Bone Growth Induction in Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA Mouse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Induction in MPS IVA Mice after CNP Peptide Gene Therapy
2.2. Induction of Chondrocyte Proliferation by the Delivery of AAV8-NPPC Vector
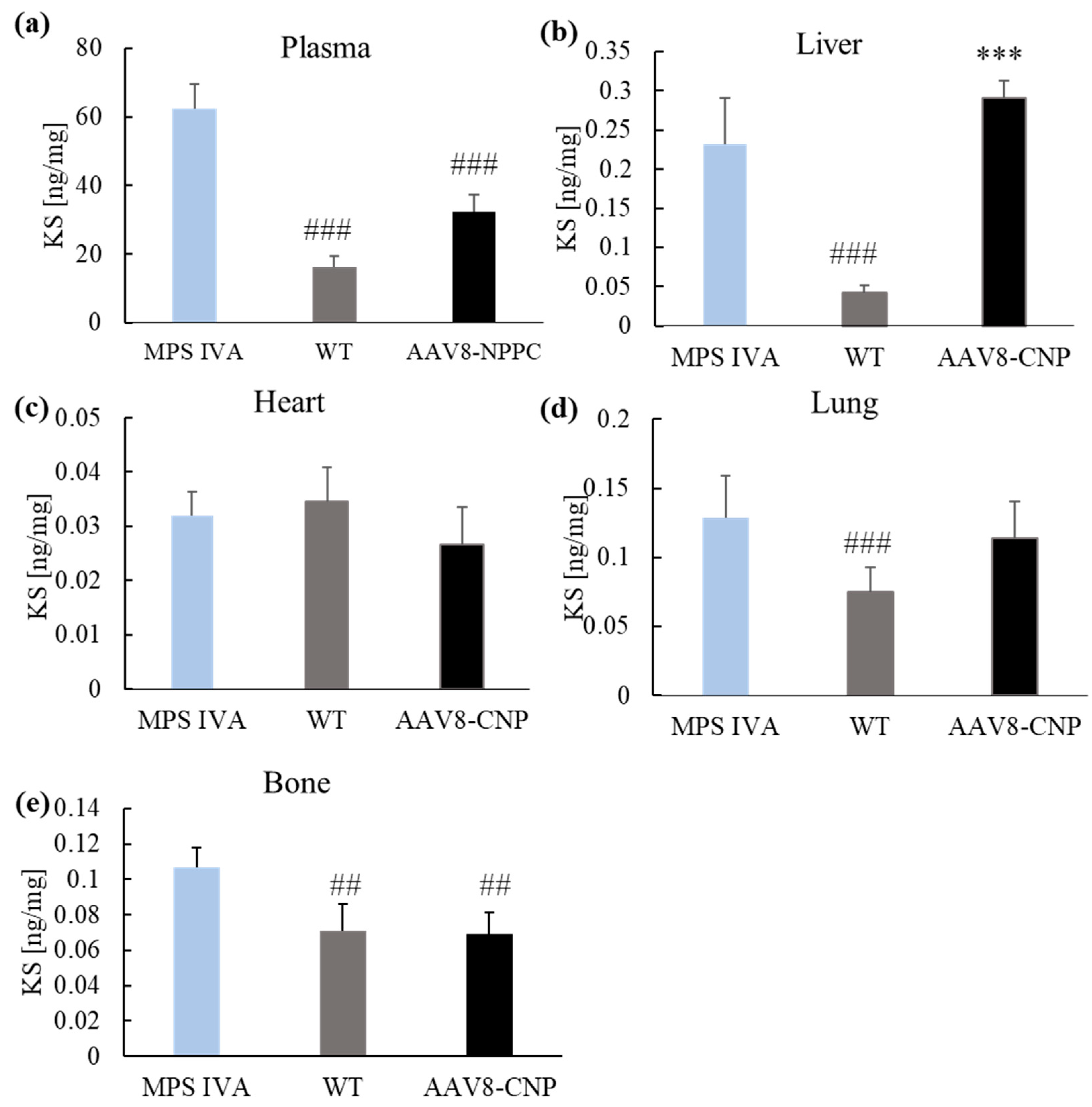
2.3. AAV Vector Biodistribution and CNP Expression
2.4. GAG Levels in the Blood and Tissues
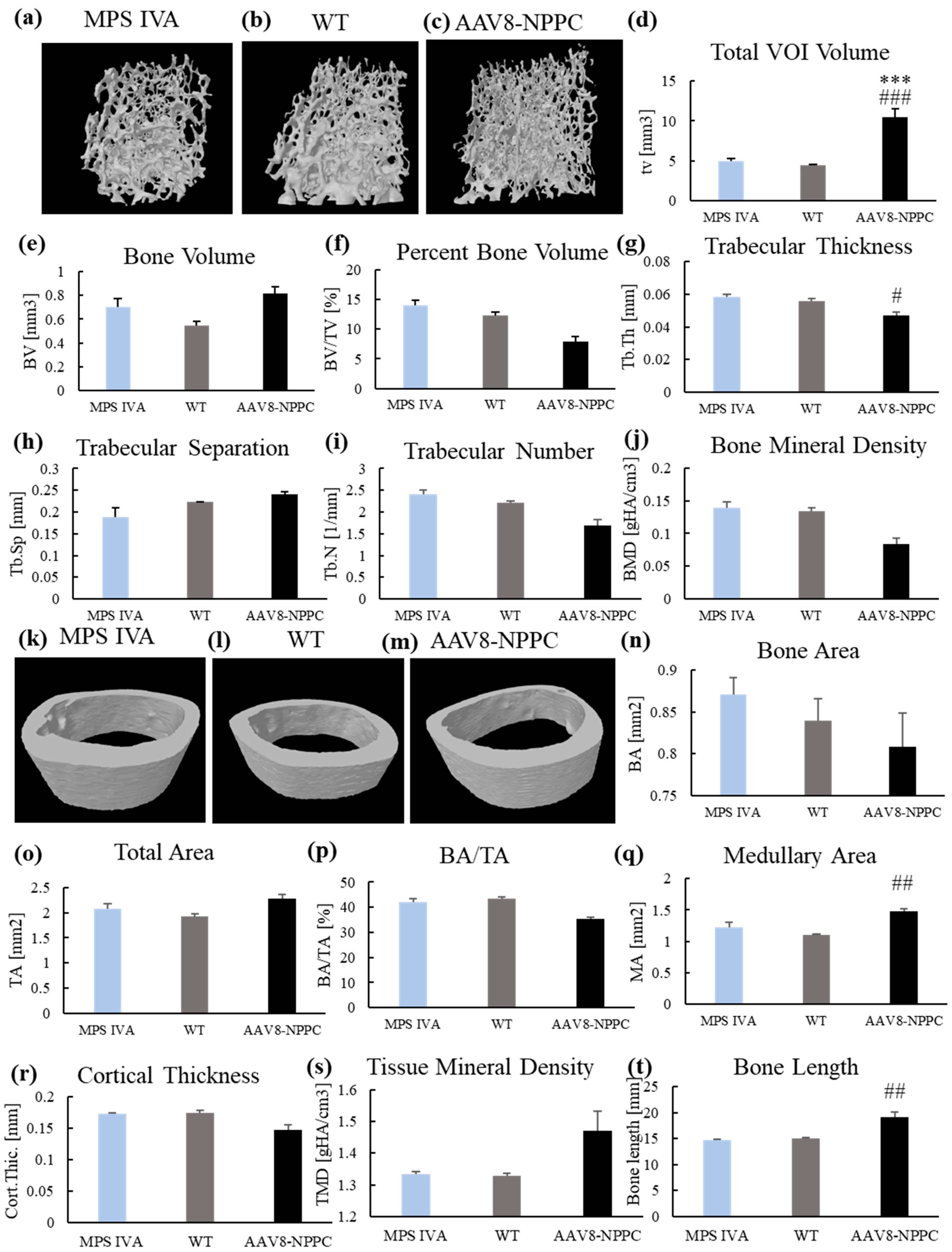
2.5. Micro-CT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Expression Vector
4.3. MPS IVA Mouse Model
4.4. GALNS Enzyme Activity Assay
4.5. Glycosaminoglycans Quantification
4.6. Gait Analysis
4.7. Bone Pathological Assessments
4.8. Trabecular and Cortical Morphometry
4.9. AAV Vector Genome Biodistribution
4.10. ELISA for NT-proCNP
4.11. Western Blot
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sabir, A.; Irving, M. Clinical trials in skeletal dysplasia: A paradigm for treating rare diseases. Br. Med. Bull. 2021, 139, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawamoto, K.; Karumuthil-Melethil, S.; Khan, S.; Stapleton, M.; Bruder, J.T.; Danos, O.; Tomatsu, S. Liver-Targeted AAV8 Gene Therapy Ameliorates Skeletal and Cardiovascular Pathology in a Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA Murine Model. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 18, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Mason, R.W.; Giugliani, R.; Orii, K.; Fukao, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Orii, T.; Tomatsu, S. Glycosaminoglycans analysis in blood and urine of patients with mucopolysaccharidosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 125, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomatsu, S.; Montaño, A.M.; Oikawa, H.; Smith, M.; Barrera, L.; Chinen, Y.; Thacker, M.M.; Mackenzie, W.G.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, T. Mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA (Morquio A disease): Clinical review and current treatment. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Alméciga-Díaz, C.J.; Sawamoto, K.; Mackenzie, W.G.; Theroux, M.C.; Pizarro, C.; Mason, R.W.; Orii, T.; Tomatsu, S. Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA and glycosaminoglycans. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, J.; Leung, W.T.; Wang, L. A basic understanding of mucopolysaccharidosis: Incidence; clinical features; diagnosis; and management. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2020, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moretto, A.; Bosatra, M.G.; Marchesini, L.; Tesoro, S. Anesthesiological risks in mucopolysaccharidoses. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44 (Suppl. S2), 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomatsu, S.; Mackenzie, W.G.; Theroux, M.C.; Mason, R.W.; Thacker, M.M.; Shaffer, T.H.; Montaño, A.M.; Rowan, D.; Sly, W.; Alméciga-Díaz, C.J.; et al. Current and emerging treatments and surgical interventions for Morquio A syndrome: A review. Res. Rep. Endocr. Disord. 2012, 2012, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doherty, C.; Stapleton, M.; Piechnik, M.; Mason, R.W.; Mackenzie, W.G.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Tomatsu, S. Effect of enzyme replacement therapy on the growth of patients with Morquio A. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Khan, S.; Stapleton, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Wynn, R.; Yabe, H.; Chinen, Y.; Boelens, J.J.; Mason, R.W.; et al. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Mucopolysaccharidoses: Past.; Present.; and Future. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, e226–e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Musson, D.G.; Schweighardt, B.; Tompkins, T.; Jesaitis, L.; Shaywitz, A.J.; Yang, K.; O’Neill, C.A. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of elosulfase alfa.; an enzyme replacement therapy in patients with Morquio A syndrome. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2014, 53, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Politei, J.; Porras-Hurtado, G.L.; Guelbert, N.; Fainboim, A.; Horovitz, D.D.G.; Satizábal, J.M. Enzyme replacement therapy interruption in mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA patients and its impact in different clinical outcomes. JIMD Rep. 2021, 58, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Tompkins, T.; Decker, C.; Jesaitis, L.; Khan, S.; Slasor, P.; Harmatz, P.; O’Neill, C.A.; Schweighardt, B. Long-term Immunogenicity of Elosulfase Alfa in the Treatment of Morquio A Syndrome: Results from MOR-005; a Phase III Extension Study. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 118–129.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schweighardt, B.; Tompkins, T.; Lau, K.; Jesaitis, L.; Qi, Y.; Musson, D.G.; Farmer, P.; Haller, C.; Shaywitz, A.J.; Yang, K.; et al. Immunogenicity of Elosulfase Alfa, an Enzyme Replacement Therapy in Patients with Morquio A Syndrome: Results from MOR-004, a Phase III Trial. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 1012–1021.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomatsu, S.; Montaño, A.M.; Ohashi, A.; Gutierrez, M.A.; Oikawa, H.; Oguma, T.; Dung, V.C.; Nishioka, T.; Orii, T.; Sly, W.S. Enzyme replacement therapy in a murine model of Morquio A syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawamoto, K.; Álvarez González, J.V.; Piechnik, M.; Otero, F.J.; Couce, M.L.; Suzuki, Y.; Tomatsu, S. Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA: Diagnosis, Treatment.; and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomatsu, S.; Sawamoto, K.; Alméciga-Díaz, C.J.; Shimada, T.; Bober, M.B.; Chinen, Y.; Yabe, H.; Montaño, A.M.; Giugliani, R.; Kubaski, F.; et al. Impact of enzyme replacement therapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with Morquio A syndrome. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2015, 9, 1937–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biffi, A. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Gene Therapy for Storage Disease: Current and New Indications. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartels, C.F.; Bükülmez, H.; Padayatti, P.; Rhee, D.K.; van Ravenswaaij-Arts, C.; Pauli, R.M.; Mundlos, S.; Chitayat, D.; Shih, L.Y.; Al-Gazali, L.I.; et al. Mutations in the transmembrane natriuretic peptide receptor NPR-B impair skeletal growth and cause acromesomelic dysplasia, type Maroteaux. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rintz, E.; Węgrzyn, G.; Fujii, T.; Tomatsu, S. Molecular Mechanism of Induction of Bone Growth by the C-Type Natriuretic Peptide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, S. Vosoritide: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 2057–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarirayan, R.; Irving, M.; Bacino, C.A.; Bostwick, B.; Charrow, J.; Cormier-Daire, V.; Le Quan Sang, K.H.; Dickson, P.; Harmatz, P.; Phillips, J.; et al. C-Type Natriuretic Peptide Analogue Therapy in Children with Achondroplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breinholt, V.M.; Rasmussen, C.E.; Mygind, P.H.; Kjelgaard-Hansen, M.; Faltinger, F.; Bernhard, A.; Zettler, J.; Hersel, U. TransCon CNP, a Sustained-Release C-Type Natriuretic Peptide Prodrug; a Potentially Safe and Efficacious New Therapeutic Modality for the Treatment of Comorbidities Associated with Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 3-Related Skeletal Dysplasias. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peracha, H.; Sawamoto, K.; Averill, L.; Kecskemethy, H.; Theroux, M.; Thacker, M.; Nagao, K.; Pizarro, C.; Mackenzie, W.; Kobayashi, H.; et al. Molecular genetics and metabolism; special edition: Diagnosis, diagnosis and prognosis of Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 125, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawale, A.A.; Church, C.; Henley, J.; Holmes, L., Jr.; Thacker, M.M.; Mackenzie, W.G.; Miller, F. Gait pattern and lower extremity alignment in children with Morquio syndrome. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2013, 22, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Torres, J.J.; Church, C.; Shields, T.; Shrader, M.W.; Fisher, L.; Mackenzie, W.G.; Mackenzie, W.G.S. Evaluation of Gait Pattern and Lower Extremity Kinematics of Children with Morquio Syndrome (MPS IV). Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouxsein, M.L.; Boyd, S.K.; Christiansen, B.A.; Guldberg, R.E.; Jepsen, K.J.; Müller, R. Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J. Bone Miner Res. 2010, 7, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, J.; Smith, P.S.; Sorby-Adams, G.; Hopwood, J. The histological and ultrastructural features of the epiphyseal plate in Morquio type A syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA). Pathology 1986, 18, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zustin, J. Morquio disease: The role of cartilage canals in the pathogenesis of chondrogenic dwarfism. Med. Hypotheses 2010, 6, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franceschi, L.; Roseti, L.; Desando, G.; Facchini, A.; Grigolo, B. A molecular and histological characterization of cartilage from patients with Morquio syndrome. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2007, 15, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bank, R.A.; Groener, J.E.; van Gemund, J.J.; Maaswinkel, P.D.; Hoeben, K.A.; Schut, H.A.; Everts, V. Deficiency in N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase results in collagen perturbations in cartilage of Morquio syndrome A patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2009, 97, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, D.J.; Tomatsu, S.; Grubb, J.H.; Montaño, A.M.; Sly, W.S. Assessment of bone dysplasia by micro-CT and glycosaminoglycan levels in mouse models for mucopolysaccharidosis type I, IIIA, IVA, and VII. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 2, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujitsuka, H.; Sawamoto, K.; Peracha, H.; Mason, R.W.; Mackenzie, W.; Kobayashi, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, K.; Orii, T.; et al. Biomarkers in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II and IV. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2019, 19, 100455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martell, L.; Lau, K.; Mei, M.; Burnett, V.; Decker, C.; Foehr, E.D. Biomarker analysis of Morquio syndrome: Identification of disease state and drug responsive markers. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2011, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haskins, M.E. Animal models for mucopolysaccharidosis disorders and their clinical relevance. Acta Paediatr. 