Mouse Models for HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T Cell Leukemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Transgenic Mouse Models for HTLV-1 Research
3. Development of Severely Immunodeficient Mice
4. Immunodeficient Mouse Models for HTLV-1 Research
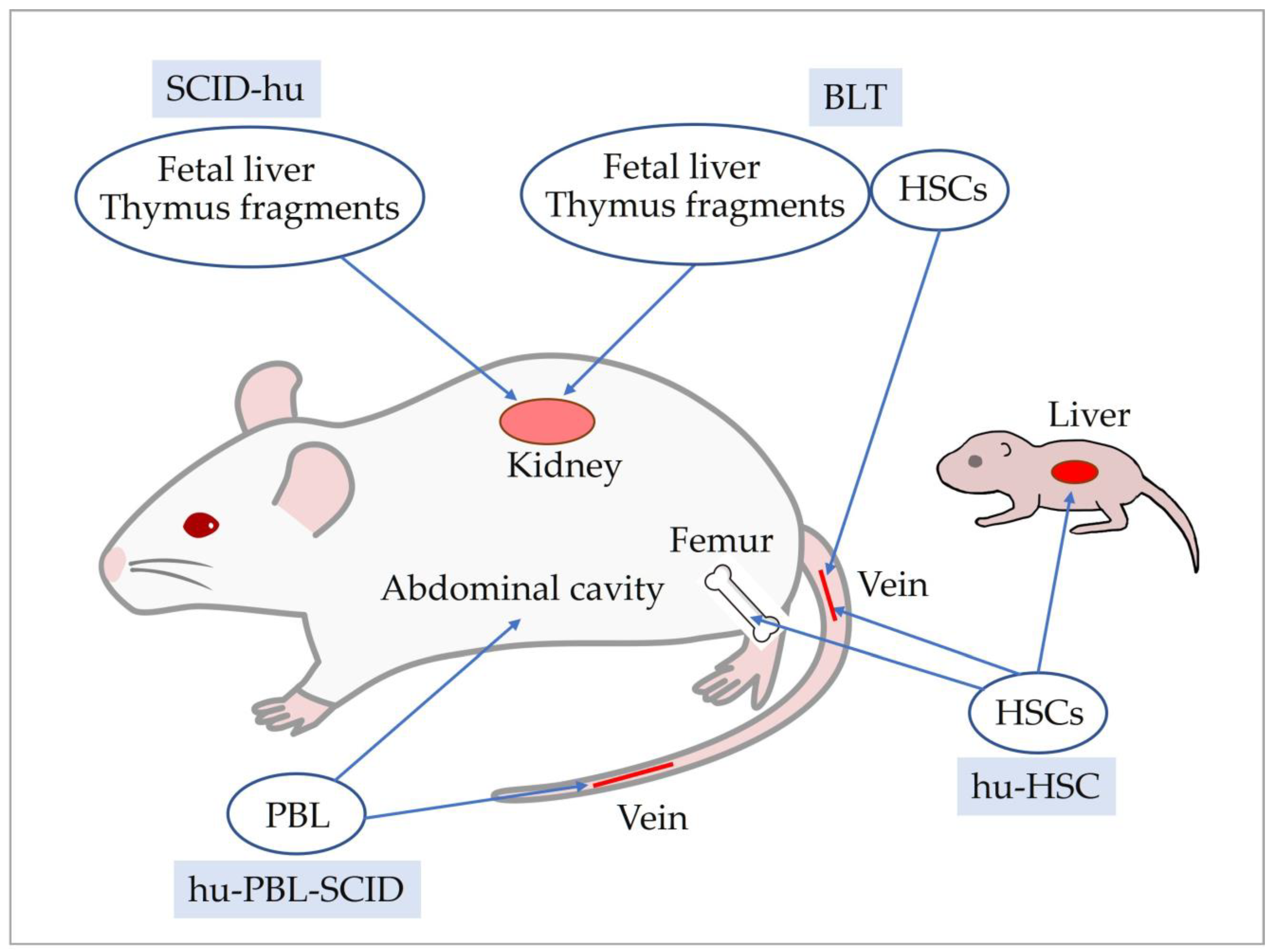
5. Development of Human Immune System Mice
6. Improvements in the hu-HSC Mice
7. Human Immune System Mouse Models for HTLV-1 Research
8. Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Mouse Model in the Development of ATL Therapeutics/Prophylaxis
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poiesz, B.J.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gazdar, A.F.; Bunn, P.A.; Minna, J.D.; Gallo, R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7415–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poiesz, B.J.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Reitz, M.S.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Gallo, R.C. Isolation of a new type C retrovirus (HTLV) in primary uncultured cells of a patient with Sézary T-cell leukaemia. Nature 1981, 294, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessain, A.; Cassar, O. Epidemiological Aspects and World Distribution of HTLV-1 Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takatsuki, K.; Uchiyama, T.; Sagawa, K.; Yodoi, J.; Seno, S.; Takaku, F.; Irino, S. Topics in hematology. In Proceedings of the The 16th International Congress of Hematology, Kyoto, Japan, 5–11 September 1976; Excerpta Medica: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; pp. 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama, T.; Yodoi, J.; Sagawa, K.; Takatsuki, K.; Uchino, H. Adult T-cell leukemia: Clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases. Blood 1977, 50, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gessain, A.; Barin, F.; Vernant, J.C.; Gout, O.; Maurs, L.; Calender, A.; de Thé, G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet 1985, 2, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanaga, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yamaguchi, K. Adult T-cell leukemia: A review of epidemiological evidence. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamano, Y.; Sato, T. Clinical pathophysiology of human T-lymphotropic virus-type 1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimoyama, M. Diagnostic criteria and classification of clinical subtypes of adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma. A report from the Lymphoma Study Group (1984–1987). Br. J. Haematol. 1991, 79, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuya, H.; Ishitsuka, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Hanada, S.; Eto, T.; Moriuchi, Y.; Saburi, Y.; Miyahara, M.; Sueoka, E.; Uike, N.; et al. Treatment and survival among 1594 patients with ATL. Blood 2015, 126, 2570–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahgoub, M.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; Iwami, S.; Nakaoka, S.; Koizumi, Y.; Shimura, K.; Matsuoka, M. Sporadic on/off switching of HTLV-1 Tax expression is crucial to maintain the whole population of virus-induced leukemic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1269–E1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, Y.; Kubota, R.; Tara, M.; Izumo, S.; Osame, M. Existence of escape mutant in HTLV-I tax during the development of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 2001, 97, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koiwa, T.; Hamano-Usami, A.; Ishida, T.; Okayama, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kamihira, S.; Watanabe, T. 5′-long terminal repeat-selective CpG methylation of latent human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 provirus in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9389–9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; Zhao, T.; Yoshida, M.; Miyazato, P.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, K.; Ohshima, K.; Green, P.L.; Ohkura, N.; et al. HTLV-1 bZIP factor induces T-cell lymphoma and systemic inflammation in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Yoshida, M.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-I basic leucine zipper factor gene mRNA supports proliferation of adult T cell leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka-Nakanishi, A.; Yasunaga, J.; Takai, K.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor suppresses apoptosis by attenuating the function of FoxO3a and altering its localization. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vernin, C.; Thenoz, M.; Pinatel, C.; Gessain, A.; Gout, O.; Delfau-Larue, M.-H.; Nazaret, N.; Legras-Lachuer, C.; Wattel, E.; Mortreux, F. HTLV-1 bZIP factor HBZ promotes cell proliferation and genetic instability by activating OncomiRs. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6082–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, P.S.; Harrington, W.J.; Kaplan, M.H.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Bennett, J.M.; Liebman, H.A.; Bernstein-Singer, M.; Espina, B.M.; Cabral, L.; Allen, S. Treatment of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma with a combination of interferon alfa and zidovudine. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1744–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermine, O.; Bouscary, D.; Gessain, A.; Turlure, P.; Leblond, V.; Franck, N.; Buzyn-Veil, A.; Rio, B.; Macintyre, E.; Dreyfus, F. Brief report: Treatment of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma with zidovudine and interferon alfa. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1749–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, J.; Utsunomiya, A.; Tanosaki, R.; Uike, N.; Sonoda, S.; Kannagi, M.; Tomonaga, M.; Harada, M.; Kimura, N.; Masuda, M.; et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation with reduced conditioning intensity as a novel immunotherapy and antiviral therapy for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 2005, 105, 4143–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; Joh, T.; Uike, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Yoshida, S.; Saburi, Y.; Miyamoto, T.; Takemoto, S.; Suzushima, H.; et al. Defucosylated anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody (KW-0761) for relapsed adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: A multicenter phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichijo, T.; Nosaka, K.; Tatetsu, H.; Higuchi, Y.; Endo, S.; Inoue, Y.; Toyoda, K.; Kikukawa, Y.; Kawakita, T.