Molecular Mechanisms of Endothelialitis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Evidence for VE-Cadherin Cleavage by ACE2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
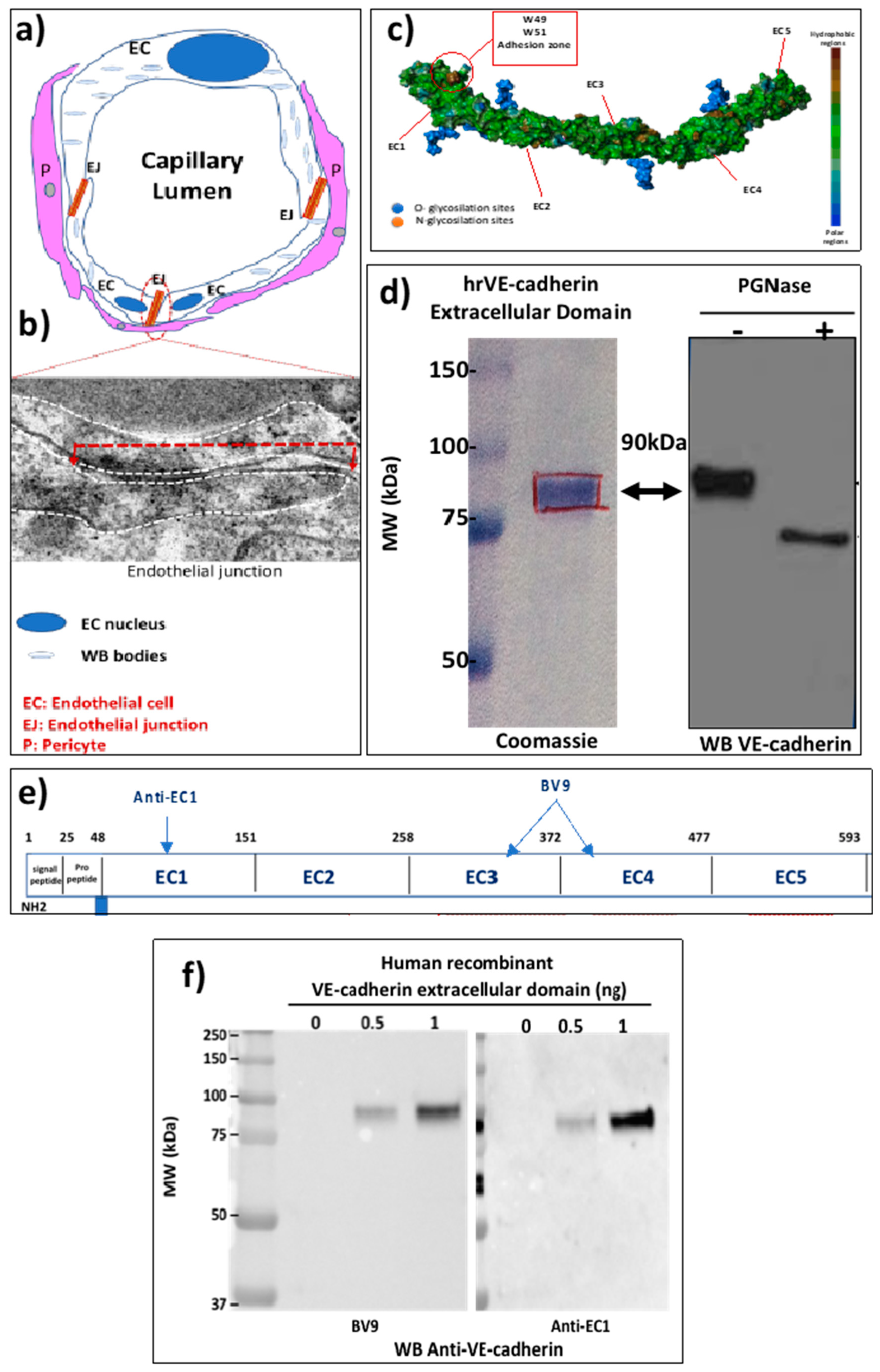
2.1. The EJ Are Cohesive Due to the Adhesive Properties of the Extracellular Domain of VE-Cadherin
2.2. VE-Cadherin Is a Direct Substrate for Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2)
2.3. Circulating ACE2 Was Detected in Blood Samples from COVID-19 Patients
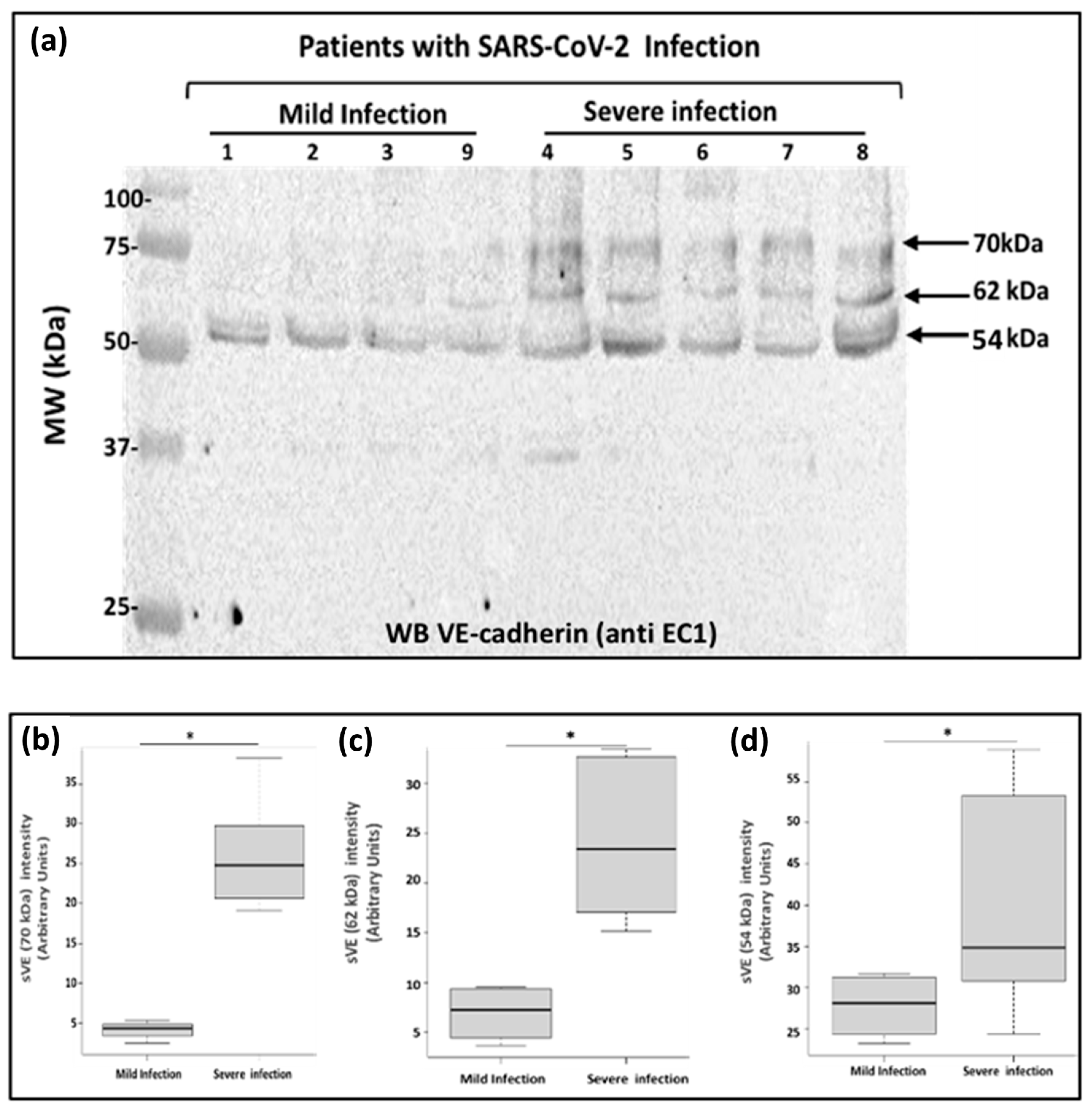
2.4. Analysis of Soluble VE-Cadherin in Blood Samples from COVID-19 Patients
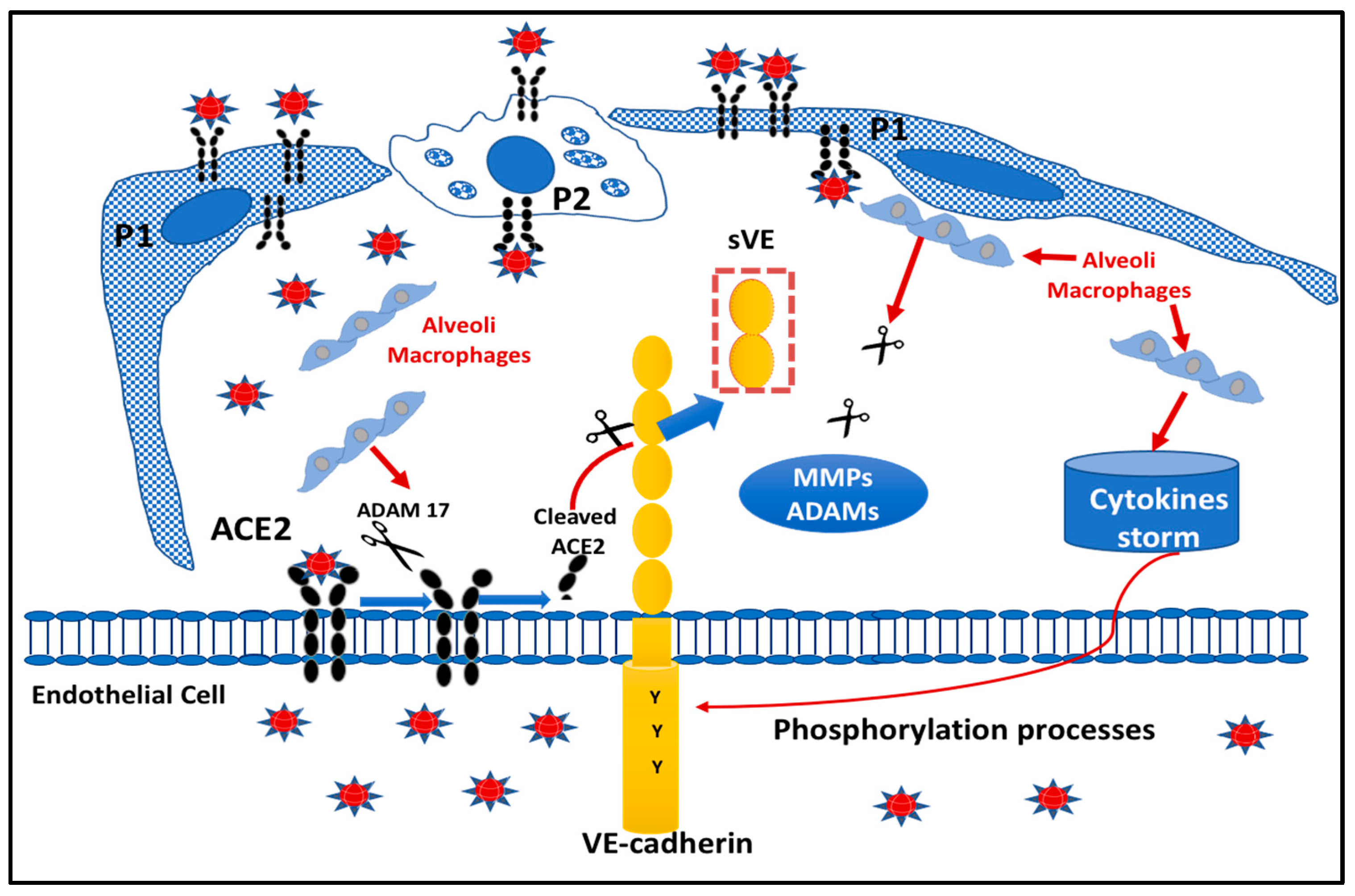
2.5. Proposed Model Scheme for Endothelial Dysfunction following SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Protein Extracts Analysis
4.4. Patient Sera
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zanini, G.; Selleri, V.; Roncati, L.; Coppi, F.; Nasi, M.; Farinetti, A.; Manenti, A.; Pinti, M.; Mattioli, A.V. Vascular “Long COVID”: A new vessel disease? Angiology 2023, 33197231153204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; et al. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, M.; Verleden, S.E.; Kuehnel, M.; Haverich, A.; Welte, T.; Laenger, F.; Vanstapel, A.; Werlein, C.; Stark, H.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhetri, S.; Khamis, F.; Pandak, N.; Al Khalili, H.; Said, E.; Petersen, E. A fatal case of COVID-19 due to metabolic acidosis following dysregulate inflammatory response (cytokine storm). IDCases 2020, 21, e00829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampugnani, M.G.; Dejana, E.; Giampietro, C. Vascular Endothelial (VE)-Cadherin, endothelial adherens junctions, and vascular disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a029322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gory-Fauré, S.; Prandini, M.H.; Pointu, H.; Roullot, V.; Pignot-Paintrand, I.; Vernet, M.; Huber, P. Role of vascular endothelial-cadherin in vascular morphogenesis. Development 1999, 126, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidibé, A.; Mannic, T.; Arboleas, M.; Subileau, M.; Gulino-Debrac, D.; Bouillet, L.; Jan, M.; Vandhuick, T.; Le Loët, X.; Vittecoq, O.; et al. Soluble VE-cadherin in rheumatoid arthritis patients correlates with disease