Low Glucose plus β-Hydroxybutyrate Induces an Enhanced Inflammatory Response in Yak Alveolar Macrophages via Activating the GPR109A/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
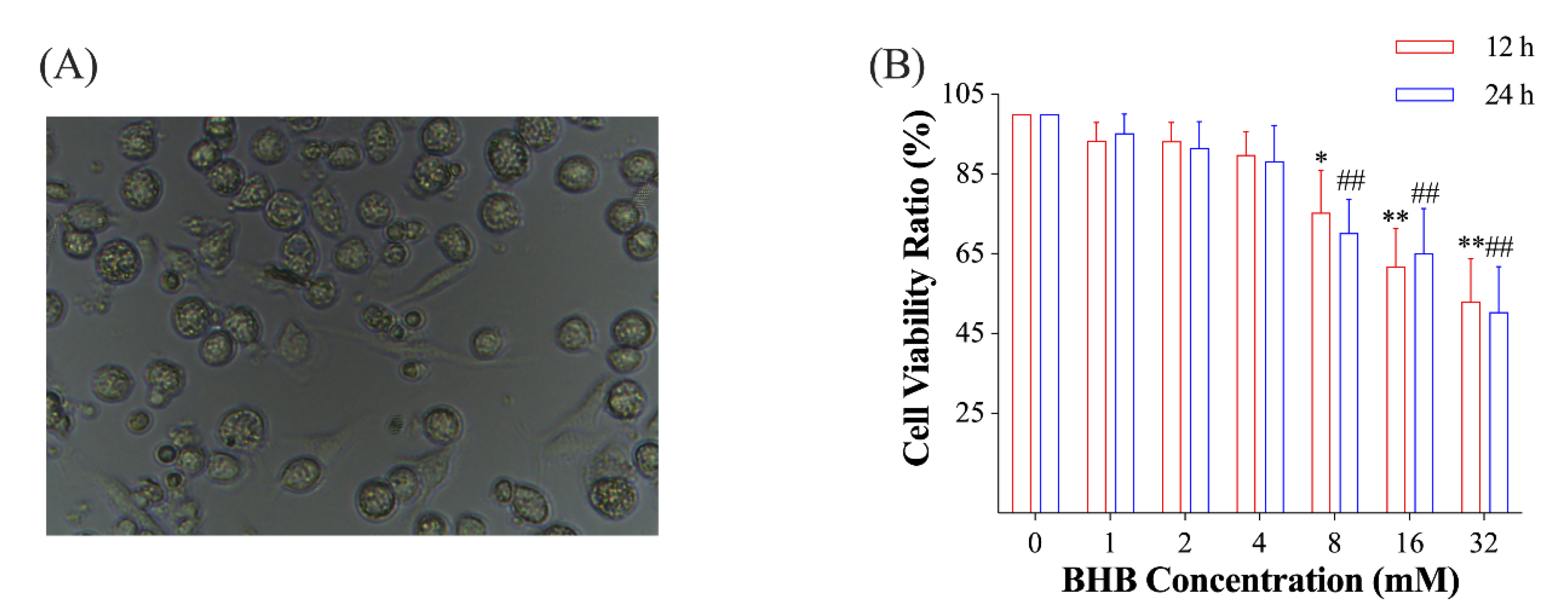
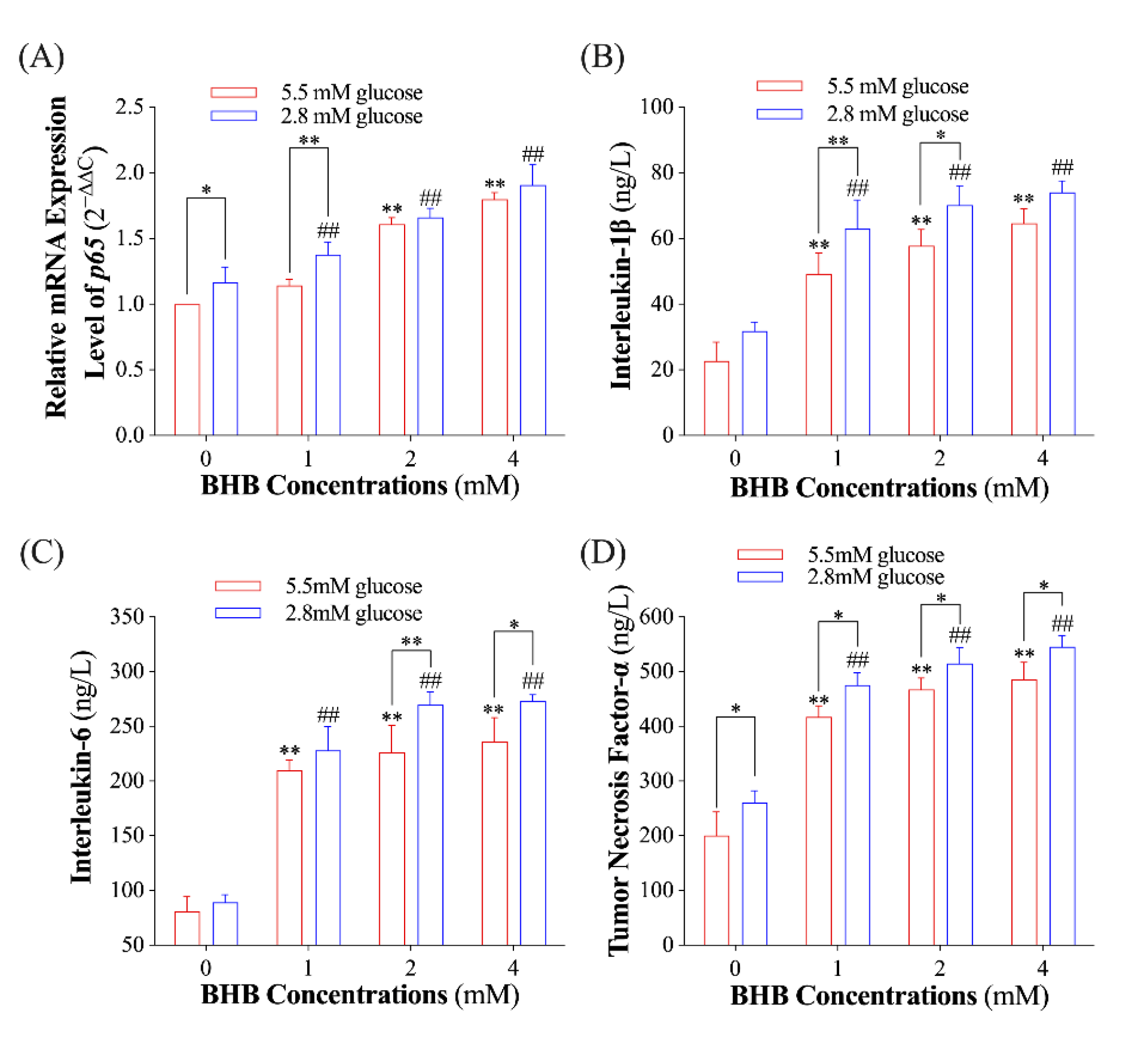
2.1. Effect of Low Glucose plus BHB on the Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
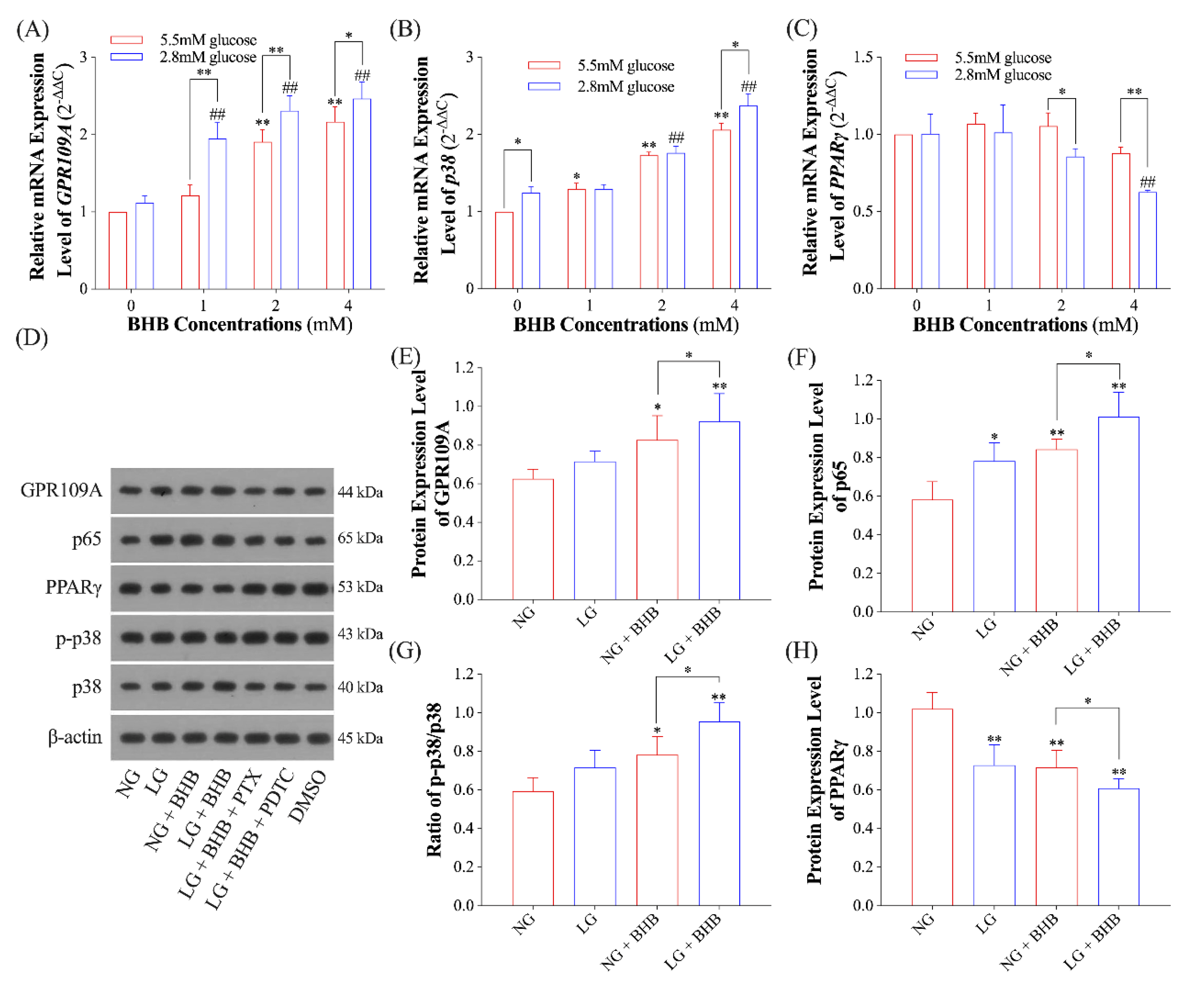
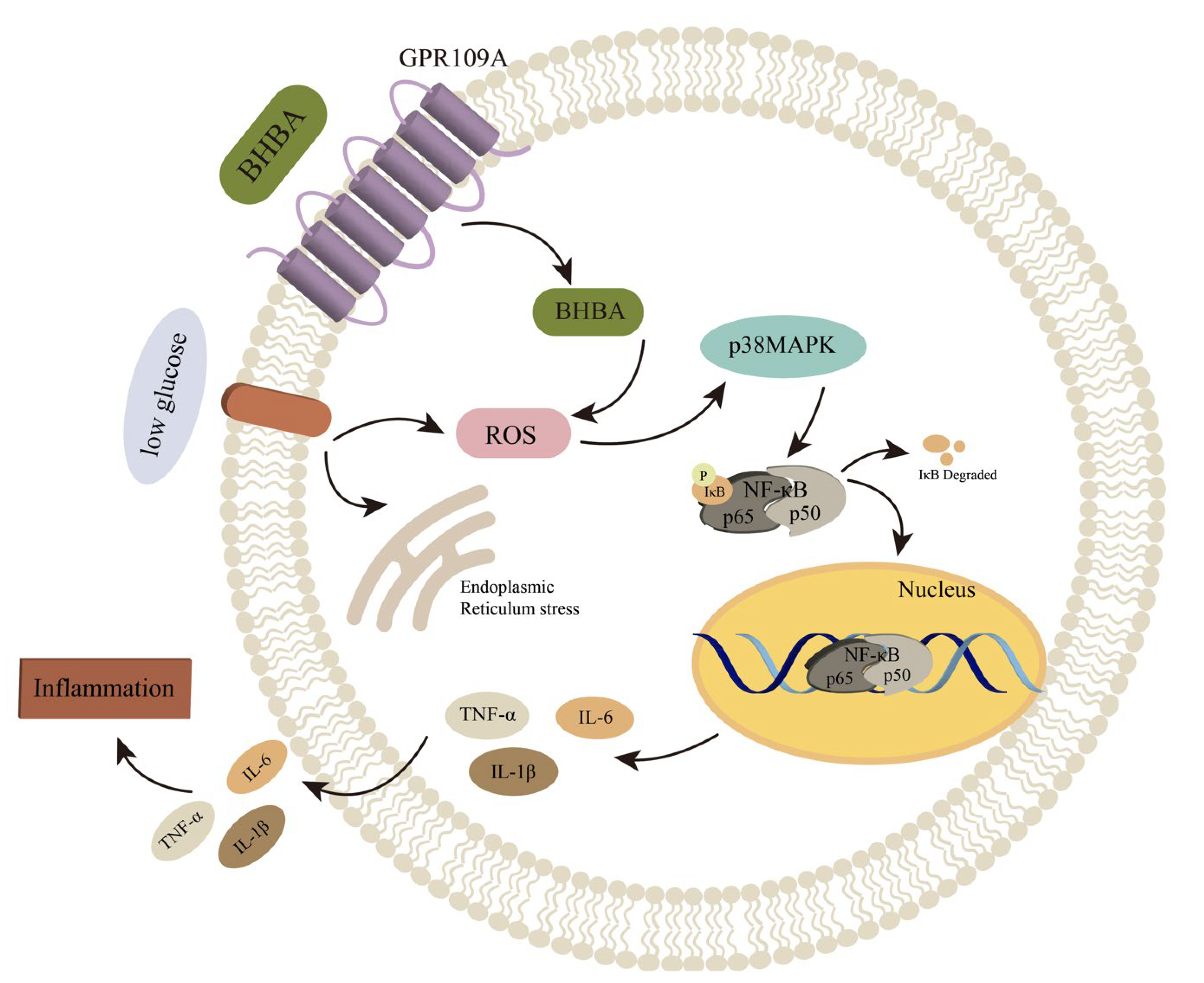
2.2. Effects of Low Glucose plus BHB on the GPR109A/p38/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
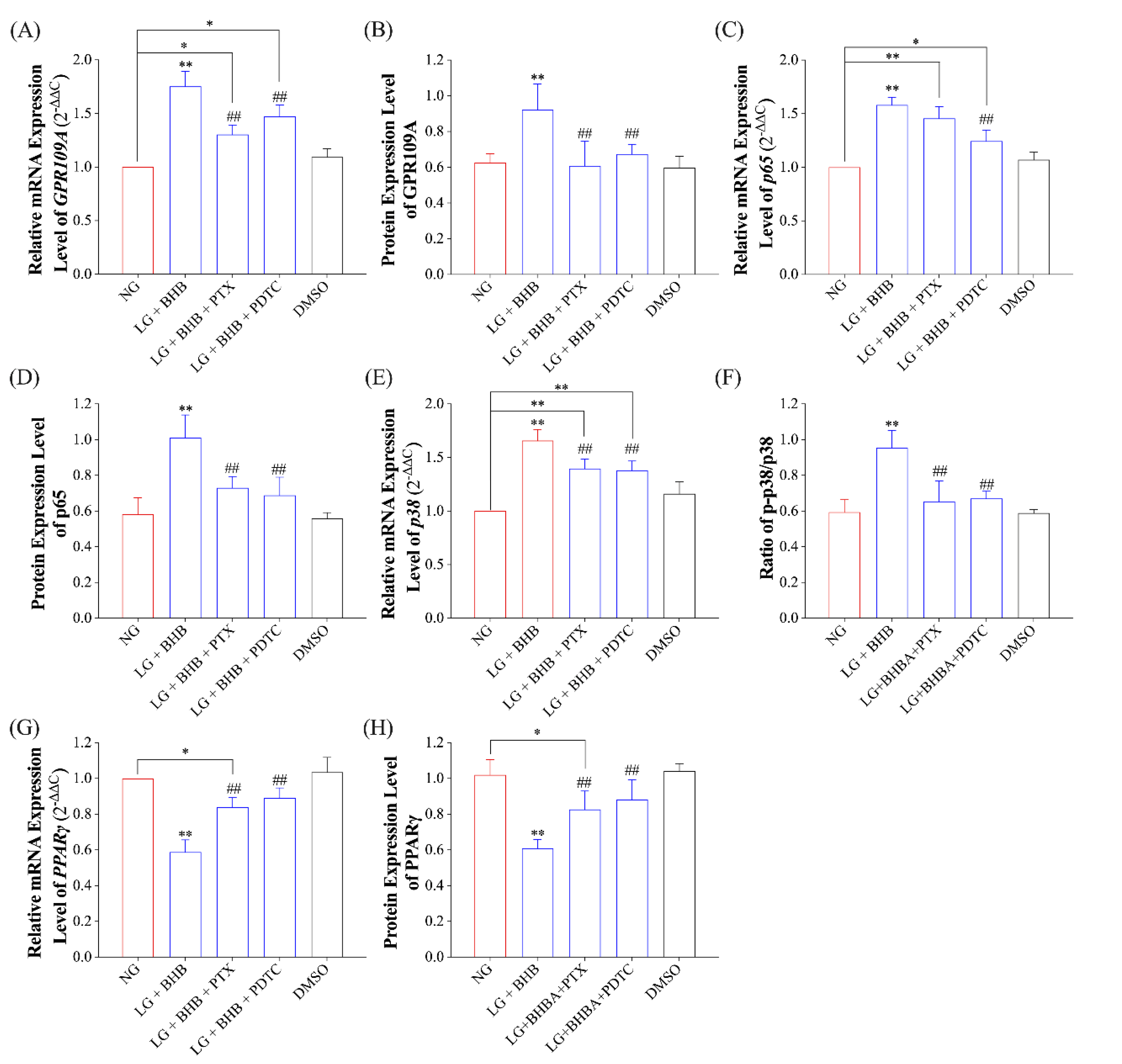
2.3. Effect of GPR109A/p38/NF-κB Signaling Pathway Inhibition on Inflammatory Response of AMs Induced by Low Glucose plus BHB
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Yak Primary AMs Isolation and Culture
4.2. BHB Preparation
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.5. Immunoblot Assay
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, X.; Ding, L.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Degen, A.; Long, R. The adaptive strategies of yaks to live in the Asian highlands. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 9, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.S. Seasonal changes in weight and body composition of yak grazing on alpine-meadow grassland in the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau of China. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 83, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Hu, R.; Wang, Z.; Shah, A.M.; Zeng, S.; Peng, Q.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Effects of Nutritional Deprivation and Re-Alimentation on the Feed Efficiency, Blood Biochemistry, and Rumen Microflora in Yaks (Bos grunniens). Animals 2019, 9, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Hu, R.; Dong, X.; Shah, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Peng, Q.