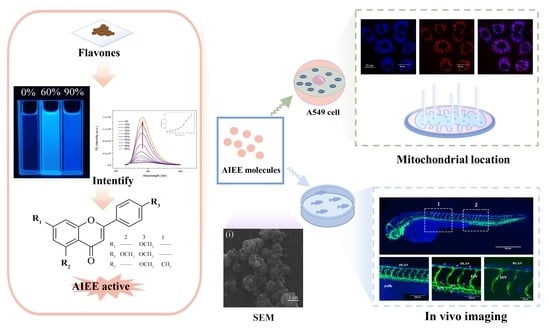
AIEE-Active Flavones as a Promising Tool for the Real-Time Tracking of Uptake and Distribution in Live Zebrafish
Abstract
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Luo, H.; Jin, T.; He, F. AIEE-Active Flavones as a Promising Tool for the Real-Time Tracking of Uptake and Distribution in Live Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210183
Wu Y, He Y, Luo H, Jin T, He F. AIEE-Active Flavones as a Promising Tool for the Real-Time Tracking of Uptake and Distribution in Live Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):10183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210183
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yi, Ying He, Huiqing Luo, Tingting Jin, and Feng He. 2023. "AIEE-Active Flavones as a Promising Tool for the Real-Time Tracking of Uptake and Distribution in Live Zebrafish" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 10183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210183
APA StyleWu, Y., He, Y., Luo, H., Jin, T., & He, F. (2023). AIEE-Active Flavones as a Promising Tool for the Real-Time Tracking of Uptake and Distribution in Live Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 10183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210183