Treatment Refractoriness in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Old and New Molecular Biomarkers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biomarkers of Refractoriness to Chemoimmunotherapy
2.1. IGHV Mutational Status
2.2. TP53 Disruption
2.3. BIRC3 Disruption
2.4. NOTCH1 Mutations
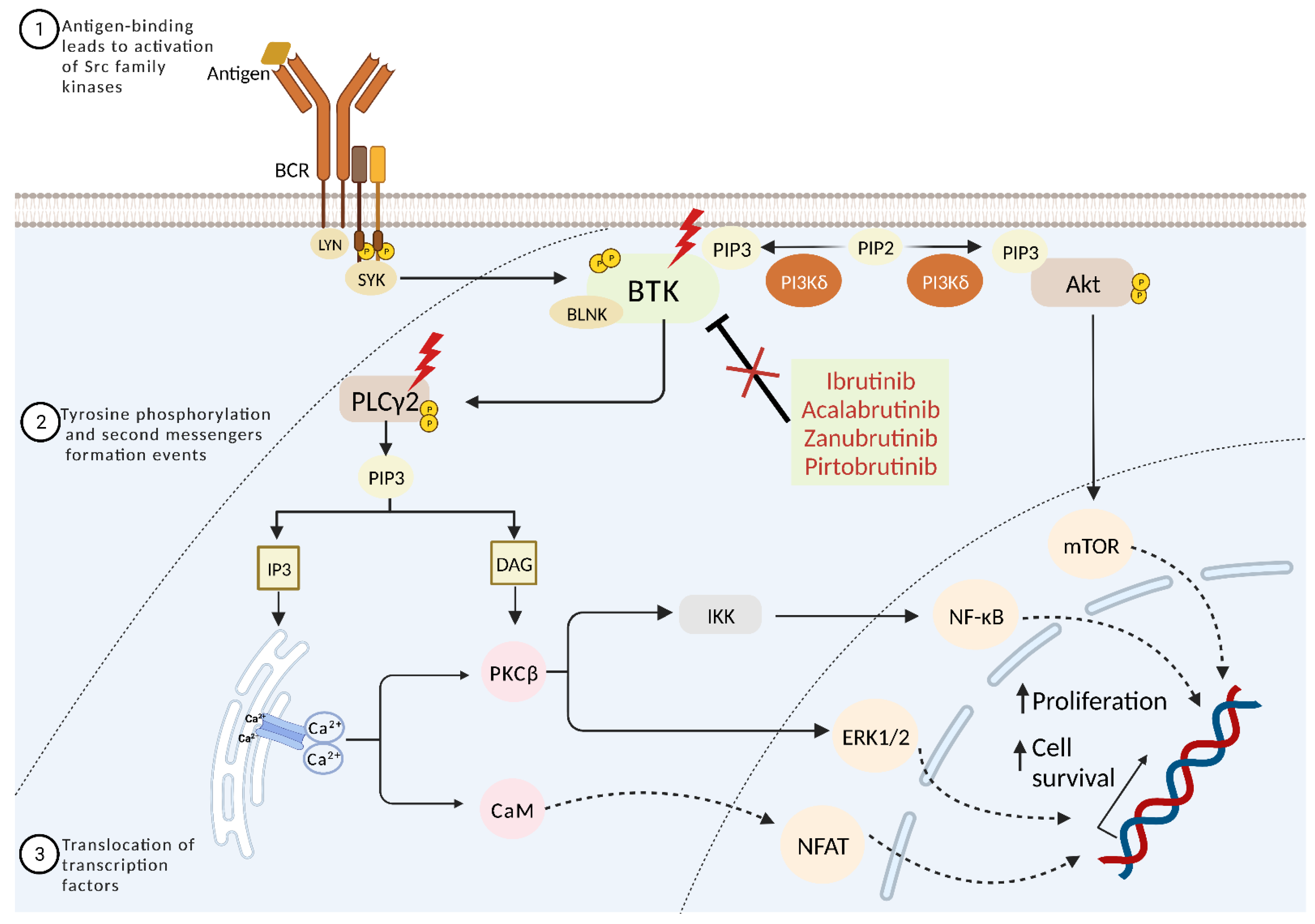
3. Biomarkers of Refractoriness to BTK Inhibitors
3.1. Refractoriness to First-Generation Covalent BTK Inhibitors
3.1.1. Primary Resistance to First-Generation Covalent BTK Inhibitors
3.1.2. Secondary Resistance to First-Generation Covalent BTK Inhibitors
3.2. Refractoriness to Second-Generation Covalent BTK Inhibitors
3.3. Strategies to Overcome Resistance to Covalent BTK Inhibitors
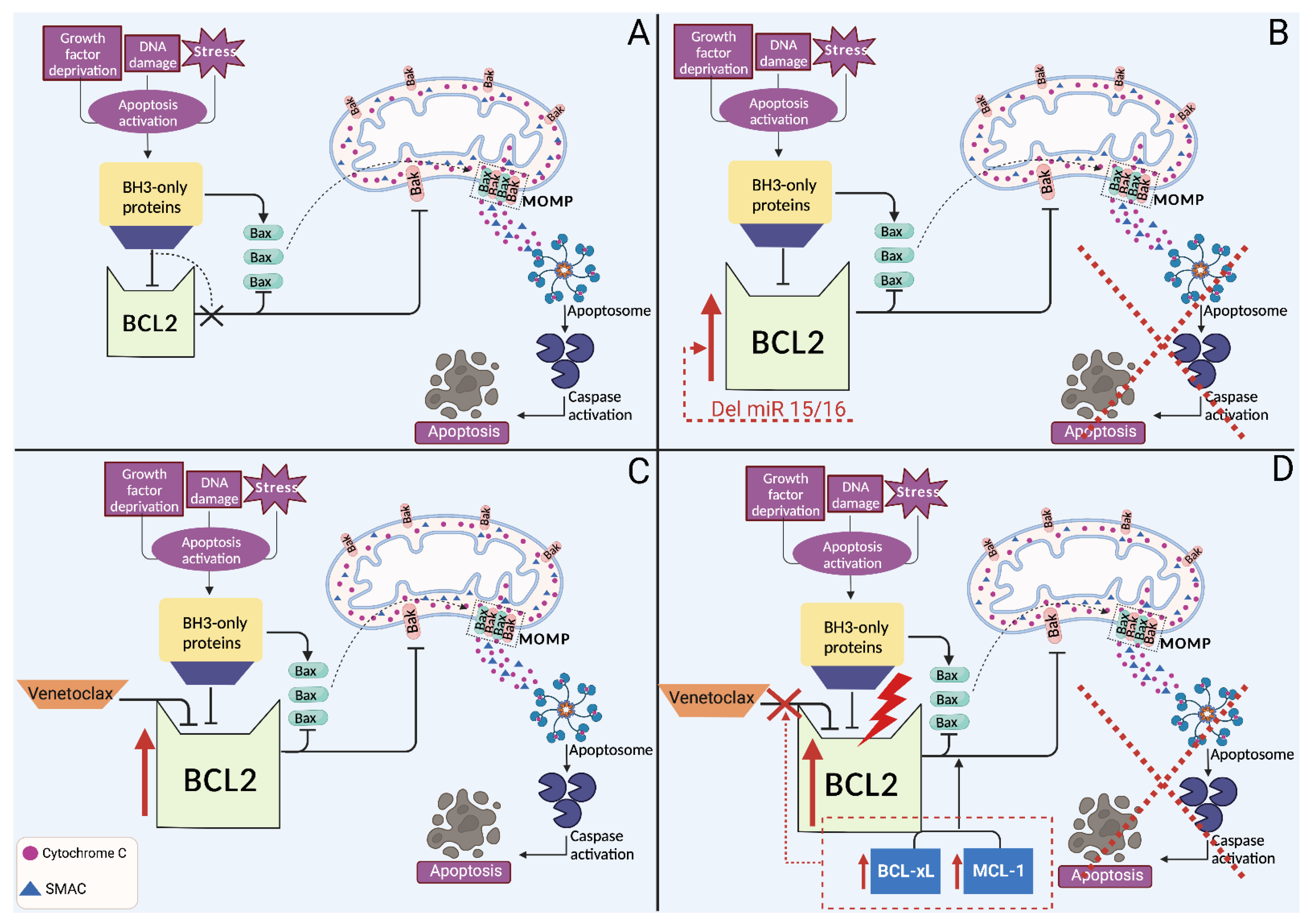
4. Biomarkers of Refractoriness to BCL2 Inhibitors
4.1. Primary Resistance to BCL2 Inhibitors
4.2. Secondary Resistance to BCL2 Inhibitors
4.3. Strategies to Overcome Resistance to BCL2 Inhibitors
5. Biomarkers of Refractoriness to Immunotherapy
5.1. Abnormal IL-10 Levels
5.2. Potential Biomarkers of Refractoriness to CAR-T Cells
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. Who Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, Revised, 4th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer Lyon: Lyon, France, 2017; Volume 2.
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, K.R. 1 Progress in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A historical perspective. Baillière’s Clin. Haematol. 1993, 6, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M.; Al-Sawaf, O. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2022 update on diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1679–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Kreuzer, K.-A.; Soosapilla, A.; Spacek, M.; Stehlikova, O.; Gambell, P.; McIver-Brown, N.; Villamor, N.; Psarra, K.; Arroz, M.; et al. Reproducible diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia by flow cytometry: An European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC) & European Society for Clinical Cell Analysis (ESCCA) Harmonisation project. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Cancer Stat Facts. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. 2023. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/clyl.html (accessed on 11 June 2023).