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Lipid Catabolism in Starved Yak Is Inhibited by Intravenous Infusion of β-Hydroxybutyrate. Animals 2020, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Peng, Q.; Luo, X.; An, T.; Guan, J.; Wang, Z. Effects of Starvation on Lipid Metabolism and Gluconeogenesis in Yak. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Cai, D.; Cui, Y.; Tan, T.; Zou, H.; Guo, W.; Xie, Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Ma, X.; et al. Metagenomics Reveals That Intravenous Injection of Beta-Hydroxybutyric Acid (BHBA) Disturbs the Nasopharynx Microflora and Increases the Risk of Respiratory Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 630280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Walter, J.M.; Misharin, A.V. Alveolar Macrophages. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 330, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Gan, L.; Fang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Guo, H.; Cai, D.; Cui, H.; Gou, L.; Deng, J.; et al. Beta-Hydroxybutyrate: A Dual Function Molecular and Immunological Barrier Function Regulator. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 805881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.C.; Verdin, E. β-Hydroxybutyrate: A Signaling Metabolite. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2017, 37, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youm, Y.-H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’Agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.D.; et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, B.J.; Koutnik, A.P.; Goldberg, E.L.; Upadhyay, V.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Verdin, E.; Newman, J.C. Investigating Ketone Bodies as Immunometabolic Countermeasures against Respiratory Viral Infections. Med 2020, 1, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, F.; Peukert, K.; Surace, L.; Michla, M.; Nikolka, F.; Fox, M.; Weiss, P.; Feuerborn, C.; Maier, P.; Schulz, S.; et al. Impaired ketogenesis ties metabolism to T cell dysfunction in COVID-19. Nature 2022, 609, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, E.L.; Molony, R.D.; Kudo, E.; Sidorov, S.; Kong, Y.; Dixit, V.D.; Iwasaki, A. Ketogenic diet activates protective γδ T cell responses against influenza virus infection. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaav2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blad, C.C.; Tang, C.; Offermanns, S. G protein-coupled receptors for energy metabolites as new therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-J.; Li, Z.-H.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, F.-Q.; Wang, W.; Cui, Z.J.; Chen, G.-Q. Ketone Body 3-Hydroxybutyrate Ameliorates Atherosclerosis via Receptor Gpr109a-Mediated Calcium Influx. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, C.L.-P.; Lai, A.C.-Y.; Ting, Y.-T.; Chi, P.-Y.; Chang, Y.-J. The ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate mitigates ILC2-driven airway inflammation by regulating mast cell function. Cell. Rep. 2022, 40, 111437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Lu, X.; Arbab, A.A.I.; Wu, X.; Mao, Y.; Loor, J.J.; Yang, Z. Metformin acts to suppress β-hydroxybutyric acid-mediated inflammatory responses through activation of AMPK signaling in bovine hepatocytes. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Deng, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Yin, L.; et al. β-Hydroxybutyrate activates the NF-κB signaling pathway to promote the expression of pro-inflammatory factors in calf hepatocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Long, M.; Yang, S.; He, J. Palmitic Acid and β-Hydroxybutyrate Induce Inflammatory Responses in Bovine Endometrial Cells by Activating Oxidative Stress-Mediated NF-κB