Metformin Prevents Cocaine Sensitization: Involvement of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Trafficking between Subcellular Compartments in the Corticostriatal Reward Circuit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
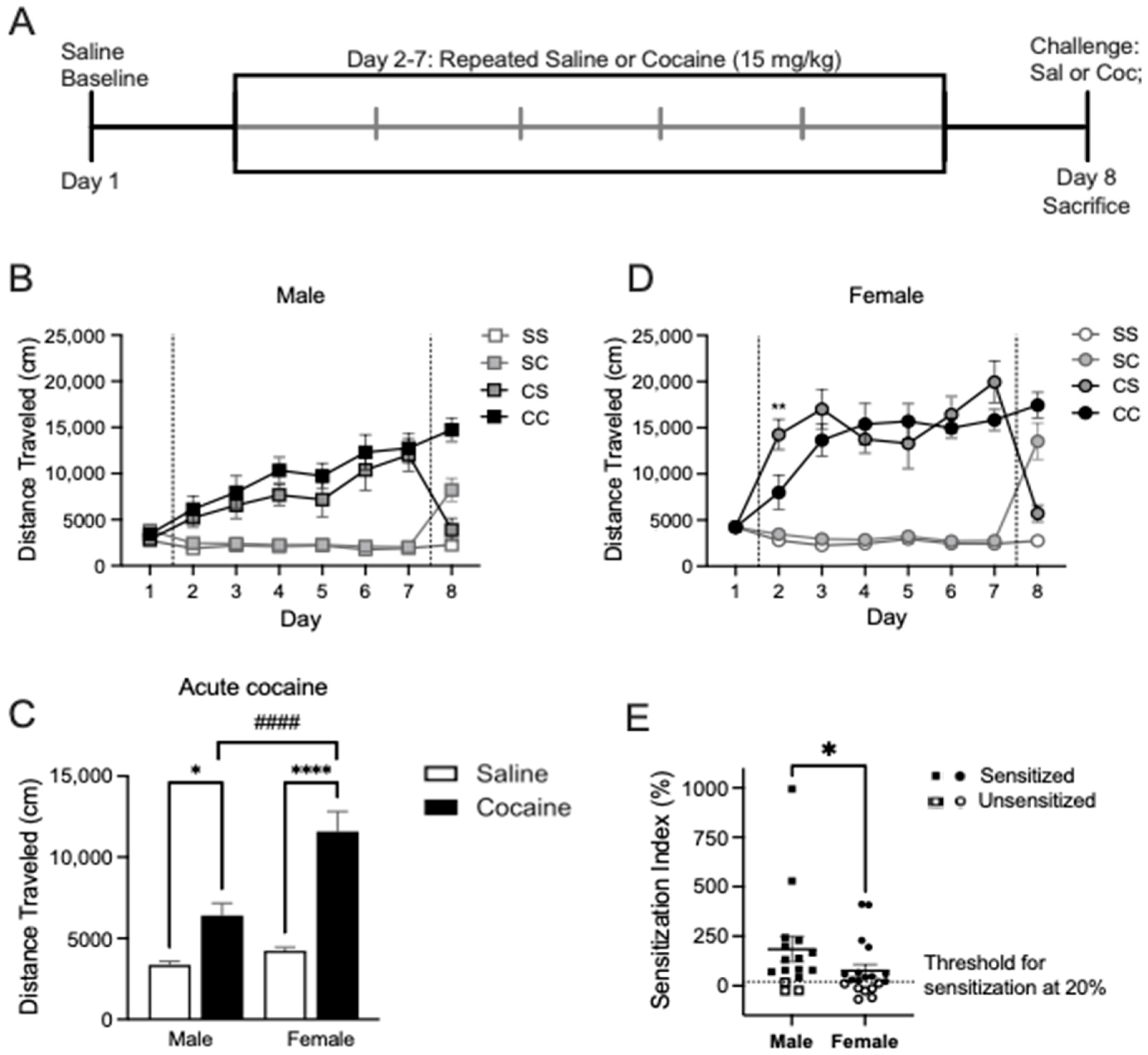
2.1. Cocaine Locomotor Sensitization
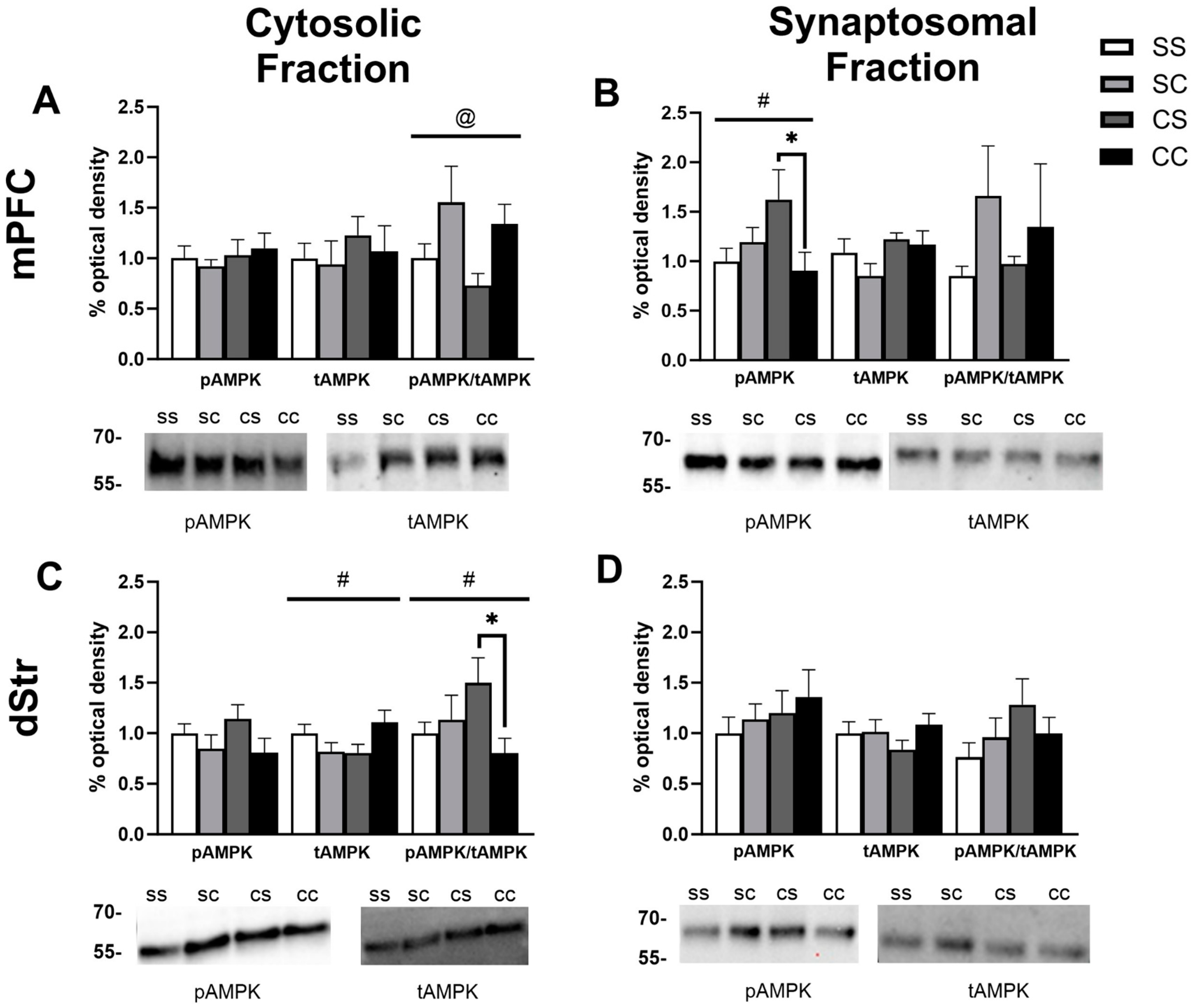
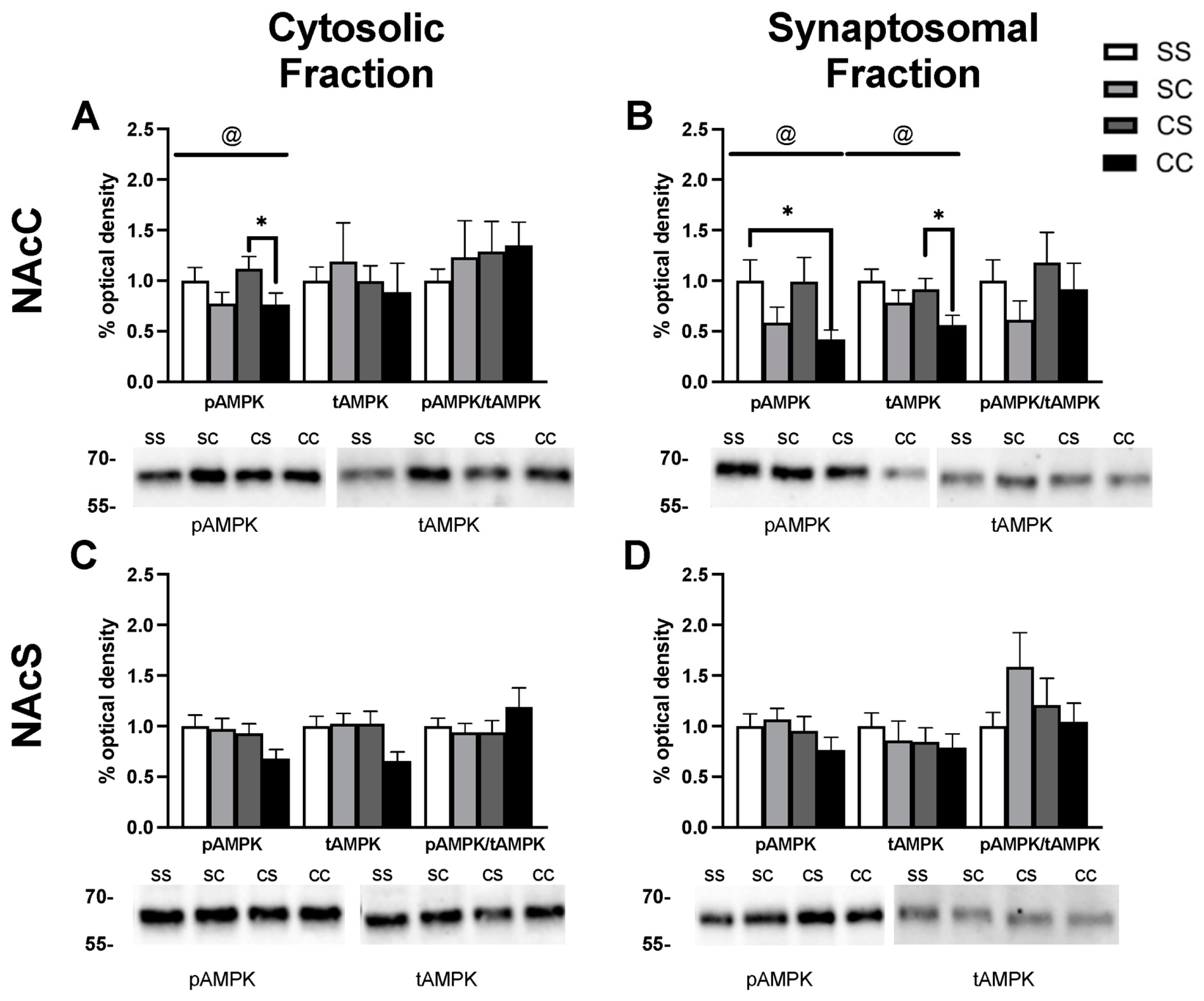
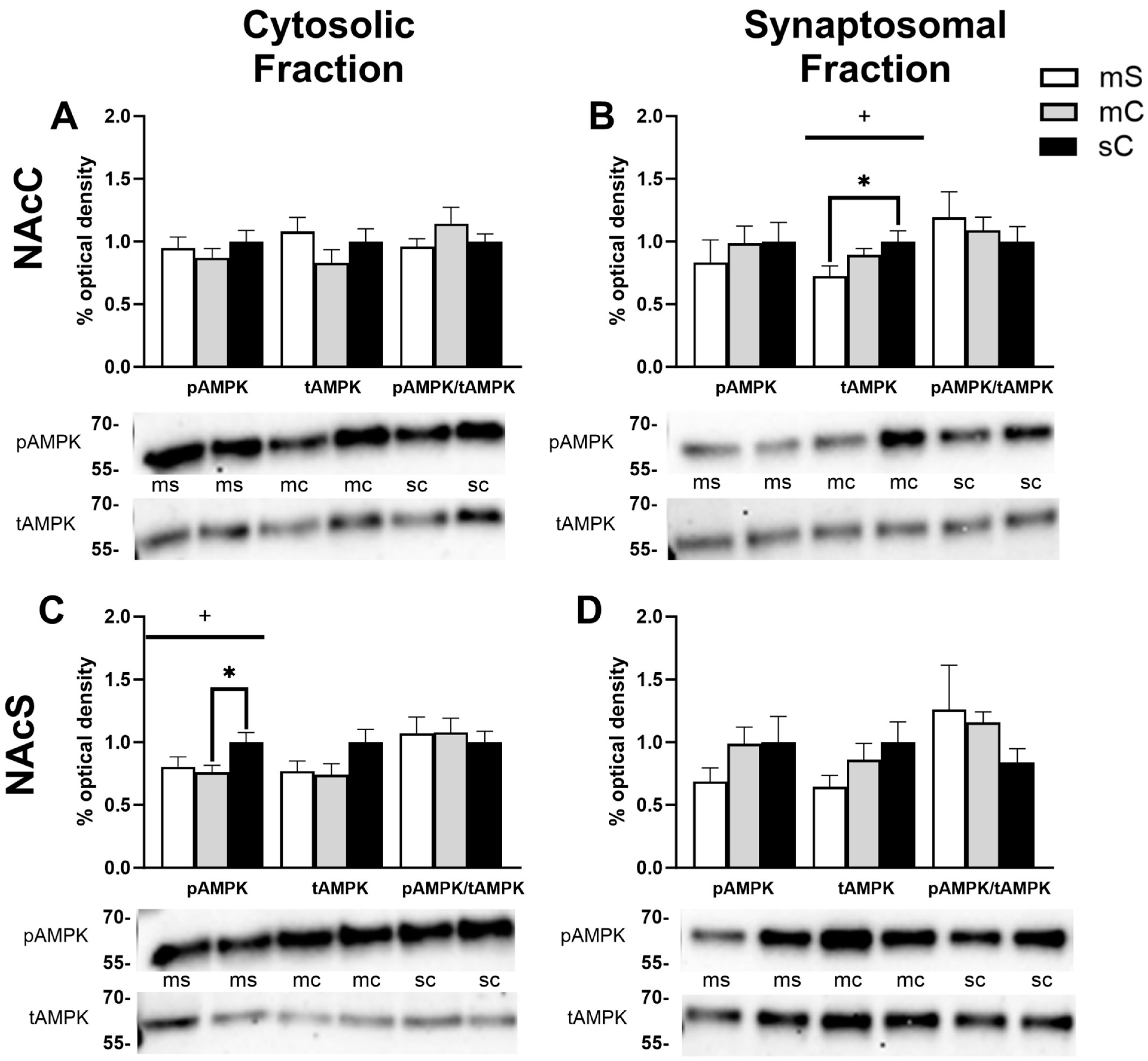
2.2. Effects of Cocaine Sensitization on AMPK Protein Levels
2.3. Effects of Metformin Pretreatment on Cocaine-Induced Locomotion and Sensitization
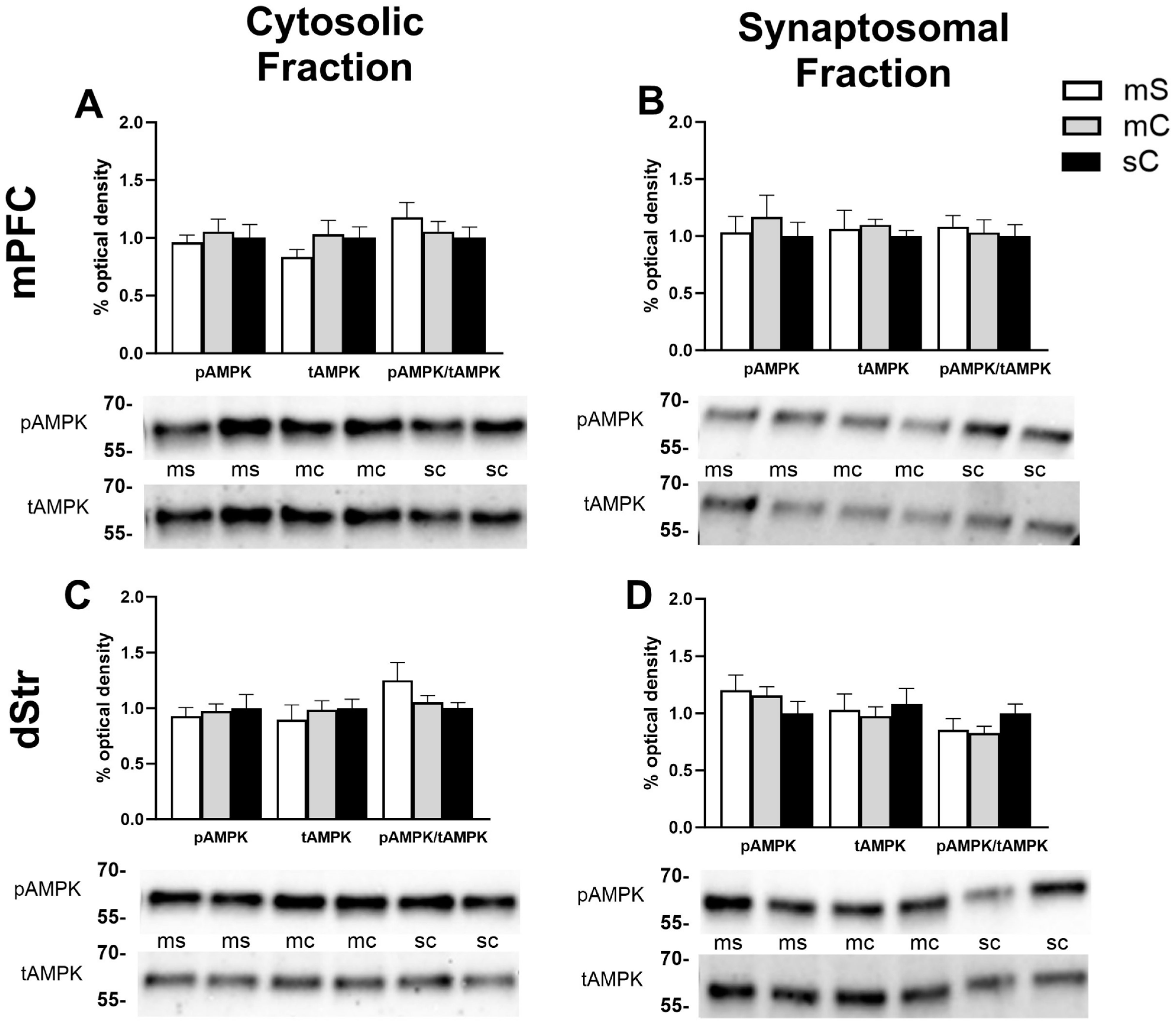
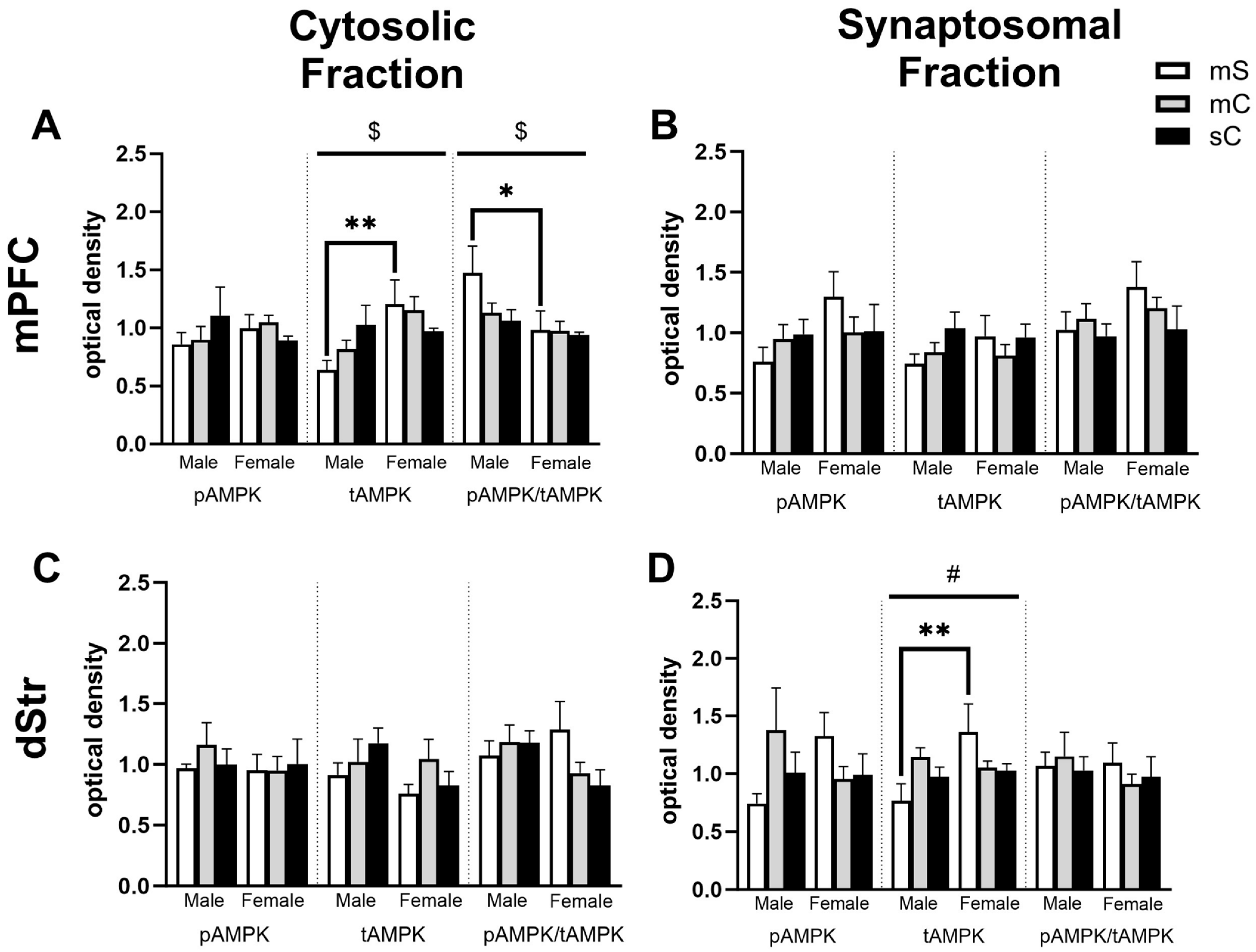
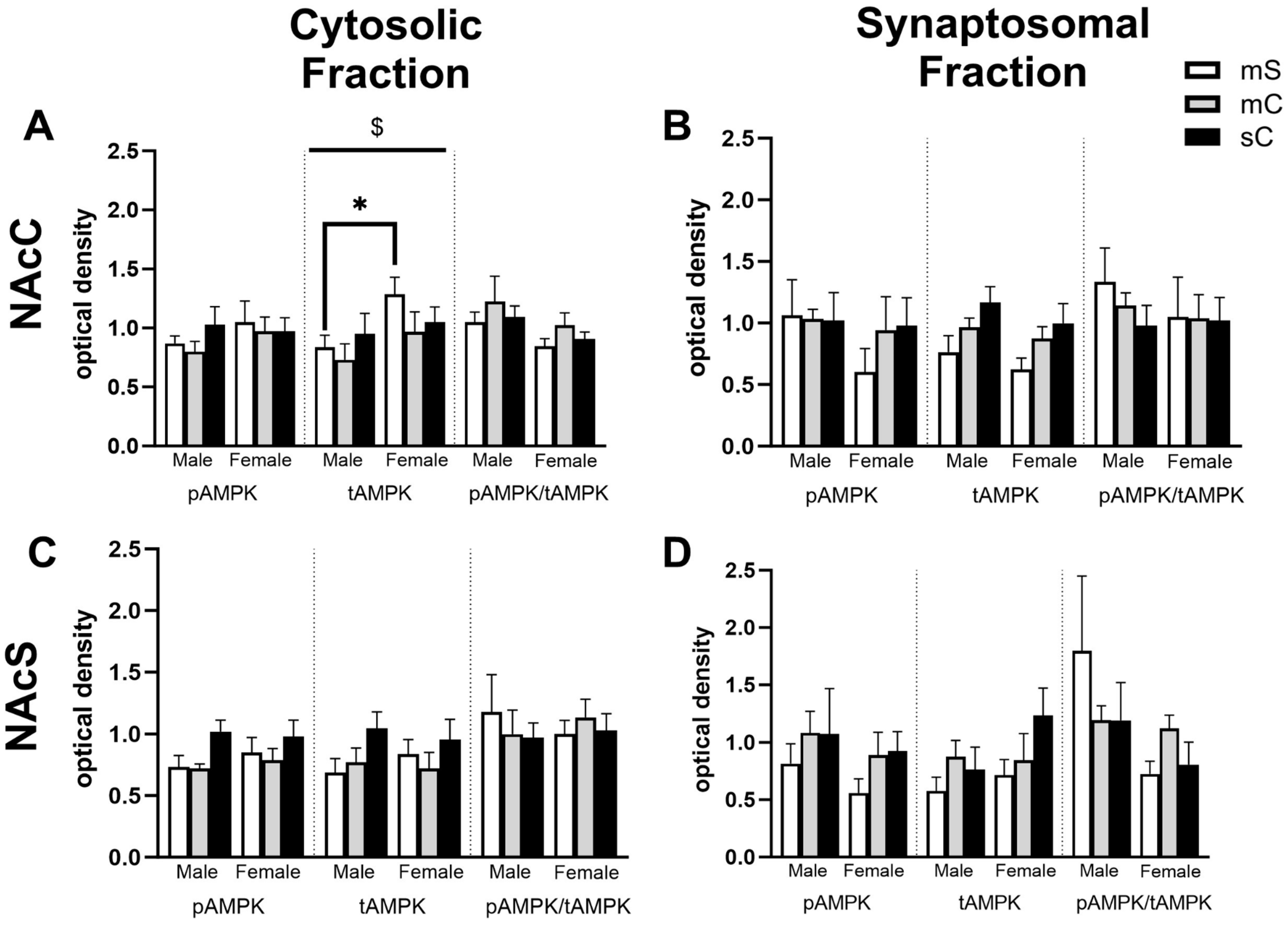
2.4. Effects of Metformin Pretreatment Followed by Cocaine on AMPK Protein Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Cocaine Sensitization
4.3.1. Experiment 1
4.3.2. Experiment 2
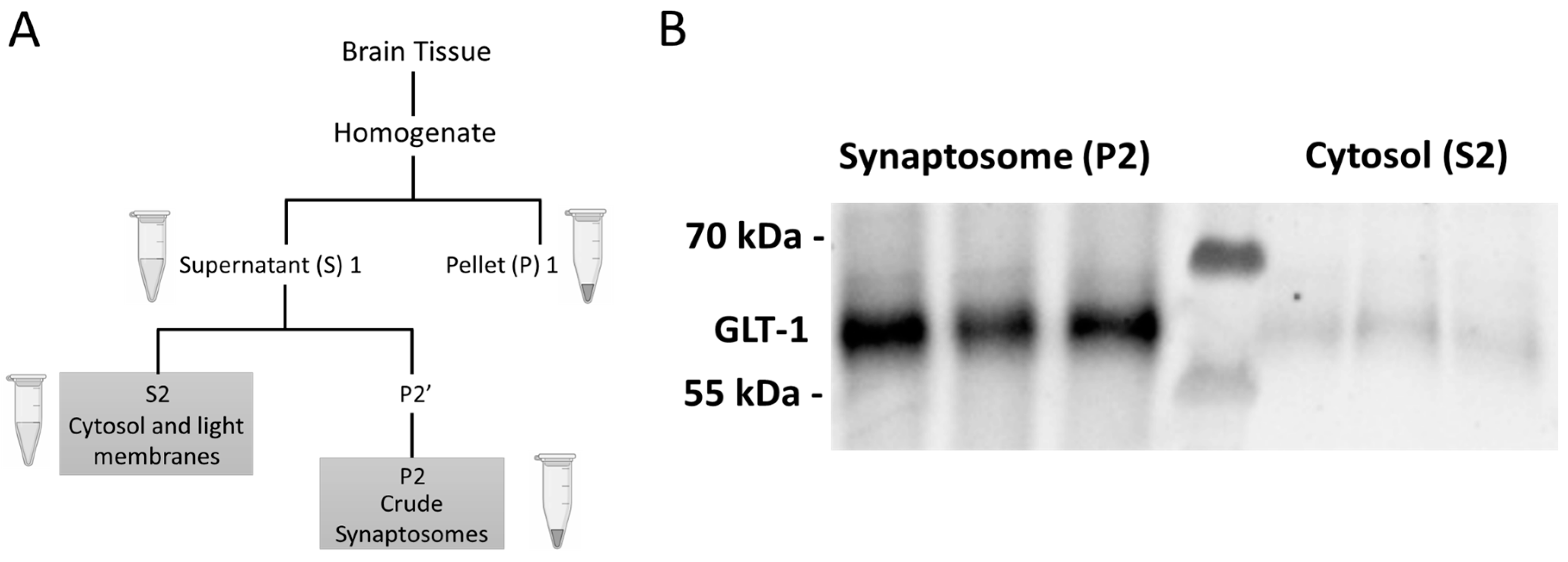
4.4. Euthanasia, Tissue Extraction, Preparation, and Western Blotting
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steketee, J.D.; Kalivas, P.W. Drug Wanting: Behavioral Sensitization and Relapse to Drug-Seeking Behavior. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 348–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.M.; Christie, M.J.; De Lecea, L.; Halford, J.C.G.; Leysen, J.E.; Meck, W.H.; Buhusi, C.V.; Bubar, M.J.; Cunningham, K.A.; Bubar, M.J.; et al. Sensitization to Drugs. In Encyclopedia of Psychopharmacology; Stolerman, I.P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1203–1208. ISBN 978-3-540-68698-9. [Google Scholar]
- Post, R.M.; Rose, H. Increasing Effects of Repetitive Cocaine Administration in the Rat. Nature 1976, 260, 731–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, D.; White, F. The Persistence of Behavioral Sensitization to Cocaine Parallels Enhanced Inhibition of Nucleus Accumbens Neurons. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6287–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, S. Sensitization to Cocaine’s Reinforcing Effects Produced by Various Cocaine Pretreatment Regimens in Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 66, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandt, B.H.; Schenk, S.; Zahniser, N.R.; Allen, R.M. Individual Differences in Cocaine-Induced Locomotor Activity in Male Sprague–Dawley Rats and Their Acquisition of and Motivation to Self-Administer Cocaine. Psychopharmacology 2008, 201, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferrario, C.R.; Gorny, G.; Crombag, H.S.; Li, Y.; Kolb, B.; Robinson, T.E. Neural and Behavioral Plasticity Associated with the Transition from Controlled to Escalated Cocaine Use. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 58, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.R.; Horger, B.A. Enhanced Responding for Conditioned Reward Produced by Intra-Accumbens Amphetamine Is Potentiated after Cocaine Sensitization. Psychopharmacology 1999, 142, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boileau, I.; Dagher, A.; Leyton, M.; Gunn, R.N.; Baker, G.B.; Diksic, M.; Benkelfat, C. Modeling Sensitization to Stimulants in Humans: An [11C]Raclopride/Positron Emission Tomography Study in Healthy Men. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Duffy, P. Time Course of Extracellular Dopamine and Behavioral Sensitization to Cocaine. I. Dopamine Axon Terminals. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, L.H.; Justice, J.B. Serotonin and Dopamine Sensitization in the Nucleus Accumbens, Ventral Tegmental Area, and Dorsal Raphe Nucleus Following Repeated Cocaine Administration. J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, R.C.; Bell, K.; Duffy, P.; Kalivas, P.W. Repeated Cocaine Augments Excitatory Amino Acid Transmission in the Nucleus Accumbens Only in Rats Having Developed Behavioral Sensitization. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.S.; Berger, S.P. Evidence for Sensitization of Cocaine-Induced Nucleus Accumbens Glutamate Release. NeuroReport 1996, 7, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, V.; Naughton, S.X.; Shi, X.; Kelley, L.K.; Yegla, B.; Tallarida, C.S.; Rawls, S.M.; Unterwald, E.M. Cocaine-Induced Neuroadaptations in the Dorsal Striatum: Glutamate Dynamics and Behavioral Sensitization. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 75, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Steketee, J.D. Repeated Exposure to Cocaine Alters Medial Prefrontal Cortex Dopamine D2-like Receptor Modulation of Glutamate and Dopamine Neurotransmission within the Mesocorticolimbic System: Sensitization and Cortical Dopamine Receptors. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, R.; Wan, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. mTOR Regulates Cocaine-Induced Behavioural Sensitization through the SynDIG1–GluA2 Interaction in the Nucleus Accumbens. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.M.; Fasano, S.; Yang, P.; Brambilla, R.; Robinson, T.E. Knockout of ERK1 Enhances Cocaine-Evoked Immediate Early Gene Expression and Behavioral Plasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 2660–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeffer, C.A.; Klann, E. mTOR Signaling: At the Crossroads of Plasticity, Memory and Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoki, K.; Zhu, T.; Guan, K.-L. TSC2 Mediates Cellular Energy Response to Control Cell Growth and Survival. Cell 2003, 115, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwinn, D.M.; Shackelford, D.B.; Egan, D.F.; Mihaylova, M.M.; Mery, A.; Vasquez, D.S.; Turk, B.E.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK Phosphorylation of Raptor Mediates a Metabolic Checkpoint. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, N.X.Y.; Kaczmarek, A.; Hoque, A.; Davie, E.; Ngoei, K.R.W.; Morrison, K.R.; Smiles, W.J.; Forte, G.M.; Wang, T.; Lie, S.; et al. mTORC1 Directly Inhibits AMPK to Promote Cell Proliferation under Nutrient Stress. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase: Maintaining Energy Homeostasis at the Cellular and Whole-Body Levels. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2014, 34, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraleedharan, R.; Dasgupta, B. AMPK in the Brain: Its Roles in Glucose and Neural Metabolism. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 2247–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gambero, A.J.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Suárez, J. Energy Sensors in Drug Addiction: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domise, M.; Vingtdeux, V. AMPK in Neurodegenerative Diseases. In AMP-Activated Protein Kinase; Cordero, M.D., Viollet, B., Eds.; Experientia Supplementum; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 107, pp. 153–177. ISBN 978-3-319-43587-9. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Kang, U.G. Region-Specific Activation of the AMPK System by Cocaine: The Role of D1 and D2 Receptors. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2016, 146–147, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.-J.; Yuan, K.; Cao, L.; Yan, W.; Luo, Y.-X.; Jian, M.; Liu, J.-F.; Fang, Q.; Wang, J.-S.; Han, Y.; et al. AMPK Signaling in the Nucleus Accumbens Core Mediates Cue-Induced Reinstatement of Cocaine Seeking. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-X.; Liu, F.-L.; Li, X.; Lu, T.-S.; Luo, Y.-X.; Jian, M.; Yuan, K.; Meng, S.-Q.; Bao, Y.-P.; Shi, J.; et al. Novel Role of AMPK in Cocaine Reinforcement via Regulating CRTC1. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, G.; Hardie, D.G.; Pearson, E.R. The Mechanisms of Action of Metformin. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; An, H.; Liu, T.; Qin, C.; Sesaki, H.; Guo, S.; Radovick, S.; Hussain, M.; Maheshwari, A.; Wondisford, F.E.; et al. Metformin Improves Mitochondrial Respiratory Activity through Activation of AMPK. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1511–1523.