Fifty Years of Animal Toxin Research at the Shemyakin–Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry RAS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural Studies of Animal Toxins
2.1. Primary Structure Determination
2.2. Toxin Spatial Structure Studies
3. Three-Finger Proteins from Snake Venoms in Research on nAChRs
3.1. Overview of α-Neurotoxin–nAChR Relationships
3.2. Interaction of α-Neurotoxins Bearing Fluorescent, Spin, or Photoactivatable Labels with the nAChRs
3.3. Recent Studies on Snake Venom α-Neurotoxins
4. Other Snake Venom Toxins
4.1. Cobra Venom Cytotoxins: Spatial Structure and Biological Activity
4.2. Non-Conventional Three-Finger Neurotoxin
4.3. Three-Finger Mammalian Proteins
4.4. Phospholipases A2
4.5. Linear Peptides
5. Marine Toxins Acting on the Ligand- or Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
5.1. α-Conotoxins in Research on nAChRs
5.2. Sea Anemone-Derived Toxins
6. Prominent Molecules from Arthropod Venoms
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, C.C.; Lee, C.Y. Isolation of Neurotoxins from the Venom of Bungarus Multicinctus and Their Modes of Neuromuscular Blocking Action. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1963, 144, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Changeux, J.P.; Kasai, M.; Lee, C.Y. Use of a Snake Venom Toxin to Characterize the Cholinergic Receptor Protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 67, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishin, E.V.; Sukhikh, A.P.; Lukyanchuk, N.N.; Slobodyan, L.N.; Lipkin, V.M.; Ovchinnikov, Y.A.; Sorokin, V.M. Amino Acid Sequence of Neurotoxin II from Naja naja oxiana Venom. FEBS Lett. 1973, 36, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishin, E.V.; Sukhikh, A.P.; Slobodyan, L.N.; Ovchinnikov, Y.A.; Sorokin, V.M. Amino Acid Sequence of Neurotoxin I from Naja naja oxiana Venom. FEBS Lett. 1974, 45, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, E.V.; Sukhikh, A.P.; Adamovich, T.B.; Ovchinnikov, Y.A. The Isolation and Sequence Determination of a Cytotoxin from the Venom of the Middle-Asian Cobra Naja naja oxiana. FEBS Lett. 1974, 48, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, E.V.; Sukhikh, A.P.; Adamovich, T.B.; Ovchinnikov, Y.A. Isolation, properties and sequence determination of the two cytotoxins from the venom of the Middle-Asian cobra Naja naja oxiana. Bioorg. Khim. 1976, 8, 1018–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Utkin, Y.N.; Kukhtina, V.V.; Maslennikov, I.V.; Eletsky, A.V.; Starkov, V.G.; Weise, C.; Franke, P.; Hucho, F.; Tsetlin, V.I. First Tryptophan-Containing Weak Neurotoxin from Cobra Venom. Toxicon 2001, 39, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukhtina, V.V.; Weise, C.; Muranova, T.A.; Starkov, V.G.; Franke, P.; Hucho, F.; Wnendt, S.; Gillen, C.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Muscarinic Toxin-like Proteins from Cobra Venom. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 6784–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, A.V.; Astapova, M.V.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. The First Representative of Glycosylated Three-Fingered Toxins. Cytotoxin from the Naja Kaouthia Cobra Venom. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazanova, A.S.; Zavada, L.L.; Starkov, V.G.; Kovyazina, I.V.; Subbotina, T.F.; Kostyukhina, E.E.; Dementieva, I.N.; Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Utkin, Y.N. Heterodimeric Neurotoxic Phospholipases A2—The First Proteins from Venom of Recently Established Species Vipera Nikolskii: Implication of Venom Composition in Viper Systematics. Toxicon 2008, 51, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.N.; Weise, C.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Andreeva, T.V.; Kryukova, E.V.; Zhmak, M.N.; Starkov, V.G.; Hoang, N.A.; Bertrand, D.; Ramerstorfer, J.; et al. Azemiopsin from Azemiops Feae Viper Venom, a Novel Polypeptide Ligand of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 27079–27086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, V.V.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Weise, C.; Dyachenko, I.; Shaykhutdinova, E.; Murashev, A.N.; Zhmak, M.; Starkov, V.; Hoang, A.N.; Tsetlin, V.; et al. Novel Bradykinin-Potentiating Peptides and Three-Finger Toxins from Viper Venom: Combined NGS Venom Gland Transcriptomics and Quantitative Venom Proteomics of the Azemiops Feae Viper. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, E.V. Structure and Function of Buthus Eupeus Scorpion Neurotoxins. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1981, 20, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.M.; Garsia, A.F.; Telezhinskaia, I.N.; Potapenko, N.A.; Grishin, E.V. [Amino acid sequence of 2 neurotoxins from the scorpion Buthus eupeus venom]. Bioorg. Khim. 1984, 10, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volkova, T.M.; Dulubova, I.E.; Telezhinskaia, I.N.; Grishin, E.V. [Toxic components of the venom of the Central Asian scorpion, Orthochirus scrobiculosus]. Bioorg. Khim. 1984, 10, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsai, I.-H.; Wang, Y.-M.; Cheng, A.C.; Starkov, V.; Osipov, A.; Nikitin, I.; Makarova, Y.; Ziganshin, R.; Utkin, Y. CDNA Cloning, Structural, and Functional Analyses of Venom Phospholipases A₂ and a Kunitz-Type Protease Inhibitor from Steppe Viper Vipera Ursinii Renardi. Toxicon 2011, 57, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, S.; Lipkin, A.; Nosyreva, E.; Blake, A.; Windass, J.D.; Grishin, E. Purification and CDNA Cloning of an Insecticidal Protein from the Venom of the Scorpion Orthochirus Scrobiculosus. Toxicon 2000, 38, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolkova, Y.V.; Kozlov, S.A.; Lipkin, A.V.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Hadley, J.K.; Filippov, A.K.; Brown, D.A.; Angelo, K.; Strøbaek, D.; Jespersen, T.; et al. An ERG Channel Inhibitor from the Scorpion Buthus Eupeus. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9868–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, E.; Korolkova, Y.; Kozlov, S.; Lipkin, A.; Nosyreva, E.; Pluzhnikov, K.; Sukhanov, S.; Volkova, T. Structure and Function of the Potassium Channel Inhibitor from Black Scorpion Venom. Pure Appl. Chem. 1996, 68, 2105–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Oparin, P.B.; Zhmak, M.N.; Egorova, N.S.; Ivanov, I.A.; Gigolaev, A.M.; Nekrasova, O.V.; Serebryakova, M.V.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Prokopev, N.A.; et al. Scorpion Toxins Interact with Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Logashina, Y.A.; Kornilov, F.D.; Lushpa, V.A.; Maleeva, E.E.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S.; et al. Peptides from the Sea Anemone Metridium Senile with Modified Inhibitor Cystine Knot (ICK) Fold Inhibit Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins 2022, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkin, A.V.; Grishin, E.V. [Variability of the structure of neurotoxins from the scorpion Orthochirus scrobiculosus from various natural habitats]. Bioorg. Khim. 1999, 25, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov, S.; Malyavka, A.; McCutchen, B.; Lu, A.; Schepers, E.; Herrmann, R.; Grishin, E. A Novel Strategy for the Identification of Toxinlike Structures in Spider Venom. Proteins 2005, 59, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, S.A.; Grishin, E.V. The Universal Algorithm of Maturation for Secretory and Excretory Protein Precursors. Toxicon 2007, 49, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, S.A.; Lazarev, V.N.