The Effect of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Central and Peripheral Nervous System Neurons—Implications for Biomaterial Applicability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. L-PRF Consists of a Porous Fibrin Network with Leukocytes and Aggregates of Activated Platelets
2.2. L-PRF Is a Reservoir for a Plethora of Growth Factors That Are Slowly Released over Time
2.3. The Proliferative and Metabolic Activity of NSCs Was Not Affected by L-PRF
2.4. Growth Factors Slowly Released by L-PRF Act as a Chemoattractant on NSCs
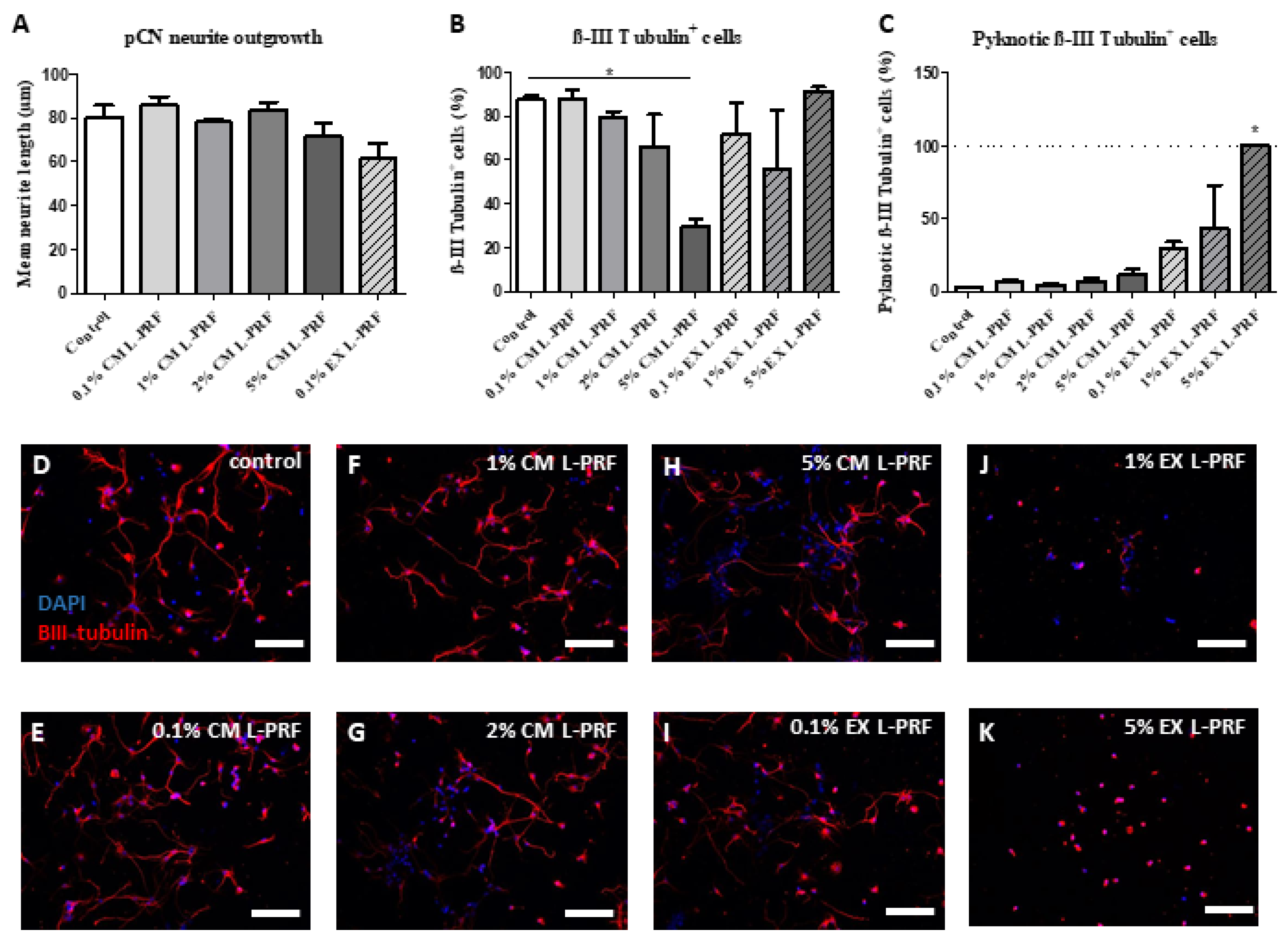
2.5. L-PRF Growth Factors Had a Detrimental Effect on pCNs and Suppressed Neurite Outgrowth
2.6. L-PRF Has a Beneficial Effect on the Survival and Neurite Outgrowth of Peripheral Neurons
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation and Processing of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF)
4.2. Preparation of Exudate and Conditioned Medium from L-PRF
4.3. (Immuno)Histological Characterization
4.4. Ultrastructural Analysis: Transmission and Scanning Electron Microscopy
4.5. Secretome Analysis: Antibody Array and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.6. Isolation and Culture of Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
4.7. Isolation and Culture of Mouse Neural Stem Cells and Primary Cortical Neurons
4.8. Metabolic Activity and Proliferation Assay
4.9. Transwell Migration Assay
4.10. Immunocytochemistry and Neurite Outgrowth Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, J.P.K.; Keane, T.J.; Roques, A.C.; Patrick, P.S.; Mooney, C.M.; Kuan, W.L.; Pisupati, V.; Oreffo, R.O.C.; Stuckey, D.J.; Watt, F.M.; et al. A blueprint for translational regenerative medicine. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, A.S.; Mooney, D.J. Regenerative medicine: Current therapies and future directions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14452–14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, K.L. Biomaterials for tissue repair. Science 2019, 363, 340–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.T.; Rosenbaum, A.J. Bone grafts, bone substitutes and orthobiologics: The bridge between basic science and clinical advancements in fracture healing. Organogenesis 2012, 8, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, G.W. Grafix(R), a Cryopreserved Placental Membrane, for the Treatment of Chronic/Stalled Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akar, B.; Jiang, B.; Somo, S.I.; Appel, A.A.; Larson, J.C.; Tichauer, K.M.; Brey, E.M. Biomaterials with persistent growth factor gradients in vivo accelerate vascularized tissue formation. Biomaterials 2015, 72, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Development of biomaterial scaffold for nerve tissue engineering: Biomaterial mediated neural regeneration. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Ding, F.; Williams, D.F. Neural tissue engineering options for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6143–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Gao, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wong, W.M.; Yuan, Q.; Su, H.; Kang, X.; Dai, X.; Zhang, W.; et al. Nanofiber scaffolds facilitate functional regeneration of peripheral nerve injury. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M.; Bliss, T.M.; Hua, T.; Lee, A.; Oh, B.; Levinson, A.; Mehta, S.; Sun, G.; Steinberg, G.K. Electrical preconditioning of stem cells with a conductive polymer scaffold enhances stroke recovery. Biomaterials 2017, 142, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisserand, L.S.; Kodama, T.; Papassin, J.; Auzely, R.; Moisan, A.; Rome, C.; Detante, O. Biomaterial Applications in Cell-Based Therapy in Experimental Stroke. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 6810562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, F.; Wang, J.; Xie, L.; Yang, C.; Pan, M.; Shao, B.; Yang, G.Y.; Yang, S.H.; ZhuGe, Q.; et al. Combining Injectable Plasma Scaffold with Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells for Repairing Infarct Cavity after Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaing, Z.Z.; Thomas, R.C.; Geissler, S.A.; Schmidt, C.E. Advanced biomaterials for repairing the nervous system: What can hydrogels do for the brain? Mater. Today 2014, 17, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.M.; Hou, S.P.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.L.; Xu, Q.Y.; Lee, I.S.; Li, H.D.; Spector, M.; Cui, F.Z. Hyaluronic acid-poly-D-lysine-based three-dimensional hydrogel for traumatic brain injury. