A Chitosan-Based Biomaterial Combined with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium for Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
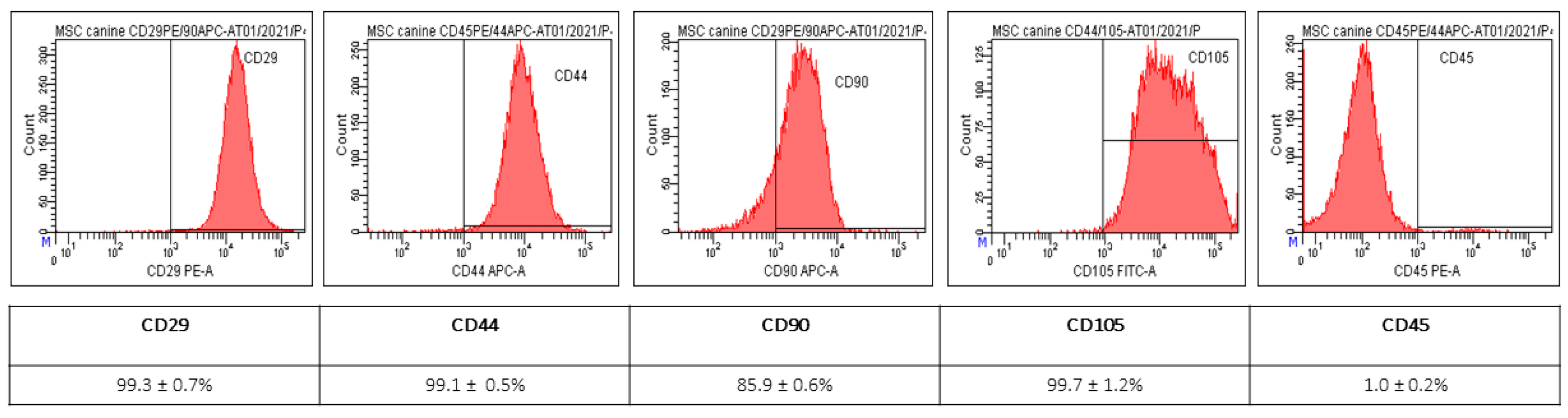
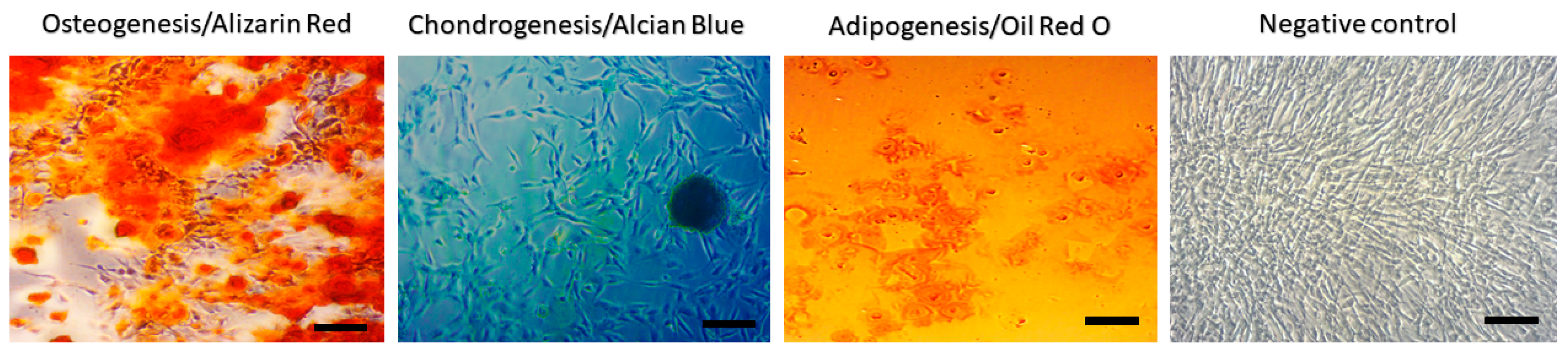
2.1. Characterization of MSC from Canine Adipose Tissue
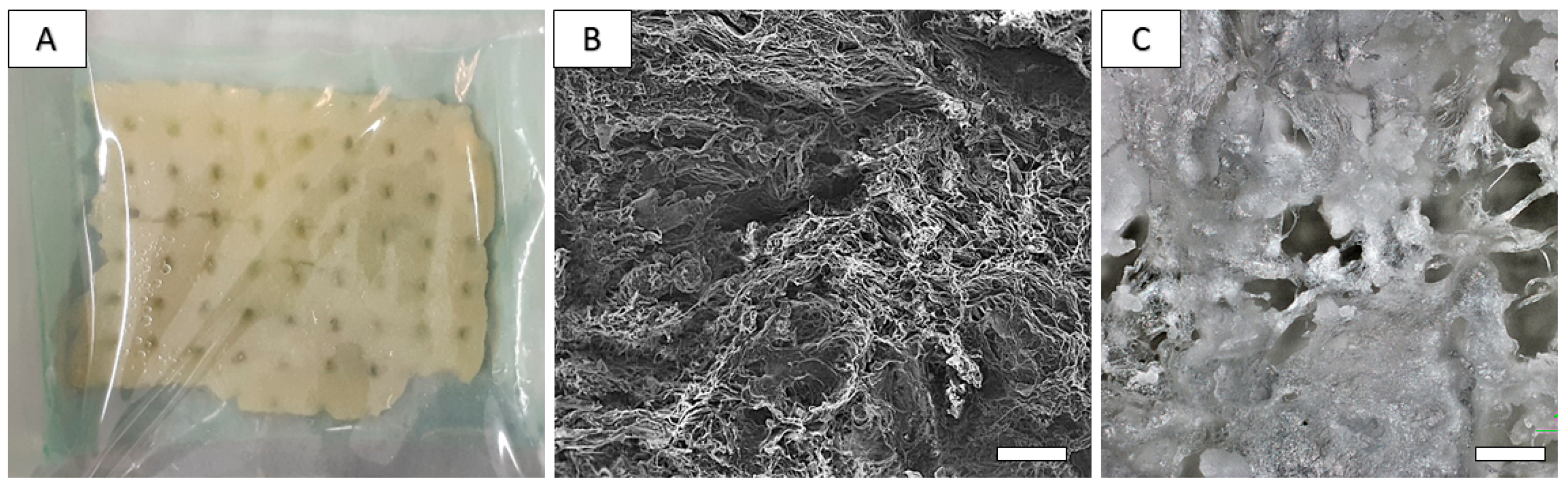
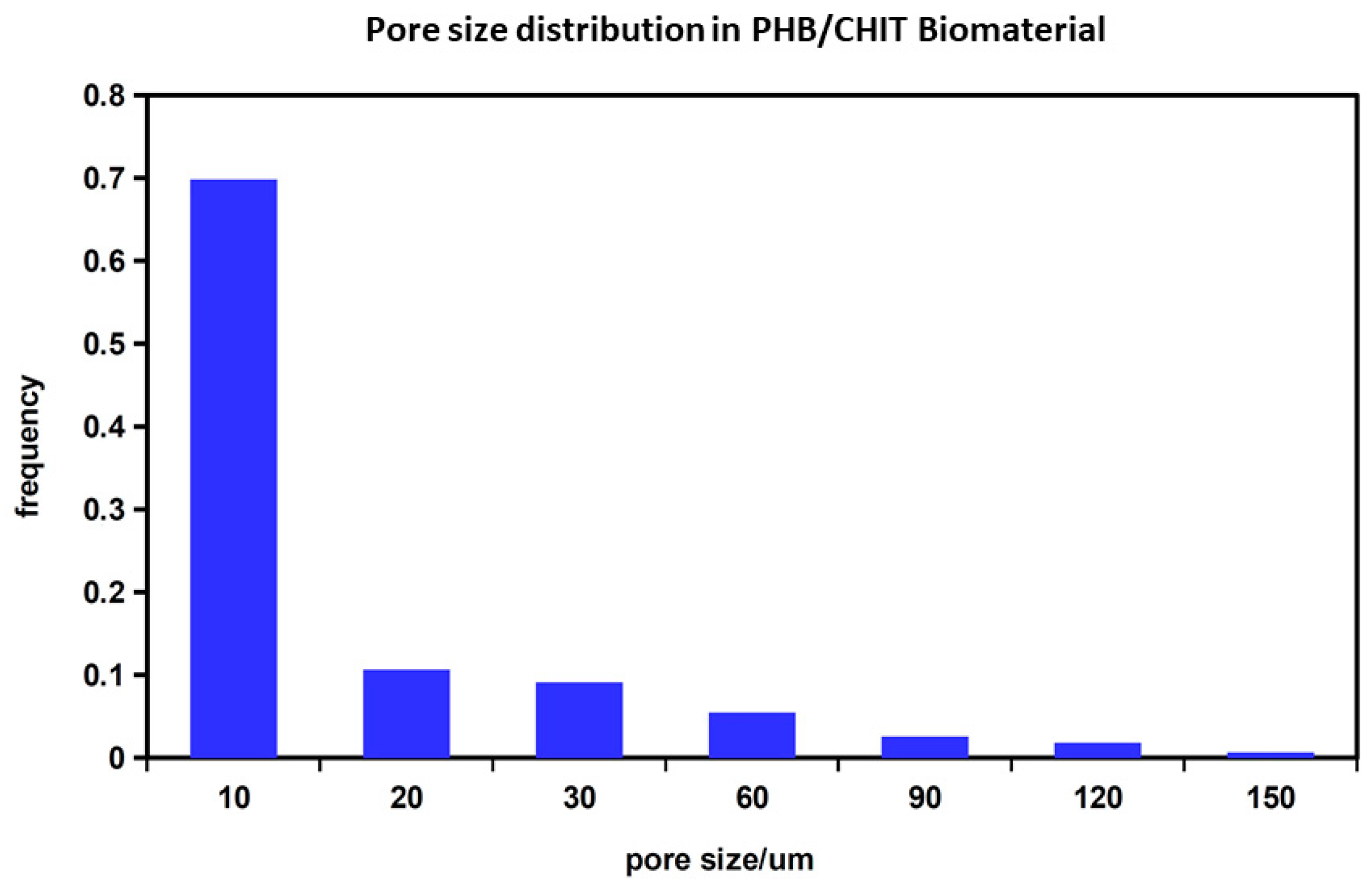
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan-Based Biopolymeric Scaffolds
2.3. Cell Seeding on the 3D Porous Polymeric Scaffolds and Cytototxicity Evaluation
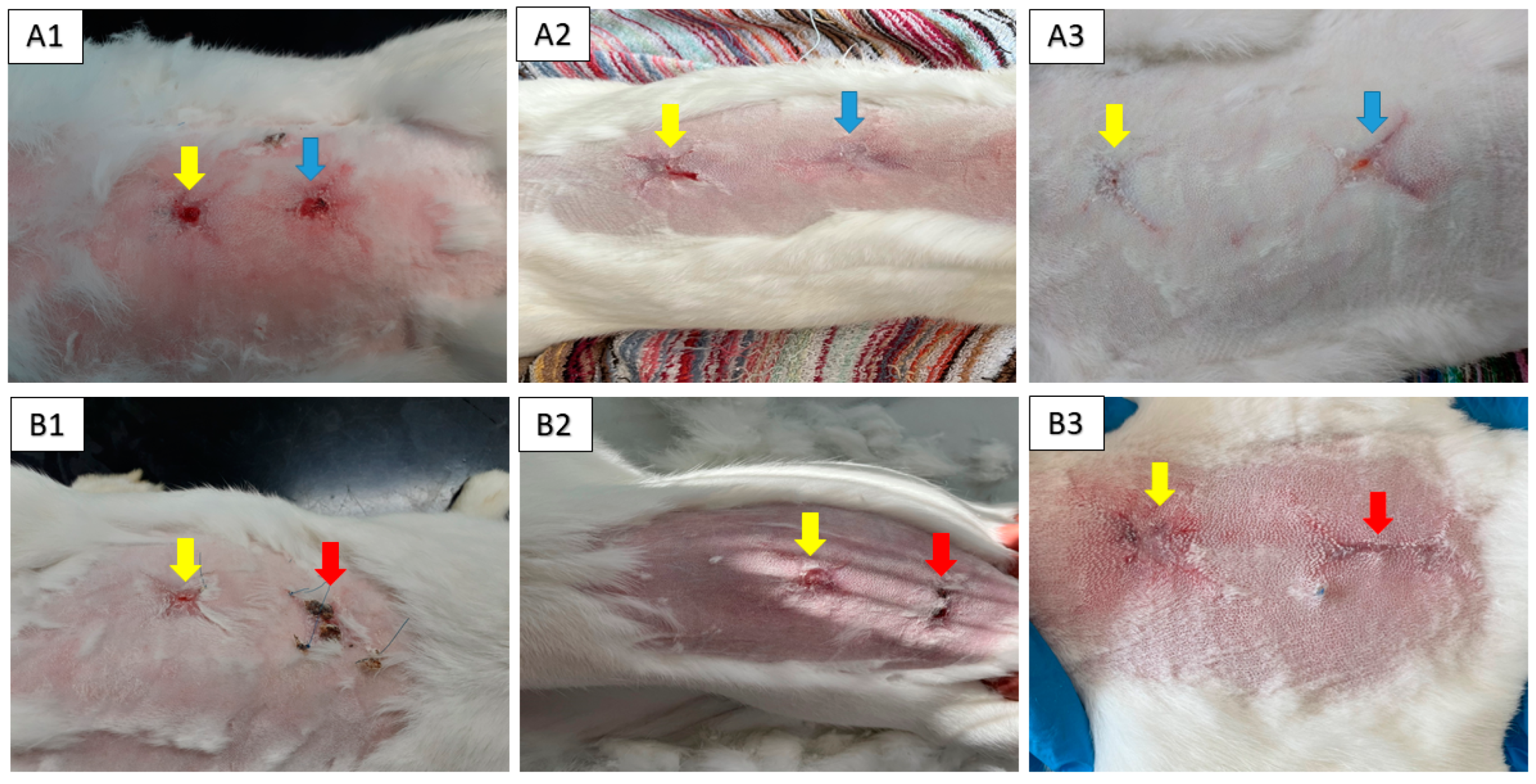
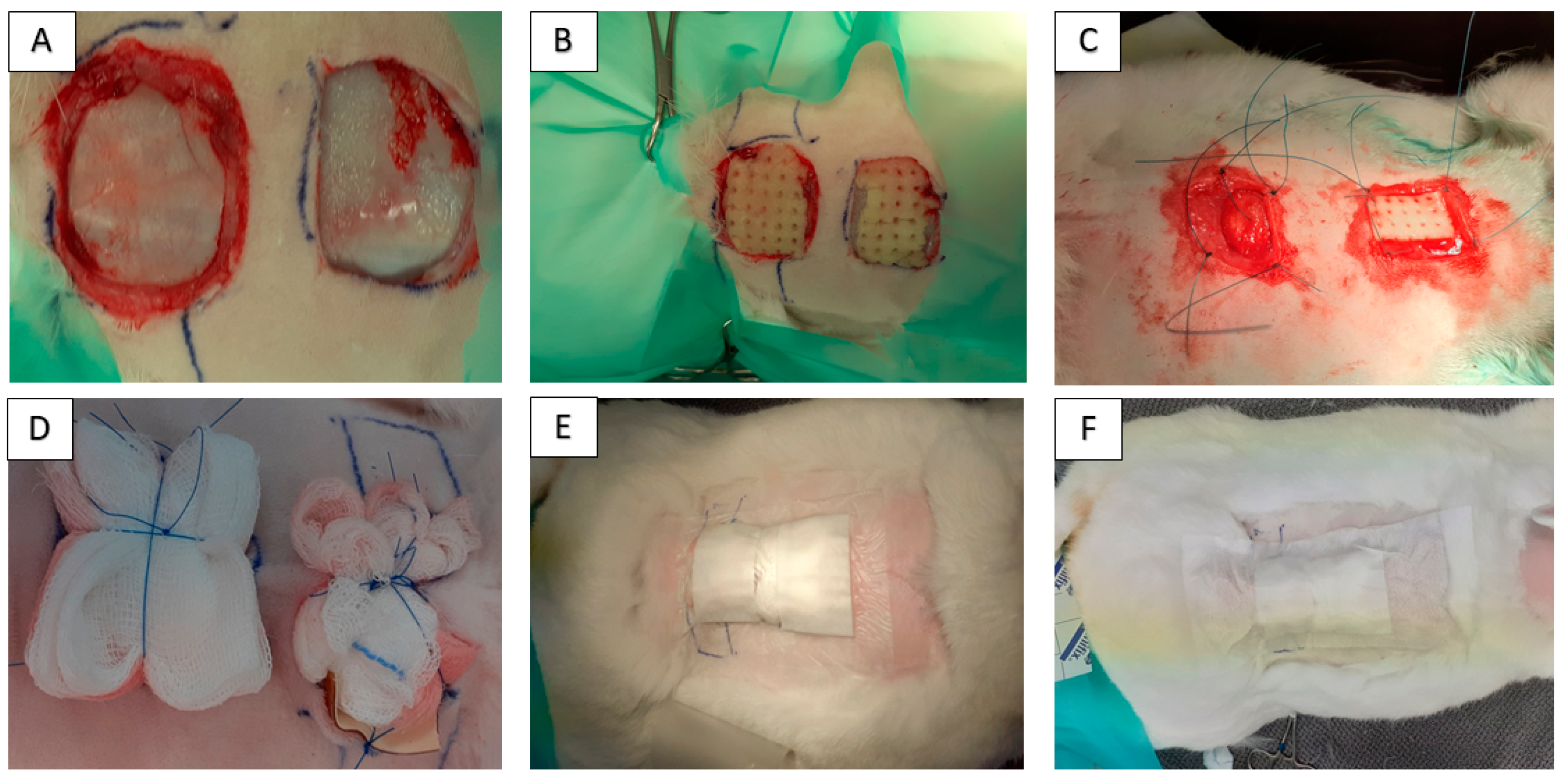
2.4. Animal Model
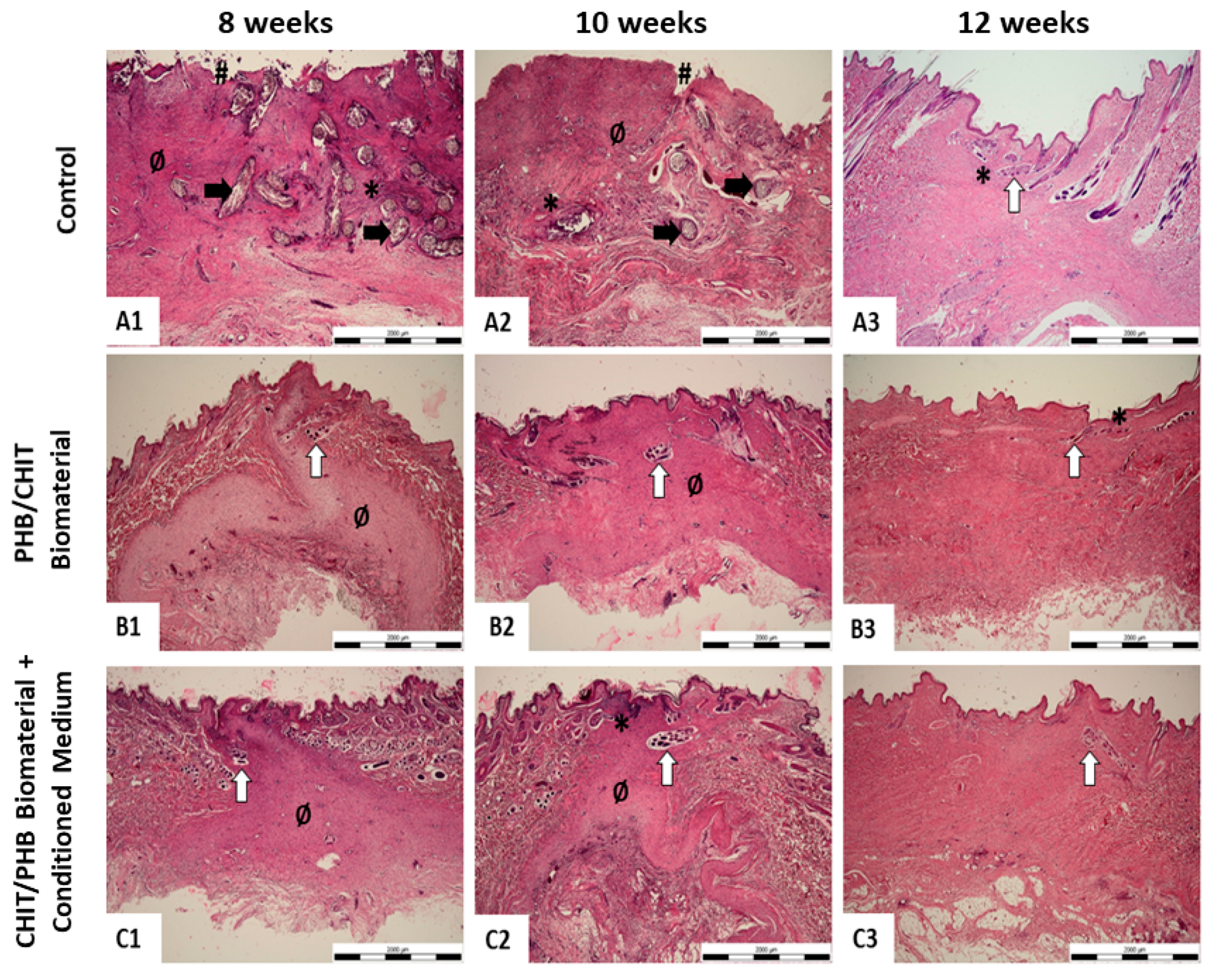
2.5. Histological Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Characterization of Canine Amniotic MSC-Conditioned Medium Harvesting
4.1.1. Isolation of MSC from Canine Adipose Tissue
4.1.2. Expression of Surface Markers
4.1.3. Preparation of AT-MSC-Conditioned Medium
4.2. Preparation and Characterization of Composite PHB/CHIT Scaffolds
4.3. Cell Seeding on the 3D Porous Polymeric Scaffolds and Cytototxicity Evaluation
4.4. In Vivo Model for Wound Healing and Surgical Technique
4.5. Histological Processing
4.6. Histopathological Score System for Wound Healing Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeschke, M.G.; van Baar, M.E.; Choudhry, M.A.; Chung, K.K.; Gibran, N.S.; Logsetty, S. Burn Injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.K. Burn Wound: How It Differs from Other Wounds? Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2012, 45, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Ceilley, R. Chronic Wound Healing: A Review of Current Management and Treatments. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, D.; Wu, Y.; Song, G.; Azizi, R.; Zamani, A. The Application of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) and Their Derivative Exosome in Skin Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, X.Y.; Wang, A.C.; Liu, X.M.; Zhu, S. Exosomes Derived from Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla Alleviate Inflammation in Rat Pulpitis by Upregulating Regulatory T Cells. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silina, E.; Manturova, N.; Stupin, V. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Application in Wound Tissue Healing in Old Animals. Stem Cells Cloning 2020, 13, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ge, S. Biomaterials Constructed for MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Loading and Delivery—A Promising Method for Tissue Regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 898394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Gould, M.; Ali, M.A. A Review of Current Advancements for Wound Healing: Biomaterial Applications and Medical Devices. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 2542–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Cai, E.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ge, X.; Wang, J.; Lan, Y.; Xu, H.; Hu, R.; Shen, J. An Immunomodulatory Hydrogel by Hyperthermia-Assisted Self-Cascade Glucose Depletion and ROS Scavenging for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Wound Therapeutics. Adv. Mater. 2023, 2306632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Xiang, Y.; Cai, E.; Ge, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Shen, J. Inorganic–Organic Hybrid Nanomaterials for Photothermal Antibacterial Therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 496, 215426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Zharkinbekov, Z.; Raziyeva, K.; Tabyldiyeva, L.; Berikova, K.; Zhumagul, D.; Temirkhanova, K.; Saparov, A. Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Man, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Wang, S. Advances in Chitosan-Based Wound Dressings: Modifications, Fabrications, Applications and Prospects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 120058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A Functional Chitosan-Based Hydrogel as a Wound Dressing and Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Wound Healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxson, S.; Lopez, E.A.; Yoo, D.; Danilkovitch-Miagkova, A.; LeRoux, M.A. Concise Review: Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Wound Repair. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Tanaka, M.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Chitosan Preparations for Wounds and Burns: Antimicrobial and Wound-Healing Effects. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 857–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Scholtemeijer, M.; Shah, K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Immunomodulation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesko, D.M.; Wilgus, T.A. Immune Cells in Cutaneous Wound Healing: A Review of Functional Data from Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z. Adipose Stem Cell-Based Treatments for Wound Healing. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 821652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; Salgado, M.; Ford, D.; Van Badiavas, E. Stimulation of Skin and Wound Fibroblast Migration by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Normal Donors and Chronic Wound Patients. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.F.; Sarkanen, J.-R.; Huttala, O.; Kaartinen, I.S.; Kuokkanen, H.O.; Ylikomi, T. Adipose Tissue Extract Shows Potential for Wound Healing: In Vitro Proliferation and Migration of Cell Types Contributing to Wound Healing in the Presence of Adipose Tissue Preparation and Platelet Rich Plasma. Cytotechnology 2018, 70, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Kodra, A.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Golinko, M.S.; Ehrlich, H.P.; Brem, H. The Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Wound Healing. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 153, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Kirsner, R.S. Angiogenesis in Wound Repair: Angiogenic Growth Factors and the Extracellular Matrix. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 60, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humenik, F.; Cizkova, D.; Cikos, S.; Luptakova, L.; Madari, A.; Mudronova, D.; Kuricova, M.; Farbakova, J.; Spirkova, A.; Petrovova, E.; et al. Canine Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Genomics, Proteomics and Functional Analyses of Paracrine Factors. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2019, 18, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.E.; Wilgus, T.A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Angiogenesis in the Regulation of Cutaneous Wound Repair. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramulu, S.; Banerjee, A.; Di Liddo, R.; Jothimani, G.; Gopinath, M.; Murugesan, R.; Marotta, F.; Pathak, S. Concise Review on Clinical Applications of Conditioned Medium Derived from Human Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cells (UC-MSCs). Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2018, 12, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Humenik, F.; Maloveska, M.; Hudakova, N.; Petrouskova, P.; Hornakova, L.; Domaniza, M.; Mudronova, D.; Bodnarova, S.; Cizkova, D. A Comparative Study of Canine Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Different Sources. Animals 2022, 12, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humenik, F.; Maloveská, M.; Hudáková, N.; Petroušková, P.; Šufliarska, Z.; Horňáková, Ľ.; Valenčáková, A.; Kožár, M.; Šišková, B.; Mudroňová, D.; et al. Impact of Canine Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Media on the Wound Healing Process: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, L.A.; León, J.; López, J.; Rojas, D.; Reyes, M.; Contreras, P.; Quest, A.F.G.; Escudero, C.; Leyton, L. The GPI-Anchored Protein Thy-1/CD90 Promotes Wound Healing upon Injury to the Skin by Enhancing Skin Perfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karina, K.; Rosadi, I.; Sobariah, S.; Afini, I.; Widyastuti, T.; Rosliana, I. Comparable Effect of Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction and Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Wound Healing: An in Vivo Study. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2019, 6, 3412–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, P.; Todd, L.; Shetye, S.; Monslow, J.; Puré, E. CD44-Dependent Inflammation, Fibrogenesis, and Collagenolysis Regulates Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Tensile Strength during Cutaneous Wound Healing. Matrix Biol. 2019, 75–76, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.S.; Borrelli, M.R.; Lorenz, H.P.; Longaker, M.T.; Wan, D.C. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Cutaneous Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review of the Background, Role, and Therapeutic Potential. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, e6901983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.T.; Aisyah, P.B.; Firmansyah, Y.; Nathasia, N.; Budi, E.; Hendrawan, S. Effectiveness of Secretome from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Gel (10% SM-hUCMSC Gel) for Chronic Wounds (Diabetic and Trophic Ulcer)–Phase 2 Clinical Trial. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2023, 16, 1763–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Cao, L.; Melino, S.; Candi, E.; Wang, Y.; Shao, C.; Melino, G.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X. Orchestration of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells and Inflammation During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2023, 12, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Hou, Q.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, X. Macrophage Related Chronic Inflammation in Non-Healing Wounds. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 681710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Dong, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Liao, L.; Jin, Y.; Yuan, L.; Li, B. MSC-Derived Exosome Promotes M2 Polarization and Enhances Cutaneous Wound Healing. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 7132708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.; Mori, M.; Yoshimura, K. Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Conditioned Medium and Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2022, 28, 830–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Schaudinn, C.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A.; Rancan, F. Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Their Conditioned Medium in a Human Ex Vivo Wound Model. Cells 2022, 11, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, R.; Mostafavinia, A.; Amini, A.; Ahmadi, H.; Ahrabi, B.; Omidi, H.; Pourhashemi, E.; Hajihosseintehrani, M.; Rezaei, F.; Mohsenifar, Z.; et al. Acceleration of a Delayed Healing Wound Repair Model in Diabetic Rats by Additive Impacts of Photobiomodulation plus Conditioned Medium of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, M.-H.; Dong, Z.; Yang, T. Prostaglandin E2 Is a Potent Inhibitor of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Interaction with Hepatocyte Growth Factor. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2006, 291, F1323–F1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillamat-Prats, R. The Role of MSC in Wound Healing, Scarring and Regeneration. Cells 2021, 10, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, L.; Lim, S.K.; Arslan, F.; Armstrong, J.S.; Hoefer, I.E.; Doevendans, P.A.; Piek, J.J.; El Oakley, R.M.; Choo, A.; Lee, C.N.; et al. Reduction of Myocardial Infarct Size by Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Medium. Stem Cell Res. 2008, 1, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temnov, A.; Rogov, K.; Zhalimov, V.; Igor, P.; Pekov, S.; Bader, A.; Sklifas, A.; Giri, S. The Effect of a Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Medium Fraction on Morphological Characteristics of Hepatocytes in Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Failure: A Preliminary Study. Hepatic Med. Evid. Res. 2019, 11, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, J.L.; de Melo, M.I.A.; da Silva Cunha, P.; de Miranda, M.C.; Barrioni, B.R.; Moreira, C.D.F.; da Fonseca Ferreira, A.; Arantes, R.M.E.; de Sá, M.A.; de Magalhães Pereira, M.; et al. Development of a Membrane and a Bilayer of Chitosan, Gelatin, and Polyhydroxybutyrate to Be Used as Wound Dressing for the Regeneration of Rat Excisional Wounds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2023, 112, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Park, S.J.; Gu, B.K.; Kim, C.H. Fabrication of Chitosan Nanofibers Scaffolds with Small Amount Gelatin for Enhanced Cell Viability. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 749, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, D.; Sanchis, A.; Blanes, M.; Pérez del Caz, M.D.; Ruiz-Saurí, A.; Piquer-Gil, M.; Pelacho, B.; Marco, B.; Garcia, N.; Ontoria-Oviedo, I.; et al. Electrospun Poly(Hydroxybutyrate) Scaffolds Promote Engraftment of Human Skin Equivalents via Macrophage M2 Polarization and Angiogenesis. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e983–e994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Vyver, M.; Boodhoo, K.; Frazier, T.; Hamel, K.; Kopcewicz, M.; Levi, B.; Maartens, M.; Machcinska, S.; Nunez, J.; Pagani, C.; et al. Histology Scoring System for Murine Cutaneous Wounds. Stem Cells Dev. 2021, 30, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgülü, T.; Olgun, A.; Torun Karadere, M.; Kargi, E. Application of N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate to Split-Thickness Skin Grafts in Rats: An Experimental Study. Dermatol. Surg. 2015, 41, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.W.