Signaling. Molecules 2019, 24, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piarulli, F.; Sartore, G.; Sechi, A.; Basso, D.; Fogar, P.; Greco, E.; Ragazzi, E.; Lapolla, A. Low Glucose Concentrations Induce a Similar Inflammatory Response in Monocytes from Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Healthy Subjects. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 9185272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugo, H.; Sukketsiri, W.; Iwamoto, K.; Suihara, S.; Moriyama, T.; Zaima, N. Low glucose and serum levels cause an increased inflammatory factor in 3T3-L1 cell through Akt, MAPKs and NF-кB activation. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, G.; Han, T.; Liu, G. Monitoring of blood biochemical indicators related to hyperketonemia in peripartum dairy cows. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 2019, 55, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, X. Non-Esterified Fatty Acids Over-Activate the TLR2/4-NF-Κb Signaling Pathway to Increase Inflammatory Cytokine Synthesis in Neutrophils from Ketotic Cows. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 48, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.-K.; Jeong, J.-K.; Choi, I.-S.; Kang, H.-G.; Hur, T.-Y.; Jung, Y.-H.; Kim, I.-H. Relationships among ketosis, serum metabolites, body condition, and reproductive outcomes in dairy cows. Theriogenology 2015, 84, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillreiner, M.; Flinspach, C.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Kliem, H. Effect of the Ketone Body Beta-Hydroxybutyrate on the Innate Defense Capability of Primary Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-P.; Wang, J.-F.; Xue, W.-J.; Liu, H.-M.; Liu, B.-r.; Zeng, Y.-L.; Li, S.-N.; Huang, B.-X.; Lv, Q.-K.; Wang, W.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of BHBA in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson’s disease models are mediated by GPR109A-dependent mechanisms. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi-Nejad, K.; Takakura, A.; Jurewicz, M.; Chandraker, A.K.; Offermanns, S.; Mount, D.; Abdi, R. The role of HCA2 (GPR109A) in regulating macrophage function. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 4366–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chai, X.; Pan, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, S. β-Hydroxybutyrate Alleviates Low Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via Modulation of ROS-Mediated p38 MAPK Signaling. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 72, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretta, M.D.; Barría, Y.; Borquez, K.; Urra, B.; Rivera, A.; Alarcón, P.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Burgos, R.A. β-hydroxybutyrate and hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 agonists activate the AKT, ERK and AMPK pathways, which are involved in bovine neutrophil chemotaxis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Assmann, J.C.; Krenz, A.; Rahman, M.; Grimm, M.; Karsten, C.M.; Köhl, J.; Offermanns, S.; Wettschureck, N.; Schwaninger, M. Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 mediates dimethyl fumarate's protective effect in EAE. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2188–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, N.; Gu, J.; Fu, S.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; et al. β-Hydroxybutyrate induces bovine hepatocyte apoptosis via an ROS-p38 signaling pathway. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9184–9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, T.; Hirschey, M.D.; Newman, J.; He, W.; Shirakawa, K.; Le Moan, N.; Grueter, C.A.; Lim, H.; Saunders, L.R.; Stevens, R.D.; et al. Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science 2013, 339, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yang, S.; Xu, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Long, M.; He, J. Proanthocyanidins Protect against β-Hydroxybutyrate-Induced Oxidative Damage in Bovine Endometrial Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerlund, R.; Kinnunen, L.; Köhler, M.; Julkunen, I.; Melén, K. NF-κB is transported into the nucleus by importin α3 and importin α4. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15942–15951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białas, N.; Müller, E.K.; Epple, M.; Hilger, I. Silica-coated calcium phosphate nanoparticles for gene silencing of NF-κB p65 by siRNA and their impact on cellular players of inflammation. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.L.; Lapadat, R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 2002, 298, 1911–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhu, B.; Cheon, I.S.; Goplen, N.P.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, R.; Peebles, R.S.; Mack, M.; Kaplan, M.H.; Limper, A.H.; et al. PPAR-γ in Macrophages Limits Pulmonary Inflammation and Promotes Host Recovery following Respiratory Viral Infection. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00030-00019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, D.; Graff, E.C.; Judd, R.L. Effects of high fat diet on GPR109A and GPR81 gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeninga, E.H.; Bugge, A.; Nielsen, R.; Kersten, S.; Hamers, N.; Dani, C.; Wabitsch, M.; Berger, R.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Mandrup, S.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma regulates expression of the anti-lipolytic G-protein-coupled receptor 81 (GPR81/Gpr81). J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26385–26393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, H.