Ganglioside GM1 and the Central Nervous System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. GM1 Metabolism
3. GM1 Distribution in the Central Nervous System
4. Biological Functions of GM1 in the Central Nervous System
5. GM1 in Central Nervous System-Related Diseases
5.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
5.2. Parkinson’s Disease
5.3. GM1 Gangliosidosis
5.4. Huntington’s Disease
5.5. Epilepsy and Seizure
5.6. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
5.7. Ischemic Stroke
5.8. Depression and Anxiety
5.9. Autism
5.10. Alcohol Dependence
5.11. Bacterial Infections
6. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Acronyms
References
- Schnaar, R.L.; Suzuki, A.; Stanley, P. Chapter 10—Glycosphingolipids. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Freeze, H.H., Stanley, P., Bertozzi, C.R., Hart, G.W., Etzler, M.E., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Latov, N. Neuropathy and Anti-Gm1 Antibodies. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27, S41–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beadon, K.; Guimarães-Costa, R.; Léger, J.M. Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sántha, P.; Dobos, I.; Kis, G.; Jancsó, G. Role of Gangliosides in Peripheral Pain Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, J.A.; Willison, H.J. Gangliosides and Autoimmune Peripheral Nerve Diseases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 156, 355–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandhoff, R.; Sandhoff, K. Emerging Concepts of Ganglioside Metabolism. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 3835–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Echten-Deckert, G.; Herget, T. Sphingolipid Metabolism in Neural Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1978–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tettamanti, G.; Bassi, R.; Viani, P.; Riboni, L. Salvage Pathways in Glycosphingolipid Metabolism. Biochimie 2003, 85, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettamanti, G. Ganglioside/Glycosphingolipid Turnover: New Concepts. Glycoconj. J. 2004, 20, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonderfeld, S.; Conzelmann, E.; Schwarzmann, G.; Burg, J.; Hinrichs, U.; Sandhoff, K. Incorporation and Metabolism of Ganglioside Gm2 in Skin Fibroblasts from Normal and Gm2 Gangliosidosis Subjects. Eur. J. Biochem. 1985, 149, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboni, L.; Viani, P.; Tettamanti, G. Estimating Sphingolipid Metabolism and Trafficking in Cultured Cells Using Radiolabeled Compounds. Methods Enzym. 2000, 311, 656–682. [Google Scholar]
- Chigorno, V.; Riva, C.; Valsecchi, M.; Nicolini, M.; Brocca, P.; Sonnino, S. Metabolic Processing of Gangliosides by Human Fibroblasts in Culture—Formation and Recycling of Separate Pools of Sphingosine. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 250, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofer, A.; Schwarzmann, G.; Futerman, A.H. The Internalization of a Short Acyl Chain Analogue of Ganglioside Gm1 in Polarized Neurons. J. Cell Sci. 1996, 109, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulsiani, D.R.; Chayko, C.A.; Orgebin-Crist, M.C.; Araki, Y. Temporal Surge of Glycosyltransferase Activities in the Genital Tract of the Hamster during the Estrous Cycle. Biol. Reprod. 1996, 54, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Yu, R.K. Role of Myelin-Associated Neuraminidase in the Ganglioside Metabolism of Rat Brain Myelin. J. Neurochem. 1992, 58, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goi, G.; Bairati, C.; Massaccesi, L.; Lovagnini, A.; Lombardo, A.; Tettamanti, G. Membrane Anchoring and Surface Distribution of Glycohydrolases of Human Erythrocyte Membranes. FEBS Lett. 2000, 473, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, R.; Riboni, L.; Tettamanti, G. Cultured Cerebellar Granule Cells, but Not Astrocytes, Produce an Ester of Ganglioside Gd1b, Presumably Gd1b Monolactone, from Exogenous Gd1b. Biochem. J. 1994, 302, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, E.; Bonten, E.; D’Azzo, A.; Bresciani, R.; Venerando, B.; Borsani, G.; Schauer, R.; Tettamanti, G. Sialidases in Vertebrates: A Family of Enzymes Tailored for Several Cell Functions. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2010, 64, 403–479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandhoff, K.; Harzer, K. Gangliosides and Gangliosidoses: Principles of Molecular and Metabolic Pathogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 10195–10208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckman, A.E.; Brockhausen, I.; Walia, J.S. Metabolism of Glycosphingolipids and Their Role in the Pathophysiology of Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolter, T.; Sandhoff, K. Principles of Lysosomal Membrane Digestion: Stimulation of Sphingolipid Degradation by Sphingolipid Activator Proteins and Anionic Lysosomal Lipids. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.K.; Bieberich, E.; Xia, T.; Zeng, G. Regulation of Ganglioside Biosynthesis in the Nervous System. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itokazu, Y.; Tsai, Y.T.; Yu, R.K. Epigenetic Regulation of Ganglioside Expression in Neural Stem Cells and Neuronal Cells. Glycoconj. J. 2017, 34, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseman, S. The Synthesis of Complex Carbohydrates by Multiglycosyltransferase Systems and Their Potential Function in Intercellular Adhesion. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1970, 5, 270–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudo, C.G.; Daniotti, J.L.; Maccioni, H.J. Physical and Functional Association of Glycolipid N-Acetyl-Galactosaminyl and Galactosyl Transferases in the Golgi Apparatus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, H.K.; Pohlentz, G.; Sandhoff, K. Tunicamycin Inhibits Ganglioside Biosynthesis in Rat Liver Golgi Apparatus by Blocking Sugar Nucleotide Transport across the Membrane Vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 7075–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, G.; Acevedo, E.; Conzelmann, E.; Nehrkorn, H.; Sandhoff, K. Model for the Interaction of Membrane-Bound Substrates and Enzymes. Hydrolysis of Ganglioside Gd1a by Sialidase of Neuronal Membranes Isolated from Calf Brain. Eur. J. Biochem. 1982, 127, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolter, T.; Proia, R.L.; Sandhoff, K. Combinatorial Ganglioside Biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25859–25862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipione, S.; Monyror, J.; Galleguillos, D.; Steinberg, N.; Kadam, V. Gangliosides in the Brain: Physiology, Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 572965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaar, R.L.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; Hildebrandt, H. Sialic Acids in the Brain: Gangliosides and Polysialic Acid in Nervous System Development, Stability, Disease, and Regeneration. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 461–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegandt, H. The Chemical Constitution of Gangliosides of the Vertebrate Nervous System. Behav. Brain Res. 1995, 66, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennerholm, L. Gangliosides and Synaptic Transmission. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1980, 125, 533–544. [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa, T.; Shumiya, S. Age-Related Alteration of Brain Gangliosides in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse (Sam)-P/8. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1991, 59, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, S.; Yu, R.K. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Trisialoganglioside, Gt1a, from Human Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 6247–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tettamanti, G.; Bonali, F.; Marchesini, S.; Zambotti, V. A New Procedure for the Extraction, Purification and Fractionation of Brain Gangliosides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1973, 296, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamori, M.; Nagai, Y. Comparative Study on Ganglioside Compositions of Various Rabbit Tissues. Tissue-Specificity in Ganglioside Molecular Species of Rabbit Thymus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 665, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledeen, R.W.; Haley, J.E.; Skrivanek, J.A. Study of Ganglioside Patterns with Two-Dimensional and Thin-Layer Chromatography and Radioautography; Detection of New Fucogangliosides and Other Minor Species in Rabbit Brain. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 112, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.K.; Tsai, Y.T.; Ariga, T. Functional Roles of Gangliosides in Neurodevelopment: An Overview of Recent Advances. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 1230–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.K.; Macala, L.J.; Taki, T.; Weinfield, H.M.; Yu, F.S. Developmental Changes in Ganglioside Composition and Synthesis in Embryonic Rat Brain. J. Neurochem. 1988, 50, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamukote, S.; Yanagisawa, M.; Ariga, T.; Ando, S.; Yu, R.K. Developmental Changes of Glycosphingolipids and Expression of Glycogenes in Mouse Brains. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 2327–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, L.N.; Hunter, G.D.; Crandall, J.E.; McCluer, R.H. Ganglioside Patterns During Cerebral Development in the Normal and Reeler Mouse. J. Neurosci. Res. 1985, 13, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajn, K.; Viljetić, B.; Degmečić, I.V.; Schnaar, R.L.; Heffer, M. Differential Distribution of Major Brain Gangliosides in the Adult Mouse Central Nervous System. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvier, J.D.; Seyfried, T.N. Ganglioside Composition of Normal and Mutant Mouse Embryos. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, T. Changes of Mouse Brain Gangliosides during Aging from Young Adult until Senescence. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1989, 50, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbig, R.; Lauke, G.; Rahmann, H. Brain Gangliosides during the Life Span (Embryogenesis to Senescence) of the Rat. Dev. Neurosci. 1983, 6, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, P.; Rao, P.S.; Vajreshwari, A.; Shankar, R. Total Gangliosides, Ganglioside Species and the Activity of Neuraminidase in Different Brain Regions and Spinal Cord of Normal and Undernourished Rats. Lipids 1984, 19, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyfus, H.; Harth, S.; Giuliani-Debernardi, A.; Roos, M.; Mack, G.; Mandel, P. Gangliosides in Various Brain Areas of Three Inbred Strains of Mice. Neurochem. Res. 1982, 7, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, J.A.; Andrés, R.; Hueso, P.; Llanillo, M.; Martínez-Zorzano, V.S.; Rodrigo, M.; Sánchez-Yagüe, J. Ganglioside and Phospholipid Composition of Forebrain, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem from Adult and Newborn Rats. Neurochem. Res. 1991, 16, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogiso, M.; Ohta, M.; Harada, Y.; Kubo, H.; Hirano, S. Developmental Change in Ganglioside Expression in Primary Culture of Rat Neurons. Neuroscience 1991, 41, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.K.; Nakatani, Y.; Yanagisawa, M. The Role of Glycosphingolipid Metabolism in the Developing Brain. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S440–S445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhoff, R.; Schulze, H.; Sandhoff, K. Ganglioside Metabolism in Health and Disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 156, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Gasa, S.; Minami, R.; Makita, A. Characterization of Neutral Glycosphingolipids from Fetal Human Brain: Evidence for Stage-Specific Expression of the Globo, Ganglio, and Neolacto Series in the Central Nervous System. J. Biochem. 1987, 101, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennerholm, L.; Rynmark, B.M.; Vilbergsson, G.; Fredman, P.; Gottfries, J.; Månsson, J.E.; Percy, A. Gangliosides in Human Fetal Brain. J. Neurochem. 1991, 56, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennerholm, L.; Boström, K.; Fredman, P.; Månsson, J.E.; Rosengren, B.; Rynmark, B.M. Human Brain Gangliosides: Developmental Changes from Early Fetal Stage to Advanced Age. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 1005, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svennerholm, L.; Boström, K.; Jungbjer, B.; Olsson, L. Membrane Lipids of Adult Human Brain: Lipid Composition of Frontal and Temporal Lobe in Subjects of Age 20 to 100 Years. J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kracun, I.; Rosner, H.; Drnovsek, V.; Heffer-Lauc, M.; Cosović, C.; Lauc, G. Human Brain Gangliosides in Development, Aging and Disease. