A Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Biosensor for the Detection of Biological Macromolecules: The Case of the Lipopolysaccharide Endotoxin Molecules
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
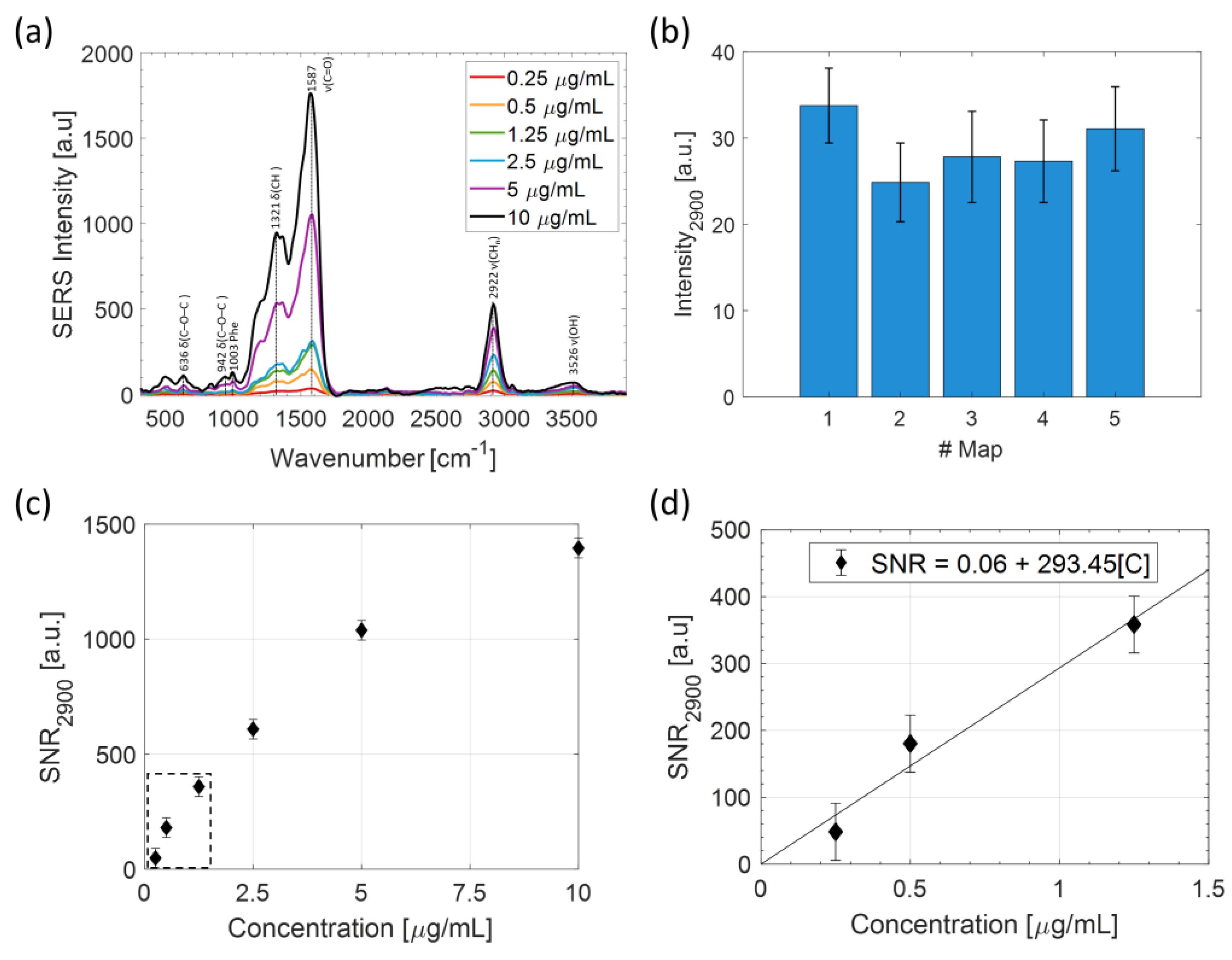
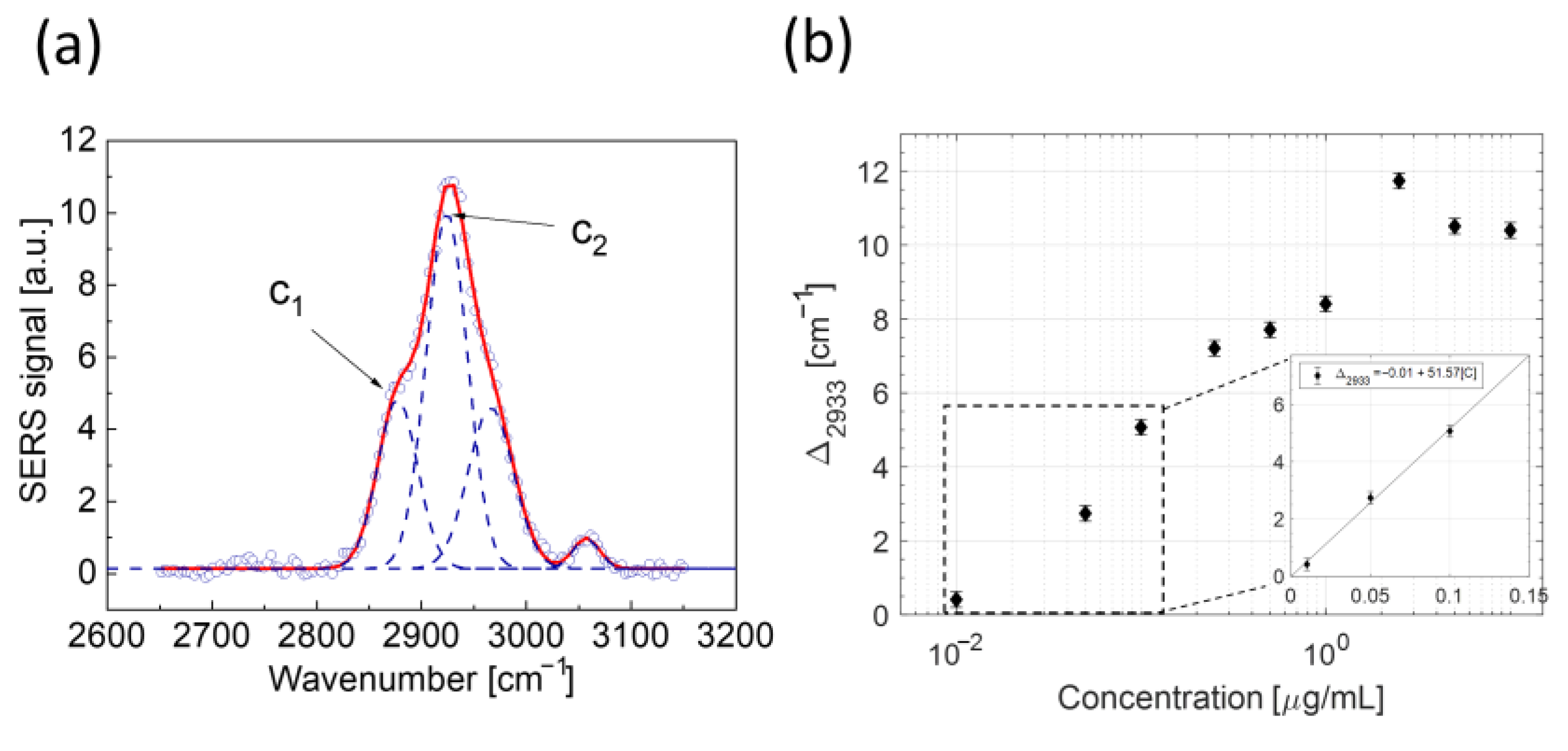
2.1. LPS Detection in Aqueous Solution
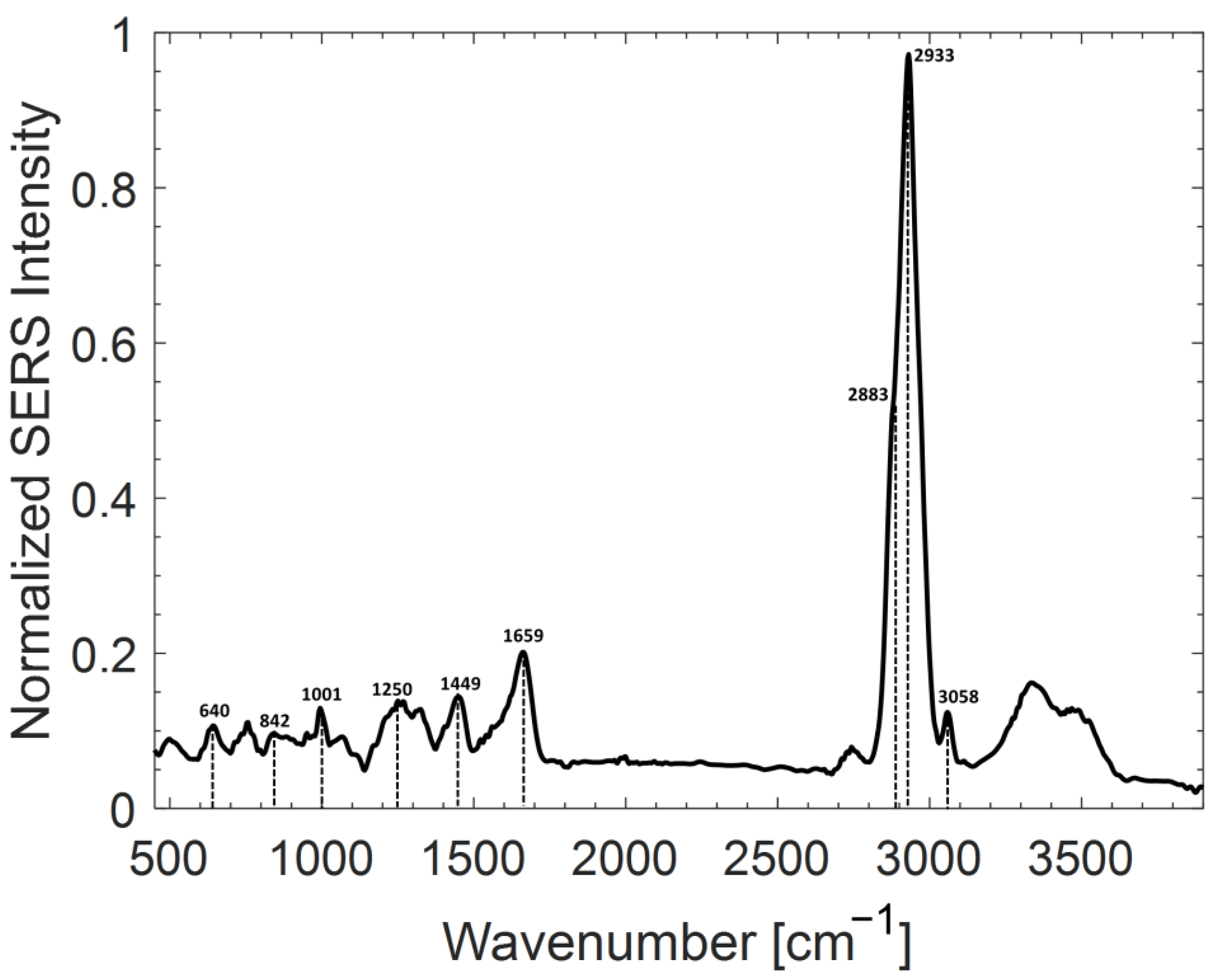
2.2. Analysis of Ab@c-SERS Substrate
2.3. LPS Detection by Ab@c-SERS
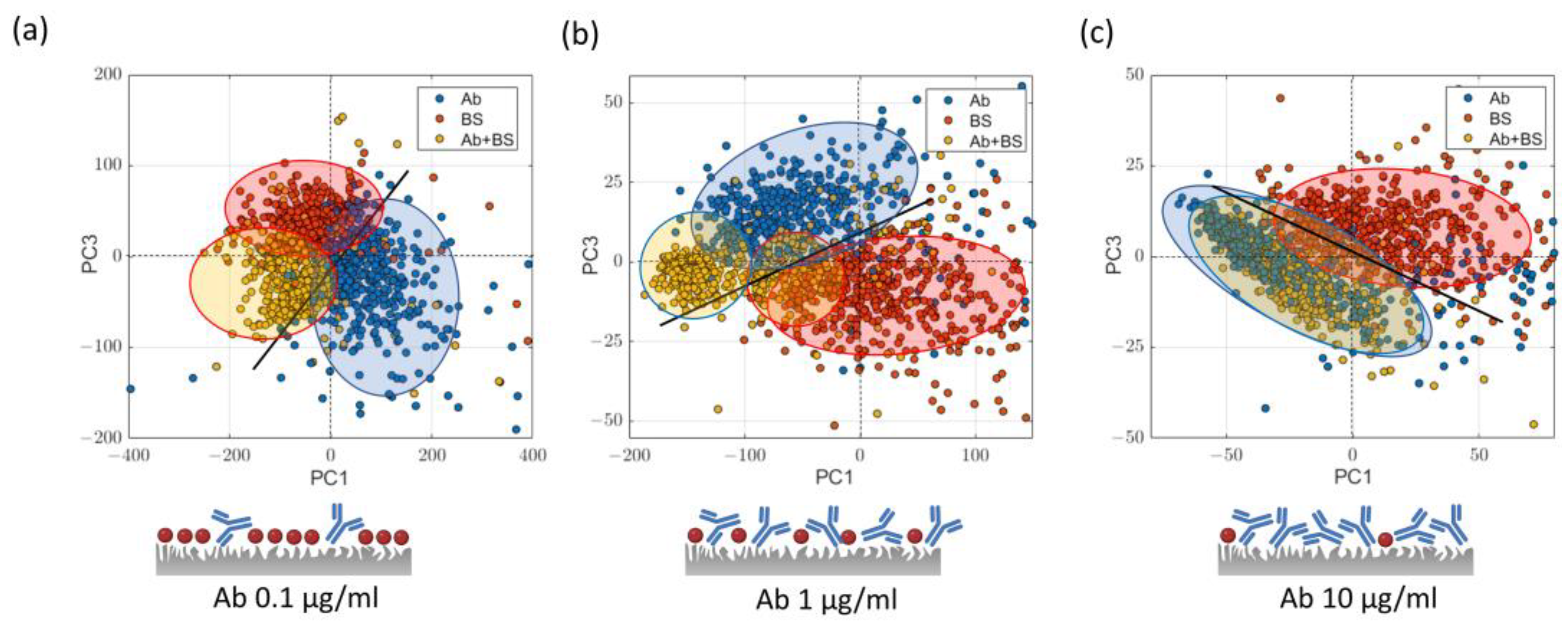
2.3.1. Analysis in the Low Wavenumber Region
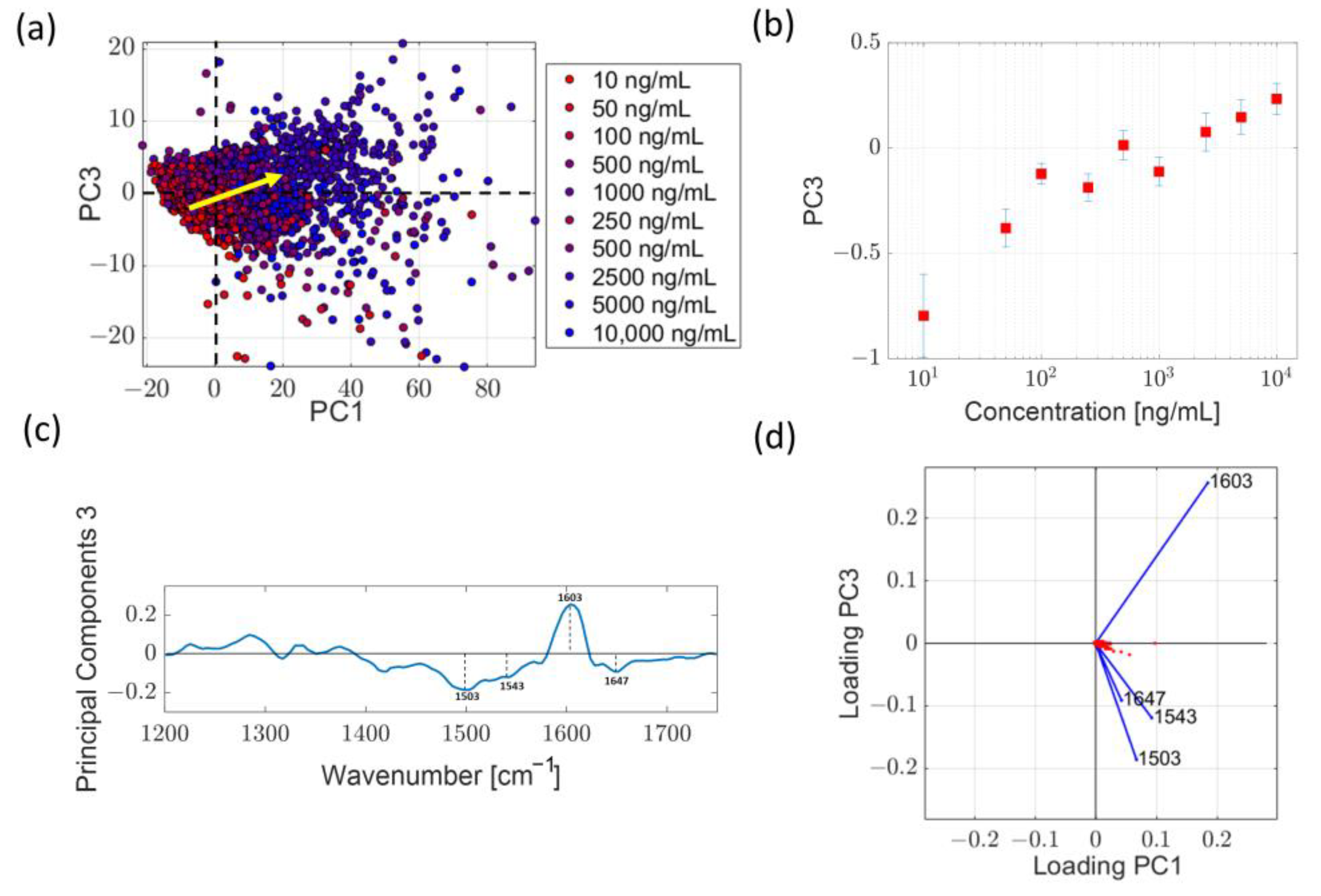
2.3.2. Analysis in the High Wavenumber Region
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Coral-like SERS Substrates
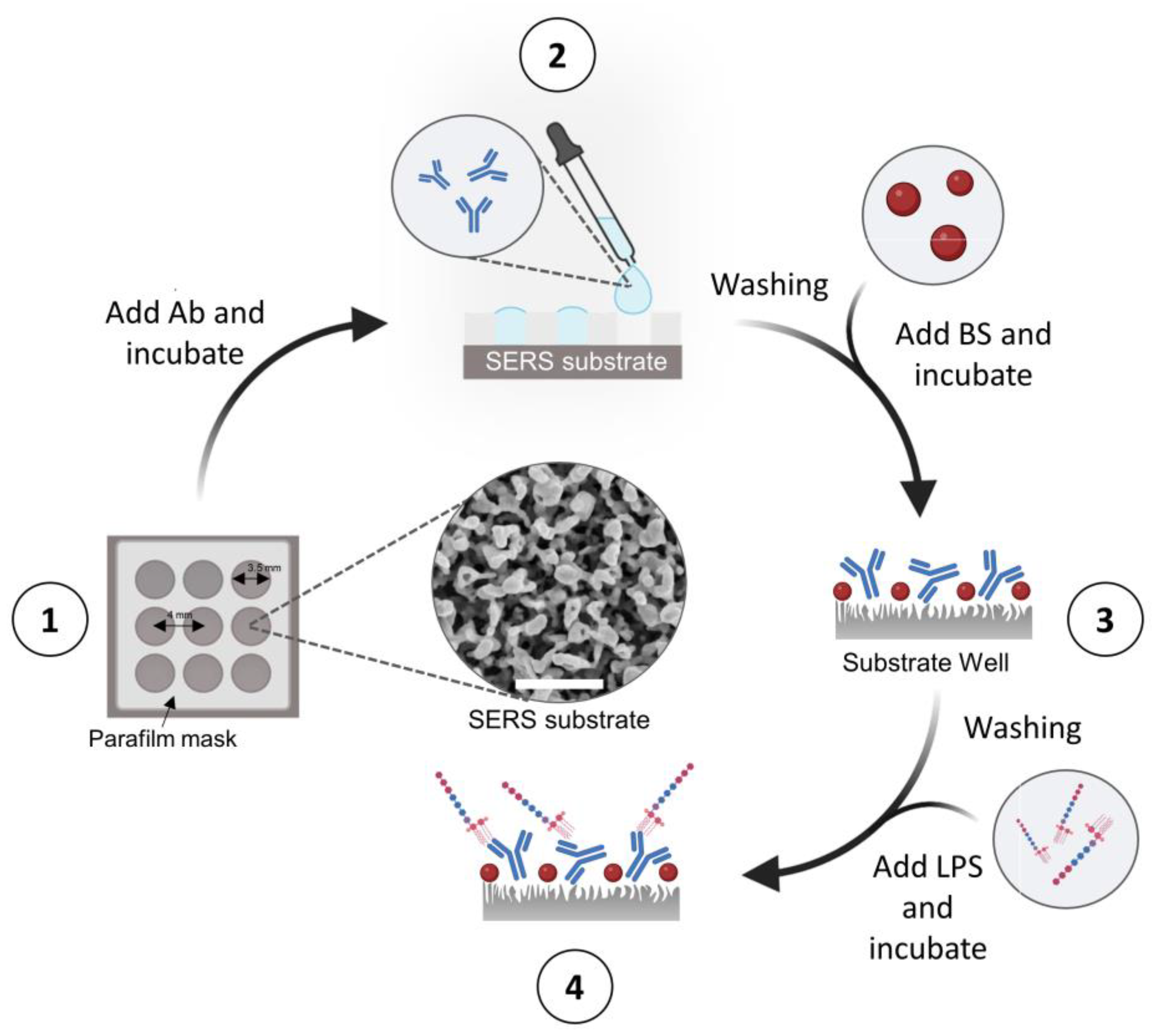
3.3. Functionalization of c-SERS Substrates for the Detection of LPS
3.4. Raman System and Signal Acquisition
3.5. Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fux, A.C.; Casonato Melo, C.; Michelini, S.; Swartzwelter, B.J.; Neusch, A.; Italiani, P.; Himly, M. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharide as source of variability in bioassays and lps-binding proteins as remedy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, R. Endotoxin in the environment--exposure and effects. J. Endotoxin Res. 2002, 8, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolden, J.S.; Warburton, R.E.; Phelan, R.; Murphy, M.; Smith, K.R.; De Felippis, M.R.; Chen, D. Endotoxin recovery using limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) assay. Biologicals 2016, 44, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, K.A.; Hadina, S.; Adamcakovadodd, A.; Weiss, J.P.; Thorne, P.S. Effect of variables in endotoxin presentation on endotoxin reactivity in the limulus amoebocyte lysate assay. In Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 2011 International Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 13–18 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann, M.; Scheibe, C.; Wellinghausen, N.; Holst, O.; Lepper, P.M. Low endotoxin release from Escherichia coli and Bacteroides fragilis during exposure to moxifloxacin. Chemotherapy 2010, 56, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakti, S.P.; Lucklum, R.; Hauptmann, P.; Bühling, F.; Ansorge, S. Disposable TSM-biosensor based on viscosity changes of the contacting medium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loreen, R.S.; Heather, M.M.; Harshini, M. Detection methods for lipopolysaccharides: Past and present. In Escherichia Coli; Amidou, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Hrvatska, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, S.; Perez-Potti, A. Applications of nanomaterials for immunosensing. Biosensors 2018, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sondhi, P.; Maruf, M.H.U.; Stine, K.J. Nanomaterials for biosensing lipopolysaccharide. Biosensors 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, W.; Ding, X. Methods of endotoxin detection. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, J.; de Aberasturi, D.J.; Aizpurua, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Auguié, B.; Baumberg, J.J.; Bazan, G.C.; Bell, S.E.J.; Boisen, A.; Brolo, A.G.; et al. Present and future of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 28–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Ru, E.C.; Etchegoin, P.G. Principles of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rusciano, G.; Capriglione, P.; Pesce, G.; Abete, P.; Carnovale, V.; Sasso, A. Raman spectroscopy as a new tool for early detection of bacteria in patients with cystic fibrosis. Laser Phys. Let. 2013, 10, 075603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusciano, G.; De Luca, A.C.; D’Alessio, A.; Minutolo, P.; Pesce, G.; Sasso, A. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering study of nano-sized organic carbon particles produced in combustion processes. Carbon 2008, 46, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cialla, D.; Pollok, S.; Steinbrücker, C.; Weber, K.; Popp, J. SERS-based detection of biomolecules. Nanophotonics 2014, 3, 383–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilot, R.; Signorini, R.; Durante, C.; Orian, L.; Bhamidipati, M.; Fabris, L. A review on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Biosensors 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Kadam, U.S.; Craig, A.P.; Irudayaraj, J. In