Synergistic Effects of Vitis vinifera L. and Centella asiatica against CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
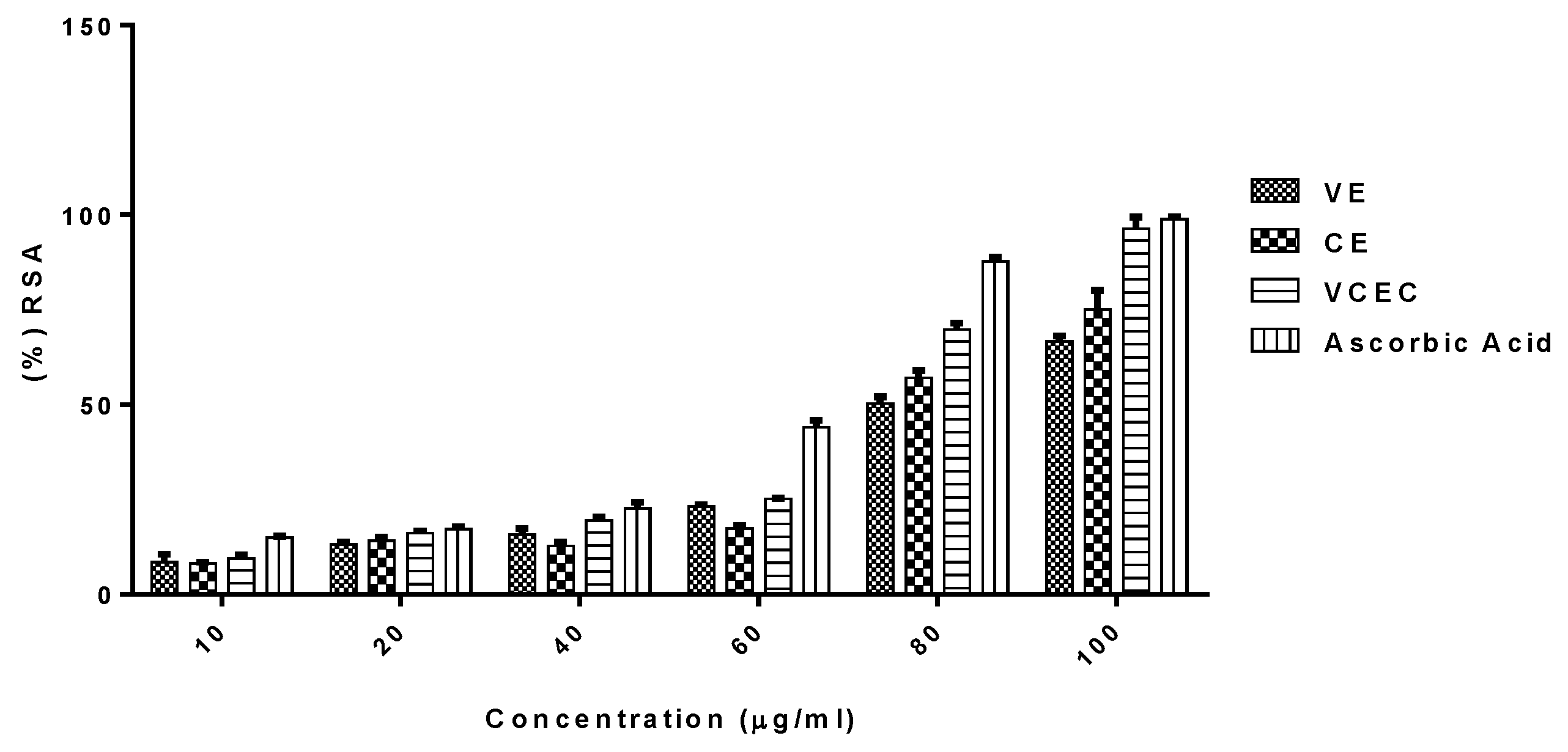
2.1. VE and CE in Combination Acted Synergistically and Demonstrated the Highest Antioxidant Activities
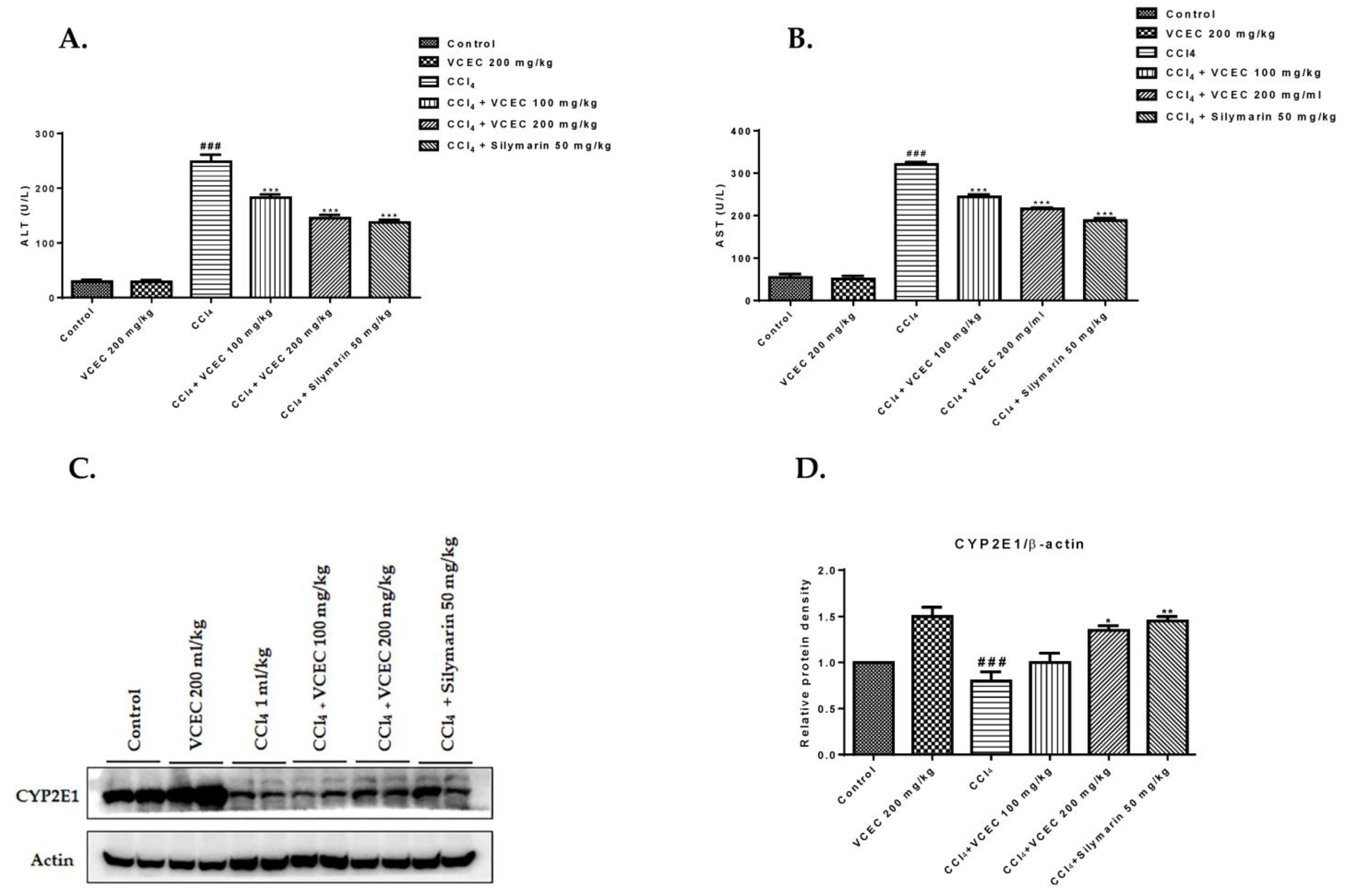
2.2. VCEC ameliorates CCl4-Induced Liver Injury
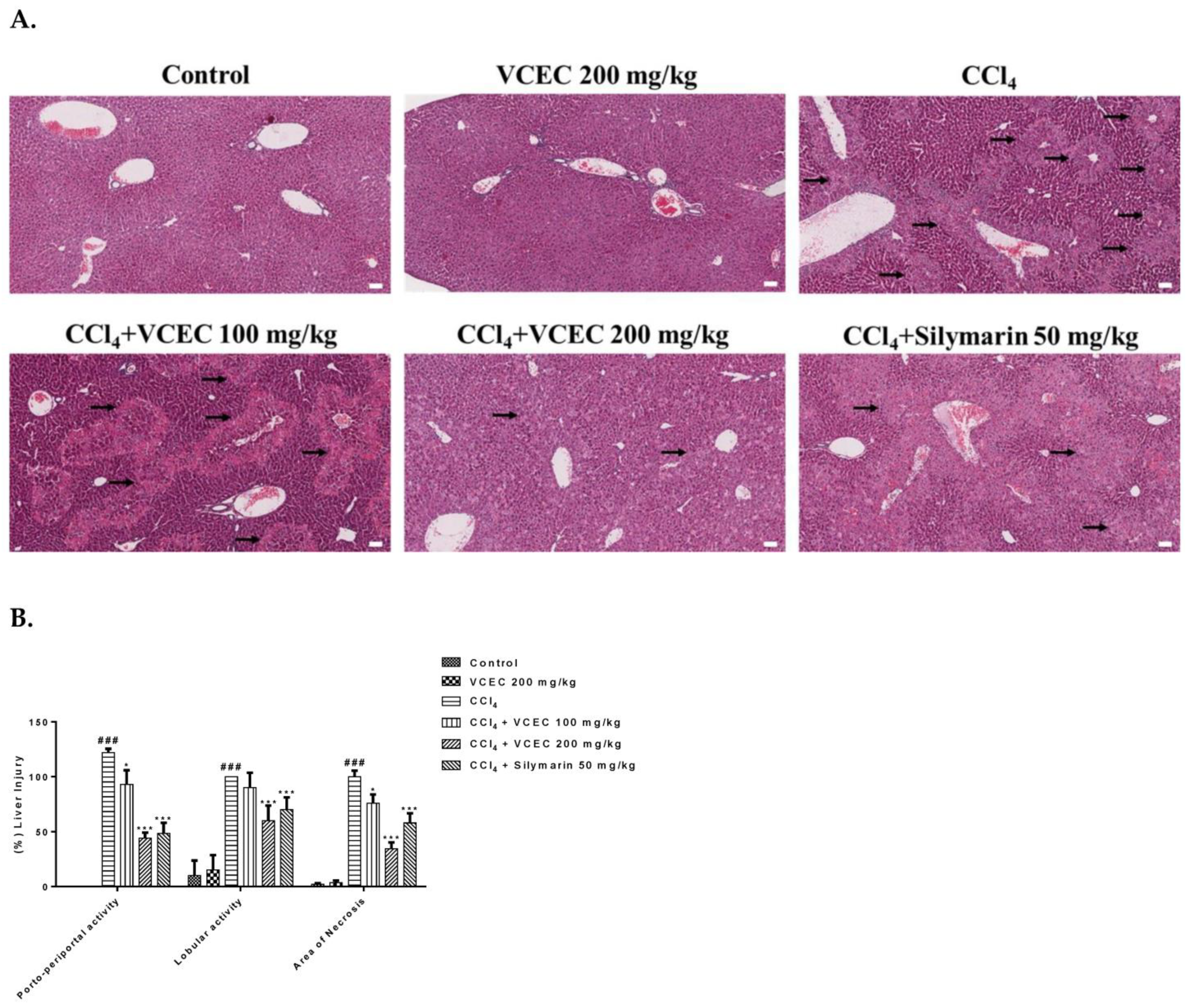
2.3. VCEC Reduces Hepatic Histopathological Damage Caused by CCl4
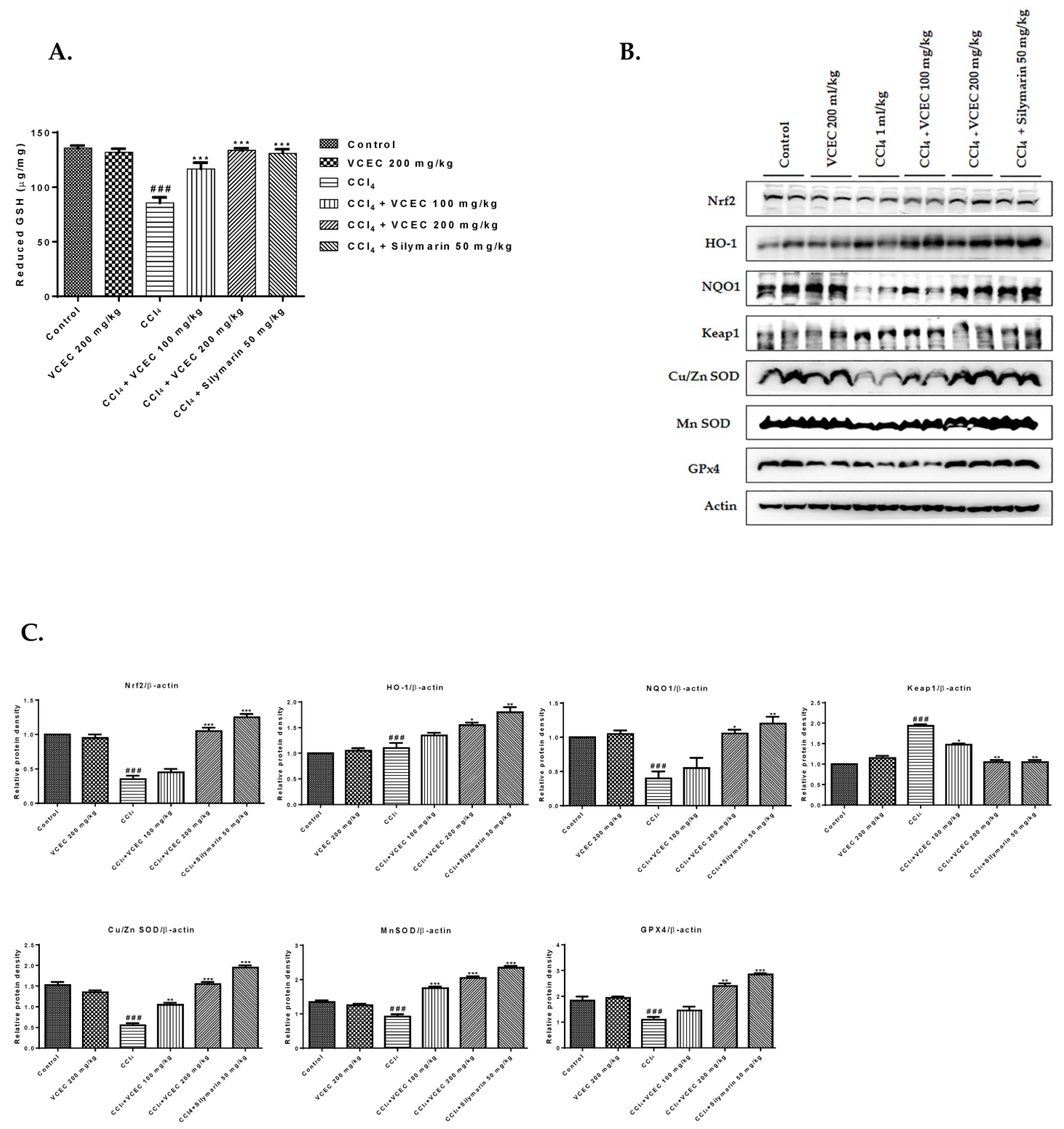
2.4. Antioxidant Properties of VCEC against CCl4-Induced Oxidative Stress
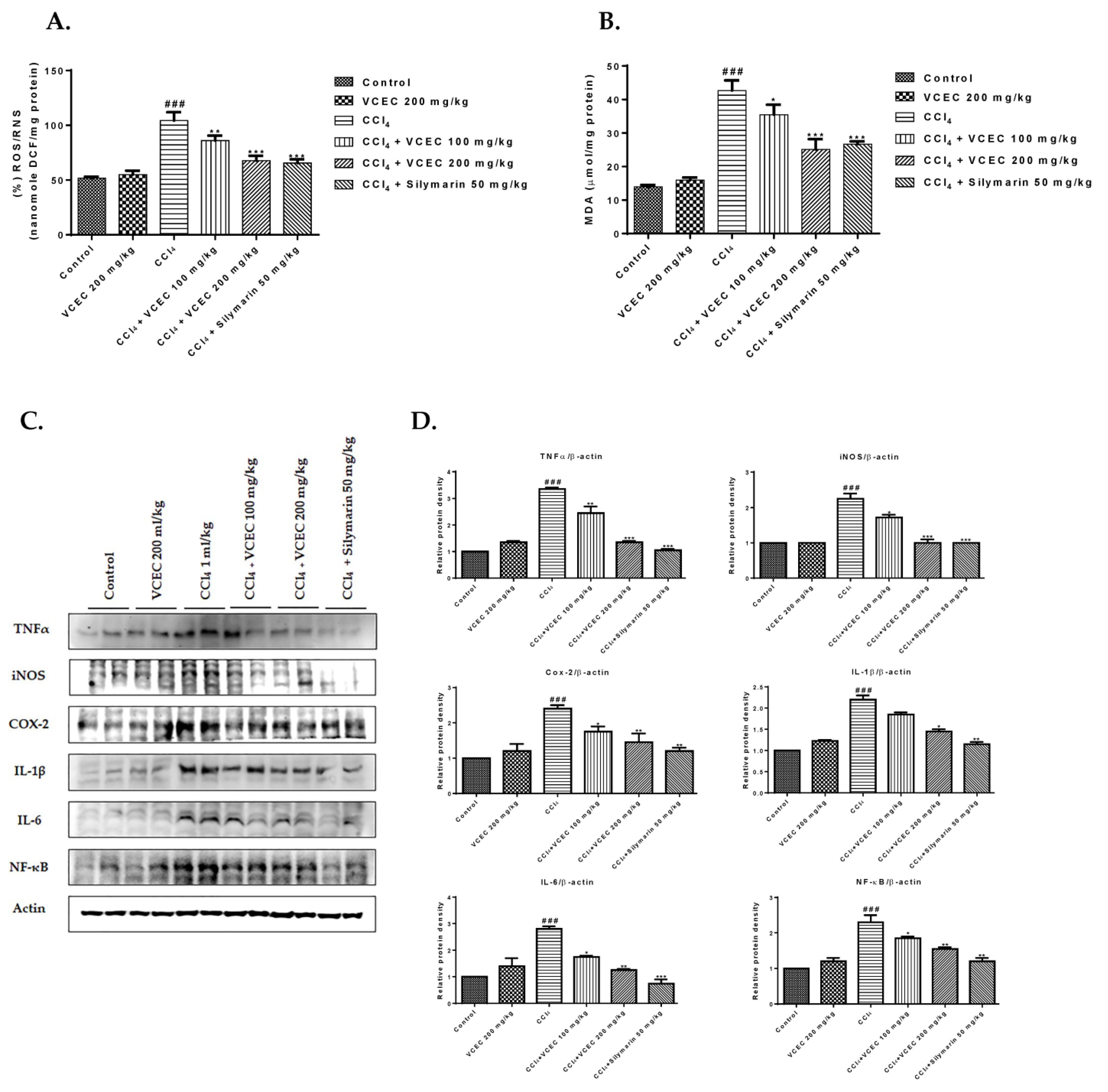
2.5. VCEC Alleviated Lipid Peroxidation, Inflammation, and ROS Production in Response to CCl4 Treatment
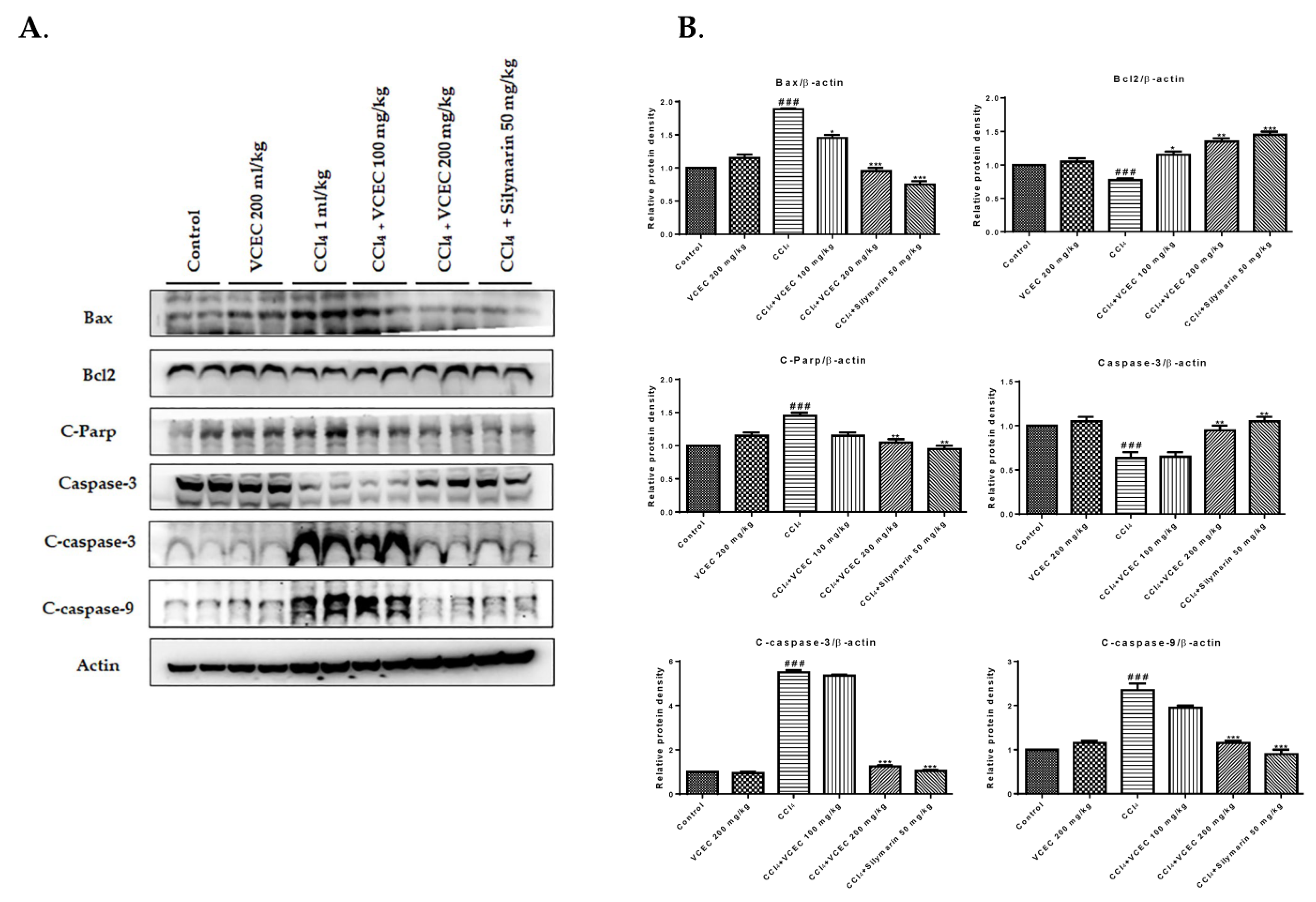
2.6. VCEC Inhibits CCl4-Induced Hepatocyte Apoptosis in Mice
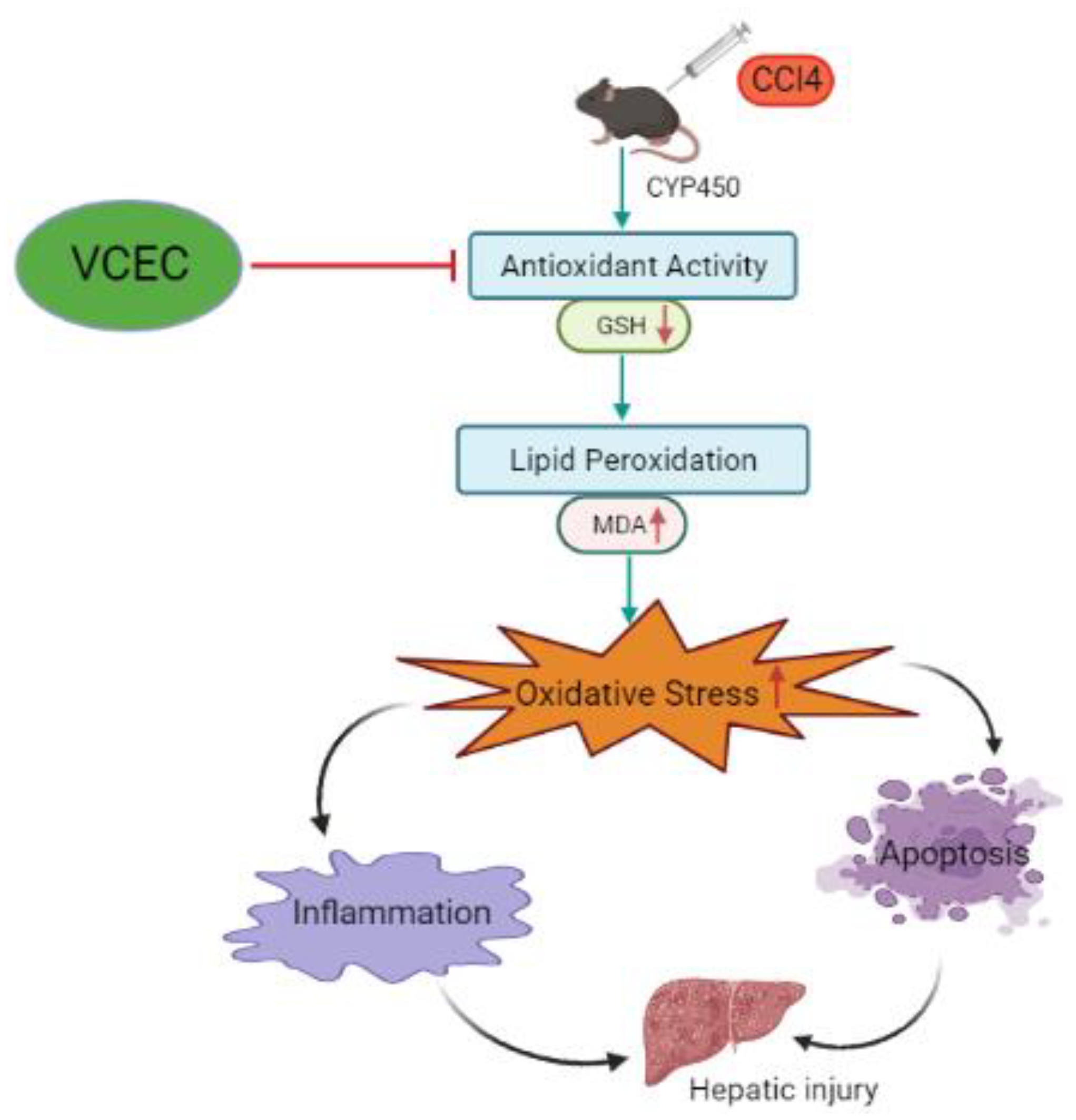
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of V. vinifera L. leaf and C. asiatica Extracts
4.3. DDPH Radical Scavenging Assays
4.4. Animals
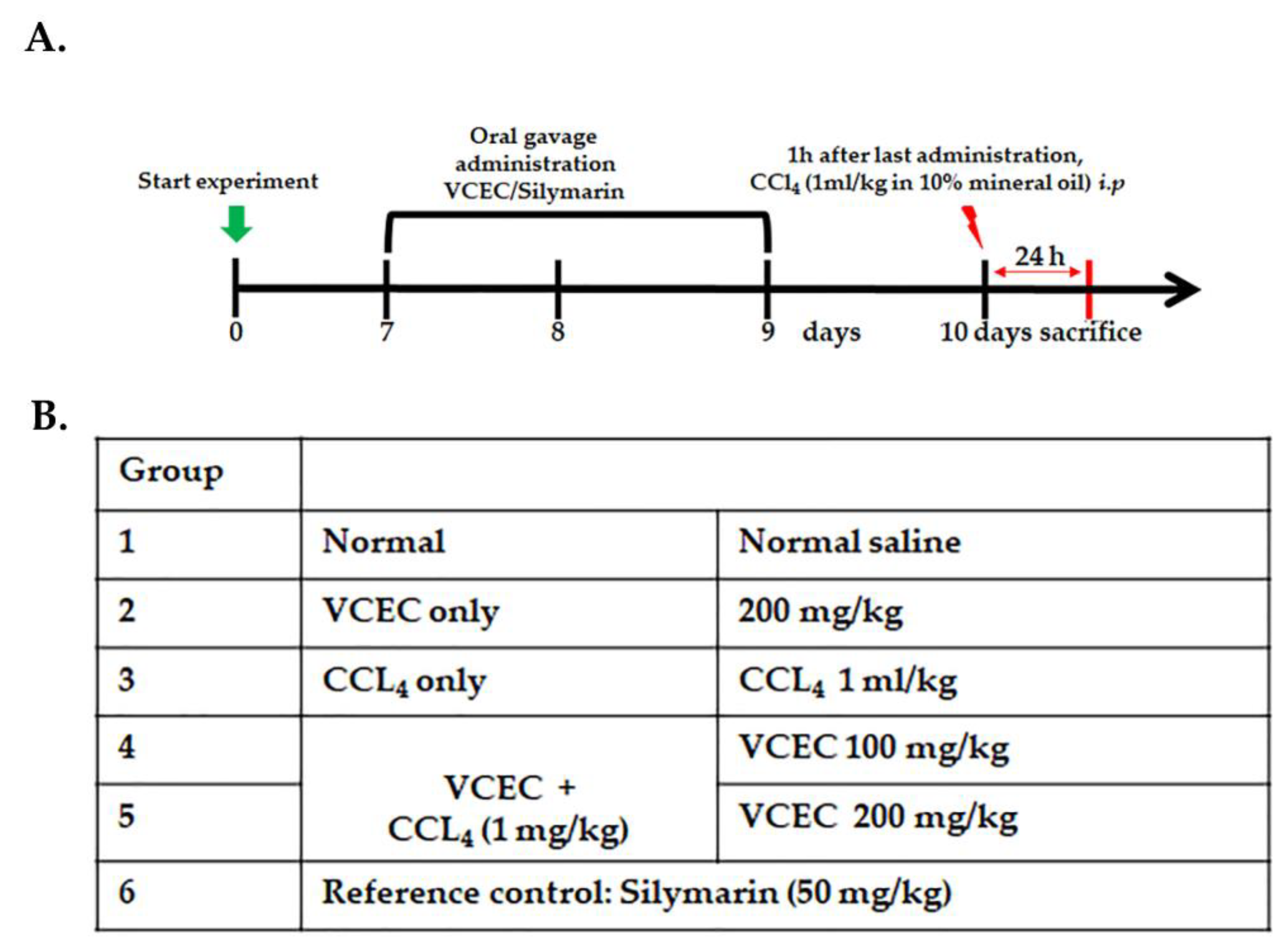
4.5. Animal Model and Drug Treatment
4.6. Determination of Biochemical Parameters
4.7. Liver Histopathological Examination
4.8. Measurements of Reduced Glutathione (GSH) and Malondialdehyde (MDA)
4.9. Determination of ROS Formation
4.10. Immunoblotting
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozougwu, J.C. Physiology of the liver. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biosci. 2017, 4, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Munakarmi, S.; Gurau, Y.; Shrestha, J.; Risal, P.; Park, H.S.; Shin, H.B.; Jeong, Y.J. Hepatoprotective Effects of a Natural Flavanol 3,3′-Diindolylmethane against CCl4-Induced Chronic Liver Injury in Mice and TGFβ1-Induced EMT in Mouse Hepatocytes via Activation of Nrf2 Cascade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11407. [Google Scholar]
