Retinal Responses to Visual Stimuli in Interphotoreceptor Retinoid Binding-Protein Knock-Out Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
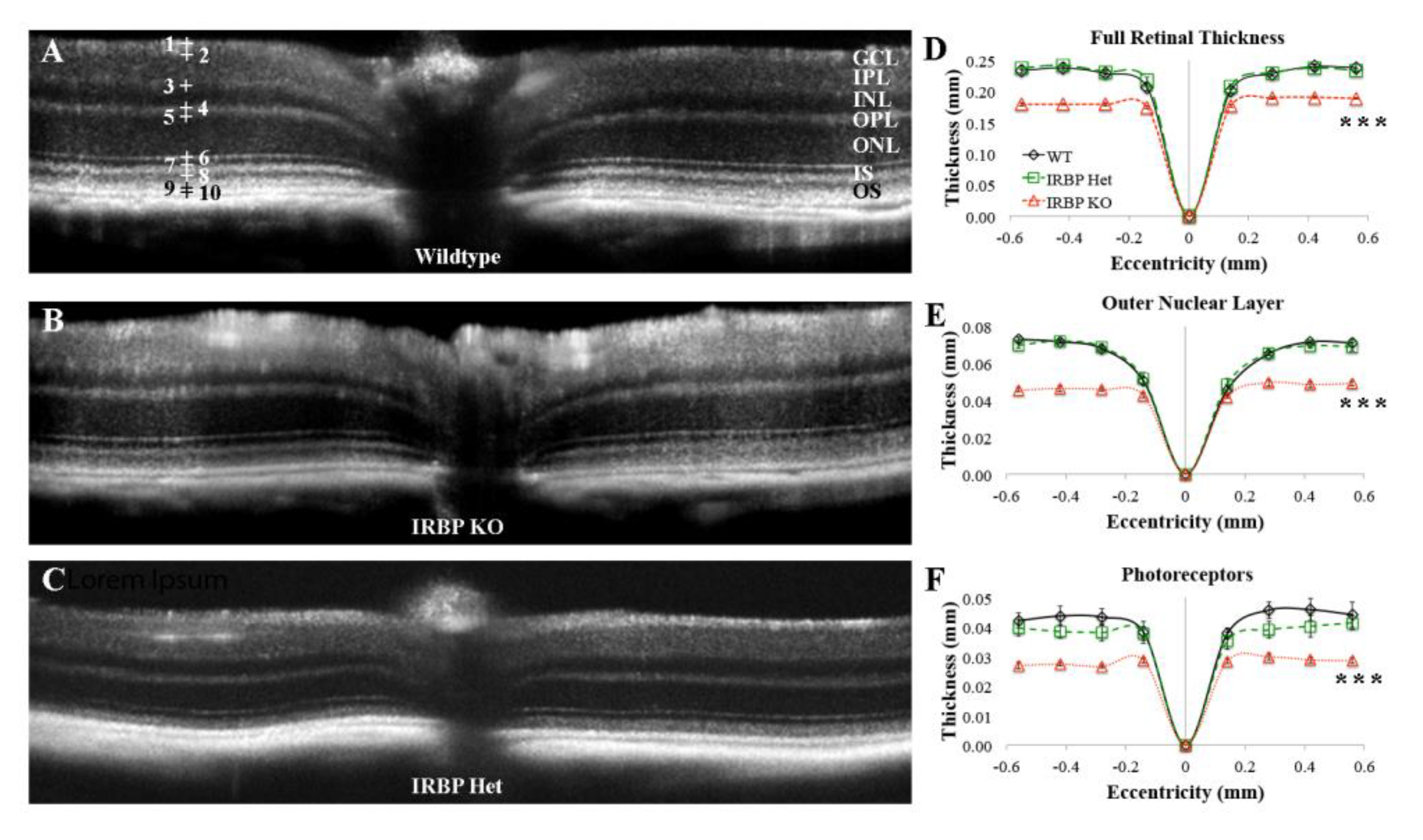
2.1. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
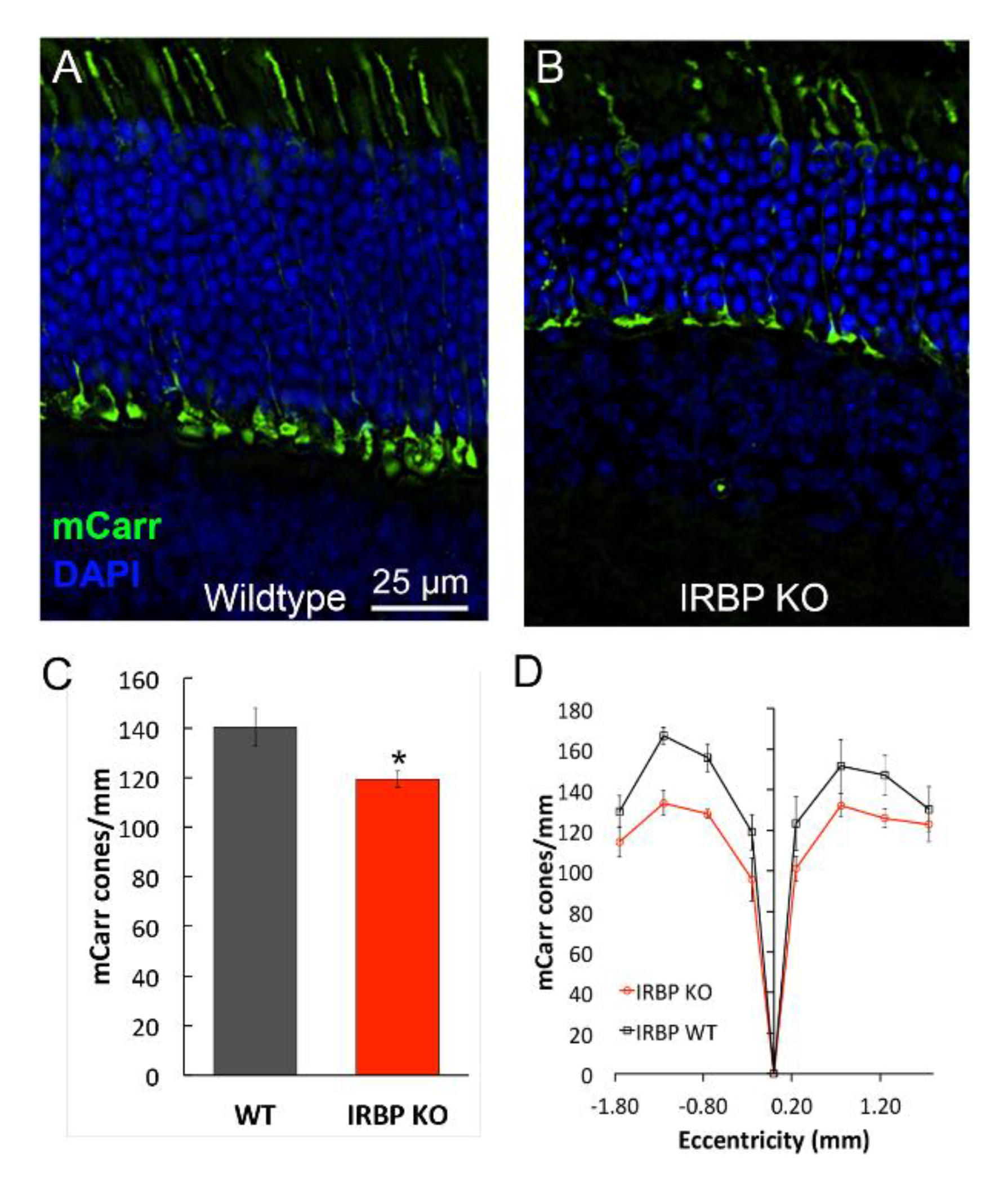
2.2. Immunohistochemistry for mCarr Assessment of Cone Density
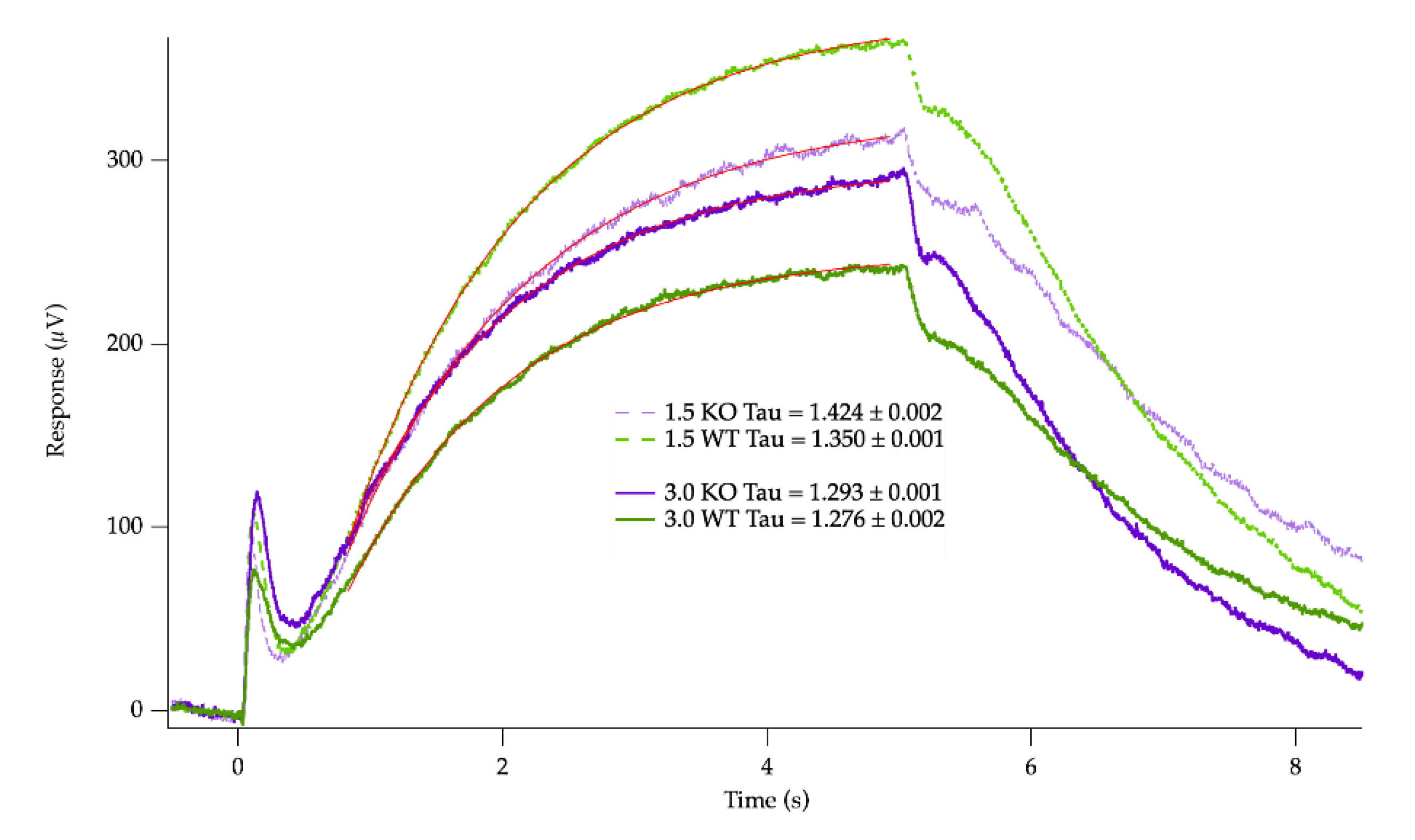
2.3. Electroretinogram (ERG)
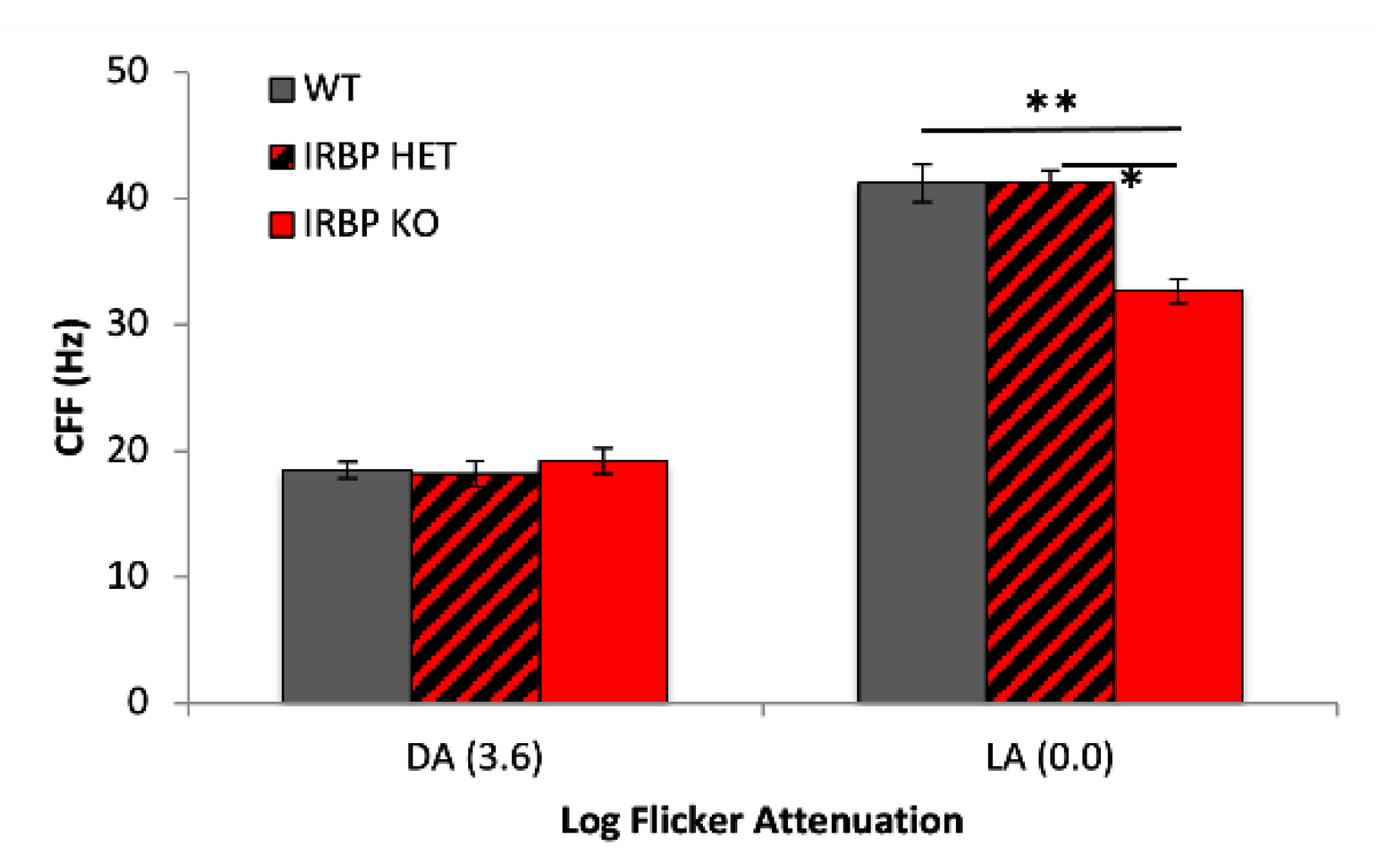
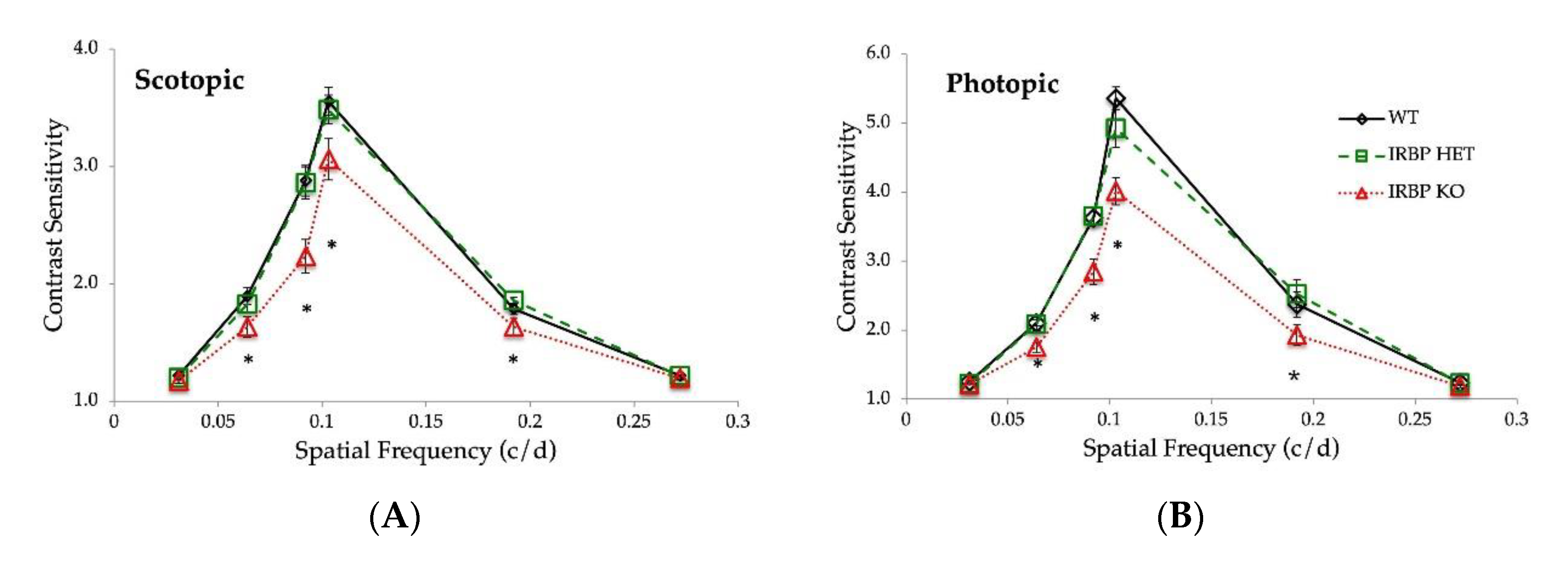
2.4. Optokinetic Reflex (OKR)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experiments with Animals
4.2. Optical Coherence Tomography
4.3. Histology
4.4. Electroretinogram
4.5. Isolated Retina Electroretinogram
4.6. Optokinetic Reflex
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adler, A.J.; Evans, C.D.; Stafford, W.F. Molecular properties of bovine interphotoreceptor retinol-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 4850–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, J.C.; Teller, D.C.; Crabb, J.W.; Bredberg, L. Properties of an interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein from bovine retina. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazan, N.G.; Reddy, T.S.; Redmond, T.M.; Wiggert, B.; Chader, G.J. Endogenous fatty acids are covalently and noncovalently bound to interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein in the monkey retina. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 13677–13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, F. Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein—An old gene for new eyes. Vis. Res. 2003, 43, 3021–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenfeld, A.J.; Bunt-Milam, A.H.; Saari, J.C. Immunocytochemical localization of retinoid-binding proteins in developing normal and RCS rats. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1985, 190, 231–240. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3901036 (accessed on 6 December 2017). [PubMed]