2007, 455, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomatsu, S.; Gutierrez, M.; Nishioka, T.; Yamada, M.; Yamada, M.; Tosaka, Y.; Grubb, J.H.; Montaño, A.M.; Vieira, M.B.; Trandafirescu, G.G.; et al. Development of MPS IVA mouse (Galnstm(hC79S.mC76S)slu) tolerant to human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 3321–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomatsu, S.; Vogler, C.; Montaño, A.M.; Gutierrez, M.; Oikawa, H.; Dung, V.C.; Orii, T.; Noguchi, A.; Sly, W.S. Murine model (Galns(tm(C76S)slu)) of MPS IVA with missense mutation at the active site cysteine conserved among sulfatase proteins. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2007, 3, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolin, J.; Sánchez, V.; Ribera, A.; Jaén, M.L.; Garcia, M.; Pujol, A.; Sánchez, X.; Muñoz, S.; Marcó, S.; Pérez, J.; et al. Treatment of skeletal and non-skeletal alterations of Mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA by AAV-mediated gene therapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, G.E.; Asokan, A. Cellular transduction mechanisms of adeno-associated viral vectors. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 21, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, B.R.; Chamberlain, J.S. Recombinant adeno-associated virus transduction and integration. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Chirmule, N.; Berta, S.C.; McCullough, B.; Gao, G.; Wilson, J.M. Gene therapy vectors based on adeno-associated virus type 1. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3994–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samulski, R.J.; Srivastava, A.; Berns, K.I.; Muzyczka, N. Rescue of adeno-associated virus from recombinant plasmids: Gene correction within the terminal repeats of AAV. Cell 1983, 33, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiorini, J.A.; Kim, F.; Yang, L.; Kotin, R.M. Cloning and characterization of adeno-associated virus type 5. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiorini, J.A.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Safer, B.; Kotin, R.M. Cloning of adeno-associated virus type 4 (AAV4) and generation of recombinant AAV4 particles. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 6823–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, S.; Wang, L.; Takeuchi, T.; Kanda, T. Two novel adeno-associated viruses from cynomolgus monkey: Pseudotyping characterization of capsid protein. Virology 2004, 330, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauck, B.; Xiao, W. Characterization of tissue tropism determinants of adeno-associated virus type 1. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2768–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Asokan, A.; Samulski, R.J. Adeno-associated virus serotypes: Vector toolkit for human gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 2006, 14, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prickett, T.C.; Espiner, E.A. Circulating products of C-type natriuretic peptide and links with organ function in health and disease. Peptides 2020, 132, 170363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wu, F.; Pan, J.; Morser, J.; Wu, Q. Furin-mediated processing of Pro-C-type natriuretic peptide. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 25847–25852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keng, B.M.H.; Gao, F.; Tan, R.S.; Ewe, S.H.; Teo, L.L.Y.; Xie, B.Q.; Goh, G.B.B.; Koh, W.P.; Koh, A.S. N-Terminal pro C-Type Natriuretic Peptide (NTproCNP) and myocardial function in ageing. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woods, A.; Khan, S.; Beier, F. C-type natriuretic peptide regulates cellular condensation and glycosaminoglycan synthesis during chondrogenesis. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5030–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tezcan, B.; Serter, S.; Kiter, E.; Tufan, A.C. Dose dependent effect of C-type natriuretic peptide signaling in glycosaminoglycan synthesis during TGF-β1 induced chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Mol. Histol. 2010, 41, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kake, T.; Kitamura, H.; Adachi, Y.; Yoshioka, T.; Watanabe, T.; Matsushita, H.; Fujii, T.; Kondo, E.; Tachibe, T.; Kawase, Y.; et al. Chronically elevated plasma C-type natriuretic peptide level stimulates skeletal growth in transgenic mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E1339–E1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorget, F.; Kaci, N.; Peng, J.; Benoist-Lasselin, C.; Mugniery, E.; Oppeneer, T.; Wendt, D.J.; Bell, S.M.; Bullens, S.; Bunting, S.; et al. Evaluation of the therapeutic potential of a CNP analog in a Fgfr3 mouse model recapitulating achondroplasia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 6, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomatsu, S.; Orii, K.O.; Vogler, C.; Nakayama, J.; Levy, B.; Grubb, J.H.; Gutierrez, M.A.; Shim, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nishioka, T.; et al. Mouse model of N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase deficiency (Galns-/-) produced by targeted disruption of the gene defective in Morquio A disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 3349–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomatsu, S.; Montaño, A.M.; Dung, V.C.; Ohashi, A.; Oikawa, H.; Oguma, T.; Orii, T.; Barrera, L.; Sly, W.S. Enhancement of drug delivery: Enzyme-replacement therapy for murine Morquio A syndrome. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertman, V.; Gromova, A.; La Spada, A.R.; Cortes, C.J. Low-Cost Gait Analysis for Behavioral Phenotyping of Mouse Models of Neuromuscular Disease. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 18, e59878. [Google Scholar]


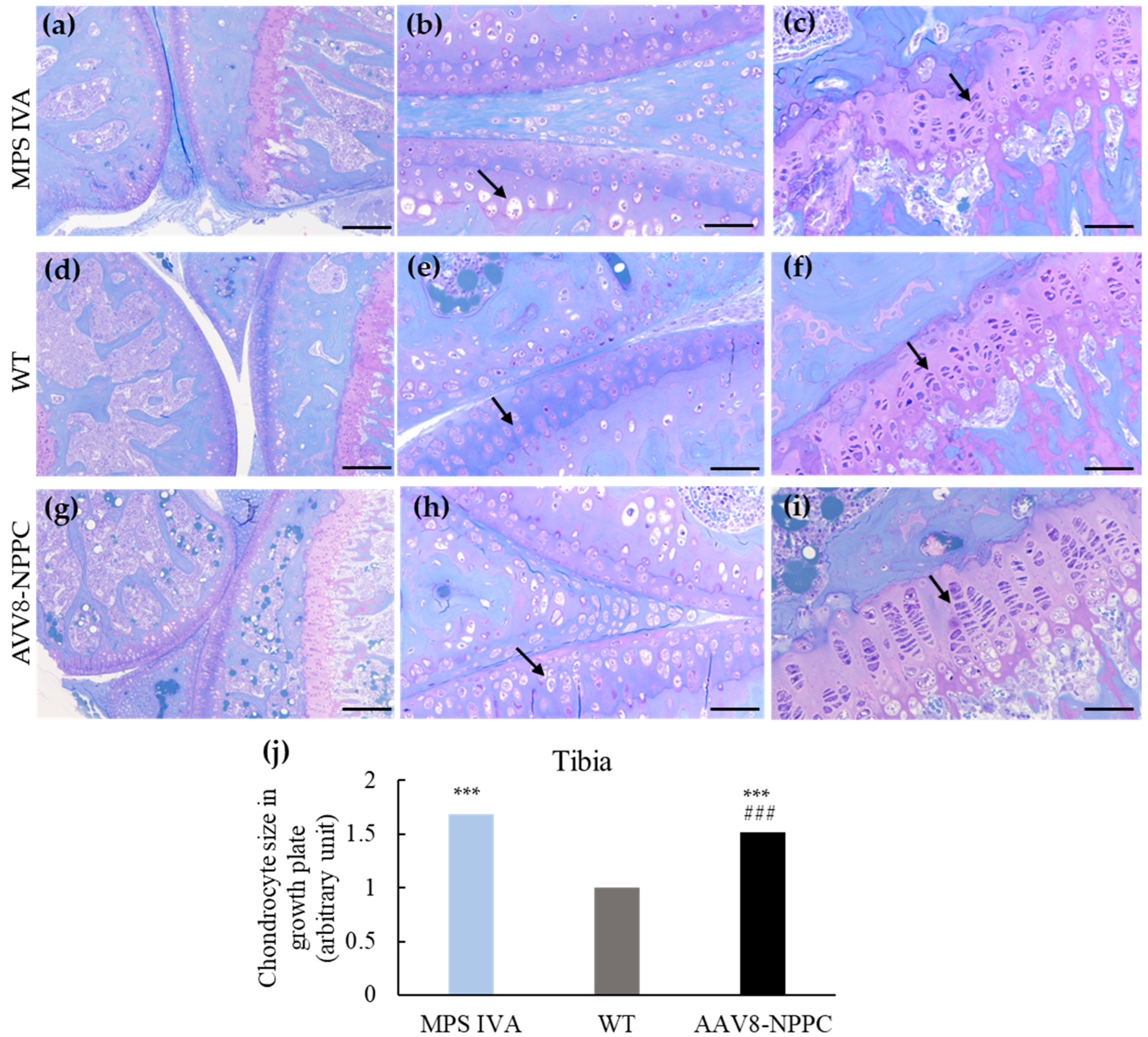

| Bone | Structure | Finding | MPS IVA | WT | AAV8-NPPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibia | Growth plate | Vacuolization | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.8 ± 0.2 |
| Column structure | 2.8 ± 0.2 | 0.0 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | ||
| Articular cartilage | Vacuolization | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.6 ± 0.1 # | |
| Column structure | 2.8 ± 0.2 | 0.0 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | ||
| Femur | Growth plate | Vacuolization | 2.8 ± 0.2 | 0.0 | 2.6 ± 0.2 |
| Column structure | 2.8 ± 0.2 | 0.0 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | ||
| Articular cartilage | Vacuolization | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | |
| Column structure | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.7 ± 0.4 | ||
| Ligament | Vacuolization | 3.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | |
| Meniscus | Vacuolization | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rintz, E.; Herreño-Pachón, A.M.; Celik, B.; Nidhi, F.; Khan, S.; Benincore-Flórez, E.; Tomatsu, S. Bone Growth Induction in Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA Mouse. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129890
Rintz E, Herreño-Pachón AM, Celik B, Nidhi F, Khan S, Benincore-Flórez E, Tomatsu S. Bone Growth Induction in Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA Mouse. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):9890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129890
Chicago/Turabian StyleRintz, Estera, Angélica María Herreño-Pachón, Betul Celik, Fnu Nidhi, Shaukat Khan, Eliana Benincore-Flórez, and Shunji Tomatsu. 2023. "Bone Growth Induction in Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA Mouse" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 9890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129890
APA StyleRintz, E., Herreño-Pachón, A. M., Celik, B., Nidhi, F., Khan, S., Benincore-Flórez, E., & Tomatsu, S. (2023). Bone Growth Induction in Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA Mouse. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 9890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129890







