Isolation and Characterization of Poeciguamerin, a Peptide with Dual Analgesic and Anti-Thrombotic Activity from the Poecilobdella manillensis Leech
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Purification of Poeciguamerin
2.2. Primary Structure of Poeciguamerin
2.3. Effect of Poeciguamerin on Protease and Coagulation
2.4. Analgesic Activity of Poeciguamerin
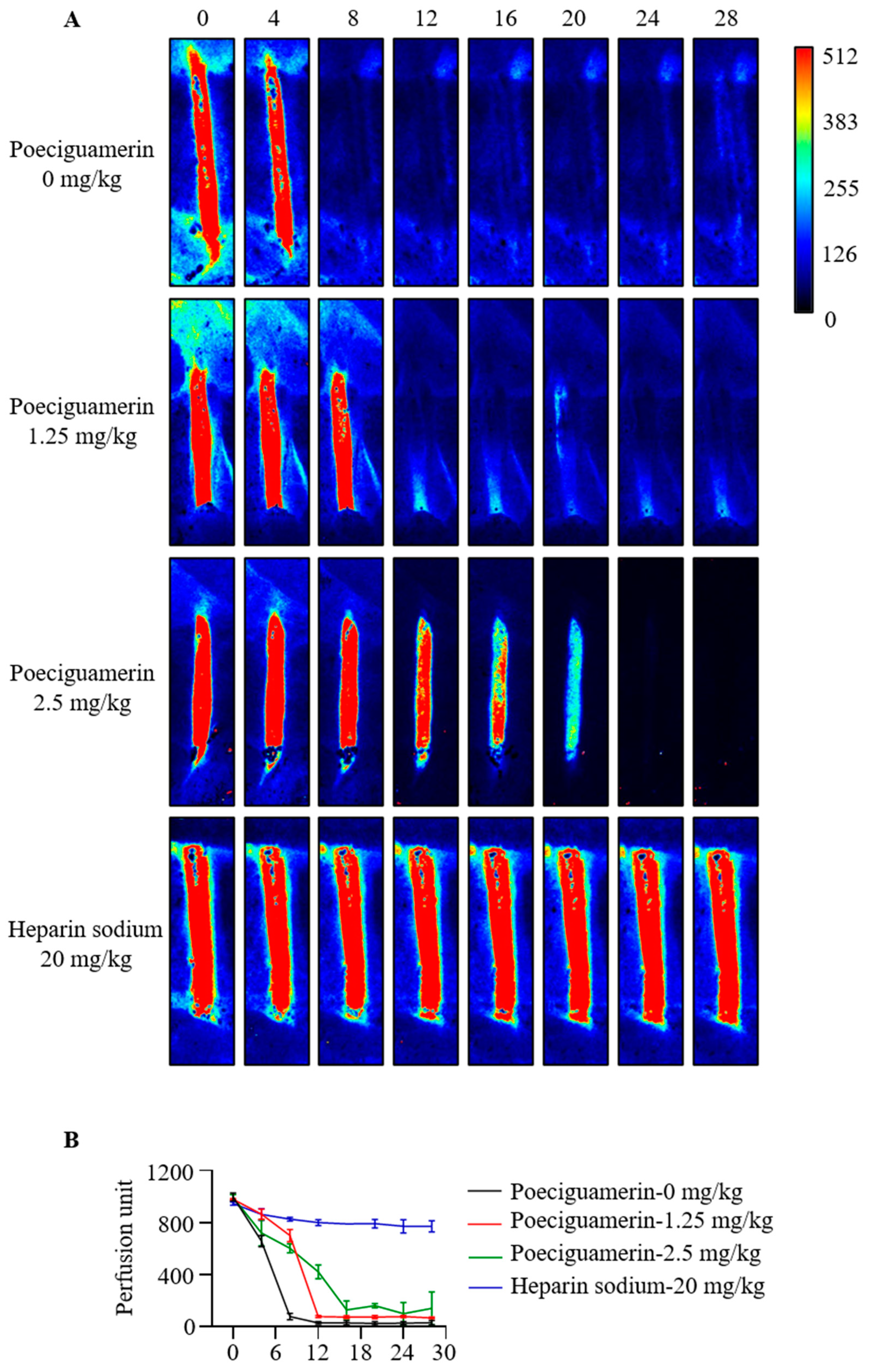
2.5. Effects of Poeciguamerin on FeCl3-Induced Carotid Artery Injury
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection of Salivary Gland Secretions from P. manillensis
4.2. Isolation and Purification of Poeciguamerin
4.3. Molecular Weight and Amino Acid Sequence Determination of Poeciguamerin
4.4. Enzyme Kinetics
4.5. Calculation of Inhibition Constant (Ki) in Enzyme Kinetics
4.6. Analgesic Activity Test
4.7. FeCl3-Induced Carotid Artery Injury Model
4.8. Animals and Ethics Statement
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woolf, C.J. What is this thing called pain? J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3742–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicuna, L.; Strochlic, D.E.; Latremoliere, A.; Bali, K.K.; Simonetti, M.; Husainie, D.; Prokosch, S.; Riva, P.; Griffin, R.S.; Njoo, C.; et al. The serine protease inhibitor SerpinA3N attenuates neuropathic pain by inhibiting T cell-derived leukocyte elastase. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bali, K.K.; Kuner, R. Therapeutic potential for leukocyte elastase in chronic pain states harboring a neuropathic component. Pain 2017, 158, 2243–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyer, A.D.; Stucky, C.L. Repurposing a leukocyte elastase inhibitor for neuropathic pain. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muley, M.M.; Reid, A.R.; Botz, B.; Bolcskei, K.; Helyes, Z.; McDougall, J.J. Neutrophil elastase induces inflammation and pain in mouse knee joints via activation of proteinase-activated receptor-2. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaneva, M.K. Neutrophil elastase and its inhibitors-overlooked players in osteoarthritis. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Lieu, T.; Barlow, N.; Sostegni, S.; Haerteis, S.; Korbmacher, C.; Liedtke, W.; Jimenez-Vargas, N.N.; Vanner, S.J.; Bunnett, N.W. Neutrophil Elastase Activates Protease-activated Receptor-2 (PAR2) and Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) to Cause Inflammation and Pain. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 13875–13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, C.; Gong, W.; Zhao, Z.; Hong, J.; Lin, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Antioxidant peptidomics reveals novel skin antioxidant system. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Kamau, P.M.; Lai, R.; Luo, L. Bioactive Peptides and Proteins from Centipede Venoms. Molecules 2022, 27, 4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Kamau, P.M.; Lai, R. Bioactive Peptides and Proteins from Wasp Venoms. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.; Lu, Q. Advanced Research on Animal Venoms in China. Toxins 2023, 15, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radis-Baptista, G.; Konno, K. Toxinologic and Pharmacological Investigation of Venomous Arthropods. Toxins 2022, 14, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacoub, T.; Rima, M.; Karam, M.; Fajloun, J. Antimicrobials from Venomous Animals: An Overview. Molecules 2020, 25, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kong, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, T.; Feng, F.; Bian, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H. A defensin-like antimicrobial peptide from the venoms of spider, Ornithoctonus hainana. J. Pept. Sci. 2011, 17, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lyu, P.; Xie, S.; Qin, H.; Pu, W.; Xu, H.