Evolutionary Landscape of Tea Circular RNAs and Its Contribution to Chilling Tolerance of Tea Plant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
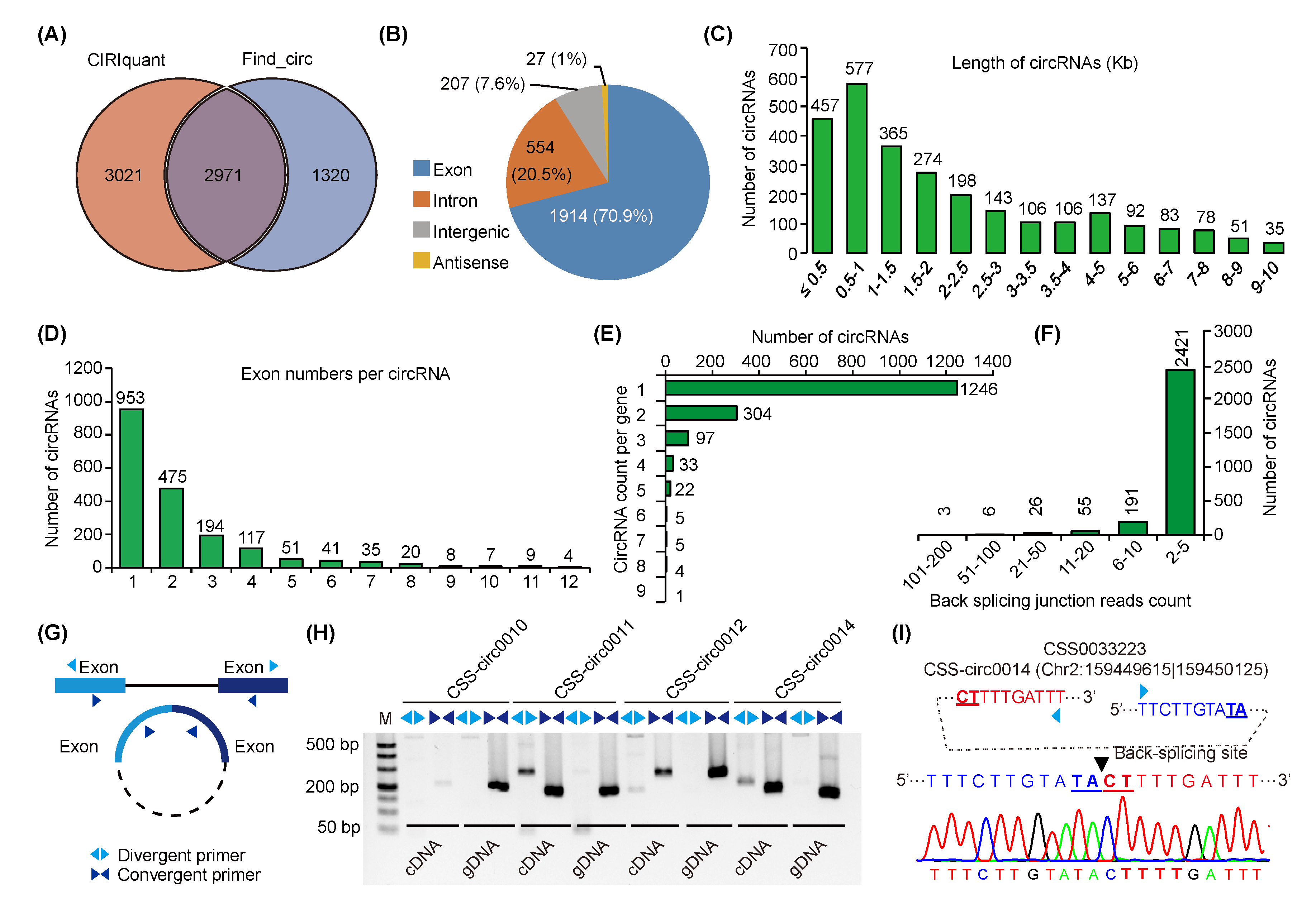
2.1. Characterization and Validation of circRNAs in Tea Plants under Chilling Stress
2.2. Conservation Assessment of circRNAs between Tea Plant and Other Plant Species
2.3. Circularization of Tea Plant circRNAs Is Affected by TE-Mediated DNA Methylation in Flanking Introns
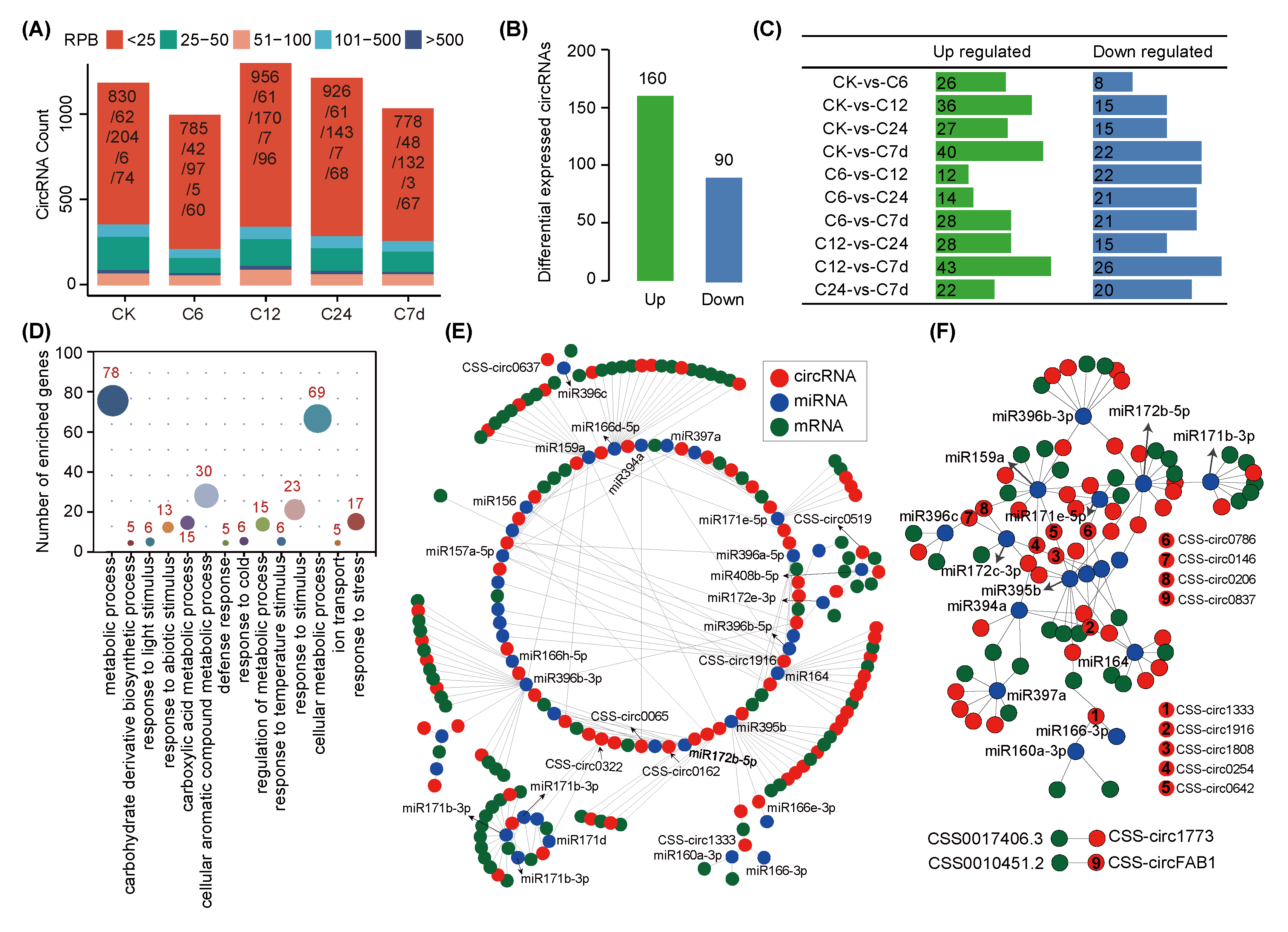
2.4. Expression Response of Tea Plant circRNAs to Chilling Stress
2.5. Tea Plant circRNAs Function as miRNAs Sponges during Chilling Stress
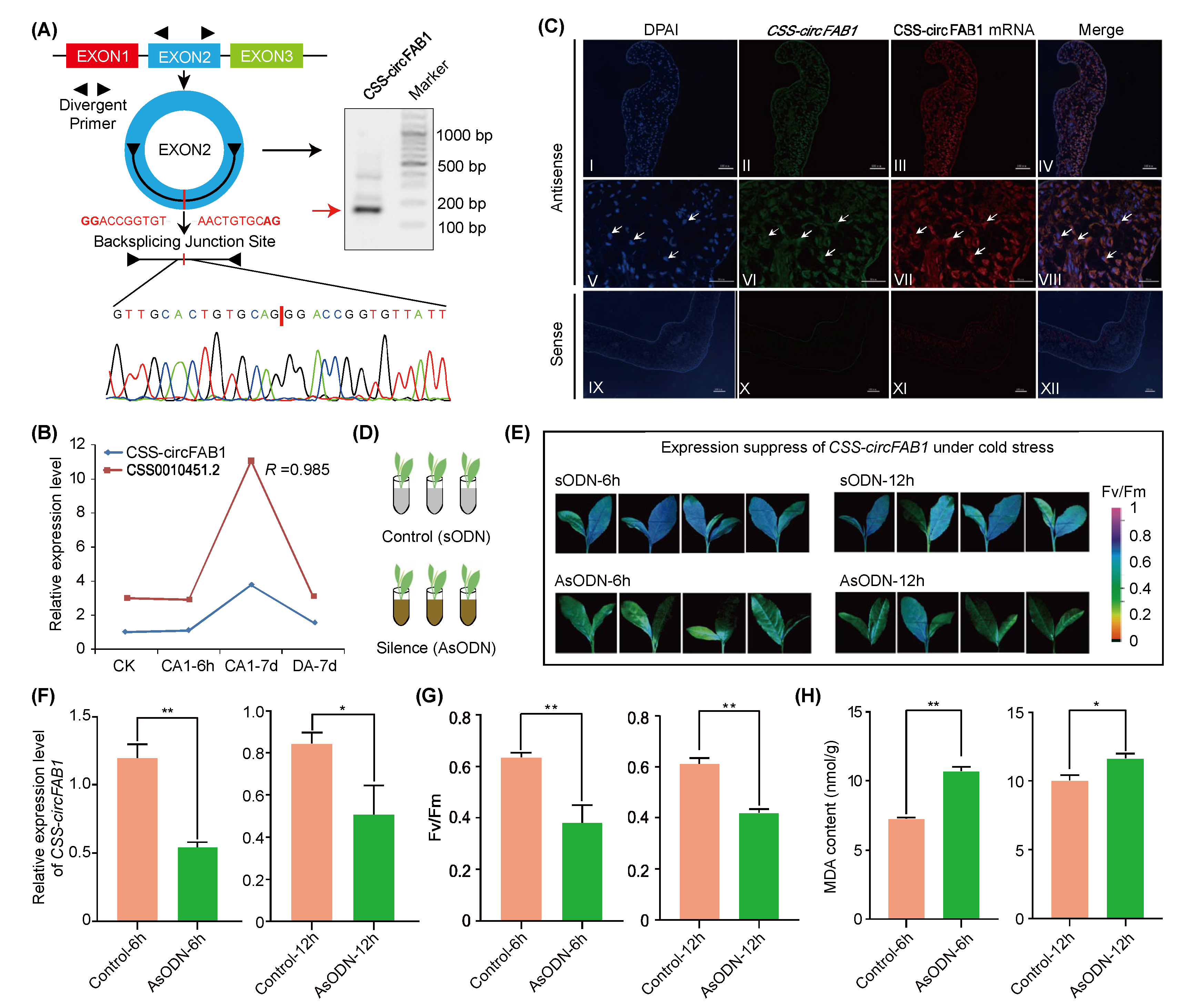
2.6. CSS-circFAB1 Contributes to Tea Plant Cold Tolerance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Chilling Treatment
4.2. CircRNA Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.3. Conservation Analysis of Tea Plant circRNAs
4.4. Sequence Validation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assays
4.5. Expression and Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.6. miRNA Identification and Prediction of Interaction Network
4.7. Gene Suppression and FISH Experiment
4.8. Statistics Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Ho, C.T.; Zhou, J.; Santos, J.S.; Armstrong, L.; Granato, D. Chemistry and Biological Activities of Processed Camellia sinensis Teas: A Comprehensive Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F 2019, 18, 1474–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, E.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Sheng, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.J.; Kim, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, W.; et al. The tea tree genome provides insights into tea flavor and independent evolution of caffeine biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, M.; Hao, Y.J.; Kapoor, A.; Dong, C.H.; Fujii, H.; Zheng, X.W.; Zhu, J.K. A R2R3 type MYB transcription factor is involved in the cold regulation of CBF genes and in acquired freezing tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37636–37645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.K. Gene regulation during cold acclimation in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2006, 126, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.J. Research progress on resistance breeding of tea plant. J. Tea Sci. 2003, 23, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.N.; Yue, C.; Cao, H.L.; Qian, W.J.; Hao, X.