activity: Evidence for tumor necrosis factor α-induced VE-cadherin cleavage. Arthritis Rheum 2012, 64, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudry-Clergeon, H.; Stengel, D.; Ninio, E.; Vilgrain, I. Platelet-activating factor increases VE-cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation in mouse endothelial cells and its association with the PtdIns3′-kinase. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallez, Y.; Vilgrain, I.; Huber, P. Angiogenesis: The VE-cadherin switch. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2006, 16, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambeng, N.; Wallez, Y.; Rampon, C.; Cand, F.; Christé, G.; Gulino-Debrac, D.; Vilgrain, I.; Huber, P. Vascular endothelial-cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation in angiogenic and quiescent adult tissues. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilgrain, I.; Sidibé, A.; Polena, H.; Cand, F.; Mannic, T.; Arboleas, M.; Boccard, S.; Baudet, A.; Gulino-Debrac, D.; Bouillet, L.; et al. Evidence for post-translational processing of vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin in brain tumors: Towards a candidate biomarker. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouillet, L.; Mannic, T.; Arboleas, M.; Subileau, M.; Massot, C.; Drouet, C.; Huber, P.; Vilgrain, I. Hereditary angioedema: Key role for kallikrein and bradykinin in vascular endothelial-cadherin cleavage and edema formation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillet, L.; Vilgrain, I. VE-cadherin, a potential marker for endothelial cell activation during hereditary angioedema attacks. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channappanavar, R.; Perlman, S. Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: Causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyerstedt, S.; Casaro, E.B.; Rangel, É.B. COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, C.; Hales, P.; Kaushik, V.; Dick, L.; Gavin, J.; Tang, J.; Godbout, K.; Parsons, T.; Baronas, E.; Hsieh, F.; et al. Hydrolysis of biological peptides by human angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14838–14843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sama, I.E.; Ravera, A.; Santema, B.T.; van Goor, H.