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, C.; Jacobs, T.F. Metformin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.; He, L. Current Understanding of Metformin Effect on the Control of Hyperglycemia in Diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 228, R97–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horakova, O.; Kroupova, P.; Bardova, K.; Buresova, J.; Janovska, P.; Kopecky, J.; Rossmeisl, M. Metformin Acutely Lowers Blood Glucose Levels by Inhibition of Intestinal Glucose Transport. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, S.; Sominsky, L.; Siskind, D.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Carvalho, A.F.; Maes, M.; Walker, A.J.; Walder, K.; Yung, A.R.; Williams, L.J.; et al. The Role of Metformin as a Treatment for Neuropsychiatric Illness. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 64, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozburn, A.R.; Spencer, S.M. Repurposing Anti-Inflammatory Medications for Alcohol and Substance Use Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.; Willard, A.; Mulloy, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Sciaccotta, A.; Schonfeld, M.; Spencer, S.M. Metformin in Nucleus Accumbens Core Reduces Cue-induced Cocaine Seeking in Male and Female Rats. Addict. Biol. 2022, 27, e13165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.C.; George, O. Advances in Smoking Cessation Pharmacotherapy: Non-Nicotinic Approaches in Animal Models. Neuropharmacology 2020, 178, 108225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.K.; Klein, K.; Majeed, A.; Khunti, K. Association of Smoking and Concomitant Metformin Use with Cardiovascular Events and Mortality in People Newly Diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes 2016, 8, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Sajja, R.K.; Kaisar, M.A.; Park, J.H.; Villalba, H.; Liles, T.; Abbruscato, T.; Cucullo, L. Role of Nrf2 and Protective Effects of Metformin against Tobacco Smoke-Induced Cerebrovascular Toxicity. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Amato, S.; Gilbert, J.; Man, H.-Y. Resveratrol Up-Regulates AMPA Receptor Expression via AMP-Activated Protein Kinase-Mediated Protein Translation. Neuropharmacology 2015, 95, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wegman-Points, L.; Alganem, K.; Imami, A.S.; Mathis, V.; Creeden, J.F.; McCullumsmith, R.; Yuan, L.