- Cichoż-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakarmi, S.; Chand, L.; Shin, H.B.; Jang, K.Y.; Jeong, Y.J. Indole-3-Carbinol Derivative DIM Mitigates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice by Inhibiting Inflammatory Response, Apoptosis and Regulating Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xu, M.; Jeong, S.; Qian, Y.; Wu, H.; Xia, Q.; Kong, X. The role of Nrf2 in liver disease: Novel molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koruk, M.; Taysi, S.; Savas, M.C.; Yilmaz, O.; Akcay, F.; Karakok, M. Oxidative stress and enzymatic antioxidant status in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2004, 34, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Minicis, S.; Brenner, D.A. Oxidative stress in alcoholic liver disease: Role of NADPH oxidase complex. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, S98–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florescu, I.E.; Georgescu, S.E.; Dudu, A.; Balaș, M.; Voicu, S.; Grecu, I.; Dediu, L.; Dinischiotu, A.; Costache, M. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense mechanisms in response to starvation and refeeding in the intestine of stellate sturgeon (Acipenser stellatus) juveniles from aquaculture. Animals 2021, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azab, K.S.; Mostafa, A.-H.A.; Ali, E.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.A. Cinnamon extract ameliorates ionizing radiation-induced cellular injury in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 2324–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjuna, K.; Shanmugam, K.; Nishanth, K.; Wu, M.-C.; Hou, C.-W.; Kuo, C.-H.; Reddy, K.S. Alcohol-induced deterioration in primary antioxidant and glutathione family enzymes reversed by exercise training in the liver of old rats. Alcohol 2010, 44, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, D.D.; Orhan, N.; Ergun, E.; Ergun, F. Hepatoprotective effect of Vitis vinifera L. leaves on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver damage in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, L.Y.; Ng, C.T.; Cheok, Z.L.; Moklas, M.A.M.; Hakim, M.N.; Ahmad, Z. Barrier protective effect of asiatic acid in TNF-α-induced activation of human aortic endothelial cells. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglisi, R.; Severgnini, A.; Tava, A.; Montedoro, M. In vitro assessment of the antioxidant properties of aqueous byproduct extracts of Vitis vinifera. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somchit, M.; Sulaiman, M.; Zuraini, A.; Samsuddin, L.; Somchit, N.; Israf, D.; Moin, S. Antinociceptive and antiinflammatory effects of Centella asiatica. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2004, 36, 377. [Google Scholar]
