Metabolomic Profile and Its Correlation with the Plasmatic Levels of Losartan, EXP3174 and Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Participants’ Characteristics
2.2. Analytical and Bioanalytical Validation
2.3. NMR Metabolomics
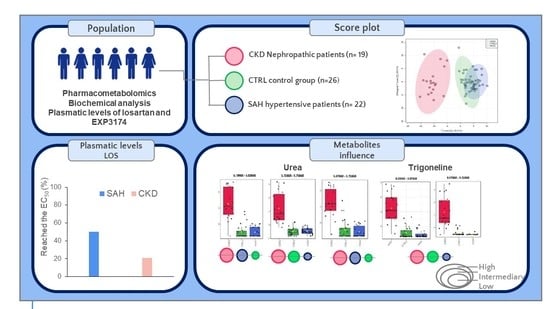
2.3.1. NMR of CTRL vs. SAH vs. CKD Groups
2.3.2. NMR of CRTL vs. CKD Groups
2.3.3. NMR of SAH vs. CKD Groups
2.3.4. NMR of CKA vs. CKN Groups
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Sample Preparation for UHPLC-ToF-MS Plasmatic Quantification
4.3. Sample Preparation and Acquisition of 1H NMR Spectra
4.4. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
4.5. Statistic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barroso, W.K.S.; Rodrigues, C.I.S.; Bortolotto, L.A.; Mota-Gomes, M.A.; Brandão, A.A.; Feitosa, A.D.M.; Machado, C.A.; Poli-de-Figueiredo, C.E.; Amodeo, C.; Mion Júnior, D.; et al. Diretrizes Brasileiras de Hipertensão Arterial—2020. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2021, 116, 516–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.G.; Aquino, M.L.A.; Brito, A.D.L.; Medeiros, C.C.M.; Simões, M.O.S.; Teixeira, A. Arterial hypertension in the elderly—Prevalent disease in this population: An integrative review. Braz. J. Dev. 2020, 6, 22590–22598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.N.; Zanella, M.T.; Kohlman, O.; Ribeiro, A.B. Treating diabetes and hypertension in the obese patient. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2002, 46, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.P.T. Sistema Renina Angiotensina, Para Além da Hipertensão Arterial. Master´s Thesis, Universidade de Fernando Pessoa, Porto, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Caixeta Neto, A.G.; Pereira, R.M.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Ribas, L.F. Comparação da tolerância e da eficácia terapêutica entre dois bloqueadores do receptor de angiotensina II no tratamento da hipertensão arterial sistêmica. Rev. De Trab. Acadêmicos–Universo Belo Horiz. 2017, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Júnior, J.M.V.; Suassuna, J.H.R. O acometimento renal na hipertensão arterial e diabetes mellitus tipo 2: Como identificar e prevenir–A visão do nefrologista. Rev. Hosp. Univ. Pedro Ernesto 2013, 12 (Suppl. S1), 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Van Buren, P.N.; Toto, R. Hypertension in diabetic nephropathy: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and management. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011, 18, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.I.S.C.R.; Almeida, F.A. Hipertensão arterial resistente. In Tratado de Nefrologia; Moura, L.R.R., Alves, M.A.R., Santos, D.R., Pecoits Filho, R., Eds.; Atheneu: São Paulo, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, J.I.S. Nefrotoxicidade Induzida por Fármacos: Caracterização da Realidade Hospitalar, Medidas Preventivas e Oportunidades de Intervenção. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dessì, A. La metabolomica in pediatria: Unascienza in continua evoluzione. INDICEN 2016, 183, 250. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Tan, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Ouyang, D.; et al. 1H NMR based pharmacometabolomics analysis of metabolic phenotype on predicting metabolism characteristics of losartan in healthy volunteers. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1095, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, T.; Horinouchi, A.; Morikawa, Y.; Tonomura, Y.; Minami, K.; Ono, A.; Yamate, J.; Yamada, H.; Ohno, Y.; Urushidani, T. Identification of metabolomic biomarkers for drug-induced acute kidney injury in rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtawa, M.; Takayama, F.; Saitoh, K.; Yoshinaga, T.; Nakashima, M. Pharmacokinetics and biochemical efficacy after single and multiple oral administration of losartan, an orally active nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist, in humans. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1993, 35, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, A.C.; Jiménez, B.; Schäfer, H.; Humpfer, E.; Spraul, M.; Lewis, M.R.; Pearce, J.T.M.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Precision high-throughput proton NMR spectroscopy of human urine, serum, and plasma for large-scale metabolic phenotyping. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9887–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignoli, A.; Ghini, V.; Meoni, G.; Licari, C.; Takis, P.G.; Tenori, L.; Turano, P.; Luchinat, C. High-throughput metabolomics by 1D NMR. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 968–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.; Carey, R.; Aronow, W.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, D.; Chellini, P.; Leite, J. Analysis of the urea and creatinine concentrations in serum and plasma with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and sodium citrate. Rev. Bras. Anal. Clin. 2017, 10, 2448–3877. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsztajn, G.M.; Bastos, M.G.; Andriolo, A. Dia Mundial do Rim 2011 Proteinúria e creatinina sérica: Testes essenciais para diagnóstico de doença renal crônica. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2011, 47, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- James, P.A.; Oparil, S.; Carter, B.L.; Cushman, W.C.; Dennison-Himmelfarb, C.; Handler, J.; Lackland, D.T.; LeFevre, M.L.; MacKenzie, T.D.; Ogedegbe, O.; et al. Diretriz baseada em evidências de 2014 para o manejo da hipertensão em adultos: Relatório dos membros do painel nomeados para o Oitavo Comitê Nacional Conjunto (JNC 8). JAMA 2014, 311, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.S.; Mitchell, G.F. Aging, arterial function, and systolic hypertension. In Hypertension Primer: The Essentials of High Blood Pressure, 4th ed.; Izzo, J.L., Sica, D.A., Black, H.R., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Thomé, F.S.; Sesso, R.C.; Lopes, A.A.; Lugon, J.R.; Martins, C.T. Inquérito brasileiro de diálise crônica 2017. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2019, 41, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, L.A. Hipertensão arterial e insuficiência renal crônica. Ver. Bras. Hipertens. 2008, 15, 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Magro, M.C.D.S.; Vattimo, M.D.F.F. Avaliação da função renal: Creatinina e outros biomarcadores. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2007, 19, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, K.F.; Yackley, K.M.; Vanamala, J.; Allred, C.D. Trigonellineis a novel phytoestrogen in coffeebeans. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1833–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, R.; Horman, I. Thermal behavior of trigonelline. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 1216–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, J.A.; Fillâtre, Y.; Martin, J.-F.; Lyan, B.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Fezeu, L.; Hercberg, S.; Comte, B.; Galan, P.; Touvier, M.; et al. New biomarkers of coffee consumption identified by the non-targeted metabolomic profiling of cohort study subjects. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagrino, P.A.; Venturini, G.; Yogi, P.S.; Dariolli, R.; Padilha, K.; Kiers, B.; Gois, T.C.; Motta-Leal-Filho, J.M.; Takimura, C.K.; Girardi, A.C.C.; et al. Metabolomic characterization of renal ischemia and reperfusion in a swine model. Life Sci. 2016, 156, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, A.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, K.-B.; Choi, W.S.; Kacew, S.; Kim, K.S.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, B.M.; Kim, S.; et al. Discovery of urinary metabolomic biomarkers for early detection of acute kidney injury. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, M.; Sugahara, K.; Kasahara, K.; Katakura, A. Metabolomic analysis of the saliva of Japanese patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, G.; Marini, D.C. Exames bioquímicos relacionados a alterações renais. FOCO Cad. Estud. Pesq. 2015, 6, 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bailys, C. Arginine, arginine analogs and oxide production in chonic kidney disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2006, 2, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranton, F.; Lundin, U.; Gayrard, N.; Mischak, H.; Aparicio, M.; Mourad, G.; Daurès, J.-P.; Weinberger, K.M.; Argilés, À. Plasma and urinary amino acid metabolomic profiling in patients with diferente levels of kidney function. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 9, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0—The Human Metabolme Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, C.; Kulkarni, K.; Hamsa, B. L-Glutamic acid and glutamine: Exciting molecules of clinical interest. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2005, 37, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsholme, P.; Procopio, J.; Lima, M.M.R.; Pithon-Curi, T.C.; Curi, R. Glutamine and glutamate—Their central role in cell metabolismo and function. Cell Biochem. 2003, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, L.H.; Lacerda, A.C.R.; Balthazar, C.H.; Marubayashi, U.; Coimbra, C.C. Central angiotensin AT1 receptors are involved in metabolic adjustments in response to graded exercise in rats. Peptides 2009, 30, 1931–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, S.; Schmidt, H.H.; Ariza, X.; Amoros, A.; Romano, A.; Hüsing-Kabar, A.; Solà, E.; Gerbes, A.; Bernardi, M.; Alessandria, C.; et al. Association Between Grade of Acute on Chronic Liver Failure and Response to Terlipressin and Albumin in Patients With Hepatorenal Syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelin, P.; Piano, S.; Solà, E.; Stanco, M.; Solé, C.; Moreira, R.; Pose, E.; Fasolato, S.; Fabrellas, N.; de Prada, G.; et al. Validation of a Staging System for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients With Cirrhosis and Association With Acute on Chronic Liver Failure. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, G.; Reboldi, G.; Verdecchia, P. High-normal serum creatinine concentration is a predictor of cardiovascular risk in essential hypertension, Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 886–891. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F. Branched-chain amino acids as predictors for individual differences of cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats: A pharmacometabonomics study. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, L.A.B.; Wandeur, V.; Matsuo, T. Preditores de lesão renal aguda e mortalidade em uma Unidade de Terapia Intensiva. Rev. Bras. Nefrol. 2015, 37, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Matsutomo, T.; Ushijima, M.; Kodera, Y.; Nakamoto, M.; Takashima, M.; Morihara, N.; Tamura, K. Metabolomic study on the antihypertensive effect of S-1-propenylcysteine in spontaneously hypertensive rats using liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1046, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeth, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Buffa, J.A.; Org, E.; Sheehy, B.T.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafidi, M.E.; Pérez, I.; GBaños, G. Is glycine effective against elevated blood pressure? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2006, 9, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, A.G.T. Desenvolvimento e Validação de Método por CLUE-EM/EM para Monitoramento Plasmático de Losartana e seu Metabólito Ativo em Pacientes com Doença Renal Crônica. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Amapá, Macapá, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guideline, I.H.T. Validation of analytical procedures: Text and methodology. Q2 (R1) 2005, 1, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Beckonert, O.; Keun, H.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Bundy, J.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ibáñez, J.; Pazos, F.; Chagoyen, M. MBROLE 2.0—Functional enrichment of chemical compounds. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, H.; Yamanaka, M.; Hagiwara, A.; Ijiri, R. Losartan and fetal toxic effect. Lancet 2001, 357, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using metaboanalyst 4.0 for comprehensive and integrative metabolomics data analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Ewald, J.; Chang, L.; Hacariz, O.; Basu, N.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 5.0 for LC–HRMS spectra processing, multi-omics integration and covariate adjustment of global metabolomics data. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 1735–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, L.; Jaworska, J.; Worth, A.P.; Cronin, M.T.D.; McDowell, R.M.; Gramatica, P. Methods for reliability and uncertainty assessment and for applicability evaluations of classification- and regression-based QSARs. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Variable | CTRL (n = 26) | SAH (n = 22) | CKD (n = 19) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 43.9 ± 10.5 a | 54.5 ± 11.6 a | 54.2 ± 11.2 a |
| Female gender (%) | 61.54 | 45.45 | 50.75 |
| Others diseases (%) | 0.0 | 9.09 | 52.63 |
| BPSYS (mmHg) 1 | 116 ± 9.6 b | B:143 ± 18.0 * A:138 ± 18.7 b | 164 ± 27.0 * |
| BPDIA (mmHg) 1 | 75 ± 8.5 c | B:91 ± 11.0 c,* A:83 ± 11.7 c | 86 ± 18.8 c |
| Patients with plasmatic levels > EC50 (%) a | - | 50.0 | 21.05 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) 2 | 0.8 ± 0.2 d | 0.9 ± 0.2 d | 10.2 ± 5.2 * |
| Urea (mg/dL) 2 | 23.8 ± 5.5 | 83.5 ± 30.8 e,* | 109.1 ± 34.2 e,* |
| PCR (mg/dL) 2 | 1.8 ± 3.4 f | 2.0 ± 3.1 f | 3.6 ± 3.9 f |
| METABOLITE (NMR Bucket, ppm) | HMDB ID | CKD | SAH | CTRL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea | HMDB0000294 | |||
| (5.79–5.83) | High | Intermediary | Low | |
| (5.71–5.75) | High | Low | Intermediary | |
| (5.67–5.71) | High | Intermediary | Low | |
| Trigonelline | HMDB0000875 | |||
| (8.03–8.07) | High | Low | Intermediary | |
| (9.07–9.11) | High | Low | Intermediary |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, I.S.R.; Martin-Pastor, M.; Tavares Júnior, A.G.; Queiroz, K.A.; da Silva Sólon, L.G.; Sousa, F.F.O.d. Metabolomic Profile and Its Correlation with the Plasmatic Levels of Losartan, EXP3174 and Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129832
Santos ISR, Martin-Pastor M, Tavares Júnior AG, Queiroz KA, da Silva Sólon LG, Sousa FFOd. Metabolomic Profile and Its Correlation with the Plasmatic Levels of Losartan, EXP3174 and Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):9832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129832
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Ingrid Souza Reis, Manuel Martin-Pastor, Alberto Gomes Tavares Júnior, Kamila Ayres Queiroz, Lílian Grace da Silva Sólon, and Francisco Fábio Oliveira de Sousa. 2023. "Metabolomic Profile and Its Correlation with the Plasmatic Levels of Losartan, EXP3174 and Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 9832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129832
APA StyleSantos, I. S. R., Martin-Pastor, M., Tavares Júnior, A. G., Queiroz, K. A., da Silva Sólon, L. G., & Sousa, F. F. O. d. (2023). Metabolomic Profile and Its Correlation with the Plasmatic Levels of Losartan, EXP3174 and Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 9832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129832