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1991, 35, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kracun, I.; Rosner, H.; Drnovsek, V.; Vukelic, Z.; Cosovic, C.; Trbojevic-Cepe, M.; Kubat, M. Gangliosides in the Human Brain Development and Aging. Neurochem. Int. 1992, 20, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberg, K.; Zisling, R.; van Echten-Deckert, G.; Futerman, A.H. Ganglioside Synthesis During the Development of Neuronal Polarity. Major Changes Occur during Axonogenesis and Axon Elongation, but Not during Dendrite Growth or Synaptogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 14876–14882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; Moretto, G.; Lee, V.; Yu, R.K. Neuroimmunology of Gangliosides in Human Neurons and Glial Cells in Culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 1986, 15, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnino, S.; Chigorno, V. Ganglioside Molecular Species Containing C18- and C20-Sphingosine in Mammalian Nervous Tissues and Neuronal Cell Cultures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1469, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palestini, P.; Masserini, M.; Sonnino, S.; Giuliani, A.; Tettamanti, G. Changes in the Ceramide Composition of Rat Forebrain Gangliosides with Age. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A.; Stern, N. Changes in Sphingosine and Fatty Acid Components of the Gangliosides in Developing Rat and Human Brain. J. Lipid Res. 1966, 7, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, N.; Taketomi, T. Variation in Sphingosine and Fatty Acid Compositions of Sphingolipids in Rabbit Brain during Development. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1969, 39, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palestini, P.; Sonnino, S.; Tettamanti, G. Lack of the Ganglioside Molecular Species Containing the C20-Long-Chain Bases in Human, Rat, Mouse, Rabbit, Cat, Dog, and Chicken Brains During Prenatal Life. J. Neurochem. 1991, 56, 2048–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansson, J.E.; Vanier, M.T.; Svennerholm, L. Changes in the Fatty Acid and Sphingosine Composition of the Major Gangliosides of Human Brain with Age. J. Neurochem. 1978, 30, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schengrund, C.L.; Garrigan, O.W. A Comparative Study of Gangliosides from Brains of Various Species. Lipids 1969, 4, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, M.; Palestini, P.; Chigorno, V.; Sonnino, S.; Tettamanti, G. Changes in the Ganglioside Long-Chain Base Composition of Rat Cerebellar Granule Cells during Differentiation and Aging in Culture. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughlin, S.; Maheshwari, S.; Weishaupt, N.; Yeung, K.K.; Cechetto, D.F.; Whitehead, S.N. Age-Dependent and Regional Heterogeneity in the Long-Chain Base of a-Series Gangliosides Observed in the Rat Brain Using Maldi Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, e16135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, M.; Palestini, P.; Chigorno, V.; Sonnino, S. Age-Related Changes of the Ganglioside Long-Chain Base Composition in Rat Cerebellum. Neurochem. Int. 1996, 28, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palestini, P.; Masserini, M.; Fiorilli, A.; Calappi, E.; Tettamanti, G. Age-Related Changes in the Ceramide Composition of the Major Gangliosides Present in Rat Brain Subcellular Fractions Enriched in Plasma Membranes of Neuronal and Myelin Origin. J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, M.; Chigorno, V.; Sonnino, S.; Tettamanti, G. Rat Cerebellar Granule Cells in Culture Associate and Metabolize Differently Exogenous Gm1 Ganglioside Molecular Species Containing a C18 or C20 Long Chain Base. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1992, 60, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnick, R. The Therapeutic Potential of Modulating the Ceramide/Sphingomyelin Pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouser, G.; Yamamoto, A. The Fatty Acid Composition of Total Gangliosides in Normal Human Whole Brain at Different Ages. J. Neurochem. 1972, 19, 2697–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielawska, A.; Crane, H.M.; Liotta, D.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A. Selectivity of Ceramide-Mediated Biology. Lack of Activity of Erythro-Dihydroceramide. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 26226–26232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencarelli, C.; Martinez-Martinez, P. Ceramide Function in the Brain: When a Slight Tilt Is Enough. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aureli, M.; Grassi, S.; Prioni, S.; Sonnino, S.; Prinetti, A. Lipid Membrane Domains in the Brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, A.S.B.; Færgeman, N.J. Sphingolipids: Membrane Microdomains in Brain Development, Function and Neurological Diseases. Open Biol. 2017, 7, e170069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witting, L.A.; Krishnan, R.S.; Sakr, A.H.; Horwitt, M.K. Brain Gangliosides of Several Species. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 22, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennerholm, L.; Raal, A. Composition of Brain Gangliosides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1961, 53, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, L.N.; Michael, D.B.; Irwin, C.C. Ganglioside Patterns of Fetal Rat and Mouse Brain. J. Neurochem. 1980, 34, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posse de Chaves, E.; Sipione, S. Sphingolipids and Gangliosides of the Nervous System in Membrane Function and Dysfunction. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinetti, A.; Chigorno, V.; Prioni, S.; Loberto, N.; Marano, N.; Tettamanti, G.; Sonnino, S. Changes in the Lipid Turnover, Composition, and Organization, as Sphingolipid-Enriched Membrane Domains, in Rat Cerebellar Granule Cells Developing In Vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 21136–21145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schengrund, C.L. The Role(S) of Gangliosides in Neural Differentiation and Repair: A Perspective. Brain Res. Bull. 1990, 24, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösner, H.; al-Aqtum, M.; Rahmann, H. Gangliosides and Neuronal Differentiation. Neurochem. Int. 1992, 20, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Biase, E.; Lunghi, G.; Fazzari, M.; Maggioni, M.; Pomè, D.Y.; Valsecchi, M.; Samarani, M.; Fato, P.; Ciampa, M.G.; Prioni, S.; et al. Gangliosides in the Differentiation Process of Primary Neurons: The Specific Role of Gm1-Oligosaccharide. Glycoconj. J. 2020, 37, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadik, S.P.; Karpiak, S.E. Gm1 Ganglioside Enhances Neonatal Cortical Development. Neurotoxicology 1986, 7, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Willinger, M.; Schachner, M. Gm1 Ganglioside as a Marker for Neuronal Differentiation in Mouse Cerebellum. Dev. Biol. 1980, 74, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carine, K.; Schengrund, C.L. Effects of Exogenous Gm1 and Gd1a on S20y Neuroblastoma Cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 1984, 12, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, J.; Tsuji, S.; Nagai, Y. Bioactive Gangliosides: Analysis of Functional Structures of the Tetrasialoganglioside Gq1b Which Promotes Neurite Outgrowth. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 876, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Skaper, S.D.; Katoh-Semba, R.; Varon, S. Gm1 Ganglioside Accelerates Neurite Outgrowth from Primary Peripheral and Central Neurons under Selected Culture Conditions. Brain Res. 1985, 355, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobue, G.; Taki, T.; Yasuda, T.; Mitsuma, T. Gangliosides Modulate Schwann Cell Proliferation and Morphology. Brain Res. 1988, 474, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmann, H.; Rösner, H.; Körtje, K.H.; Beitinger, H.; Seybold, V. Ca(2+)-Ganglioside-Interaction in Neuronal Differentiation and Development. Prog. Brain Res. 1994, 101, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, K.; Miyamoto, E.; Soderling, T.R. Regulation of Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase Ii by Brain Gangliosides. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, G.; Fabris, M.; Gorio, A. Gangliosides Enhance Neurite Outgrowth in Pc12 Cells. Brain Res. 1983, 284, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, A.J.; Rampersaud, A. Sphingolipids as Receptor Modulators. An Overview. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 845, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuello, A.C.; Garofalo, L.; Kenigsberg, R.L.; Maysinger, D. Gangliosides Potentiate in Vivo and in Vitro Effects of Nerve Growth Factor on Central Cholinergic Neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2056–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panni, M.K.; Cooper, J.D.; Sofroniew, M.V. Ganglioside Gm1 Potentiates Ngf Action on Axotomised Medial Septal Cholinergic Neurons. Brain Res. 1998, 812, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantini, G.; Fusco, M.; Bigon, E.; Leon, A. Gm1 Ganglioside Potentiates the Effect of Nerve Growth Factor in Preventing Vinblastine-Induced Sympathectomy in Newborn Rats. Brain Res. 1988, 448, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, L.; Cuello, A.C. Nerve Growth Factor and the Monosialoganglioside Gm1: Analogous and Different In Vivo Effects on Biochemical, Morphological, and Behavioral Parameters of Adult Cortically Lesioned Rats. Exp. Neurol. 1994, 125, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoh, T.; Tokuda, A.; Miyadai, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Fujiki, N. Ganglioside Gm1 Binds to the Trk Protein and Regulates Receptor Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5087–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Fukui, T.; Hikichi, C.; Ishikawa, T.; Murate, K.; Adachi, T.; Imai, H.; Fukuhara, K.; Ueda, A.; Kaplan, A.P.; et al. Neurotropin Promotes Ngf Signaling through Interaction of Gm1 Ganglioside with Trk Neurotrophin Receptor in Pc12 Cells. Brain Res. 2015, 1596, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, Y. Functional Roles of Gangliosides in Bio-Signaling. Behav. Brain Res. 1995, 66, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnino, S.; Mauri, L.; Ciampa, M.G.; Prinetti, A. Gangliosides as Regulators of Cell Signaling: Ganglioside-Protein Interactions or Ganglioside-Driven Membrane Organization? J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duchemin, A.M.; Ren, Q.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Gm1-Induced Activation of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase: Involvement of Trk Receptors. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusnati, M.; Urbinati, C.; Tanghetti, E.; Dell’Era, P.; Lortat-Jacob, H.; Presta, M. Cell Membrane Gm1 Ganglioside Is a Functional Coreceptor for Fibroblast Growth Factor 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4367–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiconstantinou, M.; Neff, N.H. Gm1 Ganglioside: In Vivo and in Vitro Trophic Actions on Central Neurotransmitter Systems. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Matinyan, N.S.; Melikyan, G.B.; Arakelyan, V.B.; Kocharov, S.L.; Prokazova, N.V.; Avakian, T.M. Interaction of Ganglioside-Containing Planar Bilayers with Serotonin and Inorganic Cations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 984, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postila, P.A.; Vattulainen, I.; Róg, T. Selective Effect of Cell Membrane on Synaptic Neurotransmission. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, e19345. [Google Scholar]
- Fantini, J.; Barrantes, F.J. Sphingolipid/Cholesterol Regulation of Neurotransmitter Receptor Conformation and Function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 2345–2361. [Google Scholar]