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; et al. Beneficial impact of first-line mogamulizumab-containing chemotherapy in adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehiro, Y.; Hasegawa, A.; Iino, T.; Sasada, A.; Watanabe, N.; Matsuoka, M.; Takamori, A.; Tanosaki, R.; Utsunomiya, A.; Choi, I.; et al. Clinical outcomes of a novel therapeutic vaccine with Tax peptide-pulsed dendritic cells for adult T cell leukaemia/lymphoma in a pilot study. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jégado, B.; Kashanchi, F.; Dutartre, H.; Mahieux, R. STLV-1 as a model for studying HTLV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2019, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezzutti, C.S.; Frazier, D.E.; Huff, L.Y.; Stromberg, P.C.; Olsen, R.G. Subunit vaccine protects Macaca nemestrina (pig-tailed macaque) against simian T-cell lymphotropic virus type I challenge. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 5687S–5691S. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, A.; Murata, M.; Fujikawa, T.; Katagiri, K.; Nagano, Y.; Masuda, T.; Kuramitsu, M.; Nakajima, S.; Fujisawa, J.-I.; Okuma, K.; et al. Vaccination with short-term-cultured autologous PBMCs efficiently activated STLV-1-specific CTLs in naturally STLV-1-infected Japanese monkeys with impaired CTL responses. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugata, K.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; Miura, M.; Akari, H.; Utsunomiya, A.; Nosaka, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Suzushima, H.; Koh, K.-R.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Enhancement of anti-STLV-1/HTLV-1 immune responses through multimodal effects of anti-CCR4 antibody. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afonso, P.V.; Mekaouche, M.; Mortreux, F.; Toulza, F.; Moriceau, A.; Wattel, E.; Gessain, A.; Bangham, C.R.M.; Dubreuil, G.; Plumelle, Y.; et al. Highly active antiretroviral treatment against STLV-1 infection combining reverse transcriptase and HDAC inhibitors. Blood 2010, 116, 3802–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanji, M.; Ureta-Vidal, A.; Ozden, S.; Tangy, F.; de Thoisy, B.; Fiette, L.; Talarmin, A.; Gessain, A.; de Thé, G. Lymphoid organs as a major reservoir for human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 in experimentally infected squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus): Provirus expression, persistence, and humoral and cellular immune responses. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4860–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valeri, V.W.; Hryniewicz, A.; Andresen, V.; Jones, K.; Fenizia, C.; Bialuk, I.; Chung, H.K.; Fukumoto, R.; Parks, R.W.; Ferrari, M.G.; et al. Requirement of the human T-cell leukemia virus p12 and p30 products for infectivity of human dendritic cells and macaques but not rabbits. Blood 2010, 116, 3809–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerenberg, M.; Hinrichs, S.H.; Reynolds, R.K.; Khoury, G.; Jay, G. The tat gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 induces mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice. Science 1987, 237, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, Y.; Aizawa, S.; Suda, Y.; Ikawa, Y.; Kishimoto, H.; Asano, Y.; Tada, T.; Hikikoshi, A.; Yoshida, M.; Seiki, M. Thymic atrophy characteristic in transgenic mice that harbor pX genes of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 3185–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, S.H.; Nerenberg, M.; Reynolds, R.K.; Khoury, G.; Jay, G. A transgenic mouse model for human neurofibromatosis. Science 1987, 237, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.E.; Hinrichs, S.H.; Vogel, J.; Jay, G. Exocrinopathy resembling Sjögren’s syndrome in HTLV-1 tax transgenic mice. Nature 1989, 341, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, E.M.I.; Takiguchi, M.; Hatanaka, M.; Yamamoto, H. Induction of Inflammatory Arthropathy Resembling Rheumatoid Artbritis. Science 1983, 253, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, H.; Sekiguchi, T.; Yamamoto, I. Histopathological observation of joint lesions of extremities in mice transferred genome. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. Off. J. Ges. Fur Toxikol. Pathol. 1993, 45, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Sekiguchi, T.; Itagaki, K.; Saijo, S.; Iwakura, Y. Inflammatory polyarthritis in mice transgenic for human T cell leukemia virus type I. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddle, N.H.; Li, C.B.; Horne, W.C.; Santiago, P.; Troiano, N.; Jay, G.; Horowitz, M.; Baron, R. Mice transgenic for HTLV-I LTR-tax exhibit tax expression in bone, skeletal alterations, and high bone turnover. Virology 1993, 197, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieberich, C.J.; King, C.M.; Tinkle, B.T.; Jay, G. A transgenic model of transactivation by the Tax protein of HTLV-I. Virology 1993, 196, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, W.J.; Kimata, J.T.; Wong, F.H.; Zutter, M.; Ley, T.J.; Ratner, L. Development of leukemia in mice transgenic for the tax gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, W.J.; Ratner, L. Cytokine Expression and Tumorigenicity of Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells From Mice Transgenic for the tax Gene of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type I. Blood 1997, 90, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Deng, H.; Zhao, H.; Hirbe, A.; Harding, J.; Ratner, L.; Weilbaecher, K. HTLV-1 Tax transgenic mice develop spontaneous osteolytic bone metastases prevented by osteoclast inhibition. Blood 2005, 106, 4294–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.P.; Irvine, J.; Blyth, K.; Cameron, E.R.; Onions, D.E.; Campbell, M.E. Tumours derived from HTLV-I tax transgenic mice are characterized by enhanced levels of apoptosis and oncogene expression. J. Pathol. 1998, 186, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Sawa, H.; Lewis, M.J.; Orba, Y.; Sheehy, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ichinohe, T.; Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Y.; Katano, H.