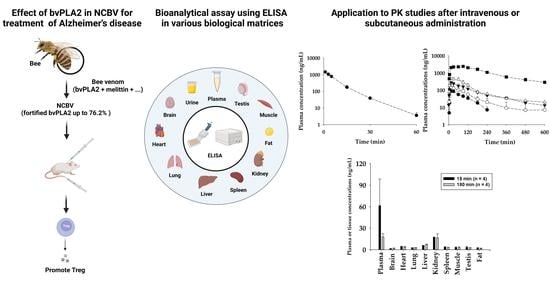
Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Bee Venom-Derived Phospholipase A2 Using a Sandwich ELISA after Subcutaneous Injection of New Composition Bee Venom in Rats
Abstract
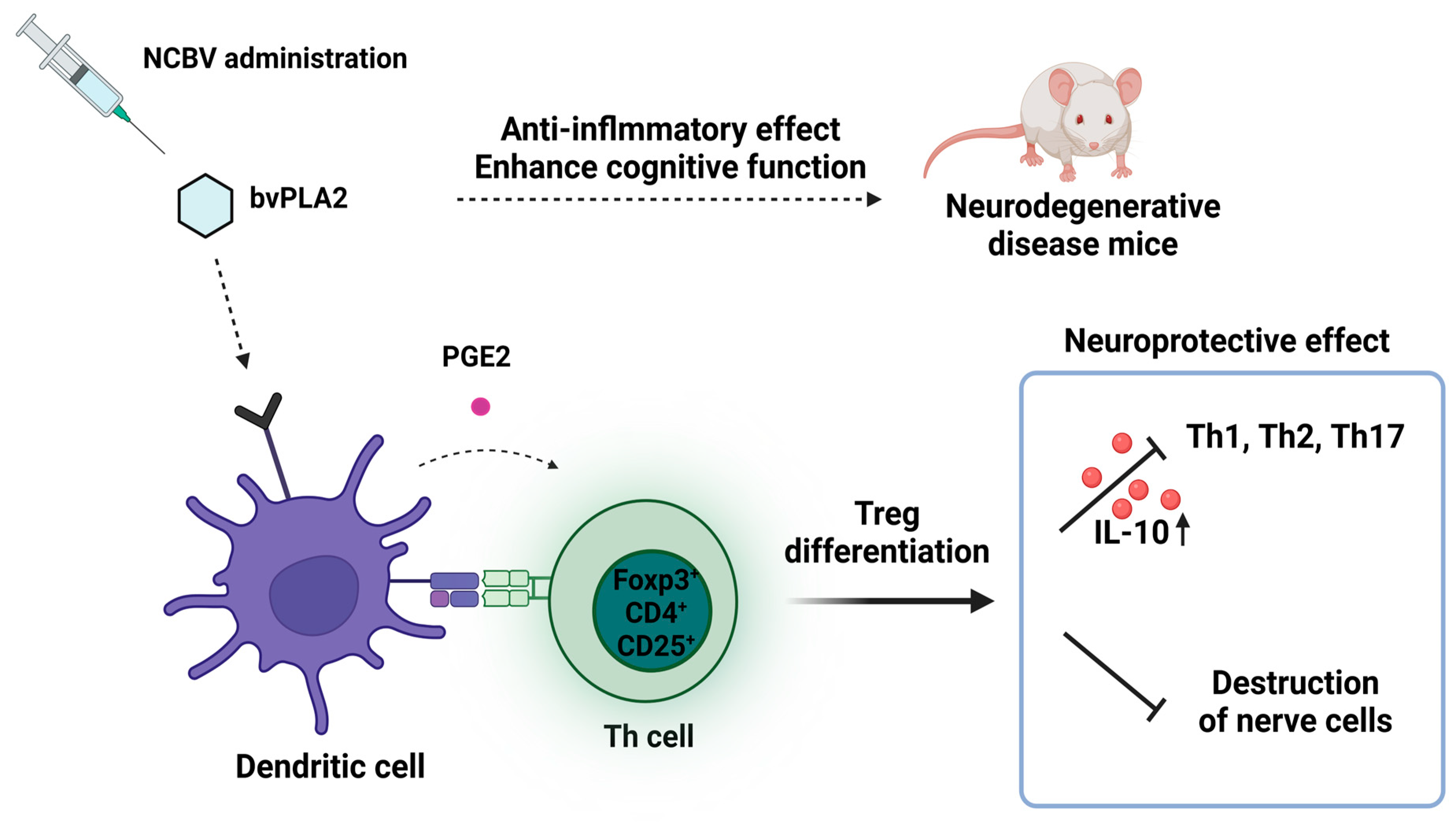
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Minimum Required Dilution for ELISA Assay
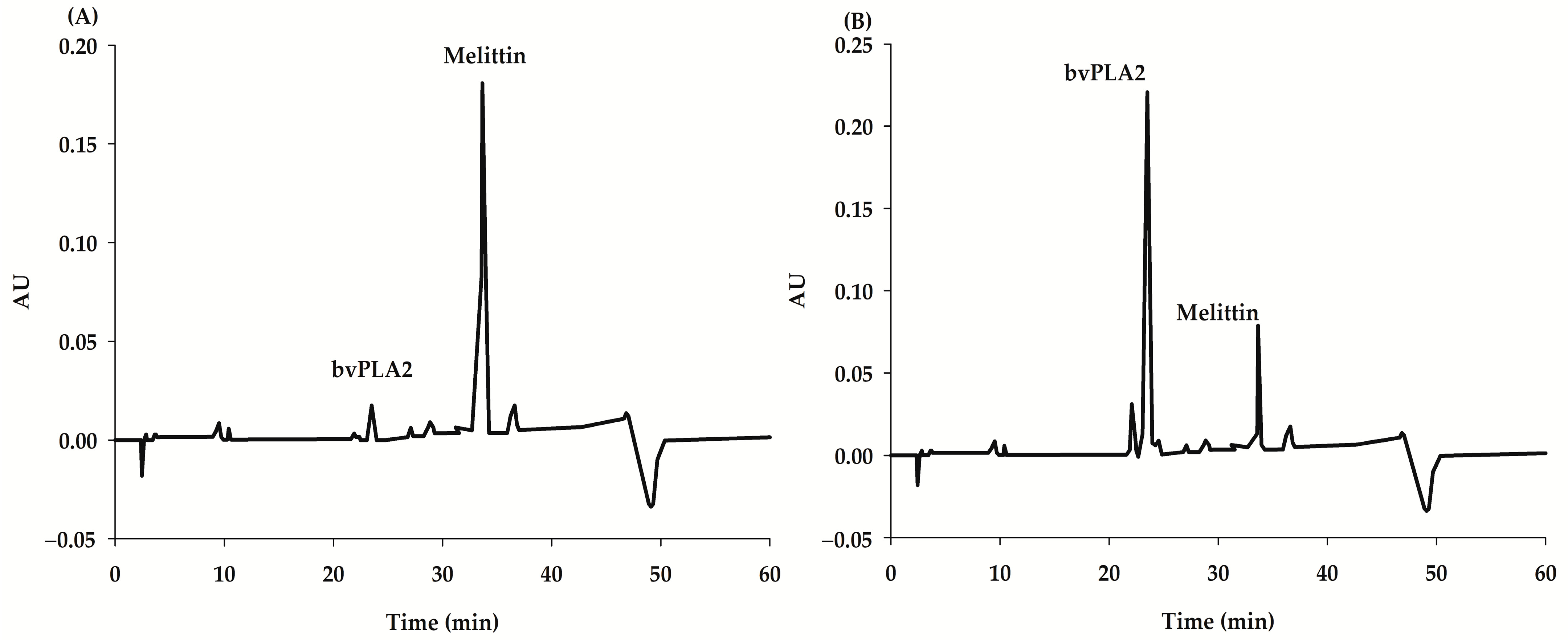
2.2. ELISA Assay Validation
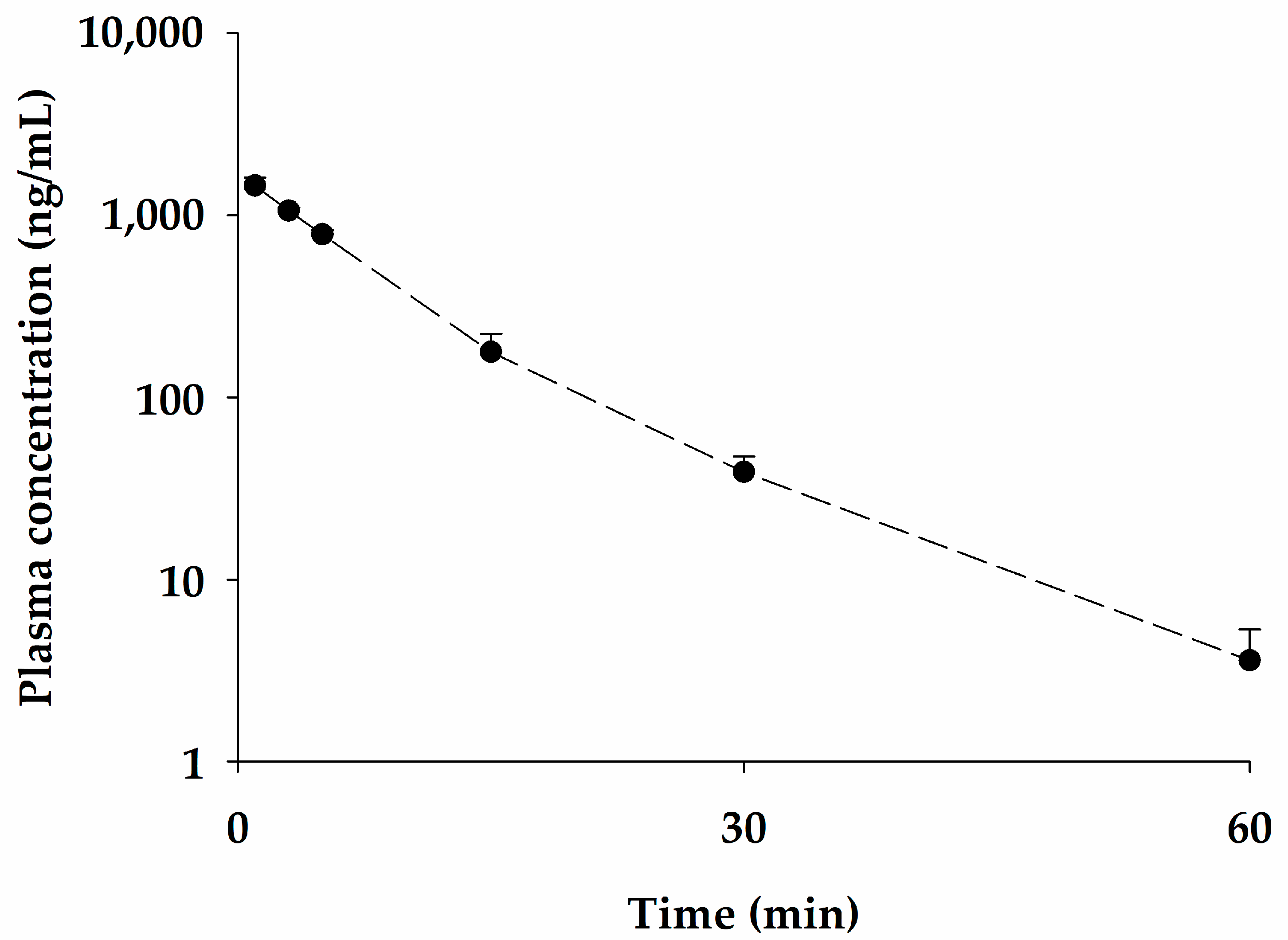
2.3. Pharmacokinetic Studies of bvPLA2 after Single Intravenous Administration of NCBV in Rats at a Dose of 0.05 mg/kg
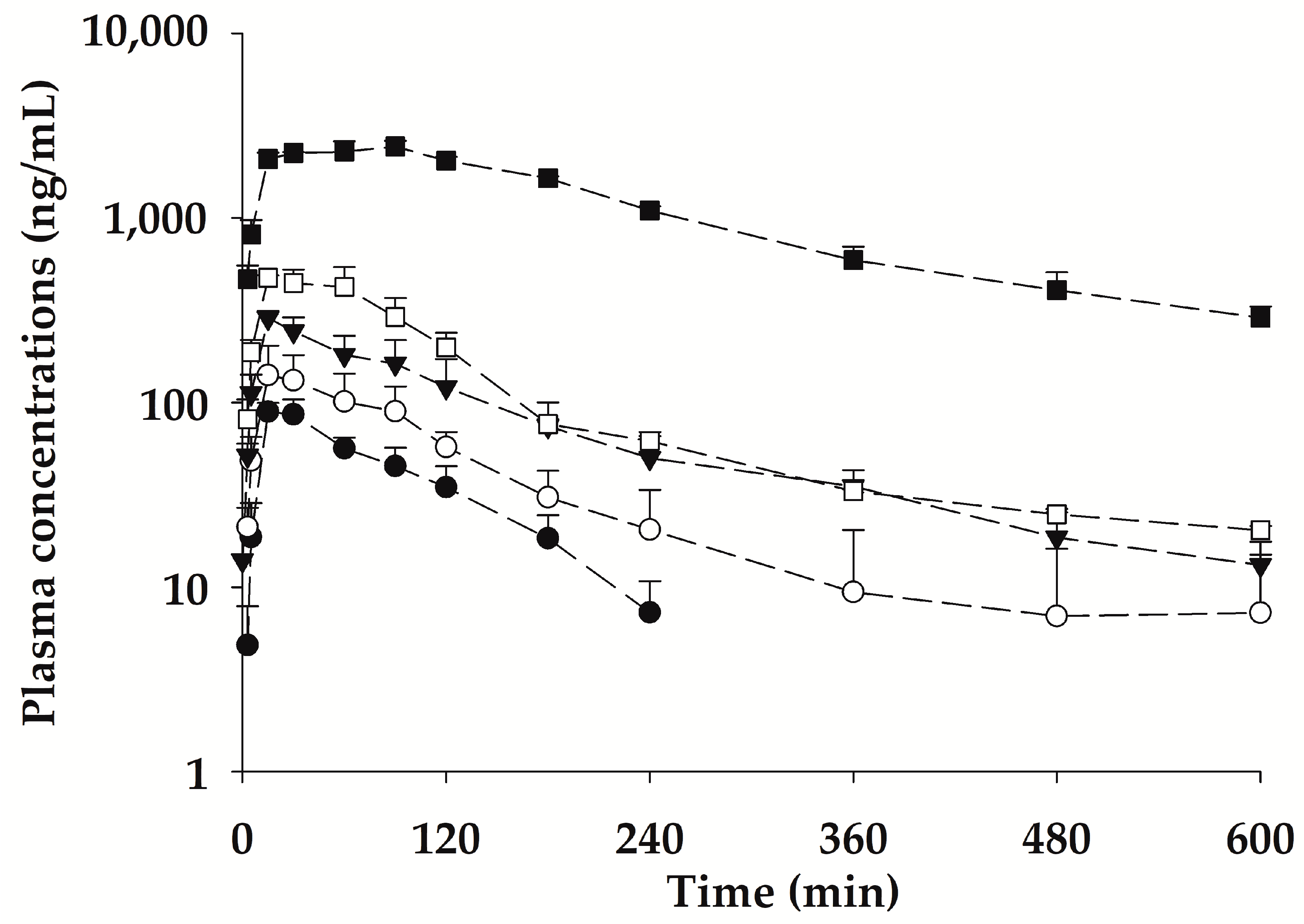
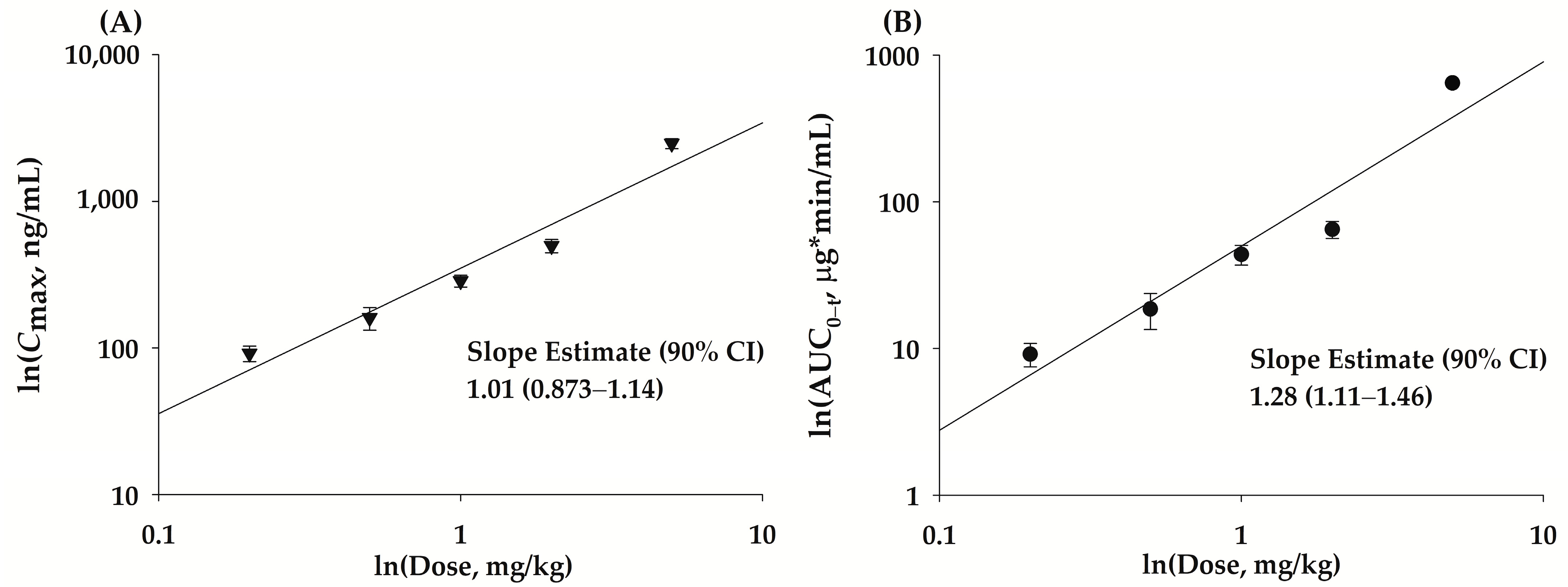
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Properties of bvPLA2 after a Single Subcutaneous Administration of NCBV in Rats at Various Doses
2.5. Multiple Subcutaneous Administration of NCBV in Rats at a Dose of 0.5 mg/kg Once a Week for Three Weeks
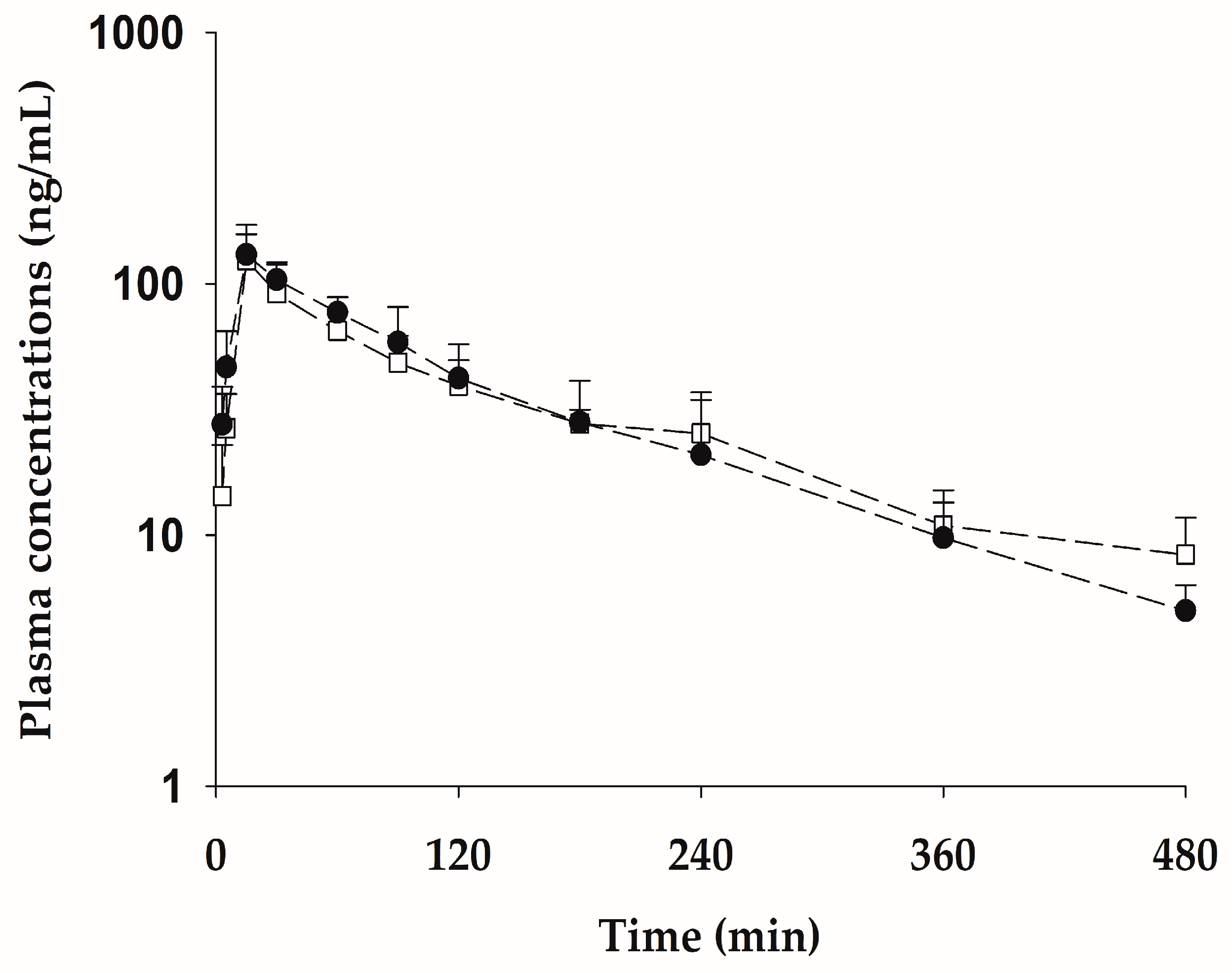
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Properties of bvPLA2 after Subcutaneous Administration of the Pure Form Equivalent to 0.5 mg/kg NCBV
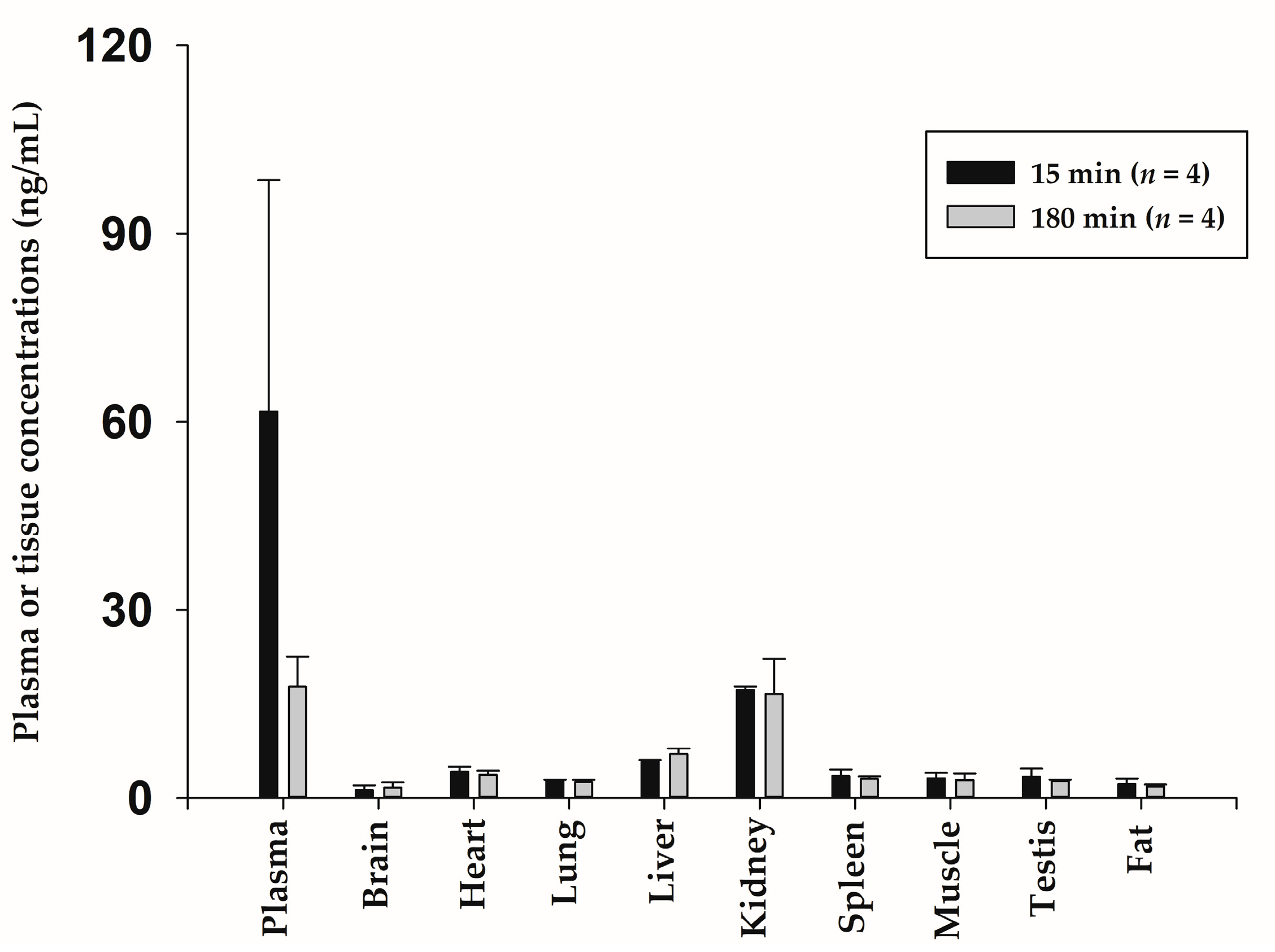
2.7. Tissue Distribution after Subcutaneous Administration of NCBV in Rats at a Dose of 0.5 mg/kg
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Calibration Standards and Quality Controls
3.3. Sandwich ELISA Procedure and Assay Validation
3.4. Animals