- Duchemin, A.M.; Ren, Q.; Mo, L.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Gm1 Ganglioside Induces Phosphorylation and Activation of Trk and Erk in Brain. J. Neurochem. 2002, 81, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemin, A.M.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Induction of Trk Phosphorylation in Rat Brain by Gm1 Ganglioside. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 845, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitto, M.; Mutoh, T.; Kuriyama, M.; Ferraretto, A.; Palestini, P.; Masserini, M. Influence of Endogenous Gm1 Ganglioside on Trkb Activity, in Cultured Neurons. FEBS Lett. 1998, 439, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricozzi, E.; Pomè, D.Y.; Maggioni, M.; Di Biase, E.; Parravicini, C.; Palazzolo, L.; Loberto, N.; Eberini, I.; Sonnino, S. Role of the Gm1 Ganglioside Oligosaccharide Portion in the Trka-Dependent Neurite Sprouting in Neuroblastoma Cells. J. Neurochem. 2017, 143, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleda, G.; Morales, L.C.; Benítez, B.; Arboleda, H. Regulation of Ceramide-Induced Neuronal Death: Cell Metabolism Meets Neurodegeneration. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 59, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, G.; Minozzi, M.C.; Zanellato, A.M.; Silvestrini, B. Gm1, Like Igf-I and Gdnf, Prevents Neuronal Apoptosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 845, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricozzi, E.; Lunghi, G.; Di Biase, E.; Fazzari, M.; Sonnino, S.; Mauri, L. Gm1 Ganglioside Is a Key Factor in Maintaining the Mammalian Neuronal Functions Avoiding Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorio, A.; Vitadello, M. Ganglioside Prevention of Neuronal Functional Decay. Prog. Brain Res. 1987, 71, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manev, H.; Favaron, M.; Vicini, S.; Guidotti, A. Ganglioside-Mediated Protection from Glutamate-Induced Neuronal Death. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1990, 50, 475–488. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, E.; Armstrong, D.M.; Guidotti, A.; Kharlamov, A.; Kiedrowski, L.; Manev, H.; Polo, A.; Wroblewski, J.T. Gangliosides in the Protection against Glutamate Excitotoxicity. Prog. Brain Res. 1994, 101, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heaton, M.B.; Paiva, M.; Swanson, D.J.; Walker, D.W. Ethanol Neurotoxicity in Vitro: Effects of Gm1 Ganglioside and Protein Synthesis Inhibition. Brain Res. 1994, 654, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Milani, D.; Leon, A. Monosialoganglioside Gm1 Protects against Anoxia-Induced Neuronal Death In Vitro. Exp. Neurol. 1989, 106, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liao, Y.J.; Hou, G.H.; Yang, Z.B.; Zuo, M.L. Monosialotetrahexosylganglioside Protect Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Upregulating the Expression of Tyrosine Hydroxylase by Inhibiting Lipid Peroxidation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, M.; Mohand-Said, S.; Hicks, D.; Dreyfus, H.; Sahel, J.A. Monosialoganglioside Gm1 Reduces Ischemia—Reperfusion-Induced Injury in the Rat Retina. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.K.; Williams, C.E.; Mallard, C.E.; Gluckman, P.D. Monosialoganglioside Gm1 Treatment after a Hypoxic-Ischemic Episode Reduces the Vulnerability of the Fetal Sheep Brain to Subsequent Injuries. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1994, 170, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janigro, D.; Di Gregorio, F.; Vyskocil, F.; Gorio, A. Gangliosides’ Dual Mode of Action: A Working Hypothesis. J. Neurosci. Res. 1984, 12, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, G.; Anderson, B.L.; Stephens, R.M.; Kaplan, D.R.; Greene, L.A. Prevention of Apoptotic Neuronal Death by Gm1 Ganglioside. Involvement of Trk Neurotrophin Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Shen, M.; Ma, X.; Li, R.; Jin, X.; Bai, H.; Gao, L. Protective Effect of Gm1 Attenuates Hippocampus and Cortex Apoptosis after Ketamine Exposure in Neonatal Rat Via Pi3k/Akt/Gsk3β Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3471–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Yao, X.Q.; Chang, R.J.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, X.; Ma, D.Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.Y. Exogenous Gm1 Ganglioside Attenuates Ketamine-Induced Neurocognitive Impairment in the Developing Rat Brain. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, J.Q.; Wang, M.; Zhu, D.M.; Tang, M.; Chen, J.T.; Wang, L.; Ruan, D.Y. Monosialoanglioside (Gm1) Prevents Lead-Induced Neurotoxicity on Long-Term Potentiation, Sod Activity, Mda Levels, and Intracellular Calcium Levels of Hippocampus in Rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2009, 379, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, C.C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.W.; Yan, C.H. Gm1 Ameliorates Lead-Induced Cognitive Deficits and Brain Damage through Activating the Sirt1/Creb/Bdnf Pathway in the Developing Male Rat Hippocampus. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Yin, L.; Yuan, L.; Sui, D.; Sun, Y.; Fu, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, X. Ganglioside Gm1 Protects against High Altitude Cerebral Edema in Rats by Suppressing the Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response via the Pi3k/Akt-Nrf2 Pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 95, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benady, A.; Freidin, D.; Pick, C.G.; Rubovitch, V. Gm1 Ganglioside Prevents Axonal Regeneration Inhibition and Cognitive Deficits in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, e13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.F.; Zhang, W.; Bao, X.F.; Wang, W.; Song, L.; Jiang, B. Gm1 Ganglioside Reverses the Cognitive Deficits Induced by Mk801 in Mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galleguillos, D.; Wang, Q.; Steinberg, N.; Zaidi, A.; Shrivastava, G.; Dhami, K.; Daskhan, G.C.; Schmidt, E.N.; Dworsky-Fried, Z.; Giuliani, F.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Role of Gm1 and Other Gangliosides on Microglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Bose, D.; Giri, R.P.; Mukhopadhyay, M.K.; Chakrabarti, A. Effects of Gm1 on Brain Spectrin-Aminophospholipid Interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, K.; Lin, X.; Malci, A.; Stojanović, M.; Puljko, B.; Rožman, M.; Vukelić, Ž.; Heffer, M.; Montag, D.; Schnaar, R.L.; et al. Plasma Membrane Calcium Atpase-Neuroplastin Complexes Are Selectively Stabilized in Gm1-Containing Lipid Rafts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Itokazu, Y.; Yu, R.K. Gm1 Ganglioside Is Involved in Epigenetic Activation Loci of Neuronal Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toffano, G.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K.G. The Effect of the Ganglioside Gm1 on Neuronal Plasticity. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1986, 4, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maysinger, D.; Leavitt, B.R.; Zorc, B.; Butula, I.; Fernandes, L.G.; Ribeiro-da-Silva, A. Inhibition of High Affinity Choline Uptake in the Rat Brain by Neurotoxins: Effect of Monosialoganglioside Gm1. Neurochem. Int. 1992, 20, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D.; Leon, A.; Facci, L. Ganglioside Gm1 Prevents Death Induced by Excessive Excitatory Neurotransmission in Cultured Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 1991, 126, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.; Facci, L.; Toffano, G.; Sonnino, S.; Tettamanti, G. Activation of (Na+, K+)-Atpase by Nanomolar Concentrations of Gm1 Ganglioside. J. Neurochem. 1981, 37, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, F.; Scherer, E.B.; Ferreira, A.G.; Petry Fdos, S.; Pereira, C.L.; Santana, F.; de Souza Wyse, A.T.; Salbego, C.G.; Trindade, V.M. Alterations on Na+,K+-Atpase and Acetylcholinesterase Activities Induced by Amyloid-Β Peptide in Rat Brain and Gm1 Ganglioside Neuroprotective Action. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadik, S.P.; Hawver, D.B.; Hungund, B.L.; Li, Y.S.; Karpiak, S.E. Gm1 Ganglioside Treatment after Global Ischemia Protects Changes in Membrane Fatty Acids and Properties of Na+, K+-Atpase and Mg2+-Atpase. J. Neurosci. Res. 1989, 24, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappagantula, S.; Andrews, M.R.; Cheah, M.; Abad-Rodriguez, J.; Dotti, C.G.; Fawcett, J.W. Neu3 Sialidase-Mediated Ganglioside Conversion Is Necessary for Axon Regeneration and Is Blocked in Cns Axons. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 2477–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newburn, E.N.; Duchemin, A.M.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Gm1 Ganglioside Enhances Ret Signaling in Striatum. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistin, L.; Cesari, A.; Galligioni, F.; Marin, G.; Massarotti, M.; Paccagnella, D.; Pellegrini, A.; Testa, G.; Tonin, P. Effects of Gm1 Ganglioside in Cerebrovascular Diseases: A Double-Blind Trial in 40 Cases. Eur. Neurol. 1985, 24, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.S.; Gollomp, S.M.; Sendek, S.; Colcher, A.; Cambi, F.; Du, W. A Randomized, Controlled, Delayed Start Trial of Gm1 Ganglioside in Treated Parkinson’s Disease Patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 324, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itokazu, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, R.K. Intracerebroventricular Infusion of Gangliosides Augments the Adult Neural Stem Cell Pool in Mouse Brain. ASN Neuro 2019, 11, e1759091419884859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeen, R.W.; Wu, G. Ganglioside Function in Calcium Homeostasis and Signaling. Neurochem. Res. 2002, 27, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmano, K.; Rowan, A.; Guillermo, R.; Guan, J.; McJarrow, P. The Role of Gangliosides in Neurodevelopment. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3891–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmann, H.; Probst, W.; Mühleisen, M. Gangliosides and Synaptic Transmission. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1982, 52, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Waki, H.; Kon, K.; Ando, S. Gangliosides Enhance Kcl-Induced Ca2+ Influx and Acetylcholine Release in Brain Synaptosomes. Neuroreport 1997, 8, 2203–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, T.G.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Gm1 Ganglioside Improves Spatial Learning and Memory of Aged Rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1997, 85, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B. Molecular Mechanism Underlying Sialic Acid as an Essential Nutrient for Brain Development and Cognition. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 465s–472s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Waki, H.; Kon, K.; Iwamoto, M.; Fukui, F. Gangliosides and Sialylcholesterol as Modulators of Synaptic Functions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 845, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorushkina, N.V.; Ratushnyak, A.S.; Egorushkin, I.V. The Influence of Exogenous Gangliosides on the Dynamics of the Development of Prolonged Posttetanic Potentiation. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 1993, 23, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieraszko, A.; Seifert, W. The Role of Monosialoganglioside Gm1 in the Synaptic Plasticity: In Vitro Study on Rat Hippocampal Slices. Brain Res. 1985, 345, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, J.Q.; Wang, M.; Zhu, D.M.; Sun, L.G.; Ruan, D.Y. Effect of Ganglioside on Synaptic Plasticity of Hippocampus in Lead-Exposed Rats In Vivo. Brain Res. 2005, 1060, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffano, G.; Savoini, G.; Moroni, F.; Lombardi, G.; Calza, L.; Agnati, L.F. Gm1 Ganglioside Stimulates the Regeneration of Dopaminergic Neurons in the Central Nervous System. Brain Res. 1983, 261, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K.; Calza, L.; Goldstein, M.; Toffano, G.; Giardino, L.; Zoli, M. Further Studies on the Effects of the Gm1 Ganglioside on the Degenerative and Regenerative Features of Mesostriatal Dopamine Neurons. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1984, 532, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Barrier, L.; Page, G.; Barc, S.; Piriou, A.; Portoukalian, J. Sulfatide and Gm1 Ganglioside Modulate the High-Affinity Dopamine Uptake in Rat Striatal Synaptosomes: Evidence for the Involvement of Their Ionic Charges. Neurochem. Int. 2003, 42, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilson, H.A.; Harry, G.J.; Nanry, K.; Hudson, P.M.; Hong, J.S. Ganglioside Interactions with the Dopaminergic System of Rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 1988, 19, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raiteri, M.; Bonanno, G.; Pende, M.; Versace, P. Gm1 Ganglioside Treatment Promotes Recovery of Electrically-Stimulated [3h]Dopamine Release in Striatal Slices from Rats Lesioned with Kainic Acid. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 136, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettl, V.M.; Wemlinger, T.A.; Fong, T.G.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Retinal Cholinergic and Dopaminergic Deficits of Aged Rats Are Improved Following Treatment with Gm1 Ganglioside. Brain Res. 2000, 877, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fadda, E.; Negro, A.; Facci, L.; Skaper, S.D. Ganglioside Gm1 Cooperates with Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor to Protect Dopaminergic Neurons from 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Degeneration. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 159, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, E.A.; Molina, V.A. Gangliosides Facilitate the Recovery of Behavioral Response Mediated by Dopaminergic Sites following Their Irreversible Blockade. Brain Res. Bull. 1993, 31, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domańska-Janik, K.; Noremberg, K.; Lazarewicz, J. Gangliosides and Synaptosomal Calcium Homeostasis. Int. J. Tissue React. 1986, 8, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spoerri, P.E.; Dozier, A.K.; Roisen, F.J. Calcium Regulation of Neuronal Differentiation: The Role of Calcium in Gm1-Mediated Neuritogenesis. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1990, 56, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tsui, Z.; Yang, F. Antagonistic Effect of Ganglioside Gm1 and Gm3 on the Activity and Conformation of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca(2+)-Atpase. FEBS Lett. 1999, 457, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X. Gangliosides Modulate the Activity of the Plasma Membrane Ca(2+)-Atpase from Porcine Brain Synaptosomes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 427, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeen, R.W.; Wu, G. Gm1 Ganglioside: Another Nuclear Lipid That Modulates Nuclear Calcium. Gm1 Potentiates the Nuclear Sodium-Calcium Exchanger. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 84, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wu, G.; Lu, Z.H.; Ledeen, R.W. Potentiation of a Sodium-Calcium Exchanger in the Nuclear Envelope by Nuclear Gm1 Ganglioside. J. Neurochem. 2002, 81, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.F.; Crain, S.M.; Ledeen, R.W. Brief Treatment of Sensory Ganglion Neurons with Gm1 Ganglioside Enhances the Efficacy of Opioid Excitatory Effects on the Action Potential. Brain Res. 1991, 559, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crain, S.M.; Shen, K.F. After Chronic Opioid Exposure Sensory Neurons Become Supersensitive to the Excitatory Effects of Opioid Agonists and Antagonists as Occurs after Acute Elevation of Gm1 Ganglioside. Brain Res. 1992, 575, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lu, Z.H.; Ledeen, R.W. Interaction of the Delta-Opioid Receptor with Gm1 Ganglioside: Conversion from Inhibitory to Excitatory Mode. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1997, 44, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.F.; Crain, S.M. Cholera Toxin-B Subunit Blocks Excitatory Effects of Opioids on Sensory Neuron Action Potentials Indicating That Gm1 Ganglioside May Regulate Gs-Linked Opioid Receptor Functions. Brain Res. 1990, 531, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamori, K.I.; Inokuchi, J.I. Roles of Gangliosides in Hypothalamic Control of Energy Balance: New Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freo, U.; Dam, M.; Pizzolato, G.; Pietrini, P.; Soncrant, T.T.; Battistin, L. The Monosialoganglioside Gm1 Dose-Dependently Reduces Regional Cerebral Metabolic Rates for Glucose in Awake Rats. Brain Res. 1993, 621, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, F.B., Jr.; Yu, R.K.; Ledeen, R.W. Myelin Gangliosides in Vertebrates. J. Neurochem. 1982, 39, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiconstantinou, M.; Neff, N.H. Gm1 and the Aged Brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 845, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schengrund, C.L. Lipid Rafts: Keys to Neurodegeneration. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 82, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masserini, M.; Palestini, P.; Freire, E. Influence of Glycolipid Oligosaccharide and Long-Chain Base Composition on the Thermotropic Properties of Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine Large Unilamellar Vesicles Containing Gangliosides. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 5029–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, M.R.; Singh, D.; Lu, D.; Grant, C.W. Glycosphingolipid Fatty Acid Arrangement in Phospholipid Bilayers: Cholesterol Effects. Biophys. J. 1995, 68, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, H.L.; Momsen, M.M.; Brown, R.E.; He, L.; Chun, J.; Byun, H.S.; Bittman, R. The 4,5-Double Bond of Ceramide Regulates Its Dipole Potential, Elastic Properties, and Packing Behavior. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and Microglial Activation in Alzheimer Disease: Where Do We Go from Here? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebecauer, M.; Hof, M.; Amaro, M. Impact of Gm(1) on Membrane-Mediated Aggregation/Oligomerization of Β-Amyloid: Unifying View. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, K. Pathological Significance of Ganglioside Clusters in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, K. Role of Gangliosides in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, T.; McDonald, M.P.; Yu, R.K. Role of Ganglioside Metabolism in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease—A Review. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1157–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, M.; Vantini, G.; Schiavo, N.; Zanotti, A.; Zanoni, R.; Facci, L.; Skaper, S.D. Gangliosides and Neurotrophic Factors in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Experimental Findings to Clinical Perspectives. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 695, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Gong, C.X.; Schuchman, E.H. Deregulation of Sphingolipid Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K. How Do Membranes Initiate Alzheimer’s Disease? Formation of Toxic Amyloid Fibrils by the Amyloid Β-Protein on Ganglioside Clusters. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, K.; Odaka, A.; Suzuki, N.; Ihara, Y. Gm1 Ganglioside-Bound Amyloid Beta-Protein (a Beta): A Possible Form of Preamyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, K.; Ihara, Y. Gm1 Ganglioside-Bound Amyloid Beta-Protein in Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. Neurobiol. Aging 1998, 19, S65–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Kimura, N.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Yokoseki, T.; Shibata, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Michikawa, M.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Terao, K.; et al. A Seed for Alzheimer Amyloid in the Brain. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4894–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, K. Gm1 Ganglioside and the Seeding of Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease: Endogenous Seed for Alzheimer Amyloid. Neuroscientist 2005, 11, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Van Nostrand, W.E.; Yanagisawa, K. Further Evidence of Local Ganglioside-Dependent Amyloid Beta-Protein Assembly in Brain. Neuroreport 2006, 17, 1735–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Matsubara, E.; Maeda, S.; Minagawa, H.; Takashima, A.; Maruyama, W.; Michikawa, M.; Yanagisawa, K. A Ganglioside-Induced Toxic Soluble Abeta Assembly. Its Enhanced Formation from Abeta Bearing the Arctic Mutation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 2646–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Fukata, Y.; Fukata, M.; Yanagisawa, K. Gm1-Ganglioside-Induced Abeta Assembly on Synaptic Membranes of Cultured Neurons. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, N.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ogino, K.; Taki, T.; Yuyama, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Shin, R.W.; Furukawa, K.; Yanagisawa, K. Gangliosides Determine the Amyloid Pathology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroreport 2009, 20, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, M.; Ariga, T.; Yu, R.K. Cytotoxic Effects of G(M1) Ganglioside and Amyloid Β-Peptide on Mouse Embryonic Neural Stem Cells. ASN Neuro 2010, 2, e00029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, K. Gm1 Ganglioside and Alzheimer’s Disease. Glycoconj. J. 2015, 32, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaro, M.; Šachl, R.; Aydogan, G.; Mikhalyov, I.I.; Vácha, R.; Hof, M. Gm1 Ganglioside Inhibits Β-Amyloid Oligomerization Induced by Sphingomyelin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9411–9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Pérez, E.J.; Sepúlveda, F.J.; Peoples, R.; Aguayo, L.G. Role of Membrane Gm1 on Early Neuronal Membrane Actions of Aβ during Onset of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 3105–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Kato, K.; Yanagisawa, K. Ganglioside-Mediated Assembly of Amyloid Β-Protein: Roles in Alzheimer’s Disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 156, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Ostaszewski, B.L.; Yang, T.; O’Malley, T.T.; Jin, M.; Yanagisawa, K.; Li, S.; Bartels, T.; Selkoe, D.J. Soluble Aβ Oligomers Are Rapidly Sequestered from Brain Isf in Vivo and Bind Gm1 Ganglioside on Cellular Membranes. Neuron 2014, 82, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuyama, K.; Yanagisawa, K. Sphingomyelin Accumulation Provides a Favorable Milieu for Gm1 Ganglioside-Induced Assembly of Amyloid Beta-Protein. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 481, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Matsubara, T.; Sato, T.; Yanagisawa, K. Age-Dependent High-Density Clustering of Gm1 Ganglioside at Presynaptic Neuritic Terminals Promotes Amyloid Beta-Protein Fibrillogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 2717–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Nishihara, M.; Yasumori, H.; Nakai, M.; Yanagisawa, K.; Sato, T. Size and Shape of Amyloid Fibrils Induced by Ganglioside Nanoclusters: Role of Sialyl Oligosaccharide in Fibril Formation. Langmuir 2017, 33, 13874–13881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakio, A.; Nishimoto, S.; Yanagisawa, K.; Kozutsumi, Y.; Matsuzaki, K. Interactions of Amyloid Beta-Protein with Various Gangliosides in Raft-Like Membranes: Importance of Gm1 Ganglioside-Bound Form as an Endogenous Seed for Alzheimer Amyloid. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 7385–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano-Sakamaki, W.; Sugiyama, E.; Hayasaka, T.; Ravid, R.; Setou, M.; Taki, T. Alzheimer’s Disease Is Associated with Disordered Localization of Ganglioside Gm1 Molecular Species in the Human Dentate Gyrus. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Tanida, M.; Kasahara, R.; Sobue, K.; Suzuki, K. Leptin Inhibits Amyloid Β-Protein Fibrillogenesis by Decreasing Gm1 Gangliosides on the Neuronal Cell Surface through Pi3k/Akt/Mtor Pathway. J. Neurochem. 2014, 131, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Wang, Q.; Min, L.; Sui, R.; Li, J.; Liu, X. Monosialoanglioside Improves Memory Deficits and Relieves Oxidative Stress in the Hippocampus of Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itokazu, Y.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Nakatani, Y.; Ariga, T.; Yu, R.K. Effects of Amyloid Β-Peptides and Gangliosides on Mouse Neural Stem Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, F.; Frozza, R.L.; Breier, A.C.; de Oliveira, V.A.; Horn, A.P.; Pettenuzzo, L.F.; Netto, C.A.; Salbego, C.G.; Trindade, V.M. Amyloid-Β Induced Toxicity Involves Ganglioside Expression and Is Sensitive to Gm1 Neuroprotective Action. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, T.V.; Zakharova, I.O.; Furaev, V.V.; Rychkova, M.P.; Avrova, N.F. Neuroprotective Effect of Ganglioside Gm1 on the Cytotoxic Action of Hydrogen Peroxide and Amyloid Beta-Peptide in Pc12 Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Hartmann, T.; Beyreuther, K.; Zhang, D. Gm1 Ganglioside Regulates the Proteolysis of Amyloid Precursor Protein. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Iijima, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Yanagisawa, K.; Sato, T. Density of Gm1 in Nanoclusters Is a Critical Factor in the Formation of a Spherical Assembly of Amyloid Β-Protein on Synaptic Plasma Membranes. Langmuir 2013, 29, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakio, A.; Nishimoto, S.I.; Yanagisawa, K.; Kozutsumi, Y.; Matsuzaki, K. Cholesterol-Dependent Formation of Gm1 Ganglioside-Bound Amyloid Beta-Protein, an Endogenous Seed for Alzheimer Amyloid. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 24985–24990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, K.; Gao, G.; Shen, L.; Sun, T. Kinetic Study of Aβ(1-42) Amyloidosis in the Presence of Ganglioside-Containing Vesicles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, e110615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Fukunaga, S.; Hoshino, M.; Matsuzaki, K. Mechanism of Amyloid Β-Protein Aggregation Mediated by Gm1 Ganglioside Clusters. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 6433–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Yi, J.S.; Ko, Y.G. Amyloid Beta Oligomerization Is Induced by Brain Lipid Rafts. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 99, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Arima, H.; Sugiura, T.; Hirate, H.; Kusama, N.; Suzuki, K.; Sobue, K. Midazolam Inhibits the Formation of Amyloid Fibrils and Gm1 Ganglioside-Rich Microdomains in Presynaptic Membranes through the Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid a Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 457, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukhinova, M.; Veremeyko, T.; Yung, A.W.Y.; Kuznetsova, I.S.; Lau, T.Y.B.; Kopeikina, E.; Chan, A.M.L.; Ponomarev, E.D. Fresh Evidence for Major Brain Gangliosides as a Target for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 77, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahi, N.; Fantini, J. Deciphering the Glycolipid Code of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Amyloid Proteins Allowed the Creation of a Universal Ganglioside-Binding Peptide. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitz, J.M. Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. Front. Biosci. 2014, 6, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.T.; Kastner, A.; Perez-Otaño, I.; Hirsch, E.C.; Luquin, M.R.; Javoy-Agid, F.; Del Río, J.; Obeso, J.A.; Agid, Y. Gangliosides and Parkinsonism. Neurology 1993, 43, 2132–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallom, K.L.; Fernández-Suárez, M.E.; Priestman, D.A.; Te Vruchte, D.; Huebecker, M.; Hallett, P.J.; Isacson, O.; Platt, F.M. Glycosphingolipid Metabolism and Its Role in Ageing and Parkinson’s Disease. Glycoconj. J. 2021, 39, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebecker, M.; Moloney, E.B.; van der Spoel, A.C.; Priestman, D.A.; Isacson, O.; Hallett, P.J.; Platt, F.M. Reduced Sphingolipid Hydrolase Activities, Substrate Accumulation and Ganglioside Decline in Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeen, R.; Chowdhury, S.; Lu, Z.H.; Chakraborty, M.; Wu, G. Systemic Deficiency of Gm1 Ganglioside in Parkinson’s Disease Tissues and Its Relation to the Disease Etiology. Glycoconj. J. 2022, 39, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Ledeen, R. The Key Role of Gm1 Ganglioside in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzari, M.; Di Biase, E.; Lunghi, G.; Mauri, L.; Chiricozzi, E.; Sonnino, S. Novel Insights on Gm1 and Parkinson’s Disease: A Critical Review. Glycoconj. J. 2022, 39, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnino, S. The Relationship between Depletion of Brain Gm1 Ganglioside and Parkinson’s Disease. FEBS Open Bio 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Lu, Z.H.; Kulkarni, N.; Ledeen, R.W. Deficiency of Ganglioside Gm1 Correlates with Parkinson’s Disease in Mice and Humans. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Lu, Z.H.; Seo, J.H.; Alselehdar, S.K.; DeFrees, S.; Ledeen, R.W. Mice Deficient in Gm1 Manifest Both Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease; Successful Treatment with Synthetic Gm1 Ganglioside. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 329, e113284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.S. Altered Expression of Genes Involved in Ganglioside Biosynthesis in Substantia Nigra Neurons in Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lu, Z.H.; Kulkarni, N.; Amin, R.; Ledeen, R.W. Mice Lacking Major Brain Gangliosides Develop Parkinsonism. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Schneider, J.S. Sirna-Mediated Knockdown of B3galt4 Decreases Gm1 Ganglioside Expression and Enhances Vulnerability for Neurodegeneration. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 95, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.S.; Aras, R.; Williams, C.K.; Koprich, J.B.; Brotchie, J.M.; Singh, V. Gm1 Ganglioside Modifies A-Synuclein Toxicity and Is Neuroprotective in a Rat A-Synuclein Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, e8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.L.; Duan, W.J.; Lu, D.H.; Ma, X.H.; Li, X.X.; Li, Z.; Bi, W.; Kurihara, H.; Liu, H.Z.; Li, Y.F.; et al. Autophagy-Dependent Removal of A-Synuclein: A Novel Mechanism of Gm1 Ganglioside Neuroprotection against Parkinson’s Disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkhawattanangkul, Y.; Maiti, P.; Xue, Y.; Aryal, D.; Wetsel, W.C.; Hamilton, D.; Fowler, S.C.; McDonald, M.P. Targeted Deletion of Gd3 Synthase Protects against Mptp-Induced Neurodegeneration. Genes Brain Behav. 2017, 16, 522–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanushkodi, A.; Xue, Y.; Roguski, E.E.; Ding, Y.; Matta, S.G.; Heck, D.; Fan, G.H.; McDonald, M.P. Lentiviral-Mediated Knock-Down of Gd3 Synthase Protects against Mptp-Induced Motor Deficits and Neurodegeneration. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 692, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, X.; Li, S. The Possible Mechanism of Parkinson’s Disease Progressive Damage and the Preventive Effect of Gm1 in the Rat Model Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine. Brain Res. 2014, 1592, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, Z.; Zhu, M.; Han, S.; Fink, A.L. Gm1 Specifically Interacts with Alpha-Synuclein and Inhibits Fibrillation. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, T.; Kim, N.C.; Luth, E.S.; Selkoe, D.J. N-Alpha-Acetylation of A-Synuclein Increases Its Helical Folding Propensity, Gm1 Binding Specificity and Resistance to Aggregation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba, X.H. Therapeutic Effects of Gm1 on Parkinson’s Disease in Rats and Its Mechanism. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.S.; Pope, A.; Simpson, K.; Taggart, J.; Smith, M.G.; DiStefano, L. Recovery from Experimental Parkinsonism in Primates with Gm1 Ganglioside Treatment. Science 1992, 256, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.S.; Yuwiler, A. Gm1 Ganglioside Treatment Promotes Recovery of Striatal Dopamine Concentrations in the Mouse Model of Mptp-Induced Parkinsonism. Exp. Neurol. 1989, 105, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.S.; Sendek, S.; Daskalakis, C.; Cambi, F. Gm1 Ganglioside in Parkinson’s Disease: Results of a Five Year Open Study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 292, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoli, E.R.; Annunziata, I.; d’Azzo, A.; Platt, F.M.; Tifft, C.J.; Stepien, K.M. Gm1 Gangliosidosis—A Mini-Review. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 734878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rha, A.K.; Maguire, A.S.; Martin, D.R. Gm1 Gangliosidosis: Mechanisms and Management. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2021, 14, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Scaglia, F. Gm1 Gangliosidosis: Review of Clinical, Molecular, and Therapeutic Aspects. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008, 94, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, H.; Yamato, O.; Asano, T.; Yonemura, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Hasegawa, D.; Orima, H.; Arai, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Maede, Y. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers Showing Neurodegeneration in Dogs with Gm1 Gangliosidosis: Possible Use for Assessment of a Therapeutic Regimen. Brain Res. 2007, 1133, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Yamato, O.; Asano, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Maede, Y. Increased Concentration of Gm1-Ganglioside in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Dogs with Gm1- and Gm2-Gangliosidoses and Its Clinical Application for Diagnosis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2004, 16, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, E.M.; Alroy, J.; Raghavan, S.S.; Schwarting, G.A.; Adelman, L.S.; Runge, V.; Gelblum, D.; Thalhammer, J.G.; Zuniga, G. Dysmyelinogenesis in Animal Model of Gm1 Gangliosidosis. Pediatr. Neurol. 1992, 8, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkerth, R.D.; Alroy, J.; Bhan, I.; Kaye, E.M. Infantile G(M1) Gangliosidosis: Complete Morphology and Histochemistry of Two Autopsy Cases, with Particular Reference to Delayed Central Nervous System Myelination. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2000, 3, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinecke, K.A.; Luoma, A.; d’Azzo, A.; Kirschner, D.A.; Seyfried, T.N. Myelin Abnormalities in the Optic and Sciatic Nerves in Mice with Gm1-Gangliosidosis. ASN Neuro 2015, 7, 1759091415568913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Voorn, J.P.; Kamphorst, W.; van der Knaap, M.S.; Powers, J.M. The Leukoencephalopathy of Infantile Gm1 Gangliosidosis: Oligodendrocytic Loss and Axonal Dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol. 2004, 107, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyakumar, M.; Thomas, R.; Elliot-Smith, E.; Smith, D.A.; van der Spoel, A.C.; d’Azzo, A.; Perry, V.H.; Butters, T.D.; Dwek, R.A.; Platt, F.M. Central Nervous System Inflammation Is a Hallmark of Pathogenesis in Mouse Models of Gm1 and Gm2 Gangliosidosis. Brain 2003, 126, 974–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessitore, A.; Martin, M.D.P.; Sano, R.; Ma, Y.; Mann, L.; Ingrassia, A.; Laywell, E.D.; Steindler, D.A.; Hendershot, L.M.; d’Azzo, A. Gm1-Ganglioside-Mediated Activation of the Unfolded Protein Response Causes Neuronal Death in a Neurodegenerative Gangliosidosis. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, M.L.; Jope, R.S.; Baker, H.J.; Lally, K.M. Reduced Ca2+ Flux in Synaptosomes from Cats with Gm1 Gangliosidosis. Brain Res. 1987, 424, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lu, Z.H.; Ledeen, R.W. Gm1 Ganglioside in the Nuclear Membrane Modulates Nuclear Calcium Homeostasis during Neurite Outgrowth. J. Neurochem. 1995, 65, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, H.S.; Coyle, J.T.; Weaver, D.L.; Kawamura, N.; Baker, H.J. Neurotransmitter Chemistry in Feline Gm1 Gangliosidosis: A Model for Human Ganglioside Storage Disease. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 12, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, A.; Higaki, K.; Kajimaki, K.; Otsuka, S.; Ninomiya, H.; Matsuda, J.; Ohno, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Nanba, E. Enhanced Autophagy and Mitochondrial Aberrations in Murine G(M1)-Gangliosidosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, A.; Higaki, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Takai, T.; Matsuda, J.; Iida, M.; Ohno, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Nanba, E. Lysosomal Accumulation of Trk Protein in Brain of GM1-Gangliosidosis Mouse and Its Restoration by Chemical Chaperone. J. Neurochem. 2011, 118, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condori, J.; Acosta, W.; Ayala, J.; Katta, V.; Flory, A.; Martin, R.; Radin, J.; Cramer, C.L.; Radin, D.N. Enzyme Replacement for GM1-Gangliosidosis: Uptake, Lysosomal Activation, and Cellular Disease Correction Using a Novel β-Galactosidase:Rtb Lectin Fusion. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 117, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybilla, M.J.; Stewart, C.; Carlson, T.W.; Ou, L.; Koniar, B.L.; Sidhu, R.; Kell, P.J.; Jiang, X.; Jarnes, J.R.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; et al. Examination of a Blood-Brain Barrier Targeting Β-Galactosidase-Monoclonal Antibody Fusion Protein in a Murine Model of Gm1-Gangliosidosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2021, 27, e100748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Pandey, H.; Sivakumar, S. Intracellular Delivery of Β-Galactosidase Enzyme Using Arginase-Responsive Dextran Sulfate/Poly-L-Arginine Capsule for Lysosomal Storage Disorder. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 9002–9012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.M.; Gross, A.L.; Martin, D.R.; Byrne, M.E. Polyethylene Glycol-B-Poly(Lactic Acid) Polymersomes as Vehicles for Enzyme Replacement Therapy. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 2591–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Luu, A.R.; Wise, N.; Angelis, R.; Agrawal, V.; Mangini, L.; Vincelette, J.; Handyside, B.; Sterling, H.; Lo, M.J.; et al. Intracerebroventricular Enzyme Replacement Therapy with Β-Galactosidase Reverses Brain Pathologies due to Gm1 Gangliosidosis in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 13532–13555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caciotti, A.; Donati, M.A.; d’Azzo, A.; Salvioli, R.; Guerrini, R.; Zammarchi, E.; Morrone, A. The Potential Action of Galactose as a “Chemical Chaperone”: Increase of Beta Galactosidase Activity in Fibroblasts from an Adult Gm1-Gangliosidosis Patient. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2009, 13, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higaki, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Nanba, E. Candidate Molecules for Chemical Chaperone Therapy of Gm1-Gangliosidosis. Futur. Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigat, B.A.; Tropak, M.B.; Buttner, J.; Crushell, E.; Benedict, D.; Callahan, J.W.; Martin, D.R.; Mahuran, D.J. Evaluation of N-Nonyl-Deoxygalactonojirimycin as a Pharmacological Chaperone for Human Gm1 Gangliosidosis Leads to Identification of a Feline Model Suitable for Testing Enzyme Enhancement Therapy. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 107, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Front, S.; Biela-Banaś, A.; Burda, P.; Ballhausen, D.; Higaki, K.; Caciotti, A.; Morrone, A.; Charollais-Thoenig, J.; Gallienne, E.; Demotz, S.; et al. (5ar)-5a-C-Pentyl-4-Epi-Isofagomine: A Powerful Inhibitor of Lysosomal Β-Galactosidase and a Remarkable Chaperone for Mutations Associated with Gm1-Gangliosidosis and Morquio Disease Type B. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, T.; Higaki, K.; Aguilar-Moncayo, M.; Mena-Barragán, T.; Hirano, Y.; Yura, K.; Yu, L.; Ninomiya, H.; García-Moreno, M.I.; Sakakibara, Y.; et al. A Bicyclic 1-Deoxygalactonojirimycin Derivative as a Novel Pharmacological Chaperone for Gm1 Gangliosidosis. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ichinomiya, S.; Kurosawa, M.; Matsuda, J.; Ogawa, S.; Iida, M.; Kubo, T.; Tabe, M.; Itoh, M.; Higaki, K.; et al. Therapeutic Chaperone Effect of N-Octyl 4-Epi-Β-Valienamine on Murine G(M1)-Gangliosidosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 106, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thonhofer, M.; Gonzalez Santana, A.; Fischer, R.; Torvisco Gomez, A.; Saf, R.; Schalli, M.; Stütz, A.E.; Withers, S.G. 5-Fluoro Derivatives of 4-Epi-Isofagomine as D-Galactosidase Inhibitors and Potential Pharmacological Chaperones for Gm1-Gangliosidosis as Well as Fabry’s Disease. Carbohydr. Res. 2016, 420, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantur, K.; Hofer, D.; Schitter, G.; Steiner, A.J.; Pabst, B.M.; Wrodnigg, T.M.; Stütz, A.E.; Paschke, E. Dlhex-Dgj, a Novel Derivative of 1-Deoxygalactonojirimycin with Pharmacological Chaperone Activity in Human G(M1)-Gangliosidosis Fibroblasts. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 100, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasperzyk, J.L.; El-Abbadi, M.M.; Hauser, E.C.; D’Azzo, A.; Platt, F.M.; Seyfried, T.N. N-Butyldeoxygalactonojirimycin Reduces Neonatal Brain Ganglioside Content in a Mouse Model of Gm1 Gangliosidosis. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperzyk, J.L.; d’Azzo, A.; Platt, F.M.; Alroy, J.; Seyfried, T.N. Substrate Reduction Reduces Gangliosides in Postnatal Cerebrum-Brainstem and Cerebellum in Gm1 Gangliosidosis Mice. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ichinomiya, S.; Kurosawa, M.; Ohkubo, M.; Watanabe, H.; Iwasaki, H.; Matsuda, J.; Noguchi, Y.; Takimoto, K.; Itoh, M.; et al. Chemical Chaperone Therapy: Clinical Effect in Murine G(M1)-Gangliosidosis. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y. Chemical Chaperone Therapy for Gm1-Gangliosidosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, K.; Li, L.; Bahrudin, U.; Okuzawa, S.; Takamuram, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Adachi, K.; Paraguison, R.C.; Takai, T.; Ikehata, H.; et al. Chemical Chaperone Therapy: Chaperone Effect on Mutant Enzyme and Cellular Pathophysiology in Β-Galactosidase Deficiency. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, J.; Suzuki, O.; Oshima, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Noguchi, A.; Takimoto, K.; Itoh, M.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Yasuda, Y.; Ogawa, S.; et al. Chemical Chaperone Therapy for Brain Pathology in G(M1)-Gangliosidosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15912–15917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot-Smith, E.; Speak, A.O.; Lloyd-Evans, E.; Smith, D.A.; van der Spoel, A.C.; Jeyakumar, M.; Butters, T.D.; Dwek, R.A.; d’Azzo, A.; Platt, F.M. Beneficial Effects of Substrate Reduction Therapy in a Mouse Model of Gm1 Gangliosidosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008, 94, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodato, F.; Procopio, E.; Rampazzo, A.; Taurisano, R.; Donati, M.A.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Caciotti, A.; Morrone, A.; Scarpa, M. The Treatment of Juvenile/Adult Gm1-Gangliosidosis with Miglustat May Reverse Disease Progression. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Hayward, C.; Patel, H.C.; Manohar, S.G.; Lyon, A.R. Gene Therapy for Gm1 Gangliosidosis: Challenges of Translational Medicine. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, S28. [Google Scholar]
- Takaura, N.; Yagi, T.; Maeda, M.; Nanba, E.; Oshima, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Yamano, T.; Tanaka, A. Attenuation of Ganglioside Gm1 Accumulation in the Brain of Gm1 Gangliosidosis Mice by Neonatal Intravenous Gene Transfer. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekman, M.L.; Baek, R.C.; Comer, L.A.; Fernandez, J.L.; Seyfried, T.N.; Sena-Esteves, M. Complete Correction of Enzymatic Deficiency and Neurochemistry in the Gm1-Gangliosidosis Mouse Brain by Neonatal Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Gene Delivery. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, R.C.; Broekman, M.L.; Leroy, S.G.; Tierney, L.A.; Sandberg, M.A.; d’Azzo, A.; Seyfried, T.N.; Sena-Esteves, M. Aav-Mediated Gene Delivery in Adult Gm1-Gangliosidosis Mice Corrects Lysosomal Storage in Cns and Improves Survival. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weismann, C.M.; Ferreira, J.; Keeler, A.M.; Su, Q.; Qui, L.; Shaffer, S.A.; Xu, Z.; Gao, G.; Sena-Esteves, M. Systemic Aav9 Gene Transfer in Adult Gm1 Gangliosidosis Mice Reduces Lysosomal Storage in Cns and Extends Lifespan. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 4353–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekman, M.L.; Tierney, L.A.; Benn, C.; Chawla, P.; Cha, J.H.; Sena-Esteves, M. Mechanisms of Distribution of Mouse Beta-Galactosidase in the Adult Gm1-Gangliosidosis Brain. Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, V.J.; Johnson, A.K.; Gray-Edwards, H.L.; Randle, A.N.; Brunson, B.L.; Morrison, N.E.; Salibi, N.; Johnson, J.A.; Hwang, M.; Beyers, R.J.; et al. Sustained Normalization of Neurological Disease after Intracranial Gene Therapy in a Feline Model. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 231ra248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foust, K.D.; Nurre, E.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hernandez, A.; Chan, C.M.; Kaspar, B.K. Intravascular Aav9 Preferentially Targets Neonatal Neurons and Adult Astrocytes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray-Edwards, H.L.; Regier, D.S.; Shirley, J.L.; Randle, A.N.; Salibi, N.; Thomas, S.E.; Latour, Y.L.; Johnston, J.; Golas, G.; Maguire, A.S.; et al. Novel Biomarkers of Human Gm1 Gangliosidosis Reflect the Clinical Efficacy of Gene Therapy in a Feline Model. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, F.O. Huntington’s Disease. Lancet 2007, 369, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, G.P.; Dorsey, R.; Gusella, J.F.; Hayden, M.R.; Kay, C.; Leavitt, B.R.; Nance, M.; Ross, C.A.; Scahill, R.I.; Wetzel, R.; et al. Huntington Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, e15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Sanchez, M.; Licitra, F.; Underwood, B.R.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Huntington’s Disease: Mechanisms of Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, e024240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.A.; Tabrizi, S.J. Huntington’s Disease: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Clinical Treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColgan, P.; Tabrizi, S.J. Huntington’s Disease: A Clinical Review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higatsberger, M.R.; Sperk, G.; Bernheimer, H.; Shannak, K.S.; Hornykiewicz, O. Striatal Ganglioside Levels in the Rat Following Kainic Acid Lesions: Comparison with Huntington’s Disease. Exp. Brain Res. 1981, 44, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desplats, P.A.; Denny, C.A.; Kass, K.E.; Gilmartin, T.; Head, S.R.; Sutcliffe, J.G.; Seyfried, T.N.; Thomas, E.A. Glycolipid and Ganglioside Metabolism Imbalances in Huntington’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 27, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglione, V.; Marchi, P.; Di Pardo, A.; Lingrell, S.; Horkey, M.; Tidmarsh, E.; Sipione, S. Impaired Ganglioside Metabolism in Huntington’s Disease and Neuroprotective Role of Gm1. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4072–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, C.A.; Desplats, P.A.; Thomas, E.A.; Seyfried, T.N. Cerebellar Lipid Differences between R6/1 Transgenic Mice and Humans with Huntington’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2010, 115, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pardo, A.; Maglione, V.; Alpaugh, M.; Horkey, M.; Atwal, R.S.; Sassone, J.; Ciammola, A.; Steffan, J.S.; Fouad, K.; Truant, R.; et al. Ganglioside Gm1 Induces Phosphorylation of Mutant Huntingtin and Restores Normal Motor Behavior in Huntington Disease Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3528–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Greiner, E.R.; Mishra, R.; Kodali, R.; Osmand, A.; Finkbeiner, S.; Steffan, J.S.; Thompson, L.M.; Wetzel, R.; Yang, X.W. Serines 13 and 16 Are Critical Determinants of Full-Length Human Mutant Huntingtin Induced Disease Pathogenesis in Hd Mice. Neuron 2009, 64, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpaugh, M.; Galleguillos, D.; Forero, J.; Morales, L.C.; Lackey, S.W.; Kar, P.; Di Pardo, A.; Holt, A.; Kerr, B.J.; Todd, K.G.; et al. Disease-Modifying Effects of Ganglioside Gm1 in Huntington’s Disease Models. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 1537–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaibva, M.; Gao, X.; Jain, P.; Campbell, W.A., 4th; Frey, S.L.; Legleiter, J. Sphingomyelin and Gm1 Influence Huntingtin Binding to, Disruption of, and Aggregation on Lipid Membranes. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, R.M.; do Nascimento, K.G.; Ferreira, P.M.; Jordán, J. Neurochemical Changes on Oxidative Stress in Rat Hippocampus During Acute Phase of Pilocarpine-Induced Seizures. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 94, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, T.; Ogawa, T.; Koizumi, H.; Fukuyama, Y. Low Levels of Csf Gangliotetraose-Series Gangliosides in West Syndrome: Implication of Brain Maturation Disturbance. Pediatr. Neurol. 1993, 9, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.A.; Cross, H.; Proukakis, C.; Priestman, D.A.; Neville, D.C.; Reinkensmeier, G.; Wang, H.; Wiznitzer, M.; Gurtz, K.; Verganelaki, A.; et al. Infantile-Onset Symptomatic Epilepsy Syndrome Caused by a Homozygous Loss-of-Function Mutation of Gm3 Synthase. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiak, S.E.; Mahadik, S.P.; Graf, L.; Rapport, M.M. An Immunological Model of Epilepsy: Seizures Induced by Antibodies to Gm1 Ganglioside. Epilepsia 1981, 22, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fighera, M.R.; Royes, L.F.; Furian, A.F.; Oliveira, M.S.; Fiorenza, N.G.; Frussa-Filho, R.; Petry, J.C.; Coelho, R.C.; Mello, C.F. Gm1 Ganglioside Prevents Seizures, Na+, K+-Atpase Activity Inhibition and Oxidative Stress Induced by Glutaric Acid and Pentylenetetrazole. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 22, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, J.; Umanah, G.K.; Yoo, S.W.; Lagerlöf, O.; Motari, M.G.; Cole, R.N.; Huganir, R.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L.; Schnaar, R.L. Ganglioside Regulation of Ampa Receptor Trafficking. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 13246–13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Es, M.A.; Hardiman, O.; Chio, A.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Pasterkamp, R.J.; Veldink, J.H.; van den Berg, L.H. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 2084–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodge, J.C.; Treleaven, C.M.; Pacheco, J.; Cooper, S.; Bao, C.; Abraham, M.; Cromwell, M.; Sardi, S.P.; Chuang, W.L.; Sidman, R.L.; et al. Glycosphingolipids Are Modulators of Disease Pathogenesis in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8100–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, A.; Croixmarie, V.; Priestman, D.A.; Rosenbohm, A.; Dirrig-Grosch, S.; D’Ambra, E.; Huebecker, M.; Hussain, G.; Boursier-Neyret, C.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; et al. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Denervation Alter Sphingolipids and up-Regulate Glucosylceramide Synthase. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 7390–7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, A.; Huebecker, M.; Blasco, H.; Keime, C.; Andres, C.R.; Corcia, P.; Priestman, D.A.; Platt, F.M.; Spedding, M.; Loeffler, J.P. Inhibition of Β-Glucocerebrosidase Activity Preserves Motor Unit Integrity in a Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, e5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, M.M. Implications of Altered Brain Ganglioside Profiles in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (Als). Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1990, 50, 505–513. [Google Scholar]