- Bunt Milam, A.H.; Saari, J.C. Immunocytochemical localization of two retinoid-binding proteins in vertebrate retina. J. Cell Biol. 1983, 97, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, G.I.; Bridges, C.; Fong, S.-L.; Alvarez, R.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, F. Vitamin A transport between retina and pigment epithelium—An interstitial protein carrying endogenous retinol (interstitial retinol-binding protein). Vis. Res. 1982, 22, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.S.; Fong, S.L.; Bridges, C.D.B. Retinoids bound to interstitial retinol-binding protein during light and dark-adaptation. Vis. Res. 1989, 29, 1699–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okajima, T.I.L.; Pepperberg, D.R.; Ripps, H.; Wiggert, B.; Chader, G.J. Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein: Role in delivery of retinol to the pigment epithelium. Exp. Eye Res. 1989, 49, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okajima, T.I.; Pepperberg, D.R.; Ripps, H.; Wiggert, B.; Chader, G.J. Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein promotes rhodopsin regeneration in toad photoreceptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6907–6911. Available online: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=54647&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract (accessed on 6 December 2017). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adler, A.J.; Spencer, S.A. Effect of light on endogenous ligands carried by interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein. Exp. Eye Res. 1991, 53, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepperberg, D.R.; Okajima, T.-I.L.; Wiggert, B.; Ripps, H.; Crouch, R.K.; Chader, G.J. Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP)—Molecular biology and physiological role in the visual cycle of rhodopsin. Mol. Neurobiol. 1993, 7, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Noy, N. Retinoid Specificity of Interphotoreceptor Retinoid-Binding Protein. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 10658–10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Houghton, L.A.; Brenna, J.T.; Noy, N. Docosahexaenoic acid modulates the interactions of the interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein with 11-cis-retinal. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20507–20515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, R.; Wang, J.-S.; Kefalov, V.J.; Crouch, R.K. Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein as the physiologically relevant carrier of 11-cis-retinol in the cone visual cycle. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 4714–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, P.H.; Kono, M.; Koutalos, Y.; Ablonczy, Z.; Crouch, R.K. New insights into retinoid metabolism and cycling within the retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2013, 32, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.L.; Wiggert, B.; Liu, Y.P.; Chader, G.J. Interphotoreceptor retinol-binding proteins: Possible transport vehicles between compartments of the retina. Nature 1982, 298, 848–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, N.S.; Noy, N. Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein contains three retinoid binding sites. Exp. Eye Res. 2001, 72, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, R.; Wald, G. Cis-trans isomers of vitamin A and retinene in the rhodopsin system. J. Gen. Physiol. 1952, 36, 269–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.R.; Bhardwaj, N.; Kjeldbye, H.; Gouras, P. Muller cells of chicken retina synthesize 11-cis-retinol. Biochem. J. 1992, 285, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mata, N.L.; Radu, R.A.; Clemmons, R.S.; Travis, G.H. Isomerization and oxidation of vitamin a in cone-dominant retinas: A novel pathway for visual-pigment regeneration in daylight. Neuron 2002, 36, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.-S.; Estevez, M.E.; Cornwall, M.C.; Kefalov, V.J. Intra-retinal visual cycle required for rapid and complete cone dark adaptation. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-S.; Kefalov, V.J. An Alternative Pathway Mediates the Mouse and Human Cone Visual Cycle. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wisard, J.; Faulkner, A.; Chrenek, M.A.; Waxweiler, T.; Waxweiler, W.; Donmoyer, C.; Liou, G.I.; Craft, C.M.; Schmid, G.F.; Boatright, J.H.; et al. Exaggerated eye growth in IRBP-deficient mice in early development. IOVS 2011, 52, 5804–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Li, S.; Gordon, W.C.; He, J.; Liou, G.I.; Hill, J.M.; Travis, G.H.; Bazan, N.G.; Jin, M. Receptor interacting protein kinase-mediated necrosis contributes to cone and rod photoreceptor degeneration in the retina lacking interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 17458–17468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ripps, H.; Peachey, N.S.; Xu, X.; Nozell, S.E.; Smith, S.B.; Liou, G.I. The rhodopsin cycle is preserved in IRBP “knockout” mice despite abnormalities in retinal structure and function. Vis. Neurosci. 2000, 17, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, G.I.; Fei, Y.; Peachey, N.S.; Matragoon, S.; Wei, S.; Blaner, W.S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Gottesman, M.E.; Ripps, H. Early onset photoreceptor abnormalities induced by targeted disruption of the interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein gene. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 4511–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.O.; Fan, J.; Nickerson, J.M.; Liou, G.I.; Crouch, R.K. Normal cone function requires the interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4616–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palczewski, K.; Van Hooser, J.P.; Garwin, G.G.; Chen, J.; Liou, G.I.; Saari, J.C. Kinetics of visual pigment regeneration in excised mouse eyes and in mice with a targeted disruption of the gene encoding interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein or arrestin. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 12012–12019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Li, S.; Nusinowitz, S.; Lloyd, M.; Hu, J.; Radu, R.A.; Bok, D.; Travis, G.H. The role of interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein on the translocation of visual retinoids and function of cone photoreceptors. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolesnikov, A.V.; Tang, P.H.; Parker, R.O.; Crouch, R.K.; Kefalov, V.J. The mammalian cone visual cycle promotes rapid M/L-cone pigment regeneration independently of the interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7900–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKeown, A.S.; Kraft, T.W. Adaptive potentiation in rod photoreceptors after light exposure. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 143, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKeown, A.S.; Kraft, T.W.; Loop, M.S. Increased visual sensitivity following periods of dim illumination. IOVS 2015, 56, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Markand, S.; Baskin, N.L.; Chakraborty, R.; Landis, E.; Wetzstein, S.A.; Donaldson, K.J.; Priyadarshani, P.; Alderson, S.E.; Sidhu, C.S.; Boatright, J.H.; et al. IRBP deficiency permits precocious ocular development and myopia. Mol. Vis. 2016, 22, 1291–1308. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27829784 (accessed on 14 April 2017). [PubMed]
- Saszik, M.S.; Robson, J.G.; Frishman, L.J. The scotopic threshold response of the dark-adapted electroretinogram of the mouse. J. Physiol. 2002, 543, 899–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benthal, M.C.; McKewon, A.S.; Kraft, T.W. Cone Photoreceptor Loss in Light-Damaged Albino Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.R.; Wen, Y.; Loop, M.S.; Kraft, T.W. ERG and Behavioral CFF in Light-Damaged Albino Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Fishkin, N.; Kong, J.; Nakanishi, K.; Allikmets, R.; Sparrow, J.R. Rpe65 Leu450Met variant is associated with reduced levels