Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Modulating CD36/AMPK/PGC-1α in RAW264.7 Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
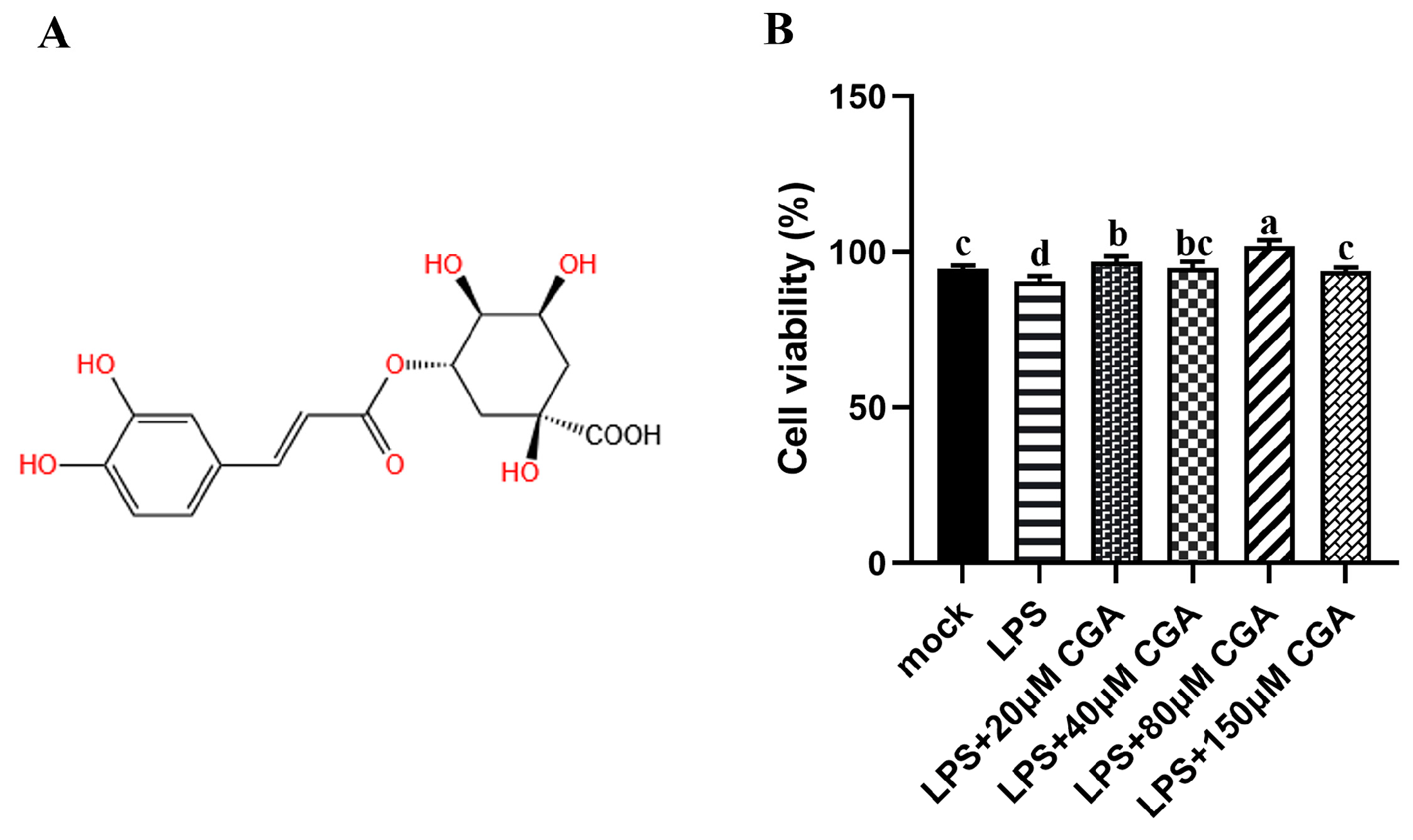
2.1. CGA Alleviated the Cell Viability Induced by LPS
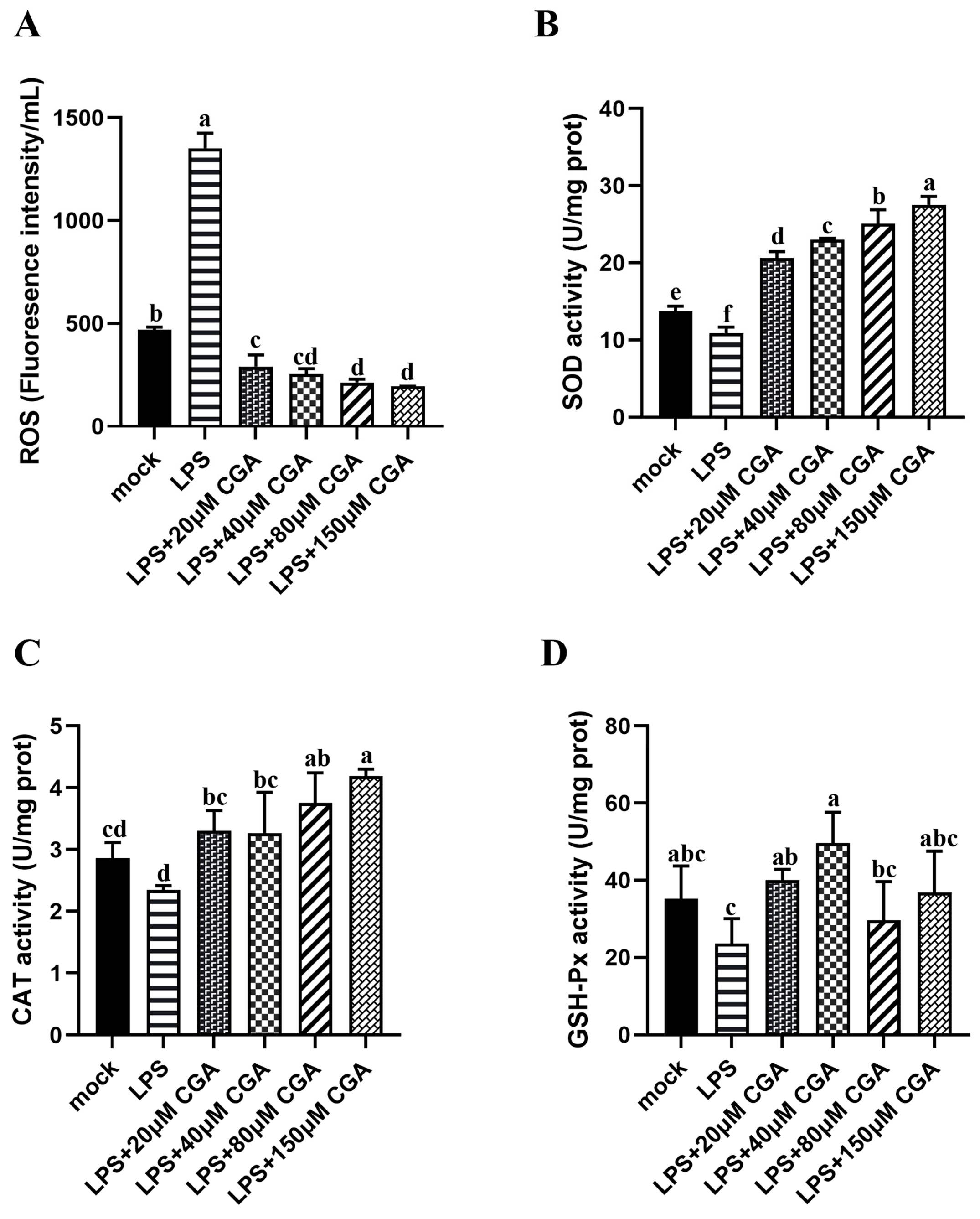
2.2. CGA Reduced LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress
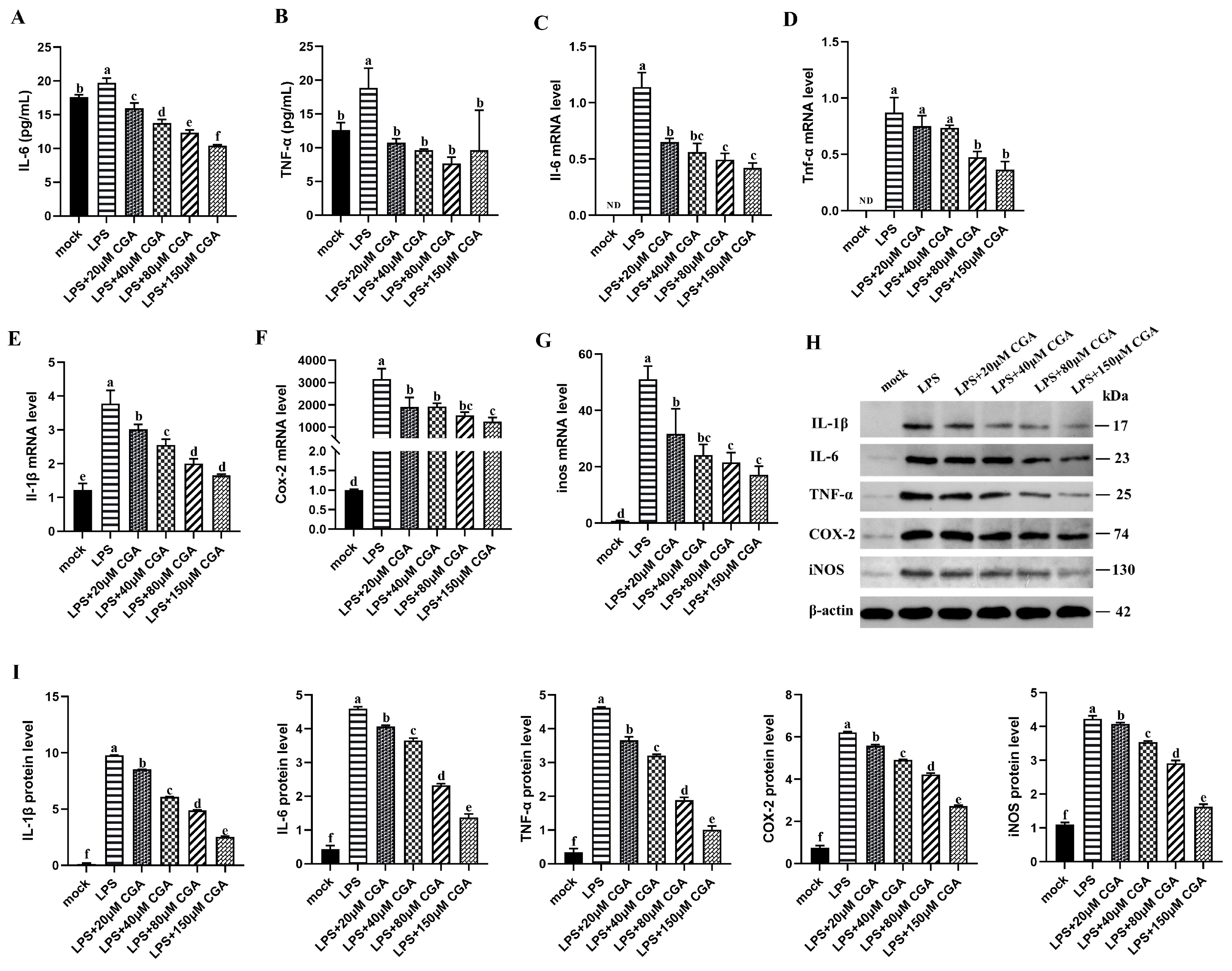
2.3. CGA Reduced LPS-Induced Inflammatory Mediators and Cytokines Expression
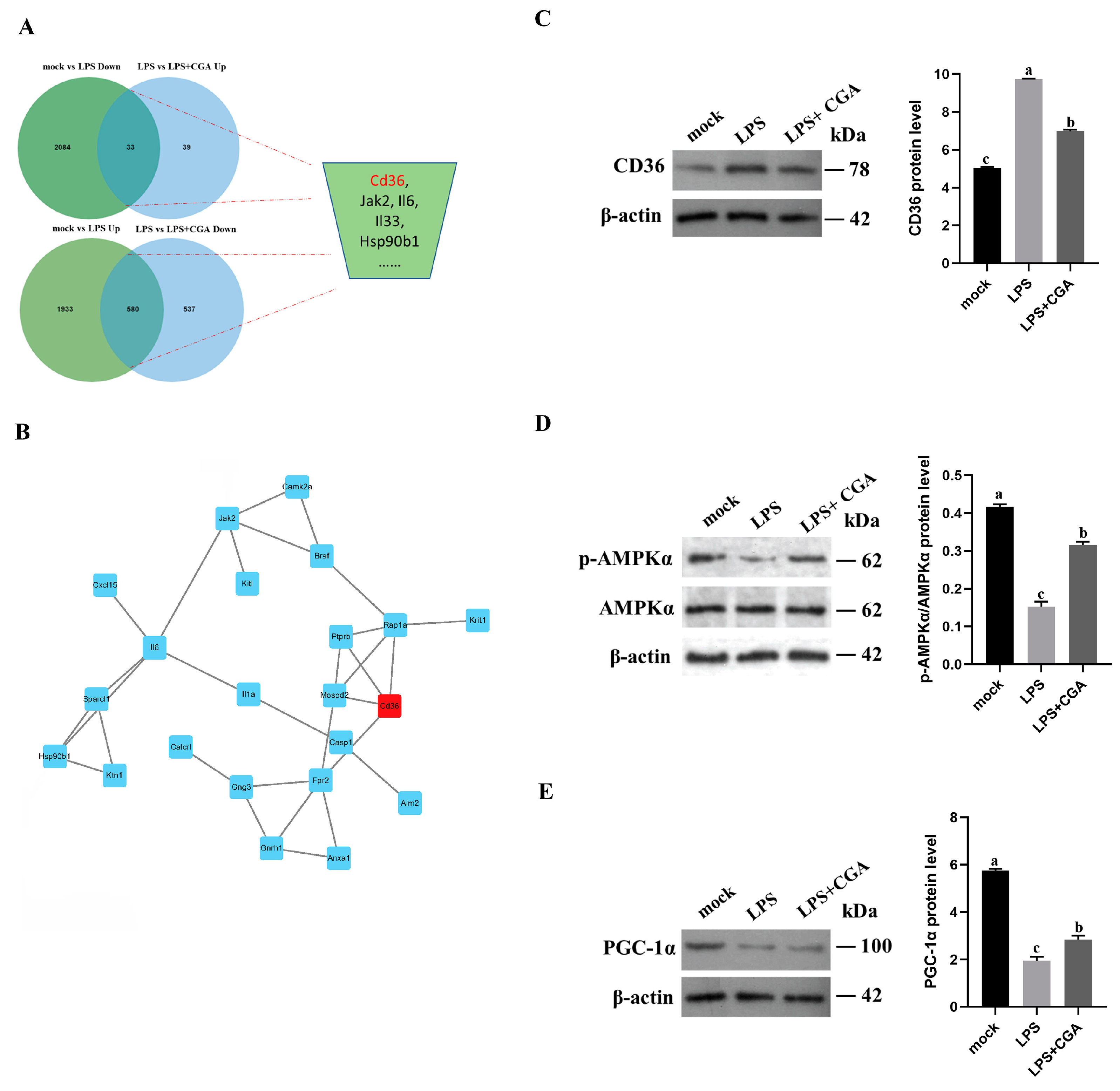
2.4. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals That CGA Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Gene Regulation
2.5. CGA Treatment Reduced CD36 Expression
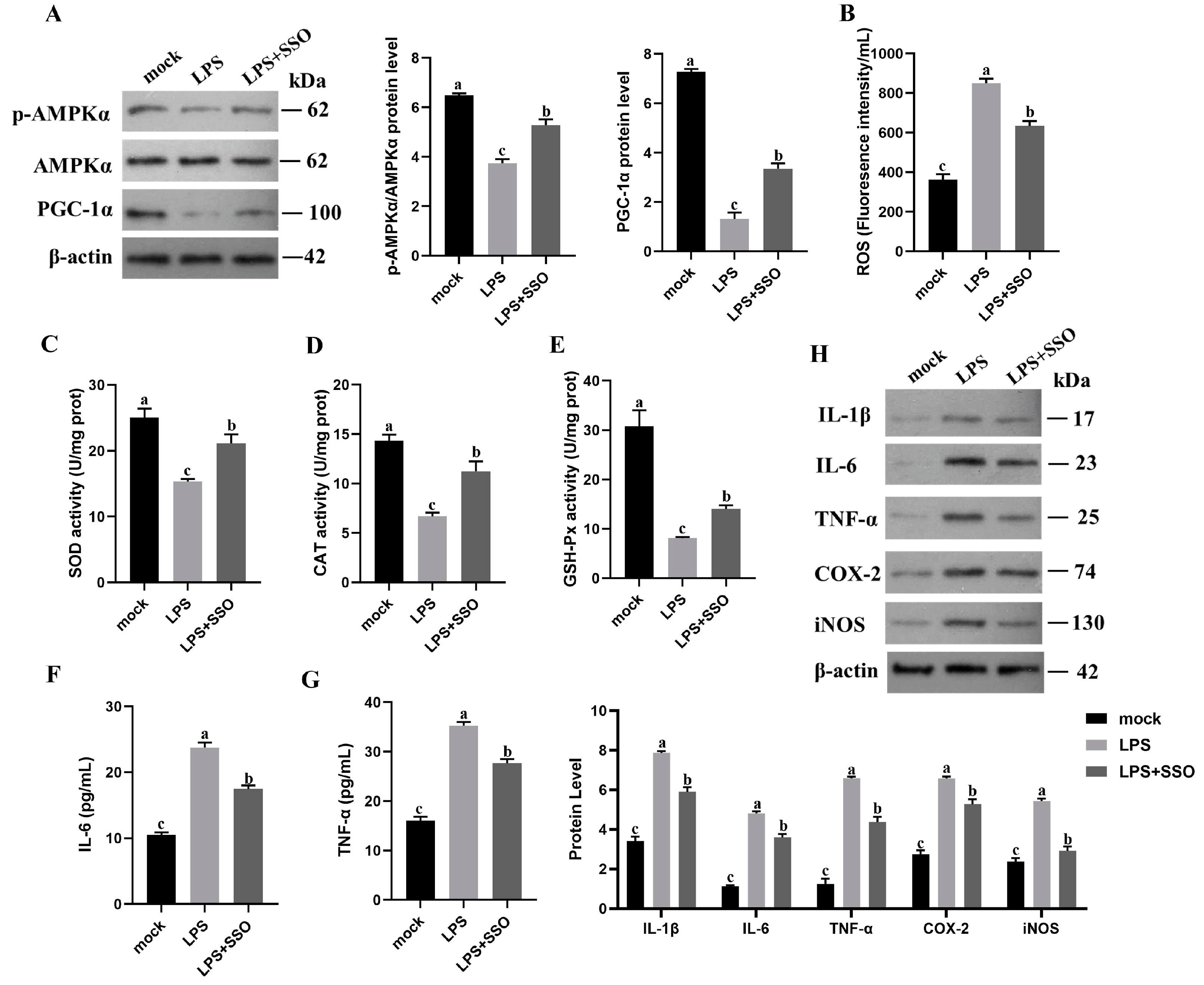
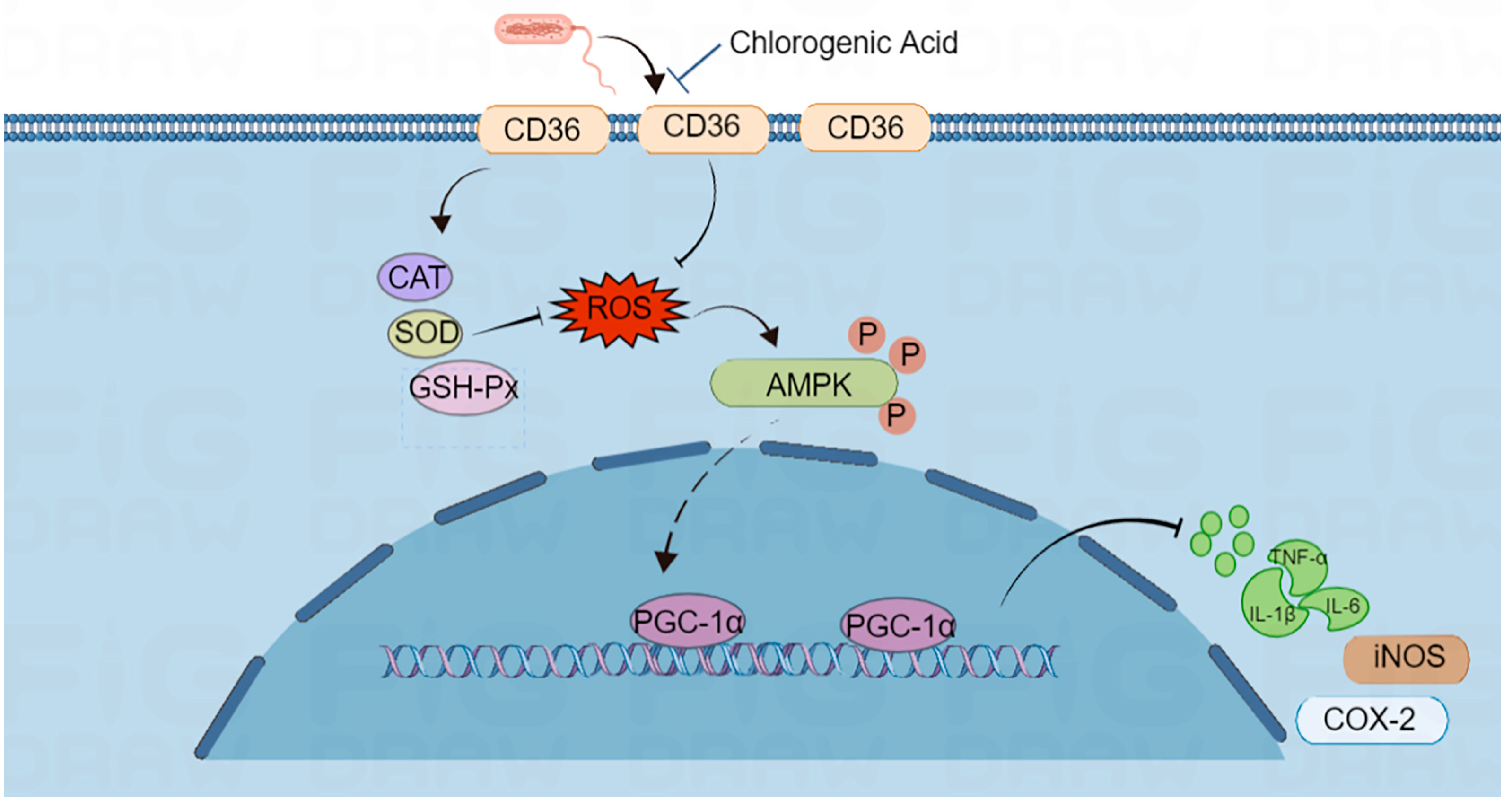
2.6. CD36 Inhibition Enabled Anti-Inflammation and Oxidative Stress through the CD36/AMPK/PGC-1α Cascade
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Regents and Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Reactive Oxygen Species Detection
4.5. Determination of GSH-Px, SOD and CAT Activities
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Transcriptomics and Validation
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, M.; Xiang, L. Pharmacological action and potential targets of chlorogenic acid. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 87, 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Naveed, M.; Hejazi, V.; Abbas, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Khan, G.J.; Shumzaid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Babazadeh, D.; FangFang, X.; Modarresi-Ghazani, F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, N.; Kang, J.W.; Lee, S.M. Protective effects of chlorogenic acid against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat liver: Molecular evidence of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joung, E.J.; Lee, B.; Gwon, W.G.; Shin, T.; Jung, B.M.; Yoon, N.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Oh, C.W.; Kim, H.R. Sargaquinoic acid attenuates inflammatory responses by regulating NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchin, M.; Colón, D.F.; da Cunha, M.G.; Castanheira, F.V.; Saraiva, A.L.; Bueno-Silva, B.; Alencar, S.M.; Cunha, T.M.; Rosalen, P.L. Neovestitol, an isoflavonoid isolated from Brazilian red propolis, reduces acute and chronic inflammation: Involvement of nitric oxide and IL-6. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.R.; Stakenborg, M.; Seok, S.H.; Matteoli, G. Macrophages in intestinal inflammation and resolution: A potential therapeutic target in IBD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yin, P.; Wan, C.; Chong, X.; Liu, M.; Cheng, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, F.; Xu, J. Punicalagin inhibits inflammation in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages via the suppression of TLR4-mediated MAPKs and NF-κB activation. Inflammation 2014, 37, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Yin, P.; Lu, Y.; Qian, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J. 7b, a novel naphthalimide derivative, exhibited anti-inflammatory effects via targeted-inhibiting TAK1 following down-regulation of ERK1/2-and p38 MAPK-mediated activation of NF-κB in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Yatsuzuka, R.; Jiang, S.; Ueda, Y.; Kamei, C. Involvement of cyclooxygenase-2 in allergic nasal inflammation in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, Y.C. Impact of oxidative stress on lung diseases. Respirology 2009, 14, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktan, F. iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Huang, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhou, J.; Wei, T. Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase increases the production of reactive oxygen species in RAW264.7 macrophages. Biosci. Rep. 2010, 30, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, J.; Starr, M.E.; Takahashi, H.; Du, J.; Chang, L.Y.; Crapo, J.D.; Evers, B.M.; Saito, H. Decreased pulmonary extracellular superoxide dismutase during systemic inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuo, M.Y.; Liao, M.F.; Chen, F.L.; Li, Y.C.; Yang, M.L.; Lin, R.H.; Kuan, Y.H. Luteolin attenuates the pulmonary inflammatory response involves abilities of antioxidation and inhibition of MAPK and NFκB pathways in mice with endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2011, 49, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants Maintain Cellular Redox Homeostasis by Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Cui, H.; Yan, X.; Fan, K. Nanozyme-based catalytic theranostics. RSC Adv. 2019, 10, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.L.; Febbraio, M. CD36, a scavenger receptor involved in immunity, metabolism, angiogenesis, and behavior. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, re3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantó, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Feige, J.N.; Lagouge, M.; Noriega, L.; Milne, J.C.; Elliott, P.J.; Puigserver, P.; Auwerx, J. AMPK regulates energy expenditure by modulating NAD+ metabolism and SIRT1 activity. Nature 2009, 458, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhong, S.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, P.; Tang, R.; et al. CD36 palmitoylation disrupts free fatty acid metabolism and promotes tissue inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatz, J.F.; Luiken, J.J.; Bonen, A. Membrane fatty acid transporters as regulators of lipid metabolism: Implications for metabolic disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 367–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, D.; Thornton, C.; Woods, A.; Sanders, M.J. AMP-activated protein kinase: New regulation, new roles? Biochem. J. 2012, 445, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zmijewski, J.W.; Lorne, E.; Liu, G.; Park, Y.J.; Tsuruta, Y.; Abraham, E. Activation of AMPK attenuates neutrophil