Ions-Induced Alginate Gelation According to Elemental Analysis and a Combinatorial Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
Experimental Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Junction Zone Structures
3.2. Application of Combinatorial Approaches to Analyze the Distribution of Cells in Connection Zones
3.3. Analysis of Results
3.3.1. Ba2+-Alginate
3.3.2. Sr2+-Alginate
3.3.3. Ca2+-Alginate
3.3.4. Zn2+-Alginate
3.3.5. Cu2+-Alginate
3.3.6. Ni2+-Alginate
3.3.7. Mn2+-Alginate
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Huang, C. Recent Advances in Sustainable Antimicrobial Food Packaging: Insights into Release Mechanisms, Design Strategies, and Applications in the Food Industry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 11806–11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, S.H.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Alginate gel particles—A review of production techniques and physical properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.O.; Bogdanova, L.R.; Zueva, O.S. Use of Natural Biopolymers to Create Nanocomposite Materials. Solid State Phenom. 2020, 299, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zueva, O.S.; Gubaidullin, A.T.; Makarova, A.O.; Bogdanova, L.R.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Zuev, Y.F. Structural Features of Composite Protein-Polysaccharide Hydrogel in the Presence of a Carbon Nanomaterial. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2020, 69, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.O.; Derkach, S.R.; Kadyirov, A.I.; Ziganshina, S.A.; Kazantseva, M.A.; Zueva, O.S.; Gubaidullin, A.T.; Zuev, Y.F. Supramolecular Structure and Mechanical Performance of κ-Carrageenan—Gelatin Gel. Polymers 2022, 14, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubaidullin, A.T.; Makarova, A.O.; Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Kadyirov, A.I.; Ziganshina, S.A.; Salnikov, V.V.; Zueva, O.S.; Zuev, Y.F. Modulation of Molecular Structure and Mechanical Properties of κ-Carrageenan-Gelatin Hydrogel with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers 2022, 14, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Geng, A.; Mei, C.; Shang, S. Graphene oxide incorporated alginate hydrogel beads for the removal of various organic dyes and bisphenol A in water. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Kamura, Y.; Koilraj, P.; Sasaki, K. Co-sorption of Sr2+ and SeO42– as the surrogate of radionuclide by alginate-encapsulated graphene oxide-layered double hydroxide beads. Environ Res. 2020, 187, 109712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lu, X.; Li, X.-Y. Selective removals of heavy metals (Pb2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+) from wastewater by gelation with alginate for effective metal recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.M.; Yang, Z. Ion-Induced Synthesis of Alginate Fibroid Hydrogel for Heavy Metal Ions Removal. Front. Chem. 2020, 7, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocher, V.; Siaugue, J.-M.; Cabuil, V.; Bee, A. Removal of organic dyes by magnetic alginate beads. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sui, K.; Liu, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.; Xia, Y. Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution by calcium alginate/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite fibers. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, H.; Xia, Y. Biocomposite fiber of calcium alginate/multi-walled carbon nanotubes with enhanced adsorption properties for ionic dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arıca, M.Y.; Kaçara, Y.; Genç, Ö. Entrapment of white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor in Ca-alginate beads: Preparation and biosorption kinetic analysis for cadmium removal from an aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 80, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoglu, G.; Tuzun, I.; Celik, G.; Yilmaz, M.; Arica, M.Y. Biosorption of mercury(II), cadmium(II) and lead(II) ions from aqueous system by microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii immobilized in alginate beads. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 81, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, L.R.; Rogov, A.M.; Zueva, O.S.; Zuev, Y.F. Lipase Enzymatic Microreactor in Polysaccharide Hydrogel: Structure and Properties. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2019, 68, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daâssi, D.; Rodríguez-Couto, S.; Nasri, M.; Mechichi, T. Biodegradation of Textile Dyes by Immobilized Laccase from Coriolopsis Gallica into Ca-Alginate Beads. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 90, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, L.R.; Makarova, A.O.; Zueva, O.S.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Zuev, Y.F. Encapsulation of diagnostic dyes in the polysaccharide matrix modified by carbon nanotubes. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2020, 69, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poncelet, D.; Neufeld, R.J.; Goosen, M.F.A.; Burgarski, B.; Babak, V. Formation of microgel beads by electric dispersion of polymer solutions. AIChE J. 1999, 45, 2018–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, L.R.; Zelenikhin, P.V.; Makarova, A.O.; Zueva, O.S.; Salnikov, V.V.; Zuev, Y.F.; Ilinskaya, O.N. Alginate-Based Hydrogel as Delivery System for Therapeutic Bacterial RNase. Polymers 2022, 14, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z. Potential applications of alginate oligosaccharides for biomedicine—A mini review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.R.; Biswal, T. Alginate and its application to tissue engineering. Springer Nat. Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Gao, X.; Cheng, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. The structural characteristics of seaweed polysaccharides and their application in gel drug delivery systems. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, A.; Patel, D.; Hickson, B.; DesRochers, J.; Hu, X. Recent Progress in Biopolymer-Based Hydrogel Materials for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühbeck, D.; Mayr, J.; Häring, M.; Hofmann, M.; Quignard, F.; Díaz Díaz, D. Evaluation of the nitroaldol reaction in the presence of metal ion-crosslinked alginates. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Sharma, B.; Verma, A.; Chaudhary, J.; Tamulevicius, S.; Thakur, V.K. Recent progress in sodium alginate based sustainable hydrogels for environmental applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspal, D.; Malviya, A. Composites for wastewater purification: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 12578846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.E.; Zaharioudakis, K.; Kollia, E.; Kopsacheili, A.; Avdylaj, L.; Georgopoulos, S.; Leontiou, A.; Karabagias, V.K.; Kehayias, G.; Ragkava, E.; et al. The Development of a Novel Sodium Alginate-Based Edible Active Hydrogel Coating and Its Application on Traditional Greek Spreadable Cheese. Gels 2023, 9, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ni, F.; Xiong, Q.; Yao, Z. Marine oligosaccharides originated from seaweeds: Source, preparation, structure, physiological activity and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Yang, X.; Yao, L.; Hu, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, X.; Lu, J. Potential Food and Nutraceutical Applications of Alginate: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Fan, Y.; Gao, X.; Gong, Y.; Dai, K.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Yu, J. The Protective Effects of Water-Soluble Alginic Acid on the N-Terminal of Thymopentin. Molecules 2023, 28, 6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łabowska, M.B.; Michalak, I.; Detyna, J. Methods of extraction, physicochemical properties of alginates and their applications in biomedical field—A review. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 738–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellimi, S.; Younes, I.; Ayed, H.B.; Maalej, H.; Montero, V.; Rinaudo, M.; Dahia, M.; Mechichi, T.; Hajji, M.; Nasri, M. Structural, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of sodium alginate isolated from a Tunisian brown seaweed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Shen, P.; Peng, Q. Structures, properties and application of alginic acid: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokova, V.; Lukova, P.; Baldzhieva, A.; Katsarov, P.; Delattre, C.; Molinié, R.; Petit, E.; Elboutachfaiti, R.; Murdjeva, M.; Apostolova, E. Extraction, Structural Characterization, and In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Alginate from Cystoseira crinita (Desf.) Borry Harvested in the Bulgarian Black Sea. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, A.; Song, S. Advances in Research on the Bioactivity of Alginate Oligosaccharides. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Parajuli, D.; Ghimire, K.N.; Biswas, B.K.; Kawakita, H.; Oshima, T.; Ohto, K. Biosorbents for Removing Hazardous Metals and Metalloids. Materials 2017, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudyal, H.; Pangeni, B.; Inoue, K.; Kawakita, H.; Ohto, K.; Ghimire, K.N.; Alam, S. Preparation of novel alginate based anion exchanger from Ulva japonica and its application for the removal of trace concentrations of fluoride from water. Bioresour Technol. 