Resveratrol Enhances Temozolomide Efficacy in Glioblastoma Cells through Downregulated MGMT and Negative Regulators-Related STAT3 Inactivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Differential Chemosensitivity of GBM Cell Lines to Res and TMZ
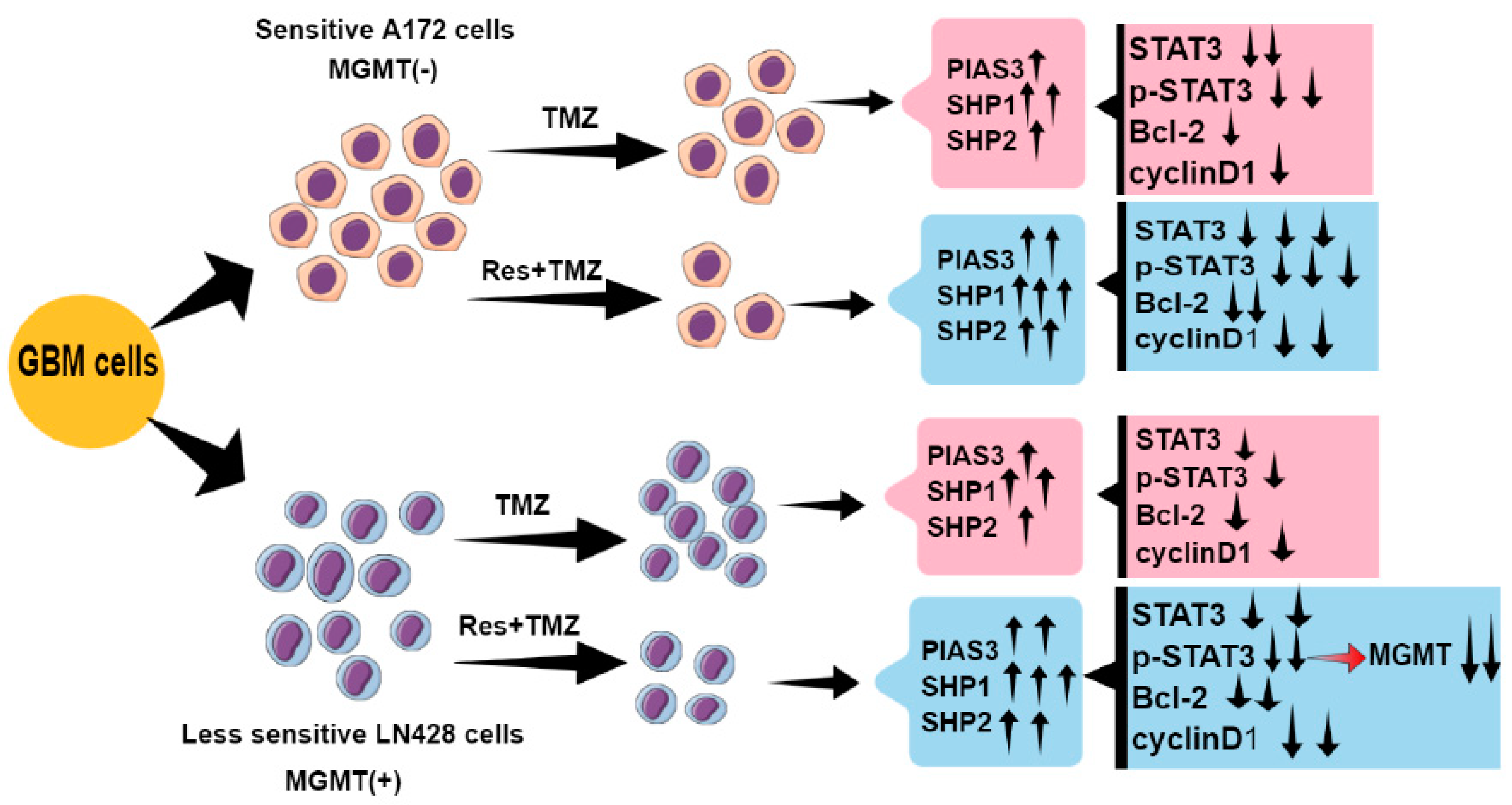
2.2. Res Improved Chemosensitivities of GBM Cells to TMZ
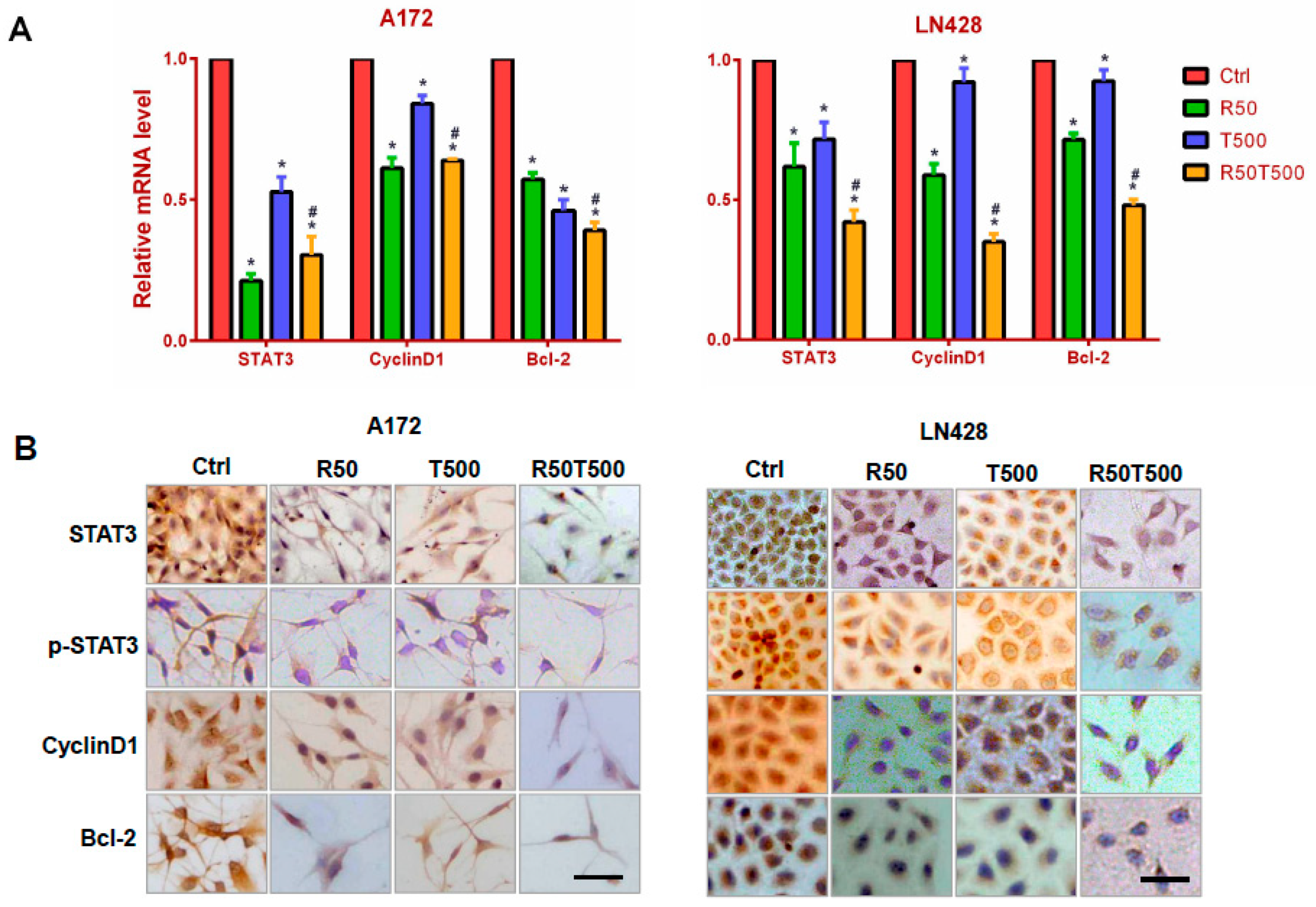
2.3. Res Increased the Inhibitory Effects of TMZ on STAT3 Signaling in GBM Cells
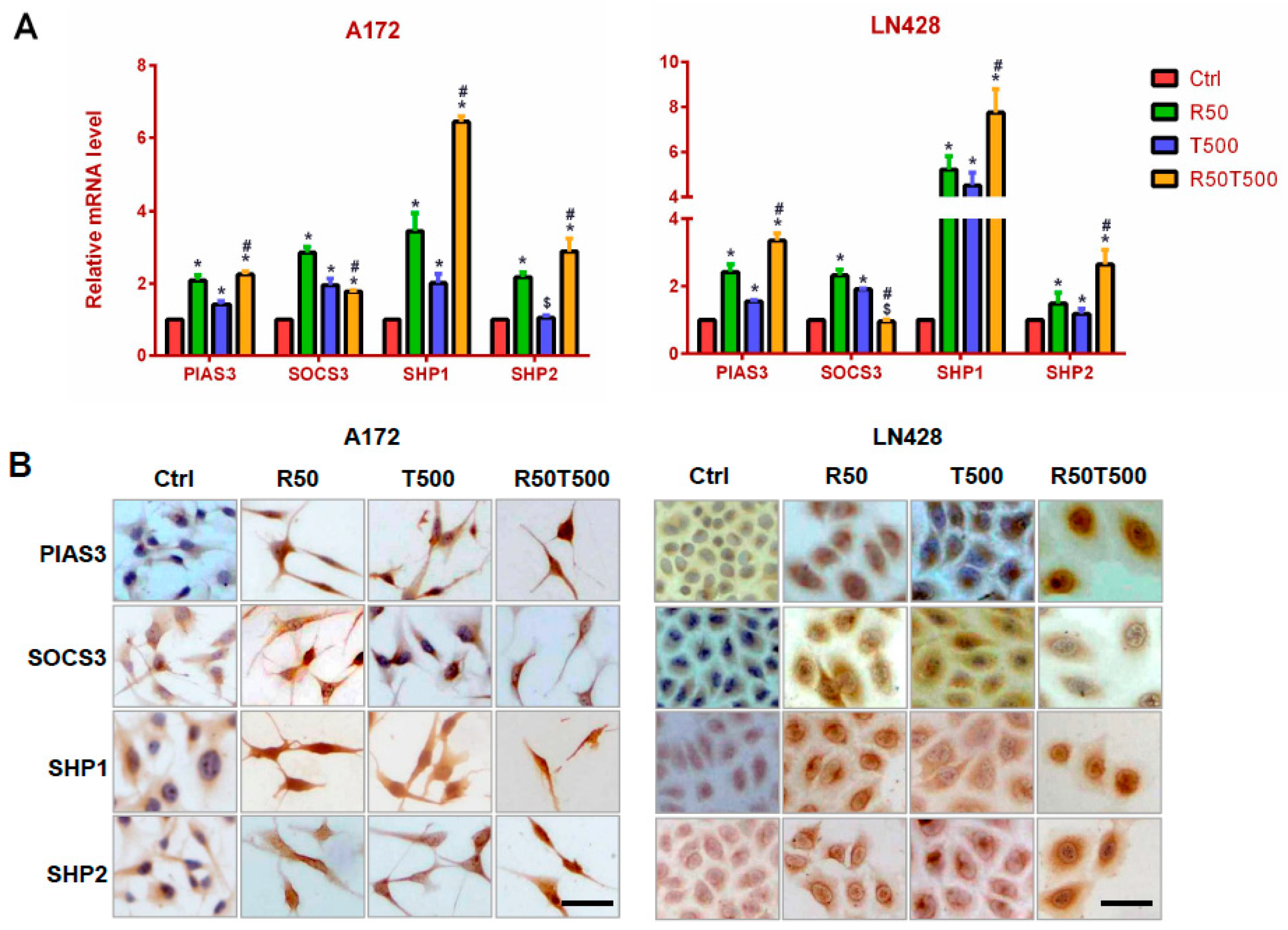
2.4. Res and TMZ Upregulated PIAS3, SOCS3, SHP1, and SHP2 Levels in GBM Cells
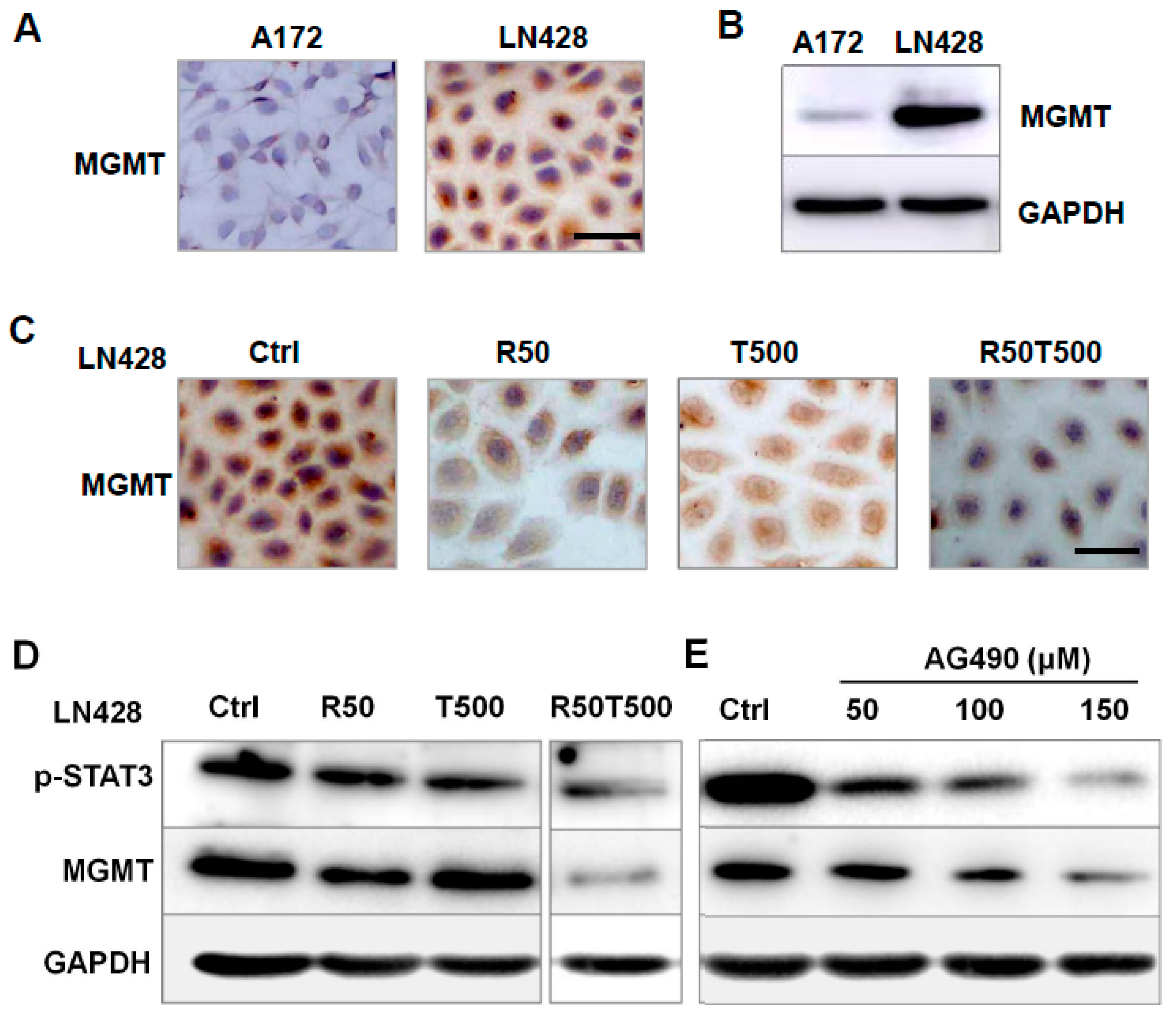
2.5. The Effects of Res on MGMT Level and Its Relevance with Different Chemosensitivities of GBM Cells to TMZ
2.6. AG490 Downregulated MGMT Level in LN428 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.2. Cell Proliferation Assays
4.3. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.4. Cell Migration Assays
4.5. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR
4.6. Immunocytochemical (ICC) Staining
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Inhibition of STAT3 Activation with AG490
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2015–2019. Neuro. Oncol. 2022, 24, v1–v95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Tanaka, M.; Trepel, J.; Reinhold, W.C.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Pommier, Y. Temozolomide in the Era of Precision Medicine. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.P.; Woodring, S.; Randazzo, D.M.; Friedman, H.S.; Desjardins, A.; Healy, P.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; McSherry, F.; Lipp, E.S.; Miller, E.; et al. Randomized open-label phase II trial of 5-day aprepitant plus ondansetron compared to ondansetron alone in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea-vomiting (CINV) in glioma patients receiving adjuvant temozolomide. Support Care Cancer 2020, 28, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, N.; Ahn, S.H.; Kong, D.S.; Lee, H.W.; Nam, D.H. The role of STAT3 in glioblastoma progression through dual influences on tumor cells and the immune microenvironment. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 451, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklossy, G.; Hilliard, T.S.; Turkson, J. Therapeutic modulators of STAT signalling for human diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Sethi, G.; Vadhan-Raj, S.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Takada, Y.; Gaur, U.; Nair, A.S.; Shishodia, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and overcomes chemoresistance through down-regulation of STAT3 and nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic and cell survival gene products in human multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2007, 109, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallàs, M.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D.; Andrés-Benito, P.; Ponce-Regalado, M.D.; Rojas-Mayorquín, A.E. Resveratrol in epilepsy: Preventive or treatment opportunities? Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.H.; Li, H.; Sun, X.X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Wu, M.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, C.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Metabolic patterns and biotransformation activities of resveratrol in human glioblastoma cells: Relevance with therapeutic efficacies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Fan, M.; Jiang, N.; Duan, Y.; Jing, D.; Xiao, W.; Fragoso, R.C.; Lam, K.S.; et al. Dual blockage of STAT3 and ERK1/2 eliminates radioresistant GBM cells. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Ma, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, G.; Ma, J. Inhibition of STAT3 reduces astrocytoma cell invasion and constitutive activation of STAT3 predicts poor prognosis in human astrocytoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Song, D.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Ma, X.; Deng, S.; Ren, C.; Shu, X. Negative regulators of STAT3 signaling pathway in cancers. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 4957–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Morales, L.D.; Jang, I.S.; Cho, Y.Y.; Kim, D.J. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases as Potential Regulators of STAT3 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.D.; Liao, J.; Liu, B.; Rao, X.; Jay, P.; Berta, P.; Shuai, K. Specific inhibition of Stat3 signal transduction by PIAS3. Science 1997, 278, 1803–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppler, L.N.; Frank, D.A. Targeting Oncogenic Transcription Factors: Therapeutic Implications of Endogenous STAT Inhibitors. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.; Pongor, L.; Su, Y.T.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Quezado, M.; Trepel, J.; Aldape, K.; Pommier, Y.; Wu, J. MGMT Status as a Clinical Biomarker in Glioblastoma. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.F.; de Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamaru, A.; Szymanski, S.; Iwado, E.; Aoki, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Fokt, I.; Hess, K.; Conrad, C.; Madden, T.; Sawaya, R.; et al. A novel inhibitor of the STAT3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.H.; Wang, L.L.; Li, H.; Song, X.; Shi, S.; Gu, J.Y.; Wu, M.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Diffusion Efficiency and Bioavailability of Resveratrol Administered to Rat Brain by Different Routes: Therapeutic Implications. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, S.O.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Haque, S.J. Aberrant Stat3 signaling by interleukin-4 in malignant glioma cells: Involvement of IL-13Ralpha2. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2956–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, B.; Fabius, A.W.; Wu, W.H.; Pedraza, A.; Brennan, C.W.; Schultz, N.; Pitter, K.L.; Bromberg, J.F.; Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C.; et al. Loss of the tyrosine phosphatase PTPRD leads to aberrant STAT3 activation and promotes gliomagenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8149–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carro, M.S.; Lim, W.K.; Alvarez, M.J.; Bollo, R.J.; Zhao, X.; Snyder, E.Y.; Sulman, E.P.; Anne, S.L.; Doetsch, F.; Colman, H.; et al. The transcriptional network for mesenchymal transformation of brain tumours. Nature 2010, 463, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.J.; Wu, M.L.; Li, H.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Inhibition of STAT3 expression and signaling in resveratrol-differentiated medulloblastoma cells. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, L.Q.; Espinoza, J.L.; An, D.T.; Viet, N.H.; Shimoda, K.; Nakao, S. Resveratrol selectively induces apoptosis in malignant cells with the JAK2V617F mutation by inhibiting the JAK2 pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.J.; Cho, B.J.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, D.H.; Song, S.H.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, I.A. Inhibition of STAT3 enhances the radiosensitizing effect of temozolomide in glioblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 130, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Bao, Z.; Li, S.; You, G.; Yan, W.; Shi, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, W.; et al. Inhibition of STAT3 reverses alkylator resistance through modulation of the AKT and β-catenin signaling pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, T.