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Selezneva, O.V.; Ospanova, E.A.; Alexeev, D.G.; Govorun, V.M.; Grishin, E.V. Comprehensive Analysis of the Venom Gland Transcriptome of the Spider Dolomedes Fimbriatus. Sci. Data 2014, 1, 140023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shliapnikov, I.M.; Kozlov, S.A.; Fedorov, A.A.; Grishin, E.V. [Comparison of polypeptide compositions from individual Agelena orientalis spider venoms]. Bioorg. Khim. 2010, 36, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kiyatkin, N.I.; Dulubova, I.E.; Chekhovskaya, I.A.; Grishin, E.V. Cloning and Structure of CDNA Encoding α-Latrotoxin from Black Widow Spider Venom. FEBS Lett. 1990, 270, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyatkin, N.; Dulubova, I.; Grishin, E. Cloning and Structural Analysis of α-Latroinsectotoxin CDNA. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 213, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulubova, I.E.; Krasnoperov, V.G.; Khvotchev, M.V.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Volkova, T.M.; Grishin, E.V.; Vais, H.; Bell, D.R.; Usherwood, P.N.R. Cloning and Structure of δ-Latroinsectotoxin, a Novel Insect-Specific Member of the Latrotoxin Family. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7535–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Südhof, T.C. Alpha-Latrotoxin and Its Receptors: Neurexins and CIRL/Latrophilins. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 933–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arseniev, A.S.; Balashova, T.A.; Utkin, Y.N.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Bystrov, V.F.; Ivanov, V.T.; Ovchinnikov, Y.A. Proton-Nuclear-Magnetic-Resonance Study of the Conformation of Neurotoxin II from Middle-Asian Cobra (Naja naja oxiana) Venom. Eur. J. Biochem. 1976, 71, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, B.W.; Preston, H.S.; Sato, A.; Rosen, L.S.; Searl, J.E.; Rudko, A.D.; Richardson, J.S. Three Dimensional Structure of Erabutoxin b Neurotoxic Protein: Inhibitor of Acetylcholine Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 2991–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsernoglou, D.; Petsko, G.A. Three-Dimensional Structure of Neurotoxin a from Venom of the Philippines Sea Snake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Schulga, A.A.; Ermolyuk, Y.S.; Mordvintsev, D.Y.; Utkin, Y.N.; Shoulepko, M.A.; Hogg, R.C.; Bertrand, D.; Dolgikh, D.A.; et al. Bacterial Expression, NMR, and Electrophysiology Analysis of Chimeric Short/Long-Chain Alpha-Neurotoxins Acting on Neuronal Nicotinic Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24784–24791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shulepko, M.A.; Tikhonov, R.V.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Paramonov, A.S.; Wulfson, A.N.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Ustich, T.L.; Utkin, Y.N.; Arseniev, A.S.; et al. Bacterial Production and Refolding from Inclusion Bodies of a “Weak” Toxin, a Disulfide Rich Protein. Biochemistry 2009, 74, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovanov, A.P.; Lomize, A.L.; Arseniev, A.S.; Utkin, Y.N.; Tsetlin, V.I. Two-Dimensional 1H-NMR Study of the Spatial Structure of Neurotoxin II from Naja naja oxiana. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 213, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Shulepko, M.A.; Paramonov, A.S.; Chugunov, A.O.; Janickova, H.; Dolejsi, E.; Dolezal, V.; Utkin, Y.N.; Tsetlin, V.I.; et al. Structural Insight into Specificity of Interactions between Nonconventional Three-Finger Weak Toxin from Naja Kaouthia (WTX) and Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 23616–23630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipov, A.V.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Makarova, Y.V.; Starkov, V.G.; Vorontsova, O.V.; Ziganshin, R.K.; Andreeva, T.V.; Serebryakova, M.V.; Benoit, A.; Hogg, R.C.; et al. Naturally Occurring Disulfide-Bound Dimers of Three-Fingered Toxins: A Paradigm for Biological Activity Diversification. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14571–14580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipov, A.V.; Rucktooa, P.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Filkin, S.Y.; Starkov, V.G.; Andreeva, T.V.; Sixma, T.K.; Bertrand, D.; Utkin, Y.N.; Tsetlin, V.I. Dimeric α-Cobratoxin X-Ray Structure: Localization of Intermolecular Disulfides and Possible Mode of Binding to Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6725–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikov, I.V.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Zhmak, M.N.; Ivanov, V.T.; Methfessel, C.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Arseniev, A.S. NMR Spatial Structure of Alpha-Conotoxin ImI Reveals a Common Scaffold in Snail and Snake Toxins Recognizing Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. FEBS Lett. 1999, 444, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmenkov, A.I.; Peigneur, S.; Nasburg, J.A.; Mineev, K.S.; Nikolaev, M.V.; Pinheiro-Junior, E.L.; Arseniev, A.S.; Wulff, H.; Tytgat, J.; Vassilevski, A.A. Apamin Structure and Pharmacology Revisited. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 977440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaravine, V.A.; Nolde, D.E.; Reibarkh, M.J.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Kozlov, S.A.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Grishin, E.V.; Arseniev, A.S. Three-Dimensional Structure of Toxin OSK1 from Orthochirus Scrobiculosus Scorpion Venom. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashkov, V.S.; Maiorov, V.N.; Bystrov, V.F.; Hoang, A.N.; Volkova, T.M.; Grishin, E.V. Solution Spatial Structure of ‘Long’ Neurotoxin M9 from the Scorpion Buthus Eupeus by 1H-NMR Spectroscopy. Biophys. Chem. 1988, 31, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsen’ev, A.S.; Kondakov, V.I.; Maĭorov, V.N.; Volkova, T.M.; Grishin, E.V. [Secondary structure and assignment of signals in two-dimensional 1H-NMR spectra of the Buthus eupeus neurotoxin I5A]. Bioorg. Khim. 1983, 9, 768–793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Korolkova, Y.V.; Bocharov, E.V.; Angelo, K.; Maslennikov, I.V.; Grinenko, O.V.; Lipkin, A.V.; Nosyreva, E.D.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Olesen, S.-P.; Arseniev, A.S.; et al. New Binding Site on Common Molecular Scaffold Provides HERG Channel Specificity of Scorpion Toxin BeKm-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 43104–43109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oparin, P.B.; Nadezhdin, K.D.; Berkut, A.A.; Arseniev, A.S.; Grishin, E.V.; Vassilevski, A.A. Structure of Purotoxin-2 from Wolf Spider: Modular Design and Membrane-Assisted Mode of Action in Arachnid Toxins. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 3113–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polz-Tejera, G.; Schmidt, J.; Karten, H.J. Autoradiographic Localisation of Alpha-Bungarotoxin-Binding Sites in the Central Nervous System. Nature 1975, 258, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, E.; Heilbronn, E.; Widlund, L. Isolation of the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor by Biospecific Chromatography on Insolubilized Naja Naja Neurotoxin. FEBS Lett. 1972, 28, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetlin, V.I.