Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Intricate Gene Networks Involved in Female Development in Melon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Proteome and Transcriptome Raw Data Analysis and Protein/Gene Identification
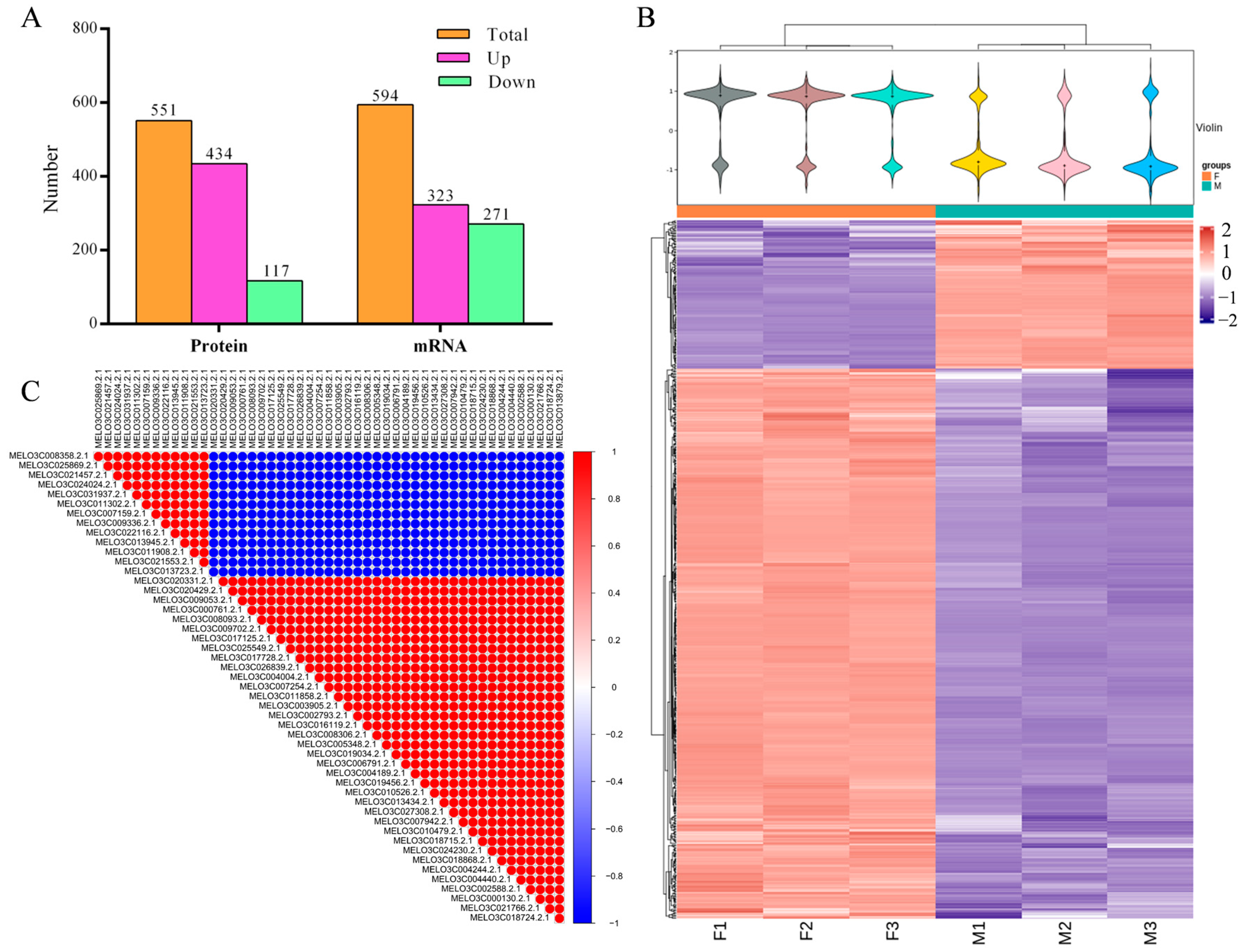
2.2. Identification and Analysis