Nitric Oxide as a Determinant of Human Longevity and Health Span
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Adaptation and Aging
3. Nutrition and Health
4. Say NO to Aging
5. Aging and Oxidative Stress
6. Chrononutrition and Synchronisation
7. Determinants of Life and Health Span
8. Nitric Oxide Boosts Protective Tryptophan Pathways
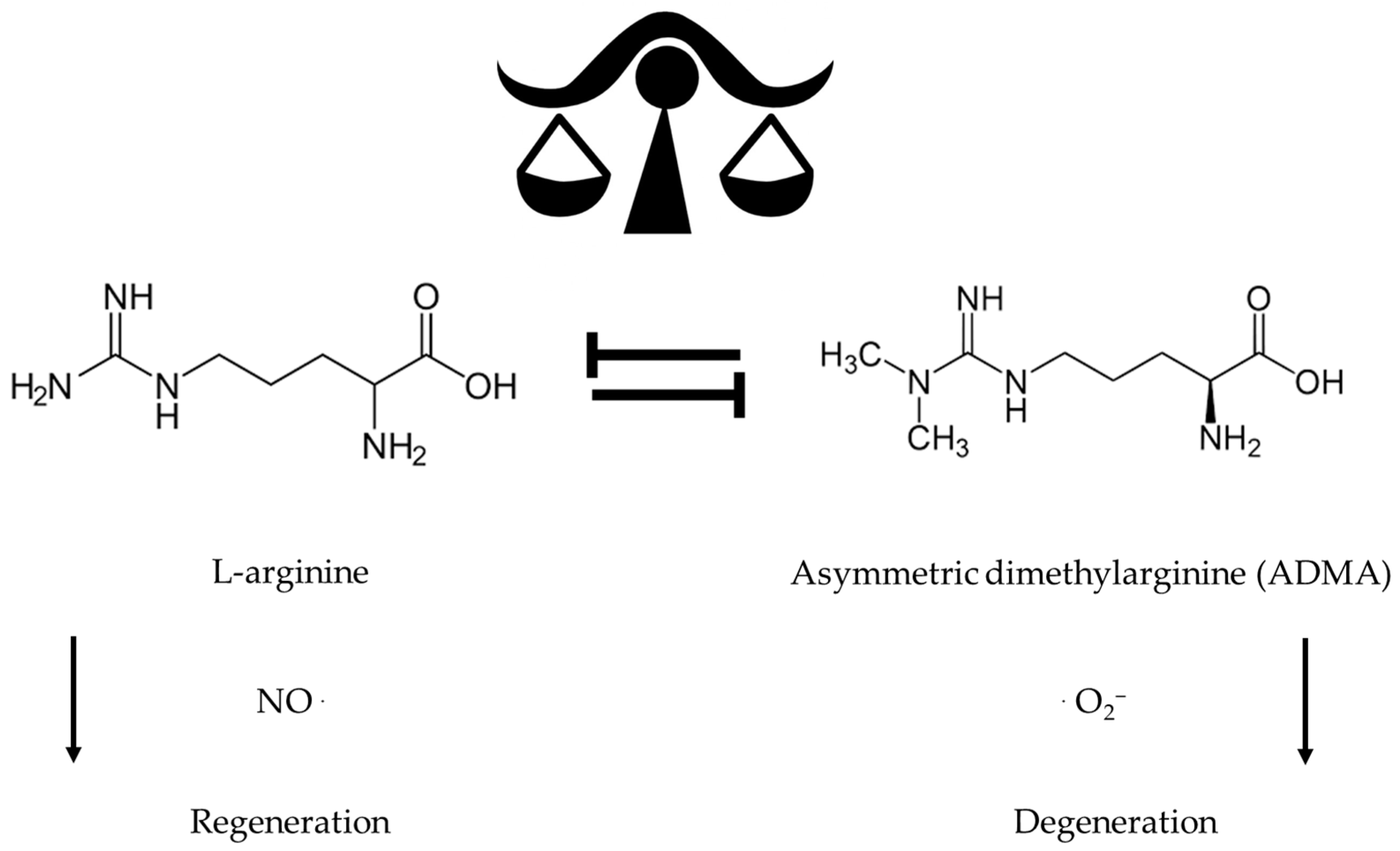
9. L-Arginine and B Vitamins Extend Health and Life Span
10. The Need for Sufficient NO Formation
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jankovic, A.; Korac, A.; Buzadzic, B.; Stanic, A.; Otasevic, V.; Ferdinandy, P.; Daiber, A.; Korac, B. Targeting the NO/superoxide ratio in adipose tissue: Relevance to obesity and diabetes management. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1570–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinkovich, A.; Livshits, G. Sarcopenic obesity or obese sarcopenia: A cross-talk between age-associated adipose tissue and skeletal muscle inflammation as a main mechanism of the pathogenesis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 200–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Han, M.; Rezaei, A.; Li, D.; Wu, G.; Ma, X. L-arginine modulates glucose and lipid metabolism in obesity and diabetes. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, T.; Senftleben, K.; Deumelandt, P.; Christen, O.; Riedel, K.; Langer, M. Healthcare costs associated with an adequate intake of sugars, salt and saturated fat in Germany: A health econometrical analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Milagro, F.I.; Allayee, H.; Chmurzynska, A.; Choi, M.S.; Curi, R.; Caterina, R.D.; Ferguson, L.R.; Goni, L.; Kang, J.X.; et al. Guide for current nutrigenetic, nutrigenomic, and nutriepigenetic approaches for precision nutrition involving the prevention and management of chronic diseases associated with obesity. J. Nutrigenet. Nutrigenom. 2017, 10, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Lluch, G.; Irusta, P.M.; Navas, P.; de Cabo, R. Mitochondrial biogenesis and healthy aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Functional amino acids in growth, reproduction, and health. Adv. Nutr. 2010, 1, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, D.A. Energy-responsive timekeeping. J. Genet. 2008, 87, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode-Böger, S.M.; Mike, J.; Surdacki, A.; Brabant, G.; Böger, R.H.; Frölich, J.C. Oral L-arginine improves endothelial function in healthy individuals older than 70 years. Vasc. Med. 2003, 8, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, C.J.; Ou, J.J.; Babish, J.G.; Lamb, J.J.; Eliason, S.; Brabazon, H.; Gao, W.; Kaadige, M.R.; Tripp, M.L. A 13-week low glycemic load diet and lifestyle modification program combining low glycemic load protein shakes and targeted nutraceuticals improved weight loss and cardio-metabolic risk factors. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 95, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic-Medic, D.; Perunicic-Pekuvic, G.; Rasic-Milotinovic, Z.; Takic, M.; Popovic, T.; Arsic, A.; Glibetic, M. Effects of dietary milled seed mixture on fatty acid status and inflammatory markers in patients on hemodialysis. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 563576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Therkildsen, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Lametsch, R. Exploration of collagen recovered from animal by-products as a precursor of bioactive peptides: Successes and challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2011–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, R.; Kerksick, C.M.; Campbell, B.I.; Cribb, P.J.; Wells, S.D.; Skwiat, T.M.; Purpura, M.; Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Ferrando, A.A.; Arent, S.M.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Protein and exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragon, A.A.