- Woyach, J.A. Management of relapsed/refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97 (Suppl. S2), S11–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolej, L. Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Therapeutic Challenge. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2016, 16, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binet, J.L.; Auquier, A.; Dighiero, G.; Chastang, C.; Piguet, H.; Goasguen, J.; Vaugier, G.; Potron, G.; Colona, P.; Oberling, F.; et al. A new prognostic classification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia derived from a multivariate survival analysis. Cancer 1981, 48, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.R.; Sawitsky, A.; Cronkite, E.P.; Chanana, A.D.; Levy, R.N.; Pasternack, B.S. Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1975, 46, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The International CLL-IPI Working Group. An international prognostic index for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL-IPI): A meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoluci, A.; Terzi di Bergamo, L.; Langerbeins, P.; Hoechstetter, M.A.; Herling, C.D.; De Paoli, L.; Delgado, J.; Rabe, K.G.; Gentile, M.; Doubek, M.; et al. International prognostic score for asymptomatic early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2020, 135, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman, M. Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Döhner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.; et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mouhssine, S.; Gaidano, G. Richter Syndrome: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Druggable Targets. Cancers 2022, 14, 4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Hanson, C.A.; Paietta, E.M.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; et al. Long-term outcomes for ibrutinib-rituximab and chemoimmunotherapy in CLL: Updated results of the E1912 trial. Blood 2022, 140, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Kay, N.E.; Hanson, C.A.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; et al. Ibrutinib–Rituximab or Chemoimmunotherapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorst, B.; Robak, T.; Montserrat, E.; Ghia, P.; Niemann, C.U.; Kater, A.P.; Gregor, M.; Cymbalista, F.; Buske, C.; Hillmen, P.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moia, R.; Dondolin, R.; De Propris, M.S.; Talotta, D.; Mouhssine, S.; Perutelli, F.; Reda, G.; Mattiello, V.; Rigolin, G.M.; Motta, M.; et al. Long-term benefit of IGHV mutated patients in a real-life multicenter cohort of FCR-treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravinetto, R.; Guenzi, P.D.; Massat, P.; Gaidano, G. Globalisation of clinical trials and ethics of benefit sharing. Lancet Haematol. 2014, 1, e54–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (Version 2.2023). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cll.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2023).
