The Roles of Zinc Finger Proteins in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
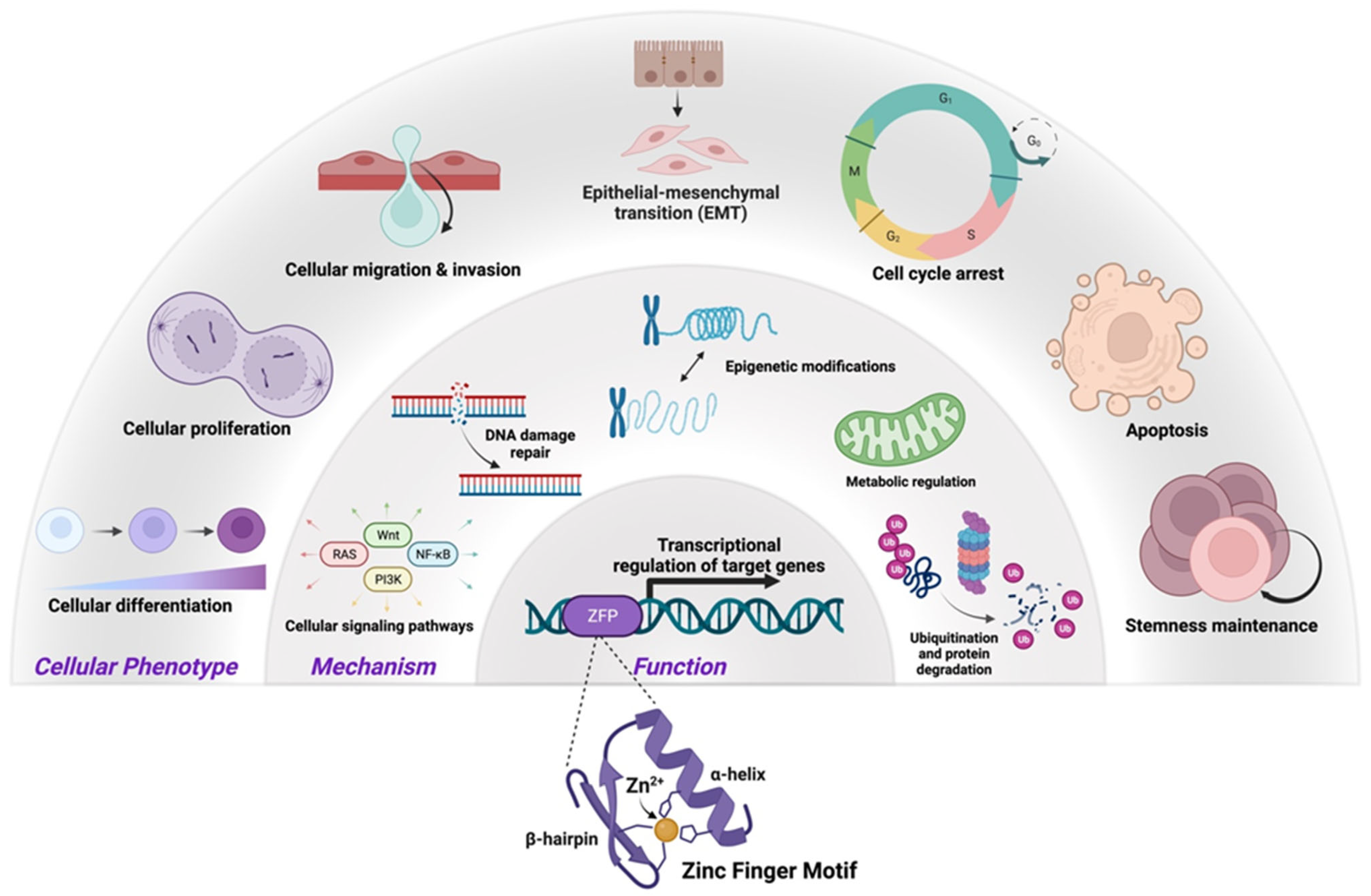
:1. Zinc Finger Proteins Are Transcriptional Regulators in Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
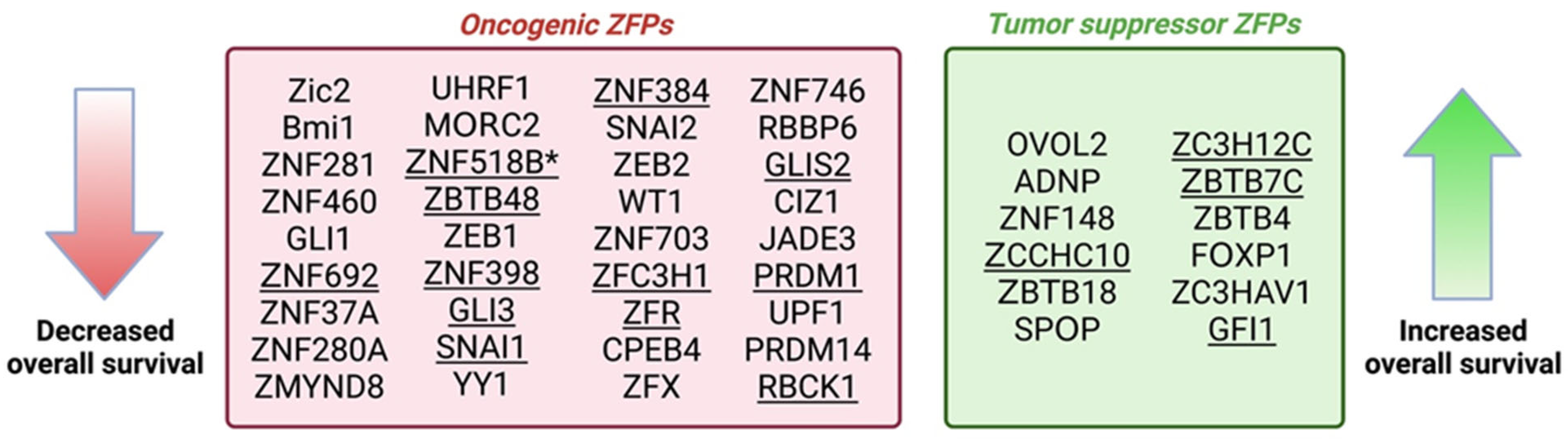
2. ZFPs Modulate CRC Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, Migration, Invasion, and EMT (Table 1)
| Molecular Mechanism | Gene | Common Alias(es) | Function | Additional Molecular Mechanisms | Cellular Targets | Role in Additional Cell Phenotypes or Behavior | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wnt/β-catenin | ZNRF3 | RNF203 | TS | Frizzled, LRP6 | [8,9] | ||
| OVOL2 | CHED; CHED1; CHED2; PPCD1; ZNF339 | TS | TCF4, SLUG; MAP3K8/AKT/NF-κB signaling, CXCL16 | [10,11] | |||
| FLYWCH1 | TS | β-catenin, TCF4, E-cadherin; γH2AX, ATM, p53 | DNA damage response | [12,13] | |||
| ZFP36 | Tristetraprolin, TIS11, TTP, NUP475, RNF162A, GOS24 | TS | MACC1, ZEB1, SOX9 | [14] | |||
| RSPO2 | HHRRD; TETAMS2; CRISTIN2 | TS | LGR5; Wnt5a/Fzd non-canonical pathway | [15,16] | |||
| ZIC2 | HPE5 | O | Axin2; cyclin D1, CD44, LGR5 | Apoptosis, cell cycle | [17] | ||
| ZBTB17 | MIZ-1, ZNF151, ZNF60, pHZ-67 | O | Myc-signaling | Dpr1, Dvl2 | Cell cycle | [18,19] | |
| BMI1 | FLVI2/BMI1, PCGF4, RNF51 | O | p16INK4a, p14ARF; IDAX, E-cadherin | [20,21,22,23] | |||
| PLAGL2 | ZNF900 | O | ASCL2, Wnt4A, Wnt5A; Wnt6; CD44 | [24,25,26] | |||
| ZNF281 | GZP1, ZBP99, ZNP-99 | O | Cell cycle | [27] | |||
| GATA6 | O | Sp1, urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) | [28] | ||||
| TRIM37 | MUL, POB1, TEF3 | O | β-catenin, c-Myc, cyclin D1 | [29] | |||
| ZNF277 | NRIF4 | O | β-catenin, p21WAF1 | Cell senescence, cell cycle | [30,31] | ||
| ADNP | ADNP1, HVDAS, MRD28 | TS | Under investigation | [32] | |||
| Ras/ERK | ZC3H13 | Xio | TS | Snail, cyclin D1, cyclin E1, occludin, Zo-1 | [33] | ||
| ZDHHC9 | DHHC9, MMSA1, MRZSR, MRXSZ, ZDHHC10, ZNF379, ZNF380 | O | [34] | ||||
| JAK/STAT | ZNF143 | SBF, STAF | TS | IL-8, ZEB1 | [35,36] | ||
| ZNF460 | HZF8, ZNF272 | O | [37] | ||||
| NF-κB | ZCCHC10 | TS | [38] | ||||
| ZFP91 | DSM8, FKSG11, PZF, ZNF757 | O | HIF-1α | Angiogenesis, cell cycle | [39] | ||
| PI3K/AKT | ZNF549 | TS | [40] | ||||
| GLI1 | PAPA8, PPD1 | O | NF-κB | Stemness | [41,42] | ||
| ZNF692 | AREBP, Zfp692 | O | cyclin D1, CDK2, MMP9, p27Kip1 | Cell cycle | [43] | ||
| ZBED6 | MGR | TS | Hippo, TGF-β, EGFR, PI3K | IGF-2 | Cell cycle | [44] | |
| TGF-β | ZNF37A | KOX21, ZNF37 | O | THSD4 | [45] | ||
| ZNF326 | ZAN75, ZIRD | O | LTBP4, p-Smad2/3, N-cadherin, Snail, Slug, vimentin, E-cadherin, Zo-1 | [46] | |||
| Hippo/YAP | ZNF367 | AFF29, CDC14B, ZFF29 | O | [47] | |||
| ZNF280A | SUHW1, ZNF280, ZNF636 | O | Cell cycle | [48] | |||
| YAP | ZMYND8 | PRKCBP1, PRO2893, RACK7 | O | Metabolism | [49,50] | ||
| DNA or histone methylation | ZBTB18 | MRD22, RP58, TAZ-1, ZNF238 | TS | [51] | |||
| GATA4 | ASD2, TACHD, TOF, VSD1 | TS | [52] | ||||
| GATA5 | CHTD5, GATAS | ||||||
| ZNF677 | TS | [53] | |||||
| ZFP82 | ZNF545 | TS | Wnt/β-catenin, PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK, NF-κB, AP1 signaling | KAP1 | Apoptosis, ribosome biogenesis | [54] | |
| SPOP | BTBD32, TEF2, NSDVS1 | TS | Hh/GLI2 pathway | SP1/PI3K axis, HDAC6; MMP2 | Apoptosis | [55,56,57] | |
| PRDM5 | BCS2, PFM2 | TS | [58] | ||||
| UHRF1 | ICBP90, Np95, RNF106, hNP95, TDRD22 | O | [59] | ||||
| Epigenetic modifications | MTA1 | O | VEGF-1, histone deacetylase | Angiogenesis | [60,61] | ||
| MORC2 | CMT2Z, DIGFAN, ZCW3, ZCWCC1 | O | NDRG1 | [62] | |||
| ZNF518B | O | Histone methyltransferases | [63] | ||||
| ZNF146 | OZF | O | hRAP | [64,65] | |||
| ZNF382 | KS1 | TS | HP1, NF-κB, and AP1 signaling | Apoptosis | [66] | ||
| KLF5 | BTEB2, CKLF, IKLF | O | SNHG12 | Stemness, DNA damage response, cell cycle | [67] | ||
| Sp1 | O | ZFAS1, VEGFA, miR-150-5p | Apoptosis | [68,69] | |||
| THAP11 | RONIN | O | HCF-1 | [70] | |||
| ZBTB48 | TZAP, HKR3, ZNF855 | O | Telomere dysregulation, mechanism under investigation | [71] | |||
| DNA Damage Response | KLF4 | EZF, GKLF | TS | Wnt, ERK signaling | p53, histone acetylases; NDRG2, cyclin D1; u-PAR | Cell cycle | [72,73,74,75] |
| ZEB1 | AREB6, BZP, DELTAEF1, FECD6, NIL2A, PPCD3, TCF8, ZFHEP, ZFHX1A | O | Wnt pathway | MPG; LOXL2; uPA, PAI-1; miR-200 | Stemness | [76,77,78,79,80] | |
| HLTF | HIP116, HIP116A, HLTF1, RNF80, SMARCA3, SNF2L3, ZBU1 | TS | [81] | ||||
| p53 | ZBTB7A | FBI1, LRF, ZBTB7, ZNF857A, pokemon, TIP21 | TS/O | ETS-1, MMPs; NF-κB | Glycolysis | [82,83,84,85] | |
| GLI3 | ACLS, GCPS, GLI3-190, GLI3FL, PAPA, PAPB, PHS, PPDIV | O | ERK1/2 cascade | [86,87] | |||
| ZNF398 | p51, p71, ZER6 | O | MDM2 | Cell cycle | [88] | ||
| E-cadherin | SNAI1 | SNAH, SLUGH2, SNAIL1, SNAIL | O | Wnt/β-catenin signaling | VDR; lncRNA WiNTRLINC1, MYB | Stemness | [89,90,91] |
| SPRY2 | SPROUTY2, IGAN3 | O | ZEB1, E-cadherin | [92] | |||
| NANOS1 | NOS1, SPGF12, ZC2HC12A | O | p120ctn | [93] | |||
| ZC3H12C | MCPIP3 | TS | Vimentin, VCAM-1, MMP2 | [94] | |||
| Metabolism | YY1 | DELTA, NF-E1, UCRBP, YIN-YANG-1 | O | Wnt/β-catenin signaling | GLUT3; p53 | Cell cycle, apoptosis | [95,96] |
| ZBTB7C | APM1, ZBTB36, ZNF857C | TS | Ras, Wnt signaling | Myc | Inflammation | [97,98] | |
| ZFP1 | ZNF475, PITA | O | p53 | Apoptosis | [99] | ||
| ZNF568 | PISA | O | p53 | Apoptosis | [99] | ||
| Angiogenesis | ZNF384 | CAGH1, CAGH1A, CIZ, ERDA2, NMP4, NP, TNRC1 | O | MMP2 | [100] | ||
| SNAI2 | SLUG, SNAIL2, WS2D, SLUGH1 | O | MMPs; MDM2, p53/p21; VDR | [89,101,102,103,104] | |||
| ZEB2 | SMADIP1, SIP1, ZFHX1B | O | miR-192, E-cadherin | MMP-2/9 | Metastasis, EMT | [105,106,107,108] | |
| ZNF24 | ZNF191, ZSCAN3, KOX17 | TS | VEGF | [109] | |||
| ZKSCAN3 | ZF47, ZFP306, ZNF306, ZNF309, ZSCAN13, ZSCAN35 | O | VEGF, integrin β4 | [110,111] | |||
| Under investigation | WT1 | AWT1, GUD, NPHS4, WAGR, WIT-2, WT33 | O | [112,113] | |||
| ZBTB4 | Kaiso-L1, ZNF903 | TS | [114] | ||||
| FOXP1 | 12CC4, HSPC215, MFH, QRF1, hFKH1B | TS | Inflammation | [115,116] | |||
| ZNF185 | SCELL | O | [117] | ||||
| ZNF217 | ZABC1 | O | [118] | ||||
| ZNF703 | NLZ1, ZEPPO1, ZNF503L, ZPO1 | O | [119] | ||||
| CRIP1 | CRHP, CRIP | O | GSK3/mTOR | [120,121] | |||
| ZFC3H1 | CCDC131, CSRC2, PSRC2 | O | [122] | ||||
| ZFR | SPG71, ZFR1 | O | FAM49B | [123] | |||
| ZNF350 | ZBRK1, ZFQR | TS | ATXN2 | [124] |
2.1. ZFPs Modulate Wnt Signaling
2.2. ZFPs Modulate Other Signaling Pathways
2.3. ZFPs Modulate Epigenetic Modifications
2.4. ZFPs and the DNA Damage Response
2.5. ZFPs Modulate p53 Levels
2.6. ZFPs Modulate E-Cadherin Expression
2.7. ZFPs Modulate CRC Cell Metabolism
2.8. ZFPs Modulate the Expression of Factors That Stimulate Angiogenesis
3. ZFPs Coordinate Cell Cycle Regulation and Apoptotic Mechanisms in CRC (Table 2)
| Molecular Mechanism | Gene | Common Alias(es) | Function | Additional Molecular Mechanisms | Cellular Targets | Role in Additional Cell Phenotypes or Behavior | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Checkpoint | ZFP36L1 | BRF1, Berg36, ERF1, RNF162B, TIS11B, cMG1 | TS | p53, cyclin A, cyclin B, cyclin D | Cell proliferation | [141] | |
| ZFP36L2 | BRF2, ERF2, OOMD13, OZEMA13, RNF162C, TIS11D | ||||||
| XAF1 | BIRC4BP, HSXIAPAF1, XIAPAF1 | TS | Cyclin B, Chk1, Cdc25; XIAP | [142,143] | |||
| KLF6 | BCD1, CBA1, COPEB, CPBP, GBF, PAC1, ST12, ZF9 | TS | p21, Bax | Cell proliferation | [144] | ||
| PATZ1 | ZNF278, MAZR, RIAZ, ZBTB19, ZSG | O | ERK/MAPK pathway | p21, p53, cyclin D1/E1 | Cell proliferation | [145] | |
| MZF1 | MZF-1, MZF1B, ZFP98, ZNF42, ZSCAN6 | O | p55PIK; Axl | Migration, invasion | [146,147,148] | ||
| Bcl-xL pathway | ZIC1 | BAIDCS, CRS6, ZIC, ZNF201 | TS | PI3K/AKT, MAPK pathways | Bcl-xL/Bad/Caspase 3 cascade; GADD45B | Cell proliferation | [149] |
| MECOM | AML1-EVI-1, EVI1, MDS1, MDS1-EVI1, PRDM3, RUSAT2, MDS1 and EVI1 complex locus, KMT8E | O | TGF-β; TIMP2, DNMT1 | BCl-xL, ΔNp63 | Cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis | [150,151,152,153] | |