Vivo Biodetection using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. In Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials and Nanodevices, 1st ed.; Li, J., Wu, N., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Verde, A.; Mangini, M.; Managò, S.; Tramontano, C.; Rea, I.; Boraschi, D.; Italiani, P.; De Luca, A.C. SERS sensing of bacterial endotoxin on gold nanoparticles. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 758410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolsky, J.; Kaur, S.; Hayashi, C.; Batra, S.K.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based immunoassay technologies for detection of disease biomarkers. Biosensors 2017, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Hutchison, J.A.; Dong, M.; Li, M. Frequency shift surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy sensing: An ultrasensitive multiplex assay for biomarkers in human health. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1704–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, K.W.; Dinish, U.S.; Kumar, A.; Olivo, M. Frequency shifts in SERS for biosensing. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4892–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, W.; Sui, H.; Kitahama, Y.; Ruan, W.; Ozaki, Y.; Zhao, B. Exploring the effect of intermolecular H-bonding: A study on charge-transfer contribution to surface-enhanced Raman scattering of p-mercaptobenzoic acid. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 10191–10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Cai, Z.; Patrow, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Benderskii, A.; Dawlaty, J.; Cronin, S.B. Monitoring local electric fields at electrode surfaces using surface enhanced Raman scattering-based stark-shift spectroscopy during hydrogen evolution reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33678–33683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubisha, D.S.; Lipert, R.J.; Park, H.-Y.; Driskell, J.; Porter, M.D. Femtomolar detection of prostate-specific antigen: an immunoassay based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering and immunogold labels. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5936–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Ma, R.; Deng, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; et al. Ultra-fast and onsite interrogation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in waters via surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Water Res. 2021, 200, 117243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Evers, T.H.; Prins, M.W. How antibody surface coverage on nanoparticles determines the activity and kinetics of antigen capturing for biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8158–8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y. Recent advances of representative optical biosensors for rapid and