, S.; Belmont, J.W.; et al. Best Practices for the Interpretation and Reporting of Clinical Whole Genome Sequencing. NPJ Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarini, N.; Biagi, E.; Uva, P.; Iovino, E.; Pippucci, T.; Seri, M.; Cavalli, A.; Ceccherini, I.; Rusmini, M.; Viti, F. Exploration of Tools for the Interpretation of Human Non-Coding Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkadi, A.; Bolze, A.; Itan, Y.; Cobat, A.; Vincent, Q.B.; Antipenko, A.; Shang, L.; Boisson, B.; Casanova, J.-L.; Abel, L. Whole-Genome Sequencing Is More Powerful Than Whole-Exome Sequencing for Detecting Exome Variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5473–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoffroy, V.; Stoetzel, C.; Scheidecker, S.; Schaefer, E.; Perrault, I.; Bär, S.; Kröll, A.; Delbarre, M.; Antin, M.; Leuvrey, A.-S.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing in Patients with Ciliopathies Uncovers a Novel Recurrent Tandem Duplication in IFT140. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.M.; Stark, Z.; Farnaes, L.; Tan, T.Y.; White, S.M.; Dimmock, D.; Kingsmore, S.F. Meta-Analysis of the Diagnostic and Clinical Utility of Genome and Exome Sequencing and Chromosomal Microarray in Children with Suspected Genetic Diseases. NPJ Genom. Med. 2018, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, C.F.; Fitzgerald, T.W.; Jones, W.D.; Clayton, S.; McRae, J.F.; van Kogelenberg, M.; King, D.A.; Ambridge, K.; Barrett, D.M.; Bayzetinova, T.; et al. Genetic Diagnosis of Developmental Disorders in the DDD Study: A Scalable Analysis of Genome-Wide Research Data. Lancet 2015, 385, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retterer, K.; Juusola, J.; Cho, M.T.; Vitazka, P.; Millan, F.; Gibellini, F.; Vertino-Bell, A.; Smaoui, N.; Neidich, J.; Monaghan, K.G.; et al. Clinical Application of Whole-Exome Sequencing across Clinical Indications. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Muzny, D.M.; Xia, F.; Niu, Z.; Person, R.; Ding, Y.; Ward, P.; Braxton, A.; Wang, M.; Buhay, C.; et al. Molecular Findings among Patients Referred for Clinical Whole-Exome Sequencing. JAMA 2014, 312, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Hernandez, V.; Pravincumar, P.; Diaz-Font, A.; May-Simera, H.; Jenkins, D.; Knight, M.; Beales, P.L. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome Proteins Control the Cilia Length through Regulation of Actin Polymerization. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3858–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, S.R.; Kretschmer, V.; Brücker, L.; Schneider, S.; Volz, A.-K.; Oancea-Castillo, L.d.R.; May-Simera, H.L. Bardet–Biedl Syndrome Proteins Regulate Cilia Disassembly during Tissue Maturation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 757–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lechtreck, K.F. The Bardet-Biedl Syndrome Protein Complex Is an Adapter Expanding the Cargo Range of Intraflagellar Transport Trains for Ciliary Export. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E934–E943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnachie, D.J.; Stow, J.L.; Mallett, A.J. Ciliopathies and the Kidney: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, C.A.B.; Larsen, L.J.; Tümer, Z.; Brøndum-Nielsen, K.; Grønskov, K.; Hjortshøj, T.D.; Møller, L.B. BBS Proteins Affect Ciliogenesis and Are Essential for Hedgehog Signaling, but Not for Formation of iPSC-Derived RPE-65 Expressing RPE-like Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley-Ford, M.R.; Engle, S.E.; Clearman, K.R.; Haycraft, C.J.; Andersen, R.S.; Croyle, M.J.; Rains, A.B.; Berbari, N.F.; Yoder, B.K. A Mouse Model of BBS Identifies Developmental and Homeostatic Effects of BBS5 Mutation and Identifies Novel Pituitary Abnormalities. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ling, K.; Hu, J. BBS4 and BBS5 Show Functional Redundancy in the BBSome to Regulate the Degradative Sorting of Ciliary Sensory Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguether, T.; Cordelieres, F.P.; Pazour, G.J. Intraflagellar Transport Is Deeply Integrated in Hedgehog Signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2018, 29, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Xing, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhong, D.; Lian, C.; Yan, M.; Chen, T.; et al. A Novel ZRS Variant Causes Preaxial Polydactyly Type I by Increased Sonic Hedgehog Expression in the Developing Limb Bud. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, E.; Haws, R.M.; Argente, J.; Beales, P.; Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Dollfus, H.; Chirila, C.; Gnanasakthy, A.; Buckley, B.C.; Mallya, U.G.; et al. Quality of Life Improvements Following One Year of Setmelanotide in Children and Adult Patients with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome: Phase 3 Trial Results. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haqq, A.M.; Chung, W.K.; Dollfus, H.; Haws, R.M.; Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Poitou, C.; Yanovski, J.A.; Mittleman, R.S.; Yuan, G.; Forsythe, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Setmelanotide, a Melanocortin-4 Receptor Agonist, in Patients with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome and Alström Syndrome: A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial with an Open-Label Period. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows–Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A Framework for Variation Discovery and Genotyping Using Next-Generation DNA Sequencing Data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmer, A.; Phan, H.; Mathieson, I.; Iqbal, Z.; Twigg, S.R.F.; Wilkie, A.O.M.; McVean, G.; Lunter, G.; WGS500 Consortium. Integrating Mapping-, Assembly- and Haplotype-Based Approaches for Calling Variants in Clinical Sequencing Applications. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffroy, V.; Pizot, C.; Redin, C.; Piton, A.; Vasli, N.; Stoetzel, C.; Blavier, A.; Laporte, J.; Muller, J. VaRank: A Simple and Powerful Tool for Ranking Genetic Variants. PeerJ 2015, 3, e796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium; Gibbs, R.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Doddapaneni, H.; Han, Y.; Korchina, V.; Kovar, C.; Lee, S.; Muzny, D.; Reid, J.G.; et al. A Global Reference for Human Genetic Variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of Protein-Coding Genetic Variation in 60,706 Humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, J.R.; Ziman, R.; Yuen, R.K.C.; Feuk, L.; Scherer, S.W. The Database of Genomic Variants: A Curated Collection of Structural Variation in the Human Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D986–D992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevers, Y.; Prasad, M.K.; Poidevin, L.; Chennen, K.; Allot, A.; Kress, A.; Ripp, R.; Thompson, J.D.; Dollfus, H.; Poch, O.; et al. Insights into Ciliary Genes and Evolution from Multi-Level Phylogenetic Profiling. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2016–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backenroth, D.; Homsy, J.; Murillo, L.R.; Glessner, J.; Lin, E.; Brueckner, M.; Lifton, R.; Goldmuntz, E.; Chung, W.K.; Shen, Y.F. CANOES: Detecting Rare Copy Number Variants from Whole Exome Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layer, R.M.; Chiang, C.; Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. LUMPY: A Probabilistic Framework for Structural Variant Discovery. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thung, D.T.; de Ligt, J.; Vissers, L.E.; Steehouwer, M.; Kroon, M.; de Vries, P.; Slagboom, E.P.; Ye, K.; Veltman, J.A.; Hehir-Kwa, J.Y. Mobster: Accurate Detection of Mobile Element Insertions in Next Generation Sequencing Data. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffroy, V.; Herenger, Y.; Kress, A.; Stoetzel, C.; Piton, A.; Dollfus, H.; Muller, J. AnnotSV: An Integrated Tool for Structural Variations Annotation. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3572–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-Performance Genomics Data Visualization and Exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2012, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidecker, S.; Etard, C.; Pierce, N.W.; Geoffroy, V.; Schaefer, E.; Muller, J.; Chennen, K.; Flori, E.; Pelletier, V.; Poch, O.; et al. Exome Sequencing of Bardet–Biedl Syndrome Patient Identifies a Null Mutation in the BBSome Subunit BBIP1 (BBS18). J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.J.; Amode, M.R.; Aneja, A.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D933–D941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, L.R.; Barber, G.P.; Benet-Pagès, A.; Casper, J.; Clawson, H.; Diekhans, M.; Fischer, C.; Gonzalez, J.N.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Lee, B.T.