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Utkin, Y.N. Three-Finger Proteins from Snakes and Humans Acting on Nicotinic Receptors: Old and New. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changeux, J.-P. Discovery of the First Neurotransmitter Receptor: The Acetylcholine Nicotinic Receptor. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirthanan, S. Snake Three-Finger α-Neurotoxins and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: Molecules, Mechanisms and Medicine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.K.; McCarthy, M.P.; Stroud, R.M. Three-Dimensional Structure of the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor and Location of the Major Associated 43-KD Cytoskeletal Protein, Determined at 22 A by Low Dose Electron Microscopy and x-Ray Diffraction to 12.5 A. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 755–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brejc, K.; van Dijk, W.J.; Klaassen, R.V.; Schuurmans, M.; van Der Oost, J.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K. Crystal Structure of an ACh-Binding Protein Reveals the Ligand-Binding Domain of Nicotinic Receptors. Nature 2001, 411, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unwin, N. Refined Structure of the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor at 4A Resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 346, 967–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilf, R.J.C.; Dutzler, R. X-Ray Structure of a Prokaryotic Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channel. Nature 2008, 452, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, N.; Nury, H.; Baaden, M.; Le Poupon, C.; Changeux, J.-P.; Delarue, M.; Corringer, P.-J. X-Ray Structure of a Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channel in an Apparently Open Conformation. Nature 2009, 457, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Perez, C.L.; Noviello, C.M.; Hibbs, R.E. X-Ray Structure of the Human A4β2 Nicotinic Receptor. Nature 2016, 538, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, Y.; Talley, T.T.; Hansen, S.B.; Taylor, P.; Marchot, P. Crystal Structure of a Cbtx-AChBP Complex Reveals Essential Interactions between Snake Alpha-Neurotoxins and Nicotinic Receptors. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Li, S.-X.; Bren, N.; Cheng, K.; Gomoto, R.; Chen, L.; Sine, S.M. Complex between α-Bungarotoxin and an A7 Nicotinic Receptor Ligand-Binding Domain Chimaera. Biochem. J. 2013, 454, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellisanti, C.D.; Yao, Y.; Stroud, J.C.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Chen, L. Crystal Structure of the Extracellular Domain of NAChR Alpha1 Bound to Alpha-Bungarotoxin at 1.94 A Resolution. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouridakis, M.; Giastas, P.; Zarkadas, E.; Chroni-Tzartou, D.; Bregestovski, P.; Tzartos, S.J. Crystal Structures of Free and Antagonist-Bound States of Human A9 Nicotinic Receptor Extracellular Domain. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Teng, J.; Worrell, B.T.; Noviello, C.M.; Lee, M.; Karlin, A.; Stowell, M.H.B.; Hibbs, R.E. Structure of the Native Muscle-Type Nicotinic Receptor and Inhibition by Snake Venom Toxins. Neuron 2020, 106, 952–962.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviello, C.M.; Gharpure, A.; Mukhtasimova, N.; Cabuco, R.; Baxter, L.; Borek, D.; Sine, S.M.; Hibbs, R.E. Structure and Gating Mechanism of the A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Cell 2021, 184, 2121–2134.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nys, M.; Zarkadas, E.; Brams, M.; Mehregan, A.; Kambara, K.; Kool, J.; Casewell, N.R.; Bertrand, D.; Baenziger, J.E.; Nury, H.; et al. The Molecular Mechanism of Snake Short-Chain α-Neurotoxin Binding to Muscle-Type Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetlin, V.I.; Karlsson, E.; Arseniev, A.S.; Utkin, Y.N.; Surin, A.M.; Pashkov, V.S.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Ivanov, V.T.; Bystrov, V.F.; Ovchinnikov, Y.A. EPR and Fluorescence Study of Interaction of Naja naja oxiana Neurotoxin II and Its Derivatives with Acetylcholine Receptor Protein from Torpedo Marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1979, 106, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreienkamp, H.J.; Utkin, Y.N.; Weise, C.; Machold, J.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Hucho, F. Investigation of Ligand-Binding Sites of the Acetylcholine Receptor Using Photoactivatable Derivatives of Neurotoxin II from Naja naja oxiana. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 8239–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machold, J.; Utkin, Y.; Kirsch, D.; Kaufmann, R.; Tsetlin, V.; Hucho, F. Photolabeling Reveals the Proximity of the Alpha-Neurotoxin Binding Site to the M2 Helix of the Ion Channel in the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7282–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.N.; Krivoshein, A.V.; Davydov, V.L.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Franke, P.; Maslennikov, I.V.; Arseniev, A.S.; Hucho, F.; Tsetlin, V.I. Labeling of Torpedo Californica Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subunits by Cobratoxin Derivatives with Photoactivatable Groups of Different Chemical Nature at Lys23. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 253, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Son, L.V.; Ojomoko, L.O.; Kryukova, E.V.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Zhmak, M.N.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Ivanov, I.A.; Kasheverov, I.E.; et al. Neurotoxins from Snake Venoms and α-Conotoxin ImI Inhibit Functionally Active Ionotropic γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 22747–22758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaragod, V.B.; Mortensen, M.; Hardwick, S.W.; Wahid, A.A.; Dorovykh, V.; Chirgadze, D.Y.; Smart, T.G.; Miller, P.S. Mechanisms of Inhibition and Activation of Extrasynaptic Aβ GABAA Receptors. Nature 2022, 602, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, L.; Kryukova, E.; Ziganshin, R.; Andreeva, T.; Kudryavtsev, D.; Kasheverov, I.; Tsetlin, V.; Utkin, Y. Novel Three-Finger Neurotoxins from Naja Melanoleuca Cobra Venom Interact with GABAA and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins 2021, 13, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkin, Y.N.; Kuch, U.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Lebedev, D.S.; Cederlund, E.; Molles, B.E.; Polyak, I.; Ivanov, I.A.; Prokopev, N.A.; Ziganshin, R.H.; et al. Novel Long-Chain Neurotoxins from Bungarus Candidus Distinguish the Two Binding Sites in Muscle-Type Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 1285–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Kuzmenkov, A.I.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Chudetskiy, I.S.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Barykin, E.P.; Ivanov, I.A.; Siniavin, A.E.