2013, 148, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X. Alginate Hydrogel Dressings for Advanced Wound Management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, E.; Lamprou, D.; Easdon, C.; McLellan, I.; Yiu, H.H.P.; Hoskins, C. Exploration of Dual Ionic Cross-Linked Alginate Hydrogels via Cations of Varying Valences towards Wound Healing. Polymers 2022, 14, 5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Jannat, F.T.; Ashfaq, T.; Santulli, C.; Rizwan, M.; Najda, A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Hussain, S.; et al. A Critical Review on the Synthesis of Natural Sodium Alginate Based Composite Materials: An Innovative Biological Polymer for Biomedical Delivery Applications. Processes 2021, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, G.; Benítez, J.J.; Ceseracciu, L.; Dastmalchi, K.; Itin, B.; Stark, R.E.; Heredia, A.; Athanassiou, A.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A. Sustainable Fabrication of Plant Cuticle-Like Packaging Films from Tomato Pomace Agro-Waste, Beeswax, and Alginate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14955–14966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekamin, M.G.; Ilkhanizadeh, S.; Latifidoost, Z.; Daemi, H.; Karimi, Z.; Barikani, M. Alginic acid: A highly efficient renewable and heterogeneous biopolymeric catalyst for one-pot synthesis of the Hantzsch 1,4-dihydropyridines. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 56658–56664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekamin, M.G.; Karimi, Z.; Latifidoost, Z.; Ilkhanizadeh, S.; Daemi, H.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R.; Barikani, M. Alginic acid: A mild and renewable bifunctional heterogeneous biopolymeric organocatalyst for efficient and facile synthesis of polyhydroquinolines. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forysenkova, A.A.; Ivanova, V.A.; Fadeeva, I.V.; Mamin, G.V.; Rau, J.V. 1H NMR and EPR Spectroscopies Investigation of Alginate Cross-Linking by Divalent Ions. Materials 2023, 16, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Malviya, R.; Singh, S.; Prajapati, B. A Critical Review on Classified Excipient Sodium-Alginate-Based Hydrogels: Modification, Characterization, and Application in Soft Tissue Engineering. Gels 2023, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Mishra, V.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Alginate: Enhancement Strategies for Advanced Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agulhon, P.; Robitzer, M.; David, L.; Quignard, F. Structural regime identification in ionotropic alginate gels: Influence of the cation nature and alginate structure. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Pianella, L.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Ottonelli, M.; Castellano, M. Alginate-based hydrogels prepared via ionic gelation: An experimental design approach to predict the crosslinking degree. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.T.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Smith, P.J.C.; Thom, D. Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: The egg-box model. FEBS Lett. 1973, 32, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, X.; Liu, T.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Chen, J.; Gao, B. Alginate-based composites for environmental applications: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brus, J.; Urbanova, M.; Czernek, J.; Pavelkova, M.; Kubova, K.; Vyslouzil, J.; Abbrent, S.; Konefal, R.; Horský, J.; Vetchy, D.; et al. Structure and Dynamics of Alginate Gels Cross-Linked by Polyvalent Ions Probed via Solid State NMR Spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2478–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Ions-induced gelation of alginate: Mechanisms and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agulhon, P.; Markova, V.; Robitzer, M.; Quignard, F.; Mineva, T. Structure of Alginate Gels: Interaction of Diuronate Units with Divalent Cations from Density Functional Calculations. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, P.; Pageni, P.; Tang, C. Recent Advances in Metal-Containing Polymer Hydrogels. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1700109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.O.; Derkach, S.R.; Khair, T.; Kazantseva, M.A.; Zuev, Y.F.; Zueva, O.S. Ion-Induced Polysaccharide Gelation: Peculiarities of Alginate Egg-Box Association with Different Divalent Cations. Polymers 2023, 15, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zueva, O.S.; Khair, T.; Derkach, S.R.; Kazantseva, M.A.; Zuev, Y.F. Strontium-Induced Gelation of Sodium Alginate in the Presence of Carbon Nanotubes: Elemental Analysis and Gel Structure. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, D.A.; Welsh, E.J. Secondary and tertiary structure of polysaccharides in solutions and gels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1977, 16, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Thom, D.; Boyd, J. Chiroptical and stoichiometric evidence of a specific, primary dimerisation process in alginate gelation. Carbohydr. Res. 1978, 66, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, W.; Perez, S.; Rizzo, R.; Taravel, F.; Vignon, M. Aspects of the conformation of polyguluronate in the solid state and in solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1983, 5, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braccini, I.; Pérez, S. Molecular Basis of Ca2+-Induced Gelation in Alginates and Pectins: The Egg-Box Model Revisited. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, I.; Holtan, S.; Mørch, Y.A.; Borgogna, M.; Dentini, M.; Gudmund, S. New hypothesis on the role of alternating sequences in calcium−alginate gels. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Al-Assaf, S.; Phillips, G.O.; Nishinari, K.; Funami, T.; Williams, P.A.; Li, L. Multiple Steps and Critical Behaviors of the Binding of Calcium to Alginate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 2456–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, P.; Mo, F.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Stokke, B.T. Evidence for Egg-Box-Compatible Interactions in Calcium—Alginate Gels from Fiber X-ray Diffraction. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2098–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Fang, Y.; Vreeker, R.; Appelqvist, I.; Mendes, E. Reexamining the egg-box model in calcium-alginate gels with X-ray diffraction. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgogna, M.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Paoletti, S.; Donati, I. On the initial binding of alginate by calcium ions. The tilted egg-box hypothesis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 7277–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, H.; Srebnik, S. Structural Characterization of Sodium Alginate and Calcium Alginate. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, H.; Srebnik, S. Sequence-dependent association of alginate with sodium and calcium counterions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wan, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zhu, J. Effect of Calcium Ions on the III Steps of Self-Assembly of SA Investigated with Atomic Force Microscopy. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Egg-box model-based gelation of alginate and pectin: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, I.; Paoletti, S. Material Properties of Alginates. In Alginates: Biology and Applications; Rehm, B.H.A., Ed.; Microbiology Monographs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 13, pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, T.; Smidsrød, O.; Larsen, B.; Haug, A.; Paasivirta, J. A Computer Study of the Changes in Composition-Distribution Occurring during Random Depolymerization of a Binary Linear Heteropolysaccharide. Acta Chem. Scand. 1968, 22, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrød, O.; Whittington, S.G. Monte Carlo Investigation of Chemical Inhomogeneity in Polymers. Macromolecules 1969, 2, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.; Painter, T.J. The periodate-oxidation limit of alginate. Carbohydr. Res. 1969, 10, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanucci, P.; Terenzi, S.; Santi, C.; Pennoni, I.; Bini, V.; Pescara, T.; Basta, G.; Calafiore, R. Insights in Behavior of Variably Formulated Alginate-Based Microcapsules for Cell Transplantation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 965804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mørch, Ý.A.; Donati, I.; Strand, B.L.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Effect of Ca2+, Ba2+ and Sr2+ on Alginate Microbeads. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, S.K.; Sharma, S. Investigation of swelling/degradation behaviour of alginate beads crosslinked with Ca2+ and Ba2+ ions. React. Funct. Polym. 2004, 59, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, U.; Mimietz, S.; Zimmermann, H.; Hillgärtner, M.; Schneider, H.; Ludwig, J.; Hasse, C.; Haase, A.; Rothmund, M.; Fuhr, G. Hydrogel-Based Non-Autologous Cell and Tissue Therapy. BioTechniques 2000, 29, 564–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-L.; Lin, Y.-S. The Size Stability of Alginate Beads by Different Ionic Crosslinkers. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 9304592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.M. Prospective and Comparative Novel Technique for Evaluation the Affinity of Alginate for Binding the Alkaline-Earth Metal Ions during Formation the Coordination Biopolymer Hydrogel Complexes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanes, D.; Teng, L.Y.; Sheng, F.S.; Coombes, A.G.A. Exploiting the Versatility of Oral Capsule Formulations Based on High M-Alginate for Targeted Delivery of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs to the Upper and Lower GI Tract. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, T.D.; Cygan, R.T.; Mitchell, R. Molecular Models of Alginic Acid: Interactions with Calcium Ions and Calcite Surfaces. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 3508–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Weng, L.; Deng, B. Strontium Ion Substituted Alginate-based Hydrogel Fibers and Its Coordination Binding Model. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaii, N.; Khodagholi, F. Evaluation of chaperone-like activity of alginate: Microcapsule and water-soluble forms. Protein J. 2009, 28, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire du Poset, A.; Lerbret, A.; Boué, F.; Zitolo, A.; Assifaoui, A.; Cousin, F. Tuning the Structure of Galacturonate Hydrogels: External Gelation by Ca, Zn, or Fe Cationic Cross-Linkers. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2864–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plazinski, W.; Drach, M. Binding of Bivalent Metal Cations by α-L-Guluronate: Insights from the DFT-MD Simulations. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 3987–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerichs, N.; Wingender, J.; Flemming, H.-C.; Mayer, C. Interaction between Alginates and Manganese Cations: Identification of Preferred Cation Binding Sites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2004, 34, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, E.; Nieduszynski, I.; Mackie, W.; Parker, K.; Smolko, E. Structural components of alginic acid. I. The crystalline structure of poly-beta-D-mannuronic acid. Results of X-ray diffraction and polarized infrared studies. Biopolymers 1973, 12, 1865. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, E.; Nieduszynski, I.; Mackie, W.; Parker, K.; Smolko, E. Structural components of alginic acid. II. The crystalline structure of poly-α-L-guluronic acid. Results of X-ray diffraction and polarized infrared studies. Biopolymers 1973, 12, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usov, A.I. Alginic acids and alginates: Analytical methods used for their estimation and characterisation of composition and primary structure. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1999, 68, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Rupérez, P. FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy as a Tool for Polysaccharide Identification in Edible Brown and Red Seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.; Park, S.A.; Lee, J.Y. Three Dimensional Cell Printing with Sulfated Alginate for Improved Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Delivery and Osteogenesis in Bone Tissue Engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zueva, O.S.; Makarova, A.O.; Zuev, Y.F. Carbon Nanotubes in Composite Hydrogels Based on Plant Carbohydrates. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 945, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paques, J.P.; van der Linden, E.; van Rijn, C.J.M.; Sagis, L.M.C. Preparation Methods of Alginate Nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
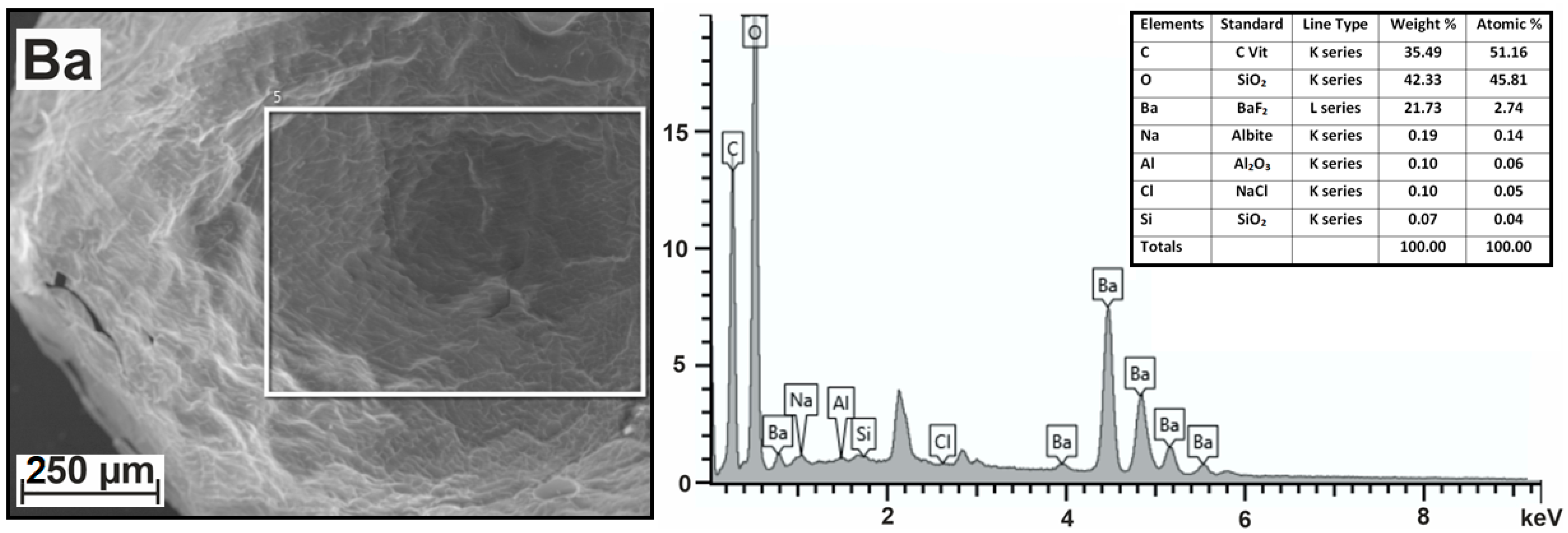
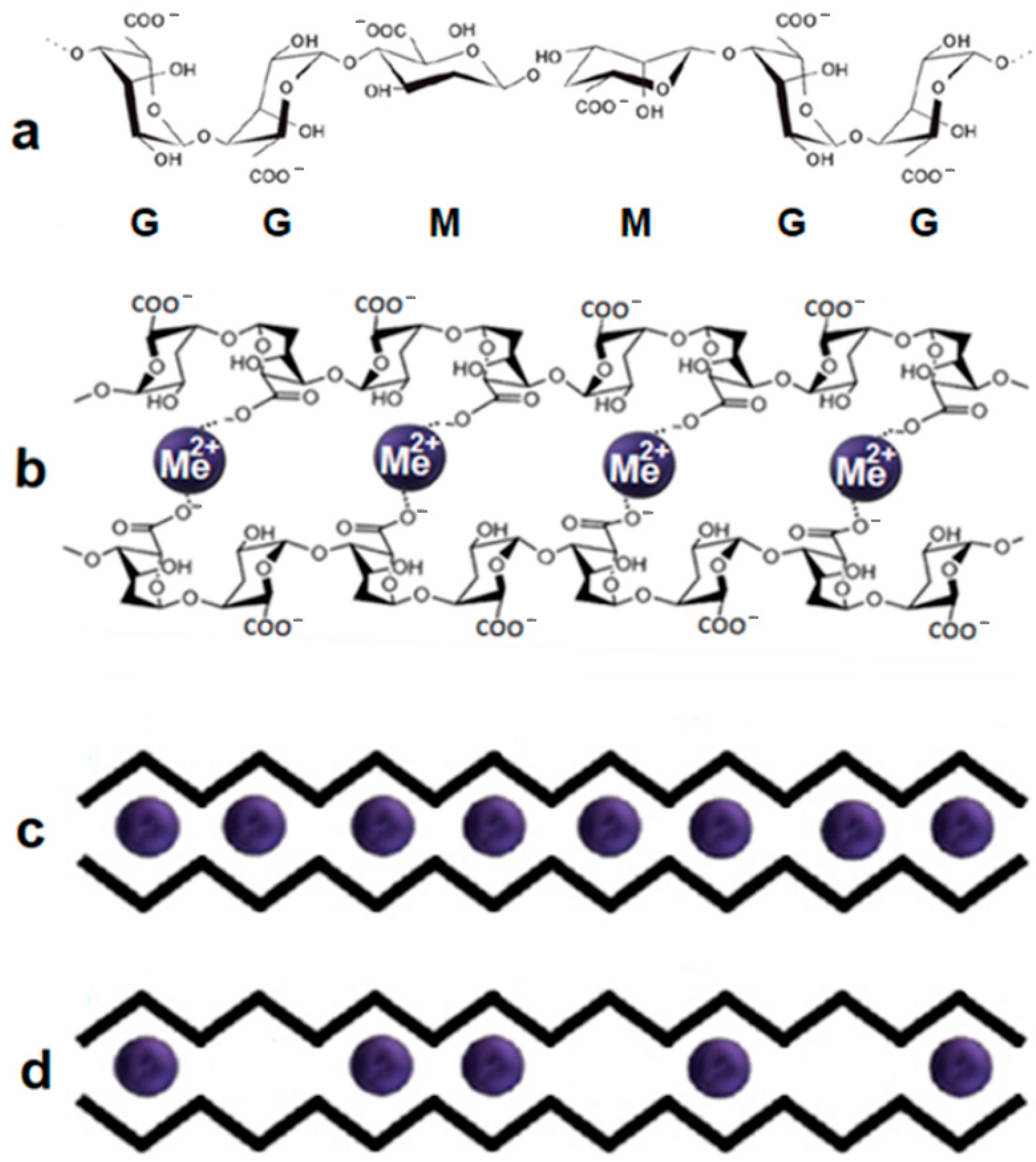
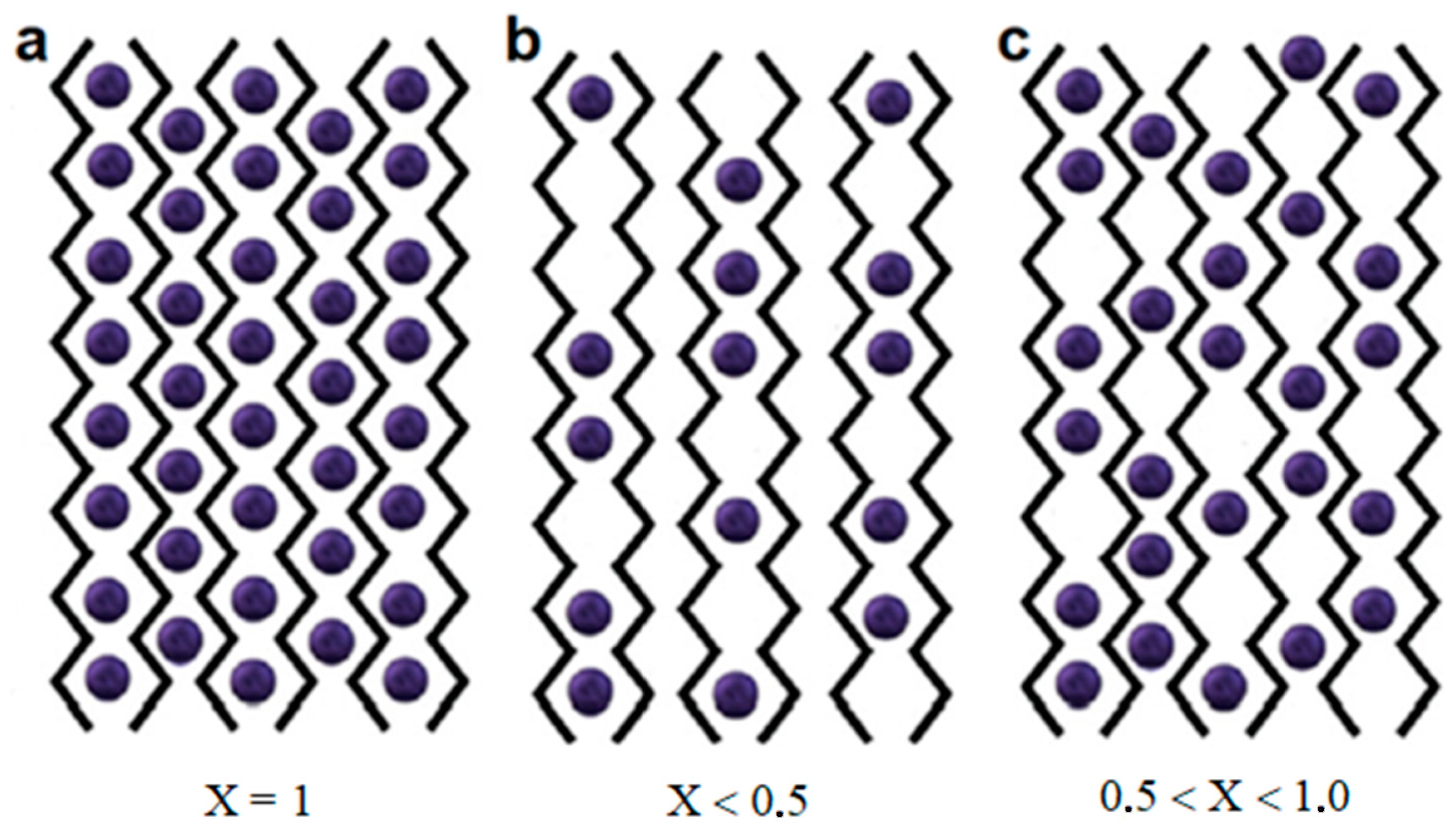
| N | rion, nm | Hydrogel | Me | C | O | Na | Cl | S | Al | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.135 | Ba2+-alginate | Ba, 2.74 | 51.16 | 45.81 | 0.14 | 0.05 | – | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| 2 | 0.113 | Sr2+-alginate | Sr, 6.47 | 43.18 | 41.73 | 0.36 | 8.27 | – | – | – |
| 3 | 0.113 | Sr2+-alginate (add. washed) | Sr, 2.71 | 50.04 | 47.25 | – | – | – | – | – |
