Characterizing the Protein Isoforms of foraging (for), the PKGI Ortholog in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The foraging Gene Encoded Eight Putative Protein Isoforms that Differed at Their N-Termini
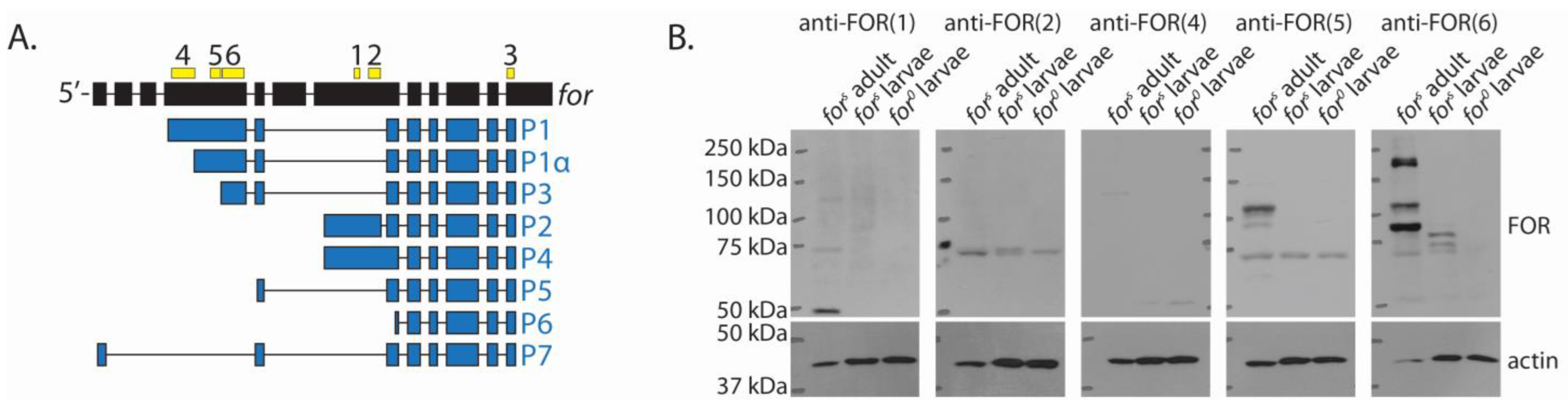
2.2. Many FOR Polypeptides Were Observed In Vivo and Their Expressions Differed between Developmental Stages
2.3. The Expression of FOR Differed between Tissues
2.4. The Majority of Whole-Body FOR Expression Was P1, P1α, and P3
2.5. LC-MS/MS of FOR Bands Corroborated Their Isoform Identity
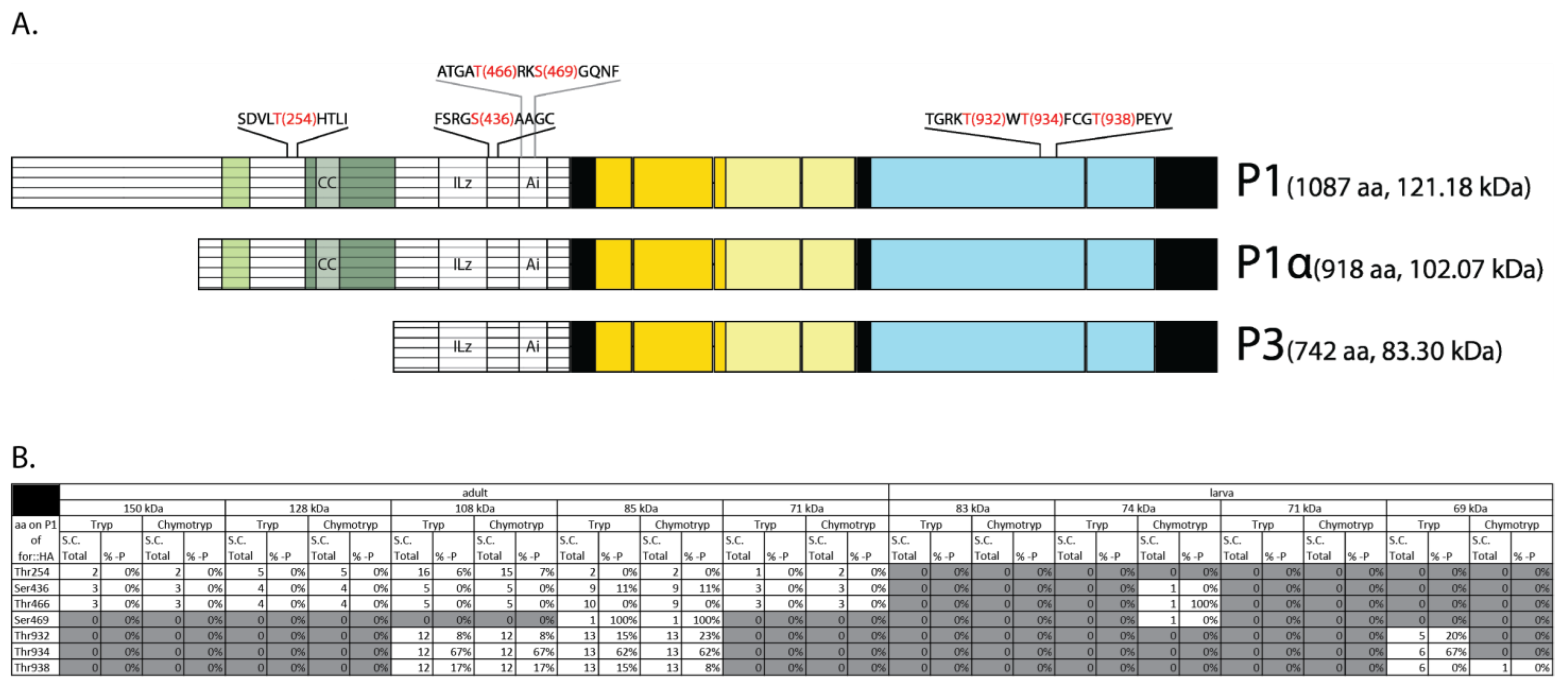
2.6. LC-MS/MS Revealed Conserved Phosphorylation of the Active Loop Residues in FOR
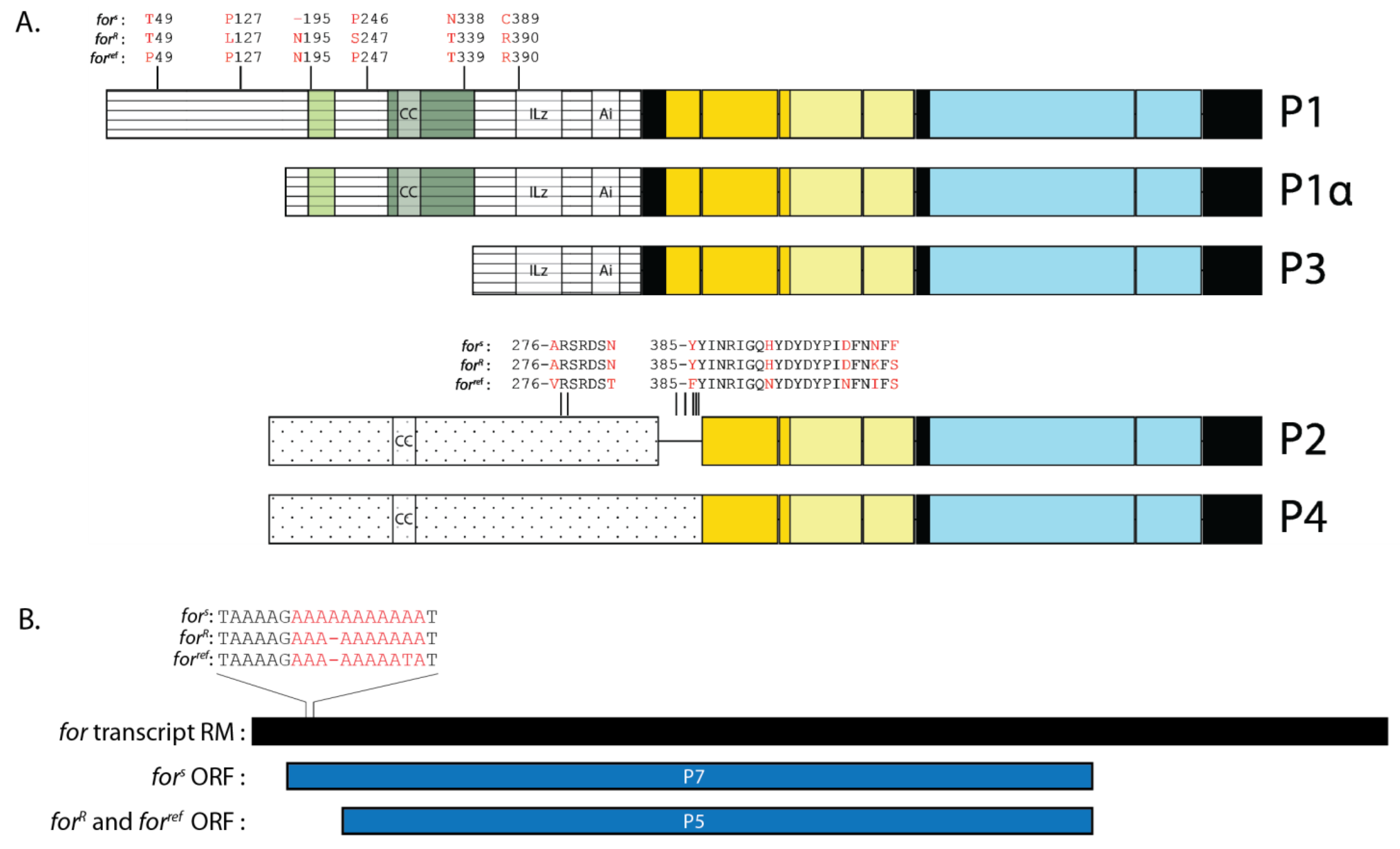
2.7. FOR Sequence Differed at Several Amino Acids in fors and forR
2.8. P7 Was a Putative FOR Isoform Specific to fors
2.9. FOR Expression Differed between fors and forR Larvae
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fly Strains and Rearing Conditions
4.2. Recombineering the forBAC::HA Allele
4.3. FOR Isoform-Specific Antibodies
4.4. Dissections
4.5. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.6. Immunoprecipitations and Mass Spectrometry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofmann, F. The cGMP system: Components and function. Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, A.; Kilić, A.; Hoffmann, L.S. Regulation of metabolism by cGMP. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 140, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.H.; Busch, J.L.; Corbin, J.D. cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cGMP phosphodiesterases in nitric oxide and cGMP action. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 525–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, F.; Bernhard, D.; Lukowski, R.; Weinmeister, P. cGMP regulated protein kinases (cGK). Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 191, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Belle, J.S.; Hilliker, A.J.; Sokolowski, M.B. Genetic localization of foraging (for): A major gene for larval behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1989, 123, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dason, J.S.; Sokolowski, M.B. A cGMP-dependent protein kinase, encoded by the Drosophila foraging gene, regulates neurotransmission through changes in synaptic structure and function. J. Neurogenet. 