Development of a Polygenic Risk Score for BMI to Assess the Genetic Susceptibility to Obesity and Related Diseases in the Korean Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
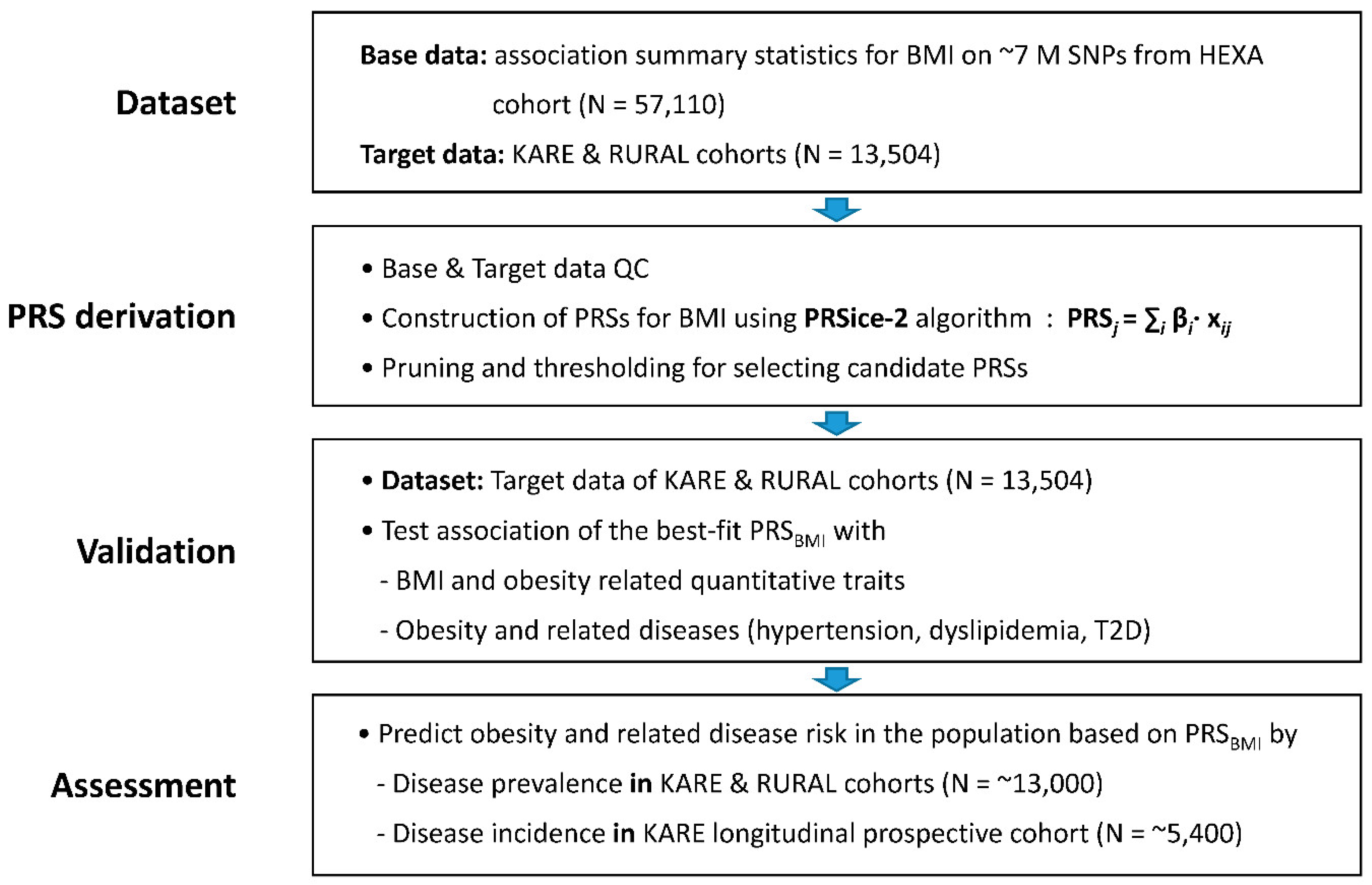
2.1. Production of Base Data for Computing BMI PRS
2.2. Derivation of PRS for BMI
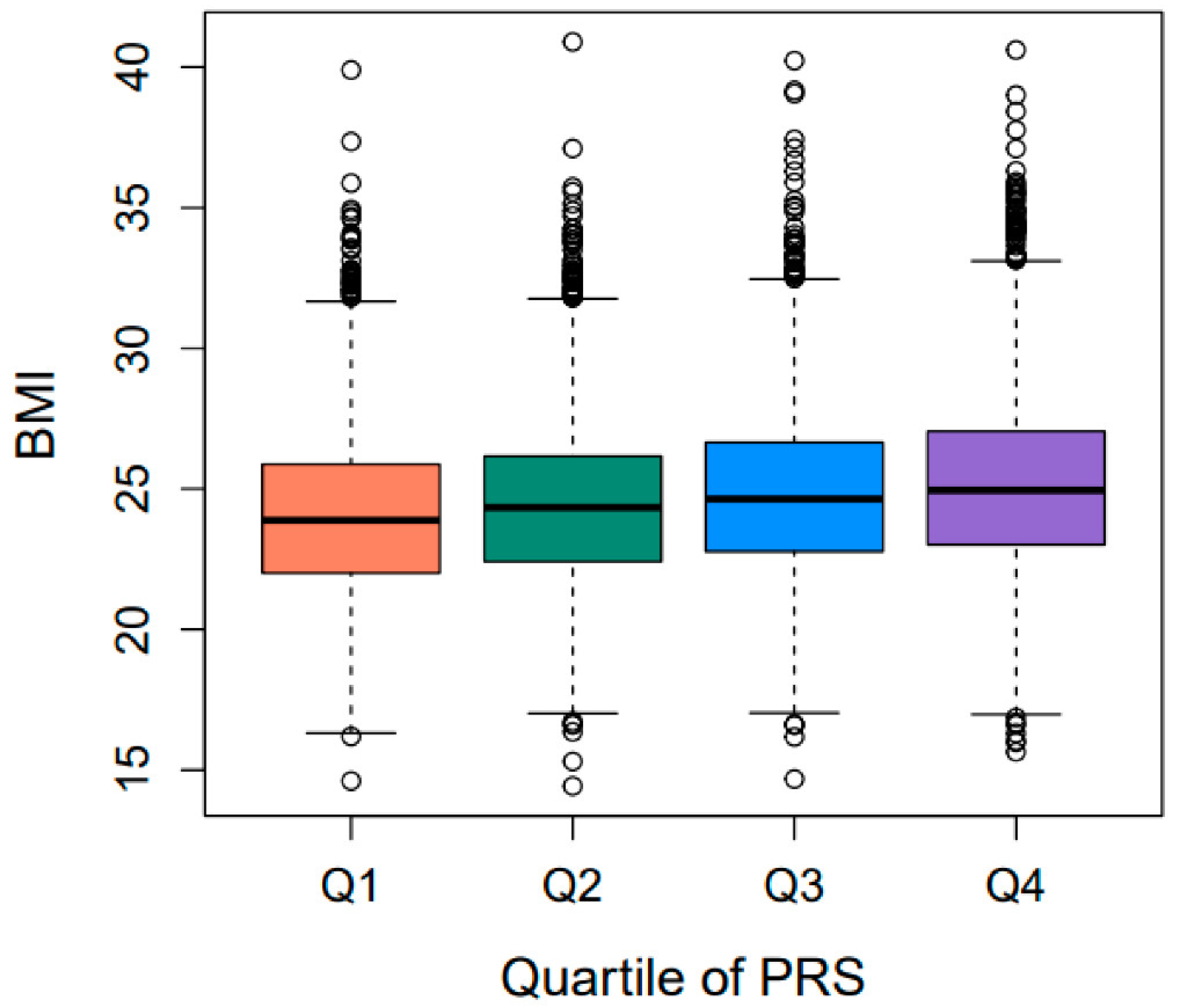
2.3. Validation of PRSBMI for Obesity-Related Quantitative Traits/Diseases
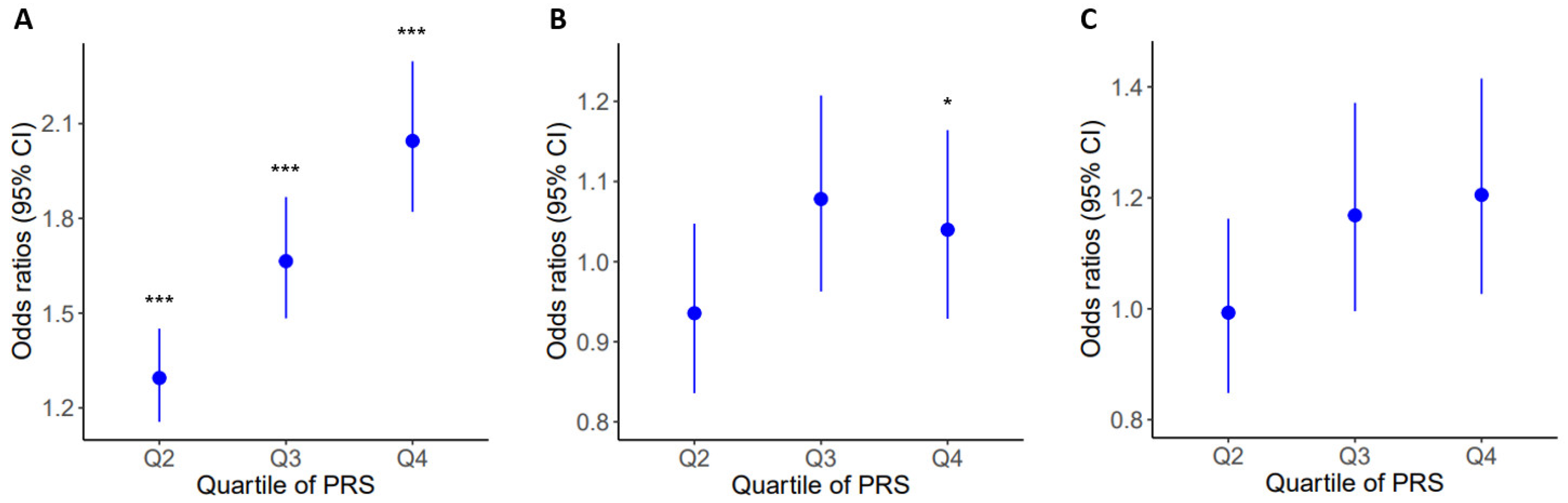
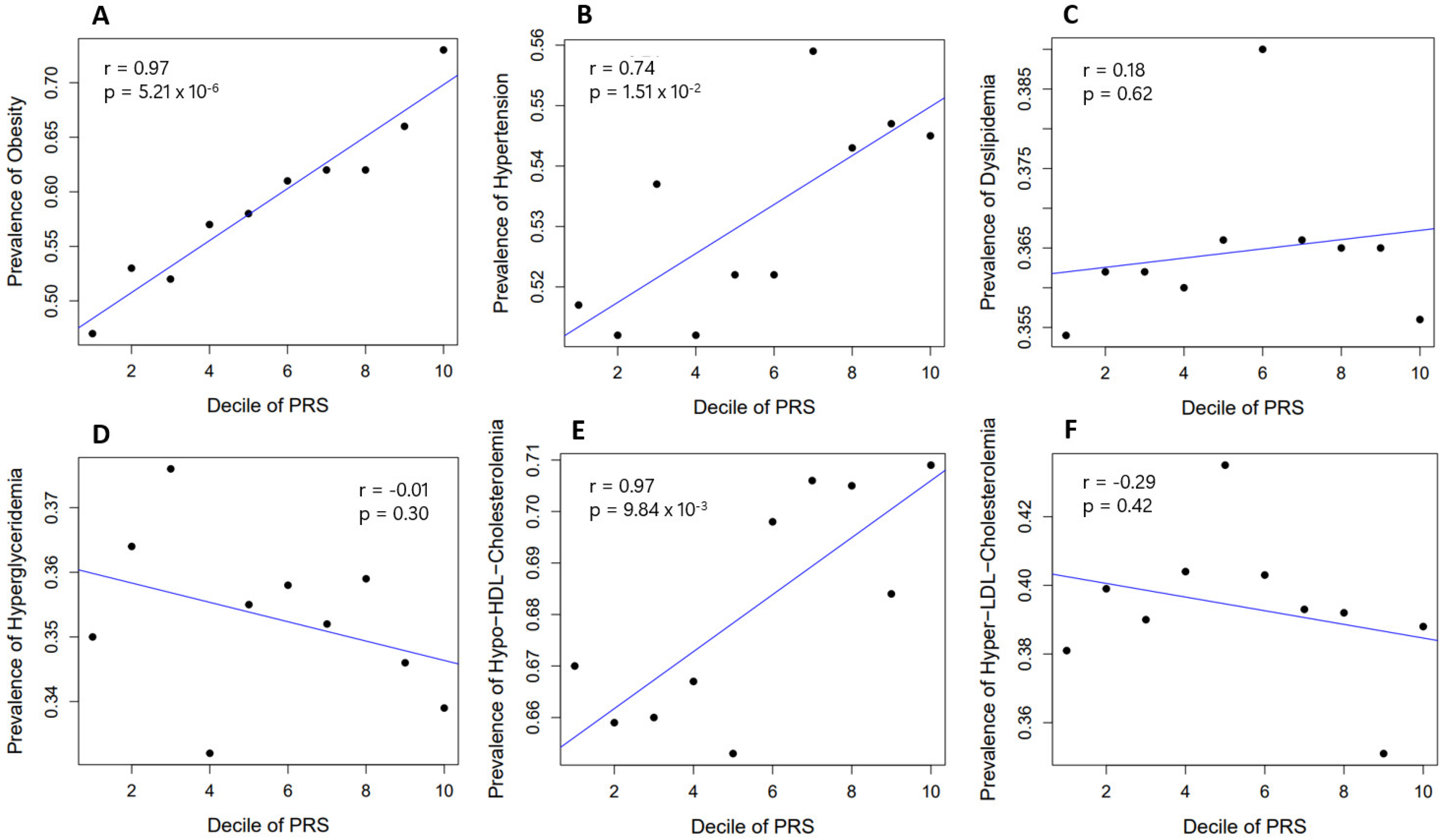
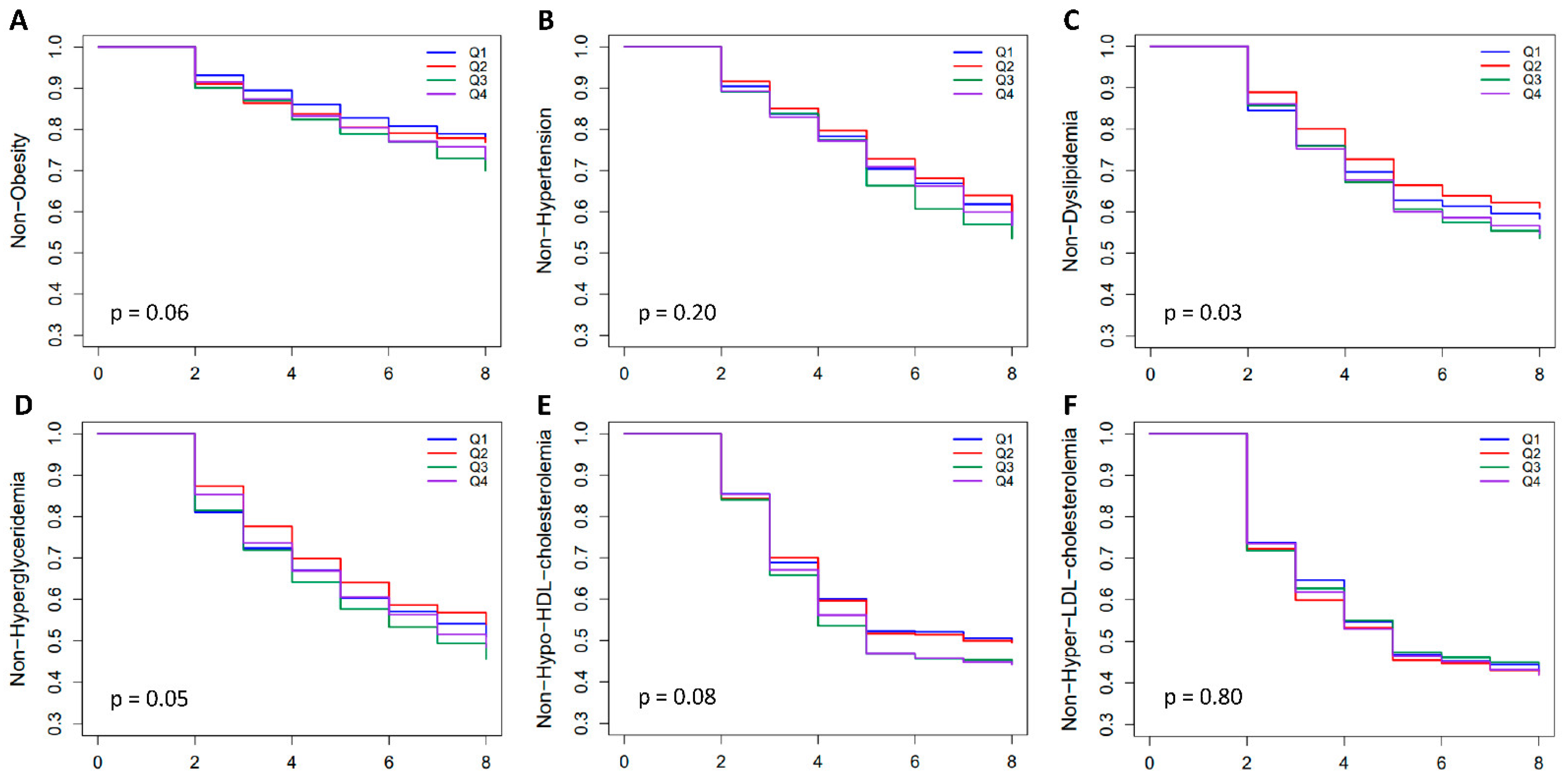
2.4. Prevalence of Obesity and Related Diseases among Genetic Risk Groups in the Population
2.5. Incidence of Obesity and Related Diseases among Genetic Risk Groups in the Population
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Subjects
4.2. Genotyping, Quality Control, and Imputation
4.3. Phenotyping
4.4. Quality Control across the Base and Target Data for PRS Derivation
4.5. Derivation of PRS
4.6. Validation of PRS
4.7. Assessment of PRS on the Prevalence and Incidence of Obesity-Related Diseases
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pi-Sunyer, X. The medical risks of obesity. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 121, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, V.S.; Willet, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Nearly a decade on-trends, risk factors and policy implications in global obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, W.; Cho, Y.S.; Zheng, W.; Dorajoo, R.; Kato, N.; Qi, L.; Chen, C.H.; Delahanty, R.J.; Okada, Y.; Tabara, Y.; et al. Meta-analysis identifies common variants associated with body mass index in east Asians. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monda, K.L.; Chen, G.K.; Taylor, K.C.; Palmer, C.; Edwards, T.L.; Lange, L.A.; Ng, M.C.; Adeyemo, A.A.; Allison, M.A.; Bielak, L.F.; et al. A meta-analysis identifies new loci associated with body mass index in individuals of African ancestry. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Zheng, W.; Okada, Y.; Takeuchi, F.; Tabara, Y.; Hwang, J.Y.; Dorajoo, R.; Li, H.; Tsai, F.J.; Yang, X.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in East Asian-ancestry populations identifies four new loci for body mass index. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 5492–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, A.E.; Kahali, B.; Berndt, S.I.; Justice, A.E.; Pers, T.H.; Day, F.R.; Powell, C.; Vedantam, S.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Yang, J.; et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 2015, 518, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, T.W.; Justice, A.E.; Graff, M.; Barata, L.; Feitosa, M.F.; Chu, S.; Czajkowski, J.; Esko, T.; Fall, T.; Kilpelainen, T.O.; et al. The Influence of Age and Sex on Genetic Associations with Adult Body Size and Shape: A Large-Scale Genome-Wide Interaction Study. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, M.; Okada, Y.; Kanai, M.; Takahashi, A.; Momozawa, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Iwata, N.; Ikegawa, S.; Hirata, M.; Matsuda, K.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 112 new loci for body mass index in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buniello, A.; MacArthur, J.A.L.; Cerezo, M.; Harris, L.W.; Hayhurst, J.; Malangone, C.; McMahon, A.; Morales, J.; Mountjoy, E.; Sollis, E.; et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog of published genome-wide association studies, targeted arrays and summary statistics 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1005–D1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Yeo, G.S.H. The genetics of obesity: From discovery to biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasco, J.A.; Holloway, K.L.; Dobbins, A.G.