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Thymus-derived leukemia-lymphoma in mice transgenic for the Tax gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsugi, T.; Kumasaka, T.; Okada, S.; Urano, T. The Tax protein of HTLV-1 promotes oncogenesis in not only immature T cells but also mature T cells. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, T. HTLV-I tax mediated activation of cellular genes in transgenic mice. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi 1991, 66, 534–543. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Winokur, T.S.; Lee, H.D.; Danielpour, D.; Kim, K.Y.; Geiser, A.G.; Chen, L.S.; Sporn, M.B.; Roberts, A.B.; Jay, G. Overexpression of transforming growth factor-beta in transgenic mice carrying the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I tax gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 5222–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwakura, Y.; Saijo, S.; Kioka, Y.; Nakayama-Yamada, J.; Itagaki, K.; Tosu, M.; Asano, M.; Kanai, Y.; Kakimoto, K. Autoimmunity induction by human T cell leukemia virus type 1 in transgenic mice that develop chronic inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in humans. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portis, T.; Harding, J.C.; Ratner, L. The contribution of NF-kappa B activity to spontaneous proliferation and resistance to apoptosis in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax-induced tumors. Blood 2001, 98, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitajima, I.; Shinohara, T.; Bilakovics, J.; Brown, D.A.; Xu, X.; Nerenberg, M. Ablation of transplanted HTLV-I Tax-transformed tumors in mice by antisense inhibition of NF-kappa B. Science 1992, 258, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Ogle, L.; Benitez, B.; Bohuslav, J.; Montano, M.; Felsher, D.W.; Greene, W.C. Lethal cutaneous disease in transgenic mice conditionally expressing type I human T cell leukemia virus Tax. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35713–35722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratner, L.; Portis, T.; Robek, M.; Harding, J.; Grossman, W. Studies of the immortalizing activity of HTLV type 1 Tax, using an infectious molecular clone and transgenic mice. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2000, 16, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portis, T.; Grossman, W.J.; Harding, J.C.; Hess, J.L.; Ratner, L. Analysis of p53 inactivation in a human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax transgenic mouse model. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 2185–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitra-Kaushik, S.; Harding, J.; Hess, J.; Schreiber, R.; Ratner, L. Enhanced tumorigenesis in HTLV-1 tax-transgenic mice deficient in interferon-gamma. Blood 2004, 104, 3305–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Hurchla, M.A.; Deng, H.; Uluçkan, O.; Bu, F.; Berdy, A.; Eagleton, M.C.; Heller, E.A.; Floyd, D.H.; Dirksen, W.P.; et al. Interferon-gamma targets cancer cells and osteoclasts to prevent tumor-associated bone loss and bone metastases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4658–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esser, A.K.; Rauch, D.A.; Xiang, J.; Harding, J.C.; Kohart, N.A.; Ross, M.H.; Su, X.; Wu, K.; Huey, D.; Xu, Y.; et al. HTLV-1 viral oncogene HBZ induces osteolytic bone disease in transgenic mice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69250–69263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto-Taguchi, N.; Satou, Y.; Miyazato, P.; Ohshima, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Katagiri, K.; Kinashi, T.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor induces inflammation through labile Foxp3 expression. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitagami, Y.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; Kinosada, H.; Ohshima, K.; Matsuoka, M. Interferon-γ Promotes Inflammation and Development of T-Cell Lymphoma in HTLV-1 bZIP Factor Transgenic Mice. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasuma, K.; Yasunaga, J.; Takemoto, K.; Sugata, K.; Mitobe, Y.; Takenouchi, N.; Nakagawa, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP Factor Impairs Anti-viral Immunity by Inducing Co-inhibitory Molecule, T Cell Immunoglobulin and ITIM Domain (TIGIT). PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinosada, H.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; Shimura, K.; Miyazato, P.; Onishi, C.; Iyoda, T.; Inaba, K.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP Factor Enhances T-Cell Proliferation by Impeding the Suppressive Signaling of Co-inhibitory Receptors. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higuchi, Y.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; Mitagami, Y.; Tsukamoto, H.; Nakashima, K.; Ohshima, K.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 induces T cell malignancy and inflammation by viral antisense factor-mediated modulation of the cytokine signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13740–13749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugata, K.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; Mitobe, Y.; Miura, M.; Miyazato, P.; Kohara, M.; Matsuoka, M. Protective effect of cytotoxic T lymphocytes targeting HTLV-1 bZIP factor. Blood 2015, 126, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, T.; Satou, Y.; Matsuoka, M. Development of T cell lymphoma in HTLV-1 bZIP factor and Tax double transgenic mice. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, J.; Mizukami, T.; Takizawa, K.; Kuramitsu, M.; Momose, H.; Masumi, A.; Ami, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Hall, W.W.; Tsujimoto, H.; et al. Identification of cancer stem cells in a Tax-transgenic (Tax-Tg) mouse model of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 2009, 114, 2709–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuribayashi, W.; Takizawa, K.; Sugata, K.; Kuramitsu, M.; Momose, H.; Sasaki, E.; Hiradate, Y.; Furuhata, K.; Asada, Y.; Iwama, A.; et al. Impact of the SCF signaling pathway on leukemia stem cell-mediated ATL initiation and progression in an HBZ transgenic mouse model. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 51027–51043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, G.C.; Custer, R.P.; Bosma, M.J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature 1983, 301, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, R.; Fujimori, A.; Hamatani, K.; Mita, K.; Saito, T.; Mori, M.; Fukumura, R.; Morimyo, M.; Muto, M.; Itoh, M.; et al. Nonsense mutation at Tyr-4046 in the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit of severe combined immune deficiency mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCune, J.M.; Namikawa, R.; Kaneshima, H.; Shultz, L.D.; Lieberman, M.; Weissman, I.L. The SCID-hu mouse: Murine model for the analysis of human hematolymphoid differentiation and function. Science 1988, 241, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, D.E.; Gulizia, R.J.; Baird, S.M.; Wilson, D.B. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature 1988, 335, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorshkind, K.; Pollack, S.B.; Bosma, M.J.; Phillips, R.A. Natural killer (NK) cells are present in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (scid). J. Immunol. 1985, 134, 3798–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, G.C.; Fried, M.; Custer, R.P.; Carroll, A.; Gibson, D.M.; Bosma, M.J. Evidence of functional lymphocytes in some (leaky) scid mice. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 167, 1016–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, L.D.; Schweitzer, P.A.; Christianson, S.W.; Gott, B.; Schweitzer, I.B.; Tennent, B.; McKenna, S.; Mobraaten, L.; Rajan, T.V.; Greiner, D.L. Multiple defects in innate and adaptive immunologic function in NOD/LtSz-scid mice. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, A.G.; Cooke, A. Complement lytic activity has no role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselton, R.M.; Greiner, D.L.; Mordes, J.P.; Rajan, T.V.; Sullivan, J.L.; Shultz, L.D. High levels of human peripheral blood mononuclear cell engraftment and enhanced susceptibility to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in NOD/LtSz-scid/scid mice. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Hiramatsu, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Suzue, K.; Kawahata, M.; Hioki, K.; Ueyama, Y.; Koyanagi, Y.; Sugamura, K.; Tsuji, K.; et al. NOD/SCID/gamma(c)(null) mouse: An excellent recipient mouse model for engraftment of human cells. Blood 2002, 100, 3175–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shultz, L.D.; Lyons, B.L.; Burzenski, L.M.; Gott, B.; Chen, X.; Chaleff, S.; Kotb, M.; Gillies, S.D.; King, M.; Mangada, J.; et al. Human lymphoid and myeloid cell development in NOD/LtSz-scid IL2R gamma null mice engrafted with mobilized human hemopoietic stem cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6477–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, S.; Harada, H.; Ito, T.; Saito, T.; Suzu, S. Early development of human hematopoietic and acquired immune systems in new born NOD/Scid/Jak3null mice intrahepatic engrafted with cord blood-derived CD34 + cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2008, 88, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, T.; Shultz, L.D.; Miller, D.; King, M.; Laning, J.; Fodor, W.; Cuthbert, A.; Burzenski, L.; Gott, B.; Lyons, B.; et al. Non-obese diabetic-recombination activating gene-1 (NOD-Rag1 null) interleukin (IL)-2 receptor common gamma chain (IL2r gamma null) null mice: A radioresistant model for human lymphohaematopoietic engraftment. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 154, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S.; Tachibana, N.; Okayama, A.; Murai, K.; Tsuda, K.; Mueller, N. Successful graft of HTLV-I-transformed human T-cells (MT-2) in severe combined immunodeficiency mice treated with anti-asialo GM-1 antibody. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1992, 83, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsugi, T.; Ishibashi, K.; Shingu, M.; Nomura, T. Engraftment of HTLV-I-transformed human T-cell line into SCID mice with NK cell function. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1994, 56, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feuer, G.; Zack, J.A.; Harrington, W.J.J.; Valderama, R.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Wachsman, W.; Baird, S.M.; Chen, I.S. Establishment of human T-cell leukemia virus type I T-cell lymphomas in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Blood 1993, 82, 722–731. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, A.; Imada, K.; Hattori, T.; Yamabe, H.; Tanaka, T.; Miyasaka, M.; Okuma, M.; Uchiyama, T. A model of in vivo cell proliferation of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 1993, 82, 2501–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imada, K.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Uchiyama, T. Analysis of in vivo cell proliferation of ATL using SCID mice. Rinsho Ketsueki. 1995, 36, 573–577. [Google Scholar]
- Watters, K.M.; Dean, J.; Hasegawa, H.; Sawa, H.; Hall, W.; Sheehy, N. Cytokine and growth factor expression by HTLV-1 Lck-tax transgenic cells in SCID mice. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2010, 26, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Grusby, M.J.; Kaisho, T. PDLIM2-mediated termination of transcription factor NF-kappaB activation by intranuclear sequestration and degradation of the p65 subunit. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Soriano, M.A.; Grusby, M.J. SLIM is a nuclear ubiquitin E3 ligase that negatively regulates STAT signaling. Immunity 2005, 22, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Muromoto, R.; Ikeda, O.; Sekine, Y.; Grusby, M.J.; Kaisho, T.; Matsuda, T. PDLIM2 inhibits T helper 17 cell development and granulomatous inflammation through degradation of STAT3. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Fu, J.; Qu, Z.; Li, S.; Tanaka, T.; Grusby, M.J.; Xiao, G. PDLIM2 suppresses human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis by targeting Tax into the nuclear matrix for proteasomal degradation. Blood 2009, 113, 4370–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeda, S.; Maeda, M.; Morikawa, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; Nosaka, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsuoka, M. Genetic and epigenetic inactivation of tax gene in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.; Zimmerman, B.; Li, M.; Lairmore, M.D.; Green, P.L. Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 antisense-encoded gene, Hbz, promotes T-lymphocyte proliferation. Blood 2008, 112, 3788–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewan, M.Z.; Terashima, K.; Taruishi, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Ito, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Mori, N.; Sata, T.; Koyanagi, Y.; Maeda, M.; et al. Rapid tumor formation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected cell lines in novel NOD-SCID/gammac(null) mice: Suppression by an inhibitor against NF-kappaB. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5286–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohsugi, T.; Horie, R.; Kumasaka, T.; Ishida, A.; Ishida, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Watanabe, T.; Umezawa, K.; Urano, T. In vivo antitumor activity of the NF-kappaB inhibitor dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin in a mouse model of adult T-cell leukemia. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, M.; Ohsugi, T.; Shoda, M.; Ishida, T.; Aizawa, S.; Maruyama-Nagai, M.; Utsunomiya, A.; Koga, S.; Yamada, Y.; Kamihira, S.; et al. Dual targeting of transformed and untransformed HTLV-1-infected T cells by DHMEQ, a potent and selective inhibitor of NF-kappaB, as a strategy for chemoprevention and therapy of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 2005, 106, 2462–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohsugi, T.; Kumasaka, T.; Ishida, A.; Ishida, T.; Horie, R.; Watanabe, T.; Umezawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K. In vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of the NF-kappaB inhibitor DHMEQ in the human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected cell line, HUT-102. Leuk. Res. 2006, 30, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsugi, T.; Kumasaka, T.; Okada, S.; Ishida, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Horie, R.; Watanabe, T.; Umezawa, K. Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin (DHMEQ) therapy reduces tumor formation in mice inoculated with tax-deficient adult T-cell leukemia-derived cell lines. Cancer Lett. 2007, 257, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, Y.; Nosaka, K.; Koya, Y.; Yasunaga, J.-I.; Toyokuni, S.; Matsuoka, M. Proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, potently inhibits the growth of adult T-cell leukemia cells both in vivo and in vitro. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, S.T.; Nadella, M.V.P.; Dirksen, W.P.; Fernandez, S.A.; Thudi, N.K.; Werbeck, J.L.; Lairmore, M.D.; Rosol, T.J. A novel bioluminescent mouse model and effective therapy for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11859–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewan, M.Z.; Uchihara, J.; Terashima, K.; Honda, M.; Sata, T.; Ito, M.; Fujii, N.; Uozumi, K.; Tsukasaki, K.; Tomonaga, M.; et al. Efficient intervention of growth and infiltration of primary adult T-cell leukemia cells by an HIV protease inhibitor, ritonavir. Blood 2006, 107, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Hajj, H.; El-Sabban, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Zaatari, G.; Ablain, J.; Saab, S.T.; Janin, A.; Mahfouz, R.; Nasr, R.; Kfoury, Y.; et al. Therapy-induced selective loss of leukemia-initiating activity in murine adult T cell leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2785–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikebe, E.; Kawaguchi, A.; Tezuka, K.; Taguchi, S.; Hirose, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Mitsui, T.; Senba, K.; Nishizono, A.; Hori, M.; et al. Oral administration of an HSP90 inhibitor, 17-DMAG, intervenes tumor-cell infiltration into multiple organs and improves survival period for ATL model mice. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, W.; Zhang, M.; Petrus, M.; Maeda, M.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Waldmann, T.A. Combination of 9-aminoacridine with Campath-1H provides effective therapy for a murine model of adult T-cell leukemia. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Ju, W.; Waldmann, T.A. Effective treatment of a murine model of adult T-cell leukemia using depsipeptide and its combination with unmodified daclizumab directed toward CD25. Blood 2009, 113, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, H.; Yamada, Y.; Tsukasaki, K.; Mori, N.; Tsuruda, K.; Sasaki, D.; Usui, T.; Osaka, A.; Atogami, S.; Ishikawa, C.; et al. LBH589, a deacetylase inhibitor, induces apoptosis in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells via activation of a novel RAIDD-caspase-2 pathway. Leukemia 2011, 25, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, B.; Sargeant, A.; Landes, K.; Fernandez, S.A.; Chen, C.-S.; Lairmore, M.D. Efficacy of novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, AR42, in a mouse model of, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 adult T cell lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishitsuka, K.; Kunami, N.; Katsuya, H.; Nogami, R.; Ishikawa, C.; Yotsumoto, F.; Tanji, H.; Mori, N.; Takeshita, M.; Miyamoto, S.; et al. Targeting Bcl-2 family proteins in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: In vitro and in vivo effects of the novel Bcl-2 family inhibitor ABT-737. Cancer Lett. 2012, 317, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneji, K.; Matsuda, T.; Tomita, M.; Kawakami, H.; Ohshiro, K.; Uchihara, J.-N.; Masuda, M.; Takasu, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohta, T.; et al. Fucoidan extracted from Cladosiphon okamuranus Tokida induces apoptosis of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukemia cells. Nutr. Cancer 2005, 52, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, Y.R.; Nakahata, S.; Chilmi, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Nueangphuet, P.; Yamaguchi, R.; Nakamura, T.; Shimoda, K.; Morishita, K. Antitumor effects of chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine mediated by inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway through abrogation of autophagic p47 degradation in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikawa, A.; Kozako, T.; Uchida, Y.; Yoshimitsu, M.; Ishitsuka, K.; Ohsugi, T.; Honda, S.