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C.; Ge, L.; Kwok, H.F. LFB: A Novel Antimicrobial Brevinin-Like Peptide from the Skin Secretion of the Fujian Large Headed Frog, Limnonectes fujianensi. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Chen, M.; Duan, Z.; Mwangi, J.; Li, P.; Lai, R. Isolation and Characterization of Poecistasin, an Anti-Thrombotic Antistasin-Type Serine Protease Inhibitor from Leech Poecilobdella manillensis. Toxins 2018, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.R.; Kang, K.W. Amino acid sequence of piguamerin, an antistasin-type protease inhibitor from the blood sucking leech Hirudo nipponia. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 254, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.I.; Kim, S.I.; Ha, K.S.; Joe, C.O.; Kang, K.W. Isolation and characterization of guamerin, a new human leukocyte elastase inhibitor from Hirudo nipponia. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 13879–13884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Kang, D.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Undheim, E.A.; Klint, J.K.; Rong, M.; Lai, R.; King, G.F. Discovery of a selective NaV1.7 inhibitor from centipede venom with analgesic efficacy exceeding morphine in rodent pain models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17534–17539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somwongin, S.; Chantawannakul, P.; Chaiyana, W. Antioxidant activity and irritation property of venoms from Apis species. Toxicon 2018, 145, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.H.; Oh, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jeong, Y.A.; Yun, H.S.; Jang, C.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S. Wasp Venom Ameliorates Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Impairment in Mice. Toxins 2022, 14, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.; Pahari, S.; Hodgson, W.C.; Kini, R.M. Hypotensive agents from snake venoms. Curr. Drug Targets Cardiovasc. Haematol. Disord. 2004, 4, 437–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Li, B.; Zhu, S.; Rong, R. Hypotensive peptides from snake venoms: Structure, function and mechanism. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, A.H.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Conotoxins: Chemistry and Biology. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 11510–11549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Santos, A.D.; Olivera, B.M. Conus peptides targeted to specific nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delafontaine, M.; Villas-Boas, I.M.; Mathieu, L.; Josset, P.; Blomet, J.; Tambourgi, D.V. Enzymatic and Pro-Inflammatory Activities of Bothrops lanceolatus Venom: Relevance for Envenomation. Toxins 2017, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, M.; Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liao, Z.; Wang, G.