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Baranov, M.S.; et al. Snake Toxins Labeled by Green Fluorescent Protein or Its Synthetic Chromophore Are New Probes for Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 753283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dement’eva, D.V.; Utkin, I.N.; Arsen’ev, A.S. [Secondary structure and conformational heterogeneity of Naja naja oxiana cytotoxin II]. Bioorg. Khim. 1996, 22, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dementieva, D.V.; Bocharov, E.V.; Arseniev, A.S. Two Forms of Cytotoxin II (Cardiotoxin) from Naja naja oxiana in Aqueous Solution: Spatial Structures with Tightly Bound Water Molecules. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 263, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovskii, P.V.; Lesovoy, D.M.; Dubinnyi, M.A.; Utkin, Y.N.; Arseniev, A.S. Interaction of the P-Type Cardiotoxin with Phospholipid Membranes. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubovskii, P.V.; Dubova, K.M.; Bourenkov, G.; Starkov, V.G.; Konshina, A.G.; Efremov, R.G.; Utkin, Y.N.; Samygina, V.R. Variability in the Spatial Structure of the Central Loop in Cobra Cytotoxins Revealed by X-Ray Analysis and Molecular Modeling. Toxins 2022, 14, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovskii, P.V.; Ignatova, A.A.; Alekseeva, A.S.; Starkov, V.G.; Boldyrev, I.A.; Feofanov, A.V.; Utkin, Y.N. Membrane-Disrupting Activity of Cobra Cytotoxins Is Determined by Configuration of the N-Terminal Loop. Toxins 2022, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feofanov, A.V.; Sharonov, G.V.; Dubinnyi, M.A.; Astapova, M.V.; Kudelina, I.A.; Dubovskii, P.V.; Rodionov, D.I.; Utkin, Y.N.; Arseniev, A.S. Comparative Study of Structure and Activity of Cytotoxins from Venom of the Cobras Naja oxiana, Naja kaouthia, and Naja haje. Biochemistry 2004, 69, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshina, O.N.; Kruykova, E.V.; Cheremnykh, E.G.; Kozlov, L.V.; Andreeva, T.V.; Starkov, V.G.; Osipov, A.V.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Screening Snake Venoms for Toxicity to Tetrahymena Pyriformis Revealed Anti-Protozoan Activity of Cobra Cytotoxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averin, A.S.; Nenov, M.N.; Starkov, V.G.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Effects of Cardiotoxins from Naja oxiana Cobra Venom on Rat Heart Muscle and Aorta: A Comparative Study of Toxin-Induced Contraction Mechanisms. Toxins 2022, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averin, A.S.; Goltyaev, M.V.; Andreeva, T.V.; Starkov, V.G.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. S- and P-Type Cobra Venom Cardiotoxins Differ in Their Action on Isolated Rat Heart. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 28, e20210110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averin, A.S.; Berezhnov, A.V.; Pimenov, O.Y.; Galimova, M.H.; Starkov, V.G.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Effects of Cobra Cardiotoxins on Intracellular Calcium and the Contracture of Rat Cardiomyocytes Depend on Their Structural Types. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.N.; Kukhtina, V.V.; Kryukova, E.V.; Chiodini, F.; Bertrand, D.; Methfessel, C.; Tsetlin, V.I. “Weak Toxin” from Naja Kaouthia Is a Nontoxic Antagonist of Alpha 7 and Muscle-Type Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 15810–15815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordvintsev, D.Y.; Polyak, Y.L.; Rodionov, D.I.; Jakubik, J.; Dolezal, V.; Karlsson, E.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Weak Toxin WTX from Naja Kaouthia Cobra Venom Interacts with Both Nicotinic and Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5065–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogay, A.Y.; Rzhevsky, D.I.; Murashev, A.N.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Weak Neurotoxin from Naja Kaouthia Cobra Venom Affects Haemodynamic Regulation by Acting on Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxicon 2005, 45, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, J.M.; Anderson, K.R.; Hoffman, K.M. Lynx Prototoxins: Roles of Endogenous Mammalian Neurotoxin-Like Proteins in Modulating Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Function to Influence Complex Biological Processes. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetlin, V.I. Three-Finger Snake Neurotoxins and Ly6 Proteins Targeting Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: Pharmacological Tools and Endogenous Modulators. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Shulepko, M.A.; Mineev, K.S.; D’Hoedt, D.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Filkin, S.Y.; Krivolapova, A.P.; Janickova, H.; Dolezal, V.; et al. NMR Structure and Action on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors of Water-Soluble Domain of Human LYNX1. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10618–10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulepko, M.A.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Paramonov, A.S.; Lobas, A.A.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Arseniev, A.S.; Kirpichnikov, M.P. Human Neuromodulator SLURP-1: Bacterial Expression, Binding to Muscle-Type Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor, Secondary Structure, and Conformational Heterogeneity in Solution. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shulepko, M.A.; Kudryavtsev, D.; Bychkov, M.L.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Astapova, M.V.; Feofanov, A.V.; Thomsen, M.S.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; et al. Human Secreted Ly-6/UPAR Related Protein-1 (SLURP-1) Is a Selective Allosteric Antagonist of A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shulepko, M.A.; Buldakova, S.L.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Reshetnikov, R.V.; Filkin, S.Y.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Ojomoko, L.O.; Kryukova, E.V.; et al. Water-Soluble LYNX1 Residues Important for Interaction with Muscle-Type and/or Neuronal Nicotinic Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 15888–15899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apsalon, U.R.; Shamborant, O.G.; Miroshnikov, A.I. Isolation and Some Properties of Phospholipase A2 from Venom of Middle-Asian Cobra Naja-Naja-Oxiana. Bioorg. Khim. 1977, 3, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov, Y.A.; Miroshnikov, A.I.; Nazimov, I.V.; Apsalon, U.R.; Soldatova, L.N. Complete Amino-Acid Sequence of Phospholipase-A2 (Isoenzyme E3) from the Venom of Middle Asian Cobra Naja-Naja-Oxiana. Bioorg. Khim. 1979, 5, 805–813. [Google Scholar]
