The Response Regulator VC1795 of Vibrio Pathogenicity Island-2 Contributes to Intestinal Colonization by Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
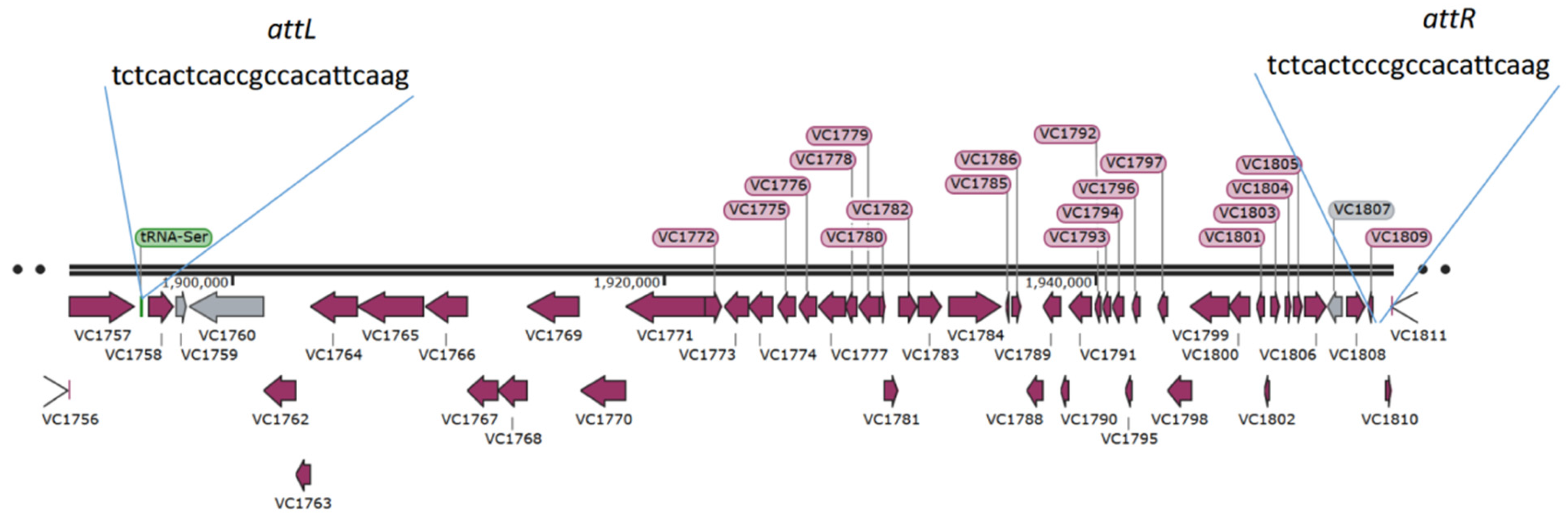
2.1. VPI-2 of Strain V. cholerae O1 EI Tor El2382
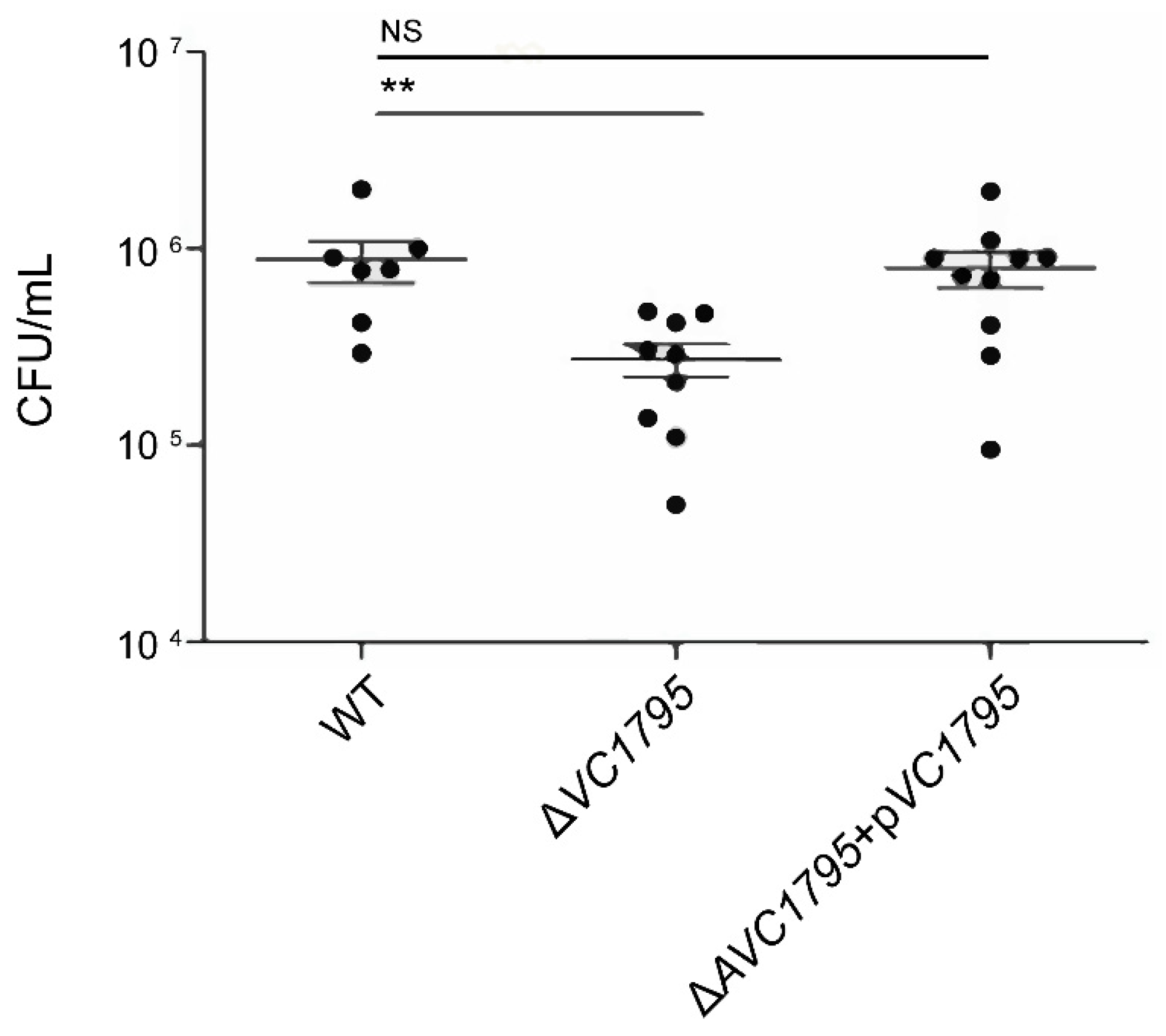
2.2. ΔVC1795 Isogenic Mutant Attenuates V. cholerae Virulence against Infant Mouse Intestinal Colonization
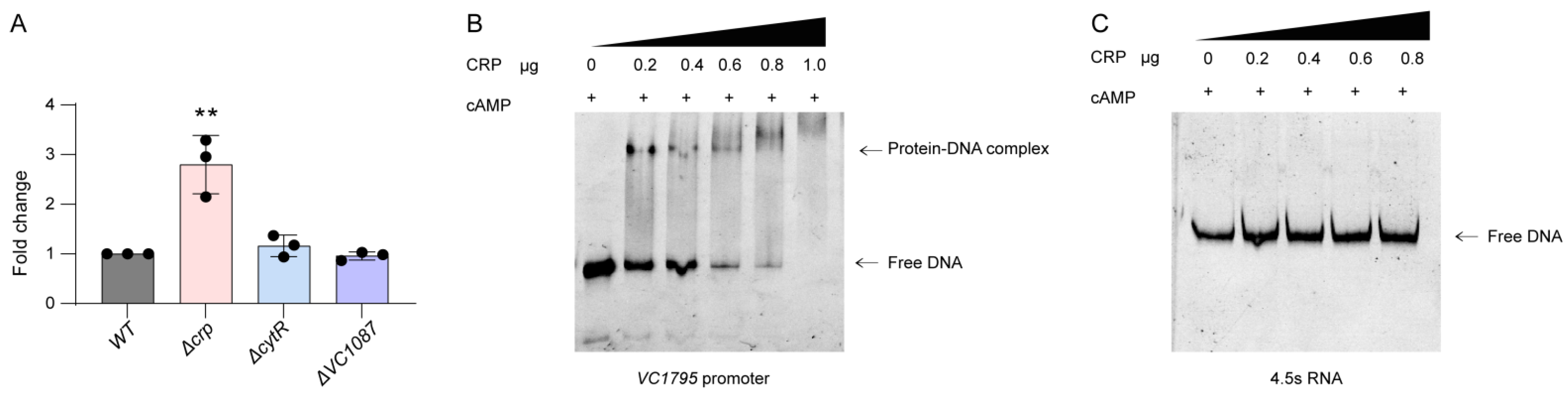
2.3. VC1795 Is Directly Represses by cAMP–CRP Complex
2.4. VC1974 Is the Downstream Target of VC1795
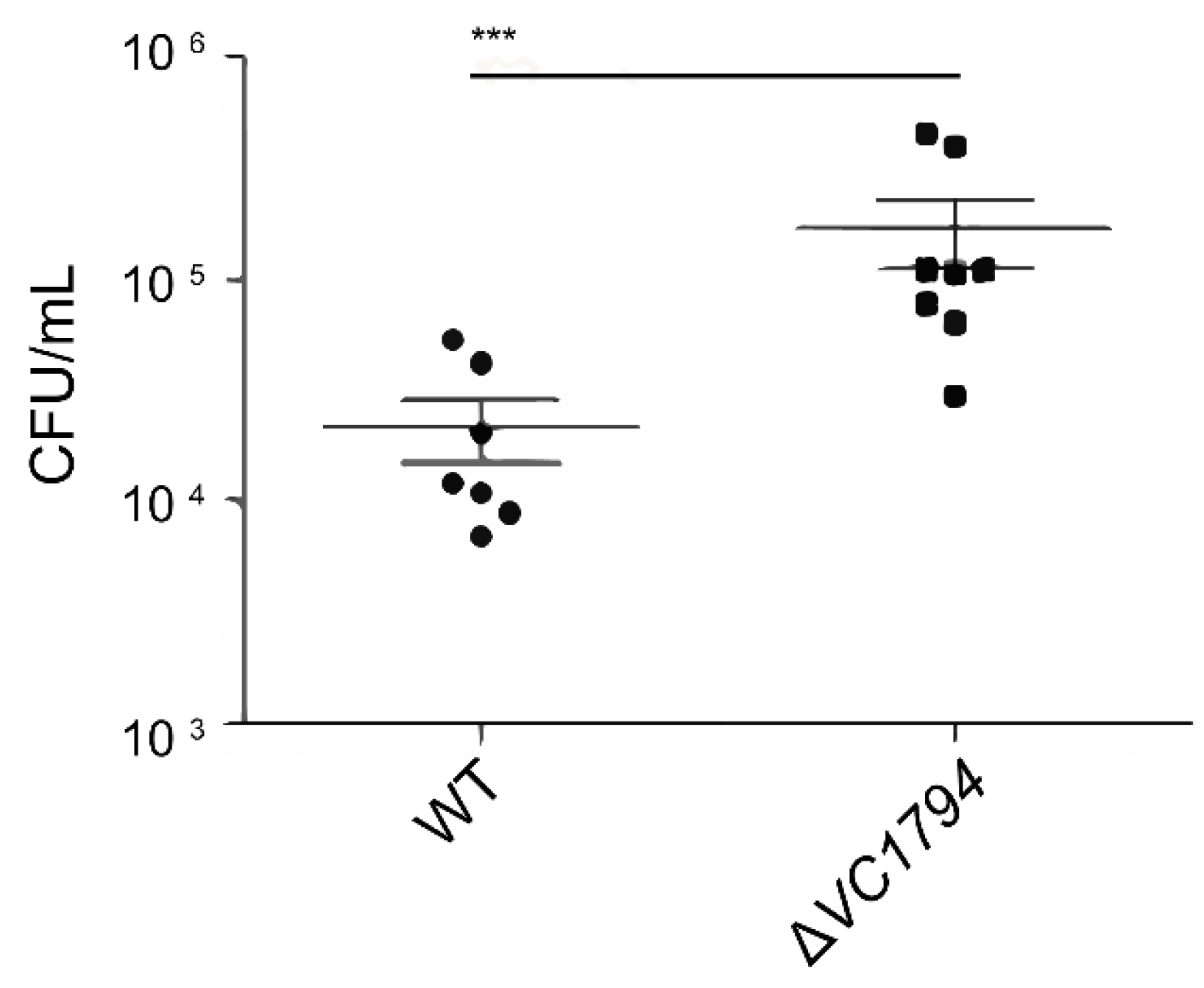
2.5. ΔVC1794 Isogenic Deletion Mutant Increased Virulence with Infant Mouse Intestinal Colonization
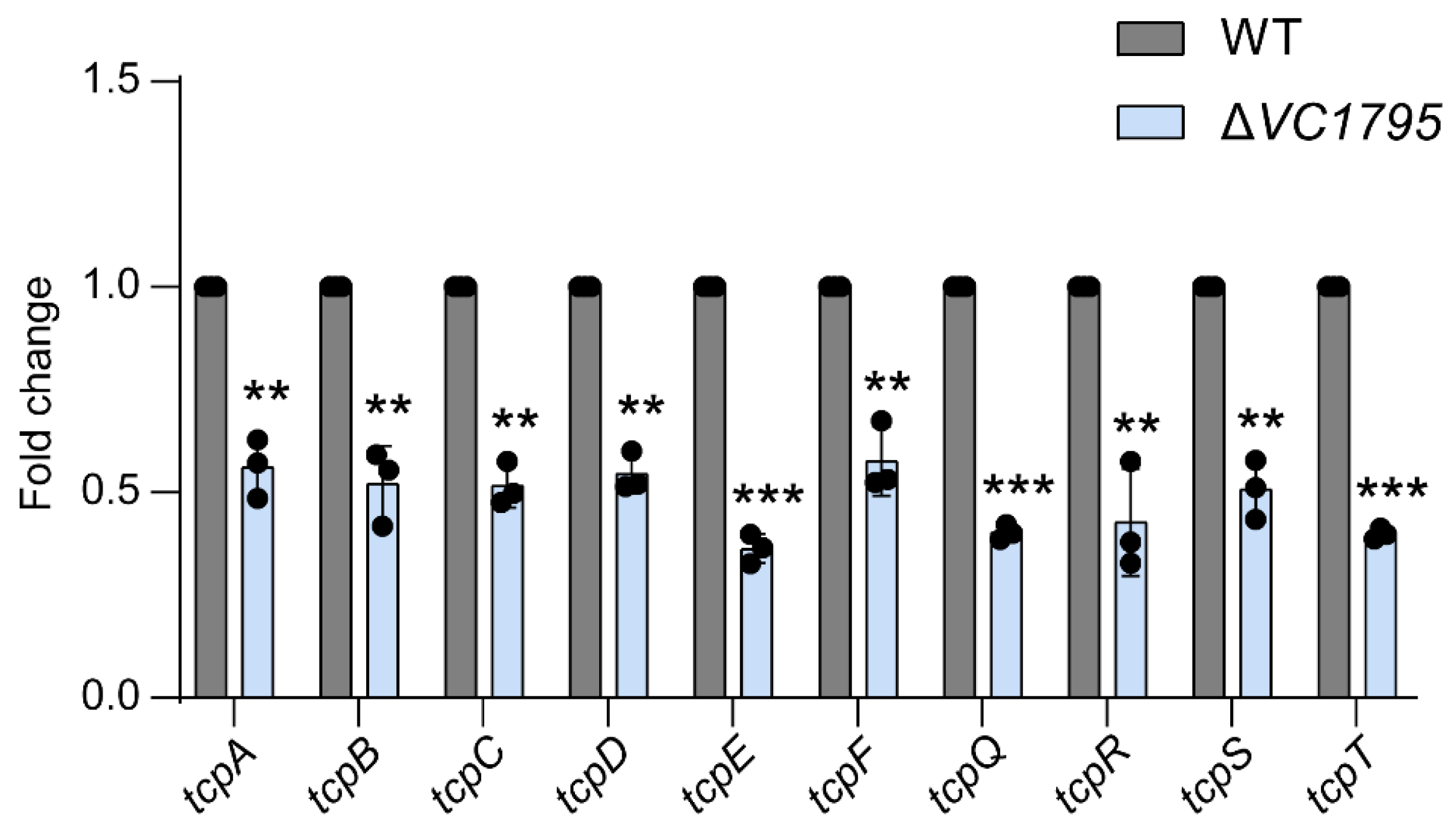
2.6. VC1795 Positively Regulates the TCP Cluster Associated with Colonization of V. cholerae
2.7. Schematic of the Proposed VC1795 Regulatory Mechanism
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
4.2. Construction of Mutant Strains and Complementation
4.3. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.4. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays (EMSAs)
4.5. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Followed by Sequencing (ChIP-seq)
4.6. DNA Pull-Down Assay
4.7. Intestinal Colonization Assay
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colwell, R.R. Global climate and infectious disease: The cholera paradigm. Science 1996, 274, 2025–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Nelson, A.R.; Lopez, A.L.; Sack, D.A. Updated global burden of cholera in endemic countries. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.R.; Huq, A. Environmental reservoir of Vibrio cholerae. The causative agent of cholera. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 740, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, V.L.; Taylor, R.K.; Mekalanos, J.J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell 1987, 48, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, D.A.; Hall, R.H.; Losonsky, G.; Mekalanos, J.J.; Taylor, R.K.; Levine, M.M. Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili, and the toxR regulon are essential for Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis in humans. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 168, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiRita, V.J.; Parsot, C.; Jander, G.; Mekalanos, J.J. Regulatory cascade controls virulence in Vibrio cholerae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5403–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häse, C.C.; Mekalanos, J.J. TcpP protein is a positive regulator of virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupski, K.; Taylor, R.K. A new level in the Vibrio cholerae ToxR virulence cascade: AphA is required for transcriptional activation of the tcpPH operon. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 31, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacikova, G.; Skorupski, K. A Vibrio cholerae LysR homolog, AphB, cooperates with AphA at the tcpPH promoter to activate expression of the ToxR virulence cascade. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4250–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziejman, M.; Balon, E.; Boyd, D.; Fraser, C.M.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Mekalanos, J.J. Comparative genomic analysis of Vibrio cholerae: Genes that correlate with cholera endemic and pandemic disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermyn, W.S.; Boyd, E.F. Characterization of a novel Vibrio pathogenicity island (VPI-2) encoding neuraminidase (nanH) among toxigenic Vibrio cholerae isolates. Microbiology 2002, 148 Pt 11, 3681–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, Y.A.; Finnan, S.; Reen, F.J.; Morrissey, J.P.; O’Gara, F.; Boyd, E.F. The