sensitive diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2. Biosensors 2022, 12, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czamara, K.; Majzner, K.; Pacia, M.Z.; Kochan, K.; Kaczor, A.; Baranska, M. Raman spectroscopy of lipids: A review. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Román, I.O.; Aroca, R.F.; Astudillo, J.; Matsuhiro, B.; Vásquez, C.; Pérez, J.M. Characterization of bacteria using its O-antigen with surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Analyst 2010, 135, 1997–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiercigroch, E.; Szafraniec, E.; Czamara, K.; Pacia, M.Z.; Majzner, K.; Kochan, K.; Kaczor, A.; Baranska, M.; Malek, K. Raman and infrared spectroscopy of carbohydrates: A review. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 185, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaccio, A.; Sasso, A.; Rusciano, G. A simple and reliable approach for the fabrication of nanoporous silver patterns for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy applications. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaccio, A.; Sasso, A.; Tarallo, O.; Rusciano, G. Coral-like plasmonic probes for tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 24376–24384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusciano, G.; Capaccio, A.; Sasso, A.; Capo, A.; Almuzara, C.M.; Staiano, M.; D’Auria, S.; Varriale, A. A Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Biosensor for the Detection of Biological Macromolecules: The Case of the Lipopolysaccharide Endotoxin Molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512099
Rusciano G, Capaccio A, Sasso A, Capo A, Almuzara CM, Staiano M, D’Auria S, Varriale A. A Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Biosensor for the Detection of Biological Macromolecules: The Case of the Lipopolysaccharide Endotoxin Molecules. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(15):12099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512099
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusciano, Giulia, Angela Capaccio, Antonio Sasso, Alessandro Capo, Carlos Murillo Almuzara, Maria Staiano, Sabato D’Auria, and Antonio Varriale. 2023. "A Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Biosensor for the Detection of Biological Macromolecules: The Case of the Lipopolysaccharide Endotoxin Molecules" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 15: 12099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512099
APA StyleRusciano, G., Capaccio, A., Sasso, A., Capo, A., Almuzara, C. M., Staiano, M., D’Auria, S., & Varriale, A. (2023). A Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Biosensor for the Detection of Biological Macromolecules: The Case of the Lipopolysaccharide Endotoxin Molecules. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(15), 12099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512099