- Osipov, A.V.; Filkin, S.Y.; Makarova, Y.V.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. A New Type of Thrombin Inhibitor, Noncytotoxic Phospholipase A2, from the Naja Haje Cobra Venom. Toxicon 2010, 55, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulfius, C.A.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Starkov, V.G.; Osipov, A.V.; Andreeva, T.V.; Filkin, S.Y.; Gorbacheva, E.V.; Astashev, M.E.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Inhibition of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors, a Novel Facet in the Pleiotropic Activities of Snake Venom Phospholipases A2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulfius, C.A.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Kryukova, E.V.; Spirova, E.N.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Starkov, V.G.; Andreeva, T.V.; Faure, G.; Zouridakis, M.; Tsetlin, V.I.; et al. Pancreatic and Snake Venom Presynaptically Active Phospholipases A2 Inhibit Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.V.; Siniavin, A.E.; Hoang, A.N.; Le, M.T.T.; Pham, C.D.; Phung, T.V.; Nguyen, K.C.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Weng, C.-F.; et al. Phospholipase A2 from Krait Bungarus Fasciatus Venom Induces Human Cancer Cell Death in Vitro. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniavin, A.E.; Streltsova, M.A.; Nikiforova, M.A.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Grinkina, S.D.; Gushchin, V.A.; Mozhaeva, V.A.; Starkov, V.G.; Osipov, A.V.; Lummis, S.C.R.; et al. Snake Venom Phospholipase A2s Exhibit Strong Virucidal Activity against SARS-CoV-2 and Inhibit the Viral Spike Glycoprotein Interaction with ACE2. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 7777–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniavin, A.; Grinkina, S.; Osipov, A.; Starkov, V.; Tsetlin, V.; Utkin, Y. Anti-HIV Activity of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2s: Updates for New Enzymes and Different Virus Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelukhina, I.V.; Zhmak, M.N.; Lobanov, A.V.; Ivanov, I.A.; Garifulina, A.I.; Kravchenko, I.N.; Rasskazova, E.A.; Salmova, M.A.; Tukhovskaya, E.A.; Rykov, V.A.; et al. Azemiopsin, a Selective Peptide Antagonist of Muscle Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor: Preclinical Evaluation as a Local Muscle Relaxant. Toxins 2018, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, S.A.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Feofanov, A.V.; Surovoy, A.Y.; Karpunin, D.V.; Grishin, E.V. Latarcins, Antimicrobial and Cytolytic Peptides from the Venom of the Spider Lachesana Tarabaevi (Zodariidae) That Exemplify Biomolecular Diversity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20983–20992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubovskii, P.V.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Kozlov, S.A.; Feofanov, A.V.; Grishin, E.V.; Efremov, R.G. Latarcins: Versatile Spider Venom Peptides. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4501–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.R.; Luque, A.; Olivera, B.M.; Barrett, J.; Cruz, L.J. Peptide Toxins from Conus Geographus Venom. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 4734–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, O.B.; Musick, J.R.; Gonzalez, C. Peptides Isolated from the Venom of Conus Geographus Block Neuromuscular Transmission. Neurosci. Lett. 1981, 25, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebbe, E.K.M.; Peigneur, S.; Wijesekara, I.; Tytgat, J. Conotoxins Targeting Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2970–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, N.; Lewis, R.J. Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Modulators from Cone Snails. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasheverov, I.; Kudryavtsev, D.; Shelukhina, I.; Nikolaev, G.; Utkin, Y.; Tsetlin, V. Marine Origin Ligands of Nicotinic Receptors: Low Molecular Compounds, Peptides and Proteins for Fundamental Research and Practical Applications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikov, I.V.; Sobol, A.G.; Gladky, K.V.; Lugovskoy, A.A.; Ostrovsky, A.G.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Ivanov, V.T.; Arseniev, A.S. Two Distinct Structures of Alpha-Conotoxin GI in Aqueous Solution. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 254, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.N.; Zhmak, M.N.; Methfessel, C.; Tsetlin, V.I. Aromatic Substitutions in Alpha-Conotoxin ImI. Synthesis of Iodinated Photoactivatable Derivative. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.; Zhmak, M.; Chivilyov, E.; Saez-Brionez, P.; Utkin, Y.; Hucho, F.; Tsetlin, V. Benzophenone-Type Photoactivatable Derivatives of Alpha-Neurotoxins and Alpha-Conotoxins in Studies on Torpedo Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 1999, 19, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasheverov, I.; Rozhkova, A.; Zhmak, M.; Utkin, Y.; Ivanov, V.; Tsetlin, V.I. Photoactivatable Alpha-Conotoxins Reveal Contacts with All Subunits as Well as Antagonist-Induced Rearrangements in the Torpedo Californica Acetylcholine Receptor. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 3664–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Chiara, D.C.; Zhmak, M.N.; Maslennikov, I.V.; Pashkov, V.S.; Arseniev, A.S.; Utkin, Y.N.; Cohen, J.B.; Tsetlin, V.I. Alpha-Conotoxin GI Benzoylphenylalanine Derivatives. (1)H-NMR Structures and Photoaffinity Labeling of the Torpedo Californica Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Zhmak, M.N.; Vulfius, C.A.; Gorbacheva, E.V.; Mordvintsev, D.Y.; Utkin, Y.N.; van Elk, R.; Smit, A.B.; Tsetlin, V.I. Alpha-Conotoxin Analogs with Additional Positive Charge Show Increased Selectivity towards Torpedo Californica and Some Neuronal Subtypes of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 4470–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Zhmak, M.N.; Khruschov, A.Y.; Tsetlin, V.I. Design of New α-Conotoxins: From Computer Modeling to Synthesis of Potent Cholinergic Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1698–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Chugunov, A.O.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Ivanov, I.A.; Zhmak, M.N.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Spirova, E.N.; Tabakmakher, V.M.; Zelepuga, E.A.; Efremov, R.G.; et al. High-Affinity α-Conotoxin PnIA Analogs Designed on the Basis of the Protein Surface Topography Method. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulfius, C.A.; Tumina, O.B.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Utkin, Y.N.; Tsetlin, V.I. Diversity of Nicotinic Receptors Mediating Cl- Current in Lymnaea Neurons Distinguished with Specific Agonists and Antagonist. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 373, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivovarov, A.S.; Palikhova, T.A.; Nikolaev, G.M.; Velikanov, A.N.; Vasilieva, N.A.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Utkin, Y.N.; Tsetlin, V.I. Atypical Acetylcholine Receptors on the Neurons of the Turkish Snail. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 491, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, L.; Lykhmus, O.; Zhmak, M.; Khruschov, A.; Tsetlin, V.; Magrini, E.; Viola, A.; Chernyavsky, A.; Qian, J.; Grando, S.; et al. Differential Involvement of A4β2, A7 and A9α10 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in B Lymphocyte Activation in Vitro. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronova, V.G.; Vulfius, C.A.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Mal’tseva, V.N.; Berezhnov, A.V.; Fedotova, E.I.; Miftahova, R.G.; Kryukova, E.V.; Grinevich, A.A.; Tsetlin, V.I. Nicotinic Receptor Involvement in Regulation of Functions of Mouse Neutrophils from Inflammatory Site. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronova, V.G.; Vulfius, C.A.; Astashev, M.E.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Serov, D.A.; Jirova, E.A.; Pershina, E.V.; Senko, D.A.; Zhmak, M.N.; Kasheverov, I.E.; et al. A9α10 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Regulate Murine Bone Marrow Granulocyte Functions. Immunobiology 2021, 226, 152047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpinskaya, T.I.; Osipov, A.V.; Balashevich, T.V.; Yanchanka, T.L.; Tamashionik, E.A.