| 4 | 0.099 | Ca2+-alginate | Ca, 6.48 | 43.30 | 38.51 | 0.49 | 11.15 | – | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| 5 | 0.074 | Zn2+-alginate | Zn, 5.02 | 40.68 | 51.33 | – | – | 2.87 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 6 | 0.073 | Cu2+-alginate | Cu, 2.68 | 32.40 | 62.23 | – | – | 2.60 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| 7 | 0.069 | Ni2+-alginate | Ni, 6.49 | 26.07 | 62.45 | – | – | 4.94 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| 8 | 0.067 | Mn2+-alginate | Mn, 11.8 | 45.80 | 24.99 | 0.12 | 17.2 | – | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| N | Hydrogel | Me | C | O | Na | Cl | S | Elemental Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ba2+-alginate | Ba, 0.64 | 12 | 10.75 | 0.03 | – | – | C12O10.75Na0.03Ba0.64 |
| 2 | Sr2+-alginate | Sr, 1.80 | 12 | 11.60 | 0.10 | 2.30 | – | C12O11.6Na0.1Sr1.80Cl2.30 |
| 3 | Sr2+-alginate (add. washed) | Sr, 0.65 | 12 | 11.33 | – | – | – | C12O11.33Sr0.65 |
| 4 | Ca2+-alginate | Ca, 1.80 | 12 | 10.67 | 0.14 | 3.09 | – | C12O10.67Na0.14Ca1.80Cl3.09 |
| 5 | Zn2+-alginate | Zn, 1.48 | 12 | 15.14 | – | – | 0.85 | C12O15.14Zn1.48S0.85 |
| 6 | Cu2+-alginate | Cu,0.99 | 12 | 23.05 | – | – | 0.96 | C12O23.05Cu0.99S0.96 |
| 7 | Ni2+-alginate | Ni, 2.99 | 12 | 28.75 | – | – | 2.27 | C12O28.75Ni2.99S2.27 |
| 8 | Mn2+-alginate | Mn, 3.09 | 12 | 6.55 | 0.03 | 4.51 | – | C12O6.55Na0.03Mn3.09Cl4.51 |
| N | Structure | Probability (Arbitrary μ) | Probability (μ = 1.56) | Probability (μ = 1.5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GG | 1/(1 + μ)2 | 0.153 | 0.16 |
| 2 | GM | μ/(1 + μ)2 | 0.238 | 0.24 |
| 3 | MG | μ/(1 + μ)2 | 0.238 | 0.24 |
| 4 | MM | μ2/(1 + μ)2 | 0.371 | 0.36 |
| N | Structure | Probability (Arbitrary μ = M/G) | Probability (μ = 1.56) | Probability (μ = 1.5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GG–GG | 1/(1 + μ)4 | 0.0233 | 0.0256 |
| 2 | GG–GM, GG–MG | 4μ/(1 + μ)4 | 0.1453 | 0.1536 |
| 3 | GG-MM | 2μ2/(1 + μ)4 | 0.1133 | 0.1152 |
| 4 | GM–GM | 2μ2/(1 + μ)4 | 0.1133 | 0.1152 |
| 5 | GM-MG | 2μ2/(1 + μ)4 | 0.1133 | 0.1152 |
| 6 | MM–GM, MM–MG | 4μ3/(1 + μ)4 | 0.3536 | 0.3456 |
| 7 | MM–MM | μ4/(1 + μ)4 | 0.1379 | 0.1296 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zueva, O.S.; Khair, T.; Kazantseva, M.A.; Latypova, L.; Zuev, Y.F. Ions-Induced Alginate Gelation According to Elemental Analysis and a Combinatorial Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216201
Zueva OS, Khair T, Kazantseva MA, Latypova L, Zuev YF. Ions-Induced Alginate Gelation According to Elemental Analysis and a Combinatorial Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(22):16201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216201
Chicago/Turabian StyleZueva, Olga S., Tahar Khair, Mariia A. Kazantseva, Larisa Latypova, and Yuriy F. Zuev. 2023. "Ions-Induced Alginate Gelation According to Elemental Analysis and a Combinatorial Approach" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 22: 16201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216201
APA StyleZueva, O. S., Khair, T., Kazantseva, M. A., Latypova, L., & Zuev, Y. F. (2023). Ions-Induced Alginate Gelation According to Elemental Analysis and a Combinatorial Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(22), 16201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216201