- Pari, L.; Suresh, A. Effect of grape (Vitis vinifera L.) leaf extract on alcohol induced oxidative stress in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-N.; Kim, H.-G.; Chon, C.-Y.; Park, J.-B.; Sohn, J.-H.; Yang, S.-H.; Yu, E.-S.; Lee, M.-S.; Jang, J.-J.; Chang, H.-K. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis standardized guideline proposed by the Korean Study Group for the Pathology of Digestive Diseases. Korean J. Pathol. 1999, 33, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.; Mehta, P. Bamboo a supplement to human health: A comprehensive review on its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activity. Nat. Prod. J. 2021, 11, 140–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul Kamdem, J.; Olalekan Abolaji, A.; Olusola Elekofehinti, O.; Olaposi Omotuyi, I.; Ibrahim, M.; Hassan, W.; Vargas Barbosa, N.; Onofre Souza, D.; Batista Teixeira da Rocha, J. Therapeutic potential of plant extracts and phytochemicals against brain ischemia-reperfusion injury: A review. Nat. Prod. J. 2016, 6, 250–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhen, X.; Jiang, X. Activatable Optical Probes for Fluorescence and Photoacoustic Imaging of Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2022, 2, 2200097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.R.; Jaeschke, H. Animal models of drug-induced liver injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hadary, A.E.; Ramadan Hassanien, M.F. Hepatoprotective effect of cold-pressed Syzygium aromaticum oil against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Han, X.; Yuan, G.; An, L.; Du, P. Screening for the protective effect target of deproteinized extract of calf blood and its mechanisms in mice with CCl4-induced acute liver injury. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clawson, G.A. Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. Pathol. Immunopathol. Res. 1989, 8, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozer, J.; Ratner, M.; Shaw, M.; Bailey, W.; Schomaker, S. The current state of serum biomarkers of hepatotoxicity. Toxicology 2008, 245, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.Y.; Kim, M.R.; Yu, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Shim, K.-S.; Shin, E.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, Y.C. Combined extract of Vitis vinifera L. and Centella asiatica synergistically attenuates oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 25, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, P.B.; Romeiro, N.C. Multi-target natural products as alternatives against oxidative stress in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 911–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Maity, N.; Nema, N.K.; Sarkar, B.K. Bioactive compounds from natural resources against skin aging. Phytomedicine 2011, 19, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizeq, B.; Gupta, I.; Ilesanmi, J.; AlSafran, M.; Rahman, M.; Ouhtit, A. The power of phytochemicals combination in cancer chemoprevention. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 4521–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.-T.; Wang, Z.J.; Chow, M.S.S.; Lam, C.W.K. Herb-herb combination for therapeutic enhancement and advancement: Theory, practice and future perspectives. Molecules 2013, 18, 5125–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhao, J.; Ma, L.; Ding, Y.; Su, D. Hepatoprotective effects of total triterpenoids and total flavonoids from Vitis vinifera L against immunological liver injury in mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 969386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giribabu, N.; Karim, K.; Kilari, E.K.; Kassim, N.M.; Salleh, N. Anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic and proproliferative effects of vitis vinifera seed ethanolic extract in the liver of streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetes in male rats. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, B.; Santhakumari, G.; Merina, B.; Sheeba, V.; Mukkadan, J. Hepatoprotective effect of Centella asiatica (L) in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 68, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.W.; Jeon, H.; Kwon, J.E.; Lee, Y.G.; So, R.; Choe, T.H.