Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients: Characterization and Cellular Effects
Abstract
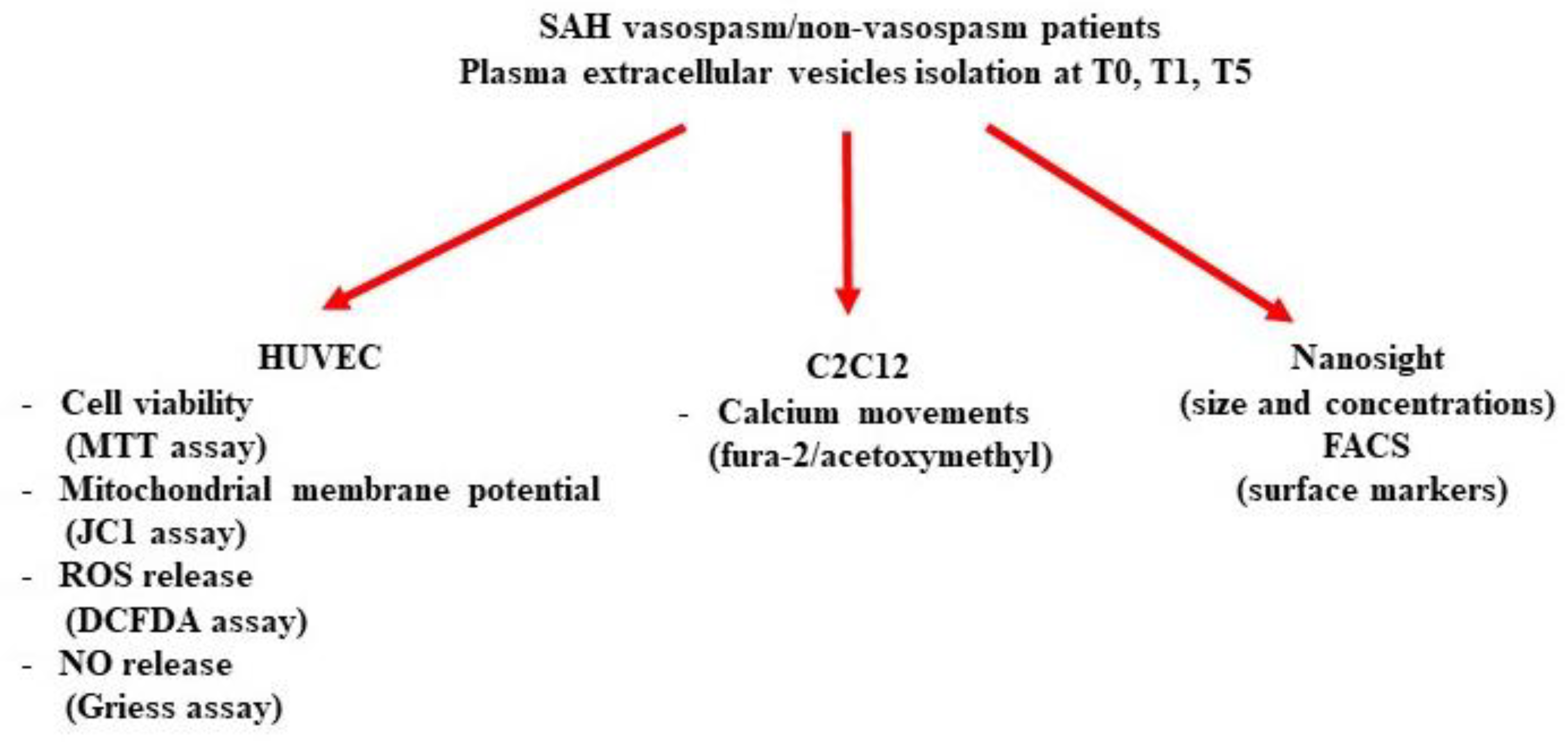
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients and Setting
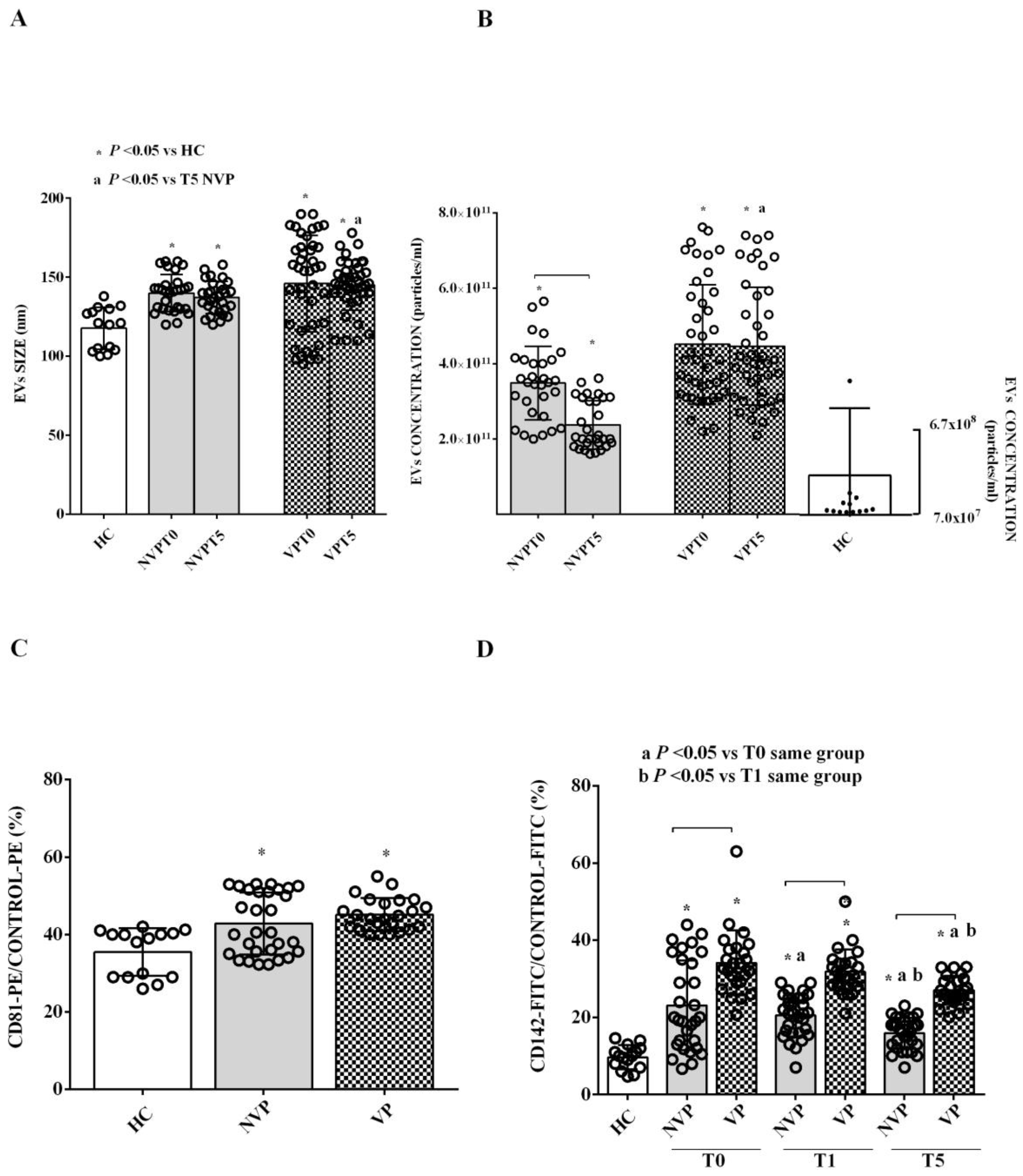
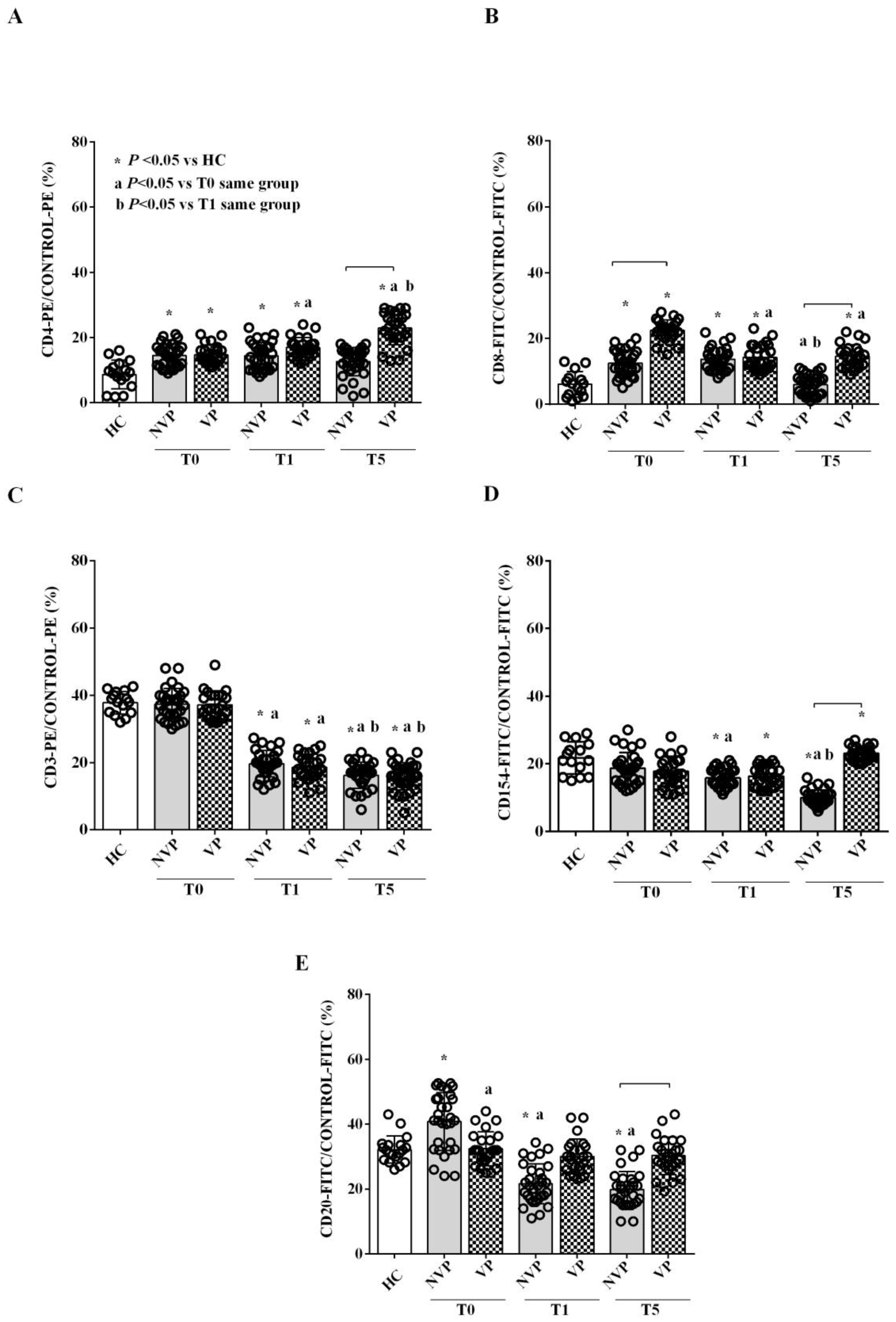
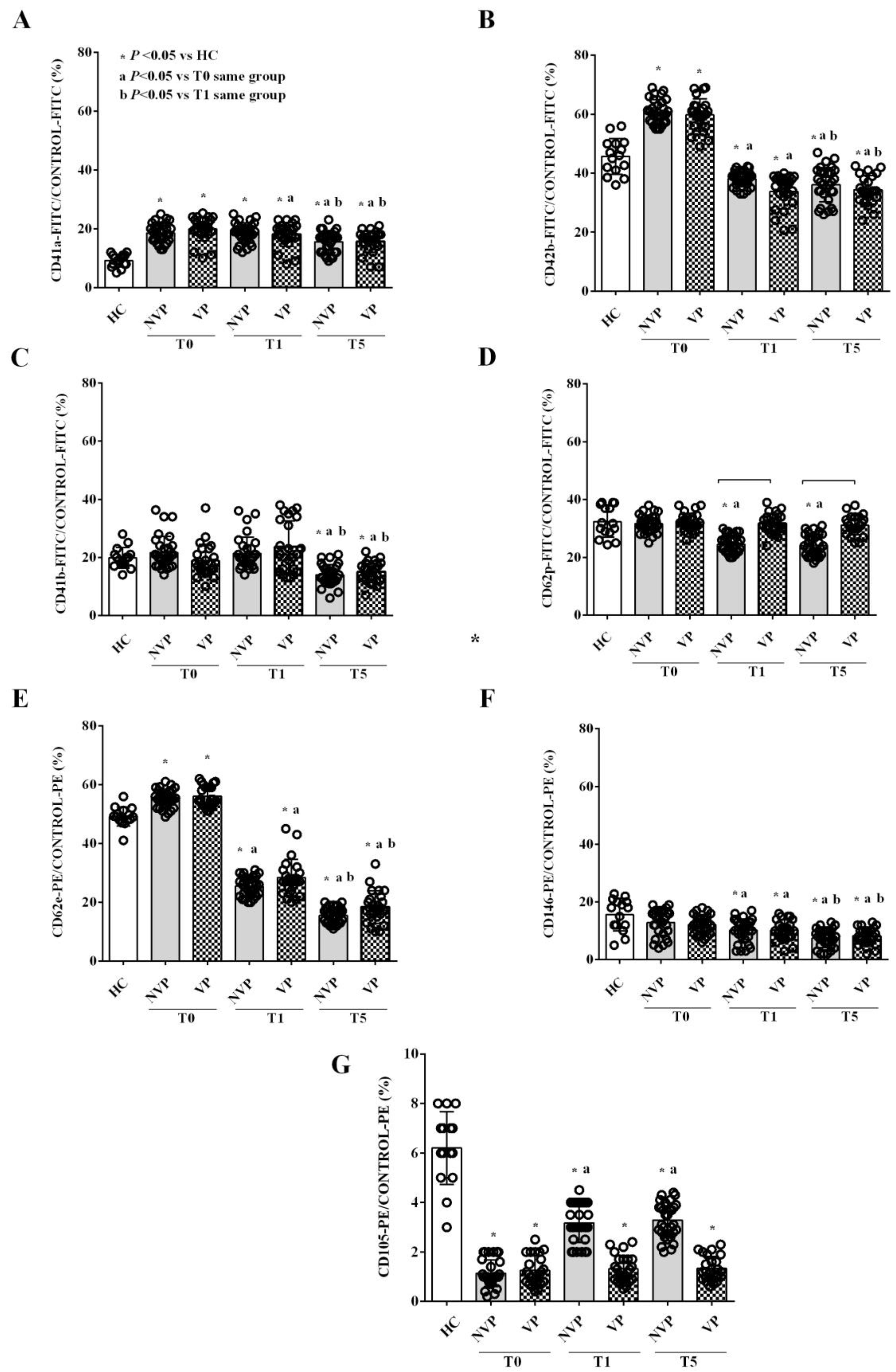
2.2. Characterization of Circulating EVs
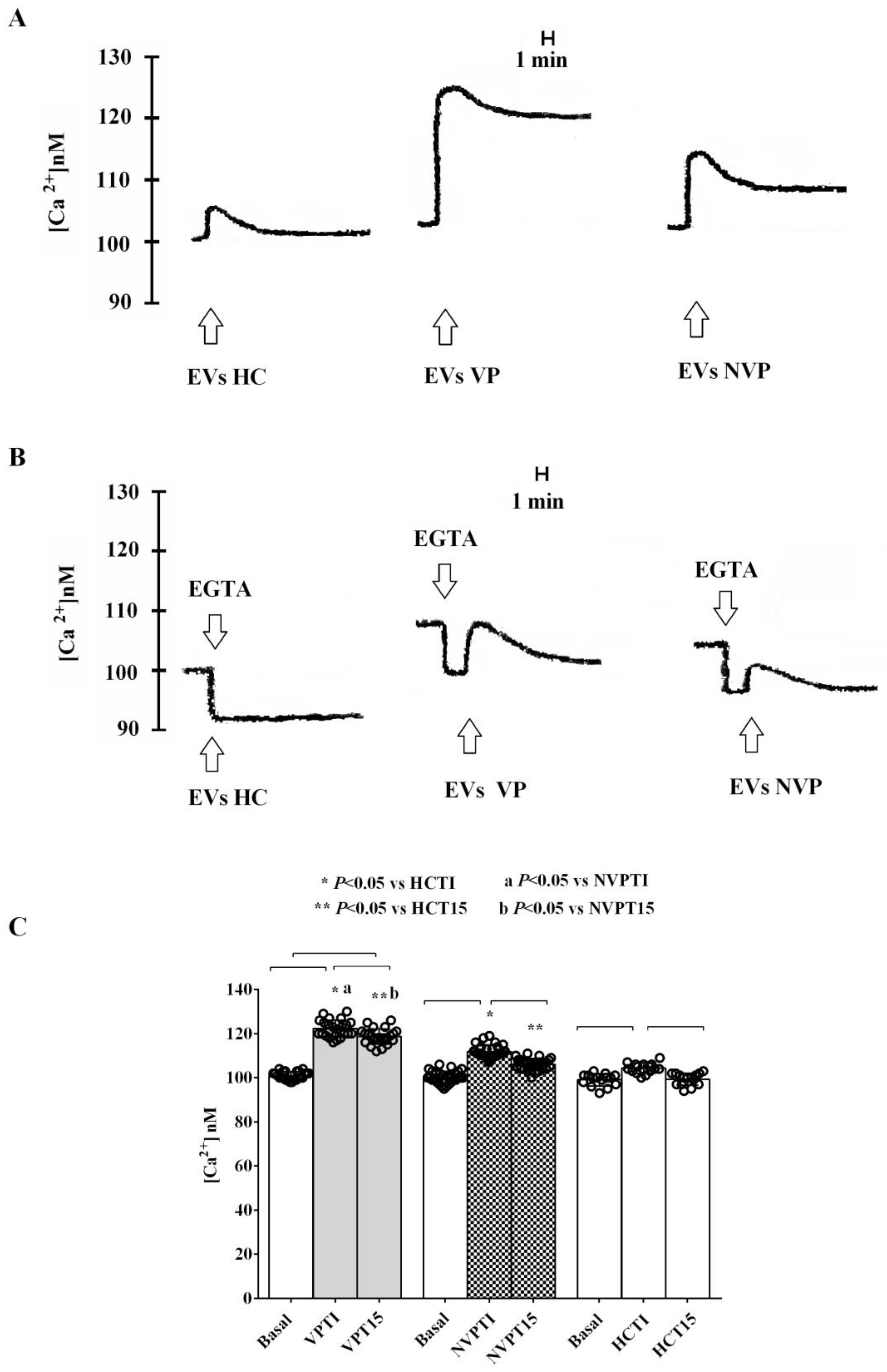
2.3. In Vitro Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Blood Sample Collection
4.3. EVs Isolation
4.4. EVs Characterization
4.5. Human Umbilical Vascular Endothelial Cells (HUVECs) and Smooth Muscle Cells (SMCs)
4.6. MTT Assay
4.7. JC-1 Assay
4.8. DCFDA Assay
4.9. NO Release
4.10. Measurement of [Ca2+]c by Fura-2 Fluorescence
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Claassen, J.; Park, S. Spontaneous Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. Lancet 2022, 400, 846–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, N.K.; Linn, F.H.H.; van der Plas, J.A.; Algra, A.; Rinkel, G.J.E. Incidence of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: A Systematic Review with Emphasis on Region, Age, Gender and Time Trends. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etminan, N. Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage--Status Quo and Perspective. Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaastra, B.; Alexander, S.; Bakker, M.K.; Bhagat, H.; Bijlenga, P.; Blackburn, S.; Collins, M.K.; Doré, S.; Griessenauer, C.; Hendrix, P.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Clinical Outcome After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: Protocol. Transl. Stroke Res. 2022, 13, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neifert, S.N.; Chapman, E.K.; Martini, M.L.; Shuman, W.H.; Schupper, A.J.; Oermann, E.K.; Mocco, J.; Macdonald, R.L. Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: The Last Decade. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021, 12, 428–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, R.L. Delayed Neurological Deterioration after Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassell, N.F.; Sasaki, T.; Colohan, A.R.; Nazar, G. Cerebral Vasospasm Following Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke 1985, 16, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budohoski, K.P.; Guilfoyle, M.; Helmy, A.; Huuskonen, T.; Czosnyka, M.; Kirollos, R.; Menon, D.K.; Pickard, J.D.; Kirkpatrick, P.J. The Pathophysiology and Treatment of Delayed Cerebral Ischaemia Following Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulters, D.; Gaastra, B.; Zolnourian, A.; Alexander, S.; Ren, D.; Blackburn, S.L.; Borsody, M.; Doré, S.; Galea, J.; Iihara, K.; et al. Haemoglobin Scavenging in Intracranial Bleeding: Biology and Clinical Implications. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, J.; Calvert, J.W.; Zhang, J.H. Mechanisms of Early Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2006, 26, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H. Inflammation: A Good Research Target to Improve Outcomes of Poor-Grade Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019, 10, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke-Wold, B.P.; Logsdon, A.F.; Manoranjan, B.; Turner, R.C.; McConnell, E.; Vates, G.E.; Huber, J.D.; Rosen, C.L.; Simard, J.M. Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Neuroinflammation: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettinger, S.; Lackner, P. Cellular Microparticles in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P. The Nature and Significance of Platelet Products in Human Plasma. Br. J. Haematol. 1967, 13, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, J.W.; Schmidtmann, M.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. The Ins and Outs of Microvesicles. FASEB Bioadv 2021, 3, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Ratajczak, J. Extracellular Microvesicles/Exosomes: Discovery, Disbelief, Acceptance, and the Future? Leukemia 2020, 34, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-H.; Chu, K.; Lee, S.-T.; Park, H.-K.; Bahn, J.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, M.; Kun Lee, S.; Roh, J.-K. Circulating Endothelial Microparticles as a Marker of Cerebrovascular Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Dong, X.-Q. High Concentrations of Procoagulant Microparticles in the Cerebrospinal Fluid and Peripheral Blood of Patients with Acute Basal Ganglia Hemorrhage Are Associated with Poor Outcome. Surg. Neurol. 2009, 72, 481–489; discussion 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanborn, M.R.; Thom, S.R.; Bohman, L.-E.; Stein, S.C.; Levine, J.M.; Milovanova, T.; Maloney-Wilensky, E.; Frangos, S.; Kumar, M.A. Temporal Dynamics of Microparticle Elevation Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, P.; Dietmann, A.; Beer, R.; Fischer, M.; Broessner, G.; Helbok, R.; Marxgut, J.; Pfausler, B.; Schmutzhard, E. Cellular Microparticles as a Marker for Cerebral Vasospasm in Spontaneous Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke 2010, 41, 2353–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter Solár, P.; Zamani, A.; Lakatosová, K.; Joukal, M. The blood-brain barrier and the neurovascular unit in subarachnoid hemorrhage: Molecular events and potential treatments. Fluids Barriers CNS 2022, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hop, J.W.; Rinkel, G.J.; Algra, A.; van Gijn, J. Quality of Life in Patients and Partners after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke 1998, 29, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Hasue, M.; Ito, H. Does Traumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Caused by Diffuse Brain Injury Cause Delayed Ischemic Brain Damage? Comparison with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Caused by Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Neurosurgery 1998, 43, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.T.; Vates, G.E. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, J.A.; Claassen, J.; Schmidt, J.M.; Wartenberg, K.E.; Temes, R.; Connolly, E.S.; MacDonald, R.L.; Mayer, S.A. Prediction of Symptomatic Vasospasm after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: The Modified Fisher Scale. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, 21–27; discussion 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsch, N.W.; King, M.T. A Review of Cerebral Vasospasm in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Part I: Incidence and Effects. J. Clin. Neurosci. 1994, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassell, N.F.; Torner, J.C.; Haley, E.C.; Jane, J.A.; Adams, H.P.; Kongable, G.L. The International Cooperative Study on the Timing of Aneurysm Surgery. Part 1: Overall Management Results. J. Neurosurg. 1990, 73, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, E.S.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Carhuapoma, J.R.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Dion, J.; Higashida, R.T.; Hoh, B.L.; Kirkness, C.J.; Naidech, A.M.; Ogilvy, C.S.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2012, 43, 1711–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, F.G.; Ogilvy, C.S. Efficacy of Prophylactic Nimodipine for Delayed Ischemic Deficit after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Metaanalysis. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 84, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Lai, N.; Tao, T.; Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Zhu, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Hang, C. Diagnosis Potential of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using MiRNA Signatures Isolated from Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1090389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichana, K.L.; Pradilla, G.; Huang, J.; Tamargo, R.J. Role of Inflammation (Leukocyte-Endothelial Cell Interactions) in Vasospasm after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2010, 73, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.A.; Turan, N.; Chau, M.; Pradilla, G. Inflammation, Vasospasm, and Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 384342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.C.; Davids, A.-M.; Brandenburg, S.; Müller, A.; Elke, A.; Magrini, S.; Atangana, E.; Turkowski, K.; Finger, T.; Gutenberg, A.; et al. Microglia Inflict Delayed Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 130, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbok, R.; Schiefecker, A.J.; Beer, R.; Dietmann, A.; Antunes, A.P.; Sohm, F.; Fischer, M.; Hackl, W.O.; Rhomberg, P.; Lackner, P.; et al. Early Brain Injury after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Multimodal Neuromonitoring Study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Yi, J.; Zhou, T.; Gong, X.; Jiang, H.; Yao, X. Toward Understanding Non-Coding RNA Roles in Intracranial Aneurysms and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Transl. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L.; Yang, L.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, X.; Tang, B.; Duan, J.; Wu, X.; et al. MiRNA Profiling of Circulating Small Extracellular Vesicles From Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Rats Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybycien-Szymanska, M.M.; Yang, Y.; Ashley, W.W. Microparticle derived proteins as potential biomarkers for cerebral vasospasm post subarachnoid hemorrhage. A preliminary study. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 141, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amabile, N.; Guérin, A.P.; Leroyer, A.; Mallat, Z.; Nguyen, C.; Boddaert, J.; London, G.M.; Tedgui, A.; Boulanger, C.M. Circulating endothelial microparticles are associated with vascular dysfunction in patients with end-stage renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 11, 3381–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Bezerra, L.M.; Filler, S.G. Endothelial Cells, Tissue Factor and Infectious Diseases. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2003, 36, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E.; Borgiani, B.; Verderio, C.; Furlan, R. Microvesicles: Novel Biomarkers for Neurological Disorders. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuharić, J.; Grabušić, K.; Tokmadžić, V.S.; Štifter, S.; Tulić, K.; Shevchuk, O.; Lučin, P.; Šustić, A. Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Induces Early Changes in the Physical Properties and Protein Composition of Intracranial Extracellular Vesicles. J. Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Chen, S.; Klebe, D.; Zhang, J.H.; Tang, J. Adhesion Molecules in CNS Disorders: Biomarker and Therapeutic Targets. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonsatti, E.; Maio, M. Highlights on Endoglin (CD105): From Basic Findings towards Clinical Applications in Human Cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2004, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- arnell, J.L.; Rieder, S.A.; Ettinger, R.; Kolbeck, R. Targeting the CD40-CD40L Pathway in Autoimmune Diseases: Humoral Immunity and Beyond. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 141, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L. Endothelial Microparticles Act as Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Biomarkers of Circulatory Hypoxia-Related Diseases: A Literature Review. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1698–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrage, A.; Loddenkemper, C.; Erben, U.; Lauer, U.; Hausdorf, G.; Jungblut, P.R.; Johnson, J.; Knolle, P.A.; Zeitz, M.; Hamann, A.; et al. Murine CD146 Is Widely Expressed on Endothelial Cells and Is Recognized by the Monoclonal Antibody ME-9F1. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshkon, A.; Heim, X.; Dubrou, C.; Bachelier, R.; Traboulsi, W.; Stalin, J.; Fayyad-Kazan, H.; Badran, B.; Foucault-Bertaud, A.; Leroyer, A.S.; et al. Role of CD146 (MCAM) in Physiological and Pathological Angiogenesis-Contribution of New Antibodies for Therapy. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Lenahan, C.; Chen, S. New Mechanisms and Targets of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Focus on Mitochondria. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 1278–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayer, R.E.; Zhang, J.H. Oxidative Stress in Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: Significance in Acute Brain Injury and Vasospasm. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2008, 104, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsushige, H.; Ostrowski, R.P.; Tsubokawa, T.; Colohan, A.; Zhang, J.H. Role of C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase in Early Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 1436–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Chen, W.; Kanamaru, K.; Zhang, J.H. Recombinant Osteopontin in Cerebral Vasospasm after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Leung, S.W. S Vascular nitric oxide: Beyond eNOS. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 129, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, S.; Osuka, K.; Takata, T.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Coordination between Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II and Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase in Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.P.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhao, R.; Lin, C.X.; Sun, K.Y.; Yan, C.P.; Zhou, X.; Cao, J.M. Silica nanomaterials induce organ injuries by Ca2+-ROS-initiated disruption of the endothelial barrier and triggering intravascular coagulation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ti-wari, M.; Prasad, S.; Shrivastav, T.G.; Chaube, S.K. Calcium signaling during meiotic cell cycle regulation and apoptosis in mammalian oocytes. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurada, R.; Odagiri, K.; Hakamata, A.; Kamiya, C.; Wei, J.; Watanabe, H. Calcium Release from Endoplasmic Reticulum In-volves Calmodulin-Mediated NADPH Oxidase-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, M.G.; Moretto, L.; Licari, I.; Esposito, T.; Capuano, L.; Olivieri, C.; Benech, A.; Brucoli, M.; Avanzi, G.C.; Cammarota, G.; et al. Osteopontin in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Severe Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Cells 2019, 8, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, W.E.; Hess, R.M. Surgical Risk as Related to Time of Intervention in the Repair of Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 1968, 28, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Report of World Federation of Neurological Surgeons Committee on a Universal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Grading Scale. J. Neurosurg. 1988, 68, 985–986. [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, G.; Jennett, B. Assessment of Coma and Impaired Consciousness. A Practical Scale. Lancet 1974, 2, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, C.M.; Kistler, J.P.; Davis, J.M. Relation of Cerebral Vasospasm to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Visualized by Computerized Tomographic Scanning. Neurosurgery 1980, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennett, B.; Bond, M. Assessment of Outcome after Severe Brain Damage. Lancet 1975, 1, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, J. Cerebral Vascular Accidents in Patients over the Age of 60. II. Prognosis. Scott. Med. J. 1957, 2, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzin, R.; Stasi, A.; Sallustio, F.; Bruno, S.; Merlotti, G.; Quaglia, M.; Grandaliano, G.; Pontrelli, P.; Thurman, J.M.; Camussi, G.