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Wang, P.; Shi, Q.; Qian, X.; Miao, F.; Shen, Z.; et al. MEX3A Impairs DNA Mismatch Repair Signaling and Mediates Acquired Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 4234–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, R.N.; Almeida, K.H.; Fornsaglio, J.L.; Schamus, S.; Sobol, R.W. The role of base excision repair in the sensitivity and resistance to temozolomide-mediated cell death. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6394–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, B.; Yao, Y.Y.; Zhong, L.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Kong, Q.Y.; Wu, M.L.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Liu, J. PIAS3, SHP2 and SOCS3 Expression patterns in Cervical Cancers: Relevance with activation and resveratrol-caused inactivation of STAT3 signaling. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 139, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Brassinin inhibits STAT3 signaling pathway through modulation of PIAS-3 and SOCS-3 expression and sensitizes human lung cancer xenograft in nude mice to paclitaxel. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6386–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.Z.; Ding, K.; Wang, Z.R.; Ding, C.H.; Lei, S.J.; Liu, J.P.; Yin, C.; Hu, P.F.; Ding, J.; Chen, W.S.; et al. SHP-1 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocarcinogenesis and HCC Progression. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4680–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Mukherjee, S.; Tucker-Burden, C.; Ross, J.L.; Chau, M.J.; Kong, J.; Brat, D.J. TRIM8 regulates stemness in glioblastoma through PIAS3-STAT3. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, E.C.; Nabors, L.B.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Palmer, C.A.; Harrison, K.; Roarty, K.; Benveniste, E.N. Loss of protein inhibitors of activated STAT-3 expression in glioblastoma multiforme tumors: Implications for STAT-3 activation and gene expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4694–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.Q.; Wang, Z.T.; Zou, M.M.; Lin, J.H.