-L. Subcellular Partitioning of Protein Kinase Activity Revealed by Functional Kinome Profiling. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalfio, A.M.; Fetterly, T.L.; Nieto, A.M.; Robinson, T.E.; Ferrario, C.R. Cocaine-Induced Sensitization and Glutamate Plasticity in the Nucleus Accumbens Core: Effects of Sex. Biol. Sex Differ. 2023, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.E.; Lee, B.R.; Mu, P.; Ferguson, D.; Dietz, D.; Ohnishi, Y.N.; Lin, Y.; Suska, A.; Ishikawa, M.; Huang, Y.H.; et al. A Silent Synapse-Based Mechanism for Cocaine-Induced Locomotor Sensitization. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8163–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.S.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B. Spatial Control of AMPK Signaling at Subcellular Compartments. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 55, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afinanisa, Q.; Cho, M.K.; Seong, H.-A. AMPK Localization: A Key to Differential Energy Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cai, Y.; Fan, X. Metformin Administration During Early Postnatal Life Rescues Autistic-Like Behaviors in the BTBR T+ Itpr3tf/J Mouse Model of Autism. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwa, M.; Egashira, T.; Nakano, H.; Sasaki, H.; Kumagai, S. Metformin Increases the PGC-1α Protein and Oxidative Enzyme Activities Possibly via AMPK Phosphorylation in Skeletal Muscle in Vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 101, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Jain, P.D.; Ghumatkar, P.J.; Tambe, R.; Sathaye, S. Neuroprotective Effect of Metformin in MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease in Mice. Neuroscience 2014, 277, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.-Y.; Ding, H.; Dunn, T.; Gao, J.-L.; Labastida, J.; Schlagal, C.; Ning, G.-Z.; Feng, S.