2021, 35, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, M.R.; Lohmann, S.M.; Davies, S.A. Analysis of Drosophila cGMP-dependent protein kinases and assessment of their in vivo roles by targeted expression in a renal transporting epithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40026–40034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, W.G.; Landgraf, W.; Hofmann, F. A catalytically active fragment of cGMP-dependent protein kinase: Occupation of its cGMP-binding sites does not affect its phosphotransferase activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 168, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgraf, W.; Hofmann, F. The amino terminus regulates binding to and activation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 181, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostmann, W.R.G.; Koep, N.; Endres, R. The catalytic domain of the cGMP-dependent protein kinase Iα modulates the cGMP-binding characteristics of its regulatory domain. FEBS Lett. 1996, 398, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Zhang, R.; Roberts, J.D. Proprotein convertases play an important role in regulating PKGI endoproteolytic cleavage and nuclear transport. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013, 305, L130–L140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, T.M.; Sheehe, J.L.; Nukareddy, P.; Nausch, L.W.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Matthews, D.E.; Blumenthal, D.K.; Dostmann, W.R. An N-terminally truncated form of cyclic GMP–dependent protein kinase I (PKG I) is monomeric and autoinhibited and provides a model for activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 7916–7929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernet, W.; Flockerzi, V.; Hofmann, F. The cDNA of the two isoforms of bovine cGMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1989, 251, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, E.; Geiger, J.; Jarchau, T.; Lohmann, S.M.; Walter, U. The cGMP-dependent protein kinase-gene, protein, and function. Neurochem. Res. 1993, 18, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surks, H.K. cGMP-dependent protein kinase I and smooth muscle relaxation: A tale of two isoforms. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anreiter, I.; Kramer, J.M.; Sokolowski, M.B. Epigenetic mechanisms modulate differences in Drosophila foraging behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12518–12523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.M.; Anreiter, I.; Vesterberg, A.; Douglas, S.J.; Sokolowski, M.B. Pleiotropy of the Drosophila melanogaster foraging gene on larval feeding-related traits. J. Neurogenet. 2018, 32, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dason, J.S.; Cheung, A.; Anreiter, I.; Montemurri, V.A.; Allen, A.M.; Sokolowski, M.B. Drosophila melanogaster foraging regulates a nociceptive-like escape behavior through a developmentally plastic sensory circuit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23286–23291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anreiter, I.; Allen, A.M.; Vasquez, O.E.; To, L.; Douglas, S.J.; Alvarez, J.V.; Ewer, J.; Sokolowski, M.B. The Drosophila foraging gene plays a vital role at the start of metamorphosis for subsequent adult emergence. J. Neurogenet. 