The QPLEX™ Plus Assay Kit for the Early Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
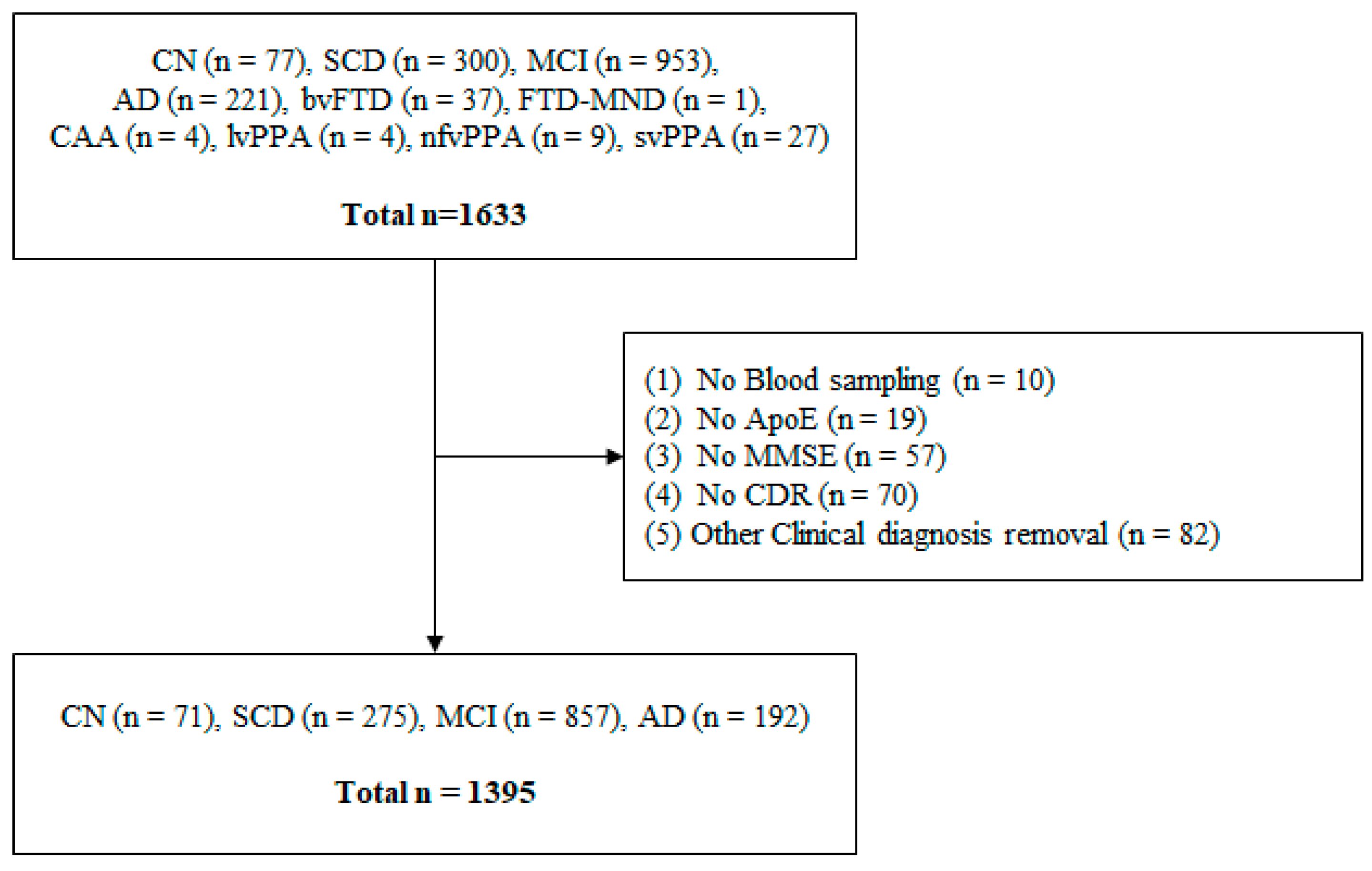
2.1. Characteristics of the Participants
2.2. Demographic Characteristics of the Two Groups Divided by the QPLEX™ Algorithm
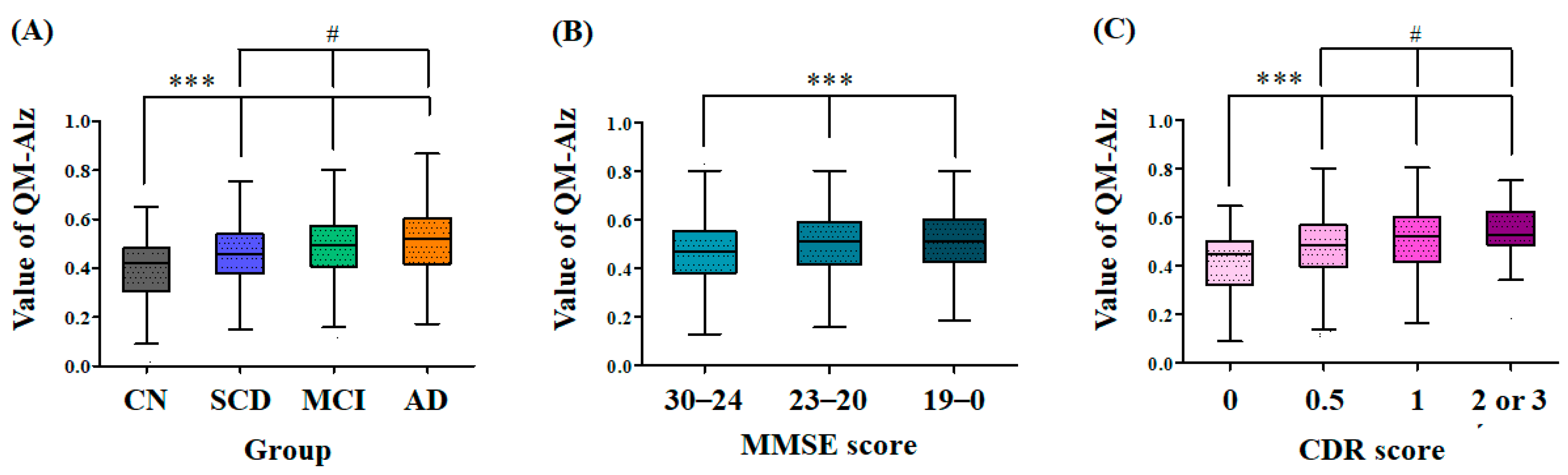
2.3. Difference in the QPLEX™ Algorithm Values among Clinically Separated, MMSE-Separated, or CDR-Separated Groups
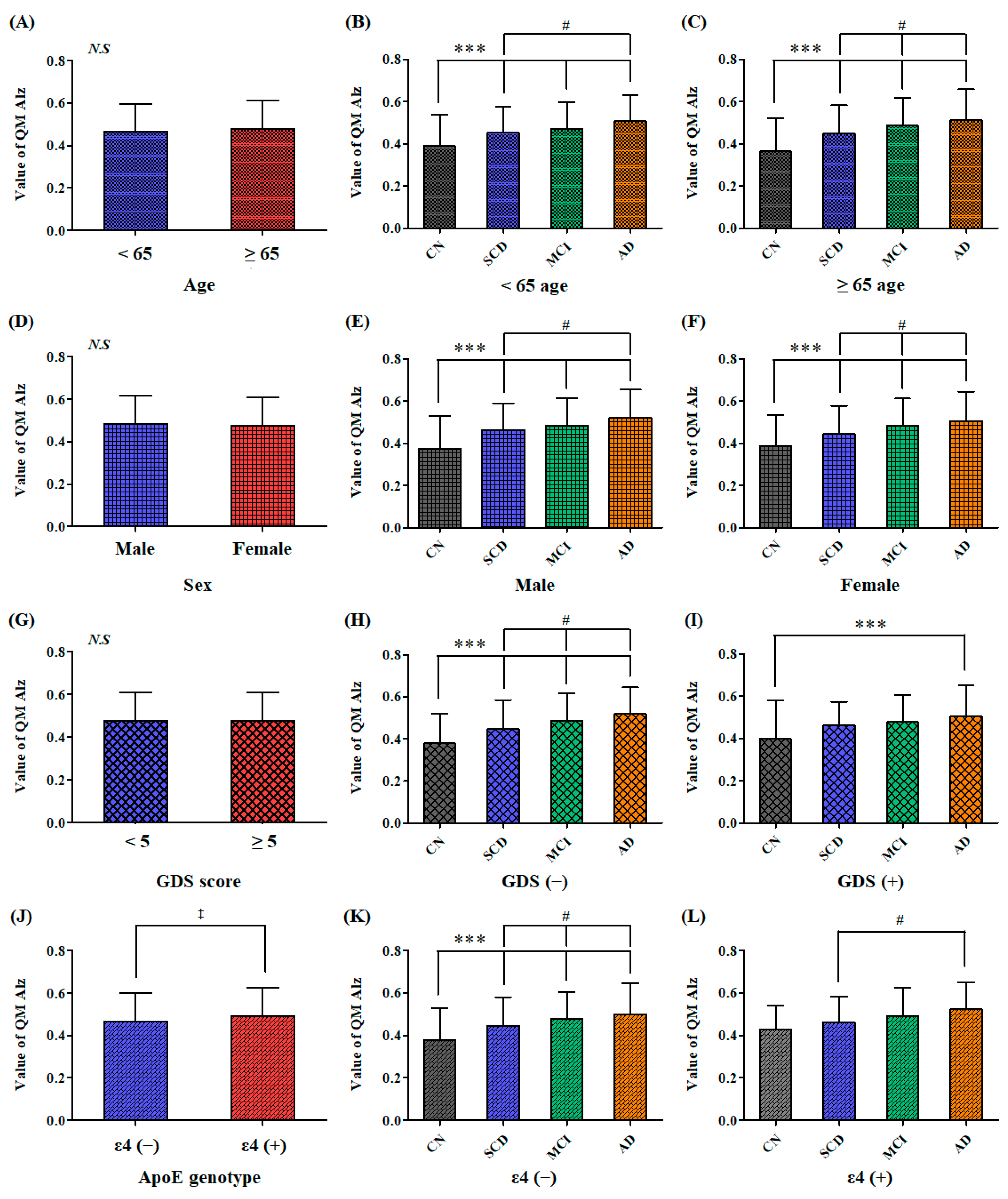
2.4. Comparison of the QPLEX™ Algorithm Values among the Individual Subgroups Fractionized by Sex, Age, Depression, or ApoE Genotype
2.5. ANCOVA Results to Adjust for Covariates, such as Age, Sex, Depression, and ApoE Genotype
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Clinical Diagnosis
4.3. Cognition Tests
4.4. Short Geriatric Depression Scale—Korean Version (SGDS-K)
4.5. Blood Sampling and Storage
4.6. Exclusion Criteria of the Participants
4.7. QPLEX™ Alz Plus Assay
4.8. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Knopman, D.S.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Weiner, M.W.; Aisen, P.S.; Shaw, L.M.; Vemuri, P.; Wiste, H.J.; Weigand, S.D.; et al. Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer’s disease: An updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Burnham, S.; Bourgeat, P.; Brown, B.; Ellis, K.A.; Salvado, O.; Szoeke, C.; Macaulay, S.L.; Martins, R.; Maruff, P.; et al. Amyloid beta deposition, neurodegeneration, and cognitive decline in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.S. Drug prescription patterns in patients with Alzheimer’s disease in an urban Neuro-speciality clinic in Western India. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World-Health-Organization. Dementia. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xia, Y.; Gui, Y. Neuronal ApoE4 in Alzheimer’s disease and potential therapeutic targets. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1199434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukull, W.A.; Bowen, J.D. Dementia epidemiology. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 86, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzavinos, V.; Alexiou, A. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2017, 14, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giacomucci, G.; Mazzeo, S.; Bagnoli, S.; Ingannato, A.; Leccese, D.; Berti, V.; Padiglioni, S.; Galdo, G.; Ferrari, C.; Sorbi, S.; et al. Plasma neurofilament light chain as a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease in Subjective Cognitive Decline and Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 4270–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, F.; Amariglio, R.E.; van Boxtel, M.; Breteler, M.; Ceccaldi, M.; Chetelat, G.; Dubois, B.; Dufouil, C.; Ellis, K.A.; van der Flier, W.M.; et al. A conceptual framework for research on subjective cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2014, 10, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, M.; O’Connell, T.; Johnson, S.; Cline, S.; Merikle, E.; Martenyi, F.; Simpson, K. Estimating Alzheimer’s Disease Progression Rates from Normal Cognition Through Mild Cognitive Impairment and Stages of Dementia. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodaty, H.; Heffernan, M.; Kochan, N.A.; Draper, B.; Trollor, J.N.; Reppermund, S.; Slavin, M.J.; Sachdev, P.S. Mild cognitive impairment in a community sample: The Sydney Memory and Ageing Study. Alzheimers Dement. 2013, 9, 310–317.e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.; Schwarz, C.; Benson, G.; Horn, N.; Buchert, R.; Lange, C.; Kobe, T.; Hetzer, S.; Maglione, M.; Michael, E.; et al. Effects of spermidine supplementation on cognition and biomarkers in older adults with subjective cognitive decline (SmartAge)-study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amariglio, R.E.; Becker, J.A.; Carmasin, J.; Wadsworth, L.P.; Lorius, N.; Sullivan, C.; Maye, J.E.; Gidicsin, C.; Pepin, L.C.; Sperling, R.A.; et al. Subjective cognitive complaints and amyloid burden in cognitively normal older individuals. Neuropsychologia 2012, 50, 2880–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandra, A.; Dervenoulas, G.; Politis, M. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. Magnetic resonance imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, Y.; Tangalos, E.G.; Petersen, R.C. Mild cognitive impairment. When is it a precursor to Alzheimer’s disease? Geriatrics 2000, 55, 62, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Busse, A.; Bischkopf, J.; Riedel-Heller, S.G.; Angermeyer, M.C. Mild cognitive impairment: Prevalence and predictive validity according to current approaches. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2003, 108, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzuegbunam, B.C.; Librizzi, D.; Hooshyar Yousefi, B. PET Radiopharmaceuticals for Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosis, the Current and Future Landscape. Molecules 2020, 25, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.C.; Jung, K.S.; Kim, J.; Jang, J.S.; Kwon, S.; Byun, M.S.; Yi, D.; Byeon, G.; Jung, G.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Performance of the QPLEX Alz plus assay, a novel multiplex kit for screening cerebral amyloid deposition. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C. Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Is MCI too late? Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2009, 6, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: Current status and prospects for the future. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 643–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, S.H.; Park, J.C.; Mook-Jung, I. Amyloid beta-interacting partners in Alzheimer’s disease: From accomplices to possible therapeutic targets. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 137, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, H.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Zetterberg, H.; Masters, C.L.; Lista, S.; Kiddle, S.J.; Batrla, R.; Blennow, K. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer disease: Mapping the road to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Han, S.H.; Mook-Jung, I. Peripheral inflammatory biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease: A brief review. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zetterberg, H.; Burnham, S.C. Blood-based molecular biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Han, S.H.; Lee, H.; Jeong, H.; Byun, M.S.; Bae, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, D.Y.; Yi, D.; Shin, S.A.; et al. Prognostic plasma protein panel for Abeta deposition in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 183, 101690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Han, S.H.; Cho, H.J.; Byun, M.S.; Yi, D.; Choe, Y.M.; Kang, S.; Jung, E.S.; Won, S.J.; Kim, E.H.; et al. Chemically treated plasma Abeta is a potential blood-based biomarker for screening cerebral amyloid deposition. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seki, T.; Kanagawa, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Kowa, H.; Yahata, N.; Maruyama, K.; Iwata, N.; Inoue, H.; Toda, T. Galectin 3-binding protein suppresses amyloid-beta production by modulating beta-cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 3678–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nassan, M.; Daghlas, I.; Piras, I.S.; Rogalski, E.; Reus, L.M.; Pijnenburg, Y.; Cuddy, L.K.; Saxena, R.; Mesulam, M.M.; Huentelman, M. Evaluating the association between genetically proxied ACE inhibition and dementias. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaisar, R.; Karim, A.; Iqbal, M.S.; Alkahtani, S.A.; Ahmad, F.; Kamli, H. ACE Inhibitors Improve Skeletal Muscle by Preserving Neuromuscular Junctions in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sanchez, J.L.; Ader, I.; Jeanson, Y.; Planat-Benard, V.; Vellas, B.; Casteilla, L.; de Souto-Barreto, P. Periostin Plasma Levels and Changes on Physical and Cognitive Capacities in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 78, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, J.C.; Jung, K.S.; Kim, J.; Jang, J.S.; Kwon, S.; Byun, M.S.; Yi, D.; Byeon, G.; Jung, G.; et al. The clinical use of blood-test factors for Alzheimer’s disease: Improving the prediction of cerebral amyloid deposition by the QPLEX(TM) Alz plus assay kit. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Park, J.C.; Jung, K.S.; Kim, J.; Jang, J.S.; Kwon, S.; Byun, M.S.; Yi, D.; Byeon, G.; Jung, G.; et al. Application of QPLEX(TM) biomarkers in cognitively normal individuals across a broad age range and diverse regions with cerebral amyloid deposition. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, M.; Mansfield, E.; Cameron, E.; Boyes, A.; Browne, W.; Dizon, J.; Sanson-Fisher, R. Depression and thoughts of self-harm and suicide among people living with dementia: Results of a cross-sectional survey. Psychogeriatrics 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psych-Congress-Network. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). 2016. Available online: https://www.hmpgloballearningnetwork.com/site/pcn/mini-mental-state-examination-mmse (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Arrighi, H.M.; Neumann, P.J.; Lieberburg, I.M.; Townsend, R.J. Lethality of Alzheimer disease and its impact on nursing home placement. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2010, 24, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.A. Interactions between ANG II, sympathetic nervous system, and baroreceptor reflexes in regulation of blood pressure. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 262, E763–E778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inagami, T. The renin-angiotensin system. Essays Biochem. 1994, 28, 147–164. [Google Scholar]
- Oba, R.; Igarashi, A.; Kamata, M.; Nagata, K.; Takano, S.; Nakagawa, H. The N-terminal active centre of human angiotensin-converting enzyme degrades Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, M.L.; Selkoe, D.J. Amyloid beta-protein is degraded by cellular angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and elevated by an ACE inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37644–37650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Igarashi, A.; Kamata, M.; Nakagawa, H. Angiotensin-converting enzyme degrades Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide (A beta ); retards A beta aggregation, deposition, fibril formation; and inhibits cytotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 47863–47868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jochemsen, H.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Ashby, E.L.; van der Flier, W.M.; Jones, R.E.; Geerlings, M.I.; Scheltens, P.; Kehoe, P.G.; Muller, M. The association of angiotensin-converting enzyme with biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, M.W.; Annis, D.S.; Mosher, D.F. alpha(M)beta(2) integrin-mediated adhesion and motility of IL-5-stimulated eosinophils on periostin. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, A.Y.; Zheng, H.; Ouyang, G. Periostin, a multifunctional matricellular protein in inflammatory and tumor microenvironments. Matrix Biol. 2014, 37, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Yagishita, S.; Itoh, Y.; Koyano, S.; Amano, N.; Matsushita, M. Eosinophilic bodies in the cerebral cortex of Alzheimer’s disease cases. Acta Neuropathol. 1996, 92, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubli, H.; Alisson-Silva, F.; Stanczak, M.A.