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, R.X. Verbascoside Inhibits Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion While Promoting Apoptosis Through Upregulation of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP-1 and Inhibition of STAT3 Phosphorylation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard-Chapeau, E.A.; Li, S.; Ding, J.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhu, H.H.; Princen, F.; Fang, D.D.; Han, T.; Bailly-Maitre, B.; Poli, V.; et al. Ptpn11/Shp2 acts as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xu, W.; Shao, J.; Zhang, F.; Chen, A.; Zheng, S. Nrf2 induces lipocyte phenotype via a SOCS3-dependent negative feedback loop on JAK2/STAT3 signaling in hepatic stellate cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, M.S.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, C.; Shrivastava, A. Elucidating the mechanisms of Temozolomide resistance in gliomas and the strategies to overcome the resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsaka, S.; Wang, L.; Yachi, K.; Mahabir, R.; Narita, T.; Itoh, T.; Tanino, M.; Kimura, T.; Nishihara, H.; Tanaka, S. STAT3 inhibition overcomes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma by downregulating MGMT expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Hu, R.; Ma, J.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, X. Resveratrol Downregulates STAT3 Expression and Astrocyte Activation in Primary Astrocyte Cultures of Rat. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.F.; Deng, W.W.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.C.; Wu, L.; Ma, S.R.; Zhang, W.F.; Bu, L.L.; Sun, Z.J. Inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 reduces tumor-induced angiogenesis and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in head and neck cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