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Engelhardt, J.F.; Wang, Y. Cloning and identification of microRNAs in bovine alveolar macrophages. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 332, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bie, J.; Marei, W.F.A.; Maillo, V.; Jordaens, L.; Gutierrez-Adan, A.; Bols, P.E.J.; Leroy, J.L.M.R. Differential effects of high and low glucose concentrations during lipolysis-like conditions on bovine in vitro oocyte quality, metabolism and subsequent embryo development. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2017, 29, 2284–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, J.; Yang, Q.; Xia, Q.; Huang, F.; Guo, H.; Cui, H.; Xie, Y.; Ren, Z.; Gou, L.; Cai, D.; et al. Low Glucose plus β-Hydroxybutyrate Induces an Enhanced Inflammatory Response in Yak Alveolar Macrophages via Activating the GPR109A/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411331
Qi J, Yang Q, Xia Q, Huang F, Guo H, Cui H, Xie Y, Ren Z, Gou L, Cai D, et al. Low Glucose plus β-Hydroxybutyrate Induces an Enhanced Inflammatory Response in Yak Alveolar Macrophages via Activating the GPR109A/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411331
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Jiancheng, Qiyuan Yang, Qing Xia, Fangyuan Huang, Hongrui Guo, Hengmin Cui, Yue Xie, Zhihua Ren, Liping Gou, Dongjie Cai, and et al. 2023. "Low Glucose plus β-Hydroxybutyrate Induces an Enhanced Inflammatory Response in Yak Alveolar Macrophages via Activating the GPR109A/NF-κB Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411331
APA StyleQi, J., Yang, Q., Xia, Q., Huang, F., Guo, H., Cui, H., Xie, Y., Ren, Z., Gou, L., Cai, D., Kumbhar, M. A., Fang, J., & Zuo, Z. (2023). Low Glucose plus β-Hydroxybutyrate Induces an Enhanced Inflammatory Response in Yak Alveolar Macrophages via Activating the GPR109A/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411331