| CPEB4 | CPE-BP4 | O | Bcl-xL, Bax | Cell proliferation, invasion | [154] | ||
| Epigenetic modifications | ZBTB33 | Kaiso, ZNF348 | O | cyclin D1/cyclin E1, MTG16 | CDKN2A | Cell proliferation | [155,156,157] |
| ZNF304 | O | p14ARF, p15INK4B, p16INK4A | [158] | ||||
| ZC3HAV1 | ZAP; ZC3H2; ARTD13; PARP13; FLB6421; ZC3HDC2 | TS | TRAILR4 | [159] | |||
| PRDM2 | HUMHOXY1, KMT8, MTB-ZF, RIZ, RIZ1, RIZ2 | TS | [160,161] | ||||
| Other | PLAGL1 | LOT1, ZAC, ZAC1 | TS | PPARγ | Cell differentiation | [162,163] | |
| KLF9 | BTEB, BTEB1 | TS | ISG15 | Cell proliferation, differentiation | [164] | ||
| ZFX | ZNF926 | O | DUSP5, MAPK signaling | Cell proliferation | [165,166,167] | ||
| ZNF746 | PARIS | O | GSK3β, FWB7, c-Myc | Cell proliferation | [168] | ||
| RBBP6 | MY038, P2P-R, PACT, RBQ-1, SNAMA | O | p53 | [169] | |||
| GLI2 | CJS, HPE9, PHS2, THP1, THP2 | O | TGF-β, HIF1-α | Stemness, cell differentiation | [170] | ||
| GLIS2 | NKL, NPHP7 | O | PUMA | Cell proliferation, migration | [171] | ||
| Under investigation | GFI1 | SCN2, ZNF163, GFI1A | TS | Cell proliferation | [172] | ||
| ZBTB16 | PLZF, ZNF145 | O | Stemness, cell proliferation | [173] | |||
| CIZ1 | LSFR1, NP94, ZNF356 | O | Cell proliferation | [174,175] |
3.1. ZFPs and Cell Cycle Checkpoint Regulation
3.2. Homeostasis Governed by the Bcl-2 Protein Family Can Be Modulated by ZFPs
3.3. Epigenetic Modifications Modulated by ZFPs
3.4. Other Mechanisms Whereby ZFPs Modulate CRC Progression
4. ZFPs Aid in Maintaining Cell Stemness to Propagate CRC-Promoting Cell Behaviors (Table 3)
| Molecular Mechanism | Gene | Common Alias(es) | Function | Additional Molecular Mechanisms | Cellular Targets | Role in Additional Cell Phenotypes or Behavior | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wnt | JADE3 | PHF16 | O | LGR5 | [178] | ||
| PRDM1 | BLIMP1, PRDI-BF1 | O | IGFBP3, ERK1/2 | [179] | |||
| SALL4 | DRRS, HSAL4, IVIC, ZNF797 | O | β-catenin, GLI2 | Metastasis | [180,181,182] | ||
| Epigenetics | ZRANB1 | Trabid | O | Wnt signaling, APC | EZH2 | Cell proliferation | [183] |
| UPF1 | HUPF1, NORF1, RENT1, UTF, pNORF1, smg-2 | O | TOP2A | [184] | |||
| SALL3 | ZNF796 | O | Under investigation | [185,186] | |||
| Under investigation | PRDM14 | PFM11 | O | Invasion | [187] | ||
| RBCK1 | HOIL1, PBMEI, PGBM1, RBCK2, RNF54, UBCE7IP3, XAP3, XAP4, ZRANB4 | O | Migration and invasion | [188] |
4.1. ZFPs Modulate Wnt Signaling
4.2. ZFPs Modulate Epigenetic Modifications
5. ZNF Structure and Function in CRC
Conserved Mutations in C2H2-Type ZFPs in CRC
6. Evaluating the Potential of ZFPs as CRC Therapeutic Targets
7. Current Limitations to Targeting ZFPs for CRC Therapy
8. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Wagle, N.S.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.J.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2023, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska, A.; Rudzki, G.; Lewandowski, T.; Stryjkowska-Gora, A.; Rudzki, S. Risk Factors for the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Control 2022, 29, 10732748211056692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, M.S.; Chung, D.C. The chromosomal instability pathway in colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2059–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laity, J.H.; Lee, B.M.; Wright, P.E. Zinc finger proteins: New insights into structural and functional diversity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2001, 11, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jen, J.; Wang, Y.C. Zinc finger proteins in cancer progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, H.X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Charlat, O.; Oster, E.; Avello, M.; Lei, H.; Mickanin, C.; Liu, D.; Ruffner, H.; et al. ZNRF3 promotes Wnt receptor turnover in an R-spondin-sensitive manner. Nature 2012, 485, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ming, T.; Tang, S.; Ren, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, M.; Tao, Q.; Xu, H. Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: Pathogenic role and therapeutic target. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, G.D.; Sun, G.B.; Jiao, P.; Chen, C.; Liu, Q.F.; Huang, X.L.; Zhang, R.; Cai, W.Y.; Li, S.N.; Wu, J.F.; et al. OVOL2, an Inhibitor of WNT Signaling, Reduces Invasive Activities of Human and Mouse Cancer Cells and Is Down-regulated in Human Colorectal Tumors. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 659–671.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Gao, J.; Ma, K.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Q.; Lian, J. OVOL2 attenuates the expression of MAP3K8 to suppress epithelial mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 224, 153493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almozyan, S.; Coulton, J.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Nateri, A.S. FLYWCH1, a Multi-Functional Zinc Finger Protein Contributes to the DNA Repair Pathway. Cells 2021, 10, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, B.A.; Almozyan, S.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Onyido, E.K.; Saadeddin, A.; Kashfi, S.H.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Ilyas, M.; Lourdusamy, A.; Behrens, A.; et al. FLYWCH1, a Novel Suppressor of Nuclear beta-Catenin, Regulates Migration and Morphology in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montorsi, L.; Guizzetti, F.; Alecci, C.; Caporali, A.; Martello, A.; Atene, C.G.; Parenti, S.; Pizzini, S.; Zanovello, P.; Bortoluzzi, S.; et al. Loss of ZFP36 expression in colorectal cancer correlates to wnt/ ss-catenin activity and enhances epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through upregulation of ZEB1, SOX9 and MACC1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59144–59157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Qiu, S.; Lu, L.; Zou, J.; Li, W.F.; Wang, O.; Zhao, H.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Chen, L.; et al. RSPO2-LGR5 signaling has tumour-suppressive activity in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Liao, W.; Zhang, L.; Tu, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, T.; Dai, X.; Xiong, Y.; Liang, W.; Ding, C.; et al. RSPO2 suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis by counteracting the Wnt5a/Fzd7-driven noncanonical Wnt pathway. Cancer Lett. 2017, 402, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Qu, C.; Yuan, L.; Cheng, C.; Sun, X.; et al. Multilevel regulation of Wnt signaling by Zic2 in colon cancer due to mutation of beta-catenin. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.G. Myc-interacting zinc-finger protein 1 positively regulates Wnt signalling by protecting Dishevelled from Dapper1-mediated degradation. Biochem. J. 2015, 466, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, K.E.; Walz, S.; von Eyss, B.; Wolf, E.; Athineos, D.; Sansom, O.; Eilers, M. The role of MIZ-1 in MYC-dependent tumorigenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a014290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zheng, J. Polycomb group protein Bmi1 expression in colon cancers predicts the survival. Med. Oncol. 2010, 27, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yoon, S.Y.; Kim, C.N.; Joo, J.H.; Moon, S.K.; Choe, I.S.; Choe, Y.K.; Kim, J.W. The Bmi-1 oncoprotein is overexpressed in human colorectal cancer and correlates with the reduced p16INK4a/p14ARF proteins. Cancer Lett. 2004, 203, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhou, C.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. BMI1 activates WNT signaling in colon cancer by negatively regulating the WNT antagonist IDAX. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bu, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Sha, W. Bmi-1 promotes the invasion and migration of colon cancer stem cells through the downregulation of E-cadherin. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Li, D.; Du, Y.; Su, C.; Yang, C.