The Interplay between Bioactive Sphingolipids in the Psoriatic Skin and the Severity of the Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Population
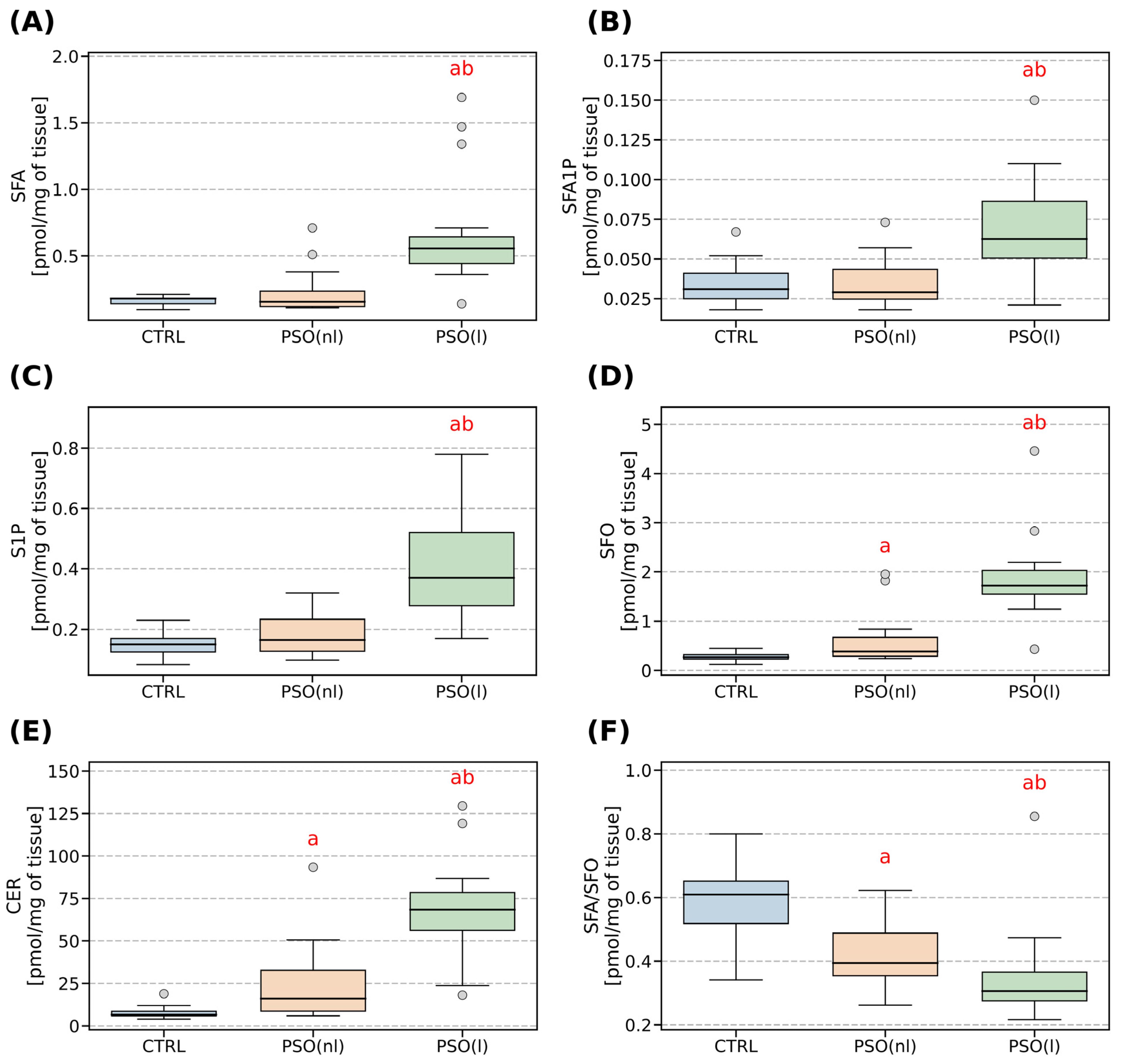
2.2. Sphingolipid Parameters
3. Discussion
3.1. The Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate
3.2. The Characteristic of Sphingosine and Sphinganine (SFA)
3.3. The Characteristic of Ceramide
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sphingolipid Analysis
4.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parisi, R.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: A systemic review of incidence and prevalence. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parisi, R.; Iskander, I.Y.K.; Kontopantelis, E.; Augustin, E.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. National, regional, and worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis: Systemic analysis and modeling study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Jullien, D.; Eyerich, E. The prevalence and Disease Characteristics of generalized Pustular Psoriasis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23 (Suppl. S1), 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon, A.; Schakel, K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowes, M.A.; Bowcock, A.M.; Krueger, J.G. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature 2007, 445, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, M.; Galand, P.; Fokan, D.; de Graef, C.; Heenen, M. Apoptosis in established and healing psoriasis. Dermatology 2000, 200, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrone-Smith, T.; Mitra, R.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Jasty, R.; Castle, V.P.; Nickoloff, B.J. Keratinocytes derived from psoriatic plaques are resistant to apoptosis compared with normal skin. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Raimondo, A.; Lembo, S.; Fausti, F.; Dini, V.; Costanzo, A.; Monfrecola, G.; Balato, N.; Ayala, F.; Romanelli, M.; et al. Crosstalk between skin inflammation and adipose tissue-derived products: Pathogenic evidence linking psoriasis to increases adiposity. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Armenteros, J.M.; Gómez-Arbonés, X.; Buti-Soler, M.; Betriu-Bars, A.; Sanmartin-Novell, V.; Ortega-Bravo, M.; Martínez-Alonso, M.; Garí, E.; Portero-Otín, M.; Santamaria-Babi, L.; et al. Psoriasis, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk factors. A population-based study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakhwa, Y.C.; Rashmi, R.; Basavaraj, K.H. Dyslipidemia in Psoriasis: A Case Controlled Study. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 729157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Sphingolipids and their metabolism in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskot, M.; Bochenska, K.; Jakobkiewiczc-Baniecka, J.; Banecki, B.; Gabig-Ciminska, M. Abnormal Sphingolipid World in Inflammation Specific for Lysosomal Storage Disease and Skin Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Checa, A.; Xu, N.; Sar, D.G.; Haeggstrom, J.Z.; Stahle, M.; Wheelock, C.E. Circulating levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate are elevated in severe, but not mild psoriasis and are unresponsive to anti-TNF-α treatment. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mysliwiec, H.; Baran, A.; Harasim-Symbor, E.; Choromanska, B.; Mysliwiec, P.; Justyna Milewska, A.; Chabowski, A.; Flisiak, I. Increase in circulating sphingosine-1-phosphate and decrease in ceramide levels in psoriatic patients. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lew, B.-L.; Cho, Y.; Kim, J.; Sim, W.Y.; Kim, N.I. Ceramides and cell signaling molecules in psoriatic epidermis: Reduced levels of ceramides, PKC-alpha, and JNK. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2006, 21, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herzinger, T.; Kleuser, B.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Christian Korting, H. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and the skin. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 8, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung-Hyuk, M.; Kim, J.Y.; Song, E.H.; Shin, M.K.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, N.I. Altered Levels of Sphingosine and Sphinganine in Psoriatic Epidermis. Ann. Dermatol. 2013, 25, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maceyka, M.; Harikumar, K.B.; Milstein, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate signaling and its role in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalski, G.M.; Carey, A.L.; Selathurai, A.; Kingwell, B.A.; Bruce, C.R. Plasma Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Is Elevated in Obesity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozłowska, D.; Harasim-Symbor, E.; Mysliwiec, H.; Milewska, A.J.; Chabowski, A.; Flisiak, I. Lipid profile disturbances may predispose psoriatic patients to liver dysfunction. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2021, 38, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, H.A.; Elshabrawy, M.M.; Ismail, N.I.; Hassan, E.T.; Jafferany, M.; Elsaie, M.L. Therapeutic implications and role of serum sphingolipids on psoriasis severity after narrow-band ultraviolet B treatment: A cross-sectional controlled study. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaclavkova, A.; Chimenti, S.; Arenberger, P.; Holló, P.; Sator, P.G.; Burcklen, M.; Stefani, M.; D’Ambrosio, D. Oral ponesimod in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambrosio, D.; Steinmann, J.; Brossard, P.; Dingemanse, J. Differential effects of ponesimod, a selective S1P1 receptor modulator, on blood-circulating human T cell subpopulations. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2015, 37, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Biase, S.; Lorenzut, S.; Barbarino, G.; Sanvilli, N.; D’Anna, L.; Dolso, P.; Valente, M.; Gigli, G.L. Clinical Remission of Psoriasis during Fingolimod Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis: A Case Report. XLVI National Congress in Genoa, 10–13.10.2015. Available online: http://congress.wooky.it/web/eventi/neuro2015/poster/pdf/pst211.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2015).