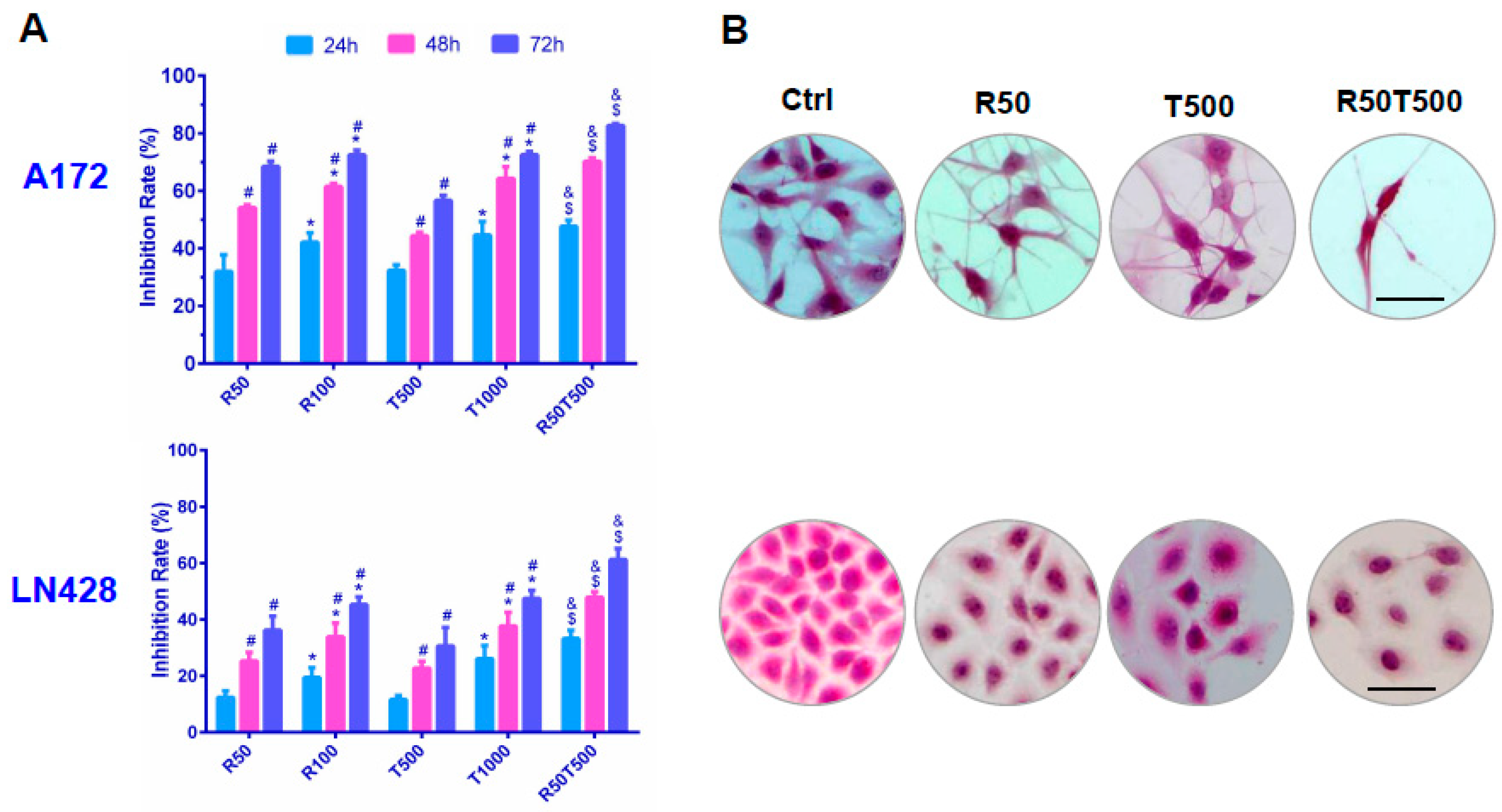

| GBM A172 Cells | |||||||||||
| Treatment | Res (μM) | TMZ (μM) | Res (μM) + TMZ (μM) | ||||||||
| Time (h) | 10 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 250 | 500 | 750 | 1000 | 50 + 500 | 100 + 500 |
| 24 | 9.1 ± 0.5 | 16.7 ± 1.2 * | 32.0 ± 2.8 * | 42.2 ± 2.6 * | 11.7 ± 0.8 | 21.4 ± 1.4 * | 32.3 ± 2.9 * | 37.8 ± 4.0 * | 44.7 ± 3.8 | 47.7 ± 2.2 ^& | 55.5 ± 2.9 ^& |
| 48 | 22.4 ± 2.0 # | 32.4 ± 2.8 *# | 54.2 ± 3.6 *# | 61.5 ± 3.6 *# | 22.1 ± 1.8 # | 30.9 ± 2.2 *# | 44.3 ± 4.0 *# | 53.3 ± 3.6 *# | 64.3 ± 4.3 *# | 70.2 ± 3.1 ^& | 76.9 ± 4.6 ^& |
| 72 | 24.8 ± 2.6 | 35.7 ± 3.1 * | 68.4 ± 4.7 *# | 72.5 ± 4.1 *# | 26.5 ± 2.4 | 37.7 ± 2.7 *# | 56.6 ± 4.8 *# | 69.7 ± 5.1 *# | 72.5 ± 4.4 *# | 82.6 ± 5.0 ^& | 84.1 ± 5.0 ^& |
| GBM LN428 cells | |||||||||||
| Treatment | Res (μM) | TMZ (μM) | Res (μM) + TMZ (μM) | ||||||||
| Time (h) | 10 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 250 | 500 | 750 | 1000 | 50 + 500 | 100 + 500 |
| 24 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 6.9 ± 0.7 * | 12.4 ± 1.0 * | 19.5 ± 2.8 * | 3.9 ± 0.6 | 5.5 ± 1.2 * | 11.6 ± 0.9 * | 15.6 ± 3.0 * | 26.1 ± 3.0 * | 33.2 ± 1.2 ^& | 33.7 ± 3.1 ^& |
| 48 | 4.7 ± 0.6 # | 17.5 ± 1.3 *# | 25.3 ± 1.5 *# | 33.9 ± 1.2 *# | 7.5 ± 0.5 # | 13.8 ± 2.3 *# | 22.8 ± 3.8 *# | 28.9 ± 2.9 *# | 37.7 ± 2.9 *# | 47.9 ± 2.4 ^& | 53.5 ± 4.2 ^& |
| 72 | 10.0 ± 1.1 # | 29.6 ± 1.4 *# | 36.2 ± 2.0 *# | 45.3 ± 2.7 *# | 20.3 ± 1.2 # | 25.6 ± 2.8 *# | 30.6 ± 3.1 *# | 37.7 ± 3.2 *# | 47.5 ± 4.1 *# | 61.3 ± 3.8 ^& | 67.8 ± 4.6 ^& |
| Parameters | Primer Sequences | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| STAT3 | F: 5′-TTCACTTGGGTGGAGAAGGACA-3′ R: 5′-CGGACTGGATCTGGGTCTTACC-3′ | 49 |