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; Hu, G. Overexpressed PLAGL2 transcriptionally activates Wnt6 and promotes cancer development in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Xie, B.; Bai, B.; Shan, L.; Zheng, W.; Huang, X.; Zhu, H. Weighted gene coexpression analysis indicates that PLAGL2 and POFUT1 are related to the differential features of proximal and distal colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 2473–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strubberg, A.M.; Veronese Paniagua, D.A.; Zhao, T.; Dublin, L.; Pritchard, T.; Bayguinov, P.O.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.J.; Madison, B.B. The Zinc Finger Transcription Factor PLAGL2 Enhances Stem Cell Fate and Activates Expression of ASCL2 in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.J.; Bu, P.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.T.; Li, Q.Y.; Liu, J.T.; Dong, H.C.; Ren, X.Q. ZNF281 Regulates Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Colorectal Cancer through Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belaguli, N.S.; Aftab, M.; Rigi, M.; Zhang, M.; Albo, D.; Berger, D.H. GATA6 promotes colon cancer cell invasion by regulating urokinase plasminogen activator gene expression. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.; Guan, H.T.; Dai, Z.J.; Ma, Y.G.; Liu, X.X.; Wang, X.J. Knockdown of Tripartite Motif-Containing Protein 37 (TRIM37) Inhibits the Proliferation and Tumorigenesis in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Xie, G.; Khurana, S.; Heath, J.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Timmons, J.; Shah, N.; Raufman, J.P. Divergent effects of muscarinic receptor subtype gene ablation on murine colon tumorigenesis reveals association of M3R and zinc finger protein 277 expression in colon neoplasia. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, G.; Peng, Z.; Liang, J.; Larabee, S.M.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Yfantis, H.; Raufman, J.P. Zinc finger protein 277 is an intestinal transit-amplifying cell marker and colon cancer oncogene. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e150894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaj, C.; Bringmann, A.; Schmidt, E.M.; Urbischek, M.; Lamprecht, S.; Frohlich, T.; Arnold, G.J.; Krebs, S.; Blum, H.; Hermeking, H.; et al. ADNP Is a Therapeutically Inducible Repressor of WNT Signaling in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2769–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, M. ZC3H13 suppresses colorectal cancer proliferation and invasion via inactivating Ras-ERK signaling. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 8899–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla, F.; Birkenkamp-Demtroder, K.; Kruhoffer, M.; Sorensen, F.B.; Andersen, C.L.; Laiho, P.; Aaltonen, L.A.; Verspaget, H.W.; Orntoft, T.F. Differential expression of DHHC9 in microsatellite stable and instable human colorectal cancer subgroups. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, V.; Paek, A.R.; Choi, B.K.; Hong, E.K.; You, H.J. Loss of zinc-finger protein 143 contributes to tumour progression by interleukin-8-CXCR axis in colon cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4043–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paek, A.R.; Lee, C.H.; You, H.J. A role of zinc-finger protein 143 for cancer cell migration and invasion through ZEB1 and E-cadherin in colon cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53 (Suppl. S1), E161–E168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, T.; Xu, J.; Fang, S.; Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; He, Y. Overexpression of ZNF460 predicts worse survival and promotes metastasis through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in patient with colon cancer. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 3198–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Shi, P.D.; Wan, B.S. MiR-410-3p activates the NF-kappaB pathway by targeting ZCCHC10 to promote migration, invasion and EMT of colorectal cancer. Cytokine 2021, 140, 155433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Mi, C.; Wang, K.S.; Lee, J.J.; Jin, X. Zinc finger protein 91 (ZFP91) activates HIF-1alpha via NF-kappaB/p65 to promote proliferation and tumorigenesis of colon cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36551–36562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Qin, X. MicroRNA-708 targeting ZNF549 regulates colon adenocarcinoma development through PI3K/AKt pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Qi, W.; Cui, Y.; Xuan, Y. GLI1 promotes cancer stemness through intracellular signaling pathway PI3K/Akt/NFkappaB in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 373, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, B.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y. Gli1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis in a Foxm1-dependent manner by activating EMT and PI3K-AKT signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86134–86147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, Y.; Ren, S.; Ai, L.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Piao, D. ZNF692 promotes colon adenocarcinoma cell growth and metastasis by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhtar Ali, M.; Younis, S.; Wallerman, O.; Gupta, R.; Andersson, L.; Sjoblom, T. Transcriptional modulator ZBED6 affects cell cycle and growth of human colorectal cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7743–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.N.; Qin, S.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, M.; Ye, Q.; Xie, N.; et al. ZNF37A promotes tumor metastasis through transcriptional control of THSD4/TGF-beta axis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3394–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, T.; Han, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wei, L.; Li, P.; Wang, E. ZNF326 promotes colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 225, 153554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Gao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhang, L.; Si, M. Inhibition of zinc finger protein 367 exerts a tumor suppressive role in colorectal cancer by affecting the activation of oncogenic YAP1 signaling. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 2278–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Tai, J.; Chen, S.; Hong, S.; Wang, L. ZNF280A Promotes Proliferation and Tumorigenicity via Inactivating the Hippo-Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2019, 12, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, Q.; Wu, P.; Fu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, K.; Xie, D.; Zhang, X. ZMYND8 expression combined with pN and pM classification as a novel prognostic prediction model for colorectal cancer: Based on TCGA and GEO database analysis. Cancer Biomark. 2020, 28, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Zhong, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yuan, H.; Lian, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. The ZMYND8-regulated mevalonate pathway endows YAP-high intestinal cancer with metabolic vulnerability. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 2736–2751.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzocco, S.; Dopeso, H.; Martinez-Barriocanal, A.; Anguita, E.; Nieto, R.; Li, J.; Garcia-Vidal, E.; Maggio, V.; Rodrigues, P.; de Marcondes, P.G.; et al. Identification of ZBTB18 as a novel colorectal tumor suppressor gene through genome-wide promoter hypermethylation analysis. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellebrekers, D.M.; Lentjes, M.H.; van den Bosch, S.M.; Melotte, V.; Wouters, K.A.; Daenen, K.L.; Smits, K.M.; Akiyama, Y.; Yuasa, Y.; Sanduleanu, S.; et al. GATA4 and GATA5 are potential tumor suppressors and biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3990–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siraj, A.K.; Parvathareddy, S.K.; Siraj, N.; Al-Obaisi, K.; Aldughaither, S.M.; AlManea, H.M.; AlHussaini, H.F.; Al-Dayel, F.; Al-Kuraya, K.S. Loss of ZNF677 expression is a predictive biomarker for lymph node metastasis in Middle Eastern Colorectal Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wong, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; Zhai, J.; Wang, G.; Wei, H.; Zhang, X.; He, H.H.; et al. ZNF545 loss promotes ribosome biogenesis and protein translation to initiate colorectal tumorigenesis in mice. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6590–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xiao, J.; Chai, Y.; Hong, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, R.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E., III; Huang, K. Speckle-Type POZ Protein Down-Regulates Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 Expression via Sp1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Pan, C.; Yan, L.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhu, X. The emerging role of SPOP protein in tumorigenesis and cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Qin, J. Properties and Clinical Relevance of Speckle-Type POZ Protein in Human Colorectal Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2015, 19, 1484–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Toyota, M.; Kondo, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Imai, T.; Ohe-Toyota, M.; Maruyama, R.; Nojima, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Sekido, Y.; et al. PRDM5 identified as a target of epigenetic silencing in colorectal and gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4786–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, W.; Brown, S.M.; Cai, Y.; Wu, K.; Fan, D.; Nie, Y.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Tiedemann, R.L.; et al. Defining UHRF1 Domains that Support Maintenance of Human Colon Cancer DNA Methylation and Oncogenic Properties. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 633–648.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, B.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhong, X.Y.; Fang, M.; Yan, Y.R.; Qi, G.L.; Pan, Y.L.; Zhou, X.L. Metastasis-associated protein 1 induces VEGF-C and facilitates lymphangiogenesis in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malisetty, V.L.; Penugurti, V.; Panta, P.; Chitta, S.K.; Manavathi, B. MTA1 expression in human cancers—Clinical and pharmacological significance. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shao, Y.; He, Y.; Ning, K.; Cui, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, F. MORC2 promotes development of an aggressive colorectal cancer phenotype through inhibition of NDRG1. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gimeno-Valiente, F.; Riffo-Campos, A.L.; Torres, L.; Tarazona, N.; Gambardella, V.; Cervantes, A.; Lopez-Rodas, G.; Franco, L.; Castillo, J. Epigenetic Mechanisms Are Involved in the Oncogenic Properties of ZNF518B in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, K.; Ferbus, D.; Kolahgar, G.; Prosperi, M.T.; Goubin, G. Zinc finger protein overexpressed in colon carcinoma interacts with the telomeric protein hRap1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 95, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, C.Y.; Hao, Y. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 acts as miR-216b-5p sponge to promote colorectal cancer progression via up-regulating ZNF146. J. Mol. Histol. 2021, 52, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Geng, H.; Cheng, S.H.; Liang, P.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Srivastava, G.; Ng, M.H.; Fukagawa, T.; Wu, X.; et al. KRAB zinc finger protein ZNF382 is a proapoptotic tumor suppressor that represses multiple oncogenes and is commonly silenced in multiple carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6516–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, N.; Xi, Y.; Hu, S.; Ng, D.M.; Ahmed, F.Y.H.; Zhao, G.; Fan, X.; Xie, Y.; et al. Network analysis of KLF5 targets showing the potential oncogenic role of SNHG12 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, R.; Nagaraju, G.P. Specificity protein 1: Its role in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 113, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zeng, K.; Xu, M.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, T.; He, B.; Pan, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. SP1-induced lncRNA-ZFAS1 contributes to colorectal cancer progression via the miR-150-5p/VEGFA axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, J.B.; Palchaudhuri, S.; Yin, H.; Wei, J.; Chakravarti, D. A transcriptional regulatory role of the THAP11-HCF-1 complex in colon cancer cell function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 1654–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.J.; Seo, Y.R.; Park, W.J.; Heo, Y.R.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.H. Clinicopathological Characteristics of TZAP Expression in Colorectal Cancers. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 12933–12942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, V.W.; Liu, Y.; Kim, J.; Shroyer, K.R.; Bialkowska, A.B. Increased Genetic Instability and Accelerated Progression of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer through Intestinal Epithelium-specific Deletion of Klf4. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Shi, W.; Liang, Y.; Yao, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J. KLF4 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation dependent on NDRG2 signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; Elkarim, E.A.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Yang, V.W. KLF4 Suppresses Tumor Formation in Genetic and Pharmacological Mouse Models of Colonic Tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Jamaluddin, M.S.; Boyd, D.D. The Kruppel-like KLF4 transcription factor, a novel regulator of urokinase receptor expression, drives synthesis of this binding site in colonic crypt luminal surface epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22674–22683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Sun, G.; Peng, C.; Chen, J.; Quan, J.; Wu, C.; Lian, X.; Tang, W.; Xiang, D. ZEB1 promotes colorectal cancer cell invasion and disease progression by enhanced LOXL2 transcription. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2021, 14, 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Tillo, E.; de Barrios, O.; Siles, L.; Amendola, P.G.; Darling, D.S.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Castells, A.; Postigo, A. ZEB1 Promotes invasiveness of colorectal carcinoma cells through the opposing regulation of uPA and PAI-1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Barrios, O.; Sanchez-Moral, L.; Cortes, M.; Ninfali, C.; Profitos-Peleja, N.; Martinez-Campanario, M.C.; Siles, L.; Del Campo, R.; Fernandez-Acenero, M.J.; Darling, D.S.; et al. ZEB1 promotes inflammation and progression towards inflammation-driven carcinoma through repression of the DNA repair glycosylase MPG in epithelial cells. Gut 2019, 68, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.W.; Lin, P.L.; Cheng, Y.W.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, L.; Lee, H. DDX3 enhances oncogenic KRAS-induced tumor invasion in colorectal cancer via the beta-catenin/ZEB1 axis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22687–22699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Pappan, L.; Galliher-Beckley, A.; Shi, J. IL-1beta promotes stemness and invasiveness of colon cancer cells through Zeb1 activation. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandhu, S.; Wu, X.; Nabi, Z.; Rastegar, M.; Kung, S.; Mai, S.; Ding, H. Loss of HLTF function promotes intestinal carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, F.; Feng, F.