-I. Cell death induced by dorsomorphin in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma is AMPK-independent. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 4005–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, C.; Senba, M.; Mori, N. Importin β1 regulates cell growth and survival during adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma therapy. Investig. New Drugs 2021, 39, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Mathews Griner, L.A.; Ju, W.; Duveau, D.Y.; Guha, R.; Petrus, M.N.; Wen, B.; Maeda, M.; Shinn, P.; Ferrer, M.; et al. Selective targeting of JAK/STAT signaling is potentiated by Bcl-xL blockade in IL-2-dependent adult T-cell leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12480–12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, C.; Senba, M.; Mori, N. Anti-adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma activity of cerdulatinib, a dual SYK/JAK kinase inhibitor. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, C.; Matsuda, T.; Okudaira, T.; Tomita, M.; Kawakami, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Masuda, M.; Ohshiro, K.; Ohta, T.; Mori, N. Bisphosphonate incadronate inhibits growth of human T-cell leukaemia virus type I-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukaemia cells by interfering with the mevalonate pathway. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 136, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machijima, Y.; Ishikawa, C.; Sawada, S.; Okudaira, T.; Uchihara, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Taira, N.; Mori, N. Anti-adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma effects of indole-3-carbinol. Retrovirology 2009, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guimaraes-Correa, A.B.; Crawford, L.B.; Figueiredo, C.R.; Gimenes, K.P.; Pinto, L.A.; Grassi, M.F.R.; Feuer, G.; Travassos, L.R.; Caires, A.C.F.; Rodrigues, E.G.; et al. C7a, a biphosphinic cyclopalladated compound, efficiently controls the development of a patient-derived xenograft model of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Viruses 2011, 3, 1041–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, C.; Jomori, T.; Tanaka, J.; Senba, M.; Mori, N. Peridinin, a carotenoid, inhibits proliferation and survival of HTLV-1-infected T-cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, C.; Senba, M.; Mori, N. Butein inhibits NF-κB, AP-1 and Akt activation in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatfat, M.; Fakhoury, I.; Habli, Z.; Mismar, R.; Gali-Muhtasib, H. Thymoquinone enhances the anticancer activity of doxorubicin against adult T-cell leukemia in vitro and in vivo through ROS-dependent mechanisms. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, A.; Orba, Y.; Kimura, T.; Iha, H.; Ogata, M.; Tsuji, T.; Ainai, A.; Sata, T.; Okamoto, T.; Hall, W.W.; et al. Inhibition of the SDF-1alpha-CXCR4 axis by the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 suppresses the migration of cultured cells from ATL patients and murine lymphoblastoid cells from HTLV-I Tax transgenic mice. Blood 2009, 114, 2961–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tary-Lehmann, M.; Saxon, A.; Lehmann, P. V The human immune system in hu-PBL-SCID mice. Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.A.; Covassin, L.; Brehm, M.A.; Racki, W.; Pearson, T.; Leif, J.; Laning, J.; Fodor, W.; Foreman, O.; Burzenski, L.; et al. Human peripheral blood leucocyte non-obese diabetic-severe combined immunodeficiency interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain gene mouse model of xenogeneic graft-versus-host-like disease and the role of host major histocompatibility complex. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 157, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, P.; Tonomura, N.; Shimizu, A.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.-G. Reconstitution of a functional human immune system in immunodeficient mice through combined human fetal thymus/liver and CD34+ cell transplantation. Blood 2006, 108, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melkus, M.W.; Estes, J.D.; Padgett-Thomas, A.; Gatlin, J.; Denton, P.W.; Othieno, F.A.; Wege, A.K.; Haase, A.T.; Garcia, J.V. Humanized mice mount specific adaptive and innate immune responses to EBV and TSST-1. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonomura, N.; Habiro, K.; Shimizu, A.; Sykes, M.; Yang, Y.-G. Antigen-specific human T-cell responses and T cell-dependent production of human antibodies in a humanized mouse model. Blood 2008, 111, 4293–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tezuka, K.; Xun, R.; Tei, M.; Ueno, T.; Tanaka, M.; Takenouchi, N.; Fujisawa, J. An animal model of adult T-cell leukemia: Humanized mice with HTLV-1-specific immunity. Blood 2014, 123, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espíndola, O.d.M.; Siteur-van Rijnstra, E.; Frankin, E.; Weijer, K.; van der Velden, Y.U.; Berkhout, B.; Blom, B.; Villaudy, J. Early Effects of HTLV-1 Infection on the Activation, Exhaustion, and Differentiation of T-Cells in Humanized NSG Mice. Cells 2021, 10, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Rauch, D.A.; Huey, D.D.; Panfil, A.R.; Cheng, X.; Esser, A.K.; Su, X.; Harding, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Fox, G.C.; et al. HTLV-1 viral oncogene HBZ drives bone destruction in adult T cell leukemia. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e128713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaatinen, T.; Hemmoranta, H.; Hautaniemi, S.; Niemi, J.; Nicorici, D.; Laine, J.; Yli-Harja, O.; Partanen, J. Global gene expression profile of human cord blood-derived CD133+ cells. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.B.; Bruno, S.; Buttiglieri, S.; Tetta, C.; Gatti, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bussolati, B.; Camussi, G. Isolation and characterization of a stem cell population from adult human liver. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 2840–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Rendon, E.; Hale, S.J.M.; Ryan, D.; Baban, D.; Forde, S.P.; Roubelakis, M.; Sweeney, D.; Moukayed, M.; Harris, A.L.; Davies, K.