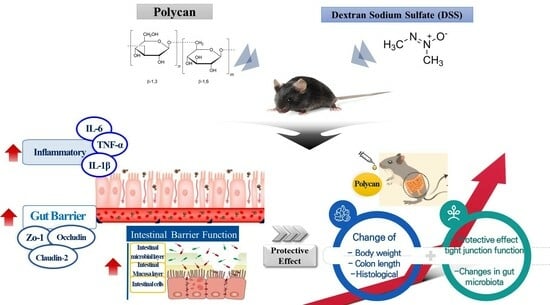
Effect of Polycan, a β-Glucan from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001, on Inflammatory Response and Intestinal Barrier Function in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Polycan of the Physiological Efficacy on DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
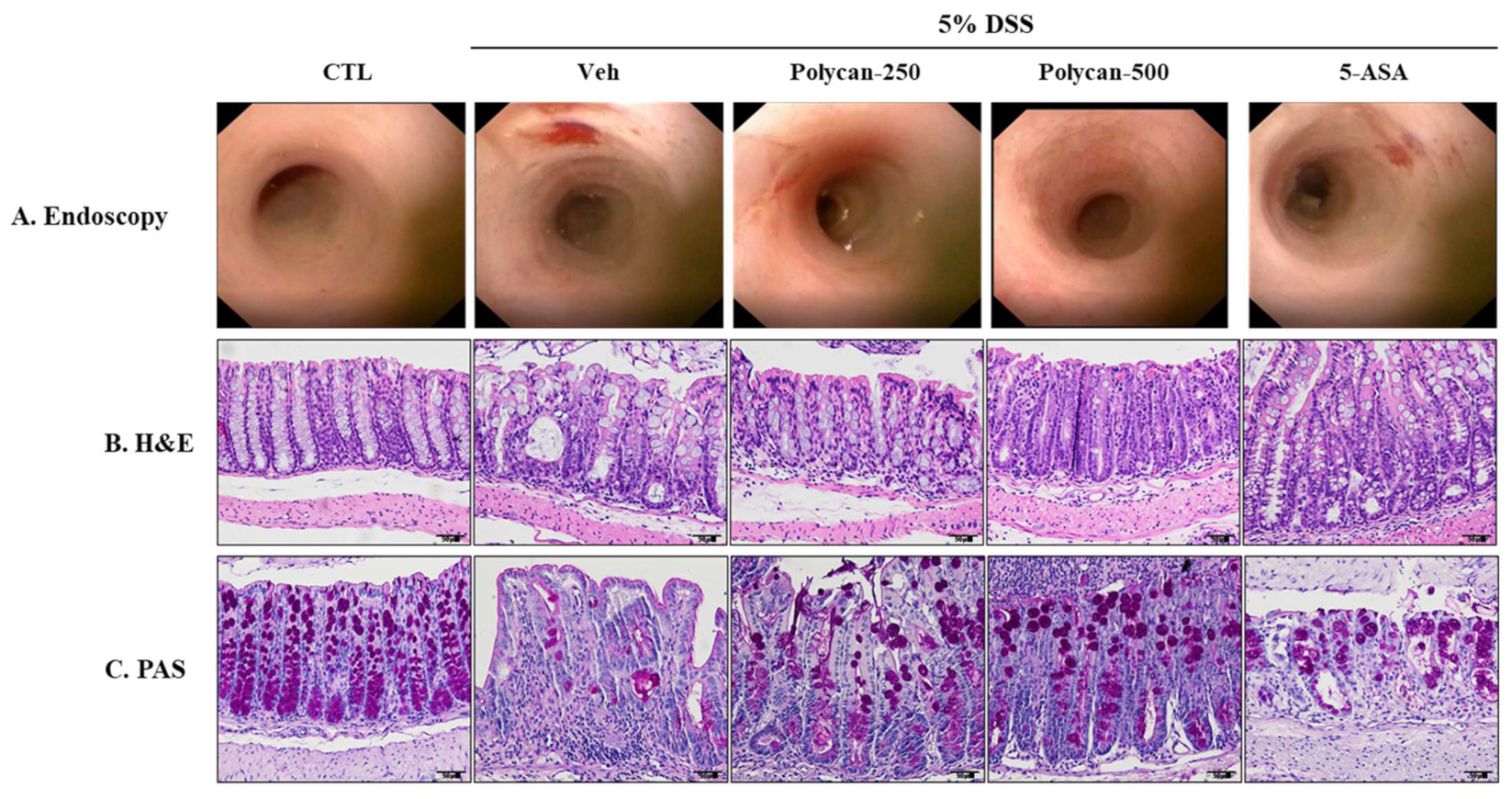
2.2. Effects of Polycan on the Histopathological Changes of DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
2.3. Effects of Polycan of Proinflammatory Cytokines in DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
2.4. Changes in the Expression of Genes Associated with Intestinal Barrier Function, Apoptosis Markers, and Tight Junction Proteins in DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
2.5. Effects of Polycan on Apoptosis in DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
2.6. Effects of Polycan on Decreasing MPO Activity in DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
2.7. Effects of Polycan on Intestinal Microbial Composition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of Polycan
4.3. Mice and Treatment
4.4. Analysis of Epithelial Paracellular Permeability
4.5. Endoscopy of the Large Intestine and Histological Analysis
4.6. Determination of Serum Cytokines of ELISA and MPO Activity
4.7. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
4.8. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) of Colon Tissue
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Feces Collection and 16S rRNA Sequencing of Intestinal Microbiota Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuoka, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Ueno, F.; Matsui, T.; Hirai, F.; Inoue, N.; Kato, J.; Kobayashi, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Koganei, K.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for inflammatory bowel disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 305–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, R.J.; Podolsky, D.K. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2007, 448, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jess, T.; Rungoe, C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: A meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.K.; Yun, S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Chang, D.K.; Kim, J.S.; Song, I.S.; Park, J.B.; et al. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in the Songpa-Kangdong district, Seoul, Korea, 1986–2005: A KASID study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.K.; Yue, G.G.L.; Chiu, P.W.Y.; Lau, C.B.S. A Review of the Effects of Natural Compounds, Medicinal Plants, and Mushrooms on the Gut Microbiota in Colitis and Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudter, J.; Neurath, M.F. IL-6 signaling in inflammatory bowel disease: Pathophysiological role and clinical relevance. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerr, R.H.; Taylor, K.D.; Brant, S.R.; Rioux, J.D.; Silverberg, M.S.; Daly, M.J.; Steinhart, A.H.; Abraham, C.; Regueiro, M.; Griffiths, A.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science 2006, 314, 1461–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Luo, Y.; Chen, W.; He, M.; Deng, J.H.; Zhao, N.; Cao, L.; Wang, L. FAM96A Protects Mice from Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS)-Induced Colitis by Preventing Microbial Dysbiosis. Front. Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019, 9, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, S.; Kumar, P.; Mohan, H.; Goyal, S.; Sharma, K.K. Inflammatory bowel disease: Tri-directional relationship between microbiota, immune system and intestinal epithelium. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, S.M.; McLean, L.P.; Cross, R.K. Adverse events in IBD therapy: The 2018 update. Expert Rev. Gastroent. 2018, 12, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, E.H.; Kim, J.H.; Sung, N.Y.; Choi, J.I.; Lim, S.T.; Kim, K.H.; Yook, H.S.; Byun, M.W.; Lee, J.W. Effects of gamma irradiation on the physical and structural properties of beta-glucan. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2008, 77, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.C.; Chan, W.K.; Sze, D.M. The effects of beta-glucan on human immune and cancer cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacha, U.; Nasir, M.; Iqbal, S.; Anjum, A.A. Nutraceutical, Anti-Inflammatory, and Immune Modulatory Effects of beta-Glucan Isolated from Yeast. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8972678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.S.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, H.R.; Moon, S.B.; Shin, H.D.; Yang, K.J.; Lee, H.S.; Kwon, Y.S.; Ku, S.K. Immunomodulatory Effects of Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001 Exopolymers on Cyclophosphamide-Treated Mice. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lim, J.M.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, K.I.; Oh, T.W. Extracellular polysaccharides purified (Polycan) from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001 improves pathophysiology of dystrophin-deficient mdx mice. Mol. Cell Toxicol. 2022, 18, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Cho, H.R.; Park, D.C.; Jung, G.W.; Ku, S.K.; Choi, J.S. Extracellular polysaccharides purified from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001 (Polycan) inhibit dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1245–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Shin, H.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Ku, S.K.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, J.W. Effect of Polycalcium, a mixture of Polycan and calcium lactate-gluconate in a 1:9 weight ratio, on rats with surgery-induced osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.A.; Yu, D.Y.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lim, J.M.; Lee, S.S.; Yun, C.H.; Choi, I.S.; et al. Effect of oral administration of beta-glucans derived from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001 in model mice and rat with atopic dermatitis-like phenotypes. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S.; Fiocchi, C. MEDICAL PROGRESS Ulcerative Colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, G.R.; Rutgeerts, P. Importance of mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, B.A.; Gokhale, R.; Cho, J.H. Clinical aspects and pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Sans, M.; Fiocchi, C. Inflammatory bowel disease: The role of environmental factors. Autoimmun. Rev. 2004, 3, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Liu, L.; Lin, P.; Dong, X.; Ni, L.; Che, H.; Xie, W. Saccharina japonica Ethanol Extract Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis via Reshaping Intestinal Microenvironment and Alleviating Inflammatory Response. Foods 2023, 12, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichele, D.D.; Kharbanda, K.K. Dextran sodium sulfate colitis murine model: An indispensable tool for advancing our understanding of inflammatory bowel diseases pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6016–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, H.; Neurath, M.F.; Atreya, R. Role of the IL23/IL17 Pathway in Crohn’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 622934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, M.H.; Neurath, M.F.; Durum, S.K. Targeting Interleukins for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease-What Lies Beyond Anti-TNF Therapy? Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, W. The Protective Role of Scorias spongiosa Polysaccharide-Based Microcapsules on Intestinal Barrier Integrity in DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Foods 2023, 12, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.C. Microbiota dysbiosis and barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancers: Exploring a common ground hypothesis. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelblum, K.L.; Turner, J.R. The tight junction in inflammatory disease: Communication breakdown. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawki, A.; McCole, D.F. Mechanisms of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction by Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 3, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarur, A.J.; Bruss, A.; Nunez, L.; Berens, B.; Beniwal-Patel, P.; Abreu, M.T.; Colombel, J.F.; Deepak, P.; Melmed, G. Therapy with Biologic: Agents Is Not Associated with Significant Changes in Body Composition Parameters in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: The Results of a Prospective Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, S960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar, S.; Engstrom, K.; Jagervall, A.; Martinez, V. Psychological stress reactivates dextran sulfate sodium-induced chronic colitis in mice. Stress 2008, 11, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, N.S.; Kim, S.; Sundby, M.; Chandran, P.; Burks, S.R.; Paz, A.H.; Frank, J.A. Temporal clinical, proteomic, histological and cellular immune responses of dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4341–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.L.; Fan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, F.; Li, M.Y.; Zhou, H.F.; Guo, W.N.; Zhang, Z.L.; Kang, Z.Y.; Gui, Y.; et al. Berberine ameliorates DSS-induced intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction through microbiota-dependence and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 1381–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.L.; Ni, J.D.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.T.; Karim, N.; Chen, W. Mulberry Anthocyanins Ameliorate DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis by Improving Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Zhao, H.A.; Cheng, N.; Cao, W. Rape bee pollen alleviates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis by neutralizing IL-1 beta and regulating the gut microbiota in mice. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, P.K.; Singh, K.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. A Review on Chemical-Induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models in Rodents. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalinger, M.R.; Schwarzfischer, M.; Hering, L.; Shawki, A.; Sayoc, A.; Santos, A.; Gottier, C.; Lang, S.; Babler, K.; Geirnaert, A.; et al. Loss of PTPN22 abrogates the beneficial effect of cohousing-mediated fecal microbiota transfer in murine colitis. Mucosal. Immunol. 2019, 12, 1336–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Son, J.D.; Hwang, S.J.; Lee, J.K.; Park, J.Y.; Park, K.I.; Oh, T.W. Fermented Glutinous Rice Extract Mitigates DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis by Alleviating Intestinal Barrier Function and Improving Gut Microbiota and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Do, H.J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Oh, T.W. Effect of Polycan, a β-Glucan from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001, on Inflammatory Response and Intestinal Barrier Function in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914773
Do HJ, Kim Y-S, Oh TW. Effect of Polycan, a β-Glucan from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001, on Inflammatory Response and Intestinal Barrier Function in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(19):14773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914773
Chicago/Turabian StyleDo, Hyun Ju, Young-Suk Kim, and Tae Woo Oh. 2023. "Effect of Polycan, a β-Glucan from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001, on Inflammatory Response and Intestinal Barrier Function in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 19: 14773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914773
APA StyleDo, H. J., Kim, Y.-S., & Oh, T. W. (2023). Effect of Polycan, a β-Glucan from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001, on Inflammatory Response and Intestinal Barrier Function in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(19), 14773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914773