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, L.; Ding, C.Q.; Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.J. Transcriptome sequencing dissection of the mechanisms underlying differential cold sensitivity in young and mature leaves of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis). J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 224, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Ban, Q.Y.; Zhu, X.X.; Jiang, C.J.; Wei, C.L.; Bennetzen, J.L. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals gene expression associated with cold adaptation in the tea plant Camellia sinensis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, W.; Li, R.P.; Huang, J.; Zhao, H.J.; Ge, R.H.; Wu, Q.; Mallano, A.I.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, F.D.; Deng, W.W.; et al. Divergent DNA methylation contributes to duplicated gene evolution and chilling response in tea plants. Plant J. 2021, 106, 1312–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Ma, C.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Cao, H.L.; Kong, Y.M.; Yue, C.; Hao, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Ma, J.Q.; et al. Global transcriptome profiles of Camellia sinensis during cold acclimation. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, S.; Li, Y.; Ding, Z. Integrated RNA-seq and sRNA-seq analysis identifies chilling and freezing responsive key molecular players and pathways in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Wei, C.L.; Deng, W.W. CsICE1 and CsCBF1: Two transcription factors involved in cold responses in Camellia sinensis. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.N.; Hao, X.Y.; Cao, H.L.; Ding, C.Q.; Yang, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.C. ABA-dependent bZIP transcription factor, CsbZIP18, from Camellia sinensis negatively regulates freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, N.; Gao, T.; Jin, J.; Jing, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wan, X.; Schwab, W.; Song, C. Sesquiterpene glucosylation mediated by glucosyltransferase UGT91Q2 is involved in the modulation of cold stress tolerance in tea plants. New Phytol. 2019, 226, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X.; Song, C.; Zou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Fang, W.; Li, X. Identification and characterization of cold-responsive microRNAs in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) and their targets using high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Xu, X.; Ye, C.Y.; Zhu, Q.H.; Guo, L.; Fan, L. Recent origination of circular RNAs in plants. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, M.