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kang, S.C. Hepatoprotective effect of Centella asiatica 50% ethanol extract against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in BALB/c mice. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 37, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hsouna, A.; Hfaiedh, M.; Ben Slima, S.; Romdhane, W.B.; Akacha, B.B.; Bouterra, M.T.; Dhifi, W.; Mnif, W.; Brini, F.; Ben Saad, R. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of novel heteropolysaccharide isolated from Lobularia maritima on CCl4-induced liver injury in rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2271–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.-W.; Chang, J.-C.; Lin, L.-W.; Tsai, F.-H.; Chang, H.-C.; Wu, C.-R. Comparison of the hepatoprotective effects of four endemic Cirsium species extracts from Taiwan on CCl4-induced acute liver damage in C57BL/6 mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusam, Y.; Louis, T.; Madhavachandran, V.; Kumar, S.; Thoprani, N.; Hamblin, M.R.; Lakshmanan, S. Antioxidant activity of the ancient herb, Holy Basil in CCl4-induced liver injury in rats. Ayurvedic 2015, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekka, E.; Kourounakis, P.N. Effect of hydroxyethyl rutosides and related compounds on lipid peroxidation and free radical scavenging activity. Some structural aspects. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1991, 43, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, C. Hepatoprotective effects of apple polyphenols on CCl4-induced acute liver damage in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6525–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Yang, T.; Chen, H.; Fu, D.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Yu, H.; Xu, W.; Xie, X. New insights into oxidative stress and inflammation during diabetes mellitus-accelerated atherosclerosis. Redox Biol. 2019, 20, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.; Talwar, P.; Parimisetty, A.; Lefebvre d’Hellencourt, C.; Ravanan, P. A molecular web: Endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-Q.; Ding, J.; Xiao, Z.