Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenol- and Flavonoid-Enriched Rice Seed Extract on Melanogenesis in Melan-a Cells via MAPK Signaling-Mediated MITF Downregulation
Abstract
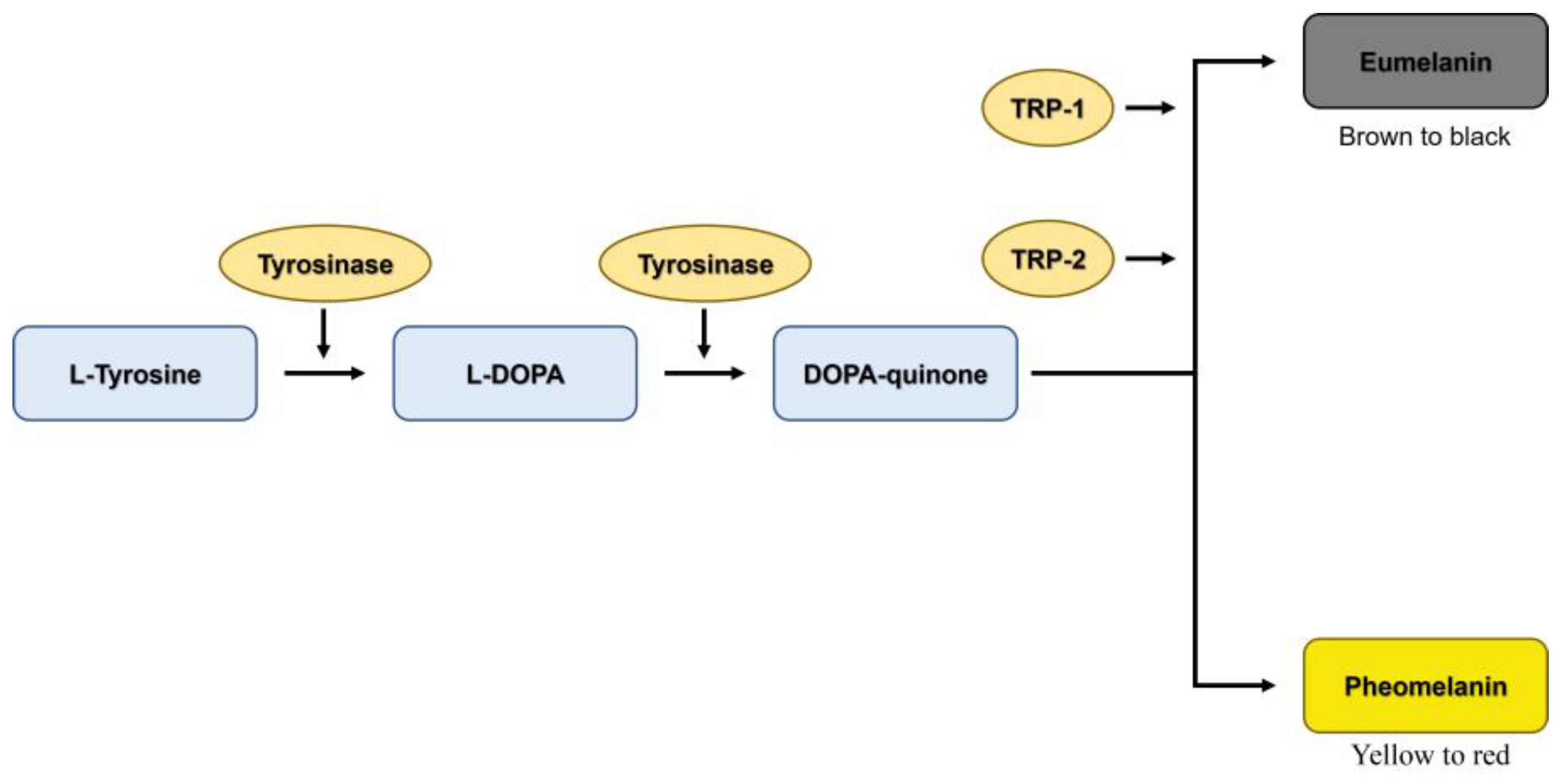
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Total Polyphenol and Flavonoid Contents of Sebok Rice Seed Extract
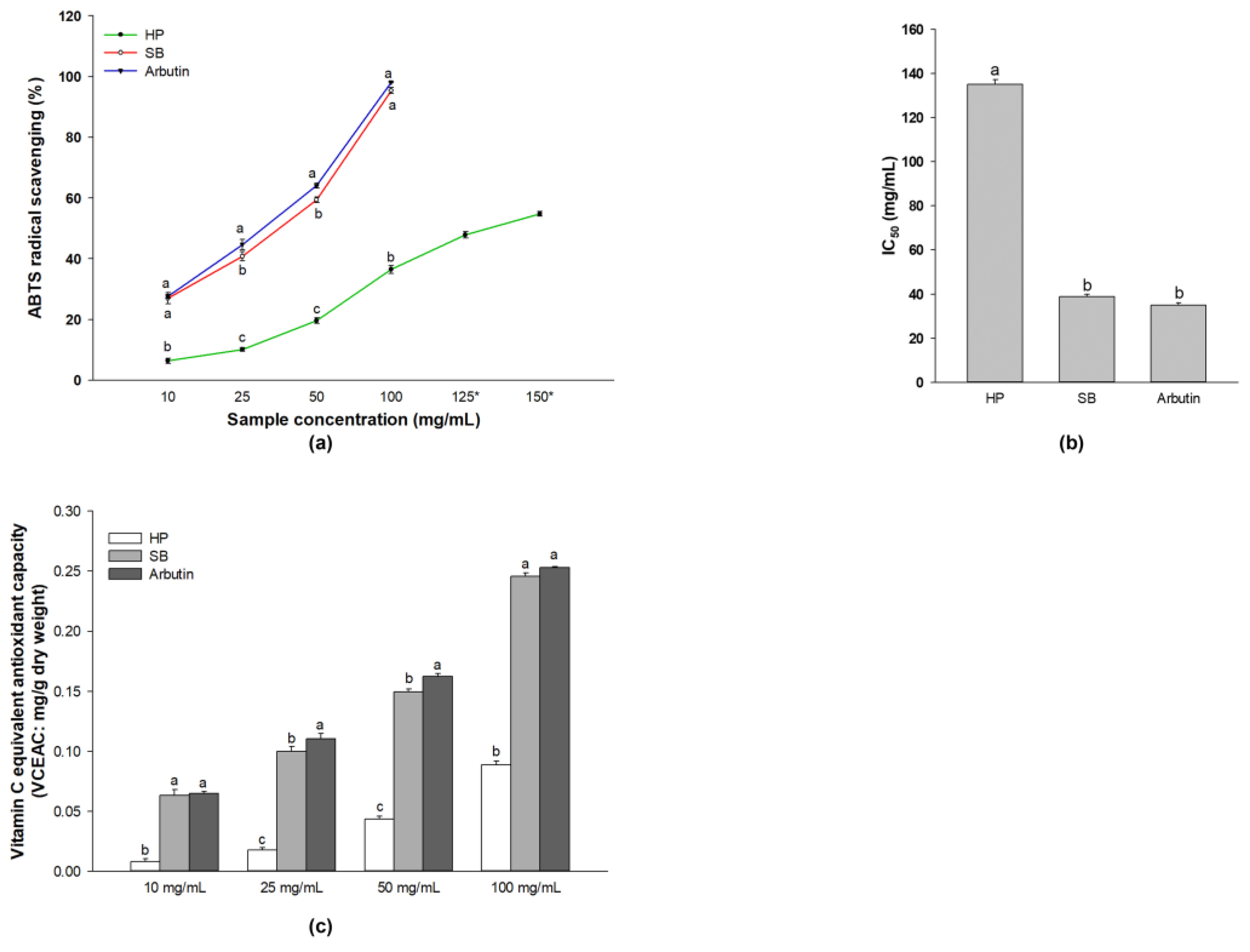
2.2. Antioxidant Activities of Sebok Rice Seed Extract
2.3. Effect of Sebok Rice Seed Extract on Cell Viability
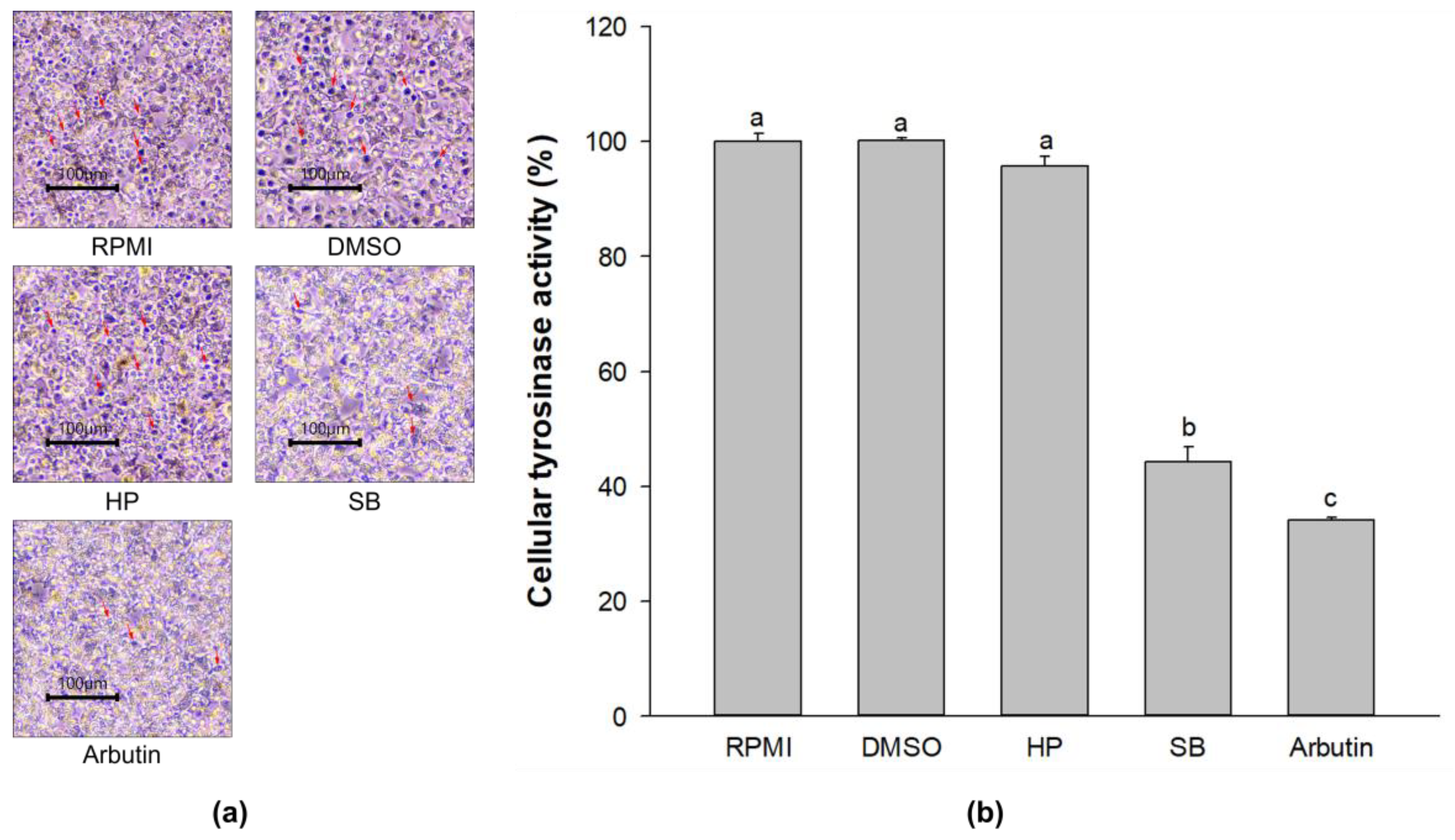
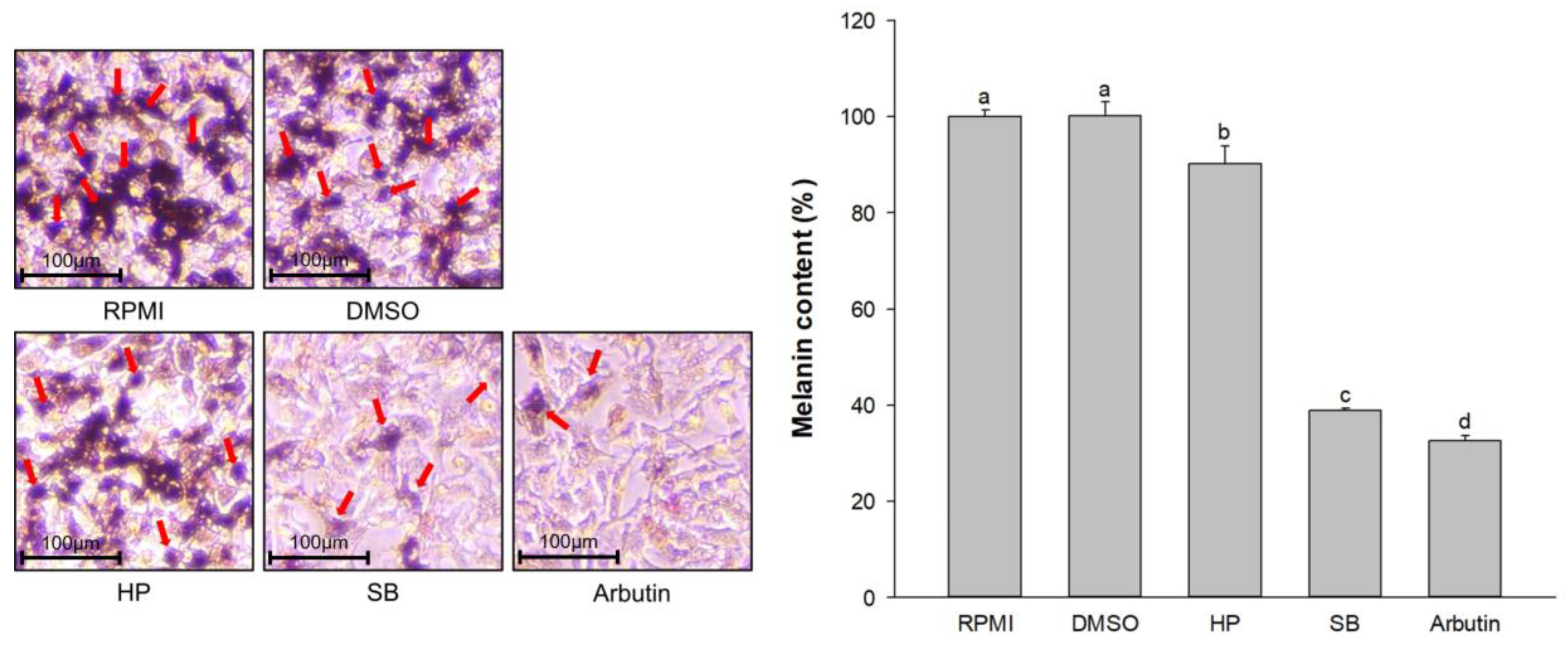
2.4. Effect of Sebok Rice Seed Extract on Melanin Content and Melanin Excretion
2.5. Effect of Sebok Rice Seed Extract on Cellular Tyrosinase Activity
2.6. Effect of Sebok Rice Seed Extract on Melanin-Containing Cells
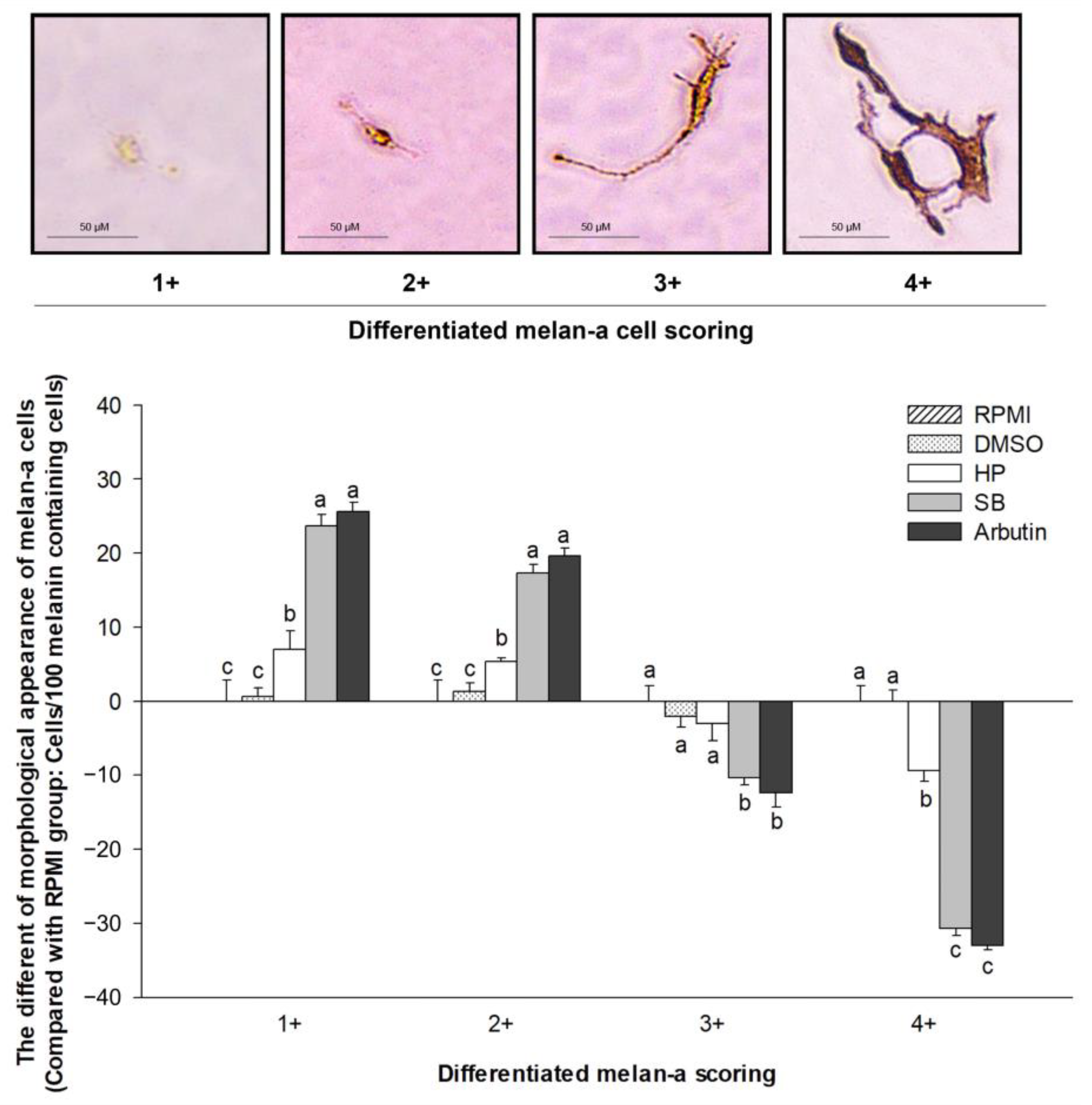
2.7. Effect of Sebok Rice Seed Extract on the Morphological Appearance of Melan-a Cells
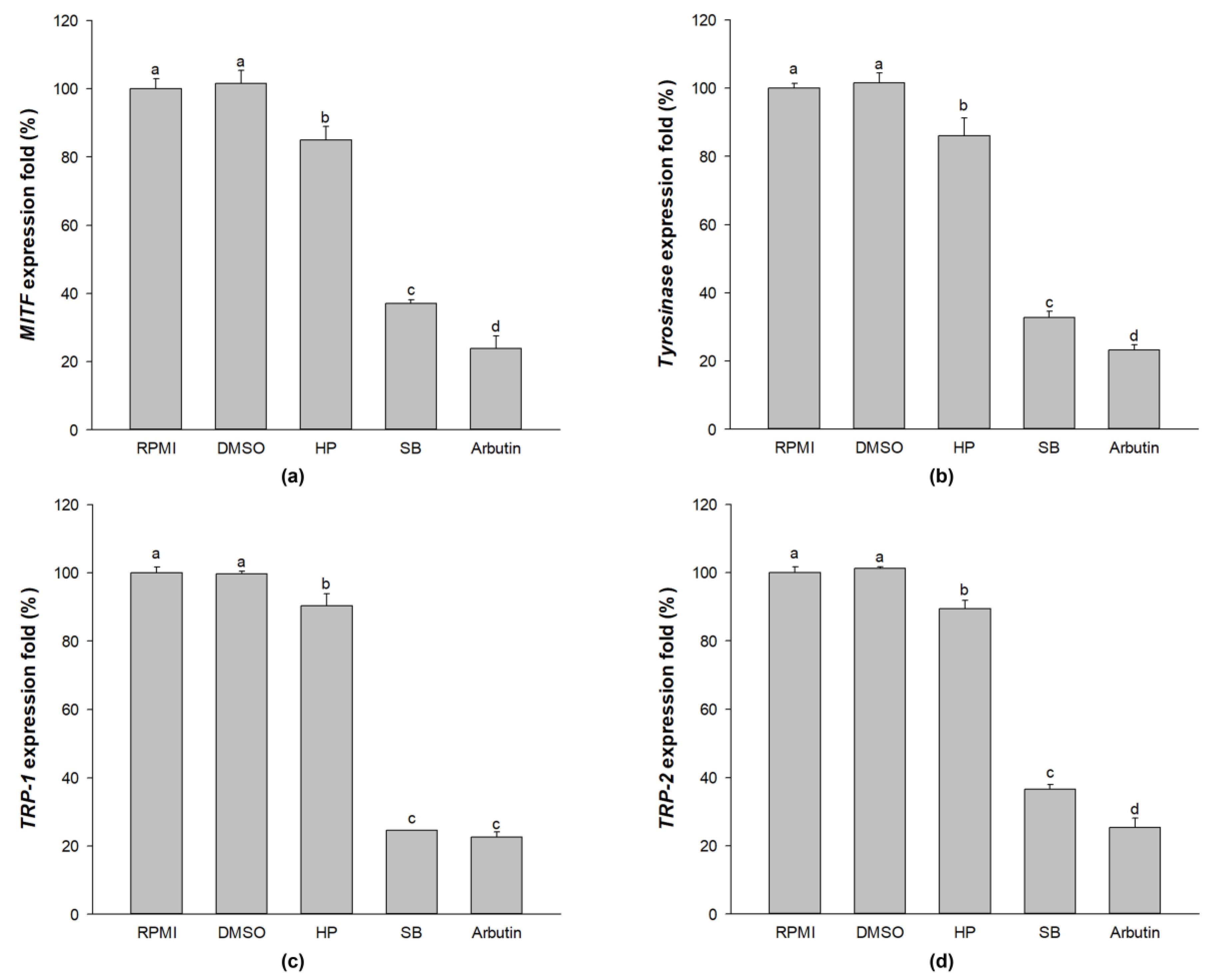
2.8. Effect of Sebok Rice Seed Extract on Melanogenic-Related Gene Expression
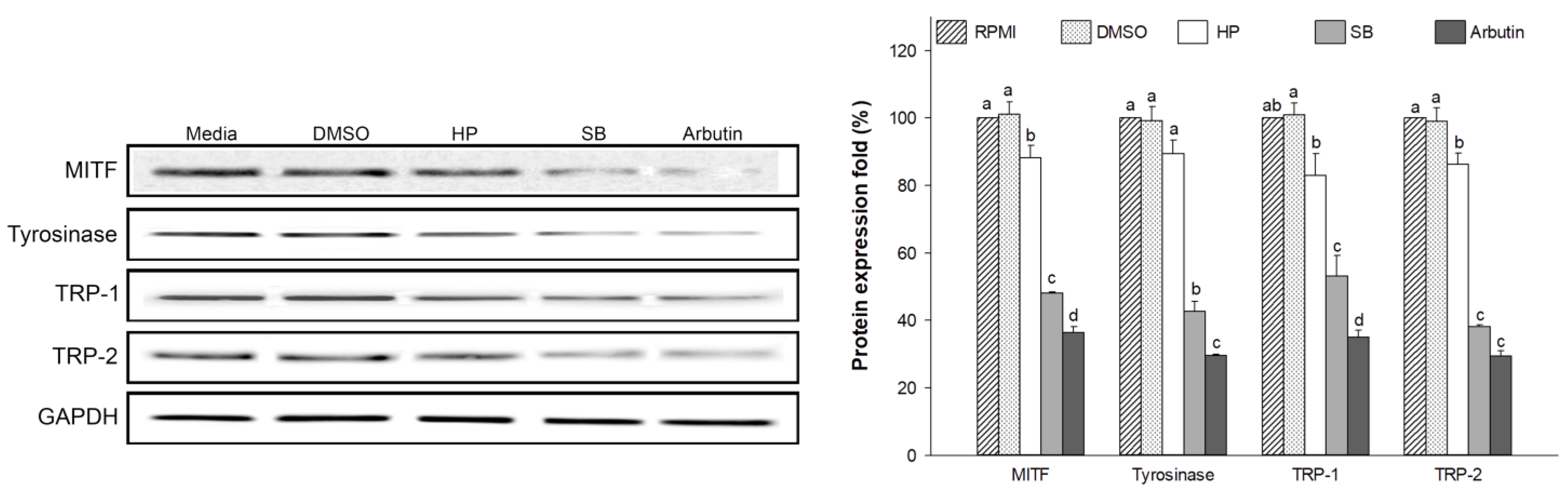
2.9. Effect of Sebok Rice Seed Extract on Melanogenesis-Related Proteins
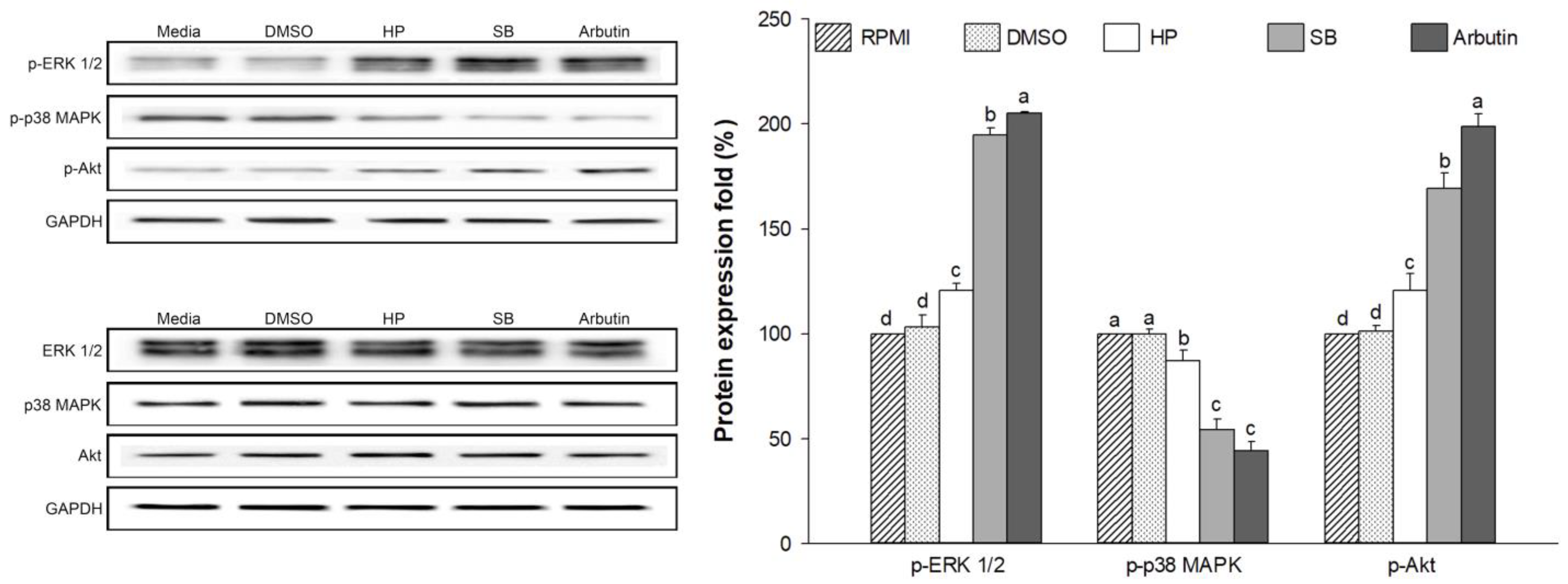
2.10. Effect of Sebok Rice Seed Extract on the MAPKs and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
4.2. Treatment Preparation
4.3. Total Polyphenol and Flavonoid Contents Determination
4.4. Antioxidant Activity Assay
4.5. Viability Assay of Melan-a Cells
4.6. Melanin Content and Melanin Excretion Assay
4.7. L-DOPA Staining and Cellular Tyrosinase Activity Assay
4.8. Morphological Appearance Assay
4.9. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Quantification
4.10. Western Blot Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefèvre-Utile, A.; Braun, C.; Haftek, M.; Aubin, F. Five functional aspects of the epidermal barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-G.; Karadeniz, F.; Seo, Y.; Kong, C.-S. Anti-melanogenic effects of flavonoid glycosides from Limonium tetragonum (Thunb.) bullock via inhibition of tyrosinase and tyrosinase-related proteins. Molecules 2017, 22, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, Y.C.; Lee, J.N.; Kim, B.S.; Hyun, C.-G. Anti-melanogenic effects of Paederia foetida L. extract via MAPK signaling-mediated MITF downregulation. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Qu, B.; Wang, M.; Yu, X.; Chen, J. Mitf involved in innate Immunity by activating tyrosinase-mediated melanin synthesis in Pteria penguin. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 626493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, T.; Hong, M.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, H.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H.; Lu, Z. Quantitative proteomic analysis uncovers inhibition of melanin synthesis by silk fibroin via MITF/tyrosinase axis in B16 melanoma cells. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, B.S.; Hyun, C.-G. Anti-melanogenic effects of bergamottin via mitogen-activated protein kinases and protein kinase B signaling pathways. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19862105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.; Yoon, J.-H.; Youn, K.; Jun, M. Decursin prevents melanogenesis by suppressing MITF expression through the regulation of PKA/CREB, MAPKs, and PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β cascades. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.B.; Park, N.H.; Song, B.-R.; Lee, S.-H. Antioxidant potential-rich betel leaves (Piper betle L.) exert depigmenting action by triggering autophagy and downregulating MITF/tyrosinase in vitro and in vivo. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Chung, Y.C.; Moon, S.-H.; Hyun, C.-G. Lincomycin induces melanogenesis through the activation of MITF via p38 MAPK, AKT, and PKA signaling pathways. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto, T.; Ohta, T.; Yamashita, A.; Fujii, S.; Shoyama, Y. Liquiritin and liquiritigenin induce melanogenesis via enhancement of p38 and PKA signaling pathways. Medicines 2019, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqui, M.F.; Jeon, S.; Kim, M.-M. CRISPR/Cas9 system mediated SIRT7 gene knockout promotes melanogenesis by MITF via MAPKS and BMP activation in melanoma cells. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2023, 59, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurpolsky, D.; Lagunov, A.; Golyshev, A. Development of device for analysis problem skin zones of the circumpolar region population. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2174, 020267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, W.; Qin, L. Melanin inspired microcapsules delivering immune metabolites for hepatic fibrosis management. Mater. Today Bio. 2023, 21, 100711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Park, H.Y.