2021, 35, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.M.; Sokolowski, M.B. Expression of the foraging gene in adult Drosophila melanogaster. J. Neurogenet. 2021, 35, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, K.A.; Robichon, A.; Burgess, E.; Butland, S.; Shaw, R.A.; Coulthard, A.; Pereira, H.S.; Greenspan, R.J.; Sokolowski, M.B. Natural behavior polymorphism due to a cGMP-dependent protein kinase of Drosophila. Science 1997, 277, 834–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalderon, D.; Rubin, G.M. cGMP-dependent protein kinase genes in Drosophila. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 10738–10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, D.K.; Murakami, M.S.; Cleghon, V. Protein kinases and phosphatases in the Drosophila genome. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, F57–F62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, M.B. Drosophila: Genetics meets behaviour. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anreiter, I.; Sokolowski, M.B. The foraging gene and its behavioral effects: Pleiotropy and plasticity. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2019, 53, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, M.B. Foraging strategies of Drosophila melanogaster: A chromosomal analysis. Behav. Genet. 1980, 10, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.M.; Anreiter, I.; Neville, M.C.; Sokolowski, M.B. Feeding-related traits are affected by dosage of the foraging gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2017, 205, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaun, K.R.; Riedl, C.A.L.; Chakaborty-Chatterjee, M.; Belay, A.T.; Douglas, S.J.; Gibbs, A.G.; Sokolowski, M.B. Natural variation in food acquisition mediated via a Drosophila cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 3547–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, E.; Harrison, M.M.; O’Connor-Giles, K.M.; Wildonger, J. Advances in engineering the fly genome with the CRISPR-Cas system. Genetics 2018, 208, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S.E.; Roman, G.; Davis, R.L. Gene expression systems in Drosophila: A synthesis of time and space. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.H.; Perrimon, N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 1993, 118, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dason, J.S.; Allen, A.M.; Vasquez, O.E.; Sokolowski, M.B. Distinct functions of a cGMP-dependent protein kinase in nerve terminal growth and synaptic vesicle cycling. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs227165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Yuan, D.; Xu, M.; Li, C.; Gong, Z.; Jiao, R.; Liu, L. cGMP-dependent protein kinase encoded by foraging regulates motor axon guidance in Drosophila by suppressing Lola function. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 4635–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belay, A.T.; Scheiner, R.; So, A.K.C.; Douglas, S.J.; Chakaborty-Chatterjee, M.; Levine, J.D.; Sokolowski, M.B. The foraging gene of Drosophila melanogaster: Spatial-expression analysis and sucrose responsiveness. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 504, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurmond, J.; Goodman, J.L.; Strelets, V.B.; Attrill, H.; Gramates, L.S.; Marygold, S.J.; Matthews, B.B.; Millburn, G.; Antonazzo, G.; Trovisco, V.; et al. FlyBase 2.0: The next generation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D759–D765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramates, L.S.; Agapite, J.; Attrill, H.; Calvi, B.R.; Crosby, M.A.; dos Santos, G.; Goodman, J.L.; Goutte-Gattat, D.; Jenkins, V.K.; Kaufman, T.; et al. FlyBase: A guided tour of highlighted features. Genetics 2022, 220, iyac035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, A.; Ruth, P.; Dostmann, W.; Sausbier, M.; Klatt, P.; Hofmann, F. Structure and function of cGMP-Dependent protein kinases. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 135, 105–149. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, S.C.; Luciani, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Park, Y.; Lopez, R.; Finn, R.D. HMMER web server: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W200–W204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, O.E.; Sokolowski, D.J.; Wilson, M.D.; Sokolowski, M.B.; Anreiter, I. Transcriptomic effects of the foraging gene shed light on pathways of pleiotropy and plasticity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, M.P.; Farnsworth, C.L.; Moritz, A.; Silva, J.C.; Jia, X.; Lee, K.A.; Guo, A.; Polakiewicz, R.D.; Comb, M.J. PTMScan Direct: Identification and quantification of peptides from critical signaling proteins by immunoaffinity enrichment coupled with LC-MS/MS. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallur, R.; Kalbacher, H.; Feil, R. Catalytic activity of cGMP-dependent protein kinase type I in intact cells is independent of N-terminal autophosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leader, D.P.; Krause, S.A.; Pandit, A.; Davies, S.A.; Dow, J.A.T. FlyAtlas 2: A new version of the Drosophila melanogaster expression atlas with RNA-seq, MiRNA-seq and sex-specific data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D809–D815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Janssens, J.; de Waegeneer, M.; Kolluru, S.S.; Davie, K.; Gardeux, V.; Saelens, W.; David, F.P.A.; Brbić, M.; Spanier, K.; et al. Fly Cell Atlas: A single-nucleus transcriptomic atlas of the adult fruit fly. Science 2022, 375, eabk2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingras, A.C.; Raught, B.; Sonenberg, N. Regulation of translation initiation by FRAP/mTOR. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShane, E.; Selbach, M. Physiological functions of intracellular protein degradation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 38, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonenberg, N.; Hinnebusch, A.G. Regulation of translation initiation in eukaryotes: Mechanisms and biological targets. Cell 2009, 136, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Sharma, R. Cyclic nucleotide selectivity of protein kinase G isozymes. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gógl, G.; Kornev, A.P.; Reményi, A.; Taylor, S.S. Disordered protein kinase regions in regulation of kinase domain cores. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Roey, K.; Gibson, T.J.; Davey, N.E. Motif switches: Decision-making in cell regulation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2012, 22, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamecna, D.; Antonny, B. Intrinsically disordered protein regions at membrane contact sites. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 159020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, I.; Shewmaker, F. The role of post-translational modifications in the phase transitions of intrinsically disordered proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhine, K.; Vidaurre, V.; Myong, S. RNA droplets. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2020, 49, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruth, P.; Landgraf, W.; Keilbach, A.; May, B.; Egleme, C.; Hofmann, F. The activation of expressed cGMP-dependent protein kinase isozymes Iα and Iβ is determined by the different amino-termini. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 202, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöhler, D.; Butt, E.; Meißner, J.; Müller, S.; Lohse, M.; Walter, U.; Lohmann, S.M.; Jarchau, T. Expression, purification, and characterization of the cGMP-dependent protein kinases Iβ and II using the baculovirus system. FEBS Lett. 1995, 374, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Francis, S.H.; Walsh, K.A.; Kumar, S.; Corbin, J.D. Autophosphorylation of type Iβ cGMP-dependent protein kinase increases basal catalytic activity and enhances allosteric activation by cGMP or cAMP. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20756–20762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, L.; Corbin, J.D.; Francis, S.H. Characterization of a novel isozyme of cGMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine aorta. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 7734–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppe, H.; Rybalkin, S.D.; Rehmann, H.; Hinds, T.R.; Tang, X.B.; Christensen, A.E.; Schwede, F.; Genieser, H.G.; Bos, J.L.; Doskeland, S.O.; et al. Cyclic nucleotide analogs as probes of signaling pathways. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keilbach, A.; Ruth, P.; Hofmann, F. Detection of cGMP dependent protein kinase isozymes by specific antibodies. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 208, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Zhou, G.P.; Kupferman, J.; Surks, H.K.; Christensen, E.N.; Chou, J.J.; Mendelsohn, M.E.; Rigby, A.C. Probing the interaction between the coiled coil leucine zipper of cGMP-dependent protein kinase Iα and the C terminus of the myosin binding subunit of the myosin light chain phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 32860–32869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, T.; Klose, F.; Kuret, A.; Hoffmann, F.; Lukowski, R.; Ueffing, M.; Boldt, K. Tissue- and isoform-specific protein complex analysis with natively processed bait proteins. J. Proteom. 2021, 231, 103947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anreiter, I.; Vasquez, O.E.; Allen, A.M.; Sokolowski, M.B. Foraging path-length protocol for Drosophila melanogaster larvae. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 2016, e53980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warming, S.; Costantino, N.; Court, D.L.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G. Simple and highly efficient BAC recombineering using GalK selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groth, A.C.; Fish, M.; Nusse, R.; Calos, M.P. Construction of transgenic Drosophila by using the site-specific integrase from phage PhiC31. Genetics 2004, 166, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Kolker, E.; Aebersold, R. Empirical statistical model to estimate the accuracy of peptide identifications made by MS/MS and database search. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5383–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Keller, A.; Kolker, E.; Aebersold, R. A statistical model for identifying proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4646–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

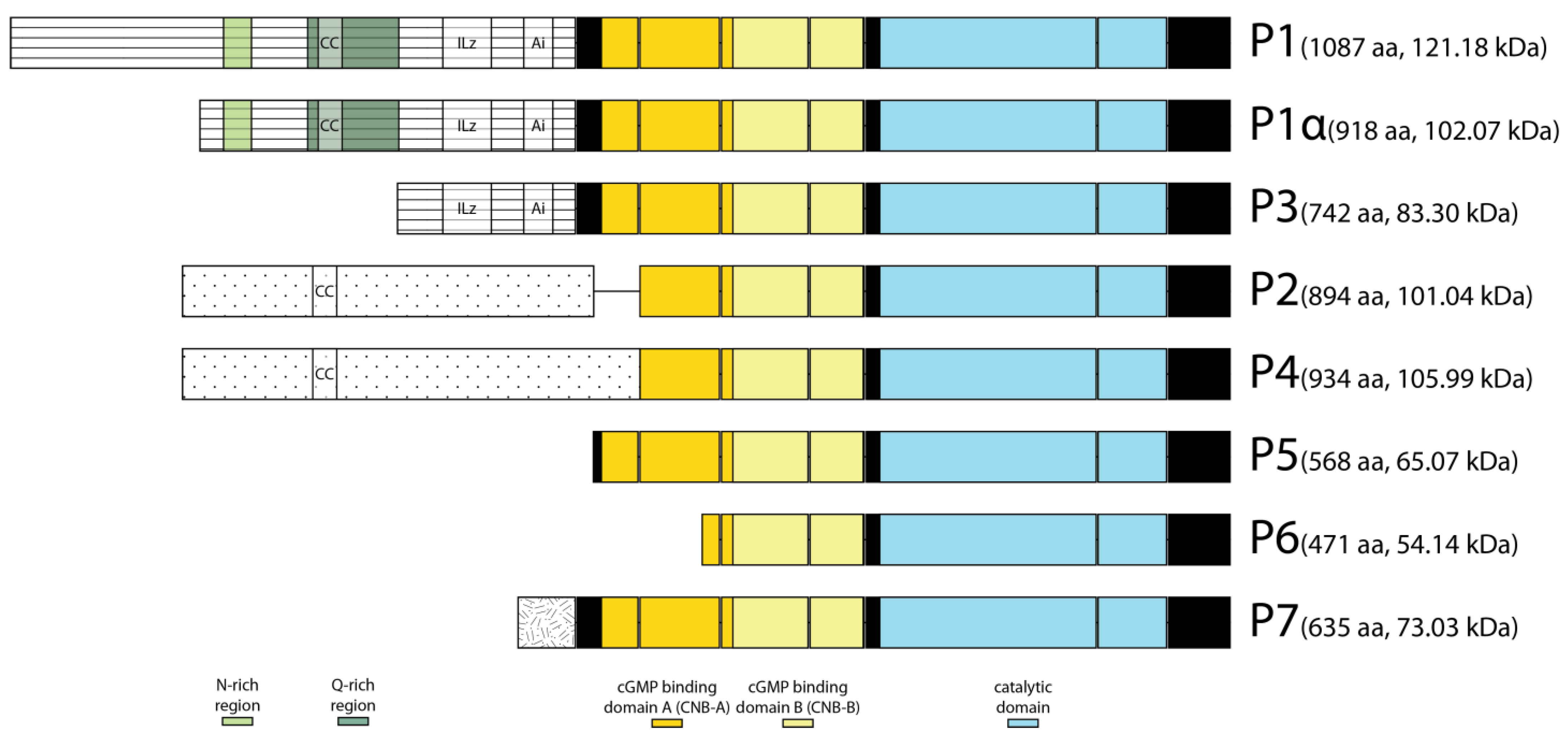




| Antibody | Antigen Sequence | Isoform Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-FOR(1) | SPPKIKENLSKSSSAYSTFSSAAEDSQDQVVICQQPQ (P2 residues 191 to 227) | P2, P4 |
| Anti-FOR(2) | RRLSLEQAIEGLKLEGEKAVRQKSPQISPAASSNGSSKDLNGEGFCIPRPRLIVPVHTYARRRRTGNLKEQSSGGQE (P2 residues 286 to 362) | P2, P4 |