-H.; Liu, C.-M. Ursolic acid ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative DNA damage and inflammation in mouse kidney by inhibiting the STAT3 and NF-κB activities. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 21, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilzer, M.; Roggel, F.; Gerbes, A.L. Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzanegi, P.; Dana, A.; Ebrahimpoor, Z.; Asadi, M.; Azarbayjani, M.A. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, M.Á.; Serrano, A.B.G.; Ramos, S.; Pulido, M.I.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L. Cocoa flavonoids up-regulate antioxidant enzyme activity via the ERK1/2 pathway to protect against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giribabu, N.; Karim, K.; Kilari, E.K.; Nelli, S.R.; Salleh, N. Oral administration of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb leave aqueous extract ameliorates cerebral oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in male rats with type-2 diabetes. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 1599–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N.; Carter-Kent, C.; Feldstein, A.E. Apoptosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 5, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qiao, B.; Jiang, S.; Shen, Q.; Han, Y.; Liu, A.; Chen, X.; Wei, L.; Zhou, L. Androgen aggravates liver fibrosis by activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in CCl4-induced liver injury mouse model. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E817–E829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelusi, O.B.; Ramachandran, A.; Lemasters, J.J.; Jaeschke, H. The role of Iron in lipid peroxidation and protein nitration during acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 445, 116043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Lan, X.-T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, D.-Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Ou-Yang, S.-X.; Zhuang, C.-L.; Shen, F.