- Roeker, L.E.; Dreger, P.; Brown, J.R.; Lahoud, O.B.; Eyre, T.A.; Brander, D.M.; Skarbnik, A.; Coombs, C.C.; Kim, H.T.; Davids, M.; et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the era of novel agents. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 3977–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman, M.; Maloney, D.G. Immune Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Allogeneic Transplant, Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Therapy, and Beyond. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 35, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoluci, A.; Rossi, D. Genetic mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Impact on clinical treatment. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2019, 12, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, L.; Thorvaldsdottir, B.; Sutton, L.A.; Karakatsoulis, G.; Meggendorfer, M.; Parker, H.; Nadeu, F.; Brieghel, C.; Laidou, S.; Moia, R.; et al. Different prognostic impact of recurrent gene mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia depending on IGHV gene somatic hypermutation status: A study by ERIC in HARMONY. Leukemia 2023, 37, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, A.; Agathangelidis, A.; Sutton, L.-A.; Ghia, P.; Rosenquist, R.; Stamatopoulos, K. Immunogenetic Studies of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Revelations and Speculations about Ontogeny and Clinical Evolution. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4211–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, K.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Goede, V.; Herling, C.D.; Cramer, P.; Langerbeins, P.; von Tresckow, J.; Engelke, A.; Maurer, C.; et al. Long-term remissions after FCR chemoimmunotherapy in previously untreated patients with CLL: Updated results of the CLL8 trial. Blood 2016, 127, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estenfelder, S.; Tausch, E.; Robrecht, S.; Bahlo, J.; Goede, V.; Ritgen, M.; van Dongen, J.J.; Langerak, A.W.; Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Kneba, M.; et al. Gene Mutations and Treatment Outcome in the Context of Chlorambucil (Clb) without or with the Addition of Rituximab (R) or Obinutuzumab (GA-101, G)—Results of an Extensive Analysis of the Phase III Study CLL11 of the German CLL Study Group. Blood 2016, 128, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, S.; Lee, J.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Galanina, N.; Sukhanova, M.; Venkataraman, G.; Sharma, S.; Long, B.; Petras, K.; Theissen, M.; et al. Clonal evolution underlying leukemia progression and Richter transformation in patients with ibrutinib-relapsed CLL. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herling, C.D.; Abedpour, N.; Weiss, J.; Schmitt, A.; Jachimowicz, R.D.; Merkel, O.; Cartolano, M.; Oberbeck, S.; Mayer, P.; Berg, V.; et al. Clonal dynamics towards the development of venetoclax resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadeu, F.; Delgado, J.; Royo, C.; Baumann, T.; Stankovic, T.; Pinyol, M.; Jares, P.; Navarro, A.; Martín-García, D.; Beà, S.; et al. Clinical impact of clonal and subclonal TP53, SF3B1, BIRC3, NOTCH1, and ATM mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Monti, S.; Ciardullo, C.; Deambrogi, C.; Khiabanian, H.; Serra, R.; Bertoni, F.; et al. Integrated mutational and cytogenetic analysis identifies new prognostic subgroups in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baliakas, P.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Sutton, L.A.; Rossi, D.; Minga, E.; Villamor, N.; Larrayoz, M.; Kminkova, J.; Agathangelidis, A.; Davis, Z.; et al. Recurrent mutations refine prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, F.; Moia, R.; Favini, C.; Spaccarotella, E.; De Paoli, L.; Bruscaggin, A.; Spina, V.; Terzi-di-Bergamo, L.; Arruga, F.; Tarantelli, C.; et al. Biological and clinical implications of BIRC3 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Zhang, C.; Tandon, M.; Sinha, A.; Fink, A.M.; Robrecht, S.; Samoylova, O.; Liberati, A.M.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Opat, S.; et al. Venetoclax plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab for previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL14): Follow-up results from a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungström, V.; Cortese, D.; Young, E.; Pandzic, T.; Mansouri, L.; Plevova, K.; Ntoufa, S.; Baliakas, P.; Clifford, R.; Sutton, L.A.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing in relapsing chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Clinical impact of recurrent RPS15 mutations. Blood 2016, 127, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedetti, D.; Tissino, E.; Pozzo, F.; Bittolo, T.; Caldana, C.; Perini, C.; Martorelli, D.; Bravin, V.; D’Agaro, T.; Rossi, F.M.; et al. NOTCH1 mutations are associated with high CD49d expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Link between the NOTCH1 and the NF-κB pathways. Leukemia 2018, 32, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, G.; Rasi, S.; Rossi, D.; Trifonov, V.; Khiabanian, H.; Ma, J.; Grunn, A.; Fangazio, M.; Capello, D.; Monti, S.; et al. Analysis of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: Role of NOTCH1 mutational activation. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Offner, F.; Robak, T.; Janssens, A.; Govind Babu, K.; Kloczko, J.; Grosicki, S.; Mayer, J.; Panagiotidis, P.; Schuh, A.; Pettitt, A.; et al. A five-year follow-up of untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with ofatumumab and chlorambucil: Final analysis of the Complement 1 phase 3 trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfiglio, S.; Sutton, L.-A.; Ljungström, V.; Capasso, A.; Pandzic, T.; Weström, S.; Foroughi-Asl, H.; Skaftason, A.; Gellerbring, A.; Lyander, A.; et al. BTK and PLCG2 remain unmutated in one third of patients with CLL relapsing on ibrutinib. Blood Adv. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Mi, X.; Thompson, M.C.; Montoya, S.; Notti, R.Q.; Afaghani, J.; Durham, B.H.; Penson, A.; Witkowski, M.T.; Lu, S.X.