3.5. Pharmacokinetic Studies of bvPLA2 after Intravenous Administration of NCBV in Rats
3.6. Pharmacokinetic Studies of bvPLA2 after Subcutaneous Administration of NCBV in Rats
3.7. Tissue Distributions of bvPLA2 following Subcutaneous Administration of NCBV
3.8. Pharmacokinetic and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, X.R.; Lin, L.T.; Xiao, L.Y.; Zhou, P.; Shi, G.X.; Liu, C.Z. Bee venom therapy: Potential mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Toxicon 2018, 148, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, D.J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Song, H.S.; Lee, C.K.; Hong, J.T. Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 115, 246–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpena, M.; Nunez-Estevez, B.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Bee Venom: An Updating Review of Its Bioactive Molecules and Its Health Applications. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bava, R.; Castagna, F.; Musella, V.; Lupia, C.; Palma, E.; Britti, D. Therapeutic Use of Bee Venom and Potential Applications in Veterinary Medicine. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidya, V.; Achar, R.R.; Himathi, M.U.; Akshita, N.; Kameshwar, V.H.; Byrappa, K.; Ramadas, D. Venom peptides—A comprehensive translational perspective in pain management. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 2, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Elesawy, B.H.; Ali, T.M.; Ahmed, O.M. Bee Venom: From Venom to Drug. Molecules 2021, 26, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.S.; Shapla, U.M.; Gan, S.H.; Khalil, M.I. Impact of Bee Venom Enzymes on Diseases and Immune Responses. Molecules 2016, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, G.; Bae, H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2: Yesterday’s Enemy Becomes Today’s Friend. Toxins 2016, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Shin, J.; Hwang, J.T.; Jeon, H.N.; Bae, H. Dose-Dependent Neuroprotective Effect of Standardized Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Against MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease in Mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, G.; Jang, H.; Kim, S.S.; Yoon, H.; Kang, G.H.; Hwang, D.S.; Kim, S.K.; Chung, H.S.; et al. Phospholipase A2 inhibits cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by modulating regulatory T cells by the CD206 mannose receptor. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, D.S.; Kim, S.K.; Bae, H. Therapeutic Effects of Bee Venom on Immunological and Neurological Diseases. Toxins 2015, 7, 2413–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, M.; Chung, H.S.; Lee, C.; Yoon, M.S.; Yu, A.R.; Kim, J.S.; Hwang, D.S.; Shim, I.; Bae, H. Neuroprotective effects of bee venom phospholipase A2 in the 3xTg AD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ham, H.J.; Han, S.B.; Yun, J.; Yeo, I.J.; Ham, Y.W.; Kim, S.H.; Park, P.H.; Choi, D.Y.; Hong, J.T. Bee venom phospholipase A2 ameliorates amyloidogenesis and neuroinflammation through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 pathway in Tg2576 mice. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Jeon, H.N.; Kim, S.H.; Bae, H. Comparison of the Protective Effects of Bee Venom Extracts with Varying PLA(2) Compositions in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Toxins 2019, 11, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, R.J.; Garcia, M.L. Therapeutic potential of venom peptides. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2003, 2, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US FDA. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation. May 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70858/download (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Diao, L.; Meibohm, B. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic correlations of therapeutic peptides. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L. Strategic approaches to optimizing peptide ADME properties. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Mager, D.E.; Kagan, L. Interspecies modeling and prediction of human exenatide pharmacokinetics. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carone, F.A. Renal handling of proteins and peptides. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1978, 8, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, S.J.; Bae, S.H.; Huang, Z.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.B.; Chae, S.U.; Park, J.B.; Kwon, M.; Chung, H.K.; Bae, S.K. Benzisothiazolinone: Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution, and Mass Balance Studies in Rats. Metabolites 2023, 13, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.P.; Vandenhende, F.R.; DeSante, K.A.; Farid, N.A.; Welch, P.A.; Callaghan, J.T.; Forgue, S.T. Confidence interval criteria for assessment of dose proportionality. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitar, L.; Jundi, D.; Rima, M.; Al Alam, J.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Fajloun, Z. Bee venom PLA2 versus snake venom PLA2: Evaluation of structural and functional properties. Venoms Toxins 2021, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, M.; Taketomi, Y.; Miki, Y.; Sato, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Lambeau, G. Emerging roles of secreted phospholipase A2 enzymes: The 3rd edition. Biochimie 2014, 107, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin, E.; Ghomashchi, F.; Gelb, M.H.; Lazdunski, M.; Lambeau, G. Novel human secreted phospholipase A(2) with homology to the group III bee venom enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 7492–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- 2022 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 700–789. [CrossRef]