-M.; Wang, P. Ferroptosis inhibitor liproxstatin-1 alleviates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in mice: Potential involvement of PANoptosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chota, A.; George, B.P.; Abrahamse, H. Interactions of multidomain pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins in cancer cell death. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y. Cell death regulation by the Bcl-2 protein family in the mitochondria. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 195, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.-G.; Jo, M.-J.; Hong, N.I.; Kim, M.J.; Shim, K.S.; Shin, E.; Lee, J.J.; Park, S.-J. Anti-inflammatory and anti-vascular leakage effects by combination of Centella asiatica and Vitis vinifera L. Leaf extracts. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 7381620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Zou, S.; Liang, D.; Luan, L. Structural characterization, antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of polysaccharides from Sophorae tonkinensis Radix. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| S.N | Target | Blocking Solution | Dilution | Secondary | Manufacturer | Catalogue Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | β-actin | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Mouse IgG | Sigma Aldrich | A5441 |
| 2 | COX-2 | 5% BSA | 1:1000 | Rabbit IgG | Cell Signaling | 4842S |
| 3 | C-Caspase-9 | 5% BSA | 1:1000 | Mouse IgG | Cell Signaling | 9508S |
| 4 | Parp | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Rabbit IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-7150 |
| 5 | Keap-1 | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Mouse IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-365626 |
| 6 | Nrf-2 | 5% BSA | 1:1000 | Rabbit IgG | Gene Tex | GTX103322 |
| 7 | NQO1 | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Mouse IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-32793 |
| 8 | HO-1 | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Mouse IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-136960 |
| 9 | GPX4 | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Mouse IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-166570 |