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Deng, L.; Verhagen, A.; Varki, N.; Varki, A. Lectin galactoside-binding soluble 3 binding protein (LGALS3BP) is a tumor-associated immunomodulatory ligand for CD33-related Siglecs. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 33481–33491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inohara, H.; Raz, A. Identification of human melanoma cellular and secreted ligands for galectin-3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 201, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Wei, J.; Shi, Z.; Rifkin, A.S.; Zheng, S.L.; Gelfman, E.; Duggan, D.; Helfand, B.T.; Hulick, P.J.; Xu, J. Refining Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease Among Heterozygous APOEvarepsilon4 Carriers. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Ren, S.; Huang, L.; He, K.; Li, J.; Hua, F.; Guan, Y.; Guo, Q.; Huang, Q.; et al. The Effect of Gender and APOE varepsilon4 Status on Brain Amyloid-beta Deposition in Different Age Groups of Mild Cognitively Impaired Individuals: A PET-CT Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomar, J.J.; Bobes-Bascaran, M.T.; Conejero-Goldberg, C.; Davies, P.; Goldberg, T.E. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. Utility of combinations of biomarkers, cognitive markers, and risk factors to predict conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer disease in patients in the Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaffer, J.L.; Petrella, J.R.; Sheldon, F.C.; Choudhury, K.R.; Calhoun, V.D.; Coleman, R.E.; Doraiswamy, P.M. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. Predicting cognitive decline in subjects at risk for Alzheimer disease by using combined cerebrospinal fluid, MR imaging, and PET biomarkers. Radiology 2013, 266, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frolich, L.; Peters, O.; Lewczuk, P.; Gruber, O.; Teipel, S.J.; Gertz, H.J.; Jahn, H.; Jessen, F.; Kurz, A.; Luckhaus, C.; et al. Incremental value of biomarker combinations to predict progression of mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s dementia. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jammeh, E.; Zhao, P.; Carroll, C.; Pearson, S.; Ifeachor, E. Identification of blood biomarkers for use in point of care diagnosis tool for Alzheimer’s disease. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Usami, R.; Ichihara, S.; Kida, H.; Satoh, M.; Tomimoto, H.; Murata, M.; Oikawa, S. Plasma protein profiling for potential biomarkers in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, N.; Andreasson, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. Association of Plasma Neurofilament Light with Neurodegeneration in Patients with Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryant, S.E.; Mielke, M.M.; Rissman, R.A.; Lista, S.; Vanderstichele, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Lewczuk, P.; Posner, H.; Hall, J.; Johnson, L.; et al. Blood-based biomarkers in Alzheimer disease: Current state of the science and a novel collaborative paradigm for advancing from discovery to clinic. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altuna-Azkargorta, M.; Mendioroz-Iriarte, M. Blood biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurologia 2021, 36, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Chun, M.Y.; Jang, H.; Cho, M.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.; Jeong, J.H.; Yoon, S.J.; Park, K.W.; et al. Transferability of Alzheimer Disease Polygenic Risk Score Across Populations and Its Association with Alzheimer Disease-Related Phenotypes. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2247162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.; Kim, D.E.; Lee, H.; Yun, J.; Lee, B.H.; Park, J.; Yeom, J.; Shin, D.S.; Na, D.L. A Validation Study of the Inbrain CST: A Tablet Computer-based Cognitive Screening Test for Elderly People with Cognitive Impairment. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinuevo, J.L.; Rabin, L.A.; Amariglio, R.; Buckley, R.; Dubois, B.; Ellis, K.A.; Ewers, M.; Hampel, H.; Kloppel, S.; Rami, L.; et al. Implementation of subjective cognitive decline criteria in research studies. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, R.C.; Smith, G.E.; Waring, S.C.; Ivnik, R.J.; Tangalos, E.G.; Kokmen, E. Mild cognitive impairment: Clinical characterization and outcome. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. Contributors. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Chang, Y.; Choe, Y.S.; Kim, J.P.; Jang, H.; Shin, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Koh, S.B.; Na, D.L.; et al. Gender-specific relationship between thigh muscle and fat mass and brain amyloid-beta positivity. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Woo, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Jang, H.; Kim, Y.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, S.J.; Shin, B.S.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Disease progression modeling of Alzheimer’s disease according to education level. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.L.; Subramaniam, M.; Abdin, E.; Wang, P.; Vaingankar, J.A.; Lee, S.P.; Shafie, S.; Seow, E.; Chong, S.A. Performance of Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in long-stay patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorders in a psychiatric institute. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 241, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, G.; Braidy, N.; Ahmed, T. Blood-Based Biomarkers for Predictive Diagnosis of Cognitive Impairment in a Pakistani Population. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftychios, A. Alzheimer Disease and Music-Therapy: An Interesting Therapeutic Challenge and Proposal. Advances in Alzheimer’s Disease 2021, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.C. Clinical dementia rating: A reliable and valid diagnostic and staging measure for dementia of the Alzheimer type. Int. Psychogeriatr. 