Vibrio seventh pandemic island-II is a 26.9 kb genomic island present in Vibrio cholerae El Tor and O139 serogroup isolates that shows homology to a 43.4 kb genomic island in V. vulnificus. Microbiology 2004, 150, 4053–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaolis, D.K.; Johnson, J.A.; Bailey, C.C.; Boedeker, E.C.; Kaper, J.B.; Reeves, P.R. A Vibrio cholerae pathogenicity island associated with epidemic and pandemic strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3134–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovach, M.E.; Shaffer, M.D.; Peterson, K.M. A putative integrase gene defines the distal end of a large cluster of ToxR-regulated colonization genes in Vibrio cholerae. Microbiology 1996, 142 Pt 8, 2165–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahmeyer-Gabbe, M.; Howe, M.M. Regulatory factors acting at the bacteriophage Mu middle promoter. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Howe, M.M. The phage Mu middle promoter Pm contains a partial UP element. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2015, 5, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaraswami, M.; Howe, M.M.; Park, H.W. Crystal structure of the Mor protein of bacteriophage Mu, a member of the Mor/C family of transcription activators. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16581–16590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, A.; Busby, S.; Buc, H.; Garges, S.; Adhya, S. Transcriptional regulation by cAMP and its receptor protein. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1993, 62, 749–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinisch, F.; Mariotti, M.; Andersen, S.H.; Lindemose, S.; Hägglund, P.; Møllegaard, N.E.; Davies, M.J. UV oxidation of cyclic AMP receptor protein, a global bacterial gene regulator, decreases DNA binding and cleaves DNA at specific sites. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, A.; Ebright, Y.W.; Ebright, R.H. DNA sequence determinants for binding of the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 14713–14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.T.; Lin, T.H.; Wu, C.C.; Wan, L.; Huang, C.F.; Peng, H.L. CRP-Cyclic AMP Regulates the Expression of Type 3 Fimbriae via Cyclic di-GMP in Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, R.; Parrack, P. Cyclic AMP-dependent functional forms of cyclic AMP receptor protein from Vibrio cholerae. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 447, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.S.; Awasthi, S.P.; Asakura, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Hinenoya, A.; Faruque, S.M.; Yamasaki, S. Suppression of Virulence of Toxigenic Vibrio cholerae by Anethole through the Cyclic AMP (cAMP)-cAMP Receptor Protein Signaling System. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaper, J.B.; Morris, J.G., Jr.; Levine, M.M. Cholera. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 8, 48–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hounmanou, Y.M.G.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Dougnon, T.V.; Mdegela, R.H.; Olsen, J.E.; Dalsgaard, A. Surveillance and Genomics of Toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 From Fish, Phytoplankton and Water in Lake Victoria, Tanzania. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 901. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, M.R.; Rozovsky, S.; Boyd, E.F. Pathogenicity Island Cross Talk Mediated by Recombination Directionality Factors Facilitates Excision from the Chromosome. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 198, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacikova, G.; Skorupski, K. Overlapping binding sites for the virulence gene regulators AphA, AphB and cAMP-CRP at the Vibrio cholerae tcpPH promoter. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Wang, K.; Zhao, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, H.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Huang, J.; Min, X. DegS protease regulates the motility, chemotaxis, and colonization of Vibrio cholerae. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1159986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzhingi, I.; Prado, C.; Sylla, M.; Diehl, F.F.; Nguyen, D.K.; Servos, M.M.; Flores Ramos, S.; Purdy, A.E. Modulation of CrbS-Dependent Activation of the Acetate Switch in Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00380–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Cao, H.; Zhu, W.; Wang, M.; Du, Y.; Yin, Z.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, B. RNA-seq-based monitoring of gene expression changes of viable but non-culturable state of Vibrio cholerae induced by cold seawater. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 10, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettiger, A.; Basler, M. Type VI Secretion System Substrates Are Transferred and Reused among Sister Cells. Cell 2016, 167, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.Z.; Liang, W.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhu, J.; Kan, B. Plasticity of regulation of mannitol phosphotransferase system operon by CRP-cAMP complex in Vibrio cholerae. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 831–840. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Qin, J.; Zhao, K.; Li, F.; Feng, X.; Li, L.; et al. Escherichia coli O157:H7 senses microbiota-produced riboflavin to increase its virulence in the gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2212436119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Meyer, C.A.; Eeckhoute, J.; Johnson, D.S.; Bernstein, B.E.; Nusbaum, C.; Myers, R.M.; Brown, M.; Li, W.; et al. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Yang, X.; Xia, H.; Wu, H.; Ye, J.; Zhang, H. sRNA EsrE Is Transcriptionally Regulated by the Ferric Uptake Regulator Fur in Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.T.; Ottemann, K.M.; Yildiz, F.H. Vibrio cholerae Response Regulator VxrB Controls Colonization and Regulates the Type VI Secretion System. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xi, D.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Cao, B. Vibrio cholerae VC1741 (PsrA) enhances the colonization of the pathogen in infant mice intestines in the presence of the long-chain fatty acid, oleic acid. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, J.; Liu, Q.; Xue, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Cao, B. The Response Regulator VC1795 of Vibrio Pathogenicity Island-2 Contributes to Intestinal Colonization by Vibrio cholerae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713523
Yan J, Liu Q, Xue X, Li J, Li Y, Su Y, Cao B. The Response Regulator VC1795 of Vibrio Pathogenicity Island-2 Contributes to Intestinal Colonization by Vibrio cholerae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713523
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Junxiang, Qian Liu, Xinke Xue, Jinghao Li, Yuehua Li, Yingying Su, and Boyang Cao. 2023. "The Response Regulator VC1795 of Vibrio Pathogenicity Island-2 Contributes to Intestinal Colonization by Vibrio cholerae" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713523
APA StyleYan, J., Liu, Q., Xue, X., Li, J., Li, Y., Su, Y., & Cao, B. (2023). The Response Regulator VC1795 of Vibrio Pathogenicity Island-2 Contributes to Intestinal Colonization by Vibrio cholerae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713523