| 10 | Cu/Zn SOD | 5% BSA | 1:1000 | Rabbit IgG | Enzo | ADI-SOD-100 |
| 11 | Mn SOD | 5% BSA | 1:3000 | Rabbit IgG | Enzo | ADI-SOD-110 |
| 12 | iNOS | 5% BSA | 1:1500 | Mouse IgG | R&D System | MAB9502 |
| 13 | NF-κB | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Rabbit IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-8008 |
| 14 | IL-1β | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Rabbit IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-7884 |
| 15 | IL-6 | 5% BSA | 1:1000 | Rabbit IgG | Bio world | BS-6419 |
| 16 | TNF-α | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Hamster IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-12744 |
| 17 | CYP2E1 | 5% BSA | 1:1000 | Rabbit IgG | Abcam | ab28146 |
| 18 | Bax | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Mouse IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-7480 |
| 19 | Bcl2 | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Mouse IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-7382 |
| 20 | Caspase-3 | 5% Skim Milk | 1:3000 | Rabbit IgG | Santa Cruz | Sc-7148 |
| 21 | C-Caspase-3 | 5% BSA | 1:1000 | Rabbit IgG | Cell Signaling | #9664 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munakarmi, S.; Gurau, Y.; Shrestha, J.; Risal, P.; Park, H.S.; Lee, G.-H.; Jeong, Y.J. Synergistic Effects of Vitis vinifera L. and Centella asiatica against CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411255
Munakarmi S, Gurau Y, Shrestha J, Risal P, Park HS, Lee G-H, Jeong YJ. Synergistic Effects of Vitis vinifera L. and Centella asiatica against CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411255
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunakarmi, Suvesh, Yamuna Gurau, Juna Shrestha, Prabodh Risal, Ho Sung Park, Geum-Hwa Lee, and Yeon Jun Jeong. 2023. "Synergistic Effects of Vitis vinifera L. and Centella asiatica against CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411255
APA StyleMunakarmi, S., Gurau, Y., Shrestha, J., Risal, P., Park, H. S., Lee, G.-H., & Jeong, Y. J. (2023). Synergistic Effects of Vitis vinifera L. and Centella asiatica against CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411255