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, D.H.; Rho, H.S.; Choi, K. Anti-melanogenic effects of kojic acid and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2020, 25, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, J.; Wan, J.; Pham, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J.; Yu, L.; Luo, Y.; Wang, T.T.Y.; Chen, P. Profiling of polyphenols and glucosinolates in kale and broccoli microgreens grown under chamber and windowsill conditions by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jia, M.; Chen, J.; Wan, H.; Dong, R.; Nie, S.; Xie, M.; Yu, Q. Removal of bound polyphenols and its effect on antioxidant and prebiotics properties of carrot dietary fiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Diana, A.B.; García-Casas, M.J.; Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; Frías, J.; Peñas, E.; Rico, D. Wheat and oat brans as sources of polyphenol compounds for development of antioxidant nutraceutical ingredients. Foods 2021, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolling, B.W. Almond polyphenols: Methods of analysis, contribution to food quality, and health promotion. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 346–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroula, A.; Amgain, N.; Kc, R.; Adhikari, S.; Acharya, J. Pigments, ascorbic acid, total polyphenols and antioxidant capacities in deetiolated barley (Hordeum vulgare) and wheat (Triticum aestivum) microgreens. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, L. Dietary plant polyphenols: Effects of food processing on their content and bioavailability. Molecules 2021, 26, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Escobar, R.; Aliaño-González, M.J.; Cantos-Villar, E. Wine polyphenol content and its influence on wine quality and properties: A review. Molecules 2021, 26, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, K.; Gantner, M.; Tatarak, A.; Hallmann, E. The content of polyphenols in coffee beans as roasting, origin and storage effect. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, L.; Zhang, H.; Qi, R.; Tsao, R.; Mine, Y. Recent advances in the understanding of the health benefits and molecular mechanisms associated with green tea polyphenols. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabini, L.; Melzi, G.; Lolli, F.; Dell’Agli, M.; Piazza, S.; Sangiovanni, E.; Marinovich, M. Effects of Vitis vinifera L. leaves extract on UV radiation damage in human keratinocytes (HaCaT). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 204, 111810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Skrzypczak, D.; Izydorczyk, G.; Mikula, K.; Szopa, D.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Antiviral properties of polyphenols from plants. Foods 2021, 10, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mssillou, I.; Bakour, M.; Slighoua, M.; Laaroussi, H.; Saghrouchni, H.; Ez-Zahra Amrati, F.; Lyoussi, B.; Derwich, E. Investigation on wound healing effect of Mediterranean medicinal plants and some related phenolic compounds: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlowski, P.; Zmigrodzka, M.; Tomaszewska, E.; Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K.; Pajak, B.; Slonska, A.; Cymerys, J.; Celichowski, G.; Grobelny, J.; Krzyzowska, M. Polyphenol-conjugated bimetallic Au@AgNPs for improved wound healing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4969–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiraguna, A.; Pangkahila, W.; Astawa, I.N.M. Antioxidant properties of topical Caulerpa sp. extract on UVB-induced photoaging in mice. Dermatol. Rep. 2018, 10, 7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latos-Brozio, M.; Masek, A. Structure-activity relationships analysis of monomeric and polymeric polyphenols (quercetin, rutin and catechin) obtained by various polymerization methods. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nani, A.; Murtaza, B.; Sayed Khan, A.; Khan, N.A.; Hichami, A. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of polyphenols contained in mediterranean diet in obesity: Molecular mechanisms. Molecules 2021, 26, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, U.; Oba, S. Polyphenol and flavonoid profiles and radical scavenging activity in leafy vegetable Amaranthus gangeticus. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Zakharov, D.V.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Terninko, I.I.; Generalova, Y.E.; Shikov, A.N. Biochemical composition, antiradical potential and human health risk of the Arctic edible brown seaweed Fucus spiralis L. J. Appl. Psychol. 2023, 35, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, S.L.; Faisal, S.; Muhammad, A.; Poulson, B.G.; Emwas, A.H.; Jaremko, M. Antiviral activities of flavonoids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Ikram, M.; Hahm, J.R.; Kim, M.O. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of citrus flavonoid hesperetin: Special focus on neurological disorders. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, L.T.; Hafeez, A.N.; Robinson, H.; Jackson, S.A.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; Tester, M.; Gao, C.; Godwin, I.D.; Hayes, B.J.; Wulff, B.B.H. Breeding crops to feed 10 billion. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, E.J.; Ha, Y.B.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.W.; Lim, S.S.; Kang, N.J. Dehydroglyasperin D suppresses melanin synthesis through MITF degradation in melanocytes. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Lyu, J.-L.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Wen, K.-C.; Chiang, H.-M. The anti-melanogenesis effect of 3,4-dihydroxybenzalacetone through downregulation of melanosome maturation and transportation in B16F10 and human epidermal melanocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, F.; Sono, Y.; Ito, T. Measurement and clinical significance of lipid peroxidation as a biomarker of oxidative stress: Oxidative stress in diabetes, atherosclerosis, and chronic inflammation. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monzani, E.; Nicolis, S.; Dell’Acqua, S.; Capucciati, A.; Bacchella, C.; Zucca, F.A.; Mosharov, E.V.; Sulzer, D.; Zecca, L.; Casella, L. Dopamine, oxidative stress and protein–quinone modifications in parkinson's and other neurodegenerative diseases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6512–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezatabar, S.; Karimian, A.; Rameshknia, V.; Parsian, H.; Majidinia, M.; Kopi, T.A.; Bishayee, A.; Sadeghinia, A.; Yousefi, M.; Monirialamdari, M.; et al. RAS/MAPK signaling functions in oxidative stress, DNA damage response and cancer progression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14951–14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfin, S.; Jha, N.K.; Jha, S.K.; Kesari, K.K.; Ruokolainen, J.; Roychoudhury, S.; Rathi, B.; Kumar, D. Oxidative stress in cancer cell metabolism. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaita, M.; Bosso, A. Polyphenolic characterization of grape skins and seeds of four Italian red cultivars at harvest and after fermentative maceration. Foods 2019, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asem, N.; Abdul Gapar, N.A.; Abd Hapit, N.H.; Omar, E.A. Correlation between total phenolic and flavonoid contents with antioxidant activity of Malaysian stingless bee propolis extract. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Del Bino, S.; Hirobe, T.; Wakamatsu, K. Improved HPLC conditions to determine eumelanin and pheomelanin contents in biological samples using an ion pair reagent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, A.; Soavi, F.; Santato, C. Eumelanin electrodes in buffered aqueous media at different pH values. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 347, 136250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Liu, L.-L.; Ren, Y.-J.; Wei, S.-D.; Yang, H.-B. Inhibitory effects and molecular mechanism on mushroom tyrosinase by condensed tannins isolation from the fruit of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. var. spinosa (Bunge) Hu ex H. F. Chow. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Oh, J.H.; Karadeniz, F.; Yang, J.; Lee, H.; Seo, Y.; Kong, C.-S. Anti-melanogenesis effect of Rosa rugosa on α-MSH-induced B16F10 cells via PKA/CREB pathway activation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, M.; Song, N.; Sun, S.; Choi, J.; Park, K. Antioxidant and anti-melanogenesis effects of colloidal gold Camellia sinensis L. extracts. Molecules 2022, 27, 5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Youn, K.; Jun, M. Discovery of pinostrobin as a melanogenic agent in cAMP/PKA and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Ahn, Y.; Park, S.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, S.H. A chemical compound from fruit extract of Juglans mandshurica inhibits melanogenesis through p-ERK-associated MITF degradation. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sakamoto, K. Pyruvic acid/ethyl pyruvate inhibits melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells through PI3K/AKT, GSK3β, and ROS-ERK signaling pathways. Genes. Cells 2019, 24, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.B.; Seo, B.-J.; Zhao, P.; Lee, S.-H. Anti-melanogenic activities of Heracleum moellendorffii via ERK1/2-mediated MITF downregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Fan, L. Antityrosinase and antioxidant activity of asparagus and its inhibition on B16F10 melanoma cells before and after hydrothermal treatment. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monmai, C.; Kim, J.-S.; Baek, S.