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Rienstra, M.; Friedrich, A.W.; Samani, N.J.; Ng, L.L.; et al. Circulating plasma concentrations of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in men and women with heart failure and effects of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 181017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragstrup, T.W.; Singh, H.S.; Grundberg, I.; Nielsen, A.L.; Rivellese, F.; Mehta, A.; Goldberg, M.B.; Filbin, M.R.; Qvist, P.; Bibby, B.M. Plasma ACE2 predicts outcome of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasch, J.; Harrison, O.J.; Ahlsen, G.; Carnally, S.M.; Henderson, R.M.; Honig, B.; Shapiro, L. Structure and binding mechanism of vascular endothelial cadherin: A divergent classical cadherin. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 408, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grobe, N.; Di Fulvio, M.; Kashkari, N.; Chodavarapu, H.; Somineni, H.K.; Singh, R.; Elased, K.M. Functional and molecular evidence for expression of the renin angiotensin system and ADAM17-mediated ACE2 shedding in COS7 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2015, 308, C767–C777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tompa, P. The principle of conformational signaling. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4252–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornilov, S.A.; Lucas, I.; Jade, K.; Dai, C.L.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Magis, A.T. Plasma levels of soluble ACE2are associated with sex, Metabolic Syndrome, and its biomarkers in a large cohort, pointing to a possible mechanism for increased severity in COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, F.J.; Smith, A.I.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2: A molecular and cellular perspective. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2704–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliou, A.G.; Keskinidou, C.; Jahaj, E.; Gallos, P.; Dimopoulou, I.; Kotanidou, A.; Orfanos, S.E. ICU Admission Levels of Endothelial Biomarkers as Predictors of Mortality in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Cells 2021, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, M.; Canonico, B.; Nordi, E.; Vandini, D.; Barocci, S.; Benedetti, S.; Carlotti, E.; Zamai, L. Which ones, when and why should renin-angiotensin system inhibitors work against COVID-19? Adv. Biol. Regul. 