- Maher-Edwards, G.; De’Ath, J.; Barnett, C.; Lavrov, A.; Lockhart, A. A 24-week study to evaluate the effect of rilapladib on cognition and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 1, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Dilution Factor | Theoretical (ng/mL) | Measured (ng/mL) | % of the Theoretical Value Accuracy (Measuresd/Theoretical × 100) | Standard Deviation (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:2 | 25 | 24.1 | 96.4 | 0.853 |
| 1:4 | 25 | 25.4 | 102 | 1.36 |
| 1:10 | 25 | 25.8 | 103 | 0.741 |
| 1:20 | 25 | 26.6 | 106 | 2.32 |
| PK Parameters | 0.05 mg/kg (n = 5) |
|---|---|
| AUC0−t (µg∙min/mL) 1 | 11.8 ± 0.869 |
| AUC0−inf (µg∙min/mL) 2 | 11.8 ± 0.866 |
| t1/2 (min) 3 | 8.10 ± 0.669 |
| Vdss (mL/kg) 4 | 49.3 ± 1.79 |
| MRT (min) 5 | 8.11 ± 1.07 |
| CL (mL/min/kg) 6 | 4.24 ± 0.291 |
| Ae24 h (% of dose) 7 | ND 8 |
| PK Parameters | 0.2 mg/kg (n = 5) | 0.5 mg/kg (n = 5) | 1 mg/kg (n = 5) | 2 mg/kg (n = 5) | 5 mg/kg (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) | 309 ± 10.9 | 314 ± 11.3 | 350 ± 14.4 | 267 ± 3.88 | 265 ± 9.84 |
| AUC0−t (µg∙min/mL) 1 | 9.16 ± 1.66 | 19.0 ± 5.09 | 43.8 ± 6.71 | 64.9 ± 8.61 | 645 ± 9.55 |
| AUC0-inf (µg∙min/mL) 2 | 9.68 ± 2.00 | 20.3 ± 6.46 | 45.4 ± 7.82 | 73.4 ± 10.2 | 715 ± 3.58 |
| t1/2 (min) 3 | 63.1 ± 8.12 | 150 ± 111 | 197 ± 88.3 | 169 ± 39.5 | 170 ± 14.6 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) 4 | 91.9 ± 11.2 | 161 ± 28.3 | 287 ± 26.3 | 498 ± 51.2 | 2480 ± 195 |