-Q.; Wu, P. Low-Dose Metformin Treatment in the Subacute Phase Improves the Locomotor Function of a Mouse Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Sahra, I.; Regazzetti, C.; Robert, G.; Laurent, K.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Auberger, P.; Tanti, J.-F.; Giorgetti-Peraldi, S.; Bost, F. Metformin, Independent of AMPK, Induces mTOR Inhibition and Cell-Cycle Arrest through REDD1. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4366–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.R.; Morrison, V.L.; Levin, D.; Mohan, M.; Forteath, C.; Beall, C.; McNeilly, A.D.; Balfour, D.J.K.; Savinko, T.; Wong, A.K.F.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Metformin Irrespective of Diabetes Status. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffner, T.G.; Hartman, J.A.; Seiden, L.S. A Rapid Method for the Regional Dissection of the Rat Brain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1980, 13, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissner, K.J.; Uys, J.D.; Schwacke, J.H.; Comte-Walters, S.; Rutherford-Bethard, J.L.; Dunn, T.E.; Blumer, J.B.; Schey, K.L.; Kalivas, P.W. AKAP Signaling in Reinstated Cocaine Seeking Revealed by iTRAQ Proteomic Analysis. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5648–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehre, K.; Levy, L.; Ottersen, O.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Danbolt, N. Differential Expression of Two Glial Glutamate Transporters in the Rat Brain: Quantitative and Immunocytochemical Observations. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1835–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genda, E.N.; Jackson, J.G.; Sheldon, A.L.; Locke, S.F.; Greco, T.M.; O’Donnell, J.C.; Spruce, L.A.; Xiao, R.; Guo, W.; Putt, M.; et al. Co-Compartmentalization of the Astroglial Glutamate Transporter, GLT-1, with Glycolytic Enzymes and Mitochondria. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 18275–18288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, T. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Regulates Gene Expression by Direct Phosphorylation of Nuclear Proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzinger, M.; Fischhuber, K.; Pölöske, D.; Mechtler, K.; Heiss, E.H. AMPK Leads to Phosphorylation of the Transcription Factor Nrf2, Tuning Transactivation of Selected Target Genes. Redox Biol. 2020, 29, 101393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teague, C.D.; Nestler, E.J. Key Transcription Factors Mediating Cocaine-Induced Plasticity in the Nucleus Accumbens. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 687–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aruldas, R.; Orenstein, L.B.; Spencer, S. Metformin Prevents Cocaine Sensitization: Involvement of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Trafficking between Subcellular Compartments in the Corticostriatal Reward Circuit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316859
Aruldas R, Orenstein LB, Spencer S. Metformin Prevents Cocaine Sensitization: Involvement of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Trafficking between Subcellular Compartments in the Corticostriatal Reward Circuit. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):16859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316859
Chicago/Turabian StyleAruldas, Rachel, Laura Buczek Orenstein, and Sade Spencer. 2023. "Metformin Prevents Cocaine Sensitization: Involvement of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Trafficking between Subcellular Compartments in the Corticostriatal Reward Circuit" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 16859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316859
APA StyleAruldas, R., Orenstein, L. B., & Spencer, S. (2023). Metformin Prevents Cocaine Sensitization: Involvement of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Trafficking between Subcellular Compartments in the Corticostriatal Reward Circuit. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 16859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316859