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Zhao, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, C.; et al. Characterization and Cloning of Grape Circular RNAs Identified the Cold Resistance-Related Vv-circATS1. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 966–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Yu, J.; Hou, Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, C.; Bennetzen, J.L. Circular RNA architecture and differentiation during leaf bud to young leaf development in tea (Camellia sinensis). Planta 2018, 248, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Fan, Y.; Lu, Q.; Li, Q.; Yan, J.; Muehlbauer, G.J.; Schnable, P.S.; Dai, M.; Li, L. Circular RNAs mediated by transposons are associated with transcriptomic and phenotypic variation in maize. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.P.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, D.W.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.B.; Huang, H.W. Identification of circular RNAs in Kiwifruit and their species-specific response to bacterial canker pathogen invasion. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Fan, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, L.; Terzaghi, W.; Bucher, E.; Li, L.; Dai, M. A large-scale circular RNA profiling reveals universal molecular mechanisms responsive to drought stress in maize and Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2019, 98, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, B.; Luo, Y.; Gao, L. Deciphering the roles of circRNAs on chilling injury in tomato. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zinta, G.; Xie, S.; Zhu, W.; Nie, W.F. Genome-Wide Identification of Circular RNAs in Response to Low-Temperature Stress in Tomato Leaves. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 591806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patop, I.L.; Wust, S.; Kadener, S. Past, present, and future of circRNAs. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Q.H.; Fan, L. Widespread noncoding circular RNAs in plants. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, Y.J.; Yan, L.Y.; Hu, B.Q.; Fan, X.Y.; Ren, Y.X.; Li, R.; Lian, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, Q.Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Tracing the expression of circular RNAs in human pre-implantation embryos. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sharpless, N.E. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.M.; Wilusz, J.E. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, N.; Xu, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhu, L.; Min, L.; et al. microRNAs involved in auxin signalling modulate male sterility under high-temperature stress in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Plant J. 2017, 91, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Muleke, E.M.; Liu, L. Identification of microRNAs and Their Target Genes Explores miRNA-Mediated Regulatory Network of Cytoplasmic Male Sterility Occurrence during Anther Development in Radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Xie, F.; Hua, Q.; Zur, N.T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J.; Hu, G.; Qin, Y. Integrated sRNAome and RNA-Seq analysis reveals miRNA effects on betalain biosynthesis in pitaya. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Tian, Y.; Tan, C.; Bai, S.; Hao, J.; Hasi, A. Genome-wide identification of microRNAs involved in the regulation of fruit ripening and climacteric stages in melon (Cucumis melo). Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Guo, P.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, D.; Li, Y.; Acheampong, A.; Wu, P.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, W. Genome-Wide Identification of Copper Stress-Regulated and Novel MicroRNAs in Mulberry Leaf. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.L.; Bao, Y.; Yee, M.C.; Barrett, S.P.; Hogan, G.J.; Olsen, M.N.; Dinneny, J.R.; Brown, P.O.; Salzman, J. Circular RNA is expressed across the Eukaryotic tree of life. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Litholdo, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.C. Circular RNAs and Plant Stress Responses. Circ. Rnas Biog. Funct. 2018, 1087, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.H.; Ren, Y.Z.; Lin, T.B.; Cui, D.Q. Identification and characterization of CircRNAs involved in the regulation of wheat root length. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, H.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Xi, F.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Kohnen, M.V.; Gao, P.F.; Wei, W.T.; Chen, K.; Liu, X.Q.; et al. Whole-genome characterization of chronological age-associated changes in methylome and circular RNAs in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) from vegetative to floral growth. Plant J. 2021, 106, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.; Memczak, S.; Wyler, E.; Torti, F.; Porath, H.T.; Orejuela, M.R.; Piechotta, M.; Levanon, E.Y.; Landthaler, M.; Dieterich, C.; et al. Analysis of Intron Sequences Reveals Hallmarks of Circular RNA Biogenesis in Animals. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, T.