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Wildmann, R.; Kleiner, S.; VanDusseldorp, T.; Taylor, L.; Earnest, C.P.; Arciero, P.J.; Wilborn, C.; Kalman, D.S.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Diets and body composition. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukagawa, N.K. Protein and amino acid supplementation in older humans. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 1493–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristina, K.; Langerholc, T.; Trapecar, M. Novel metabolic roles of L-arginine in body energy metabolism and possible clinical applications. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2014, 18, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Assar, M.; Angulo, J.; Santoz-Ruis, M.; de Adana, J.C.R.; Pindado, M.L.; Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Hernández, A.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) elevation and arginase up-regulation contribute to endothelial dysfunction related to insulin resistance in rats and morbidly obese humans. Physiol. J. 2016, 594, 3045–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, R.; Engelen, M.P.; Deutz, N.E. Role of specific dietary amino acids in clinical conditions. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S139–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiking, Y.C.; Ten Have, G.A.M.; Wolfe, R.R.; Deutz, N.E.P. Arginine de novo and nitric oxide production in disease states. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E1177–E1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, H. Site-specific antioxidative therapy for prevention of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 796891. [Google Scholar]
- Poeggeler, B. L-Arginin schützt vor nitrosativem Stress. [L-Arginine protects against nitrosative stress]. Perfusion 2012, 25, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Menzel, D.; Haller, H.; Wilhelm, M.; Robenek, H. L-Arginine and B vitamins improve endothelial function in subjects with mild to moderate blood pressure elevation. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reule, C.A.; Goyvaerts, B.; Schoen, C. Effects of an L-arginine-based multi ingredient product on endothelial function in subjects with mild to moderate hypertension and hyperhomocysteinemia—A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashtabi, A.; Mazloom, Z.; Fararouei, M.; Hejazi, N. Oral L-arginine administration improves anthropometric and biochemical indices associated with cardiovascular diseases in obese patients: A randomized, single blind placebo controlled clinical trial. Res. Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 5, e29419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeggeler, B. Melatonin, aging, and age-related diseases. Endocrine 2005, 27, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeggeler, B.; Sambamurti, K.; Siedlak, S.L.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Pappolla, M.A. A novel endogenous indole protects rodent mitochondria and extends rotifer lifespan. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosselin, M.; Poeggeler, B.; Durand, G. Nitrone derivatives as therapeutics: From chemical modification to specific-targeting. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 2006–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzarelli, F.; Maas, R.; Dattolo, P.; Tripepi, G.; Michelassi, S.; D’Arrigo, G.; Mieth, M.; Bandinelli, S.; Ferrucci, L.; Zoccali, C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine predicts survival in the elderly. Age 2013, 35, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverdlov, A.L.; Ngo, D.T.; Chan, W.P.; Chirkov, Y.Y.; Horowitz, J.D. Aging of the nitric oxide system: Are we as old as our NO? J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seljeflot, I.; Nilsson, B.B.; Westheim, A.S.; Bratseth, V.; Arnesen, H. The L-arginine–asymmetric dimethylarginine ratio is strongly related to the severity of chronic heart failure. No effects of exercise training. J. Card. Fail. 2011, 3, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Boit, M.; Tommasi, S.; Elliot, D.; Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Sibson, R.; Meakin, J.R.; Aspden, R.M.; Carru, C.; Mangoni, A.A.; et al. Sex Differences in the Associations between L-Arginine Pathway Metabolites, Skeletal Muscle Mass and Function, and their Responses to Resistance Exercise, in Old Age. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisoli, E.; Clementi, E.; Paolucci, C.; Cozzi, V.; Tonello, C.; Sciorati, C.; Bracale, R.; Valerio, A.; Francolini, M.; Moncada, S.; et al. Mitochondrial biogenesis in mammals: The role of endogenous nitric oxide. Science 2003, 299, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, C.F.; Ledo, A.; Barbosa, R.M.; Laranjinha, J. Neurovascular-neuroenergetic coupling axis in the brain: Master regulation by nitric oxide and consequences in aging and neurodegeneration. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangge, H.; Becker, K.; Fuchs, D.; Gostner, J.M. Antioxidants, inflammation and cardiovascular disease. World J. Cardiol. 2014, 6, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, A.B.; Engin, A. The Interactions Between Kynurenine, Folate, Methionine and Pteridine Pathways in Obesity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.W.; Terentis, A.C.; King, N.J.; Thomas, S.R. Role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in health and disease. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 601–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxenkrug, G. Interferon-gamma—Inducible Inflammation: Contribution to Aging and Aging-Associated Psychiatric Disorders. Aging Dis. 2011, 2, 474–486. [Google Scholar]
- Pappolla, M.; Sambamurti, K.; Vidal, R.; Pacheco-Quinto, J.; Poeggeler, B.; Matsubara, E. Evidence for lymphatic Aβ clearance in Alzheimer’s transgenic mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 71, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappolla, M.A.; Matsubara, E.; Vidal, R.; Pacheco-Quinto, J.; Poeggeler, B.; Zagorski, M.; Sambamurti, K. Melatonin Treatment Enhances Aβ Lymphatic Clearance in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Amyloidosis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondanelli, G.; Iacono, A.; Allegrucci, M.; Puccetti, P.; Grohmann, U. Immunoregulatory Interplay Between Arginine and Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, I.D.C.G.; Marchioni, D.M.L.; Carioca, A.A.F.; Bueno, V.; Colleoni, G.W.B. May critical molecular cross-talk between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) and arginase during human aging be targets for immunosenescence control? Immun. Aeging 2021, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A. Role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) and kynurenine pathway in the regulation of the aging process. Aeging Res. Rev. 2022, 75, 101573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappolla, M.A.; Perry, G.; Fang, X.; Zagorski, M.; Sambamurti, K.; Poeggeler, B. Indoles as essential mediators in the gut-brain axis. Their role in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 156, 105403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappolla, M.A.; Carare, R.O.; Poeggeler, B.; Wisniewski, T.; Sambamurti, K. The lymphatic system in neurological disease and Alzheimer’s disease. A brief editorial. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2022, 19, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeggeler, B.; Pappolla, M.A. Lupinenprotein mit Sanddorn und Acerola für eine optimale Stoffwechselsteuerung und Hirnleistung. [Lupin seed with sea buckthorn and acerola extract improves cognition and health]. FHM Bielef. 2020, 13, 107–150. [Google Scholar]
- Poeggeler, B.; Pappolla, M.A. Eine explorative Anwendungsbeobachtung zur Nährstoffergänzung in der Sportmedizin. Lupinenprotein mit Sanddorn und Acerola schützt vor gefährlicher RF-EMF Strahlung. [Lupin protein with sea buckthorn and acerola extract protects against RF-EMF radiation]. FHM Bielef. 2020, 13, 151–167. [Google Scholar]