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance to Noncovalent Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinquenel, A.; Fornecker, L.M.; Letestu, R.; Ysebaert, L.; Fleury, C.; Lazarian, G.; Dilhuydy, M.S.; Nollet, D.; Guieze, R.; Feugier, P.; et al. Prevalence of BTK and PLCG2 mutations in a real-life CLL cohort still on ibrutinib after 3 years: A FILO group study. Blood 2019, 134, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Furman, R.R.; Liu, T.M.; Ozer, H.G.; Zapatka, M.; Ruppert, A.S.; Xue, L.; Li, D.H.; Steggerda, S.M.; Versele, M.; et al. Resistance mechanisms for the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blombery, P.; Thompson, E.R.; Nguyen, T.; Birkinshaw, R.W.; Gong, J.N.; Chen, X.; McBean, M.; Thijssen, R.; Conway, T.; Anderson, M.A.; et al. Multiple BCL2 mutations cooccurring with Gly101Val emerge in chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression on venetoclax. Blood 2020, 135, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayappa, K.D.; Portell, C.A.; Gordon, V.L.; Capaldo, B.J.; Bekiranov, S.; Axelrod, M.J.; Brett, L.K.; Wulfkuhle, J.D.; Gallagher, R.I.; Petricoin, E.F.; et al. Microenvironmental agonists generate de novo phenotypic resistance to combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax in CLL and MCL. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guièze, R.; Liu, V.M.; Rosebrock, D.; Jourdain, A.A.; Hernández-Sánchez, M.; Martinez Zurita, A.; Sun, J.; Ten Hacken, E.; Baranowski, K.; Thompson, P.A.; et al. Mitochondrial Reprogramming Underlies Resistance to BCL-2 Inhibition in Lymphoid Malignancies. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 369–384.e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, J.R.; Liu, Y.; Alhakeem, S.S.; Eckenrode, J.M.; Marti, F.; Collard, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Shaaban, K.A.; Muthusamy, N.; Hildebrandt, G.C.; et al. Interleukin-10 suppression enhances T-cell antitumor immunity and responses to checkpoint blockade in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3188–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraietta, J.A.; Lacey, S.F.; Orlando, E.J.; Pruteanu-Malinici, I.; Gohil, M.; Lundh, S.; Boesteanu, A.C.; Wang, Y.; O’Connor, R.S.; Hwang, W.T.; et al. Determinants of response and resistance to CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, S.; Ma, S. Frontline Treatment for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL/SLL): Targeted Therapy vs. Chemoimmunotherapy. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2021, 16, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Fischer, K.; Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Fink, A.M.; Busch, R.; Mayer, J.; Hensel, M.; Hopfinger, G.; Hess, G.; von Grünhagen, U.; et al. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goede, V.; Fischer, K.; Busch, R.; Engelke, A.; Eichhorst, B.; Wendtner, C.M.; Chagorova, T.; de la Serna, J.; Dilhuydy, M.S.; Illmer, T.; et al. Obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in patients with CLL and coexisting conditions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dal Porto, J.M.; Gauld, S.B.; Merrell, K.T.; Mills, D.; Pugh-Bernard, A.E.; Cambier, J. B cell antigen receptor signaling 101. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 41, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizels, N. Immunoglobulin Gene Diversification. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Noia, J.M.; Neuberger, M.S. Molecular mechanisms of antibody somatic hypermutation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, F.; Dalla-Favera, R. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: From genetics to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, U.; Tu, Y.; Stolovitzky, G.A.; Mattioli, M.; Cattoretti, G.; Husson, H.; Freedman, A.; Inghirami, G.; Cro, L.; Baldini, L.; et al. Gene expression profiling of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia reveals a homogeneous phenotype related to memory B cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visentin, A.; Facco, M.; Gurrieri, C.; Pagnin, E.; Martini, V.; Imbergamo, S.; Frezzato, F.; Trimarco, V.; Severin, F.; Raggi, F.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Effect of IGHV Mutational Status and Load in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Focus on FCR and BR Treatments. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, 678–685.e674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, R.N.; Wasil, T.; Fais, F.; Ghiotto, F.; Valetto, A.; Allen, S.L.; Buchbinder, A.; Budman, D.; Dittmar, K.; Kolitz, J.; et al. Ig V Gene Mutation Status and CD38 Expression As Novel Prognostic Indicators in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Presented in part at the 40th Annual Meeting of The American Society of Hematology, held in Miami Beach, FL, December 4–8, 1998. Blood 1999, 94, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; Oscier, D.G.; Stevenson, F.K. Unmutated Ig VH Genes Are Associated With a More Aggressive Form of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Terzi-di-Bergamo, L.; De Paoli, L.; Cerri, M.; Ghilardi, G.; Chiarenza, A.; Bulian, P.; Visco, C.; Mauro, F.R.; Morabito, F.; et al. Molecular prediction of durable remission after first-line fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2015, 126, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Cramer, P.; Busch, R.; Böttcher, S.; Bahlo, J.; Schubert, J.; Pflüger, K.H.; Schott, S.; Goede, V.; Isfort, S.; et al. Bendamustine in combination with rituximab for previously untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A multicenter phase II trial of the German Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3209–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, M.; Zirlik, K.; Ciolli, S.; Mauro, F.R.; Di Renzo, N.; Mastrullo, L.; Angrilli, F.; Molica, S.; Tripepi, G.; Giordano, A.; et al. Combination of bendamustine and rituximab as front-line therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Multicenter, retrospective clinical practice experience with 279 cases outside of controlled clinical trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 60, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Hillmen, P.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; Barr, P.M.; et al. Long-term follow-up of the RESONATE phase 3 trial of ibrutinib vs ofatumumab. Blood 2019, 133, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cull, G.; Burger, J.A.; Opat, S.; Gottlieb, D.; Verner, E.; Trotman, J.; Marlton, P.; Munoz, J.; Johnston, P.; Simpson, D.; et al. Zanubrutinib for treatment-naïve and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Long-term follow-up of the phase I/II AU-003 study. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Efficacy and safety in a 4-year follow-up of the ELEVATE-TN study comparing acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in treatment-naïve chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; Synnott, N.C.; Crown, J. Mutant p53 as a target for cancer treatment. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 83, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norbury, C.J.; Zhivotovsky, B. DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2797–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buccheri, V.; Barreto, W.G.; Fogliatto, L.M.; Capra, M.; Marchiani, M.; Rocha, V. Prognostic and therapeutic stratification in CLL: Focus on 17p deletion and p53 mutation. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 2269–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G. The clinical implications of gene mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malcikova, J.; Tausch, E.; Rossi, D.; Sutton, L.A.; Soussi, T.; Zenz, T.; Kater, A.P.; Niemann, C.U.; Gonzalez, D.; Davi, F.; et al. ERIC recommendations for TP53 mutation analysis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia—Update on methodological approaches and results interpretation. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarnegar, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Mahoney, D.J.; Dempsey, P.W.; Cheung, H.H.; He, J.; Shiba, T.; Yang, X.; Yeh, W.C.; Mak, T.W.; et al. Noncanonical NF-kappaB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, R.; Niu, M.Y.; Pratt, M.A. cIAP2 represses IKKα/β-mediated activation of MDM2 to prevent p53 degradation. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 4009–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asslaber, D.; Wacht, N.; Leisch, M.; Qi, Y.; Maeding, N.; Hufnagl, C.; Jansko, B.; Zaborsky, N.; Villunger, A.; Hartmann, T.N.; et al. BIRC3 Expression Predicts CLL Progression and Defines Treatment Sensitivity via Enhanced NF-κB Nuclear Translocation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tausch, E.; Schneider, C.; Robrecht, S.; Zhang, C.; Dolnik, A.; Bloehdorn, J.; Bahlo, J.; Al-Sawaf, O.; Ritgen, M.; Fink, A.-M.; et al. Prognostic and predictive impact of genetic markers in patients with CLL treated with obinutuzumab and venetoclax. Blood 2020, 135, 2402–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Robak, T.; Demirkan, F.; Bairey, O.; Moreno, C.; Simpson, D.; Munir, T.; Stevens, D.A.; Dai, S.; Cheung, L.W.K.; et al. Outcomes of First-Line Ibrutinib in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and High-Risk Genomic Features with up to 6.5 Years Follow-up: Integrated Analysis of Two Phase 3 Studies (RESONATE-2 and iLLUMINATE). Blood 2020, 136, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moia, R.; Gaidano, G.; Rossi, D. Reply to Aron P. Kater et al. Haematologica 2020, 105, e384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woyach, J.A.; Barr, P.M.; Kipps, T.J.; Barrientos, J.C.; Ahn, I.E.; Ghia, P.; Girardi, V.; Hsu, E.; Jermain, M.; Burger, J.A. Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma Receiving Ibrutinib for ≥5 Years in the RESONATE-2 Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobry, C.; Oh, P.; Aifantis, I. Oncogenic and tumor suppressor functions of Notch in cancer: It’s NOTCH what you think. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1931–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosati, E.; Baldoni, S.; De Falco, F.; Del Papa, B.; Dorillo, E.; Rompietti, C.; Albi, E.; Falzetti, F.; Di Ianni, M.; Sportoletti, P. NOTCH1 Aberrations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Ianni, M.; Baldoni, S.; Rosati, E.; Ciurnelli, R.; Cavalli, L.; Martelli, M.F.; Marconi, P.; Screpanti, I.; Falzetti, F. A new genetic lesion in B-CLL: A NOTCH1 PEST domain mutation. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 146, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, E.; Sabatini, R.; Rampino, G.; Tabilio, A.; Di Ianni, M.; Fettucciari, K.; Bartoli, A.; Coaccioli, S.; Screpanti, I.; Marconi, P. Constitutively activated Notch signaling is involved in survival and apoptosis resistance of B-CLL cells. Blood 2009, 113, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Robak, T.; Janssens, A.; Babu, K.G.; Kloczko, J.; Grosicki, S.; Doubek, M.; Panagiotidis, P.; Kimby, E.; Schuh, A.; et al. Chlorambucil plus ofatumumab versus chlorambucil alone in previously untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (COMPLEMENT 1): A randomised, multicentre, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzo, F.; Bittolo, T.; Arruga, F.; Bulian, P.; Macor, P.; Tissino, E.; Gizdic, B.; Rossi, F.M.; Bomben, R.; Zucchetto, A.; et al. NOTCH1 mutations associate with low CD20 level in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Evidence for a NOTCH1 mutation-driven epigenetic dysregulation. Leukemia 2016, 30, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.E.; Brown, J.R. Targeting Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase in CLL. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 687458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal Singh, S.; Dammeijer, F.; Hendriks, R.W. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A. Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Present and Future. Cancer J. 2019, 25, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Wiestner, A. Targeting B cell receptor signalling in cancer: Preclinical and clinical advances. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Chiorazzi, N. B cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burger, J.A.; Tedeschi, A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Ghia, P.; Bairey, O.; Hillmen, P.; Bartlett, N.L.; Li, J.; et al. Ibrutinib as Initial Therapy for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Kay, N.E.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Ibrutinib versus ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Z.; Scheerens, H.; Li, S.J.; Schultz, B.E.; Sprengeler, P.A.; Burrill, L.C.; Mendonca, R.V.; Sweeney, M.D.; Scott, K.C.; Grothaus, P.G.; et al. Discovery of selective irreversible inhibitors for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Chem. Med. Chem. 2007, 2, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarini, A.; Chiaretti, S.; Tavolaro, S.; Maggio, R.; Peragine, N.; Citarella, F.; Ricciardi, M.R.; Santangelo, S.; Marinelli, M.; De Propris, M.S.; et al. BCR ligation induced by IgM stimulation results in gene expression and functional changes only in IgV H unmutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. Blood 2008, 112, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganatra, S.; Sharma, A.; Shah, S.; Chaudhry, G.M.; Martin, D.T.; Neilan, T.G.; Mahmood, S.S.; Barac, A.; Groarke, J.D.; Hayek, S.S.; et al. Ibrutinib-Associated Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, V.; Swami, A. Ibrutinib in CLL: A focus on adverse events, resistance, and novel approaches beyond ibrutinib. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holohan, C.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Wang, Y.L. Prognostic and Predictive Molecular Biomarkers in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.I.E.; Burger, J.A. Resistance Mutations to BTK Inhibitors Originate From the NF-κB but Not From the PI3K-RAS-MAPK Arm of the B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 689472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, E.; Cymbalista, F.; Ghia, P.; Jäger, U.; Pospisilova, S.; Rosenquist, R.; Schuh, A.; Stilgenbauer, S. TP53 aberrations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An overview of the clinical implications of improved diagnostics. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1956–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maddocks, K.J.; Ruppert, A.S.; Lozanski, G.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Abruzzo, L.; Lozanski, A.; Davis, M.; Gordon, A.; Smith, L.L.; et al. Etiology of Ibrutinib Therapy Discontinuation and Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, I.E.; Tian, X.; Ipe, D.; Cheng, M.; Albitar, M.; Tsao, L.C.; Zhang, L.; Ma, W.; Herman, S.E.M.; Gaglione, E.M.; et al. Prediction of Outcome in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treated With Ibrutinib: Development and Validation of a Four-Factor Prognostic Model. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, T.G.; Kyung, D.; O’Brien, S. Mechanisms of ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and alternative treatment strategies. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2020, 13, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhoda, S.; Vistarop, A.; Wang, Y.L. Resistance to Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibition in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Guo, A.; Lu, P.; Ma, J.; Coleman, M.; Wang, Y.L. Functional characterization of BTK(C481S) mutation that confers ibrutinib resistance: Exploration of alternative kinase inhibitors. Leukemia 2015, 29, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Zhong, Y.; Lozanski, A.; Lozanski, G.; Dong, S.; Strattan, E.; Lehman, A.; Zhang, X.; Jones, J.A.; et al. Hypermorphic mutation of phospholipase C, γ2 acquired in ibrutinib-resistant CLL confers BTK independency upon B-cell receptor activation. Blood 2015, 126, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, I.E.; Underbayev, C.; Albitar, A.; Herman, S.E.; Tian, X.; Maric, I.; Arthur, D.C.; Wake, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Guinn, D.; Lehman, A.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, A.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Coleman, J.; Jones, D.; et al. BTK(C481S)-Mediated Resistance to Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burger, J.A.; Landau, D.A.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Bozic, I.; Zhang, H.; Sarosiek, K.; Wang, L.; Stewart, C.; Fan, J.; Hoellenriegel, J.; et al. Clonal evolution in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia developing resistance to BTK inhibition. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrd, J.C.; Hillmen, P.; Ghia, P.; Kater, A.P.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Furman, R.R.; O’Brien, S.; Yenerel, M.N.; Illés, A.; Kay, N.; et al. Acalabrutinib Versus Ibrutinib in Previously Treated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results of the First Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3441–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; Jurczak, W.; Kaźmierczak, M.; Lamanna, N.; O’Brien, S.M.; Tam, C.S.; Qiu, L.; Zhou, K.; et al. Zanubrutinib or Ibrutinib in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, K.; Bhat, S.A.; Grever, M.R.; Lozanski, A.; Doong, T.-J.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, G.; Jones, D.; et al. Resistance to Acalabrutinib in CLL Is Mediated Primarily By BTK Mutations. Blood 2019, 134, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handunnetti, S.M.; Tang, C.P.S.; Nguyen, T.; Zhou, X.; Thompson, E.; Sun, H.; Xing, H.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.; Sutton, L.A.; et al. BTK Leu528Trp—A Potential Secondary Resistance Mechanism Specific for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treated with the Next Generation BTK Inhibitor Zanubrutinib. Blood 2019, 134, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.A.; Woyach, J.A. Targeting BTK in CLL: Beyond Ibrutinib. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2019, 14, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puła, B.; Gołos, A.; Górniak, P.; Jamroziak, K. Overcoming Ibrutinib Resistance in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2019, 11, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frustaci, A.M.; Deodato, M.; Zamprogna, G.; Cairoli, R.; Montillo, M.; Tedeschi, A. Next Generation BTK Inhibitors in CLL: Evolving Challenges and New Opportunities. Cancers 2023, 15, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Shah, N.N.; Jurczak, W.; Cheah, C.Y.; Pagel, J.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Fakhri, B.; Eyre, T.A.; Lamanna, N.; Patel, M.R.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (BRUIN): A phase 1/2 study. Lancet 2021, 397, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blombery, P.; Thompson, E.R.; Lew, T.E.; Tiong, I.S.; Bennett, R.; Cheah, C.Y.; Lewis, K.L.; Handunnetti, S.M.; Tang, C.P.S.; Roberts, A.; et al. Enrichment of BTK Leu528Trp mutations in patients with CLL on zanubrutinib: Potential for pirtobrutinib cross-resistance. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 5589–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awan, F.T.; Thirman, M.J.; Patel-Donnelly, D.; Assouline, S.; Rao, A.V.; Ye, W.; Hill, B.; Sharman, J.P. Entospletinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia previously treated with B-cell receptor inhibitors: Results of a phase 2 study. Leuk Lymphoma 2019, 60, 1972–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buhimschi, A.D.; Armstrong, H.A.; Toure, M.; Jaime-Figueroa, S.; Chen, T.L.; Lehman, A.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Johnson, A.J.; Byrd, J.C.; Crews, C.M. Targeting the C481S Ibrutinib-Resistance Mutation in Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Using PROTAC-Mediated Degradation. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 3564–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, A.R.; Wierda, W.G.; Ai, W.Z.; Flinn, I.W.; Tees, M.; Patel, M.R.; Patel, K.; O’Brien, S.; Bond, D.A.; Roeker, L.E.; et al. NX-2127-001, a First-in-Human Trial of NX-2127, a Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase-Targeted Protein Degrader, in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and B-Cell Malignancies. Blood 2022, 140, 2329–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, I.; Bodo, J.; Hill, B.T.; Hsi, E.D.; Almasan, A. Targeting BCL-2 in B-cell malignancies and overcoming therapeutic resistance. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruefli-Brasse, A.; Reed, J.C. Therapeutics targeting Bcl-2 in hematological malignancies. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 3643–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasica, M.; Anderson, M.A. Review of Venetoclax in CLL, AML and Multiple Myeloma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Assouline, S.; Owen, C.; Gerecitano, J.; Robak, T.; De la Serna, J.; et al. Venetoclax-Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, F.; Landau, D.A. A BAX door to venetoclax resistance. Blood 2022, 139, 1124–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D.A.; Carter, S.L.; Stojanov, P.; McKenna, A.; Stevenson, K.; Lawrence, M.S.; Sougnez, C.; Stewart, C.; Sivachenko, A.; Wang, L.; et al. Evolution and impact of subclonal mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cell 2013, 152, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutierrez, C.; Wu, C.J. Clonal dynamics in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3759–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guièze, R.; Wu, C.J. Genomic and epigenomic heterogeneity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2015, 126, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blombery, P.; Anderson, M.A.; Gong, J.N.; Thijssen, R.; Birkinshaw, R.W.; Thompson, E.R.; Teh, C.E.; Nguyen, T.; Xu, Z.; Flensburg, C.; et al. Acquisition of the Recurrent Gly101Val Mutation in BCL2 Confers Resistance to Venetoclax in Patients with Progressive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tausch, E.; Close, W.; Dolnik, A.; Bloehdorn, J.; Chyla, B.; Bullinger, L.; Döhner, H.; Mertens, D.; Stilgenbauer, S. Venetoclax resistance and acquired BCL2 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2019, 104, e434–e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blombery, P. Mechanisms of intrinsic and acquired resistance to venetoclax in B-cell lymphoproliferative disease. Leuk Lymphoma 2020, 61, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, E.M.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Choi, M.Y.; Quijada-Álamo, M.; Chu, E.; Widhopf, G.F., 2nd; Kipps, T.J. High expression level of ROR1 and ROR1-signaling associates with venetoclax resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorcari, S.; Maffei, R.; Atene, C.G.; Mesini, N.; Maccaferri, M.; Leonardi, G.; Martinelli, S.; Paolini, A.; Nasillo, V.; Debbia, G.; et al. Notch2 Increases the Resistance to Venetoclax-Induced Apoptosis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia B Cells by Inducing Mcl-1. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 777587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, V.S.; Lew, T.E.; Handunnetti, S.M.; Blombery, P.; Nguyen, T.; Westerman, D.A.; Kuss, B.J.; Tam, C.S.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; et al. BTK inhibitor therapy is effective in patients with CLL resistant to venetoclax. Blood 2020, 135, 2266–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, A.R.; Roeker, L.E.; Jacobs, R.; Hill, B.T.; Lamanna, N.; Brander, D.; Shadman, M.; Ujjani, C.S.; Yazdy, M.S.; Perini, G.F.; et al. Assessment of the Efficacy of Therapies Following Venetoclax Discontinuation in CLL Reveals BTK Inhibition as an Effective Strategy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3589–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lew, T.E.; Anderson, M.A.; Lin, V.S.; Handunnetti, S.M.; Came, N.A.; Blombery, P.; Westerman, D.A.; Wall, M.; Tam, C.S.; Roberts, A.W.; et al. Undetectable peripheral blood MRD should be the goal of venetoclax in CLL, but attainment plateaus after 24 months. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, G.; Kaestner, C.L.; Licht, J.D.; Bennett, R.L. Targeting epigenetic mechanisms to overcome venetoclax resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 119047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrà, G.; Nicoli, P.; Lingua, M.F.; Maffeo, B.; Cartellà, A.; Circosta, P.; Brancaccio, M.; Parvis, G.; Gaidano, V.; Guerrasio, A.; et al. Inhibition of bromodomain and extra-terminal proteins increases sensitivity to venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, X.; Sarkar, A.; Kismali, G.; Aslan, B.; Ayres, M.; Iles, L.R.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Long, J.P.; Bertilaccio, M.T.S.; et al. AMG-176, an Mcl-1 Antagonist, Shows Preclinical Efficacy in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3856–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillman, R.O. Cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2011, 26, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perutelli, F.; Jones, R.; Griggio, V.; Vitale, C.; Coscia, M. Immunotherapeutic Strategies in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Advances and Challenges. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 837531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggio, V.; Perutelli, F.; Salvetti, C.; Boccellato, E.; Boccadoro, M.; Vitale, C.; Coscia, M. Immune Dysfunctions and Immune-Based Therapeutic Interventions in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayad, L.; Keating, M.J.; Reuben, J.M.; O’Brien, S.; Lee, B.-N.; Lerner, S.; Kurzrock, R. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Correlation with phenotypic characteristics and outcome. Blood 2001, 97, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alhakeem, S.S.; McKenna, M.K.; Oben, K.Z.; Noothi, S.K.; Rivas, J.R.; Hildebrandt, G.C.; Fleischman, R.A.; Rangnekar, V.M.; Muthusamy, N.; Bondada, S. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Derived IL-10 Suppresses Antitumor Immunity. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 4180–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanna, B.S.; Llaó-Cid, L.; Iskar, M.; Roessner, P.M.; Klett, L.C.; Wong, J.K.L.; Paul, Y.; Ioannou, N.; Öztürk, S.; Mack, N.; et al. Interleukin-10 receptor signaling promotes the maintenance of a PD-1(int) TCF-1(+) CD8(+) T cell population that sustains anti-tumor immunity. Immunity 2021, 54, 2825–2841.e2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagala, M.; Ysebaert, L.; Ligat, L.; Lopez, F.; Fournié, J.J.; Laurent, C.; Poupot, M. IL-10 Rescues CLL Survival through Repolarization of Inflammatory Nurse-like Cells. Cancers 2021, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Xu, A.; Xu, J. Roles of PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: Signaling, Cancer, and Beyond. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1248, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flies, D.B.; Sandler, B.J.; Sznol, M.; Chen, L. Blockade of the B7-H1/PD-1 pathway for cancer immunotherapy. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2011, 84, 409–421. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Brusa, D.; Serra, S.; Coscia, M.; Rossi, D.; D’Arena, G.; Laurenti, L.; Jaksic, O.; Fedele, G.; Inghirami, G.; Gaidano, G.; et al. The PD-1/PD-L1 axis contributes to T-cell dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2013, 98, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; LaPlant, B.R.