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Blockers of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Delay Tumor Growth and Increase Antitumor Activity of Mouse Splenocytes. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 491, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpinskaya, T.I.; Osipov, A.V.; Kuznetsova, T.E.; Ryzhkovskaya, E.L.; Ulaschik, V.S.; Ivanov, I.A.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. α-Conotoxins Revealed Different Roles of Nicotinic Cholinergic Receptor Subtypes in Oncogenesis of Ehrlich Tumor and in the Associated Inflammation. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 463, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipov, A.V.; Terpinskaya, T.I.; Yanchanka, T.; Balashevich, T.; Zhmak, M.N.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. α-Conotoxins Enhance Both the In Vivo Suppression of Ehrlich Carcinoma Growth and In Vitro Reduction in Cell Viability Elicited by Cyclooxygenase and Lipoxygenase Inhibitors. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpinskaya, T.I.; Osipov, A.V.; Kryukova, E.V.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Kopylova, N.V.; Yanchanka, T.L.; Palukoshka, A.F.; Gondarenko, E.A.; Zhmak, M.N.; Tsetlin, V.I.; et al. α-Conotoxins and α-Cobratoxin Promote, While Lipoxygenase and Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors Suppress the Proliferation of Glioma C6 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celie, P.H.N.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Mordvintsev, D.Y.; Hogg, R.C.; van Nierop, P.; van Elk, R.; van Rossum-Fikkert, S.E.; Zhmak, M.N.; Bertrand, D.; Tsetlin, V.; et al. Crystal Structure of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Homolog AChBP in Complex with an Alpha-Conotoxin PnIA Variant. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulens, C.; Hogg, R.C.; Celie, P.H.; Bertrand, D.; Tsetlin, V.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K. Structural Determinants of Selective Alpha-Conotoxin Binding to a Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Homolog AChBP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3615–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Xu, M.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Hu, Y.; Xiang, S.-H.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Tsetlin, V.I.; et al. From Crystal Structure of α-Conotoxin GIC in Complex with Ac-AChBP to Molecular Determinants of Its High Selectivity for A3β2 NAChR. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Kudryavtsev, D.; Kasheverov, I.; Lei, Y.; Zhangsun, D.; Tsetlin, V.; Luo, S. Species Specificity of Rat and Human A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors towards Different Classes of Peptide and Protein Antagonists. Neuropharmacology 2018, 139, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Pan, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Kasheverov, I.E.; et al. High Selectivity of an α-Conotoxin LvIA Analogue for A3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Is Mediated by Β2 Functionally Important Residues. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13656–13668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouridakis, M.; Papakyriakou, A.; Ivanov, I.A.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Tsetlin, V.; Tzartos, S.; Giastas, P. Crystal Structure of the Monomeric Extracellular Domain of A9 Nicotinic Receptor Subunit in Complex With α-Conotoxin RgIA: Molecular Dynamics Insights Into RgIA Binding to A9α10 Nicotinic Receptors. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, H.K.; Christensen, S.B.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Gajewiak, J.; Ramachandra, R.; Elmslie, K.S.; Vetter, D.E.; Ghelardini, C.; Iadonato, S.P.; Mercado, J.L.; et al. Inhibition of A9α10 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Prevents Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1825–E1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Christensen, S.B.; Dowell, C.; Purushottam, L.; Skalicky, J.J.; McIntosh, J.M.; Chou, D.H. Discovery of Methylene Thioacetal-Incorporated α-RgIA Analogues as Potent and Stable Antagonists of the Human A9α10 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 9513–9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedev, D.S.; Kryukova, E.V.; Ivanov, I.A.; Egorova, N.S.; Timofeev, N.D.; Spirova, E.N.; Tufanova, E.Y.; Siniavin, A.E.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Kasheverov, I.E.; et al. Oligoarginine Peptides, a New Family of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 96, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyachenko, I.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Palikov, V.A.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Kazakov, V.A.; Egorova, N.S.; Garifulina, A.I.; Utkin, Y.N.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Kryukova, E.V. α-Conotoxin RgIA and Oligoarginine R8 in the Mice Model Alleviate Long-Term Oxaliplatin Induced Neuropathy. Biochimie 2022, 194, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, I.N.; Klimovich, A.A.; Kalina, R.S.; Kozhevnikova, Y.V.; Khasanov, T.A.; Osmakov, D.I.; Koshelev, S.G.; Monastyrnaya, M.M.; Andreev, Y.A.; Leychenko, E.V.; et al. Anxiolytic, Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Peptides Hmg 1b-2 and Hmg 1b-4 from the Sea Anemone Heteractis Magnifica. Toxins 2023, 15, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, R.; Gladkikh, I.; Dmitrenok, P.; Chernikov, O.; Koshelev, S.; Kvetkina, A.; Kozlov, S.; Kozlovskaya, E.; Monastyrnaya, M. New APETx-like Peptides from Sea Anemone Heteractis Crispa Modulate ASIC1a Channels. Peptides 2018, 104, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, R.S.; Koshelev, S.G.; Zelepuga, E.A.; Kim, N.Y.; Kozlov, S.A.; Kozlovskaya, E.P.; Monastyrnaya, M.M.; Gladkikh, I.N. APETx-Like Peptides from the Sea Anemone Heteractis Crispa, Diverse in Their Effect on ASIC1a and ASIC3 Ion Channels. Toxins 2020, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, R.S.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Koshelev, S.G.; Sintsova, O.V.; Peigneur, S.; Pinheiro-Junior, E.L.; Popov, R.S.; Chausova, V.E.; Monastyrnaya, M.M.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; et al. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Are Novel Targets of APETx-like Toxins from the Sea Anemone Heteractis Magnifica. Toxins 2022, 14, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, Y.A.; Kozlov, S.A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Ivanova, E.A.; Monastyrnaya, M.M.; Kozlovskaya, E.P.; Grishin, E.V. Analgesic Compound from Sea Anemone Heteractis Crispa Is the First Polypeptide Inhibitor of Vanilloid Receptor 1 (TRPV1). J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23914–23921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, S.A.; Andreev, I.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Skobtsov, D.I.; D’iachenko, I.A.; Grishin, E.V. [New polypeptide components from the Heteractis crispa sea anemone with analgesic activity]. Bioorg. Khim. 2009, 35, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logashina, Y.A.; Mosharova, I.V.