2021, 81, 100820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, M.; Vertui, V.; Pandolfi, L.; Bozzini, S.; Fossali, T.; Colombo, R.; Aliberti, A.; Fumagalli, M.; Iadarola, P.; Didò, C.; et al. Investigating the link between Alpha-1 Antitrypsin and human neutrophil elastase in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of COVID-19 patients. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 2122–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, S.; Burkard, N.; Renschler, M.; Vielmuth, F.; Meir, M.; Schick, M.A.; Wunder, C.; Germer, C.T.; Spindler, V.; Waschke, J.; et al. Soluble VE-cadherin is involved in endothelial barrier breakdown in systemic inflammation and sepsis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harki, O.; Tamisier, R.; Pépin, J.L.; Bailly, S.; Mahmani, A.; Gonthier, B.; Salomon, A.; Vilgrain, I.; Faury, G.; Briançon-Marjollet, A. VE-cadherin cleavage in sleep apnea: New insights into intermittent hypoxia-related endothelial permeability. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2004518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, S.; Polena, H.; Vilgrain, I. Soluble vascular endothelial-cadherin and auto-antibodies to human vascular endothelial-cadherin in human diseases: Two new biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction. Vasc. Med. 2015, 20, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hooper, N.M. Angiotensin converting enzyme: Implications from molecular biology for its physiological functions. Int. J. Biochem. 1991, 23, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.B.; Clarke, N.; Wang, Z.; Fan, D.; Parajuli, N.; Basu, R.; Putko, B.; Kassiri, Z.; Turner, A.J.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin II induced proteolytic cleavage of myocardial ACE2 is mediated by TACE/ADAM-17: A positive feedback mechanism in the RAS. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2014, 66, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.P.; Look, D.C.; Tan, P.; Shi, L.; Hickey, M.; Gakhar, L.; Chappell, M.C.