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhang, D.; Linghu, E. FBI-1 enhances ETS-1 signaling activity and promotes proliferation of human colorectal carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, C.; Zhou, M.; Liu, R.; Xu, G.; et al. ZBTB7 evokes 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer through the NFkappaB signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.S.; Liu, Z.; Gerarduzzi, C.; Choi, D.E.; Ganapathy, S.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Yuan, Z.M. Somatic human ZBTB7A zinc finger mutations promote cancer progression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3071–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.K.; Verma, S.; Kushwaha, P.P.; Prajapati, K.S.; Shuaib, M.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, S. Role of ZBTB7A zinc finger in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4703–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.N.; Oh, S.C.; Kim, J.S.; Yoo, Y.A. Abrogation of Gli3 expression suppresses the growth of colon cancer cells via activation of p53. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P. GLI3 Promotes Invasion and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8889986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wu, S.; Li, W.; Herkilini, A.; Miyagishi, M.; Zhao, H.; Kasim, V. Zinc-finger protein p52-ZER6 accelerates colorectal cancer cell proliferation and tumour progression through promoting p53 ubiquitination. EBioMedicine 2019, 48, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brzozowa, M.; Michalski, M.; Wyrobiec, G.; Piecuch, A.; Dittfeld, A.; Harabin-Slowinska, M.; Boron, D.; Wojnicz, R. The role of Snail1 transcription factor in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 19, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyes, S.; Andrieux, G.; Schrempp, M.; Aicher, D.; Wenzel, J.; Anton-Garcia, P.; Boerries, M.; Hecht, A. Genome-wide mapping of DNA-binding sites identifies stemness-related genes as directly repressed targets of SNAIL1 in colorectal cancer cells. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6647–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, S.; Torshizi Esfahani, A.; Karimpour, R.; Bakhshian, F.; Mortazavi Tabatabaei, S.A.; Laleh, A.; Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad, E. High expression of Snail1 is associated with EMAST and poor prognosis in CRC patients. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2019, 12, S30–S36. [Google Scholar]
- Barbachano, A.; Ordonez-Moran, P.; Garcia, J.M.; Sanchez, A.; Pereira, F.; Larriba, M.J.; Martinez, N.; Hernandez, J.; Landolfi, S.; Bonilla, F.; et al. SPROUTY-2 and E-cadherin regulate reciprocally and dictate colon cancer cell tumourigenicity. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4800–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strumane, K.; Bonnomet, A.; Stove, C.; Vandenbroucke, R.; Nawrocki-Raby, B.; Bruyneel, E.; Mareel, M.; Birembaut, P.; Berx, G.; van Roy, F. E-cadherin regulates human Nanos1, which interacts with p120ctn and induces tumor cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10007–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suk, F.M.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, R.J.; Lin, S.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Liang, Y.C. MCPIP3 as a Potential Metastasis Suppressor Gene in Human Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Kasim, V. Yin Yang 1 promotes the Warburg effect and tumorigenesis via glucose transporter GLUT3. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2423–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Li, X.; Wu, C.W.; Dong, Y.; Cai, M.; Mok, M.T.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Ng, S.S.; Chen, M.; et al. microRNA-7 is a novel inhibitor of YY1 contributing to colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5078–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Pu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xiang, L.; Jiang, Z. Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing 7C (ZBTB7C) expression as an independent prognostic factor for colorectal cancer and its relevant molecular mechanisms. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 4141–4159. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Z. The prognostic and immunological effects of ZBTB7C across cancers: Friend or foe? Aging 2021, 13, 12849–12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Z.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X.; Song, S.; Pei, P.; Tian, C.; Yan, H.; et al. KRAB-type zinc-finger proteins PITA and PISA specifically regulate p53-dependent glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 572–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Li, P.; Tian, H.; Tang, X.; Zhang, G. Zinc finger protein 384 enhances colorectal cancer metastasis by upregulating MMP2. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, U.; Park, J.K.; Um, H.D. Slug promotes p53 and p21 protein degradation by inducing Mdm2 expression in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shioiri, M.; Shida, T.; Koda, K.; Oda, K.; Seike, K.; Nishimura, M.; Takano, S.; Miyazaki, M. Slug expression is an independent prognostic parameter for poor survival in colorectal carcinoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welch-Reardon, K.M.; Ehsan, S.M.; Wang, K.; Wu, N.; Newman, A.C.; Romero-Lopez, M.; Fong, A.H.; George, S.C.; Edwards, R.A.; Hughes, C.C. Angiogenic sprouting is regulated by endothelial cell expression of Slug. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Ngo, V.N.; Marani, M.; Yang, Y.; Wright, G.; Staudt, L.M.; Downward, J. Critical role for transcriptional repressor Snail2 in transformation by oncogenic RAS in colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4658–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Chaudhuri, A.; Talmon, G.; Wisecarver, J.L.; Are, C.; Brattain, M.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-192 suppresses liver metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5332–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahlert, C.; Lahes, S.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Dutta, S.; Mogler, C.; Herpel, E.; Brand, K.; Steinert, G.; Schneider, M.; Mollenhauer, M.; et al. Overexpression of ZEB2 at the invasion front of colorectal cancer is an independent prognostic marker and regulates tumor invasion in vitro. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7654–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.Z.; Wang, J.J.; Yang, S.B.; Li, W.F.; Xiao, L.B.; He, Y.L.; Song, X.M. ZEB2 promotes tumor metastasis and correlates with poor prognosis of human colorectal cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2838–2851. [Google Scholar]
- Sreekumar, R.; Harris, S.; Moutasim, K.; DeMateos, R.; Patel, A.; Emo, K.; White, S.; Yagci, T.; Tulchinsky, E.; Thomas, G.; et al. Assessment of Nuclear ZEB2 as a Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer Outcome and TNM Risk Stratification. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e183115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harper, J.; Yan, L.; Loureiro, R.M.; Wu, I.; Fang, J.; D’Amore, P.A.; Moses, M.A. Repression of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by the zinc finger transcription factor ZNF24. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8736–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.W.; Roh, S.A.; Tak, K.H.; Koh, B.M.; Ha, Y.J.; Cho, D.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.C. ZKSCAN3 Facilitates Liver Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer Associated with CEA-expressing Tumor. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 2397–2406. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Hamilton, S.R.; Sood, A.; Kuwai, T.; Ellis, L.; Sanguino, A.