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Hu, M.; Shi, S.J.; Li, Z.W.; Wu, G.L.; Cui, H.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles/Chitosan Oligosaccharide/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofiber Promotes Wound Healing by Activating TGFβ1/Smad Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moura Estevão, L.R.; Cassini-Vieira, P.; Leite, A.G.B.; de Carvalho Bulhões, A.A.V.; da Silva Barcelos, L.; Evêncio-Neto, J. Morphological Evaluation of Wound Healing Events in the Excisional Wound Healing Model in Rats. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-X.; Zhao, W.-Y.; Fang, Q.-Q.; Wang, X.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Shi, B.-H.; Zheng, B.; Wang, S.-J.; Tan, W.-Q.; Wu, L.-H. Effects of Chitosan-Collagen Dressing on Wound Healing In Vitro and In Vivo Assays. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2021, 19, 2280800021989698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, N.; Meng, G.; He, J.; Wu, F. The Effect of Form of Carboxymethyl-Chitosan Dressings on Biological Properties in Wound Healing. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 194, 111191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, K.; Ishihara, M.; Ishizuka, T.; Fujita, M.; Ozeki, Y.; Maehara, T.; Saito, Y.; Yura, H.; Matsui, T.; Hattori, H.; et al. Photocrosslinkable Chitosan Hydrogel Containing Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Stimulates Wound Healing in Healing-Impaired Db/Db Mice. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, S.A.; Pawde, A.M.; Sharun, K.; Kalaiselvan, E.; Shivaramu, S.; Mathesh, K.; Chandra, V.; Kumar, R.; Maiti, S.K.; Verma, M.R.; et al. Evaluation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Eggshell Membrane for Full-Thickness Wound Healing in a Rabbit Model. Cell Tissue Bank. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelizzo, G.; Avanzini, M.A.; Icaro Cornaglia, A.; Osti, M.; Romano, P.; Avolio, L.; Maccario, R.; Dominici, M.; De Silvestri, A.; Andreatta, E.; et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Cutaneous Wound Healing in a Rabbit Model: Pre-Clinical Study Applicable in the Pediatric Surgical Setting. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giretova, M.; Medvecky, L.; Petrovova, E.; Cizkova, D.; Danko, J.; Mudronova, D.; Slovinska, L.; Bures, R. Polyhydroxybutyrate/Chitosan 3D Scaffolds Promote In Vitro and In Vivo Chondrogenesis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 189, 556–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BS EN ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. Available online: https://www.en-standard.eu/bs-en-iso-10993-5-2009-biological-evaluation-of-medical-devices-tests-for-in-vitro-cytotoxicity/ (accessed on 5 November 2023).

| Experimental Group | Healing Period | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 Weeks | 10 Weeks | 12 Weeks | |
| Control | 3 | 3 | 0/0- |
| Implant | 1- | 1- | 0-/1 |
| Implant + medium | 1/1- | 1- | 0/0- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Humenik, F.; Danko, J.; Krešáková, L.; Vdoviaková, K.; Vrabec, V.; Vasilová, E.; Giretová, M.; Tóth, Š.; Fagová, Z.; Babík, J.; et al. A Chitosan-Based Biomaterial Combined with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium for Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216080
Humenik F, Danko J, Krešáková L, Vdoviaková K, Vrabec V, Vasilová E, Giretová M, Tóth Š, Fagová Z, Babík J, et al. A Chitosan-Based Biomaterial Combined with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium for Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(22):16080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216080
Chicago/Turabian StyleHumenik, Filip, Ján Danko, Lenka Krešáková, Katarína Vdoviaková, Vladimír Vrabec, Emília Vasilová, Mária Giretová, Štefan Tóth, Zuzana Fagová, Ján Babík, and et al. 2023. "A Chitosan-Based Biomaterial Combined with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium for Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 22: 16080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216080
APA StyleHumenik, F., Danko, J., Krešáková, L., Vdoviaková, K., Vrabec, V., Vasilová, E., Giretová, M., Tóth, Š., Fagová, Z., Babík, J., & Medvecký, Ľ. (2023). A Chitosan-Based Biomaterial Combined with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium for Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(22), 16080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216080