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; McCray, P.B., Jr. Ectodomain shedding of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in human airway epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L84–L96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramchand, J.; Burrell, L.M. Circulating ACE2: A novel biomarker of cardiovascular risk. Lancet 2020, 396, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scialo, F.; Daniele, A.; Amato, F.; Pastore, L.; Matera, M.G.; Cazzola, M.; Castaldo, G.; Bianco, A. ACE2: The Major Cell Entry Receptor for SARS-CoV-2. Lung 2020, 198, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteil, V.; Kwon, H.; Prado, P.; Hagelkrüys, A.; Wimmer, R.A.; Stahl, M.; Leopoldi, A.; Garreta, E.; Hurtado Del Pozo, C.; Prosper, F.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Engineered Human Tissues Using Clinical-Grade Soluble Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S. Soluble ACE2 in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelman, S.; Tang, W.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Van Lente, F.; Francis, G.S.; Sen, S. Detection of soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in heart failure: Insights into the endogenous counter-regulatory pathway of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilgrain, I.; Cand, F.; Pelletier, L. Circulating VE-Cadherin as a Predictive Marker of Sensitivity or Resistance to Anti-Tumoral Treatment and Improved Method for the Detection of soluble Proteins. U.S. Patent 20100121171A10, 23 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, D.W.; Yarski, M.; Warner, F.J.; Thornhill, P.; Parkin, E.T.; Smith, A.I.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2). J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30113–30119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Patients | Age | Management Protocol | ICUA | Background | Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 88 | - | No | Hypertension, hyperuricaemia, Benine Prostate Hypertropnhia, chronic renal failure | Allopurinol, bétaxolol, fénofibrate, lercanidipine, alfuzosine |
| 2 | 80 | - | No | Hypertension, hyperuricaemia, Benine Prostate Hypertropnhia, chronic renal failure | bisoprolol, amiloride |
| 3 | 67 | - | No | OSAS, Benine Prostate Hypertropnhia, Rotator cuff surgery, sigmoidectomy for diverticular disease | none |
| 9 | 63 | - | No | Appendicitis | none |