| Anti-FOR(3) [34] | WFDGFYWWGLQNCTLEPPIKPAVKSVVDTTNFDDYPPDPEGPPP (catalytic domain) | P1, P1α, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 |
| Anti-FOR(4) | HSSTTVDAPPRPADVDVATVPVATTAPPPQQPVSNLFYADYQKLQPAIIDRDWERDRDTDTDTRSEAKPPDIVEHIEPVEEQRQIHTQIQSPAEIQIQIPPTPPAPSIQIQIQQRYRRHSSAEDRNLNTRRNDSNITEALRKAASMQ (P1 residues 25 to 171) | P1 |
| Anti-FOR(5) | QQELQLQQRYQQLQQLQAQTQGLYTSQGSPVLYHQPSPGSSQPVAIPGATCHSPTQLQPPNTL (P1 residues 278 to 340) | P1, P1α |
| Anti-FOR(6) | ISGCTPSGTGGSATPSPVGLVDPNFIVSNYVAASPQEECFIQIIQAKELKIQEMQRALQFKDNEIAELKSHLDKFQSVFPFSRGSAAGCAGTGGASGSGAGGSGGSGPGTATGATRKSGQNFQRQRALGISAEPQSESSLLL (P1 residues 351 to 492) | P1, P1α, P3 |
| CNS | Carcass | Fat Body | Intestine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOR isoform expression by for promoter Gal4 expression [17] | P1, P5, P7 * (pr1) P1, P5 (pr2) P1α, P3 (pr3) P2, P4, P6 (pr4) | P1α, P3 (pr3) P2, P4, P6 (pr4) | P1α, P3 (pr3) | P1, P5, P7 * (pr1) P1, P5 (pr2) P1α, P3 (pr3) P2, P4, P6 (pr4) |
| FOR isoform expression by modENCODE RNA-seq by region (FlyBase) | P1/P1α/P3 (exon 4) P2/P4 (exon 7) | P1/P1α/P3 (exon 4) P2/P4 (exon 7) | P1/P1α/P3 (exon 4) P2/P4 (exon 7) | P1/P1α/P3 (exon 4) P2/P4 (exon 7) |
| FOR isoform expression | P1, P1α, P3 | P1, P1α, P2, P3, P4 | P1α, P2, P3, P4 | No detectable expression |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasquez, O.E.; Allen, A.M.; So, A.K.-C.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Krause, H.M.; Levine, J.D.; Sokolowski, M.B. Characterizing the Protein Isoforms of foraging (for), the PKGI Ortholog in Drosophila melanogaster. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210219
Vasquez OE, Allen AM, So AK-C, Nguyen QH, Krause HM, Levine JD, Sokolowski MB. Characterizing the Protein Isoforms of foraging (for), the PKGI Ortholog in Drosophila melanogaster. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):10219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210219
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasquez, Oscar E., Aaron M. Allen, Anthony K.-C. So, Quynh H. Nguyen, Henry M. Krause, Joel D. Levine, and Marla B. Sokolowski. 2023. "Characterizing the Protein Isoforms of foraging (for), the PKGI Ortholog in Drosophila melanogaster" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 10219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210219
APA StyleVasquez, O. E., Allen, A. M., So, A. K.-C., Nguyen, Q. H., Krause, H. M., Levine, J. D., & Sokolowski, M. B. (2023). Characterizing the Protein Isoforms of foraging (for), the PKGI Ortholog in Drosophila melanogaster. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 10219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210219