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Williams, L.J.; Brennan, S.L. Body mass index and measures of body fat for defining obesity and underweight: A cross-sectional, population-based study. BMC Obes. 2014, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Jimenez, E. Genes and obesity: A cause and effect relationship. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2011, 58, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Ahima, R.S. Physiology of leptin: Energy homeostasis, neuroendocrine function and metabolism. Metabolism 2015, 64, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpelainen, T.O.; Carli, J.F.; Skowronski, A.A.; Sun, Q.; Kriebel, J.; Feitosa, M.F.; Hedman, A.K.; Drong, A.W.; Hayes, J.E.; Zhao, J.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis uncovers novel loci influencing circulating leptin levels. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudbridge, F. Polygenic Epidemiology. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Benyamin, B.; McEvoy, B.P.; Gordon, S.; Henders, A.K.; Nyholt, D.R.; Madden, P.A.; Heath, A.C.; Martin, N.G.; Montgomery, G.W.; et al. Common SNPs explain a large proportion of the heritability for human height. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Finucane, H.K.; Anttila, V.; Gusev, A.; Day, F.R.; Loh, P.R.; ReproGen Consortium; Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; Genetic Consortium for Anorexia Nervosa of the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 3; Duncan, L.; et al. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkamani, A.; Wineinger, N.E.; Topol, E.J. The personal and clinical utility of polygenic risk scores. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, N.R.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. Prediction of individual genetic risk to disease from genome-wide association studies. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, A.V.; Chaffin, M.; Aragam, K.G.; Haas, M.E.; Roselli, C.; Choi, S.H.; Natarajan, P.; Lander, E.S.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. Genome-wide polygenic scores for common diseases identify individuals with risk equivalent to monogenic mutations. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.H.T.; Lim, C.K.P.; Luk, A.O.Y.; Ng, A.C.W.; Lee, H.M.; Jiang, G.; Lau, E.S.H.; Fan, B.; Wan, R.; Kong, A.P.S.; et al. Development of genome-wide polygenic risk scores for lipid traits and clinical applications for dyslipidemia, subclinical atherosclerosis, and diabetes cardiovascular complications among East Asians. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Sakoda, L.C.; Hoffmeister, M.; Rosenthal, E.A.; Lee, J.K.; van Duijnhoven, F.J.B.; Platz, E.A.; Wu, A.H.; Dampier, C.H.; de la Chapelle, A.; et al. Genome-wide Modeling of Polygenic Risk Score in Colorectal Cancer Risk. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, I.S.; Chaudhary, K.; Paranjpe, I.; Vy, H.M.T.; Marquez-Luna, C.; Rocheleau, G.; Saha, A.; Chan, L.; Van Vleck, T.; Loos, R.J.F.; et al. Genome-wide polygenic risk score for retinopathy of type 2 diabetes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilhjalmsson, B.J.; Yang, J.; Finucane, H.K.; Gusev, A.; Lindstrom, S.; Ripke, S.; Genovese, G.; Loh, P.R.; Bhatia, G.; Do, R.; et al. Modeling Linkage Disequilibrium Increases Accuracy of Polygenic Risk Scores. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 576–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, T.S.H.; Porsch, R.M.; Choi, S.W.; Zhou, X.; Sham, P.C. Polygenic scores via penalized regression on summary statistics. Genet. Epidemiol. 2017, 41, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; O’Reilly, P.F. PRSice-2: Polygenic Risk Score software for biobank-scale data. Gigascience 2019, 8, giz082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, P.; Livstone, M.S.; Lewis, S.E.; Thomas, P.D. Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform. 2011, 12, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.J.F. 15 years of genome-wide association studies and no signs of slowing down. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.J.; Yeo, G.S. The bigger picture of FTO: The first GWAS-identified obesity gene. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Kovacs, P.; Guiu-Jurado, E. Genetics of Obesity in East Asians. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 575049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.M.; Heid, I.; Buechler, C.; Steege, A.; Resch, M.; Birner, C.; Endemann, D.H.; Riegger, G.A.; Luchner, A. Expression of fourteen novel obesity-related genes in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Cho, Y.S. Identification of female-specific genetic variants for metabolic syndrome and its component traits to improve the prediction of metabolic syndrome in females. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Han, B.G.; KoGES Group. Cohort Profile: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) Consortium. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Go, M.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Ban, H.J.; Yoon, D.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, D.J.; Park, M.; et al. A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.Y.; Lee, H.; Cho, Y.S. Identification of genetic variants for blood insulin level in sex-stratified Korean population and evaluation of the causal relationship between blood insulin level and polycystic ovary syndrome. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Go, M.J.; Hu, C.; Hong, C.B.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, J.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, N.H.; et al. Large-scale genome-wide association studies in East Asians identify new genetic loci influencing metabolic traits. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, S.; Hwang, M.Y.; Shin, D.M.; Park, M.Y.; Lu, Y.; Yoon, K.; Jang, H.M.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. The Korea Biobank Array: Design and Identification of Coding Variants Associated with Blood Biochemical Traits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.U.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Hwang, Y.I.; Kim, T.H.; Lim, S.Y.; Yoo, K.H.; Jung, K.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Rhee, C.K. Comparison of World Health Organization and Asia-Pacific body mass index classifications in COPD patients. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2017, 12, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopfholz, J.; Disserol, C.C.; Pierin, A.J.; Schirr, F.L.; Streisky, L.; Takito, L.L.; Massucheto Ledesma, P.; Faria-Neto, J.R.; Olandoski, M.; da Cunha, C.L.; et al. Validation of the friedewald formula in patients with metabolic syndrome. Cholesterol 2014, 2014, 261878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Mak, T.S.; O’Reilly, P.F. Tutorial: A guide to performing polygenic risk score analyses. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2759–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Base Dataset | Target Dataset | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HEXA | RURAL | KARE | |