- Poeggeler, B.; Robenek, H.; Pappolla, M.A. Editorial: Pharmacology of L-arginine and L-arginine-rich food. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 743788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeggeler, B.; Singh, S.K.; Pappolla, M.A. Tryptophan in nutrition and health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquarone, E.; Argyrousi, E.K.; van den Berg, M.; Gulisano, W.; Fà, M.; Staniszewski, A.; Calcagno, E.; Zuccarello, E.; D’Adamio, L.; Deng, S.-X.; et al. Synaptic and memory dysfunction induced by tau oligomers is rescued by upregulation of the nitric oxide cascade. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, B.S. The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway on healthy ageing: A review of pre-clinical and clinical data on the impact of dietary nitrate in the elderly. Front. Aging 2021, 2, 778467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendra, A.; Bondonno, N.P.; Rainey-Smith, S.R.; Gardener, S.L.; Hodgson, J.M.; Bondonno, C.P. Potential role of dietary nitrate in relation to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular health, cognition, cognitive decline and dementia: A review. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12572–12589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tropea, M.R.; Gulisano, W.; Vacanti, V.; Arancio, O.; Puzzo, D.; Palmeri, A. Nitric oxide/cGMP/CREB pathway and amyloid-beta crosstalk: From physiology to Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 193, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, Z.S.; Craighead, D.H.; Darvish, S.; Coppock, M.; Ludwig, K.R.; Brunt, V.E.; Seals, D.R.; Rossman, M.J. Promoting healthy cardiovascular aging: Emerging topics. J. Cardiovasc. Aging 2022, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresnajati, S.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Mündel, T.; Bernard, J.R.; Lin, H.-S.; Liao, Y.-H. Changes in arterial stiffness in response to various types of exercise modalities: A narrative review on physiological and endothelial senescence perspectives. Cells 2022, 11, 3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, O.M.; Clifford, T.; Seals, D.R.; Craighead, D.H.; Rossman, M.J. Nitric oxide, aging and aerobic exercise: Sedentary individuals to Master’s athletes. Nitric Oxide 2022, 125-126, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cai, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W.; Cui, C.; Ouyang, D.; Ye, J. Effect of seabuckthorn seed protein and its arginine-enriched peptides on combating memory impairment in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.O.; Mahoney, S.A.; Venkatasubramanian, R.; Seals, D.R.; Clayton, Z.S. Aging, aerobic exercise, and cardiovascular health: Barriers, alternative strategies and future directions. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 173, 112105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neacsu, M.; Vaughan, N.J.; Multari, S.; Haljas, E.; Scobbie, L.; Duncan, G.J.; Cantlay, L.; Fyfe, C.; Anderson, S.; Horgan, G.; et al. Hemp and buckwheat are valuable sources of dietary amino acids, beneficially modulating gastrointestinal hormones and promoting satiety in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeggeler, B.; Singh, S.K.; Sambamurti, K.; Pappolla, M.A. Umkehrung des Alterungsprozesses durch eine neuartige Supplementation mit Aminosäuren und Ketosäuren. [Rejuvenation by a supplementation with amino and keto acids]. FHM Bielef. 2023, 15, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka, Y.; Nakaya, J. Effect of oral administration of L-arginine on senile dementia. Am. J. Med. 2000, 108, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirodaria, C.; Antoniades, C.; Lee, J.; Jackson, C.E.; Robson, M.D.; Francis, J.M.; Moat, S.J.; Ratnatunga, C.; Pillai, R.; Refsum, H.; et al. Global improvement of vascular function and redox state with low-dose folic acid. Implications for folate therapy in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 2007, 115, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, J.; Khondkar, W.; Morelli, M.; Wang, X.; Santulli, G.; Trimarco, V. Arginine and Endothelial Function. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosroshahi, M.Z.; Asbaghi, O.; Moradi, S.; Kelishadi, M.R.; Kaviani, M.; Mardani, M.; Jalili, C. The effects of supplementation with L-arginine on anthropometric indices and body composition in overweight or obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 71, 104022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Talebi, M.; Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Samarghandian, S.; Bernatoniene, J. An Overview of NO Signaling Pathways in Aging. Molecules 2021, 26, 4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Wan, S.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Xu, T.; He, J.; Mechanick, J.I.; Wu, W.-C.; et al. Micronutrient Supplementation to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 2269–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraseb, F.; Asbaghi, O.; Bagheri, R.; Wong, A.; Figueroa, A.; Mirzaei, K. Effect of l-arginine supplementation on blood pressure in adults: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 1226–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A. Activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in Alzheimer’s disease: Role of tryptophan metabolites generated by gut host-microbiota. J. Mol. Med 2023, 101, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Song, J.; Gao, J.; Cheng, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Adipocyte-derived kynurenine promotes obesity and insulin resistance by activating the AhR/STAT3/IL-6 signaling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bie, J.; Guest, J.; Guillemin, G.J.; Grant, R. Central kynurenine pathway shift with age in woman. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y.; Guo, Y.-C.; Zhou, H.-F.; Yue, T.-T.; Wang, F.-X.; Sun, F.; Wang, W.-Z. Arginine metabolism regulates the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 81, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannur, J.; Harel, S.; Granit, R. Nitric oxide as an antioxidant. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1991, 289, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, J.; Osaki, T. Involvement of nitric oxide in protecting against radical species and autoregulation of M1-polarized macrophages through metabolic remodeling. Molecules 2023, 28, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhir, A.; Kulkarni, S.K. Nitric oxide and major depression. Nitric Oxide 2011, 24, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Kaimori, J.-Y.; Isaka, Y. Plant-dominant low protein diet: A potential alternative dietary practice for patients with chronic kidney disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorissen, S.H.M.; Crombag, J.J.R.; Senden, J.M.G.; Waterval, W.A.H.; Bierau, J.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.C. Protein content and amino acid composition of commercially available plant-based protein isolates. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Klebach, M.; Visser, M.; Hofman, Z. Amino acid availability of a dairy and vegetable protein blend compared to single casein, whey, soy, and pea proteins: A double-blind, cross-over trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.D.; Mah, E.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Dey, P.; Labyk, A.N.; Villamena, F.A.; Volek, J.S.; Bruno, R.S. Dairy milk proteins attenuate hyperglycemia-induced impairments in vascular endothelial function in adults with prediabetes by limiting increases in glycemia and oxidative stress that reduce nitric oxide bioavailability. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 63, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.Z. Anti-aging effects of L-arginine. J. Adv. Res. 2010, 1, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, C.A.; Bradshaw, P.C. Amino acids in the regulation of aging and aging-related diseases. Transl. Med. Aging 2019, 3, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allerton, T.D.; Proctor, D.N.; Stephens, J.M.; Tammy, R.; Dugas, T.R.; Spielmann, G.; Irving, B.A. L-Citrulline supplementation: Impact on cardiometabolic health. Nutrients 2018, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Homoarginine in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2023, 26, 42–49, online ahead of print, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katic, Z.S.; d’Uscio, L.V.; He, T. Emerging roles of endothelial nitric oxide in preservation of cognitive health. Stroke 2023, 54, 686–696. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, A.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Q. LC-MS/MS insight into vitamin C restoration to metabolic disorder evoked by amyloid in Caenorhabditis elegans CL2006. Metabolites 2022, 12, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondanelli, G.; Bianchi, R.; Pallotta, M.T.; Orabona, C.; Albini, E.; Iacono, A.; Belladonna, M.L.; Vacca, C.; Fallarino, F.; Macchiarulo, A.; et al. A Relay Pathway between Arginine and Tryptophan Metabolism Confers Immunosuppressive Properties on Dendritic Cells. Immunity 2017, 46, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaric, B.L.; Radovanovic, J.N.; Gluvic, Z.; Stewart, A.J.; Essack, M.; Motwalli, O.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Atherosclerosis linked to aberrant amino acid metabolism and immunosuppressive amino acid catabolizing enzymes. Front. Immunol. 2000, 11, 551758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Miranda, R.B.; Weimer, P.; Rossi, R.C. Effects of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation on skin aging: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Puig, D.; Costa-Larrión, E.; Rubio-Rodríguez, N.; Gálvez-Martín, P. Collagen supplementation for joint health: The link between composition and scientific knowledge. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, M.; Naughton, R.J.; Clifford, T.; Harper, L.D.; Corr, L. The effects of collagen peptide supplementation on body composition, collagen synthesis, and recovery from joint injury and exercise: A systematic review. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghshi, S.; Sadeghi, O.; Willett, W.C.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Dietary intake of total, animal, and plant proteins and risk of all cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: Systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2020, 370, m2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lépine, G.; Fouillet, H.; Rémond, D.; Huneau, J.F.; Mariotti, F.; Polakof, S. A Scoping Review: Metabolomics Signatures Associated with Animal and Plant Protein Intake and Their Potential Relation with Cardiometabolic Risk. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 2112–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poeggeler, B.; Singh, S.K.; Sambamurti, K.; Pappolla, M.A. Nitric Oxide as a Determinant of Human Longevity and Health Span. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914533
Poeggeler B, Singh SK, Sambamurti K, Pappolla MA. Nitric Oxide as a Determinant of Human Longevity and Health Span. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(19):14533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914533
Chicago/Turabian StylePoeggeler, Burkhard, Sandeep Kumar Singh, Kumar Sambamurti, and Miguel A. Pappolla. 2023. "Nitric Oxide as a Determinant of Human Longevity and Health Span" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 19: 14533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914533
APA StylePoeggeler, B., Singh, S. K., Sambamurti, K., & Pappolla, M. A. (2023). Nitric Oxide as a Determinant of Human Longevity and Health Span. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(19), 14533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914533