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Pan, S.; Dangaria, S.J.; Gopinathan, G.; Kolokythas, A.; Chu, S.; Geng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Luan, X. Platelet-rich fibrin promotes periodontal regeneration and enhances alveolar bone augmentation. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 638043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumstein, M.A.; Rumian, A.; Lesbats, V.; Schaer, M.; Boileau, P. Increased vascularization during early healing after biologic augmentation in repair of chronic rotator cuff tears using autologous leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF): A prospective randomized controlled pilot trial. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2014, 23, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan, D.M.; Choukroun, J.; Diss, A.; Dohan, S.L.; Dohan, A.J.; Mouhyi, J.; Gogly, B. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: Platelet-related biologic features. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2006, 101, e45–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Corso, M.; Vervelle, A.; Simonpieri, A.; Jimbo, R.; Inchingolo, F.; Sammartino, G.; Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M. Current knowledge and perspectives for the use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) in oral and maxillofacial surgery part 1: Periodontal and dentoalveolar surgery. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1207–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan, D.M.; Choukroun, J.; Diss, A.; Dohan, S.L.; Dohan, A.J.; Mouhyi, J.; Gogly, B. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: Technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2006, 101, e37–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukroun, J.; Diss, A.; Simonpieri, A.; Girard, M.O.; Schoeffler, C.; Dohan, S.L.; Dohan, A.J.; Mouhyi, J.; Dohan, D.M. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: Clinical effects on tissue healingOral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2006, 101, e56–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Reed, D.A.; Min, L.; Gopinathan, G.; Li, S.; Dangaria, S.J.; Li, L.; Geng, Y.; Galang, M.T.; Gajendrareddy, P.; et al. Lyophilized platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) promotes craniofacial bone regeneration through Runx2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8509–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaretti, F.; Tia, M.; D’Esposito, V.; De Pascale, M.; Del Corso, M.; Sepulveres, R.; Liguoro, D.; Valentino, R.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P.; et al. Growth-promoting action and growth factor release by different platelet derivatives. Platelets 2014, 25, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade Aldana, C.; Ugarte Amenabar, F.; Inostroza Silva, C.; Diaz Calderon, P.; Rosenberg Messina, D.; Pinto Carrasco, N.; Quirynen, M. The impact of gender and peripheral blood parameters on the characteristics of L-PRF membranes. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2022, 12, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.B.; Cortellini, S.; Temmerman, A.; Li, X.; Pinto, N.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Characterization of the Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Block: Release of Growth Factors, Cellular Content, and Structure. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.B.; Andrade, C.; Li, X.; Pinto, N.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Impact of g force and timing on the characteristics of platelet-rich fibrin matrices. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schar, M.O.; Diaz-Romero, J.; Kohl, S.; Zumstein, M.A.; Nesic, D. Platelet-rich concentrates differentially release growth factors and induce cell migration in vitro. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuki, H.; Okudera, T.; Watanebe, T.; Suzuki, M.; Nishiyama, K.; Okudera, H.; Nakata, K.; Uematsu, K.; Su, C.Y.; Kawase, T. Growth factor and pro-inflammatory cytokine contents in platelet-rich plasma (PRP), plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF), advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), and concentrated growth factors (CGF). Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2016, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumstein, M.A.; Berger, S.; Schober, M.; Boileau, P.; Nyffeler, R.W.; Horn, M.; Dahinden, C.A. Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) for long-term delivery of growth factor in rotator cuff repair: Review, preliminary results and future directions. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; Jeon, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Choung, Y.H.; Choung, H.W.; Kim, E.S.; Choung, P.H. Platelet-rich fibrin is a Bioscaffold and reservoir of growth factors for tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfest, D.M.D.; Bielecki, T.; Jimbo, R.; Barbe, G.; Del Corso, M.; Inchingolo, F.; Sammartino, G. Do the Fibrin Architecture and Leukocyte Content Influence the Growth Factor Release of Platelet Concentrates? An Evidence-based Answer Comparing a Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma (P-PRP) Gel and a Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF). Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.V.; Shubhashini, N. Platelet rich fibrin: A new paradigm in periodontal regeneration. Cell Tissue Bank. 2013, 14, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pascale, M.R.; Sommese, L.; Casamassimi, A.; Napoli, C. Platelet derivatives in regenerative medicine: An update. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Rasmusson, L.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of platelet concentrates: From pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenzi, G.; Riccitiello, F.; Tia, M.; di Lauro, A.; Sammartino, G. Influence of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) in the Healing of Simple Postextraction Sockets: A Split-Mouth Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 369273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, F.; Jimenez, C.; Espinoza, D.; Vervelle, A.; Beugnet, J.; Haidar, Z. Use of leukocyte and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) in periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics (PAOO): Clinical effects on edema and pain. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2016, 8, e119–e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.B.; Van Dessel, J.; Temmerman, A.; Jacobs, R.; Quirynen, M. Effect of different platelet-rich fibrin matrices for ridge preservation in multiple tooth extractions: A split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molemans, B.; Cortellini, S.; Jacobs, R.; Pinto, N.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Simultaneous sinus floor elevation and implant placement using leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin as a sole graft material. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.Y.; Vy, V.P.T.; Tang, S.L.; Hung, T.N.K.; Wang, C.W.; Liang, J.Y.; Wong, C.C.; Chan, W.P. Current Progress of Platelet-Rich Derivatives in Cartilage and Joint Repairs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, N.R.; Ubilla, M.; Zamora, Y.; Del Rio, V.; Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Quirynen, M. Leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) as a regenerative medicine strategy for the treatment of refractory leg ulcers: A prospective cohort study. Platelets 2018, 29, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G. Impact of a Novel Hydrogel with Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Diabetic Wound Healing. J. Diabetes Res. 2023, 2023, 7532637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Pan, R.; Chen, Y. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma for Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehlawat, T.; Karia, U.K.; Shah, S.R.; Vyas, H.R.; Parghi, M.B.; Doshi, Y.J.; Shah, B.J. A Comparative Study on Therapeutic Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma, Autologous Platelet-rich Fibrin Matrix, Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor, and Collagen Particles in Nonhealing Leg Ulcers. J. Cutan. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 16, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Bornstein, M.M.; Lambrichts, I.; Yu, H.Y.; Politis, C.; Jacobs, R. Platelet-rich plasma for regeneration of neural feedback pathways around dental implants: A concise review and outlook on future possibilities. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenfels, M.; Colome, L.; Sebben, A.D.; Braga-Silva, J. Effect of Platelet Rich Plasma and Platelet Rich Fibrin on sciatic nerve regeneration in a rat model. Microsurgery 2013, 33, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Anitua, E.; Delgado, D.; Sanchez, P.; Prado, R.; Orive, G.; Padilla, S. Platelet-rich plasma, a source of autologous growth factors and biomimetic scaffold for peripheral nerve regeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; He, C.; Jiang, L.; Quan, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Z. Effect of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) concentration on proliferation, neurotrophic function and migration of Schwann cells in vitro. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiyama-Elbert, S.E.; Hubbell, J.A. Controlled release of nerve growth factor from a heparin-containing fibrin-based cell ingrowth matrix. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2000, 69, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.J.; Rosenzweig, E.S.; McDonald, J.W., 3rd; Sakiyama-Elbert, S.E. Delivery of neurotrophin-3 from fibrin enhances neuronal fiber sprouting after spinal cord injury. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2006, 113, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Tatara, A.; McCreedy, D.A.; Shiu, A.; Sakiyama-Elbert, S.E. Tissue-engineered fibrin scaffolds containing neural progenitors enhance functional recovery in a subacute model of SCI. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 5127–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, J.; Vangansewinkel, T.; Gervois, P.; Merckx, G.; Hilkens, P.; Quirynen, M.; Lambrichts, I.; Bronckaers, A. Angiogenic Properties of ‘Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin’. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falnikar, A.; Stratton, J.; Lin, R.; Andrews, C.E.; Tyburski, A.; Trovillion, V.A.; Gottschalk, C.; Ghosh, B.; Iacovitti, L.; Elliott, M.B.; et al. Differential Response in Novel Stem Cell Niches of the Brain after Cervical Spinal Cord Injury and Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaj, V.; Butti, E.; Martino, G.; Panina-Bordignon, P. Endogenous neural stem cells characterization using omics approaches: Current knowledge in health and disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1125785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adugna, D.G.; Aragie, H.; Kibret, A.A.; Belay, D.G. Therapeutic Application of Stem Cells in the Repair of Traumatic Brain Injury. Stem Cells Cloning 2022, 15, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, H.J. The influence of platelet-rich fibrin on angiogenesis in guided bone regeneration using xenogenic bone substitutes: A study of rabbit cranial defects. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatova, L.; Campbell, R.G.; Elkhatib, A.H.; Schmidt, T.W.; Pinto, N.R.; Pinto, J.M.; Prevedello, D.M.; Ditzel Filho, L.F.; Otto, B.A.; Carrau, R.L. Role of Leukocyte-Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Endoscopic Endonasal Skull Base Surgery Defect Reconstruction. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2017, 78, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Jin, K.; Xie, L.; Childs, J.; Mao, X.O.; Logvinova, A.; Greenberg, D.A. VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapel, P.; Frielingsdorf, H.; Haggblad, J.; Zachrisson, O.; Brundin, P. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-BB) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) induce striatal neurogenesis in adult rats with 6-hydroxydopamine lesions. Neuroscience 2005, 132, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobolyi, A.; Vincze, C.; Pal, G.; Lovas, G. The neuroprotective functions of transforming growth factor beta proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8219–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Fan, Y.; Hao, Q.; Shen, F.; Hashimoto, T.; Yang, G.Y.; Gasmi, M.; Bartus, R.T.; Young, W.L.; Chen, Y. Postischemic IGF-1 gene transfer promotes neurovascular regeneration after experimental stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogister, B.; Delree, P.; Leprince, P.; Martin, D.; Sadzot, C.; Malgrange, B.; Munaut, C.; Rigo, J.M.; Lefebvre, P.P.; Octave, J.N.; et al. Transforming Growth-Factor-Beta as a Neuronoglial Signal during Peripheral Nervous-System Response to Injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 1993, 34, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Takagawa, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Shirakawa, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Sasahara, M. Platelet-derived growth factor-b expression induced after rat peripheral nerve injuries. Glia 2002, 38, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolin, L.M.; Verity, A.N.; Silver, J.E.; Shooter, E.M.; Abrams, J.S. Interleukin-6 production by Schwann cells and induction in sciatic nerve injury. J. Neurochem. 