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Tan, Z.; et al. An inhibitor of leukotriene-A(4) hydrolase from bat salivary glands facilitates virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2110647119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, C.; Fang, M.; Han, Y.; Long, C.; Liu, W.; Yang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Cao, Q.; et al. Novel contact-kinin inhibitor sylvestin targets thromboinflammation and ameliorates ischemic stroke. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Long, C.; Liu, W.; Xu, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.; Lu, Q.; Meng, P.; Li, D.; Rong, M.; et al. Novel Sodium Channel Inhibitor From Leeches. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMahon, K.L.; Tay, B.; Deuis, J.R.; Tanaka, B.S.; Peigneur, S.; Jin, A.H.; Tytgat, J.; Waxman, S.G.; Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Vetter, I.; et al. Pharmacological activity and NMR solution structure of the leech peptide HSTX-I. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Chen, Y.; Bai, X.W.; Yao, H.M.; Zhang, X.G.; Yan, X.W.; Lai, R. Identification and characterization of a novel neuropeptide (neuropeptide Y-HS) from leech salivary gland of Haemadipsa sylvestris. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.H.; Zhou, M.; Wu, F.L.; Tang, X.P.; Lu, Q.M.; Lai, R.; Long, C.B. Identification and characterization of a novel elastase inhibitor from Hirudinaria manillensis. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, W.; Huber, R. Natural protein proteinase inhibitors and their interaction with proteinases. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 204, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electricwala, A.; Von Sicard, N.A.; Sawyer, R.T.; Atkinson, T. Biochemical characterisation of a pancreatic elastase inhibitor from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis. J. Enzym. Inhib. 1992, 6, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollner, C.; Mentele, R.; Eckerskorn, C.; Fritz, H.; Sommerhoff, C.P. Isolation and characterization of hirustasin, an antistasin-type serine-proteinase inhibitor from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 219, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, A.; Magalhaes, H.P.; Richardson, M.; Gontijo, S.; Ferreira, R.N.; Almeida, A.P.; Sanchez, E.F. Purification and properties of a coagulant thrombin-like enzyme from the venom of Bothrops leucurus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 146, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Tang, X.; Chen, W.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Z.; He, K.; Li, Q.; Duan, Z.; He, X.; Kamau, P.M.; et al. Shrew’s venom quickly causes circulation disorder, analgesia and hypokinesia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.E.; Bindokas, V.P.; Hasegawa, L.; Venema, V.J. Omega-agatoxins: Novel calcium channel antagonists of two subtypes from funnel web spider (Agelenopsis aperta) venom. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.G.; Van Renterghem, C.; Martin-Moutot, N.; Mansuelle, P.; Cordeiro, M.N.; Diniz, C.R.; Mori, Y.; De Lima, M.E.; Seagar, M. Phoneutria nigriventer omega-phonetoxin IIA blocks the Cav2 family of calcium channels and interacts with omega-conotoxin-binding sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 13856–13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, R.J.; Nielsen, K.J.; Craik, D.J.; Loughnan, M.L.; Adams, D.A.; Sharpe, I.A.; Luchian, T.; Adams, D.J.; Bond, T.; Thomas, L.; et al. Novel omega-conotoxins from Conus catus discriminate among neuronal calcium channel subtypes. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 35335–35344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, F.