| Female (%) | 38,407 (65.4) | 5010 (62.3) | 2863 (52.4) |
| Age (year) | 53.8 ± 8.0 | 58.5 ± 8.8 | 51.6 ± 8.5 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.9 ± 2.9 | 24.5 ± 3.0 | 24.6 ± 3.0 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 122.5 ± 14.8 | 124.6 ± 17.4 | 120.9 ± 18.0 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 75.8 ± 9.7 | 78.6 ± 10.8 | 80.1 ± 11.2 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 95.1 ± 19.8 | 98.1 ± 20.6 | 92.2 ± 21.2 |
| OGTT120 (mg/dL) | NA | NA | 132.4 ± 51.7 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.7 ± 0.7 | 5.7 ± 0.8 | 5.8 ± 0.9 |
| INS0 (μIU/mL) | NA | 8.1 ± 4.8 | 7.5 ± 4.5 |
| HDLC (mg/dL) | 53.8 ± 13.2 | 45.1 ± 10.9 | 49.3 ± 11.5 |
| LDLC (mg/dL) | 119.3 ± 32.1 | 123.7 ± 31.6 | 120.5 ± 32.2 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 125.1 ± 85.6 | 146.2 ± 94.5 | 153.0 ± 110.4 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 197.4 ± 35.7 | 196.9 ± 35.3 | 199.0 ± 35.8 |
| PRS | Related Disease | Trait | No of Samples | Correlation with QT | Linear Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson r | β | SE | p | ||||
| PRSBMI | Obesity | BMI | 13,504 | 0.1590 | 0.0021 | 0.0001 | 1.36 × 10−73 |
| Hypertension | SBP | 13,499 | 0.0289 | 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 2.63 × 10−6 | |
| DBP | 13,499 | 0.0299 | 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 2.90 × 10−5 | ||
| T2D | FPG | 12,802 | 0.0029 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 4.39 × 10−1 | |
| OGTT120 | 5192 | −0.0104 | −0.0002 | 0.0005 | 7.13 × 10−1 | ||
| HbA1c | 6794 | −0.0040 | 0.0000 | 0.0002 | 8.23 × 10−1 | ||
| INS0 | 5929 | 0.0490 | 0.0022 | 0.0008 | 8.15 × 10−3 | ||