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser Database: 2023 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1188–D1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; Funk, K.; Kelly, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Database Resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D20–D26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talevich, E.; Shain, A.H.; Botton, T.; Bastian, B.C. CNVkit: Genome-Wide Copy Number Detection and Visualization from Targeted DNA Sequencing. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvakov, M.; Panda, A.; Diesh, C.; Holmes, I.; Abyzov, A. CNVpytor: A Tool for Copy Number Variation Detection and Analysis from Read Depth and Allele Imbalance in Whole-Genome Sequencing. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, T.; Zichner, T.; Schlattl, A.; Stütz, A.M.; Benes, V.; Korbel, J.O. DELLY: Structural Variant Discovery by Integrated Paired-End and Split-Read Analysis. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, i333–i339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Schulz-Trieglaff, O.; Shaw, R.; Barnes, B.; Schlesinger, F.; Källberg, M.; Cox, A.J.; Kruglyak, S.; Saunders, C.T. Manta: Rapid Detection of Structural Variants and Indels for Germline and Cancer Sequencing Applications. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1220–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartenhagen, C.; Dugas, M. Robust and Exact Structural Variation Detection with Paired-End and Soft-Clipped Alignments: SoftSV Compared with Eight Algorithms. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 17, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Szklarczyk, D.; Forslund, K.; Cook, H.; Heller, D.; Walter, M.C.; Rattei, T.; Mende, D.R.; Sunagawa, S.; Kuhn, M.; et al. EggNOG 4.5: A Hierarchical Orthology Framework with Improved Functional Annotations for Eukaryotic, Prokaryotic and Viral Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D286–D293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Gui, M.; Koh, F.; Yip, M.C.; Brown, A. Structure and Activation Mechanism of the BBSome Membrane Protein Trafficking Complex. Elife 2020, 9, e53322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2--a Multiple Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, LLC. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Ng, P.C. SIFT Indel: Predictions for the Functional Effects of Amino Acid Insertions/Deletions in Proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Mort, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. DDIG-in: Discriminating between Disease-Associated and Neutral Non-Frameshifting Micro-Indels. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Chan, A.P. PROVEAN Web Server: A Tool to Predict the Functional Effect of Amino Acid Substitutions and Indels. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karam, A.; Delvallée, C.; Estrada-Cuzcano, A.; Geoffroy, V.; Lamouche, J.-B.; Leuvrey, A.-S.; Nourisson, E.; Tarabeux, J.; Stoetzel, C.; Scheidecker, S.; et al. WGS Revealed Novel BBS5 Pathogenic Variants, Missed by WES, Causing Ciliary Structure and Function Defects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108729
Karam A, Delvallée C, Estrada-Cuzcano A, Geoffroy V, Lamouche J-B, Leuvrey A-S, Nourisson E, Tarabeux J, Stoetzel C, Scheidecker S, et al. WGS Revealed Novel BBS5 Pathogenic Variants, Missed by WES, Causing Ciliary Structure and Function Defects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108729
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaram, Adella, Clarisse Delvallée, Alejandro Estrada-Cuzcano, Véronique Geoffroy, Jean-Baptiste Lamouche, Anne-Sophie Leuvrey, Elsa Nourisson, Julien Tarabeux, Corinne Stoetzel, Sophie Scheidecker, and et al. 2023. "WGS Revealed Novel BBS5 Pathogenic Variants, Missed by WES, Causing Ciliary Structure and Function Defects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108729
APA StyleKaram, A., Delvallée, C., Estrada-Cuzcano, A., Geoffroy, V., Lamouche, J.-B., Leuvrey, A.-S., Nourisson, E., Tarabeux, J., Stoetzel, C., Scheidecker, S., Porter, L. F., Génin, E., Redon, R., Sandron, F., Boland, A., Deleuze, J.-F., Le May, N., Dollfus, H., & Muller, J. (2023). WGS Revealed Novel BBS5 Pathogenic Variants, Missed by WES, Causing Ciliary Structure and Function Defects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108729