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Kozlov, S.A.; Stensvåg, K.; et al. Peptide from Sea Anemone Metridium Senile Affects Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin-Repeat 1 (TRPA1) Function and Produces Analgesic Effect. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 2992–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logashina, Y.A.; Solstad, R.G.; Mineev, K.S.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Mosharova, I.V.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Arseniev, A.S.; et al. New Disulfide-Stabilized Fold Provides Sea Anemone Peptide to Exhibit Both Antimicrobial and TRPA1 Potentiating Properties. Toxins 2017, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Kozlov, S.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Sanamyan, N.P.; Sanamyan, K.E.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Bondarenko, D.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Mineev, K.S.; et al. Sea Anemone Peptide with Uncommon β-Hairpin Structure Inhibits Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3 (ASIC3) and Reveals Analgesic Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23116–23127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreev, Y.A.; Osmakov, D.I.; Koshelev, S.G.; Maleeva, E.E.; Logashina, Y.A.; Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Kozlov, S.A. Analgesic Activity of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3 (ASIC3) Inhibitors: Sea Anemones Peptides Ugr9-1 and APETx2 versus Low Molecular Weight Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintsova, O.; Gladkikh, I.; Klimovich, A.; Palikova, Y.; Palikov, V.; Styshova, O.; Monastyrnaya, M.; Dyachenko, I.; Kozlov, S.; Leychenko, E. TRPV1 Blocker HCRG21 Suppresses TNF-α Production and Prevents the Development of Edema and Hypersensitivity in Carrageenan-Induced Acute Local Inflammation. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, S.M.; Grishin, E.V.; Magazanik, L.G.; Shupliakov, O.V.; Vesselkin, N.P.; Volkova, T.M. Argiopin Blocks the Glutamate Responses and Sensorimotor Transmission in Motoneurones of Isolated Frog Spinal Cord. Neurosci. Lett. 1987, 83, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiskin, N.I.; Kryshtal, O.A.; Tsyndrenko, A.; Volkova, T.M.; Grishin, E.V. [Argiopine, Argiopinines and Pseudoargiopinines--Blockers of the Glutamate Receptors in Hippocampal Neurons]. Neirofiziologiia Neurophysiol. 1989, 21, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, E.C.; Yelshanskaya, M.V.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Sobolevsky, A.I. Mechanisms of Channel Block in Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors. Neuron 2018, 99, 956–968.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishin, E.V.; Savchenko, G.A.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Boychuk, Y.A.; Viatchenko-Karpinski, V.Y.; Nadezhdin, K.D.; Arseniev, A.S.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Kulyk, V.B.; et al. Novel Peptide from Spider Venom Inhibits P2X3 Receptors and Inflammatory Pain. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Männikkö, R.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Thor, M.G.; Berkut, A.A.; Myshkin, M.Y.; Paramonov, A.S.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Kuzmin, D.A.; Sampedro Castañeda, M.; King, L.; et al. Spider Toxin Inhibits Gating Pore Currents Underlying Periodic Paralysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4495–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudina, E.E.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Bocharova, N.E.; Koshelev, S.G.; Egorov, T.A.; Huys, I.; Tytgat, J.; Grishin, E.V. OsK2, a New Selective Inhibitor of Kv1.2 Potassium Channels Purified from the Venom of the Scorpion Orthochirus Scrobiculosus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 286, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmenkov, A.I.; Nekrasova, O.V.; Peigneur, S.; Tabakmakher, V.M.; Gigolaev, A.M.; Fradkov, A.F.; Kudryashova, K.S.; Chugunov, A.O.; Efremov, R.G.; Tytgat, J.; et al. KV1.2 Channel-Specific Blocker from Mesobuthus Eupeus Scorpion Venom: Structural Basis of Selectivity. Neuropharmacology 2018, 143, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmenkov, A.I.; Nekrasova, O.V.; Kudryashova, K.S.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Stepanov, A.V.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Grishin, E.V.; Feofanov, A.V.; Vassilevski, A.A. Fluorescent Protein-Scorpion Toxin Chimera Is a Convenient Molecular Tool for Studies of Potassium Channels. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billen, B.; Vassilevski, A.; Nikolsky, A.; Debaveye, S.; Tytgat, J.; Grishin, E. Unique Bell-Shaped Voltage-Dependent Modulation of Na+ Channel Gating by Novel Insect-Selective Toxins from the Spider Agelena Orientalis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 18545–18554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikov, A.N.; Fedorova, I.M.; Potapieva, N.N.; Maleeva, E.E.; Andreev, Y.A.; Zaitsev, A.V.; Kim, K.K.; Bocharov, E.V.; Bozin, T.N.; Altukhov, D.A.; et al. ω-Tbo-IT1-New Inhibitor of Insect Calcium Channels Isolated from Spider Venom. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovskii, P.V.; Lesovoy, D.M.; Dubinnyi, M.A.; Konshina, A.G.; Utkin, Y.N.; Efremov, R.G.; Arseniev, A.S. Interaction of Three-Finger Toxins with Phospholipid Membranes: Comparison of S- and P-Type Cytotoxins. Biochem. J. 2005, 387, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippov, A.K.; Kozlov, S.A.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Grishin, E.V.; Brown, D.A. M-Type K+ Current Inhibition by a Toxin Fron the Scorpion Buthus Eupeus. FEBS Lett. 1996, 384, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishin, E.V.; Volkova, T.M.; Arseniev, A.S. Isolation and Structure Analysis of Components from Venom of the Spider Argiope Lobata. Toxicon 1989, 27, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovskii, P.V.; Volynsky, P.E.; Polyansky, A.A.; Karpunin, D.V.; Chupin, V.V.; Efremov, R.G.; Arseniev, A.S. Three-Dimensional Structure/Hydrophobicity of Latarcins Specifies Their Mode of Membrane Activity. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 3525–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovskii, P.V.; Volynsky, P.E.; Polyansky, A.A.; Chupin, V.V.; Efremov, R.G.; Arseniev, A.S. Spatial Structure and Activity Mechanism of a Novel Spider Antimicrobial Peptide. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10759–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryashova, K.S.; Nekrasova, O.V.; Kuzmenkov, A.I.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Ignatova, A.A.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Grishin, E.V.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Feofanov, A.V. Fluorescent System Based on Bacterial Expression of Hybrid KcsA Channels Designed for Kv1.3 Ligand Screening and Study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 2379–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryukova, E.V.; Ivanov, I.A.; Lebedev, D.S.; Spirova, E.N.; Egorova, N.S.; Zouridakis, M.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Tzartos, S.J.; Tsetlin, V.I. Orthosteric and/or Allosteric Binding of α-Conotoxins to Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors and Their Models. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

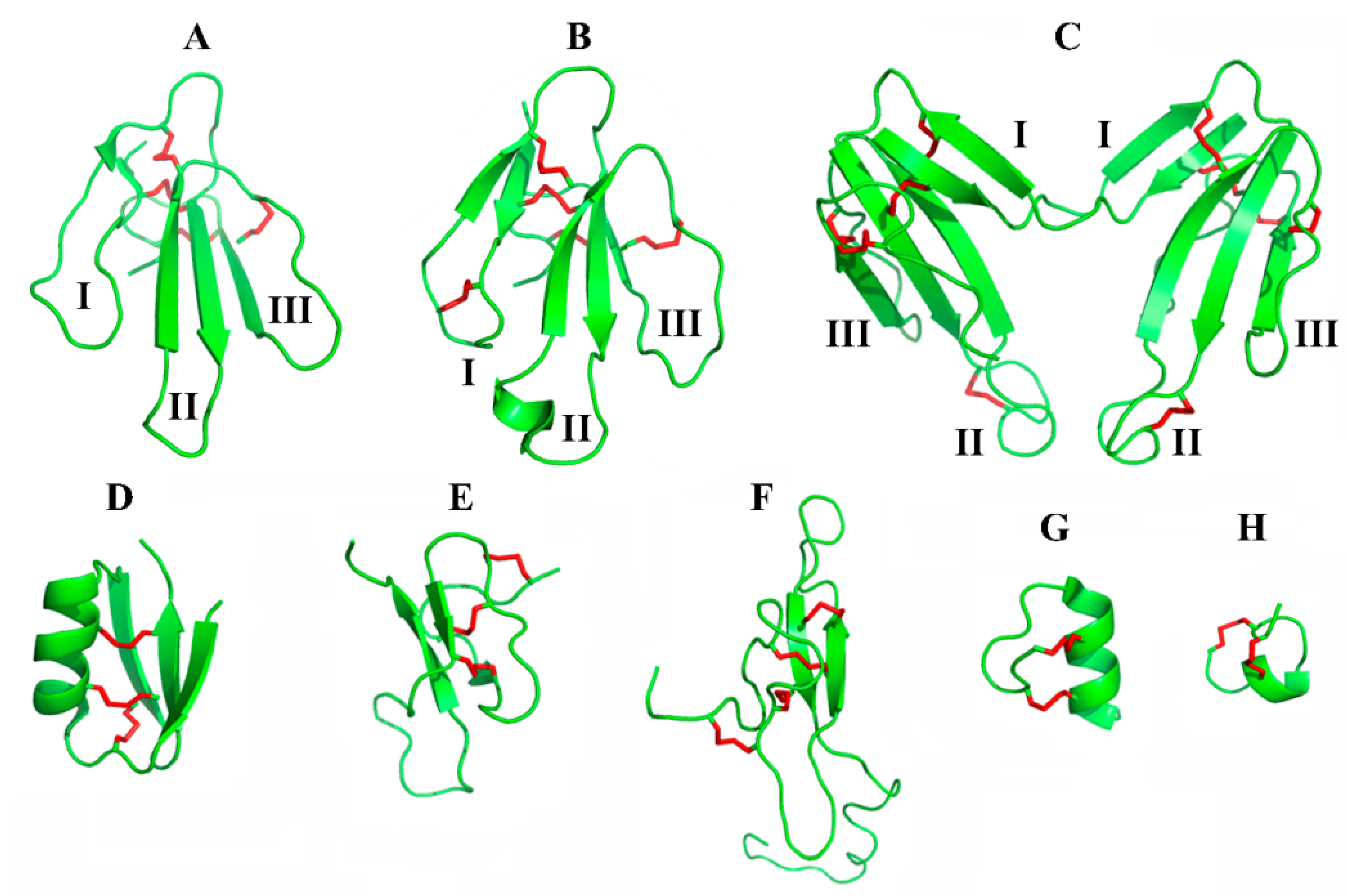