| Tmax (min) 5 | 22.5 (15–30) | 15 (15–90) | 15 (15–15) | 15 (15–60) | 60 (30–90) |
| Ae24 h (% of dose) 6 | ND 7 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Vdss/F (L/kg) 8 | 1.93 ± 0.376 | 4.49 ± 2.37 | 5.23 ± 3.31 | 6.95 ± 1.24 | 1.34 ± 0.111 |
| F (%) 9 | 20.4 | 17.1 | 19.2 | 15.5 | 60.4 |
| Parameter | Linearity Range (mg/kg) | R2 | Dose Proportionality Coefficient (β) | 90% CI 3 | Acceptance Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax1 | 0.2–5 | 0.914 | 1.01 ± 0.0774 | 0.873–1.14 | 0.93–1.06 |
| AUC0−t 2 | 0.2–5 | 0.907 | 1.28 ± 0.102 | 1.11–1.46 | 0.93–1.06 |
| PK Parameters | Multiple (n = 5) | Single (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|
| AUC0−t (µg∙min/mL) 1 | 19.0 ± 9.13 | 14.2 ± 4.46 |
| t1/2 (min) 2 | 95.4 ± 18.0 | 110 ± 44.2 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) 3 | 154 ± 38.8 | 145 ± 37.6 |
| Tmax (min) 4 | 15 (15–15) | 15 (15–15) |
| Ae24 h (% of dose) 5 | ND 6 | ND |
| PK Parameters | NCBV (n = 5) | bvPLA2 Pure form (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|
| AUC0−t (µg∙min/mL) 1 | 14.0 ± 1.04 | 14.8 ± 4.22 |
| t1/2 (min) 2 | 146 ± 53.4 | 114 ± 34.9 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) 3 | 124 ± 47.4 | 134 ± 25.8 |
| Tmax (min) 4 | 15 (15–15) | 15 (15–30) |