- Okura, I.; Kamata, M.; Asano, Y.; Mitsui, A.; Shimizu, T.; Sato, S.; Tada, Y. Fingolimod ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasiform dermatitis by sequastrating interleukin-17 producing ?d cells in secondary lymph nodes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2021, 102, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, A.V.; Domenichiello, A.F.; Dey, A.K.; Yuan, Z.K.; Goyal, A.; Rose, S.M.; Playford, M.P.; Ramsden, C.E.; Mehta, N.N. Bioactive Lipid Mediator Profiles in Human Psoriasis Skin and Blood. J. Invest.Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toncic, R.J.; Jakasa, I.; Hadzavdic, S.L.; Goorden, S.M.; Ghauharali-van der Vlugt, K.M.; Stet, F.S.; Balic, A.; Petkovic, M.; Pavicic, B.; Zuzul, K.; et al. Altered Levels of Sphingosine, Sphinganine, and Their Ceramides in Atopic Dermatitis Are Related to Skin Barrier Function, Disease Severity and Local Cytokine Milieu. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arikawa, J.; Ishibashi, M.; Kawashima, M.; Takagi, Y.; Ichikawa, Y.; Imokawa, G. Decreased levels of sphingosine, a natural antimicrobial agent, may be associated with vulnerability of the stratum corneum from patients with atopic dermatitis to colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawada, C.; Kanoh, H.; Nakamura, M.; Mizutani, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Banno, Y.; Seishima, M. Interferon-γ decreases ceramides with long-chain fatty acids: Possible involvement in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alessandrini, F.; Stachowitz, S.; Ring, J.; Behrendt, H. The level of prosaposin is decreased in the skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.; Lew, B.L.; Seong, K.; Kim, N.I. An Inverse Relationship Between Ceramide Synthesis and Clinical Severity in Patients with Psoriasis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2004, 19, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Zou, S.; Zhou, P.; Hu, Y.-W.; Zhao, Q.-X.; Gu, L.-N.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Metabolic Syndrome and Psoriasis: Mechanisms and Future Directions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 711060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.A.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Hong, G.; Hong, J.; Choi, K.; Eom, C.S.; Baik, S.; Lee, M.K.; et al. Genetic Variants Associated with Elevated Plasma Ceramides in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome. Genes 2022, 13, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, J.; Wozel, G. The psoriasis area and severity index is the adequate criterion to define severity in chronic plaque-type psoriasis. Dermatology 2005, 210, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Min, J.K.; Yoo, H.S.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, Y.M. Simultaneous quantitative analysis of sphingoid base 1-phosphates in biological samples by o-phthalaldehyde precolumn derivatization after dephosphorylation with alkaline phosphatase. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 303, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowski, M.; Zabielski, P.; Blachnio, A.; Gorski, J. Effect of exercise duration on ceramide metabolism in the rat heart. Acta Physiol. 2008, 192, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical and Laboratory Features | CTRL (n = 17) | PSO (n = 15) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 42.0 (35.5–55.0) | 51.0 (43.0–66.0) |
| Body mass (kg) | 75.0 (67.5–78.0) | 87.0 (82.0–94.0) a |
| Height (cm) | 174.0 (166.5–176.0) | 174.0 (162.0–176.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.06 (23.75–27.31) | 28.74 (27.72–30.35) a |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 1.0 (1.0–1.45) | 4.65 (3.06–8.11) a |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 93.0 (88.5–100.0) | 84.0 (81.0–94.0) |
| TAG (mg/dL) | 73.0 (67.5–82.0) | 122.0 (85.0–135.0) a |
| AST (U/L) | 22.0 (17.5–28.5) | 20.0 (19.0–32.0) |
| ALT (U/L) | 17.0 (13.0–22.0) | 18.0 (15.0–27.0) |
| Sex (no. female/no. male) | 6/11 | 8/7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matwiejuk, M.; Mysliwiec, H.; Lukaszuk, B.; Lewoc, M.; Malla, H.; Mysliwiec, P.; Dadan, J.; Chabowski, A.; Flisiak, I. The Interplay between Bioactive Sphingolipids in the Psoriatic Skin and the Severity of the Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411336
Matwiejuk M, Mysliwiec H, Lukaszuk B, Lewoc M, Malla H, Mysliwiec P, Dadan J, Chabowski A, Flisiak I. The Interplay between Bioactive Sphingolipids in the Psoriatic Skin and the Severity of the Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411336
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatwiejuk, Mateusz, Hanna Mysliwiec, Bartłomiej Lukaszuk, Marta Lewoc, Hend Malla, Piotr Mysliwiec, Jacek Dadan, Adrian Chabowski, and Iwona Flisiak. 2023. "The Interplay between Bioactive Sphingolipids in the Psoriatic Skin and the Severity of the Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411336
APA StyleMatwiejuk, M., Mysliwiec, H., Lukaszuk, B., Lewoc, M., Malla, H., Mysliwiec, P., Dadan, J., Chabowski, A., & Flisiak, I. (2023). The Interplay between Bioactive Sphingolipids in the Psoriatic Skin and the Severity of the Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411336