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Boyd, D.D. The previously undescribed ZKSCAN3 (ZNF306) is a novel “driver” of colorectal cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4321–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bejrananda, T.; Phukaoloun, M.; Boonpipattanapong, T.; Wanitsuwan, W.; Kanngern, S.; Sangthong, R.; Sangkhathat, S. WT1 expression as an independent marker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancers. Cancer Biomark. 2010, 8, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oji, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Nomura, M.; Nakano, Y.; Ikeba, A.; Nakatsuka, S.; Abeno, S.; Kiyotoh, E.; Jomgeow, T.; Sekimoto, M.; et al. Overexpression of the Wilms’ tumor gene WT1 in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, T.; He, K.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Li, H. Expression of Zinc Finger and BTB Domain-Containing 4 in Colorectal Cancer and Its Clinical Significance. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 9621–9626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banham, A.H.; Beasley, N.; Campo, E.; Fernandez, P.L.; Fidler, C.; Gatter, K.; Jones, M.; Mason, D.Y.; Prime, J.E.; Trougouboff, P.; et al. The FOXP1 winged helix transcription factor is a novel candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8820–8829. [Google Scholar]
- De Smedt, L.; Palmans, S.; Govaere, O.; Moisse, M.; Boeckx, B.; De Hertogh, G.; Prenen, H.; Van Cutsem, E.; Tejpar, S.; Tousseyn, T.; et al. Expression of FOXP1 and Colorectal Cancer Prognosis. Lab. Med. 2015, 46, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, D.; Chijiwa, T.; Matsuyama, M.; Mukai, M.; Matsuo, E.I.; Nishimura, O.; Kawai, K.; Suemizu, H.; Hiraoka, N.; Nakagohri, T.; et al. Zinc finger protein 185 is a liver metastasis-associated factor in colon cancer patients. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Zheng, L.Q.; Pan, L.J.; Guo, J.X.; Yang, G.S. ZNF217 is overexpressed and enhances cell migration and invasion in colorectal carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 2459–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, F.; Bi, L.; Yang, G.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y. ZNF703 promotes tumor cell proliferation and invasion and predicts poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, G.; Zou, L.; Zhou, L.; Gao, P.; Qian, X.; Cui, J. Cysteine-Rich Intestinal Protein 1 Silencing Inhibits Migration and Invasion in Human Colorectal Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhu, H.; Yao, Y.; Chai, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Fu, S.; Wang, Y. Cysteine-rich intestinal protein 1 silencing alleviates the migration and invasive capability enhancement induced by excessive zinc supplementation in colorectal cancer cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3578–3588. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Chen, W.; Wei, J.; Yao, H.; Shi, J.; Hou, X.; Deng, Y.; Ou, M. Zinc finger C3H1-type containing serves as a novel prognostic biomarker in human pan-cancer. Gene 2022, 820, 146251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Marian, T.A.; Wei, Z. ZFR promotes cell proliferation and tumor development in colorectal and liver cancers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallen, L.; Klein, H.; Stoschek, C.; Wehrmeyer, S.; Nonhoff, U.; Ralser, M.; Wilde, J.; Rohr, C.; Schweiger, M.R.; Zatloukal, K.; et al. The KRAB-containing zinc-finger transcriptional regulator ZBRK1 activates SCA2 gene transcription through direct interaction with its gene product, ataxin-2. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gujral, T.S.; Chan, M.; Peshkin, L.; Sorger, P.K.; Kirschner, M.W.; MacBeath, G. A noncanonical Frizzled2 pathway regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cell 2014, 159, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gargalionis, A.N.; Papavassiliou, K.A.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Targeting STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, A.; Rahmani, F.; Ferns, G.A.; Ryzhikov, M.; Avan, A.; Hassanian, S.M. Role of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Gene 2020, 726, 144132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, S.A.; Eide, P.W.; Nesbakken, A.; Guren, T.; Leithe, E.; Lothe, R.A. Portrait of the PI3K/AKT pathway in colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1855, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Pasche, B. TGF-beta signaling alterations and susceptibility to colorectal cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, R14–R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lao, V.V.; Grady, W.M. Epigenetics and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Guo, M. Epigenetic changes in colorectal cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groelly, F.J.; Fawkes, M.; Dagg, R.A.; Blackford, A.N.; Tarsounas, M. Targeting DNA damage response pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhmoud, J.F.; Woolley, J.F.; Al Moustafa, A.E.; Malki, M.I. DNA Damage/Repair Management in Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebl, M.C.; Hofmann, T.G. The Role of p53 Signaling in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschos, K.A.; Canovas, D.; Bird, N.C. The role of cell adhesion molecules in the progression of colorectal cancer and the development of liver metastasis. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.E.; Short, S.P.; Williams, C.S. Colorectal Cancer and Metabolism. Curr. Colorectal. Cancer Rep. 2018, 14, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, L.; Salem, M.E.; Mikhail, S. Biomarkers of Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer. Biomark. Cancer 2015, 7, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, K.J.; O’Connell, M.J. Cell cycle regulation by checkpoints. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1170, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, J. Role of apoptosis in colon cancer biology, therapy, and prevention. Curr. Colorectal. Cancer Rep. 2013, 9, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suk, F.M.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, R.J.; Lin, S.Y.; Liu, S.C.; Jau, C.F.; Liang, Y.C. ZFP36L1 and ZFP36L2 inhibit cell proliferation in a cyclin D-dependent and p53-independent manner. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liston, P.; Fong, W.G.; Kelly, N.L.; Toji, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Conte, D.; Tamai, K.; Craig, C.G.; McBurney, M.W.; Korneluk, R.G. Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-Caspase activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gu, Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Yang, M.; Zou, B.; Chan, S.; Qiao, L.; Jiang, B.; Tu, S.; et al. Identification of XAF1 as a novel cell cycle regulator through modulating G(2)/M checkpoint and interaction with checkpoint kinase 1 in gastrointestinal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, D.D.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wu, Y.A. Expression of KLF6-SV2 in colorectal cancer and its impact on proliferation and apoptosis. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 27, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.Q.; Guo, F.F.; Sun, D.F.; Wang, Y.C.