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Wu, F.; Wang, G.; Feng, X.; Ombati, R.; Zuo, R.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; et al. Prostaglandin E1 Is an Efficient Molecular Tool for Forest Leech Blood Sucking. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 615915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, N.; Zhao, Q.; Duan, Z.; Ji, M.; Xing, M.; Zhu, T.; Mwangi, J.; Rong, M.; Liu, J.; Lai, R. Identification and Characterization of ShSPI, a Kazal-Type Elastase Inhibitor from the Venom of Scolopendra hainanum. Toxins 2019, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Padrines, M.; Schneider-Pozzer, M.; Bieth, J.G. Inhibition of neutrophil elastase by alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor oxidized by activated neutrophils. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, M.S.; Levin, R.I.; Garry, K. Human neutrophil elastase modulates platelet function by limited proteolysis of membrane glycoproteins. J. Clin. Investig. 1985, 75, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legrand, Y.; Pignaud, G.; Caen, J.P. Human blood platelet elastase and proelastase. Activation of proelastase and release of elastase after ahesion of platelets to collagen. Haemostasis 1977, 6, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Renesto, P.; Chignard, M. Enhancement of cathepsin G-induced platelet activation by leukocyte elastase: Consequence for the neutrophil-mediated platelet activation. Blood 1993, 82, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selak, M.A. Neutrophil elastase potentiates cathepsin G-induced platelet activation. Thromb. Haemost. 1992, 68, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gob, E.; Reymann, S.; Langhauser, F.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Kraft, P.; Thielmann, I.; Gobel, K.; Brede, M.; Homola, G.; Solymosi, L.; et al. Blocking of plasma kallikrein ameliorates stroke by reducing thromboinflammation. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 784–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Lu, X.; Yang, S.; Yang, M.; Fang, Y.; Lai, R.; Duan, Z. Isolation and Characterization of Poeciguamerin, a Peptide with Dual Analgesic and Anti-Thrombotic Activity from the Poecilobdella manillensis Leech. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311097
Wang C, Chen M, Lu X, Yang S, Yang M, Fang Y, Lai R, Duan Z. Isolation and Characterization of Poeciguamerin, a Peptide with Dual Analgesic and Anti-Thrombotic Activity from the Poecilobdella manillensis Leech. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):11097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311097
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chaoming, Mengrou Chen, Xiaoyu Lu, Shuo Yang, Min Yang, Yaqun Fang, Ren Lai, and Zilei Duan. 2023. "Isolation and Characterization of Poeciguamerin, a Peptide with Dual Analgesic and Anti-Thrombotic Activity from the Poecilobdella manillensis Leech" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 11097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311097
APA StyleWang, C., Chen, M., Lu, X., Yang, S., Yang, M., Fang, Y., Lai, R., & Duan, Z. (2023). Isolation and Characterization of Poeciguamerin, a Peptide with Dual Analgesic and Anti-Thrombotic Activity from the Poecilobdella manillensis Leech. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 11097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311097