of the retinal pigment epithelium lipofuscin fluorophores A2E and iso-A2E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11668–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeRamus, M.L.; Stacks, D.A.; Zhang, Y.; Huisingh, C.E.; McGwin, G.; Pittler, S.J. GARP2 accelerates retinal degeneration in rod cGMP-gated cation channel β-subunit knockout mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Li, A.; Brown, B.; Weiss, E.R.; Osawa, S.; Craft, C.M. Mouse cone arrestin expression pattern: Light induced translocation in cone photoreceptors. Mol. Vis. 2002, 8, 462–471. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12486395 (accessed on 6 December 2017).
- Clark, M.E.; Kraft, T.W. Measuring rodent electroretinograms to assess retinal function. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 884, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.R.; Kraft, T.W. Flicker assessment of rod and cone function in a model of retinal degeneration. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2007, 115, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyubarsky, A.L.; Daniele, L.L.; Pugh, E.N. From candelas to photoisomerizations in the mouse eye by rhodopsin bleaching in situ and the light-rearing dependence of the major components of the mouse ERG. Vis. Res. 2004, 44, 3235–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyubarsky, A.L.; Pugh, E.N. Recovery phase of the murine rod photoresponse reconstructed from electroretinographic recordings. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, H.A.; Kraft, T.W. Human oscillatory potentials: Intensity-dependence of timing and amplitude. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2008, 117, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, H.A.; Kraft, T.W. Oscillatory potential analysis and ERGs of normal and diabetic rats. IOVS 2004, 45, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brockway, L.M.; Benos, D.J.; Keyser, K.T.; Kraft, T.W. Blockade of amiloride-sensitive sodium channels alters multiple components of the mammalian electroretinogram. Vis. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRamus, M.L.; Kraft, T.W. Optimizing ERG Measures of Scotopic and Photopic Critical Flicker Frequency. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1074, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinilla, I.; Lund, R.D.; Sauvé, Y. Cone function studied with flicker electroretinogram during progressive retinal degeneration in RCS rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2005, 80, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowey, A.; Franzini, C. The retinal origin of uncrossed optic nerve fibres in rats and their role in visual discrimination. Exp. Brain Res. 1979, 35, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, R.D. Review of optokinetic nystagmus from 1954–1960. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1961, 65, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.M.; Altimus, C.M.; Douglas, R.M.; Hattar, S.; Prusky, G.T. Photoreceptor Regulation of Spatial Visual Behavior. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 1842–1849. Available online: http://www.iovs.org/cgi/doi/10.1167/iovs.14-15644 (accessed on 6 December 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Segura, F.; Sánchez-Cano, A.; Jarabo, S.; De La Fuente, C.L.; Cuenca, N.; Villegas-Pérez, M.P.; Pinilla, I. Assessment of Visual and Chromatic Functions in a Rodent Model of Retinal Degeneration. IOVS 2015, 56, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deming, J.D.; Pak, J.S.; Brown, B.M.; Kim, M.K.; Aung, M.H.; Eom, Y.S.; Shin, J.-A.; Lee, E.-J.; Pardue, M.T.; Craft, C.M. Visual Cone Arrestin 4 Contributes to Visual Function and Cone Health. IOVS 2015, 56, 5407–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelli, D.G. Measuring contrast sensitivity. Vision Res. 2014, 90, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Genotype | a-Wave (µV) | b-Wave (µV) | a-Wave ttp (ms) | b-Wave ttp (ms) | a/b Ratio (%) | CFF (Hz) | OP Area (µV*ms) | I ½ (R* Per Rod) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark-adapted | ||||||||