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Leis, J.F.; He, R.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Sinha, S.; Le-Rademacher, J.; Feldman, A.L.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood 2017, 129, 3419–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Riddell, S.R. Engineering CAR-T cells: Design concepts. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miliotou, A.N.; Papadopoulou, L.C. CAR T-cell Therapy: A New Era in Cancer Immunotherapy. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2018, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, M.; Abken, H. TRUCKs: The fourth generation of CARs. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2015, 15, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorovic, Z.; Todorovic, D.; Markovic, V.; Ladjevac, N.; Zdravkovic, N.; Djurdjevic, P.; Arsenijevic, N.; Milovanovic, M.; Arsenijevic, A.; Milovanovic, J. CAR T Cell Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Successes and Shortcomings. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3647–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Rivière, I.; Gonen, M.; Wang, X.; Sénéchal, B.; Curran, K.J.; Sauter, C.; Wang, Y.; Santomasso, B.; Mead, E.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of CD19 CAR Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riches, J.C.; Ramsay, A.G.; Gribben, J.G. Immune dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: The role for immunotherapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 3389–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.J.; Lucien, F.; Sakemura, R.; Boysen, J.C.; Kim, Y.; Horvei, P.; Manriquez Roman, C.; Hansen, M.J.; Tapper, E.E.; Siegler, E.L.; et al. Leukemic extracellular vesicles induce chimeric antigen receptor T cell dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalabi, H.; Kraft, I.L.; Wang, H.W.; Yuan, C.M.; Yates, B.; Delbrook, C.; Zimbelman, J.D.; Giller, R.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Sequential loss of tumor surface antigens following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2018, 103, e215–e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachonikola, E.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Chatzidimitriou, A. T Cells in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Two-Edged Sword. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 612244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M.; Herishanu, Y.; Katz, B.Z.; Dezorella, N.; Sun, C.; Kay, S.; Polliack, A.; Avivi, I.; Wiestner, A.; Perry, C. Lymphocyte activation gene 3: A novel therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2017, 102, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.H.; Li, W.; Dong, H.; Han, F. Current state of NK cell-mediated immunotherapy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1077436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, L.; Santos, S.; Vesga, M.A.; Anguita, J.; Martin-Ruiz, I.; Carrascosa, T.; Juan, M.; Eguizabal, C. Adult peripheral blood and umbilical cord blood NK cells are good sources for effective CAR therapy against CD19 positive leukemic cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fürstenau, M.; Eichhorst, B. Novel Agents in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: New Combination Therapies and Strategies to Overcome Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biomarker | Prevalence before Treatment | Prevalence at Progression | Mechanism of Resistance | Predictive Value | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unmutated IGHV gene | ~40% | 70–80% | Increased BCR signaling capacity | Poor response to CIT | [24,25,26] |
| Del(17p) | 5% | ~30% | Genomic instability, survival advantage, and reduced DNA damage response | Poor response to CIT, BTKi, and BCL2i | [24,25,27,28,29,30] |
| TP53 mutations | 7% | 30–40% | Genomic instability, survival advantage, and reduced DNA damage response | Poor response to CIT, BTKi, and BCL2i | [24,25,27,28,29,30] |
| BIRC3 mutations | 2–6% | ~8% | Upregulation of non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway | Poor response to CIT | [24,31,32,33,34,35,36] |
| NOTCH1 mutations | 8–10% | 30% | Transcriptional activation of cell survival and proliferation and reduced expression of CD20 | Poor response to CIT and anti-CD20 mAbs | [24,25,27,37,38,39] |
| BTK point mutations of C481: C481S/R/Y/G | N/A | ~50% | Reduced affinity for covalent BTKi | Poor response to covalent BTKi | [40] |
| BTK point mutations of the tyrosine kinase domain: L528W, V416L, T474I, M437R, A428D | N/A | ~16% | Binding impairment of non-covalent BTKi | Poor response to covalent and non-covalent BTKi | [41] |
| PLCG2 mutations: R665W, L845G, C849R, D993H | N/A | 13% | Constitutively active PLCγ2 | Poor response to BTKi | [42,43] |
| BCL2 mutations: G101V, D103Y, F104I | N/A | ~15% | Binding impairment of BCL2is | Poor response to BCL2i | [44] |
| Upregulation of MCL-1 and/or BCL-xL | N/A | N/A | Enhanced apoptosis evasion | Poor response to BCL2i | [45,46] |
| High serum [IL-10] | N/A | N/A | Reduced T cell response through IL-10R stimulation | Poor response to PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors | [47] |
| Low serum [IL-6] | N/A | N/A | CAR-T cell exhaustion due to defective IL-6R stimulation | Poor response to CAR-T cells | [48] |
| Low levels of CD27+CD45RO− CD8+ T cells | N/A | N/A | Reduced population of active CAR-T cells | Poor response to CAR-T cells | [48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maher, N.; Mouhssine, S.; Matti, B.F.; Alwan, A.F.; Gaidano, G. Treatment Refractoriness in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Old and New Molecular Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210374
Maher N, Mouhssine S, Matti BF, Alwan AF, Gaidano G. Treatment Refractoriness in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Old and New Molecular Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):10374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210374
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaher, Nawar, Samir Mouhssine, Bassam Francis Matti, Alaa Fadhil Alwan, and Gianluca Gaidano. 2023. "Treatment Refractoriness in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Old and New Molecular Biomarkers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 10374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210374
APA StyleMaher, N., Mouhssine, S., Matti, B. F., Alwan, A. F., & Gaidano, G. (2023). Treatment Refractoriness in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Old and New Molecular Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 10374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210374