| Toxin(s) | Species | Structure Type | Structural and Functional Characterization: Sequence/Spatial Structure/Functional Characterization | UniProt Code | Year of Discovery | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snake venom-derived toxins | ||||||
| Neurotoxin II | Naja oxiana | TFT: Short-type α-neurotoxin | +/+/+ | 3S11_NAJOX | 1973 | [3,31,34,36,69] |
| Neurotoxin I | N. oxiana | TFT: Long-type α-neurotoxin | +/−/+ | 3L21_NAJOX | 1974 | [4,69,71] |
| Cytotoxins | N. oxiana, N. kaouthia | TFT | +/+/+ | 3SA1(2)_NAJOX, 3SA3(7A,8)_NAJKA | 1974–2022 | [5,6,9,38,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,157] |
| Muscarinic toxin-like protein 1 | N. kaouthia, N. melanoleuca | TFT | +/−/+ | 3SUC1_NAJKA, 3SUC1_NAJME | 2000–2021 | [8,71] |
| WTX | N. kaouthia | Non-conventional TFT | +/+/+ | 3NO2_NAJKA | 2001 | [7,35,37,69,84,85,86] |
| Homodimer of α-cobratoxin | N. kaouthia | TFT: Dimer of long-type α-neurotoxin | +/+/+ | 3L21_NAJKA | 2008 | [38,39] |
| Heterodimeric neurotoxic phospholipase A2 | Vipera nikolskii | Secreted PLA2 of group II | +/−/+ | PA2B1(2)_VIPBN PA2H_VIPBN | 2008 | [10] |
| Phospholipases A2 | V. ursinii renardi, Bungarus fasciatus, Bitis arietans, N. oxiana, N. haje | Secreted PLA2 of group I and II | +/−/+ | PA2A2(A3,B)_VIPRE PA2B_BITAR PA2B6_BUNFA PA2TI_NAJHH | 1977–2011 | [16,93,94] |
| Azemiopsin | Azemiops feae | Linear peptide | +/−/+ | AON_AZEFE | 2012 | [11,101] |
| αδ-Bungarotoxin (αδ-BgTx-1) | Bungarus candidus | TFT: Long-type α-neurotoxin | +/−/+ | 3L21_BUNCA | 2019 | [72] |
| Bradykinin- potentiating peptides | A. feae | Linear peptide | +/−/+ | No code | 2020 | [12] |
| Tx-NM2, Tx-NM3-1 | N. melanoleuca | TFT: Long-type α-neurotoxin | +/−/+ | 3L23(24)_NAJME | 2021 | [71] |
| Scorpion venom-derived toxins | ||||||
| Neurotoxin BeKm-1 | Mesobuthus eupeus | α-helix and a triple-stranded antiparallel β-sheet | +/+/+ | KGX21_MESEU | 1996 | [45,158] |
| Spider venom-derived toxins | ||||||
| β/δ-Agatoxin-5 | Agelena orientalis | ICK | +/−/+ | T5G1A_AGEOR | 2010 | [155] |
| Argiopin, argiopinins, and pseudoargiopinins | Argiope lobata | Acylpolyamines | +/+/+ | CID: 122294 189479 189486 * | 1989 | [159] |
| Latarcin-1 | Lachesana tarabaevi | Linear peptide | +/+/+ | LAT1_LACTA | 2006 | [102,160] |
| Latarcin-2a | L. tarabaevi | Linear peptide | +/+/+ | LAT2A_LACTA | 2006 | [102,161] |
| Purotoxin-1 (PT1) | Alopecosa marikovskyi | ICK | +/+/+ | TXPR1_ALOMR | 2010 | [150] |
| α-Latrototoxin-Lt1a | Latrodectus mactans tredecimguttatus | Multidomain organization | +/−/+ | LATA_LATTR | 1990 | [27] |
| α-Latroinsectotoxin- Lt1a | L. mactans tredecimguttatus | Multidomain organization | +/−/+ | LITA_LATTR | 1993 | [28] |
| Sea anemone venom-derived toxins | ||||||
| Analgesic polypeptide HC1 (τPI-SHTX-Hcr2b) | Heteractis crispa | Kunitz-type | +/−/+ | VKT2B_HETCR | 2008 | [140] |
| π-AnmTX Ugr 9a-1 | Urticina grebelnyi | β-hairpin structure | +/+/+ | TX9A_URTGR | 2013 | [144] |
| τ-AnmTX Ms 9a-1 | Metridium senile | β-hairpin structure | +/−/+ | TX91O_METSE | 2017 | [142] |
| Ms11a-1/4 | M. senile | ICK | +/+/+ | No code | 2023 | [21] |
| Native Toxin (Species) | Modifications | Target(s)/Activity | Tasks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Bungarotoxin (Bungarus multicinctus) | Radiolabeled and fluorescent derivatives | αβδγ/ε-, α7-, α9(α10) nAChRs; AChBPs; GABA-A | Detection of respective targets in different preparations, cells, tissues Radioligand in radioligand assay | [7,11,35,38,39,69,71,73] |
| Other long-type α-neurotoxins | Radiolabeled, photoactivatable, and fluorescent derivatives, analogs | αβδγ/ε-, α7-, α9(α10) nAChRs; AChBPs; GABA-A | Detection of respective targets in different preparations, cells, tissues Radioligand in radioligand assay Structure–function characterization Mapping of ligand-binding sites of T. californica nAChR | [4,34,68,69,71,73] |
| κ-Bungarotoxin (Bungarus multicinctus) | α7-, α3β2 nAChRs | Detection of respective targets in different preparations | [38] | |
| Short-type α-neurotoxins | Radiolabeled and photoactivatable derivatives, analogs | αβδγ/ε nAChRs | Detection of respective targets in different preparations Determination of the spatial structure Structure–function characterization Mapping of ligand-binding sites of T. californica nAChR | [3,34,65,66,67,69] |
| Phospholipases A2 | Cytotoxicity, antiviral activity, thrombin inhibitor, αβδγ/ε-, α7-nAChRs | Detection of respective targets in different preparations, cells, tissues Revealing the different biological activity | [95,96,97,98,99,100] | |
| Cytotoxins | Fluorescent derivatives | Cytotoxicity | Determination of the spatial structure Determination of the cytotoxicity mechanism | [138] |
| Azemiopsin (Azemiops feae) | Ala analogs, fluorescent derivative | αβδγ/ε nAChRs | Binding and functional characterization Structure–function characterization Preclinical trials as myorelaxant | [11,101] |
| Agitoxin-2 and OSK-1 | Toxin fused with fluorescent proteins | Voltage-gated potassium channels (KV) | Ligand screening in the spheroplast binding assay | [154] |
| Agitoxin-2 | Fluorescently labeled derivatives | Spheroplasts with the embedded KcsA-Kv1.3 hybrid protein | Screening of prospective compounds recognized by Kv1.3 | [162] |
| Toxin PT1 | Pure pharmacological substance | P2X3 | Preclinical trials as analgesic | - |
| APHC3 | Pure pharmacological substance | TRPV1 | Preclinical trials as analgesic | - |
| Different α-conotoxins (Conidae) | Different analogs, radiolabeled, photoactivatable, and fluorescent derivatives | Different nAChR subtypes; AChBPs; GABA-A | Determination of the spatial structure Detection of respective targets in different preparations, cells, tissues Radioligand in radioligand assay Design of new analogs Mapping of ligand-binding sites of T. californica nAChR X-ray studies of AChPB complexes In vivo studies on neuropathy models | [40,69,72,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,135] |
| αO-Conotoxin GXIVA (Conus geographus) | Isomers, radiolabeled derivative | α9(α10) nAChR; AChBPs | Binding and functional characterization | [163] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsetlin, V.; Shelukhina, I.; Kozlov, S.; Kasheverov, I. Fifty Years of Animal Toxin Research at the Shemyakin–Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry RAS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813884
Tsetlin V, Shelukhina I, Kozlov S, Kasheverov I. Fifty Years of Animal Toxin Research at the Shemyakin–Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry RAS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(18):13884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813884
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsetlin, Victor, Irina Shelukhina, Sergey Kozlov, and Igor Kasheverov. 2023. "Fifty Years of Animal Toxin Research at the Shemyakin–Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry RAS" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 18: 13884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813884
APA StyleTsetlin, V., Shelukhina, I., Kozlov, S., & Kasheverov, I. (2023). Fifty Years of Animal Toxin Research at the Shemyakin–Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry RAS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(18), 13884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813884