| WT | 434 ± 39 | 819 ± 58 | 9.7 ± 0.8 | 67.8 ± 2.6 | 52.1 ± 1.7 | 18.5 ± 0.7 | 3.98 ± 0.23 | 21.9 ± 0.11 |
| IRBP Het | 420 ± 41 | 821 ± 86 | 8.0 ± 0.3 | 73.4 ± 3.4 | 51.6 ± 1.7 | 18.2 ± 1.0 | 3.97 ± 0.38 | 13.8 ± 0.16 |
| IRBP KO | 195 ± 17 **†† | 616 ± 58 * | 11.0 ± 0.9 † | 93.4 ± 3.3 **†† | 32.0 ± 0.9 **†† | 19.2 ± 0.9 | 2.19 ± 0.24 *† | 15.6 ± 0.03 |
| Light-adapted | ||||||||
| WT | 252 ± 31 | 384 ± 46 | 10.6 ± 0.6 | 53.9 ± 3.7 | 67.9 ± 42 | 41.2 ± 1.5 | 2.64 ± 0.21 | -- |
| IRBP Het | 196 ± 26 | 291 ± 31 | 10.6 ± 0.5 | 50.1 ± 1.6 | 66.3 ± 2.2 | 41.2 ± 2.6 | 2.26 ± 017 | -- |
| IRBP KO | 109 ± 13 **† | 233 ± 28 * | 12.5 ± 0.7 | 62.8 ± 0.1 | 49.4 ± 1.3 **†† | 32.7 ± 2.1 *† | 1.89 ± 0.19 * | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DeRamus, M.L.; Jasien, J.V.; Eppstein, J.M.; Koala, P.; Kraft, T.W. Retinal Responses to Visual Stimuli in Interphotoreceptor Retinoid Binding-Protein Knock-Out Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310655
DeRamus ML, Jasien JV, Eppstein JM, Koala P, Kraft TW. Retinal Responses to Visual Stimuli in Interphotoreceptor Retinoid Binding-Protein Knock-Out Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):10655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310655
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeRamus, Marci L., Jessica V. Jasien, Jess M. Eppstein, Pravallika Koala, and Timothy W. Kraft. 2023. "Retinal Responses to Visual Stimuli in Interphotoreceptor Retinoid Binding-Protein Knock-Out Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 10655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310655
APA StyleDeRamus, M. L., Jasien, J. V., Eppstein, J. M., Koala, P., & Kraft, T. W. (2023). Retinal Responses to Visual Stimuli in Interphotoreceptor Retinoid Binding-Protein Knock-Out Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 10655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310655