- Palomo, V.; Nozal, V.; Rojas-Prats, E.; Gil, C.; Martinez, A. Protein Kinase Inhibitors for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Therapy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 1316–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggiag, S.; Steiner-Birmanns, B.; Wirguin, I.; Sicsic, C.; Brenner, T.; Steiner, I. Seroconversion of Anti-Gm1 Antibodies in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurology 2004, 63, 755–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Kuntzer, T.; Burger, D.; Chofflon, M.; Magistris, M.R.; Regli, F.; Steck, A.J. Predictive Value of Anti-Gm1 Ganglioside Antibodies in Neuromuscular Diseases: A Study of 180 Sera. J. Neuroimmunol. 1991, 32, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.; Weller, M.; Wiethölter, H. A Characteristic Ganglioside Antibody Pattern in the Csf of Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1993, 56, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollewe, K.; Wurster, U.; Sinzenich, T.; Körner, S.; Dengler, R.; Mohammadi, B.; Petri, S. Anti-Ganglioside Antibodies in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Revisited. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankey, G.J. Stroke. Lancet 2017, 389, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Xue, Q.M. Ganglioside Levels in Hypoxic Brains from Neonatal and Premature Infants. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 1991, 14, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, M.R.; Muraro, F.; Zylbersztejn, D.S.; Abel, C.R.; Arteni, N.S.; Lavinsky, D.; Netto, C.A.; Trindade, V.M. Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Reduces Ganglioside, Phospholipid and Cholesterol Contents in the Rat Hippocampus. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 46, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, S.N.; Chan, K.H.; Gangaraju, S.; Slinn, J.; Li, J.; Hou, S.T. Imaging Mass Spectrometry Detection of Gangliosides Species in the Mouse Brain Following Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia and Long-Term Recovery. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughlin, S.; Hepburn, J.D.; Park, D.H.; Jurcic, K.; Yeung, K.K.; Cechetto, D.F.; Whitehead, S.N. Increased Expression of Simple Ganglioside Species Gm2 and Gm3 Detected by Maldi Imaging Mass Spectrometry in a Combined Rat Model of Aβ Toxicity and Stroke. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.U.; Jung, K.Y.; Seo, B.B.; Choo, Y.K. Differential Expression Patterns of Gangliosides in the Ischemic Cerebral Cortex Produced by Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Mol. Cells 2005, 20, 354–360. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.R.; Ding, M.P.; Wei, E.Q.; Luo, J.H.; Song, Y.; Huang, J.Z.; Ge, Q.F.; Hu, H.; Zhu, L.J. Gm1 Stabilizes Expression of Nmda Receptor Subunit 1 in the Ischemic Hemisphere of Mcao/Reperfusion Rat. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2005, 6, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Xu, R. The Possible Damaged Mechanism and the Preventive Effect of Monosialotetrahexosylganglioside in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.K.; Williams, C.E.; Gunn, A.J.; Mallard, E.C.; Gluckman, P.D. Pretreatment with Monosialoganglioside Gm1 Protects the Brain of Fetal Sheep against Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury without Causing Systemic Compromise. Pediatr. Res. 1993, 34, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajnc, D.; Wemlinger, T.A.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Neonatal Hypoxia: Early Neurotransmitter Responses and the Consequences of Treatment with Gm1 Ganglioside. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 271, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Jing, L.; Ma, Y.; Guo, F.Y.; Chang, Y.; Li, P.A. Monosialotetrahexosy-1 Ganglioside Attenuates Diabetes-Enhanced Brain Damage after Transient Forebrain Ischemia and Suppresses Phosphorylation of Erk1/2 in the Rat Brain. Brain Res. 2010, 1344, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Kang, Y.; Lv, M.; Li, Y. Monosialotetrahexosy-1 Ganglioside Attenuates Diabetes-Associated Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Suppression of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 41, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadik, S.P.; Hungund, B.L.; Gokhale, V.S.; Ortiz, A.; Makar, T.K.; Karpiak, S.E. Monosialoganglioside (Gm1) Restores Membrane Fatty Acid Levels in Ischemic Tissue after Cortical Focal Ischemia in Rat. Neurochem. Int. 1993, 23, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Krafft, P.R.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.H.; Li, L.; Tang, J. Pathophysiology of Ganglioside Gm1 in Ischemic Stroke: Ganglioside Gm1: A Critical Review. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharucha, V.A.; Wakade, C.G.; Mahadik, S.P.; Karpiak, S.E. Gm1 Ganglioside Treatment Reduces Functional Deficits Associated with Cortical Focal Ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 1991, 114, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.; MacDonall, J.S.; Wakade, C.G.; Karpiak, S.E. Gm1 Ganglioside Reduces Cognitive Dysfunction after Focal Cortical Ischemia. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1990, 37, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D.; Heidinger, V.; Mohand-Said, S.; Sahel, J.; Dreyfus, H. Growth Factors and Gangliosides as Neuroprotective Agents in Excitotoxicity and Ischemia. Gen. Pharmacol. 1998, 30, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, G.; Maniero, G.; Toffano, G. New Perspectives in the Treatment of Hypoxic and Ischemic Brain Damage: Effect of Gangliosides. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1990, 61, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tian, J.; Long, M.K.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, T. Protection against Experimental Stroke by Ganglioside Gm1 Is Associated with the Inhibition of Autophagy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0144219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seren, M.S.; Lazzaro, A.; Yang, C.L.; Canella, R.; Bassan, M.; Zanoni, R.; Manev, H. Orally Administered Glycolipid Derivative Liga20 Reduces Infarct Volume and Behavioral Impairment after Focal Cerebral Ischemia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 268, 460–465. [Google Scholar]
- Karpiak, S.E.; Li, Y.S.; Mahadik, S.P. Gangliosides Reduce Mortality due to Global Ischemia: Membrane Protection. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1986, 9 (Suppl. S4), 338–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jesulola, E.; Micalos, P.; Baguley, I.J. Understanding the Pathophysiology of Depression: From Monoamines to the Neurogenesis Hypothesis Model—Are We There Yet? Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 341, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, H.C.; Byard, C.; Sims, W.; Wilson, R. Gangliosides and Other Lipid Micelles. A Study of Amine Binding by a Dialysis/Fluorescence Method. Neurochem. Res. 1979, 4, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry-Kravis, E.; Dawson, G. Possible Role of Gangliosides in Regulating an Adenylate Cyclase-Linked 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-Ht1) Receptor. J. Neurochem. 1985, 45, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Paila, Y.D.; Shrivastava, S.; Tiwari, S.; Singh, P.; Fantini, J. Sphingolipid-Binding Domain in the Serotonin(1a) Receptor. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 749, 279–293. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore, N.; Cherian, L.; Klemm, W.R. Ganglioside or Sialic Acid Attenuates Ethanol-Induced Decrements in Locomotion, Nose-Poke Exploration, and Anxiety, but Not Body Temperature. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1991, 15, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, C.J.; Rezazadeh, S.M.; Lal, H. Gm1 Ganglioside Reduces Ethanol Intoxication and the Development of Ethanol Dependence. Alcohol 1995, 12, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Song, L.; Wang, C.N.; Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Tong, L.J. Antidepressant-Like Effects of Gm1 Ganglioside Involving the Bdnf Signaling Cascade in Mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, pyw046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhola, H.; Postila, P.A.; Rissanen, S.; Lolicato, F.; Vattulainen, I.; Róg, T. Negatively Charged Gangliosides Promote Membrane Association of Amphipathic Neurotransmitters. Neuroscience 2018, 384, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekman, A.; Skjeldal, O.; Sponheim, E.; Svennerholm, L. Gangliosides in Children with Autism. Acta Paediatr. 1995, 84, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, V.; Lekman, A.; Johansson, M.; Fredman, P.; Gillberg, C. Gangliosides in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1998, 40, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, G.A.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y. Increased Serum Levels of Anti-Ganglioside M1 Auto-Antibodies in Autistic Children: Relation to the Disease Severity. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, S.; Lau, N.M.; Green, P.H.; Hellberg, D.; Higgins, J.J.; Rajadhyaksha, A.M.; Alaedini, A. Lack of Association between Autism and Anti-Gm1 Ganglioside Antibody. Neurology 2013, 81, 1640–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laev, H.; Karpiak, S.E.; Gokhale, V.S.; Hungund, B.L. In Utero Ethanol Exposure Retards Growth and Alters Morphology of Cortical Cultures: Gm1 Reverses Effects. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1995, 19, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.A.; Groh, G.I.; Baxter, D.M.; Hitzemann, R.J. Gangliosides Enhance the Membrane Actions of Ethanol and Pentobarbital. Mol. Pharmacol. 1984, 25, 410–417. [Google Scholar]
- Vrbaski, S.R.; Grujić-Injac, B.; Ristić, M. Phospholipid and Ganglioside Composition in Rat Brain after Chronic Intake of Ethanol. J. Neurochem. 1984, 42, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbaski, S.R. Region Distribution of the Gangliosides in Rat Brain after Chronic Ethanol Treatment. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 1995, 25, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Saito, M.; Cooper, T.B.; Vadasz, C. Alcohol Reduces Gm1 Ganglioside Content in the Serum of Inbred Mouse Strains. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, L.D.; Szabó, G.; Tabakoff, B.; Hoffman, P.L. Gangliosides Reduce the Development of Ethanol Dependence without Affecting Ethanol Tolerance. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 279, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, M.; Saito, M.; Berg, M.J.; Guidotti, A.; Marks, N. Gangliosides Attenuate Ethanol-Induced Apoptosis in Rat Cerebellar Granule Neurons. Neurochem. Res. 1999, 24, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Mao, R.F.; Wang, R.; Vadasz, C.; Saito, M. Effects of Gangliosides on Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration in the Developing Mouse Brain. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungund, B.L.; Ross, D.C.; Gokhale, V.S. Ganglioside Gm1 Reduces Fetal Alcohol Effects in Rat Pups Exposed to Ethanol in Utero. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1994, 18, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungund, B.L.; Gokhale, V.S. Reduction of Fatty Acid Ethyl Ester Accumulation by Ganglioside Gm1 in Rat Fetus Exposed to Ethanol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laev, H.; Hungund, B.L.; Karpiak, S.E. Cortical Cell Plasma Membrane Alterations after In Vitro Alcohol Exposure: Prevention by Gm1 Ganglioside. Alcohol 1996, 13, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungund, B.L.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, L.; Barkai, A.I. Ganglioside Gm1 Reduces Ethanol Induced Phospholipase A2 Activity in Synaptosomal Preparations from Mice. Neurochem. Int. 1994, 25, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Barkai, A.I.; Hungund, B.L. Effect of Ganglioside Gm1 on Ethanol-Induced Changes in the Incorporation of Free Fatty Acids into Membrane Phospholipids in Mouse Brain. Alcohol Alcohol. 1997, 32, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, P.H. Role of Membrane Gangliosides in the Binding and Action of Bacterial Toxins. J. Membr. Biol. 1982, 69, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernick, N.L.; Chinnapen, D.J.; Cho, J.A.; Lencer, W.I. Cholera Toxin: An Intracellular Journey into the Cytosol by Way of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Toxins 2010, 2, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubran, M.M. Bacterial Toxins. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1988, 18, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chinnapen, D.J.; Hsieh, W.T.; te Welscher, Y.M.; Saslowsky, D.E.; Kaoutzani, L.; Brandsma, E.; D’Auria, L.; Park, H.; Wagner, J.S.; Drake, K.R.; et al. Lipid Sorting by Ceramide Structure from Plasma Membrane to Er for the Cholera Toxin Receptor Ganglioside Gm1. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.A.; Kenworthy, A.K. Functions of Cholera Toxin B-Subunit as a Raft Cross-Linker. Essays Biochem. 2015, 57, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuverink, M.; Barbieri, J.T. Protein Toxins That Utilize Gangliosides as Host Receptors. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 156, 325–354. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Xie, X.; Ledeen, R.W.; Wu, G. Characterization of Cholera Toxin B Subunit-Induced Ca(2+) Influx in Neuroblastoma Cells: Evidence for a Voltage-Independent Gm1 Ganglioside-Associated Ca(2+) Channel. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 69, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelkoska, L.; Benjamins, J.A. Binding of Cholera Toxin B Subunit: A Surface Marker for Murine Microglia but Not Oligodendrocytes or Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 53, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fu, Z.; Kim, J.J.; Barbieri, J.T.; Baldwin, M.R. Gangliosides as High Affinity Receptors for Tetanus Neurotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26569–26577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, D.R.; Habig, W.H.; Fishman, P.H. Reevaluation of the Role of Gangliosides as Receptors for Tetanus Toxin. J. Neurochem. 1986, 47, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, H.R.; Smejkal, C.W.; Glister, C.; Kemp, F.; van den Heuvel, E.; de Slegte, J.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Sialyloligosaccharides Inhibit Cholera Toxin Binding to the Gm1 Receptor. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 2589–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingwood, C. Therapeutic Uses of Bacterial Subunit Toxins. Toxins 2021, 13, e378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.S. Gangliosides and Glycolipids in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Adv. Neurobiol. 2014, 9, 449–461. [Google Scholar]
- Aureli, M.; Mauri, L.; Ciampa, M.G.; Prinetti, A.; Toffano, G.; Secchieri, C.; Sonnino, S. Gm1 Ganglioside: Past Studies and Future Potential. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1824–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipartiti, M.; Lazzaro, A.; Zanoni, R.; Mazzari, S.; Toffano, G.; Leon, A. Monosialoganglioside Gm1 Reduces Nmda Neurotoxicity in Neonatal Rat Brain. Exp. Neurol. 1991, 113, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipartiti, M.; Lazzaro, A.; Manev, H. Ganglioside Derivative Liga20 Reduces Nmda Neurotoxicity in Neonatal Rat Brain. Neuroreport 1992, 3, 919–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarewicz, J.W.; Salińska, E.; Matyja, E. Ganglioside Gm1 Prevents N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Neurotoxicity in Rabbit Hippocampus in Vivo. Effects on Calcium Homeostasis. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 1995, 24, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzini, E.; Durso, R.; Davoudi, H.; Szabo, G.K.; Albert, M.L. Gm1 Gangliosides Alter Acute Mptp-Induced Behavioral and Neurochemical Toxicity in Mice. J. Neurol. Sci. 1990, 99, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellot, R.G.; Vital, M.A.; Palermo-Neto, J.; Frussa-Filho, R. Repeated Monosialoganglioside Administration Attenuates Behavioral Sensitization to Amphetamine. Brain Res. 1997, 747, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fighera, M.R.; Bonini, J.S.; de Oliveira, T.G.; Frussa-Filho, R.; Rocha, J.B.; Dutra-Filho, C.S.; Rubin, M.A.; Mello, C.F. Gm1 Ganglioside Attenuates Convulsions and Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances Production Induced by the Intrastriatal Injection of Methylmalonic Acid. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G.; Zanoni, R.; Moroni, F. Systemic Treatments with Gm1 Ganglioside Reduce Quinolinic Acid-Induced Striatal Lesions in the Rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1989, 174, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, H.; Yamada, S.; Yokoo, H.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nishi, S.; Inanaga, K.; Nagatsu, I.; Jonsson, G.; Toffano, G. The Effects of Exogenous Gm1 Ganglioside on Neurotoxin Induced Damage of Cerebral Serotonin Nerve Terminals in Adult Rats. Kurume Med. J. 1988, 35, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Leon, A. Gangliosides Attenuate the Delayed Neurotoxicity of Aspartic Acid In Vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 1990, 117, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabel, B.A.; DelMastro, R.; Dunbar, G.L.; Stein, D.G. Reduction of Anterograde Degeneration in Brain Damaged Rats by Gm1-Gangliosides. Neurosci. Lett. 1987, 77, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelman, L.R.; Zorrilla Zubilete, M.A.; Ríos, H.; Dopico, A.M.; Zieher, L.M. Gm1 Ganglioside Treatment Protects against Long-Term Neurotoxic Effects of Neonatal X-Irradiation on Cerebellar Cortex Cytoarchitecture and Motor Function. Brain Res. 2000, 858, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelman, L.R.; Zieher, L.M.; Fiszman, M.L. The Effect of X-Radiation on Cerebellar Granule Cells Grown in Culture. Ganglioside Gm1 Neuroprotective Activity. Neurochem. Int. 1996, 29, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goettl, V.M.; Lindsey, A.E.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Gm1 Ganglioside Restores Abnormal Responses to Acute Thermal and Mechanical Stimuli in Aged Rats. Brain Res. 2000, 858, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sautter, J.; Schwartz, M.; Duvdevani, R.; Sabel, B.A. Gm1 Ganglioside Treatment Reduces Visual Deficits after Graded Crush of the Rat Optic Nerve. Brain Res. 1991, 565, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasier, M.M.; Janis, L.S.; Goncalves, M.I.; Stein, D.G. Gm1 Produces Attenuation of Short-Term Memory Deficits in Hebb-Williams Maze Performance after Unilateral Entorhinal Cortex Lesions. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 66, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, E.E.; Brock, M.V.; Lange, M.S.; Troncoso, J.C.; Blue, M.E.; Lowenstein, C.J.; Johnston, M.V.; Baumgartner, W.A. Monosialoganglioside Gm1 Inhibits Neurotoxicity after Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest. Surgery 1998, 124, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, W.A.; Redmond, J.M.; Zehr, K.J.; Brock, M.V.; Tseng, E.E.; Blue, M.E.; Troncoso, J.C.; Johnston, M.V. The Role of the Monosialoganglioside, Gm1 as a Neuroprotectant in an Experimental Model of Cardiopulmonary Bypass and Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 845, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oderfeld-Nowak, B.; Brosnan, C.; Cervone, A.; Oderfeld, J.; Ledeen, R.W. Gangliosides Improve the Outcome of Experimental Allergic Neuritis (Ean). Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1990, 50, 495–504. [Google Scholar]
- Laev, H.; Mahadik, S.P.; Bonheur, J.L.; Hernandez, N.; Karpiak, S.E. Gm1 Ganglioside Reduces Glutamate Toxicity to Cortical Cells. Lowered Ldh Release and Preserved Membrane Integrity. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 1993, 20, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, T.G.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Systemic Administration of Gm1 Ganglioside Increases Choline Acetyltransferase Activity in the Brain of Aged Rats. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 132, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjiconstantinou, M.; Karadsheh, N.S.; Rattan, A.K.; Tejwani, G.A.; Fitkin, J.G.; Neff, N.H. Gm1 Ganglioside Enhances Cholinergic Parameters in the Brain of Senescent Rats. Neuroscience 1992, 46, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelsberg, V.; Fong, T.G.; Neff, N.H.; Hadjiconstantinou, M. Cholinergic Deficits in Aged Rat Spinal Cord: Restoration by Gm1 Ganglioside. Brain Res. 1997, 761, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Patre, P.L.; Abbamondi, A.; Bartolini, L.; Pepeu, G. Gm1 Ganglioside Counteracts Cholinergic and Behavioral Deficits Induced in the Rat by Intracerebral Injection of Vincristine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1989, 162, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjiconstantinou, M.; Neff, N.H. Treatment with Gm1 Ganglioside Restores Striatal Dopamine in the 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine-Treated Mouse. J. Neurochem. 1988, 51, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiconstantinou, M.; Mariani, A.P.; Neff, N.H. Gm1 Ganglioside-Induced Recovery of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons after Mptp: An Immunohistochemical Study. Brain Res. 1989, 484, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiconstantinou, M.; Weihmuller, F.; Neff, N.H. Treatment with Gm1 Ganglioside Reverses Dopamine D-2 Receptor Supersensitivity Induced by the Neurotoxin Mptp. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1989, 168, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Cavallaro, S.; Bruno, V.; Virgili, M.; Catania, M.V.; Contestabile, A.; Canonico, P.L. Gangliosides Attenuate Nmda Receptor-Mediated Excitatory Amino Acid Release in Cultured Cerebellar Neurons. Neuropharmacology 1989, 28, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.S.; DiStefano, L. Liga 20 Increases Striatal Dopamine Levels in Aged Mptp-Treated Mice Refractory to Gm1 Ganglioside Treatment. Neuroreport 1993, 5, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffano, G.; Savoini, G.; Aldinio, C.; Valenti, G.; Dal Toso, R.; Leon, A.; Calza, L.; Zini, I.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K. Effects of Gangliosides on the Functional Recovery of Damaged Brain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1984, 174, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubovitch, V.; Zilberstein, Y.; Chapman, J.; Schreiber, S.; Pick, C.G. Restoring Gm1 Ganglioside Expression Ameliorates Axonal Outgrowth Inhibition and Cognitive Impairments Induced by Blast Traumatic Brain Injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, e41269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.T.; Perez-Otaño, I.; Oset, C.; Kastner, A.; Hirsch, E.C.; Agid, Y.; Luquin, M.R.; Obeso, J.A.; Del Rio, J. Gm-1 Ganglioside Promotes the Recovery of Surviving Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons in Mptp-Treated Monkeys. Neuroscience 1993, 56, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stull, N.D.; Schneider, J.S.; Iacovitti, L. Gm1 Ganglioside Partially Rescues Cultured Dopaminergic Neurons from Mpp(+)-Induced Damage: Dependence on Initial Damage and Time of Treatment. Brain Res. 1994, 640, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weihmuller, F.B.; Hadjiconstantinou, M.; Bruno, J.P.; Neff, N.H. Administration of Gm1 Ganglioside Eliminates Neuroleptic-Induced Sensorimotor Deficits in Mptp-Treated Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 1988, 92, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
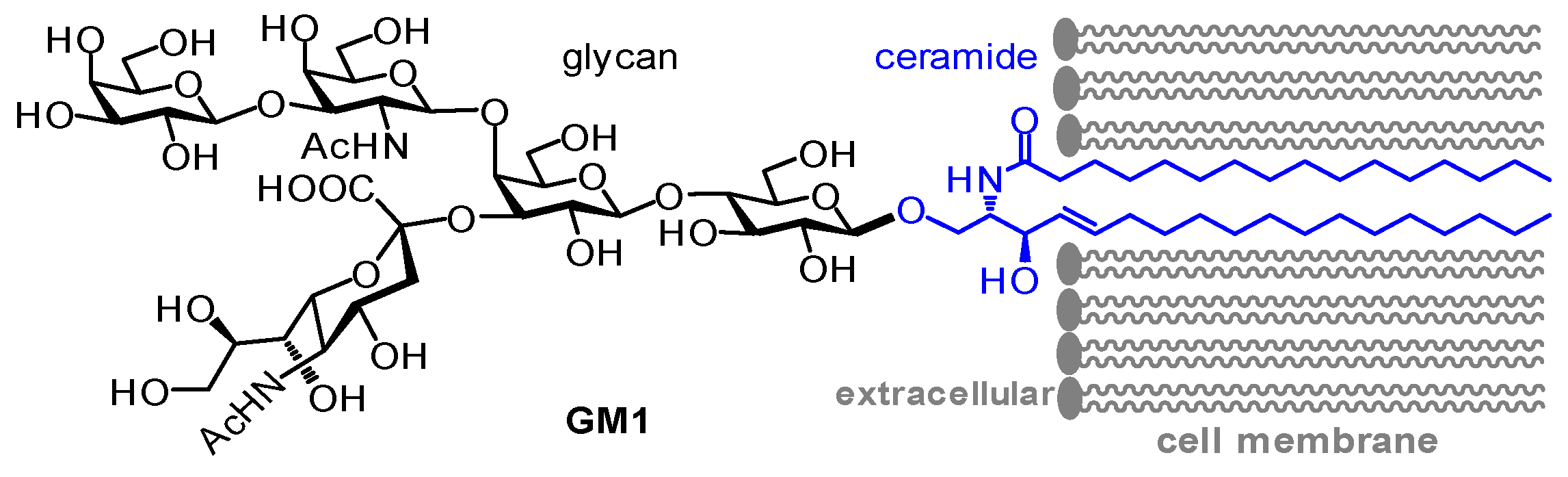
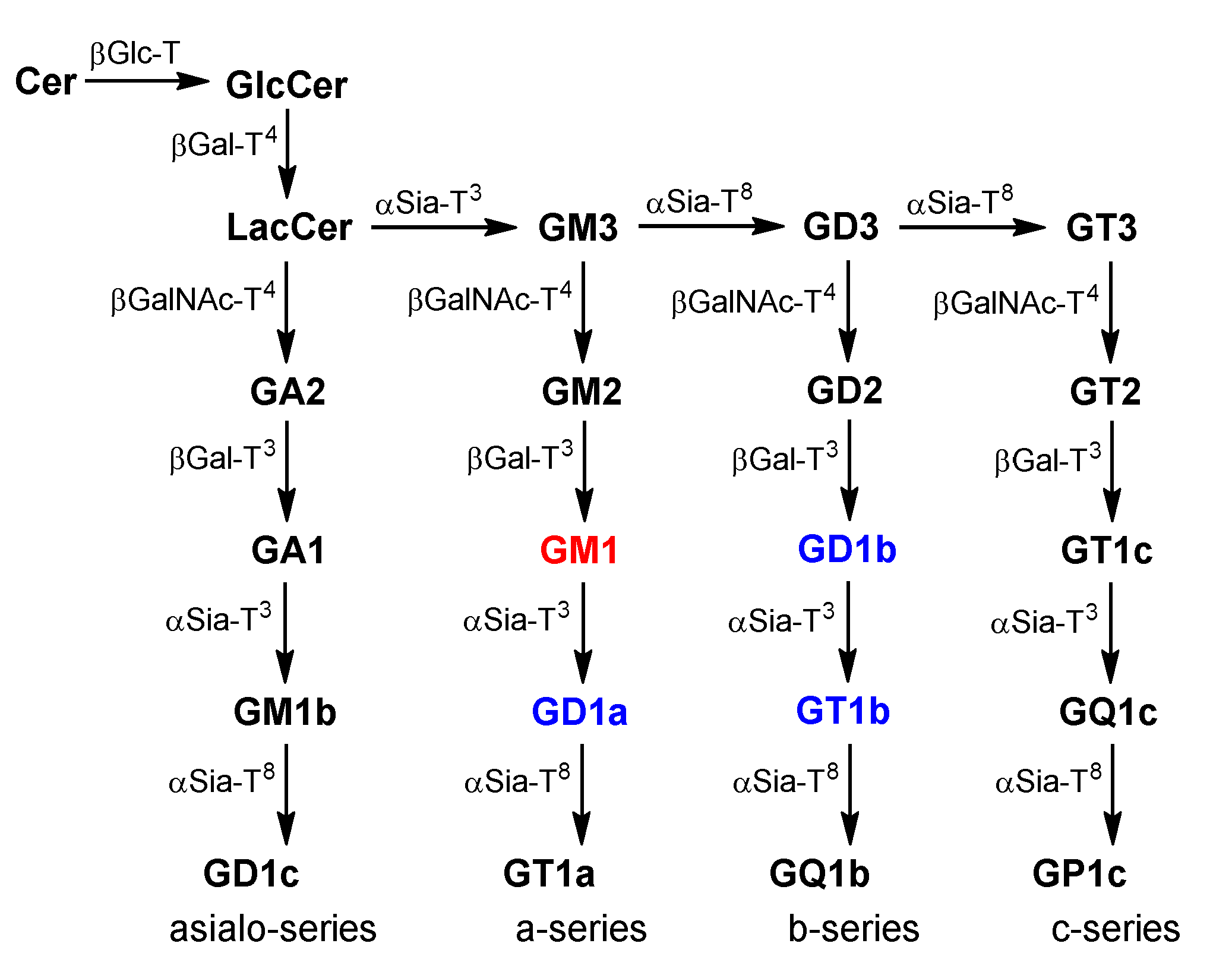
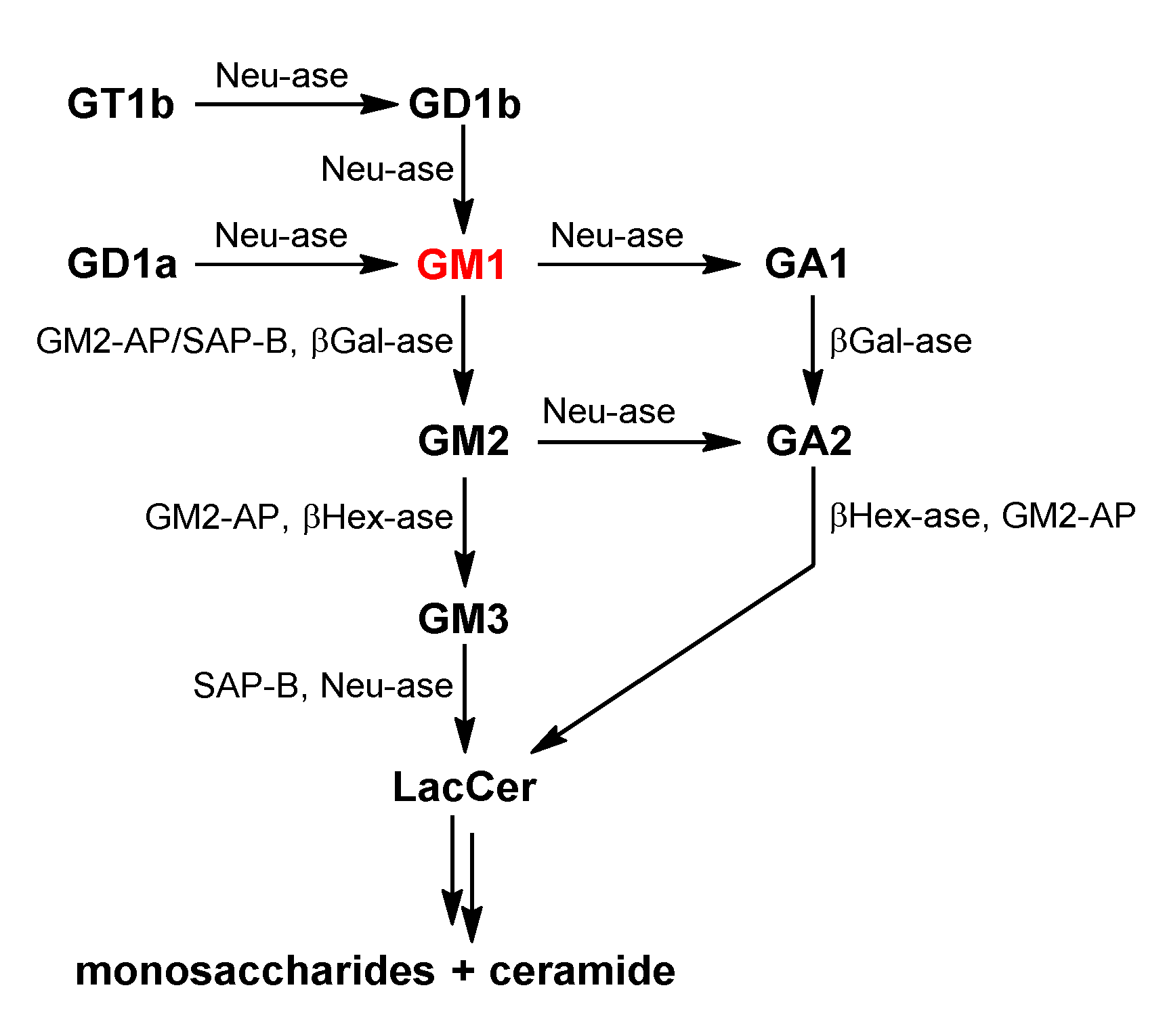
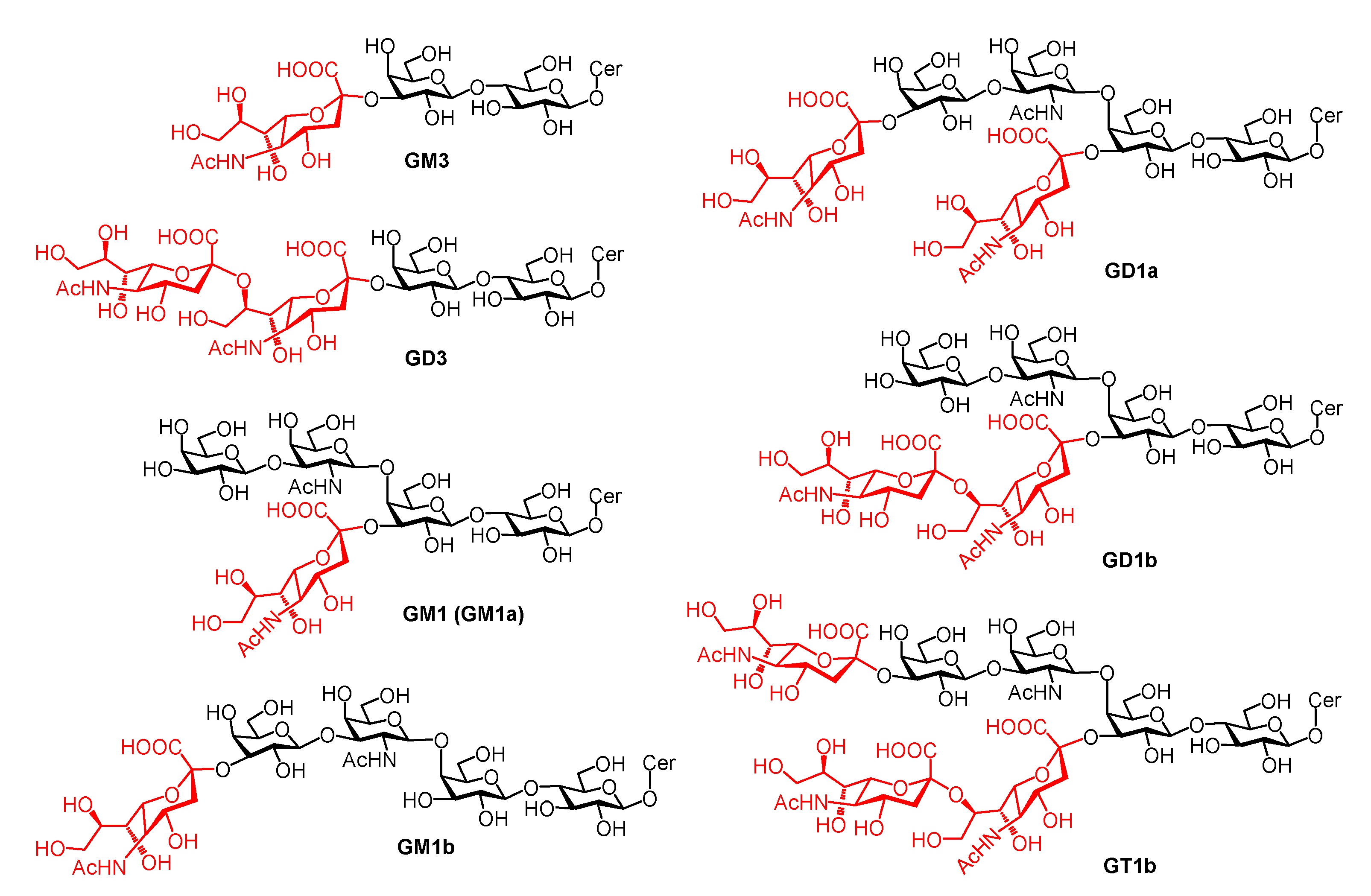

| CNS Functions That Involve GM1 | References |
|---|---|
| [87] [83,84,92] [88,89] [90] [102,103] [115] [117] [116,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125] [32,149,150] |
| Diseases | Correlation of GM1 with the Disease | References |
|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s disease |
| [208] [211] [203,206] [210,219,220,221,222] |
| Parkinson’s disease |
| [234,235,236] [239,240] |
| GM1 gangliosidosis |
| [250,251,253,254] |
| Huntington’s disease |
| [301,302,303] [305,306,307] |
| Epilepsy, seizure |
| [310] [312] |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| [316] |
| Ischemic stroke |
| [326] [328,329] |
| Depression, anxiety |
| [107,161,347] [349] |
| Autism |
| [354,355,356] |
| Alcohol dependence |
| [362] [366,368] |
| Bacterial infections |
| [371,372,373] [374] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z. Ganglioside GM1 and the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119558
Guo Z. Ganglioside GM1 and the Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119558
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhongwu. 2023. "Ganglioside GM1 and the Central Nervous System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119558
APA StyleGuo, Z. (2023). Ganglioside GM1 and the Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119558