1997, 9 (Suppl. 1), 173–176, discussion 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.N.; Cho, M.J. Development of the Korean version of the Geriatric Depression Scale and its short form among elderly psychiatric patients. J. Psychosom. Res. 2004, 57, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, J.I.; Yesavage, J.A. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS): Recent evidence and development of a shorter version. Clin. Gerontol. J. Aging Ment. Health 1986, 5, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jang, H.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, H.J.; Moon, S.H.; Ewers, M.; Im, K.; et al. Vascular Effects on Depressive Symptoms in Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 65, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.C.; Kim, E.H.; Woo, H.S.; Song, C.S. Effectiveness of an Online Dementia Prevention Program on Cognitive Function and Depression in Community-Dwelling Older Adults during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.P.; Shrivastava, S.R.; Ramasamy, J. Depression in an older adult rural population in India. MEDICC Rev. 2013, 15, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikmat, A.W.; Azhar, Z.I.; Shuib, N.; Hashim, N.A. Psychometric Properties of Geriatric Depression Scale (Malay Version) in Elderly with Cognitive Impairment. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 28, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.G.; Heinz, A.J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, H. Optofluidic in situ maskless lithography of charge selective nanoporous hydrogel for DNA preconcentration. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 43014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, L.N.; Kim, M.; Jung, K.; Bae, H.J.; Jang, J.; Jung, Y.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S. Shape-encoded silica microparticles for multiplexed bioassays. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12130–12133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CN | SCD | MCI | AD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 71 (5%) | 275 (20%) | 857 (61%) | 192 (14%) |
| Age | 61.49 ± 9.44 | 69.79 ± 7.80 a | 72.86 ± 8.15 a | 70.26 ± 9.44 a |
| Sex (M/F) | 24/47 | 81/194 | 297/560 | 78/114 |
| ApoE genotype (ε4 +/−) | 8/63 | 71/204 | 314/543 | 92/100 |
| MMSE total | 27.93 ± 2.24 | 27.92 ± 1.91 | 24.31 ± 4.06 a | 19.33 ± 4.73 a |
| Orientation | 9.85 ± 0.36 | 9.84 ± 0.43 | 8.59 ± 1.69 a | 5.94 ± 2.07 a |
| Immediate recall | 2.96 ± 0.20 | 2.96 ± 0.22 | 2.90 ± 0.37 | 2.81 ± 0.49 a |
| Attention and Calculation | 4.21 ± 1.12 | 4.17 ± 1.03 | 3.32 ± 1.51 a | 2.36 ± 1.75 a |
| Memory recall | 2.37 ± 0.76 | 2.27 ± 0.96 | 1.35 ± 1.11 a | 0.66 ± 0.99 a |
| Language | 7.59 ± 0.77 | 7.74 ± 0.56 | 7.32 ± 1.01 a | 6.92 ± 1.34 a |
| Copying | 0.94 ± 0.23 | 0.94 ± 0.24 | 0.81 ± 0.39 a | 0.65 ± 0.48 a |