| Ae24 h (% of dose) 5 | ND 6 | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chae, S.U.; Jo, S.J.; Lee, C.B.; Lee, S.; Park, J.-H.; Jung, J.-S.; Park, E.-S.; Bae, H.; Bae, S.K. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Bee Venom-Derived Phospholipase A2 Using a Sandwich ELISA after Subcutaneous Injection of New Composition Bee Venom in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210214
Chae SU, Jo SJ, Lee CB, Lee S, Park J-H, Jung J-S, Park E-S, Bae H, Bae SK. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Bee Venom-Derived Phospholipase A2 Using a Sandwich ELISA after Subcutaneous Injection of New Composition Bee Venom in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):10214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210214
Chicago/Turabian StyleChae, Soon Uk, Seong Jun Jo, Chae Bin Lee, Sangyoung Lee, Ji-Hyun Park, Jin-Su Jung, Eui-Suk Park, Hyunsu Bae, and Soo Kyung Bae. 2023. "Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Bee Venom-Derived Phospholipase A2 Using a Sandwich ELISA after Subcutaneous Injection of New Composition Bee Venom in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 10214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210214
APA StyleChae, S. U., Jo, S. J., Lee, C. B., Lee, S., Park, J.-H., Jung, J.-S., Park, E.-S., Bae, H., & Bae, S. K. (2023). Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Bee Venom-Derived Phospholipase A2 Using a Sandwich ELISA after Subcutaneous Injection of New Composition Bee Venom in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 10214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210214