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.L.; Hong, J.; Fang, J.Y. Downregulation of ZNF278 arrests the cell cycle and decreases the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells via inhibition of the ERK/MAPK pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3685–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Jin, Y.; Luo, X.; Xia, X.; Gong, J.; Hu, J. p55PIK transcriptionally activated by MZF1 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 868131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horinaka, M.; Yoshida, T.; Tomosugi, M.; Yasuda, S.; Sowa, Y.; Sakai, T. Myeloid zinc finger 1 mediates sulindac sulfide-induced upregulation of death receptor 5 of human colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mudduluru, G.; Vajkoczy, P.; Allgayer, H. Myeloid zinc finger 1 induces migration, invasion, and in vivo metastasis through Axl gene expression in solid cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, L.; Chen, S.; Zhong, J.; Wang, X.; Lam, E.K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, T.; Yu, J.; Si, J.; et al. ZIC1 is downregulated through promoter hypermethylation, and functions as a tumor suppressor gene in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeepa; Suresh, V.; Singh, V.K.; Nayak, K.B.; Senapati, S.; Chakraborty, S. EVI1 promotes metastasis by downregulating TIMP2 in metastatic colon and breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 142, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Wang, J. EVI1 in Leukemia and Solid Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, K.B.; Kuila, N.; Das Mohapatra, A.; Panda, A.K.; Chakraborty, S. EVI1 targets DeltaNp63 and upregulates the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p21 independent of p53 to delay cell cycle progression and cell proliferation in colon cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Sambandam, K.; Rajaraman, S.; Perkins, A.S.; Fields, A.P.; Hellmich, M.R.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; et al. Overexpression of Evi-1 oncoprotein represses TGF-beta signaling in colorectal cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C.; Wei, X.; Hu, C.; Ling, X.; Liu, X. MicroRNA-203-mediated posttranscriptional deregulation of CPEB4 contributes to colorectal cancer progression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 466, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, C.W.; Smith, J.J.; Lu, L.C.; Markham, N.; Stengel, K.R.; Short, S.P.; Zhang, B.; Hunt, A.A.; Fingleton, B.M.; Carnahan, R.H.; et al. Kaiso directs the transcriptional corepressor MTG16 to the Kaiso binding site in target promoters. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozner, A.; Terooatea, T.W.; Buck-Koehntop, B.A. Cell-specific Kaiso (ZBTB33) Regulation of Cell Cycle through Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E1. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 24538–24550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, E.C.; Valls, E.; Figueroa, M.E.; Mazur, A.; Meng, F.G.; Chiosis, G.; Laird, P.W.; Schreiber-Agus, N.; Greally, J.M.; Prokhortchouk, E.; et al. Kaiso contributes to DNA methylation-dependent silencing of tumor suppressor genes in colon cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7258–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serra, R.W.; Fang, M.; Park, S.M.; Hutchinson, L.; Green, M.R. A KRAS-directed transcriptional silencing pathway that mediates the CpG island methylator phenotype. Elife 2014, 3, e02313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, W.; Wong, C.W.; Zhu, W.; Lin, Y.; Hu, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Sander, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. Zinc-finger antiviral protein acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 5995–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Carling, T.; Fang, W.; Piao, Z.; Sheu, J.C.; Huang, S. Hypermethylation in human cancers of the RIZ1 tumor suppressor gene, a member of a histone/protein methyltransferase superfamily. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8094–8099. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.L.; Huang, S. Adenovirus expressing RIZ1 in tumor suppressor gene therapy of microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1796–1798. [Google Scholar]
- Barz, T.; Hoffmann, A.; Panhuysen, M.; Spengler, D. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is a Zac target gene mediating Zac antiproliferation. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11975–11982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalczyk, A.E.; Krazinski, B.E.; Godlewski, J.; Kiewisz, J.; Kwiatkowski, P.; Sliwinska-Jewsiewicka, A.; Kiezun, J.; Wierzbicki, P.M.; Bodek, G.; Sulik, M.; et al. Altered expression of the PLAGL1 (ZAC1/LOT1) gene in colorectal cancer: Correlations to the clinicopathological parameters. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, A.R.; Simmen, R.C.; Raj, V.R.; Van, T.T.; MacLeod, S.L.; Simmen, F.A. Kruppel-like factor 9 (KLF9) prevents colorectal cancer through inhibition of interferon-related signaling. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, L.Y. Zinc finger protein X-linked is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and is associated with poor prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Shan, Z.; Yan, L.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, L.; Xu, B.; Liu, S.; Jin, Z.; Gao, Y. High expression of Zinc-finger protein X-linked promotes tumor growth and predicts a poor outcome for stage II/III colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19680–19692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Yan, L.; Su, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, S.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y. Zinc-finger protein X-linked is a novel predictor of prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3150–3157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Jung, D.B.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Kang, S.E.; Srivastava, S.K.; Yun, M.; Kim, S.H. Zinc finger protein 746 promotes colorectal cancer progression via c-Myc stability mediated by glycogen synthase kinase 3beta and F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3715–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tang, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, T.; Xue, Y.; Huang, G.; Yan, D.; Peng, Z. Overexpression of RBBP6, alone or combined with mutant TP53, is predictive of poor prognosis in colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.A.; Chen, Y.F.; Bao, Y.; Mahara, S.; Yatim, S.; Oguz, G.; Lee, P.L.; Feng, M.; Cai, Y.; Tan, E.Y.; et al. Hypoxic tumor microenvironment activates GLI2 via HIF-1alpha and TGF-beta2 to promote chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5990–E5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, J.; Lei, P.J.; Li, Q.L.; Chen, J.; Tang, S.B.; Xiao, Q.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Li, L.Y.; Wu, M. GLIS2 promotes colorectal cancer through repressing enhancer activation. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Lo, Y.H.; Chen, X.; Williams, C.S.; Donnelly, J.M.; Criss, Z.K., 2nd; Patel, S.; Butkus, J.M.; Dubrulle, J.; Finegold, M.J.; et al. Growth Factor-Independent 1 Is a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, C.; St-Jean, S.; Frechette, I.; Bergeron, D.; Rivard, N.; Boudreau, F. Identification of a novel promyelocytic leukemia zinc-finger isoform required for colorectal cancer cell growth and survival. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Q.; Wang, K.; Yan, D.W.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Li, M.X.; Wang, X.W.; Liu, J.; Peng, Z.H.; Li, G.X.; et al. Ciz1 is a novel predictor of survival in human colon cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, C.; Tang, X.; Sun, H.; Shao, Q.; Yang, X.; Qu, X. CIZ1 regulates the proliferation, cycle distribution and colony formation of RKO human colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thoma, O.M.; Neurath, M.F.; Waldner, M.J. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors and Their Therapeutic Potential in Colorectal Cancer Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 757120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, P.M.; Caicedo, A. Stemness in Cancer: Stem Cells, Cancer Stem Cells, and Their Microenvironment. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 5619472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, R.; Zhu, Z.; Ou, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, X.; Ding, Y.; Song, L.; et al. Jade family PHD finger 3 (JADE3) increases cancer stem cell-like properties and tumorigenicity in colon cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 428, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Moon, Y. Mucosal ribosomal stress-induced PRDM1 promotes chemoresistance via stemness regulation. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Xu, L.; Bi, W.; Ou, W.B. SALL4 Oncogenic Function in Cancers: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Relevance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Deng, R.; Wu, C.; Zhang, P.; Wu, K.; Shi, L.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Deng, M.; Gao, J.; et al. Inhibition of SALL4 suppresses carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer via regulating Gli1 expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10092–10101. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhang, X.; He, T.; Song, S.; Sun, S.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; et al. Expression and clinical significance of SALL4 and beta-catenin in colorectal cancer. J. Mol. Histol. 2016, 47, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Wang, F.; Han, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, B. The oncogenic role of LncRNA FAM83C-AS1 in colorectal cancer development by epigenetically inhibits SEMA3F via stabilizing EZH2. Aging 2020, 12, 20396–20412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; Dai, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Sheng, W.; Xu, Y. UPF1 promotes chemoresistance to oxaliplatin through regulation of TOP2A activity and maintenance of stemness in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, C.; Quiroz, A.; Benitez-Riquelme, D.; Riffo, E.; Castro, A.F.; Pincheira, R. SALL Proteins; Common and Antagonistic Roles in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Sohn, I.; Do, I.G.; Jang, J.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, I.H.; Park, J.O.; Park, Y.S.; Talasaz, A.; Lee, J.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of CD133-positive stem cells and prognostic value of survivin in colorectal cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2014, 11, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Nosho, K.; Ishigami, K.; Koide, H.; Mitsuhashi, K.; Okita, K.; Takemasa, I.; Imai, K.; Nakase, H. PRDM14 promotes malignant phenotype and correlates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Zang, F.; Zhang, S.J. RBCK1 contributes to chemoresistance and stemness in colorectal cancer (CRC). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassandri, M.; Smirnov, A.; Novelli, F.; Pitolli, C.; Agostini, M.; Malewicz, M.; Melino, G.; Raschella, G. Zinc-finger proteins in health and disease. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fedotova, A.A.; Bonchuk, A.N.; Mogila, V.A.; Georgiev, P.G. C2H2 Zinc Finger Proteins: The Largest but Poorly Explored Family of Higher Eukaryotic Transcription Factors. Acta Nat. 2017, 9, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munro, D.; Ghersi, D.; Singh, M. Two critical positions in zinc finger domains are heavily mutated in three human cancer types. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbehausen, C. Zinc finger domains as therapeutic targets for metal-based compounds—An update. Metallomics 2019, 11, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Aiba, I.; Chen, H.H.; Kuo, M.T. Effects of Cu(II) and cisplatin on the stability of Specific protein 1 (Sp1)-DNA binding: Insights into the regulation of copper homeostasis and platinum drug transport. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 161, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimberg, G.D.; Ok, K.; Neu, H.M.; Splan, K.E.; Michel, S.L.J. Cu(I) Disrupts the Structure and Function of the Nonclassical Zinc Finger Protein Tristetraprolin (TTP). Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 6838–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sievers, Q.L.; Petzold, G.; Bunker, R.D.; Renneville, A.; Slabicki, M.; Liddicoat, B.J.; Abdulrahman, W.; Mikkelsen, T.; Ebert, B.L.; Thoma, N.H. Defining the human C2H2 zinc finger degrome targeted by thalidomide analogs through CRBN. Science 2018, 362, eaat0572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, T.; Shi, S.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; Xu, D.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Xi, Y. A pan-cancer study of spalt-like transcription factors 1/2/3/4 as therapeutic targets. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 711, 109016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Bartom, E.; Marshall, S.; Rendleman, E.; Ryan, C.; Shilati, A.; Savas, J.; Chandel, N.; Shilatifard, A. beta-Catenin/Tcf7l2-dependent transcriptional regulation of GLUT1 gene expression by Zic family proteins in colon cancer. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax0698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satow, R.; Inagaki, S.; Kato, C.; Shimozawa, M.; Fukami, K. Identification of zinc finger protein of the cerebellum 5 as a survival factor of prostate and colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 2405–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, W.; Gao, X.; Kuang, F. Regulation between two alternative splicing isoforms ZNF148(FL) and ZNF148(DeltaN), and their roles in the apoptosis and invasion of colorectal cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essien, B.E.; Sundaresan, S.; Ocadiz-Ruiz, R.; Chavis, A.; Tsao, A.C.; Tessier, A.J.; Hayes, M.M.; Photenhauer, A.; Saqui-Salces, M.; Kang, A.J.; et al. Transcription Factor ZBP-89 Drives a Feedforward Loop of beta-Catenin Expression in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6877–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.H.; Liu, Q.Z.; Chang, W.; Xu, X.D.; Du, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.Q.; Zuo, Z.G.; Xing, J.J.; et al. Expression of ZNF148 in different developing stages of colorectal cancer and its prognostic value: A large Chinese study based on tissue microarray. Cancer 2013, 119, 2212–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Lin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lian, J. ZNF750 facilitates carcinogenesis via promoting the expression of long non-coding RNA CYTOR and influences pharmacotherapy response in colon adenocarcinoma. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2022, 23, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhang, X.; Lv, X. Zinc finger protein 750(ZNF750), negatively regulated by miR-17-5p, inhibits proliferation, motility and invasion of colonic cancer cells. J. Gene Med. 2020, 22, e3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z. Zinc finger antisense 1: A long noncoding RNA with complex roles in human cancers. Gene 2019, 688, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Jing, Y.M.; Lou, H.Z.; Lou, Q.A. Effect and mechanism of long non-coding RNA ZEB2-AS1 in the occurrence and development of colon cancer. Math Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 8109–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Chen, B. LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 Regulates Colorectal Cancer Cells by MiR-205/YAP1 Axis. Open. Med. 2020, 15, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iyer, A.S.; Shaik, M.R.; Raufman, J.-P.; Xie, G. The Roles of Zinc Finger Proteins in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210249
Iyer AS, Shaik MR, Raufman J-P, Xie G. The Roles of Zinc Finger Proteins in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):10249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210249
Chicago/Turabian StyleIyer, Aishwarya S., Mohammed Rifat Shaik, Jean-Pierre Raufman, and Guofeng Xie. 2023. "The Roles of Zinc Finger Proteins in Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 10249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210249
APA StyleIyer, A. S., Shaik, M. R., Raufman, J. -P., & Xie, G. (2023). The Roles of Zinc Finger Proteins in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 10249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210249