proinflammatory activity and decreases the severity of acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L497–L504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Li, J.; Zha, D.; Zhang, L.; Gao, P.; Yao, T.; Wu, X. Chlorogenic acid prevents diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation through modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-ĸB pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Park, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.W. Anti-inflammatory effects of chlorogenic acid in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Inflamm. Res. Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. 2014, 63, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.; Adcock, I.M. Oxidative stress and redox regulation of lung inflammation in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Yang, S.R.; Kode, A.; Rajendrasozhan, S.; Caito, S.; Adenuga, D.; Henry, R.; Edirisinghe, I.; Rahman, I. Redox regulation of lung inflammation: Role of NADPH oxidase and NF-kappaB signalling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janakiram, N.B.; Rao, C.V. iNOS-selective inhibitors for cancer prevention: Promise and progress. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 2193–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y. CD36 tango in cancer: Signaling pathways and functions. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4893–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, W.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Y.; Schulte, M.L.; Volberding, P.; Gerbec, Z.; Zimmermann, M.T.; Zeighami, A.; et al. Mitochondrial Metabolic Reprogramming by CD36 Signaling Drives Macrophage Inflammatory Responses. Circ. Res. 2019, 125, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Shen, Z.Y.; Zhan, Y.Z.; Feng, X.C.; Chen, K.L.; Li, Y.S.; Deng, H.J.; Pan, S.M.; Wu, D.H.; Ding, Y. CD36 inhibits β-catenin/c-myc-mediated glycolysis through ubiquitination of GPC4 to repress colorectal tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Su, C.; Luo, X.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, L.; Wei, L.; Zhang, X.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F.; Chen, Y.; et al. Dietary oleic acid-induced CD36 promotes cervical cancer cell growth and metastasis via up-regulation Src/ERK pathway. Cancer Lett. 2018, 438, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Yao, Y.; Huang, C.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Miao, Y.; Feng, X.; Gao, X.; et al. CD36 regulates LPS-induced acute lung injury by promoting macrophages M1 polarization. Cell. Immunol. 2022, 372, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Febbraio, M.; Reddy, S.P.; Yu, D.Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Silverstein, R.L. CD36 participates in a signaling pathway that regulates ROS formation in murine VSMCs. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3996–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Ren, L.; Zhi, L.; Yu, Z.; Lv, F.; Xu, F.; Peng, W.; Bai, X.; Cheng, K.; Quan, L.; et al. Negative regulation of AMPK signaling by high glucose via E3 ubiquitin ligase MG53. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 629–637.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sag, D.; Carling, D.; Stout, R.D.; Suttles, J. Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase promotes macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory functional phenotype. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8633–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′ to 3′) | Annealing (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18s | Forward (sense) | GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG | ||
| Il-1β | Forward (sense) | GGCAGGCAGTATCACTCATTGTG | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | GCTCATGTCCTCATCCTGGAAG | ||
| Il-6 | Forward (sense) | TCTACTCGGCAAACCTAGTGCGTTA | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | TTCTGACCACAGTGAGGAATGTCCA | ||
| Tnf-α | Forward (sense) | GACCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG | ||
| COX-2 | Forward (sense) | GGCAGGAAGTCTTTGGTCTGGT | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | CTGGTTTGGAATAGTTGCTCATCAC | ||
| iNOS | Forward (sense) | TGCCACGGACGAGACGGATA | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | AGGAAGGCAGCGGGCACAT | ||
| Il7r | Forward (sense) | GCATCCCCAACCAACTGAGG | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | GCATCTTCTAGGTCTCTTTTGAGC | ||
| Casp4 | Forward (sense) | TGTCTCATGGCACACTGCAT | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | TTCTCCAGAGTTCCCACCTC | ||
| Cpt1a | Forward (sense) | TCGGTGAGCCTGGCCT | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | TTGAGTGGTGACCGAGTCTG | ||
| Eef2k | Forward (sense) | CACCTGGAAGATATTGCCACC | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | GCTTCGCCACGTAGTTGGA | ||
| Stat1 | Forward (sense) | CGCTGCCTATGATGTCTC | 60 |
| Reverse (antisense) | TTTCCGTATGTTGTGCTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Tian, Y.; Xu, W.; Zeng, T.; Wu, W.; Lu, L. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Modulating CD36/AMPK/PGC-1α in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713516
Gu T, Zhang Z, Liu J, Chen L, Tian Y, Xu W, Zeng T, Wu W, Lu L. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Modulating CD36/AMPK/PGC-1α in RAW264.7 Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713516
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Tiantian, Zhiguo Zhang, Jinyu Liu, Li Chen, Yong Tian, Wenwu Xu, Tao Zeng, Weicheng Wu, and Lizhi Lu. 2023. "Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Modulating CD36/AMPK/PGC-1α in RAW264.7 Macrophages" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713516
APA StyleGu, T., Zhang, Z., Liu, J., Chen, L., Tian, Y., Xu, W., Zeng, T., Wu, W., & Lu, L. (2023). Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Modulating CD36/AMPK/PGC-1α in RAW264.7 Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713516