| Dyslipedemia | HDLC | 13,501 | −0.0236 | −0.0006 | 0.0002 | 9.07 × 10−3 | |
| LDLC | 13,177 | −0.0026 | −0.0001 | 0.0003 | 7.02 × 10−1 | ||
| TG | 13,501 | 0.0078 | 0.0011 | 0.0005 | 2.50 × 10−2 | ||
| TC | 13,501 | −0.0062 | −0.0001 | 0.0002 | 4.93 × 10−1 | ||
| PRS | Variable | N | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRSBMI | Obesity | 9671 | 1.031 | 1.027–1.035 | 8.73 × 10−45 |
| Hypertension | 9757 | 1.008 | 1.003–1.013 | 6.84 × 10−4 | |
| Type 2 Diabetes | 3464 | 1.006 | 0.997–1.015 | 2.08 × 10−1 | |
| Dyslipidemia | 9283 | 1.001 | 0.996–1.006 | 6.52 × 10−1 | |
| Hyperglyceridemia | 13,501 | 1.002 | 0.998–1.006 | 3.15 × 10−1 | |
| Hypo-HDL Cholesterolemia | 5554 | 1.008 | 1.001–1.014 | 2.75 × 10−2 | |
| Hyper-LDL Cholesterolemia | 13,177 | 0.997 | 0.993–1.001 | 1.07 × 10−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, N.; Cho, Y.S. Development of a Polygenic Risk Score for BMI to Assess the Genetic Susceptibility to Obesity and Related Diseases in the Korean Population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411560
Yoon N, Cho YS. Development of a Polygenic Risk Score for BMI to Assess the Genetic Susceptibility to Obesity and Related Diseases in the Korean Population. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411560
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Nara, and Yoon Shin Cho. 2023. "Development of a Polygenic Risk Score for BMI to Assess the Genetic Susceptibility to Obesity and Related Diseases in the Korean Population" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411560
APA StyleYoon, N., & Cho, Y. S. (2023). Development of a Polygenic Risk Score for BMI to Assess the Genetic Susceptibility to Obesity and Related Diseases in the Korean Population. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411560