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D.; Gong, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, D.; et al. Transcriptome-wide investigation of circular RNAs in rice. RNA 2015, 21, 2076–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, L.Y.; Li, S.; Xu, M.; Guan, X.Y.; Zhou, B.L. Characterization of conserved circular RNA in polyploid Gossypium species and their ancestors. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 3660–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, T.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Deng, G.; Lin, H.; Wang, S. Heat stress alters genome-wide profiles of circular RNAs in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 96, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnatreya, D.B.; Agarwala, N.; Gill, S.S.; Bandyopadhyay, T. Understanding the role of miRNAs for improvement of tea quality and stress tolerance. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 328, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, G.C.; Flores-Vergara, M.A.; Krasnyanski, S.; Kumar, S.; Thompson, W.F. A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; et al. SOAPnuke: A MapReduce acceleration-supported software for integrated quality control and preprocessing of high-throughput sequencing data. Gigascience 2018, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, E.; Tong, W.; Hou, Y.; An, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Li, R.; et al. The Reference Genome of Tea Plant and Resequencing of 81 Diverse Accessions Provide Insights into Its Genome Evolution and Adaptation. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F. Accurate quantification of circular RNAs identifies extensive circular isoform switching events. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, W.; Kojima, K.K.; Kohany, O. Repbase Update, a database of repetitive elements in eukaryotic genomes. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Du, T.; Mao, W.; Li, X.; Ye, C.Y.; Zhu, Q.H.; Fan, L.; Chu, Q. PlantcircBase 7.0: Full-length transcripts and conservation of plant circRNAs. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, N.; Dawson, J.A.; Thomson, J.A.; Ruotti, V.; Rissman, A.I.; Smits, B.M.; Haag, J.D.; Gould, M.N.; Stewart, R.M.; Kendziorski, C. EBSeq: An empirical Bayes hierarchical model for inference in RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klopfenstein, D.V.; Zhang, L.; Pedersen, B.S.; Ramirez, F.; Warwick Vesztrocy, A.; Naldi, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Yunes, J.M.; Botvinnik, O.; Weigel, M.; et al. GOATOOLS: A Python library for Gene Ontology analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: A plant small RNA target analysis server (2017 release). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W49–W54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zeng, X.; Lin, N.; Yu, S.; Fernie, A.R.; Zhao, J. CsbZIP1-CsMYB12 mediates the production of bitter-tasting flavonols in tea plants (Camellia sinensis) through a coordinated activator-repressor network. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lu, M.; Wu, Y.; Jing, T.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, T.; et al. Salicylic acid carboxyl glucosyltransferase UGT87E7 regulates disease resistance in Camellia sinensis. Plant Physiol 2022, 188, 1507–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, L.H.; Yan, M.L.; Hu, J.; Lin, Q.Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Ni, D.J.; et al. A rapid and efficient transient expression system for gene function and subcellular localization studies in the tea plant (Camellia sinensis) leaves. Sci. Hortic-Amst. 2022, 297, 110927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijuan, Z.; Ali Inayat, M.; Fangdong, L.; Penghui, L.; Qiong, W.; Yanli, W.; Yunze, L.; Naveed, A.; Wei, T.; Yeyun, L.; et al. Characterization of CsWRKY29 and CsWRKY37 transcription factors and the functional roles in cold tolerance of tea plant. Beverage Plant Res. 2022, 2, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Castellano, S.; Nic-Can, G.I.; De-la-Peña, C. Localization of miRNAs by In Situ Hybridization in Plants Using Conventional Oligonucleotide Probes. In Plant Epigenetics: Methods and Protocols; Kovalchuk, I., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Yi, L.; Li, Y.; Xie, N.; Wu, Q.; Samarina, L.; Tong, W.; et al. Evolutionary Landscape of Tea Circular RNAs and Its Contribution to Chilling Tolerance of Tea Plant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021478
Huang J, Wang Y, Yu J, Li F, Yi L, Li Y, Xie N, Wu Q, Samarina L, Tong W, et al. Evolutionary Landscape of Tea Circular RNAs and Its Contribution to Chilling Tolerance of Tea Plant. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021478
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jin, Yanli Wang, Jie Yu, Fangdong Li, Lianghui Yi, Yunze Li, Na Xie, Qiong Wu, Lidiia Samarina, Wei Tong, and et al. 2023. "Evolutionary Landscape of Tea Circular RNAs and Its Contribution to Chilling Tolerance of Tea Plant" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021478
APA StyleHuang, J., Wang, Y., Yu, J., Li, F., Yi, L., Li, Y., Xie, N., Wu, Q., Samarina, L., Tong, W., & Xia, E. (2023). Evolutionary Landscape of Tea Circular RNAs and Its Contribution to Chilling Tolerance of Tea Plant. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021478





