The Prognostic Biomarkers of Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Short-Chain Fatty Acids for Recanalization Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Demographics
2.2. Details of Recanalization Therapy
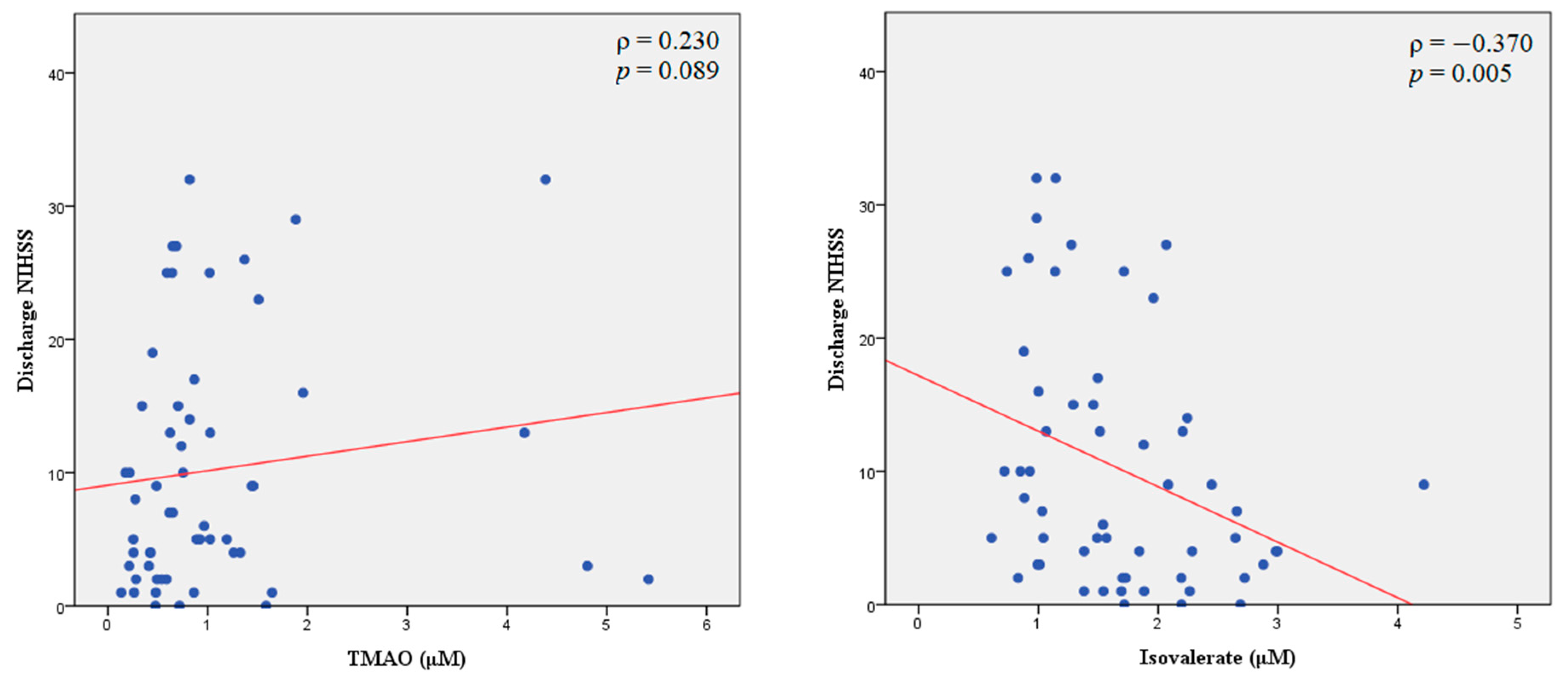
2.3. Plasma TMAO Levels and Stroke Outcomes
| Spearman Rank Correlation | All Enrolled Patients with Stroke (n = 56) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial NIHSS | p Value | Discharge NIHSS | p Value | |
| TMAO | 0.087 | 0.524 | 0.230 | 0.089 |
| Formate | 0.089 | 0.516 | −0.028 | 0.836 |
| Acetate | 0.077 | 0.578 | −0.003 | 0.983 |
| Propionate | 0.019 | 0.891 | 0.078 | 0.566 |
| Isobutyrate | 0.182 | 0.179 | 0.099 | 0.468 |
| Butyrate | 0.090 | 0.511 | 0.165 | 0.225 |
| 2-methylbutyrate | 0.250 | 0.063 | 0.209 | 0.122 |
| Isovalerate | −0.329 | 0.013 * | −0.370 | 0.005 ** |
| Valerate | 0.168 | 0.217 | 0.185 | 0.173 |
| Characteristic | Total | Mild-to-Moderate Disability (n = 23) | Severe Disability (n = 33) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMAO, μM, mean (±SD) | 1.1 ± 1.1 | 1.1 ± 1.4 | 1.1 ± 0.9 | 0.983 |
| Formate, μM, mean (±SD) | 75.2 ± 17.0 | 76.8 ± 18.5 | 74.1 ± 16.0 | 0.564 |
| Acetate, μM, mean (±SD) | 136.0 ± 58.8 | 137.0 ± 59.4 | 135.3 ± 59.3 | 0.916 |
| Propionate, μM, mean (±SD) | 10.1 ± 3.4 | 10.3 ± 3.7 | 9.9 ± 3.2 | 0.688 |
| Isobutyrate, μM, mean (±SD) | 17.4 ± 6.1 | 17.4 ± 5.9 | 17.4 ± 6.3 | 0.972 |
| Butyrate, μM, mean (±SD) | 4.1 ± 5.8 | 5.1 ± 9.0 | 3.5 ± 1.3 | 0.310 |
| 2-methylbutyrate, μM, mean (±SD) | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 0.797 |
| Isovalerate, μM, mean (±SD) | 1.7 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0.013 * |
| Valerate, μM, mean (±SD) | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 0.765 |

2.4. Plasma SCFA Levels and Stroke Outcomes
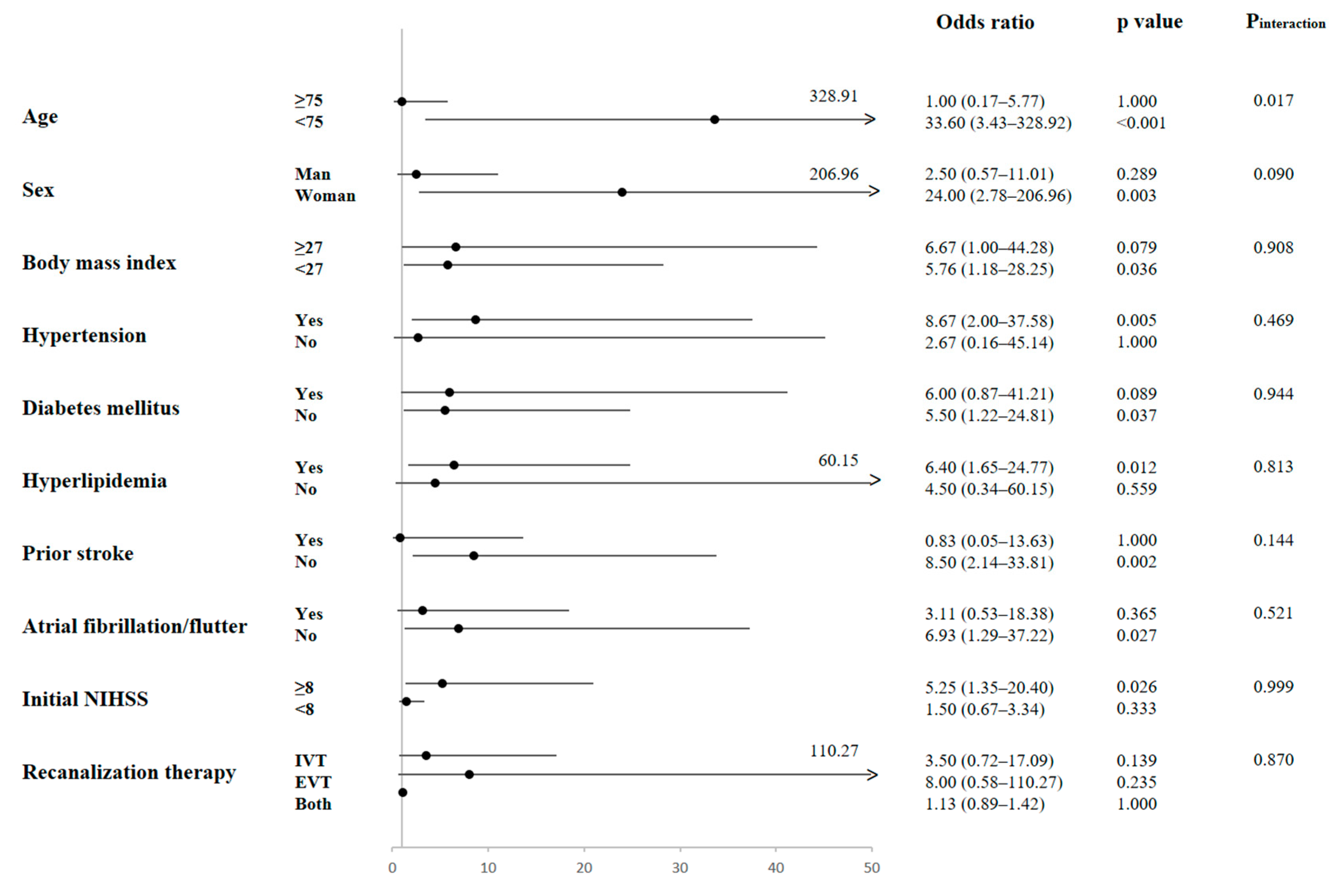
2.5. Subgroup Analysis of the Effect of Isovalerate on Functional Outcomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Stroke Severity, Functional Outcomes, and Reperfusion Assessment
4.3. Sampling and Measurements of Plasma TMAO and SCFA Levels
4.4. Statistical Analyses
4.5. Ethical Approval
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donkor, E.S. Stroke in the 21st Century: A Snapshot of the Burden, Epidemiology, and Quality of Life. Stroke Res. Treat. 2018, 2018, 3238165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019, 50, e344–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.; Kitai, T.; Hazen, S.L. Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.H.W.; Backhed, F.; Landmesser, U.; Hazen, S.L. Intestinal Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2089–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durgan, D.J.; Lee, J.; McCullough, L.D.; Bryan, R.M., Jr. Examining the Role of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 2270–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Roth, S.; Llovera, G.; Sadler, R.; Garzetti, D.; Stecher, B.; Dichgans, M.; Liesz, A. Microbiota Dysbiosis Controls the Neuroinflammatory Response after Stroke. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7428–7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, G.H.; You, C.; Gao, X.X.; Zeng, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Xu, K.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Xu, R.T.; Wu, Q.H.; Zhou, H.W.; et al. Stroke Dysbiosis Index (SDI) in Gut Microbiome Are Associated with Brain Injury and Prognosis of Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Cao, R.; Dang, Y.; Yu, B. Imbalance of Microbacterial Diversity Is Associated with Functional Prognosis of Stroke. Neural Plast. 2023, 2023, 6297653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H. A Gut Feeling about Thrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2494–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nam, H.S. Gut Microbiota and Ischemic Stroke: The Role of Trimethylamine N-Oxide. J. Stroke 2019, 21, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, M.A.; Vajdi, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Gut microbiota-associated metabolite trimethylamine N-Oxide and the risk of stroke: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Cheng, A.; Song, B.; Zhao, M.; Xue, J.; Wang, A.; Dai, L.; Jing, J.; Meng, X.; Li, H.; et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Stroke Recurrence Depends on Ischemic Stroke Subtypes. Stroke 2022, 53, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Xu, J.; Zhao, M.; Jin, A.; Cheng, A.; Jiang, X.; Li, K.; Lin, J.; Meng, X.; Li, H.; et al. Residual Risk of Trimethylamine-N-Oxide and Choline for Stroke Recurrence in Patients with Intensive Secondary Therapy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e027265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.S.; Preston, T.; Frost, G.; Morrison, D.J. Role of Gut Microbiota-Generated Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2018, 7, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Xu, R.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, H.; He, Y.; et al. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Acute Ischemic Stroke and the Subsequent Risk for Poor Functional Outcomes. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Xu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhou, H.; Lasanajak, Y.; Fang, Y.; Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Li, X.; Cai, Z.; et al. Transplantation of fecal microbiota rich in short chain fatty acids and butyric acid treat cerebral ischemic stroke by regulating gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, N.; Frank, J.; McLouth, C.; Trout, A.L.; Morris, A.; Chen, J.; Stowe, A.M.; Fraser, J.F.; Pennypacker, K. Short Chain Fatty Acids Taken at Time of Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients Are Independent of Stroke Severity but Associated with Inflammatory Markers and Worse Symptoms at Discharge. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 797302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xue, F.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Xie, N.; Chang, W.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Wei, W.; et al. Relationship between elevated plasma trimethylamine N-oxide levels and increased stroke injury. Neurology 2020, 94, e667–e677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X. Prognostic Value of Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide Levels in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexidamu, M.; Li, H.; Jin, H.; Huang, J. Serum levels of Trimethylamine-N-oxide in patients with ischemic stroke. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, C.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Xu, R.; Zeng, X.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Q.; Xia, G.; Zhou, H.; et al. Dynamic Changes and Prognostic Value of Gut Microbiota-Dependent Trimethylamine-N-Oxide in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, C.; Okun, J.G.; Schwarz, K.V.; Hauke, J.; Zorn, M.; Nurnberg, C.; Ungerer, M.; Ringleb, P.A.; Mundiyanapurath, S. Trimethylamine-N-oxide is elevated in the acute phase after ischaemic stroke and decreases within the first days. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.Y.; Li, X.S.; Chaikijurajai, T.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Hazen, S.L.; Tang, W.H.W. Relation of Statin Use to Gut Microbial Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Cardiovascular Risk. Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 178, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Chen, M.; Qian, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. The Bridge Between Ischemic Stroke and Gut Microbes: Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Wu, X.; Lu, M.; Si, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, T.; Yu, X.; Zhao, X.; et al. Change of intestinal microbiota in cerebral ischemic stroke patients. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamashiro, K.; Tanaka, R.; Urabe, T.; Ueno, Y.; Yamashiro, Y.; Nomoto, K.; Takahashi, T.; Tsuji, H.; Asahara, T.; Hattori, N. Gut dysbiosis is associated with metabolism and systemic inflammation in patients with ischemic stroke. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Gu, M.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Acute Ischemic Stroke Associated with 3-Month Unfavorable Outcome. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 799222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafasova, A.; Fosbol, E.L.; Johnsen, S.P.; Kruuse, C.; Petersen, J.K.; Alhakak, A.; Vinding, N.E.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gislason, G.H.; Kober, L.; et al. Time to Thrombolysis and Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Nationwide Study. Stroke 2021, 52, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panni, P.; Gory, B.; Xie, Y.; Consoli, A.; Desilles, J.P.; Mazighi, M.; Labreuche, J.; Piotin, M.; Turjman, F.; Eker, O.F.; et al. Acute Stroke with Large Ischemic Core Treated by Thrombectomy. Stroke 2019, 50, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spychala, M.S.; Venna, V.R.; Jandzinski, M.; Doran, S.J.; Durgan, D.J.; Ganesh, B.P.; Ajami, N.J.; Putluri, N.; Graf, J.; Bryan, R.M.; et al. Age-related changes in the gut microbiota influence systemic inflammation and stroke outcome. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; d’Aigle, J.; Atadja, L.; Quaicoe, V.; Honarpisheh, P.; Ganesh, B.P.; Hassan, A.; Graf, J.; Petrosino, J.; Putluri, N.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Promote Poststroke Recovery in Aged Mice. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.H.; Kaiser, E.E.; Waters, E.S.; Yang, X.; Lourenco, J.M.; Fagan, M.M.; Scheulin, K.M.; Sneed, S.E.; Shin, S.K.; Kinder, H.A.; et al. Tanshinone IIA-loaded nanoparticles and neural stem cell combination therapy improves gut homeostasis and recovery in a pig ischemic stroke model. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total | Mild-to-Moderate Disability (n = 23) | Severe Disability (n = 33) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean (±SD) | 70.7 ± 13.0 | 69.0 ± 12.7 | 71.9 ± 13.3 | 0.410 |
| Sex, male, n (%) | 32 (57.1%) | 13 (56.5%) | 19 (57.6%) | 0.938 |
| BMI, mean (±SD) | 25.9 ± 3.6 | 26.3 ± 3.6 | 25.6 ± 3.6 | 0.501 |
| Prior vascular risk factors | ||||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 46 (82.1%) | 16 (69.6%) | 30 (90.9%) | 0.040 * |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 23 (41.1%) | 8 (34.8%) | 15 (45.5%) | 0.425 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 42 (75.0%) | 19 (82.6%) | 23 (69.7%) | 0.272 |
| Prior stroke, n (%) | 11 (19.6%) | 3 (13.0%) | 8 (24.2%) | 0.299 |
| Atrial fibrillation/flutter, n (%) | 27 (48.2%) | 7 (30.4%) | 20 (60.6%) | 0.026 * |
| Smoking, n (%) | 10 (17.9%) | 2 (8.7%) | 8 (24.2%) | 0.135 |