-H. Transgenic rice seed extracts exert immunomodulatory effects by modulating immune-related biomarkers in RAW264.7 bacrophage cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4143–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, Y.C. Arbutin as a skin depigmenting agent with antimelanogenic and antioxidant properties. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Dai, G.F.; Hsu, J.L.; Lin, J.J.; Wu, W.T.; Su, C.C.; Wu, Y.J. Antimelanogenesis effect of methyl gallate through the regulation of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK in B16F10 melanoma cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 5092655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Mori, M.; Nakayama, D.; Sato, J.; Kim, I.-H.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Sugahara, T. Anti-melanogenic activity of methanolic extract from leaves of Sorbaria sorbifolia var. stellipila Max. on α-MSH-stimulated B16 melanoma 4A5 cells. Biomed. Dermatol. 2020, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Le, T.; Xue, J.; Engelhardt, U.H.; Jiang, H. Kojic acid showed consistent inhibitory activity on tyrosinase from mushroom and in cultured B16F10 cells compared with arbutins. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkök, A.; Keskin, M.; Tanuğur Samancı, A.E.; Yorulmaz Önder, E.; Takma, Ç. Determination of antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds for basic standardization of Turkish propolis. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.-D.; Cho, H.; Leo, A.P.; Shin, H.; Lee, S. Development of an analytical approach for the utilization of edible tree sprouts. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2022, 28, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotek, Z.; Białecka, B.; Pilarczyk, B.; Drozd, R.; Pilarczyk, R.; Tomza-Marciniak, A.; Kruzhel, B.; Lysak, H.; Bąkowska, M.; Vovk, S. Antioxidant activity and selenium and polyphenols content from selected medicinal plants natives from various areas abundant in Selenium (Poland, Lithuania, and Western Ukraine). Processes 2019, 7, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monmai, C.; Kim, J.-S.; Promyot, K.; Baek, S.-H. Protopanaxadiol-enriched rice extracts suppressed oxidative and melanogenic activities in melan-a cells. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-Y.; Song, M.W.; Kim, K.-T.; Paik, H.-D. Improved antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antimelanogenic effects of fermented hydroponic ginseng with Bacillus strains. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodboon, T.; Okada, S.; Suwannalert, P. Germinated riceberry rice enhanced protocatechuic acid and vanillic acid to suppress melanogenesis through cellular oxidant-related tyrosinase activity in B16 cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Extract | Total Polyphenols Content (mg TAE/g Extract) | Total Flavonoids Content (mg QE/g Extract) |
|---|---|---|
| HP | 12.5 ± 0.6 | 3.1 ± 1.1 |
| SB | 21.6 ± 1.2 | 14.1 ± 1.5 |
| Gene | Accession Number | Sequence (5′-3′) | Target Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MITF | NM_001113198.2 | Forward: AGC GTG TAT TTT CCC CAC AG Reverse: CCT TAG CTC GTT GCT GTT CC | 239 |
| Tyrosinase | D00131.1 | Forward: CCA GAA GCC AAT GCA CCT AT Reverse: CCA GAT ACG ACT GGC CTT GT | 193 |
| TRP-1 | NM_031202.3 | Forward: TCT GGC CTC CAG TTA CCA AC Reverse: TCA GTG AGG AGA GGC TGG TT | 223 |
| TRp-2 | X63349.1 | Forward: ACC CTG TGT TTG TGG TCC TC Reverse: GTT GCT CTG CGG TTA GGA AG | 186 |
| GAPDH | NM_001289726.2 | Forward: AAC TTT GGC ATT GTG GAA GG Reverse: ACA CAT TGG GGG TAG GAA CA | 223 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monmai, C.; Kim, J.-S.; Chin, J.H.; Lee, S.; Baek, S.-H. Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenol- and Flavonoid-Enriched Rice Seed Extract on Melanogenesis in Melan-a Cells via MAPK Signaling-Mediated MITF Downregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411841
Monmai C, Kim J-S, Chin JH, Lee S, Baek S-H. Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenol- and Flavonoid-Enriched Rice Seed Extract on Melanogenesis in Melan-a Cells via MAPK Signaling-Mediated MITF Downregulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411841
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonmai, Chaiwat, Jin-Suk Kim, Joong Hyoun Chin, Sanghyun Lee, and So-Hyeon Baek. 2023. "Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenol- and Flavonoid-Enriched Rice Seed Extract on Melanogenesis in Melan-a Cells via MAPK Signaling-Mediated MITF Downregulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411841
APA StyleMonmai, C., Kim, J.-S., Chin, J. H., Lee, S., & Baek, S.-H. (2023). Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenol- and Flavonoid-Enriched Rice Seed Extract on Melanogenesis in Melan-a Cells via MAPK Signaling-Mediated MITF Downregulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411841