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from patients with antibody-mediated rejection induce tu-bular senescence and endothelial to mesenchymal transition in renal cells. Am. J. Transplant. 2022, 22, 2139–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Koch, B.; Morikawa, K.; Suda, G.; Sakamoto, N.; Rueschenbaum, S.; Akhras, S.; Dietz, J.; Hildt, E.; Zeuzem, S.; et al. Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Induce Long-Lasting Immunity Against Hepatitis C Virus Which Is Blunted by Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossini, E.; Smirne, C.; Venkatesan, S.; Tonello, S.; D’Onghia, D.; Minisini, R.; Cantaluppi, V.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Comi, C.; Tanzi, A.; et al. Plasma Pattern of Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Hepatitis C Virus Patients and Their Effects on Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudia Cavallari, C.; Dellepiane, S.; Fonsato, V.; Medica, D.; Marengo, M.; Migliori, M.; Quercia, A.D.; Pitino, A.; Formica, M.; Panichi, V.; et al. Online Hemodiafiltration Inhibits Inflammation-Related Endothelial Dysfunction and Vascular Calcification of Uremic Patients Modulating miR-223 Expression in Plasma Extracellular Vesicles. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 2372–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossini, E.; Garhwal, D.; Venkatesan, S.; Ferrante, D.; Mele, A.; Saraceno, M.; Scognamiglio, A.; Mandrioli, J.; Amedei, A.; De Marchi, F.; et al. The Potential Role of Peripheral Oxidative Stress on the Neurovascular Unit in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Pathogenesis: A Preliminary Report from Human and In Vitro Evaluations. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossini, E.; Concina, D.; Rinaldi, C.; Russotto, S.; Garhwal, D.; Zeppegno, P.; Gramaglia, C.; Kul, S.; Panella, M. Association Between Plasma Redox State/Mitochondria Function and a Flu-Like Syndrome/COVID-19 in the Elderly Admitted to a Long-Term Care Unit. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 707587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossini, E.; Garhwal, D.P.; Calamita, G.; Romito, R.; Rigamonti, C.; Minisini, R.; Smirne, C.; Surico, D.; Bellan, M.; Pirisi, M. Exposure to Plasma From Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients Affects Hepatocyte Viability, Generates Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Modulates Pathways Involved in Fat Accumulation and Inflammation. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 693997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farruggio, S.; Cocomazzi, G.; Marotta, P.; Romito, R.; Surico, D.; Calamita, G.; Bellan, M.; Pirisi, M.; Grossini, E. Genistein and 17β-Estradiol Protect Hepatocytes from Fatty Degeneration by Mechanisms Involving Mitochondria, Inflammasome and Kinases Activation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 54, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surico, D.; Ercoli, A.; Farruggio, S.; Raina, G.; Filippini, D.; Mary, D.; Minisini, R.; Surico, N.; Pirisi, M.; Grossini, E. Modulation of Oxidative Stress by 17 β-Estradiol and Genistein in Human Hepatic Cell Lines In Vitro. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cillà, S.; Farruggio, S.; Cocomazzi, G.; Mary, D.; Alkabes, M.; Rossetti, L.; Vujosevic, S.; Grossini, E. Aflibercept and Ranibizumab Modulate Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Function by Acting on Their Cross Talk with Vascular Endothelial Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 54, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grynkiewicz, G.; Poenie, M.; Tsien, R.Y. A New Generation of Ca2+ Indicators with Greatly Improved Fluorescence Properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossini, E.; Molinari, C.; Sigaudo, L.; Biella, M.; Mary, D.S.G.; Vacca, G. Calcium Handling in Porcine Coronary Endothelial Cells by Gastrin-17. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 50, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossini, E.; Caimmi, P.P.; Platini, F.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F.; Cattaneo, M.; Valente, G.; Mary, D.A.S.G.; Vacca, G.; Tessitore, L. Modulation of Programmed Forms of Cell Death by Intracoronary Levosimendan during Regional Myocardial Ischemia in Anesthetized Pigs. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2010, 24, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lötvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzás, E.I.; Di Vizio, D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, J.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell Vesicles. 2014, 22, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Demographic and Clinical Characteristics | All Patients n = 18 | Healthy Controls n = 5 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 54.5 (71–47.5) | 53 (46.5–61.5) | 0.5 |
| Sex | >0.99 | ||
| Male (%) | 8 (44) | 2 (40) | |
| Female (%) | 10 (56) | 3 (60) | |
| Comorbidities | >0.99 | ||
| Hypertension (%) | 6 (33) | 1 (20) | |
| Cardiovascular disease (%) | 2 (11) | 0 (0) | |
| Respiratory disease (%) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | |
| Chronic kidney disease (%) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | |
| Cancer (%) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | |
| Other (%) | 4 (22) | 1 (20) |
| Demographic and Clinical Characteristics | All Patients n = 18 | Vasospasm Patients n = 8 | Non-Vasospasm Patients n = 10 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 54.5 (71–47.5) | 49.5 (52.8–43.5) * | 70.5 (73.5–57.8) * | 0.003 |
| Sex | 0.19 | |||
| Male (%) | 8 (44) | 2 (25) | 6 (60) | |
| Female (%) | 10 (56) | 6 (75) | 4 (40) | |
| Aneurysm site | 0.08 | |||
| MCA (%) | 4 (22) | 3 (37.5) | 1 (10) | |
| ACA (%) | 6 (33) | 4 (50) | 2 (20) | |
| BA (%) | 3 (17) | 1 (12.5) | 2 (20) | |
| Other (%) | 5 (28) | 0 (0) | 5 (50) | |
| Aneurysm treatment | 0.61 | |||
| Surgical clipping (%) | 5 (28) | 3 (38) | 2 (20) | |
| Endovascular coiling (%) | 13 (72) | 5 (62) | 8 (80) | |
| GCS at ICU admission | 7 (9–6) | 8 (9–4) | 7 (10–6) | 0.71 |
| WFNS scale at ICU admission | 4.5 (5–4) | 4 (5–4) | 5 (5–3.5) | 0.63 |
| Fisher scale at ICU admission | 3.5 (4–3) | 3 (3–3) | 4 (4–3.8) | 0.06 |