| 4 | 65 | Mechanical ventilatory assistance, Prone position, NO/Pulmonary embolism thrombolysis | Yes | Deep vein thrombosis, obesity, OSAS, Umbilical hernia with prosthesis | none |
| 5 | 86 | Atrial Fibrillation, Pneumopathy (S aureus and enterobacter) | Yes | Hypertension, Atrial fibrillation treated with anti-clotting medication | - |
| 6 | 52 | Mechanical ventilatory assistance, Prone position, Pumonary embolism | Yes | Hiatal hernia, clavicle fracture | none |
| 7 | 53 | Mechanical ventilatory assistance, Prone position, Cardiopulmonary bypass | Yes | Hypertension, dyslipidemia, obesity | none |
| 8 | 73 | Mechanical ventilatory assistance, Prone position | Yes | Hypertension, diabetes | bisoprolol, vildagliptine/metformine, gliclazide, kardegic, pravastatine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouillet, L.; Deroux, A.; Benmarce, M.; Guérin, C.; Bouvet, L.; Garnier, O.; Martin, D.K.; Vilgrain, I. Molecular Mechanisms of Endothelialitis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Evidence for VE-Cadherin Cleavage by ACE2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512525
Bouillet L, Deroux A, Benmarce M, Guérin C, Bouvet L, Garnier O, Martin DK, Vilgrain I. Molecular Mechanisms of Endothelialitis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Evidence for VE-Cadherin Cleavage by ACE2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(15):12525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512525
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouillet, Laurence, Alban Deroux, Meryem Benmarce, Chloé Guérin, Laura Bouvet, Olivia Garnier, Donald K. Martin, and Isabelle Vilgrain. 2023. "Molecular Mechanisms of Endothelialitis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Evidence for VE-Cadherin Cleavage by ACE2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 15: 12525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512525
APA StyleBouillet, L., Deroux, A., Benmarce, M., Guérin, C., Bouvet, L., Garnier, O., Martin, D. K., & Vilgrain, I. (2023). Molecular Mechanisms of Endothelialitis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Evidence for VE-Cadherin Cleavage by ACE2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(15), 12525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512525