| CDR score | 0.18 ± 0.24 | 0.46 ± 0.14 a | 0.50 ± 0.16 a | 0.94 ± 0.49 a |
| CDR SB | 0.21 ± 0.30 | 0.67 ± 0.48 a | 1.63 ± 1.35 a | 5.65 ± 2.87 a |
| Memory | 0.18 ± 0.24 | 0.46 ± 0.15 a | 0.60 ± 0.28 a | 1.24 ± 0.57 a |
| Orientation | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.18 | 0.32 ± 0.36 a | 1.07 ± 0.55 a |
| Judgment and Problem-solving | 0.01 ± 0.06 | 0.07 ± 0.18 | 0.28 ± 0.33 a | 0.95 ± 0.53 a |
| Community Affairs | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.12 | 0.19 ± 0.32 a | 0.97 ± 0.61 a |
| Home and Hobbies | 0.02 ± 0.10 | 0.06 ± 0.17 | 0.20 ± 0.32 a | 0.95 ± 0.61 a |
| Personal care | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.05 | 0.04 ± 0.23 | 0.47 ± 0.68 a |
| QM Alz-N | QM Alz-P | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 595 | 800 | |
| Age | 70.71 ± 9.04 | 71.76 ± 8.49 | p = 0.0283 |
| Sex (M/F) | 212/383 | 268/532 | |
| ApoE genotype (ε4 +/−) | 184/411 | 301/499 | |
| MMSE total | 25.15 ± 4.28 | 24.05 ± 4.70 | p < 0.0001 |
| Orientation | 8.80 ± 1.75 | 8.34 ± 2.03 | p < 0.0001 |
| Immediate recall | 2.92 ± 0.34 | 2.90 ± 0.38 | N.S. |
| Attention and Calculation | 3.53 ± 1.50 | 3.31 ± 1.58 | p = 0.0068 |
| Memory recall | 1.62 ± 1.13 | 1.39 ± 1.18 | p = 0.0002 |
| Language | 7.43 ± 0.94 | 7.31 ± 1.07 | p = 0.0289 |
| Copying | 0.84 ± 0.36 | 0.81 ± 0.40 | N.S. |
| CDR score | 0.50 ± 0.24 | 0.57 ± 0.32 | p < 0.0001 |
| CDR SB | 1.60 ± 1.82 | 2.16 ± 2.38 | p < 0.0001 |
| Memory | 0.58 ± 0.37 | 0.68 ± 0.43 | p < 0.0001 |
| Orientation | 0.29 ± 0.43 | 0.40 ± 0.49 | p < 0.0001 |
| Judgment and Problem-solving | 0.25 ± 0.38 | 0.36 ± 0.46 | p < 0.0001 |
| Community Affairs | 0.20 ± 0.38 | 0.30 ± 0.49 | p < 0.0001 |
| Home and Hobbies | 0.21 ± 0.37 | 0.31 ± 0.49 | p < 0.0001 |
| Personal care | 0.06 ± 0.27 | 0.11 ± 0.39 | p = 0.0059 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Na, H.; Shin, K.Y.; Lee, D.; Yoon, C.; Han, S.-H.; Park, J.-C.; Mook-Jung, I.; Jang, J.; Kwon, S. The QPLEX™ Plus Assay Kit for the Early Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311119
Na H, Shin KY, Lee D, Yoon C, Han S-H, Park J-C, Mook-Jung I, Jang J, Kwon S. The QPLEX™ Plus Assay Kit for the Early Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):11119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311119
Chicago/Turabian StyleNa, Hunjong, Ki Young Shin, Dokyung Lee, Changsik Yoon, Sun-Ho Han, Jong-Chan Park, Inhee Mook-Jung, Jisung Jang, and Sunghoon Kwon. 2023. "The QPLEX™ Plus Assay Kit for the Early Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 11119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311119
APA StyleNa, H., Shin, K. Y., Lee, D., Yoon, C., Han, S.-H., Park, J.-C., Mook-Jung, I., Jang, J., & Kwon, S. (2023). The QPLEX™ Plus Assay Kit for the Early Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 11119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311119