| PIAS3 | F: 5′-ACTACATGAGTACCCACCTGCCTTC-3′ R: 5′-CCAAGGGCATCCTGTTCATCTA-3′ | 135 |
| SOCS3 | F: 5′-CAGGAATGTAGCAGCGATGGAA-3′ R: 5′-CCTGTCCAGCCCAATACCTGA-3′ | 125 |
| SHP1 | F: 5′-GGGATTTCTATGACCTGTATGGAG-3′ R: 5′-CCAGACATGTGGCCATGGTA-3′ | 178 |
| SHP2 | F: 5′-AAGAATATGGCGTCATGCGTGTTA-3′ R: 5′-GCCAGGTCCGAAAGTGGTATTG-3′ | 150 |
| Bcl-2 | F: 5′-CCCGTTGCTTTTCCTCTGG-3′ R: 5′-ATCCCACTCGTAGCCCCTCT-3′ | 117 |
| CyclinD1 | F: 5′-TGTTCGTGGCCTCTAAGATGAA-3′ R: 5′-TCGGTGTAGATGCACAGCTTCT-3′ | 67 |
| GAPDH | F: 5′-GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC-3′ R: 5′-TGGTGAAGACGCCAGTGGA-3′ | 138 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, M.; Song, D.; Li, H.; Ahmad, N.; Xu, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Deng, S.; Shu, X. Resveratrol Enhances Temozolomide Efficacy in Glioblastoma Cells through Downregulated MGMT and Negative Regulators-Related STAT3 Inactivation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119453
Wu M, Song D, Li H, Ahmad N, Xu H, Yang X, Wang Q, Cheng X, Deng S, Shu X. Resveratrol Enhances Temozolomide Efficacy in Glioblastoma Cells through Downregulated MGMT and Negative Regulators-Related STAT3 Inactivation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119453
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Moli, Danyang Song, Hui Li, Nisar Ahmad, Hong Xu, Xiaobo Yang, Qian Wang, Xiaoxin Cheng, Sa Deng, and Xiaohong Shu. 2023. "Resveratrol Enhances Temozolomide Efficacy in Glioblastoma Cells through Downregulated MGMT and Negative Regulators-Related STAT3 Inactivation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119453
APA StyleWu, M., Song, D., Li, H., Ahmad, N., Xu, H., Yang, X., Wang, Q., Cheng, X., Deng, S., & Shu, X. (2023). Resveratrol Enhances Temozolomide Efficacy in Glioblastoma Cells through Downregulated MGMT and Negative Regulators-Related STAT3 Inactivation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119453