| Initial NIHSS, median (IQR) | 15 (10.3–21) | 10 (6–15) | 18 (14–22.5) | 0.002 ** |
| Discharge NIHSS, median (IQR) | 7 (3–15) | 2 (1–4) | 13 (8.8–25) | <0.001 ** |
| Recanalization therapy, n (%) | 0.006 ** | |||
| IVT only | 30 (53.6%) | 18 (78.3%) | 12 (36.4%) | |
| EVT only | 15 (26.8%) | 4 (17.4%) | 11 (33.3%) | |
| Both IVT and EVT | 11 (19.6%) | 1 (4.3%) | 10 (30.3%) |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Isovalerate | 0.32 | 0.13–0.79 | 0.013 * | 0.27 | 0.09–0.79 | 0.017 * | 0.32 | 0.11–0.95 | 0.041 * |
| Age | 1.02 | 0.97–1.07 | 0.565 | 1.02 | 0.96–1.08 | 0.590 | 1.05 | 0.98–1.12 | 0.196 |
| Sex, male vs. female | 1.80 | 0.51–6.45 | 0.364 | 1.43 | 0.35–5.85 | 0.620 | 2.38 | 0.47–12.09 | 0.296 |
| Body mass index | 0.92 | 0.77–1.11 | 0.378 | 0.84 | 0.68–1.04 | 0.113 | 0.86 | 0.68–1.09 | 0.213 |
| Hypertension | 3.29 | 0.52–20.98 | 0.208 | 2.92 | 0.42–20.29 | 0.279 | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 2.71 | 0.62–11.90 | 0.188 | 2.66 | 0.48–14.64 | 0.260 | |||
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.38 | 0.06–2.37 | 0.297 | 0.56 | 0.07–4.34 | 0.577 | |||
| Smoking | 6.22 | 0.71–53.95 | 0.097 | 11.85 | 0.94–148.83 | 0.056 | |||
| Prior stroke | 1.21 | 0.21–7.01 | 0.831 | 1.16 | 0.15–8.71 | 0.889 | |||
| EVT, vs. IVT only | 10.19 | 1.71–60.78 | 0.011 * | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chou, P.-S.; Yang, I.-H.; Kuo, C.-M.; Wu, M.-N.; Lin, T.-C.; Fong, Y.-O.; Juan, C.-H.; Lai, C.-L. The Prognostic Biomarkers of Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Short-Chain Fatty Acids for Recanalization Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310796
Chou P-S, Yang I-H, Kuo C-M, Wu M-N, Lin T-C, Fong Y-O, Juan C-H, Lai C-L. The Prognostic Biomarkers of Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Short-Chain Fatty Acids for Recanalization Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):10796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310796
Chicago/Turabian StyleChou, Ping-Song, I-Hsiao Yang, Chia-Ming Kuo, Meng-Ni Wu, Tzu-Chao Lin, Yi-On Fong, Chi-Hung Juan, and Chiou-Lian Lai. 2023. "The Prognostic Biomarkers of Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Short-Chain Fatty Acids for Recanalization Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 10796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310796
APA StyleChou, P.-S., Yang, I.-H., Kuo, C.-M., Wu, M.-N., Lin, T.-C., Fong, Y.-O., Juan, C.-H., & Lai, C.-L. (2023). The Prognostic Biomarkers of Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Short-Chain Fatty Acids for Recanalization Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 10796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310796