1995, 64, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, P.J.; Ma, J.; Callahan, M.; Northam, C.N.; Alton, T.B.; Sonntag, W.E.; Li, Z. Effect of locally delivered IGF-1 on nerve regeneration during aging: An experimental study in rats. Muscle Nerve 2010, 41, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Lopes, F.R.; Lisboa, B.C.; Frattini, F.; Almeida, F.M.; Tomaz, M.A.; Matsumoto, P.K.; Langone, F.; Lora, S.; Melo, P.A.; Borojevic, R.; et al. Enhancement of sciatic nerve regeneration after vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene therapy. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2011, 37, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.M. Biological responses to materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2001, 31, 81–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, M.A.; Waser, J.; Milleret, V.; Gerber, I.; Emmert, M.Y.; Foolen, J.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Schlottig, F.; Vogel, V. Synergistic interactions of blood-borne immune cells, fibroblasts and extracellular matrix drive repair in an in vitro peri-implant wound healing model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Swieringa, F.; de Laat, B.; de Groot, P.G.; Roest, M.; Heemskerk, J.W.M. Reversible Platelet Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 Activation and Thrombus Instability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, R.I.; Farrell, D.H.; Weisel, J.W.; Bennett, J.S. The Platelet Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 Differentially Interacts with Fibrin Versus Fibrinogen. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 7858–7867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Andia, I.; Zumstein, M.A.; Zhang, C.Q.; Pinto, N.R.; Bielecki, T. Classification of platelet concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF) for topical and infiltrative use in orthopedic and sports medicine: Current consensus, clinical implications and perspectives. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashank, B.; Bhushan, M. Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): The newest biomaterial and its use in various dermatological conditions in our practice: A case series. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollapudi, M.; Bajaj, P.; Oza, R.R. Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin—A Revolution in Periodontal Regeneration. Cureus 2022, 14, e28647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockerman, A.; Hendrickx, A.; Willekens, W.; Fehervary, H.; Vastmans, J.; Coucke, W.; Verhamme, P.; Politis, C.; Vanassche, T.; Braem, A.; et al. Mechanical properties and cellular content of leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin membranes of patients on antithrombotic drugs. J. Periodontal Res. 2022, 57, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downen, M.; Amaral, T.D.; Hua, L.L.; Zhao, M.L.; Lee, S.C. Neuronal death in cytokine-activated primary human brain cell culture: Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Glia 1999, 28, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theys, T.; Van Hoylandt, A.; Broeckx, C.E.; Van Gerven, L.; Jonkergouw, J.; Quirynen, M.; van Loon, J. Plasma-rich fibrin in neurosurgery: A feasibility study. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, W.M.; Mantuano, E.; Azmoon, P.; Henry, K.; Banki, M.; Kim, J.H.; Pizzo, D.P.; Gonias, S.L. Ionotropic glutamate receptors activate cell signaling in response to glutamate in Schwann cells. FASEB J. 2016, 31, 1744–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, W.; Song, L.; Fu, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Neuregulin-1beta regulates tyrosine kinase receptor expression in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons with excitotoxicity induced by glutamate. Regul. Pept. 2013, 180, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, F.; Fernandes, M.; Valente, S.G.; Santos, J.B.G.; Furukawa, R.B.; Fernandes, C.H.; Leite, V.M.; Faloppa, F. Platelet-Rich Fibrin Conduits as an Alternative to Nerve Autografts for Peripheral Nerve Repair. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2017, 33, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vares, P.; Dehghan, M.M.; Bastami, F.; Biazar, E.; Shamloo, N.; Heidari Keshel, S.; Khojasteh, A. Effects of Platelet-Rich Fibrin/Collagen Membrane on Sciatic Nerve Regeneration. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves Atti, V.; Fernandes, M.; Santiago de Lima Figueiredo, G.; Roth, F.; Gomes Valente, S.; Nakachima, L.R.; Fernandes, C.H.; Gomes Dos Santos, J.B. Peripheral nerve regeneration in rats using nerve graft in a vein conduit pre-filled with platelet-rich fibrin (PRF). Hand Surg. Rehabil. 2023, 42, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, C.W.; Barber, M.J.; Martin, J.; Mayfield, J.J.; Valenzuela, C.F. The mouse-equivalent of the human BDNF VAL66MET polymorphism increases dorsal hippocampal volume and does not interact with developmental ethanol exposure. Alcohol 2020, 86, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, F.; Malerba, F.; Ercole, B.B.; Lamba, D.; Cattaneo, A. A comparative analysis of the structural, functional and biological differences between Mouse and Human Nerve Growth Factor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1854, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilkens, P.; Bronckaers, A.; Ratajczak, J.; Gervois, P.; Wolfs, E.; Lambrichts, I. The Angiogenic Potential of DPSCs and SCAPs in an In Vivo Model of Dental Pulp Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 2582080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervois, P.; Ratajczak, J.; Wolfs, E.; Vangansewinkel, T.; Dillen, Y.; Merckx, G.; Bronckaers, A.; Lambrichts, I. Preconditioning of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells with Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin-Derived Factors Does Not Enhance Their Neuroregenerative Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 8589149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, W.; Sanen, K.; Georgiou, M.; Struys, T.; Bronckaers, A.; Ameloot, M.; Phillips, J.; Lambrichts, I. Human dental pulp stem cells can differentiate into Schwann cells and promote and guide neurite outgrowth in an aligned tissue-engineered collagen construct in vitro. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, L.; Pollard, S.M.; Gorba, T.; Reitano, E.; Toselli, M.; Biella, G.; Sun, Y.; Sanzone, S.; Ying, Q.L.; Cattaneo, E.; et al. Niche-independent symmetrical self-renewal of a mammalian tissue stem cell. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reekmans, K.P.; Praet, J.; De Vocht, N.; Tambuyzer, B.R.; Bergwerf, I.; Daans, J.; Baekelandt, V.; Vanhoutte, G.; Goossens, H.; Jorens, P.G.; et al. Clinical potential of intravenous neural stem cell delivery for treatment of neuroinflammatory disease in mice? Cell Transplant. 2011, 20, 851–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banker, G.; Goslin, K. Culturing Nerve Cells, 2nd ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; p. 666. [Google Scholar]
- Vangansewinkel, T.; Lemmens, S.; Tiane, A.; Geurts, N.; Dooley, D.; Vanmierlo, T.; Pejler, G.; Hendrix, S. Therapeutic administration of mouse mast cell protease 6 improves functional recovery after traumatic spinal cord injury in mice by promoting remyelination and reducing glial scar formation. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lambrichts, I.; Wolfs, E.; Bronckaers, A.; Gervois, P.; Vangansewinkel, T. The Effect of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Central and Peripheral Nervous System Neurons—Implications for Biomaterial Applicability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814314
Lambrichts I, Wolfs E, Bronckaers A, Gervois P, Vangansewinkel T. The Effect of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Central and Peripheral Nervous System Neurons—Implications for Biomaterial Applicability. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(18):14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814314
Chicago/Turabian StyleLambrichts, Ivo, Esther Wolfs, Annelies Bronckaers, Pascal Gervois, and Tim Vangansewinkel. 2023. "The Effect of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Central and Peripheral Nervous System Neurons—Implications for Biomaterial Applicability" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 18: 14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814314
APA StyleLambrichts, I., Wolfs, E., Bronckaers, A., Gervois, P., & Vangansewinkel, T. (2023). The Effect of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Central and Peripheral Nervous System Neurons—Implications for Biomaterial Applicability. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(18), 14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814314





