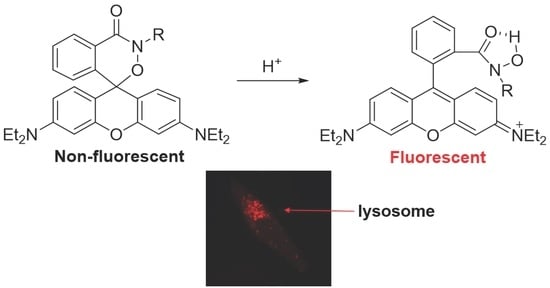
Rhodamine-Based Cyclic Hydroxamate as Fluorescent pH Probe for Imaging of Lysosomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Design and Synthesis of Probe 1
2.2. Optical Properties of Probe 1
2.3. Fluorescence and Imaging in Live PC3 and A549 Cells
2.4. In Vivo Zebrafish Imaging
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Probe 1
4.2. Cytotoxicity of Probe 1
4.3. Real-Time Monitoring of Changes in Intracellular Fluorescence
4.4. Measurement of Intracellular Fluorescence in a Dose-Dependent or Time-Dependent Manner
4.5. Imaging of Mammalian Cells Incubated with pH Probe
4.6. Imaging of Zebrafish Incubated with pH Probe
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casey, J.R.; Grinstein, S.; Orlowski, J. Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Burgess, K. Fluorescent indicators for intracellular pH. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2709–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegesna, G.K.; Janjanam, J.; Bi, J.; Luo, F.-T.; Zhang, J.; Olds, C.; Tiwari, A.; Liu, H. pH-activatable near-infrared fluorescent probes for detection of lysosomal pH inside living cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4500–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.-L.; Chen, X.-P.; Zhang, X.-F.; Miao, J.-Y.; Zhao, B.-X. A rhodamine B-based lysosomal pH probe. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaurex, N. pH Homeostasis of cellular organelles. Physiology 2002, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitner, E.B.; Platt, F.M.; Futerman, A.H. Common and uncommon pathogenic cascades in lysosomal storage diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 20423–20427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boya, P. Lysosomal function and dysfunction: Mechanism and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.-S.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, B.-X.; Miao, J.-Y. Highly selective and sensitive pH-responsive fluorescent probe in living Hela and HUVEC cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-T.; Ren, W.X.; Li, K.; Seo, J.; Sharma, A.; Yu, X.-Q.; Kim, J.S. Fluorescent bioimaging of pH: From design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2076–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Kwon, N.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, J.; Shin, I. Synthetic ratiometric fluorescent probes for detection of ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 143–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Huang, C.; Emery, B.P.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Bull, S.D.; He, X.-P.; Tian, H.; Yoon, J.; Sessler, J.L.; James, T.D. Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based small-molecule sensors and imaging agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5110–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, P.E.; Shelke, Y.G.; Datta, A.; Gharpure, S.J. Recent Advances in small molecule-based intracellular ph probes. ChemBioChem 2022, 23, e202100448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Huang, L.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; James, T.D.; Lin, W. Small molecule based fluorescent chemosensors for imaging the microenvironment within specific cellular regions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 12098–12150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-L.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L. Small-molecule fluorescent probes for specific detection and imaging of chemical species inside lysosomes. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6629–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pradhan, T.; Wang, F.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent chemosensors based on spiroring-opening of xanthenes and related derivatives. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1910–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, S.; Han, J.; Han, S. Imaging of intracellular acidic compartments with a sensitive rhodamine based fluorogenic pH sensor. Analyst 2011, 136, 3698–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-L.; Mao, G.-J.; Zhang, X.-B.; Liu, H.-W.; Gong, Y.-J.; Wu, Y.-X.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Tan, W. Rhodamine-based fluorescent probe for direct bio-imaging of lysosomal pH changes. Talanta 2014, 130, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.-S.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhao, B.-X.; Miao, J.-Y. A new rhodamine B-based lysosomal pH fluorescent indicator. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 788, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.-S.; Huang, S.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Dai, X.; Miao, J.-Y.; Zhao, B.-X. A new fluorescent pH probe for imaging lysosomes in living cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-K.; Li, K.; Hou, J.-T.; Qin, H.-H.; Xie, Y.-M.; Qian, C.-H.; Yu, X.-Q. Rhodamine-based lysosome-targeted fluorescence probes: High pH sensitivity and their imaging application in living cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 33975–33980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; She, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Two rhodamine lactam modulated lysosome-targetable fluorescence probes for sensitively and selectively monitoring subcellular organelle pH change. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 900, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Qiu, L.; Lu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.-B. An efficient ratiometric fluorescent probe for tracking dynamic changes in lysosomal pH. Analyst 2015, 140, 5563–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wu, S.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Han, S. Resolution of lysosomes in living cells with a ratiometric molecular pH-meter. Talanta 2013, 114, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Lin, C.; Li, H.; Zhan, P.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.; Hu, M.; Cheng, G.; Peng, X. A ratiometric lysosomal pH chemosensor based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Dyes Pigments 2013, 99, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Zhang, T.; Shen, S.-L.; Miao, J.-Y.; Zhao, B.-X. A ratiometric lysosomal pH probe based on the naphthalimide–rhodamine system. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3260–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Zhang, T.; Shen, S.-L.; Miao, J.-Y.; Zhao, B.-X. A ratiometric lysosomal pH probe based on the coumarin–rhodamine FRET system. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 49115–49121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Xiao, Y. pKa modulation of rhodamine alkylamides by hydrogen-bond and application in bio-imaging. Dyes Pigments 2021, 188, 109173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yu, H.; Yang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Li, N.; Bian, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Song, Y.; Zhang, M. Strategy to lengthen the on-time of photochromic rhodamine spirolactam for super-resolution photoactivated localization microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6527–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, Y.; Niu, M.; Li, Y.; Ye, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Y. Always-on and water-soluble rhodamine amide designed by positive charge effect and application in mitochondrion-targetable imaging of living cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 286, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, Y. A neutral pH probe of rhodamine derivatives inspired by effect of hydrogen bond on pKa and its organelle-targetable fluorescent imaging. Dyes Pigments 2016, 133, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-X.; Ge, D.; Dai, X.; Wu, W.-L.; Miao, J.-Y.; Zhao, B.-X. A water-soluble pH fluorescence probe based on quaternary ammonium salt for bioanalytical applications. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 151, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Fan, J.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Gao, P.; Peng, X. Imaging of lysosomal pH changes with a fluorescent sensor containing a novel lysosome-locating group. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 11766–11768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratton, S.G.; Taumoefolau, G.H.; Purnell, G.E.; Rasooly, M.; Czaplyski, W.L.; Harbron, E.J. Tuning the pKa of fluorescent rhodamine pH probes through substituent effects. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 14064–14072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, H. A single rhodamine spirolactam probe for localization and pH monitoring of mitochondrion/lysosome in living cells. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 11102–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Swamy, K.; Hong, J.; Lee, S.; Yoon, J. A rhodamine-based fluorescent probe for the detection of lysosomal pH changes in living cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Best, Q.A.; Suarez, B.; Pertile, J.; McCarroll, M.E.; Scott, C.N. Cycloalkyl-aminomethylrhodamines: pH dependent photophysical properties tuned by cycloalkane ring size. J. Fluoresc. 2015, 25, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, A.; Woydziak, Z.R.; Fu, L.; Branden, M.; Zhou, Z.; Ackley, B.D.; Peterson, B.R. Novel acid-activated fluorophores reveal a dynamic wave of protons in the intestine of Caenorhabditis elegans. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, X.; Han, J.; Han, S. Rhodamine-deoxylactam functionalized poly [styrene-alter-(maleic acid)] s as lysosome activatable probes for intraoperative detection of tumors. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2941–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poronik, Y.M.; Vygranenko, K.V.; Gryko, D.; Gryko, D.T. Rhodols–synthesis, photophysical properties and applications as fluorescent probes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5242–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- For Comprehensive pKa Values. Available online: https://organicchemistrydata.org/hansreich/resources/pka/ (accessed on 19 July 2023).
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Tae, J.; Shin, I. For 6-membered rhodamine probe, see: Rhodamine-based cyclic hydrazide derivatives as fluorescent probes for selective and rapid detection of formaldehyde. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 22435–22439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ko, S.-K.; Kim, H.; Shin, I.; Tae, J. Rhodamine cyclic hydrazide as a fluorescent probe for the detection of hydroxyl radicals. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7959–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Park, J.; Tae, J. Fluorescent probes based on rhodamine hydrazides and hydroxamates. Chem. Rec. 2016, 16, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-K.; Lee, S.; Tae, J. A gold (III) ion-selective fluorescent probe and its application to bioimagings. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5610–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuma, S.; Poole, B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 3327–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, L.-Q.; Branchaud, B.P. Selective labeling and monitoring pH changes of lysosomes in living cells with fluorogenic pH sensors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 3546–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berstad, M.; Cheung, L.; Berg, K.; Peng, Q.; Fremstedal, A.; Patzke, S.; Rosenblum, M.; Weyergang, A. Design of an EGFR-targeting toxin for photochemical delivery: In vitro and in vivo selectivity and efficacy. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5582–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Grassmé, H.; Döring, G.; Gulbins, E. Alterations in ceramide concentration and pH determine the release of reactive oxygen species by Cftr-deficient macrophages on infection. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5104–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, N.B.; Bi, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Yan, X.; Mandalapu, S.R.; Faucett, M.; Jockusch, S.; Ju, J.; Gibson, K.M. Highly stable and sensitive fluorescent probes (LysoProbes) for lysosomal labeling and tracking. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Tae, J. Rhodamine-hydroxamate-based fluorescent chemosensor for FeIII. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5389–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.J. Concerning the relationship between the strength of acids and their capacity to preserve neutrality. Am. J. Physiol. 1908, 21, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magde, D.; Rojas, G.E.; Seybold, P. Solvent dependence of the fluorescence lifetimes of xanthene dyes. Photochem. Photobiol. 1999, 70, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.R.; Winfield, S.A.; Miller, J.N. Relative fluorescence quantum yields using a computer-controlled luminescence spectrometer. Analyst 1983, 108, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.J.; Jang, M.; Roh, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Moon, H.J.; Byun, J.; Wi, J.; Ko, S.-K.; Tae, J. Rhodamine-Based Cyclic Hydroxamate as Fluorescent pH Probe for Imaging of Lysosomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015073
Kim YJ, Jang M, Roh J, Lee YJ, Moon HJ, Byun J, Wi J, Ko S-K, Tae J. Rhodamine-Based Cyclic Hydroxamate as Fluorescent pH Probe for Imaging of Lysosomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(20):15073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015073
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young Ju, Mina Jang, Jongtae Roh, Yoon Jeong Lee, Hee Jung Moon, Jimin Byun, Jihyun Wi, Sung-Kyun Ko, and Jinsung Tae. 2023. "Rhodamine-Based Cyclic Hydroxamate as Fluorescent pH Probe for Imaging of Lysosomes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 20: 15073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015073
APA StyleKim, Y. J., Jang, M., Roh, J., Lee, Y. J., Moon, H. J., Byun, J., Wi, J., Ko, S.-K., & Tae, J. (2023). Rhodamine-Based Cyclic Hydroxamate as Fluorescent pH Probe for Imaging of Lysosomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(20), 15073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015073