| HHS at ICU admission | 4 (5–3) | 4 (5–3) | 4.5 (5–3) | 0.64 |
| ICU LOS (d) | 21 (33.5–11) | 18.5 (34.5–11) | 22 (33–12.3) | 0.88 |
| Hospital LOS (d) | 29 (46.3–14) | 19 (42.5–11) | 36.5 (50–12.3) | 0.25 |
| mRS | >0.99 | |||
| 3 months | 6 (6–4) | 6 (6–5.3) | 5 (6–3.5) | |
| 6 months | 6 (6–4) | 6 (6–4.5) | 5 (6–3.5) | |
| GOS-E | >0.99 | |||
| 3 months | 1 (3–1) | 1 (2.5–1) | 3 (3–1) | |
| 6 months | 1 (3–1) | 1 (2.5–1) | 3 (3–1) |
| T0 | T1 | T5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NVP | VP | NVP | VP | NVP | VP | |
| CD4 | 5.8 | 6 | 4.2 | 4.9 | 3 | 5 |
| CD8 | 5 | 5.6 | 5.8 | 6.5 | 3 | 6 |
| CD42b | 14 | 15 | 13.4 | 16.4 | 11 | 13.5 |
| CD142 | 11 | 13 | 8.3 | 14.5 | 9 | 11 |
| CD20 | 10.7 | 11 | 10.5 | 11.3 | 10 | 11.3 |
| CD41a | 4,7 | 7 | 6.5 | 7 | 4 | 5.7 |
| CD41b | 8 | 11 | 8.4 | 9.6 | 5 | 5.9 |
| CD3 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 7.7 | 6.8 | 8.5 | 6.6 |
| CD154 | 5.3 | 4.8 | 6,1 | 6.3 | 4.6 | 6.5 |
| CD62e | 14 | 5 | 11.1 | 4 | 17 | 7.3 |
| CD62p | 8.7 | 10.4 | 9.2 | 11.5 | 8.9 | 15 |
| CD146 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 6 | 2 |
| CD105 | 1 | 0.5 | 5 | 1 | 10 | 4.2 |
| T0 | T1 | T5 | p | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basal | EGTA | EVs | Basal | EGTA | EVs | Basal | EGTA | EVs | ||
| VP | 100 ± 3.4 | 91.5 ± 2.4 * | 99.4 ± 3.1 * | 101 ± 2.9 | 93 ± 3.2 * | 100.8 ± 2.7 * | 100.4 ± 2.7 | 92.2 ± 3.2 * | 93.3 ± 3.3 * | * <0.05 |
| NVP | 99.4 ± 2 | 91.2 ± 2.3 * | 95.5 ± 1.6 * | 100 ± 2.1 | 91.7 ± 1.8 * | 94.8 ± 1.7 * | 100.8 ± 2.7 | 92.4 ± 3.1 * | 92.6 ± 3 * | * <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grossini, E.; Esposito, T.; Viretto, M.; Venkatesan, S.; Licari, I.; Surico, D.; Della Corte, F.; Castello, L.; Bruno, S.; Quaglia, M.; et al. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients: Characterization and Cellular Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914913
Grossini E, Esposito T, Viretto M, Venkatesan S, Licari I, Surico D, Della Corte F, Castello L, Bruno S, Quaglia M, et al. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients: Characterization and Cellular Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(19):14913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914913
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrossini, Elena, Teresa Esposito, Michela Viretto, Sakthipriyan Venkatesan, Ilaria Licari, Daniela Surico, Francesco Della Corte, Luigi Castello, Stefania Bruno, Marco Quaglia, and et al. 2023. "Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients: Characterization and Cellular Effects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 19: 14913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914913
APA StyleGrossini, E., Esposito, T., Viretto, M., Venkatesan, S., Licari, I., Surico, D., Della Corte, F., Castello, L., Bruno, S., Quaglia, M., Comi, C., Cantaluppi, V., & Vaschetto, R. (2023). Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients: Characterization and Cellular Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(19), 14913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914913