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of human cord blood CD133+ and cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in response to hypoxia. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Okajima, A.; Shiokawa, M.; Ishii, N.; Katano, I.; Ito, R.; Ito, M.; Minegishi, M.; Minegishi, N.; et al. The analysis of the functions of human B and T cells in humanized NOD/shi-scid/gammac(null) (NOG) mice (hu-HSC NOG mice). Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 843–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danner, R.; Chaudhari, S.N.; Rosenberger, J.; Surls, J.; Richie, T.L.; Brumeanu, T.-D.; Casares, S. Expression of HLA class II molecules in humanized NOD.Rag1KO.IL2RgcKO mice is critical for development and function of human T and B cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, M.; Takahashi, T.; Katano, I.; Ito, R.; Ito, M.; Harigae, H.; Ishii, N.; Sugamura, K. Induction of human humoral immune responses in a novel HLA-DR-expressing transgenic NOD/Shi-scid/γcnull mouse. Int. Immunol. 2012, 24, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strowig, T.; Gurer, C.; Ploss, A.; Liu, Y.-F.; Arrey, F.; Sashihara, J.; Koo, G.; Rice, C.M.; Young, J.W.; Chadburn, A.; et al. Priming of protective T cell responses against virus-induced tumors in mice with human immune system components. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, L.D.; Saito, Y.; Najima, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Ochi, T.; Tomizawa, M.; Doi, T.; Sone, A.; Suzuki, N.; Fujiwara, H.; et al. Generation of functional human T-cell subsets with HLA-restricted immune responses in HLA class I expressing NOD/SCID/IL2r gamma(null) humanized mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13022–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willinger, T.; Rongvaux, A.; Takizawa, H.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Murphy, A.J.; Auerbach, W.; Eynon, E.E.; Stevens, S.; Manz, M.G.; et al. Human IL-3/GM-CSF knock-in mice support human alveolar macrophage development and human immune responses in the lung. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2390–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billerbeck, E.; Barry, W.T.; Mu, K.; Dorner, M.; Rice, C.M.; Ploss, A. Development of human CD4+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in human stem cell factor-, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-, and interleukin-3-expressing NOD-SCID IL2Rγ(null) humanized mice. Blood 2011, 117, 3076–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huntington, N.D.; Legrand, N.; Alves, N.L.; Jaron, B.; Weijer, K.; Plet, A.; Corcuff, E.; Mortier, E.; Jacques, Y.; Spits, H.; et al. IL-15 trans-presentation promotes human NK cell development and differentiation in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Khoury, M.; Chen, J. Expression of human cytokines dramatically improves reconstitution of specific human-blood lineage cells in humanized mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21783–21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, I.; Takahashi, T.; Ito, R.; Kamisako, T.; Mizusawa, T.; Ka, Y.; Ogura, T.; Suemizu, H.; Kawakami, Y.; Ito, M. Predominant development of mature and functional human NK cells in a novel human IL-2-producing transgenic NOG mouse. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3513–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, T.; Katano, I.; Ito, R.; Goto, M.; Abe, H.; Mizuno, S.; Kawai, K.; Sugiyama, F.; Ito, M. Enhanced Antibody Responses in a Novel NOG Transgenic Mouse with Restored Lymph Node Organogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyazato, P.; Yasunaga, J.; Taniguchi, Y.; Koyanagi, Y.; Mitsuya, H.; Matsuoka, M. De novo human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection of human lymphocytes in NOD-SCID, common gamma-chain knockout mice. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10683–10691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takajo, I.; Umeki, K.; Morishita, K.; Yamamoto, I.; Kubuki, Y.; Hatakeyama, K.; Kataoka, H.; Okayama, A. Engraftment of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 carriers in NOD/SCID/gammac(null) (NOG) mice. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaudy, J.; Wencker, M.; Gadot, N.; Gillet, N.A.; Scoazec, J.-Y.; Gazzolo, L.; Manz, M.G.; Bangham, C.R.M.; Dodon, M.D. HTLV-1 propels thymic human T cell development in “human immune system” Rag2−/− gamma c−/− mice. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérès, E.; Blin, J.; Ricci, E.P.; Artesi, M.; Hahaut, V.; Van den Broeke, A.; Corbin, A.; Gazzolo, L.; Ratner, L.; Jalinot, P.; et al. PDZ domain-binding motif of Tax sustains T-cell proliferation in HTLV-1-infected humanized mice. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimova, V.; Smith, S.; Seth, J.; Phelps, C.; Niewiesk, S.; Satou, Y.; Green, P.L.; Panfil, A.R. HTLV-1 intragenic viral enhancer influences immortalization phenotype in vitro, but is dispensable for persistence and disease development in animal models. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 954077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyoshi, M.; Okuma, K.; Tateyama, S.; Takizawa, K.; Saito, M.; Kuramitsu, M.; Araki, K.; Morishita, K.; Okada, S.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Furin-dependent CCL17-fused recombinant toxin controls HTLV-1 infection by targeting and eliminating infected CCR4-expressing cells in vitro and in vivo. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inocencio, N.M.; Moehring, J.M.; Moehring, T.J. Furin activates Pseudomonas exotoxin A by specific cleavage in vivo and in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 31831–31835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percher, F.; Curis, C.; Pérès, E.; Artesi, M.; Rosewick, N.; Jeannin, P.; Gessain, A.; Gout, O.; Mahieux, R.; Ceccaldi, P.-E.; et al. HTLV-1-induced leukotriene B4 secretion by T cells promotes T cell recruitment and virus propagation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tezuka, K.; Okuma, K.; Kuramitsu, M.; Matsuoka, S.; Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Hamaguchi, I. Control of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) Infection by Eliminating Envelope Protein-Positive Cells with Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Viruses Encoding HTLV-1 Primary Receptor. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01885-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madugula, K.K.; Joseph, J.; DeMarino, C.; Ginwala, R.; Teixeira, V.; Khan, Z.K.; Sales, D.; Wilson, S.; Kashanchi, F.; Rushing, A.W.; et al. Regulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 antisense promoter by myocyte enhancer factor-2C in the context of adult T-cell leukemia and lymphoma. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2928–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkhanis, V.; Hu, Y.-J.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Imbalzano, A.N.; Sif, S. Versatility of PRMT5-induced methylation in growth control and development. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ernzen, K.; Melvin, C.; Yu, L.; Phelps, C.; Niewiesk, S.; Green, P.L.; Panfil, A.R. The PRMT5 inhibitor EPZ015666 is effective against HTLV-1-transformed T-cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strain | Genotype | Characteristics | Limitation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCID | PrkdcSCID | T cell and B cell defect | T cell and B cell leakage Radiosensitive | [66] |
| NOD/SCID | NOD/PrkdcSCID | T cell and B cell defect Decreased NK cell, DC and macrophage activity Functional C5 complement deficiency | T cell and B cell leakage Radiosensitive Spontaneous lymphoma | [72] |
| NOG | NOD/PrkdcSCID/Il2rgnull | T cell, B cell and NK cell defect Decreased DC and macrophage activity Functional C5 complement deficiency | Radiosensitive | [75] |
| NSG | NOD/PrkdcSCID/Il2rgnull | T cell, B cell and NK cell defect Decreased DC and macrophage activity Functional C5 complement deficiency | Radiosensitive | [76] |
| NOJ | NOD/PrkdcSCID/JAK3null | T cell, B cell and NK cell defect Decreased DC and macrophage activity Functional C5 complement deficiency | Radiosensitive | [77] |
| NRG | NOD/Rag1null/Il2rgnull | T cell, B cell and NK cell defect Decreased DC and macrophage activity Functional C5 complement deficiency | - | [78] |
| Candidates | Target/Function | Mouse | Efficacy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bay 11-7082 | NF-κB inhibitor | NOG mouse | Inhibits tumor growth and invasion | [91] |
| DHMEQ | NF-κB inhibitor | NK(-)SCID mouse SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth and invasion | [92,93,94,95] |
| Ritonavir | HIV protease inhibitor | NOG mouse | Inhibits tumor growth and invasion | [98] |
| Fucoidan | Survivin inhibitor | SCID mouse | Partially inhibits tumor growth | [106] |
| Incadronate | Mevalonate pathway inhibitor | SCID mouse | Reduces tumor formation | [112] |
| PS-341 | Proteasome inhibitor | SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [96] |
| PS-341 Zoledronic acid | Proteasome inhibitor Osteoclast inhibitor | NOD/SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [97] |
| 9-aminoacridine (9AA) Campath-1H | Increase p53 transcription activity NF-κB activation inhibitor Humanized anti-CD52 antibody | NOD/SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth Extends survival | [101] |
| Depsipeptide Daclizumab | HDAC inhibitor Anti-IL-2Rα antibody | NOD/SCID mouse | Extends survival | [102] |
| LBH589 | HDAC inhibitor | SCID mouse | Induces tumor cell apoptosis Extends survival | [103] |
| AR-42 | HDAC inhibitor | NOD/SCID mouse | Extends survival | [104] |
| ABT-737 | Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L), and Bcl-w inhibitor | SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [105] |
| 17-DMAG | HSP90 inhibitor | NOG mouse | Inhibits tumor invasion Extends survival | [100] |
| As(2)O(3) IFN-α | Proteolysis of Tax Antiviral | SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor cell immortality | [99] |
| C7a | Antitumor effect | NSG mouse | Extends survival | [114] |
| Indole-3-carbinol | Antitumor effect | SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [113] |
| AMD3100 | CXCR4 antagonist | SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor cell infiltration into liver and lung tissue | [118] |
| Chloroquine Hydroxychloroquine | Autophagy inhibitor | NOG mouse | Inhibits tumor growth Extends survival | [107] |
| Dorsomorphin | AMPK inhibitor | NOD/SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [108] |
| Ivermectin | IPOα/β1 inhibitor | SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [109] |
| Ruxolitinib Navitoclax | JAK inhibitor Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor | NSG mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [110] |
| Cerdulatinib | Dual SYK/JAK inhibitor | SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [111] |
| Peridinin | Antitumor effect | SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [115] |
| Butein | Antitumor effect | SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [116] |
| Thymoquinone Doxorubicin | Antitumor effect Anticancer drug | NOD/SCID mouse | Inhibits tumor growth | [117] |
| Candidates | Target/Function | Mouse | Efficacy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TARC-PE38 | CCR4 | HIS NOJ mouse | Eliminate HTLV-1-infected cells | [146] |
| MK886 | LTB4 secretion inhibitor | HIS NSG-HLA-A2/HDD mouse | Reduce both PVL and the number of infected clones | [148] |
| VSVΔG-GL VSVΔG-NP | GLUT1 NRP1 | HIS NOJ mouse | Eliminate HTLV-1-infected Env-expressing cells | [149] |
| MC1568 | HDAC inhibitor (MEF-2 inhibitor) | HIS NOG mouse | Reduce PVL | [150] |
| EPZ015666 | PRMT5 inhibitor | HIS NSG mouse | Extends survival | [152] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakajima, S.; Okuma, K. Mouse Models for HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T Cell Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411737
Nakajima S, Okuma K. Mouse Models for HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T Cell Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411737
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakajima, Shinsuke, and Kazu Okuma. 2023. "Mouse Models for HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T Cell Leukemia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411737
APA StyleNakajima, S., & Okuma, K. (2023). Mouse Models for HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T Cell Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411737