of Differential Proteins and Differential Genes
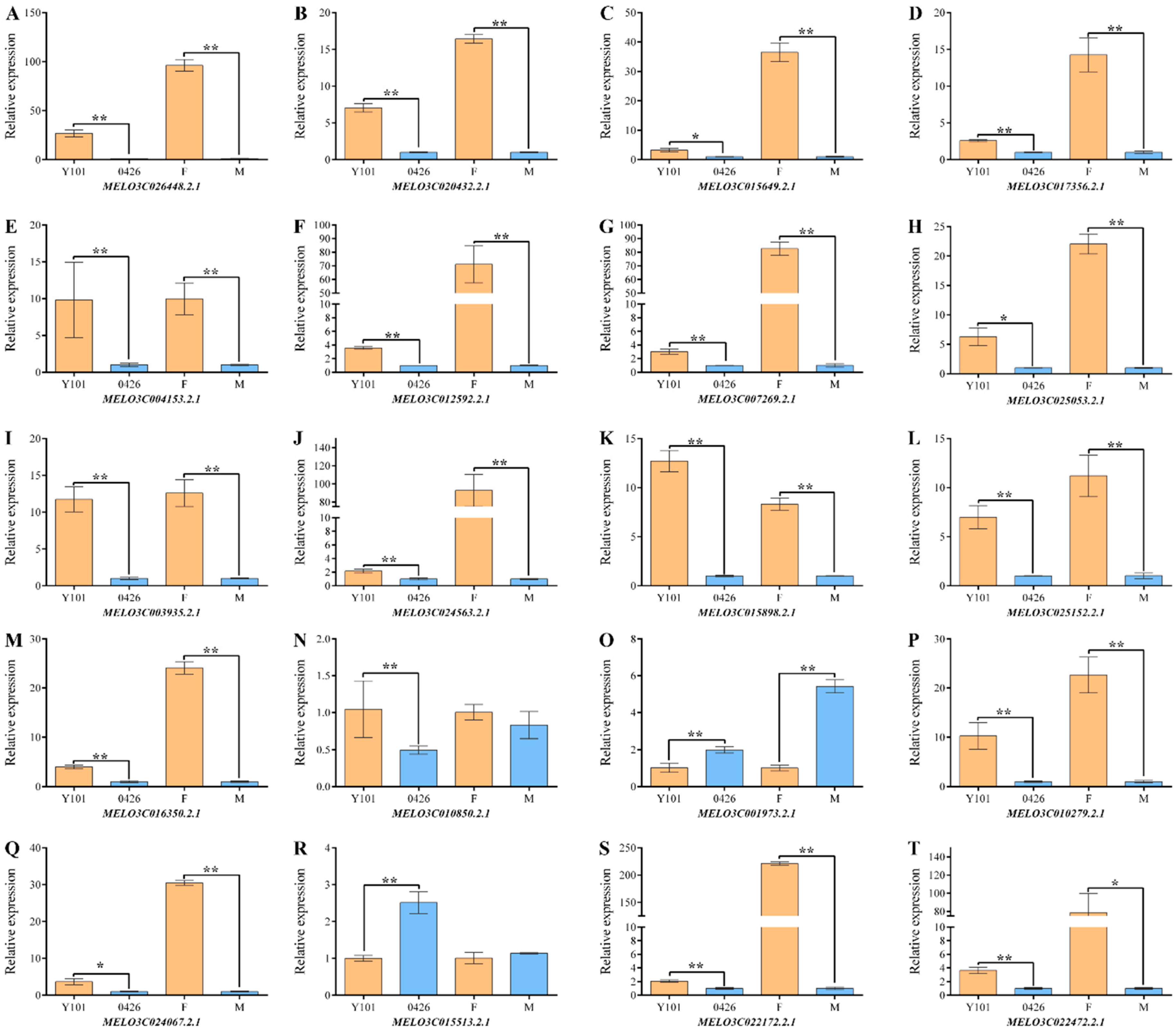
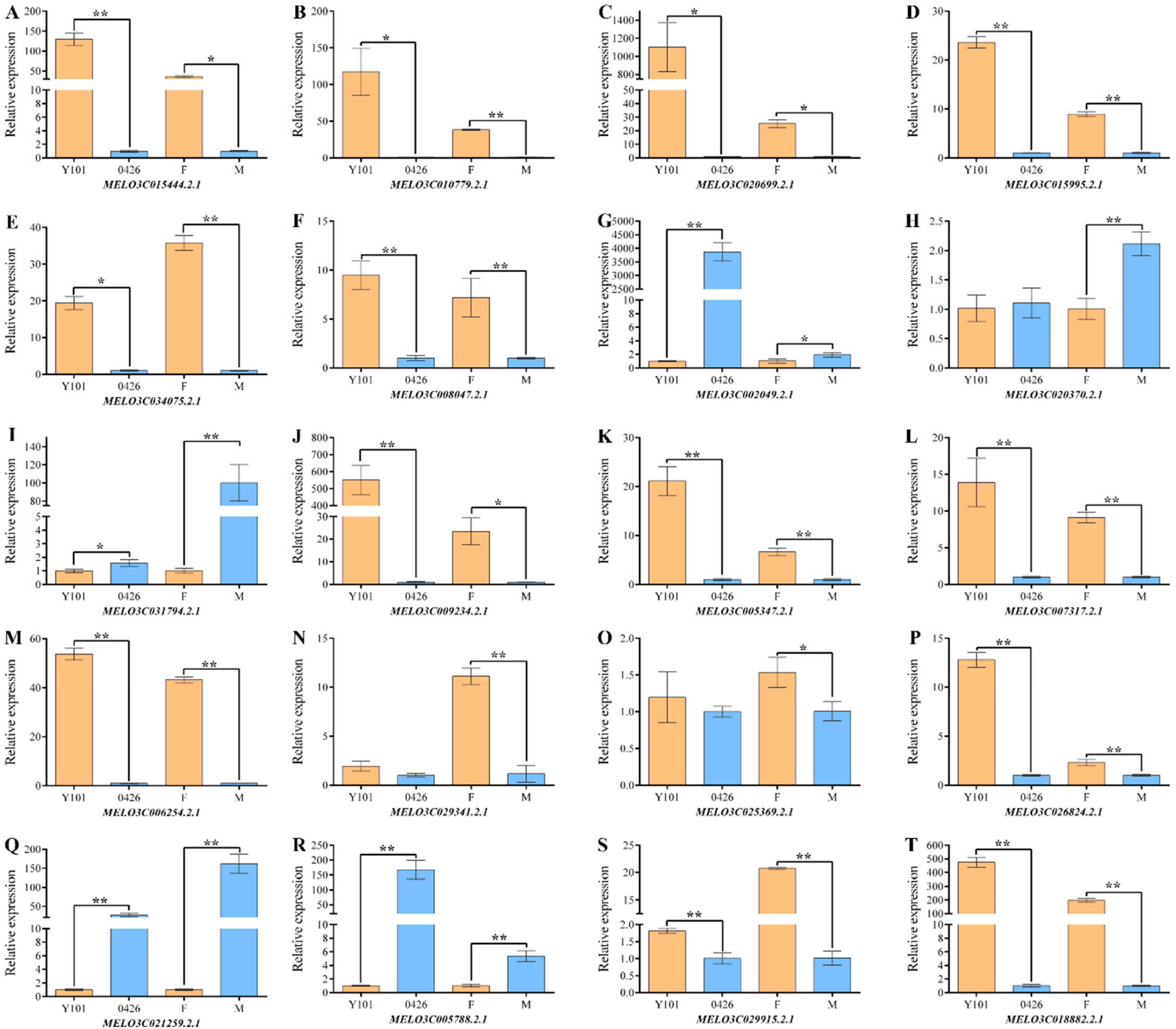
2.3. Omics Data Validation Test
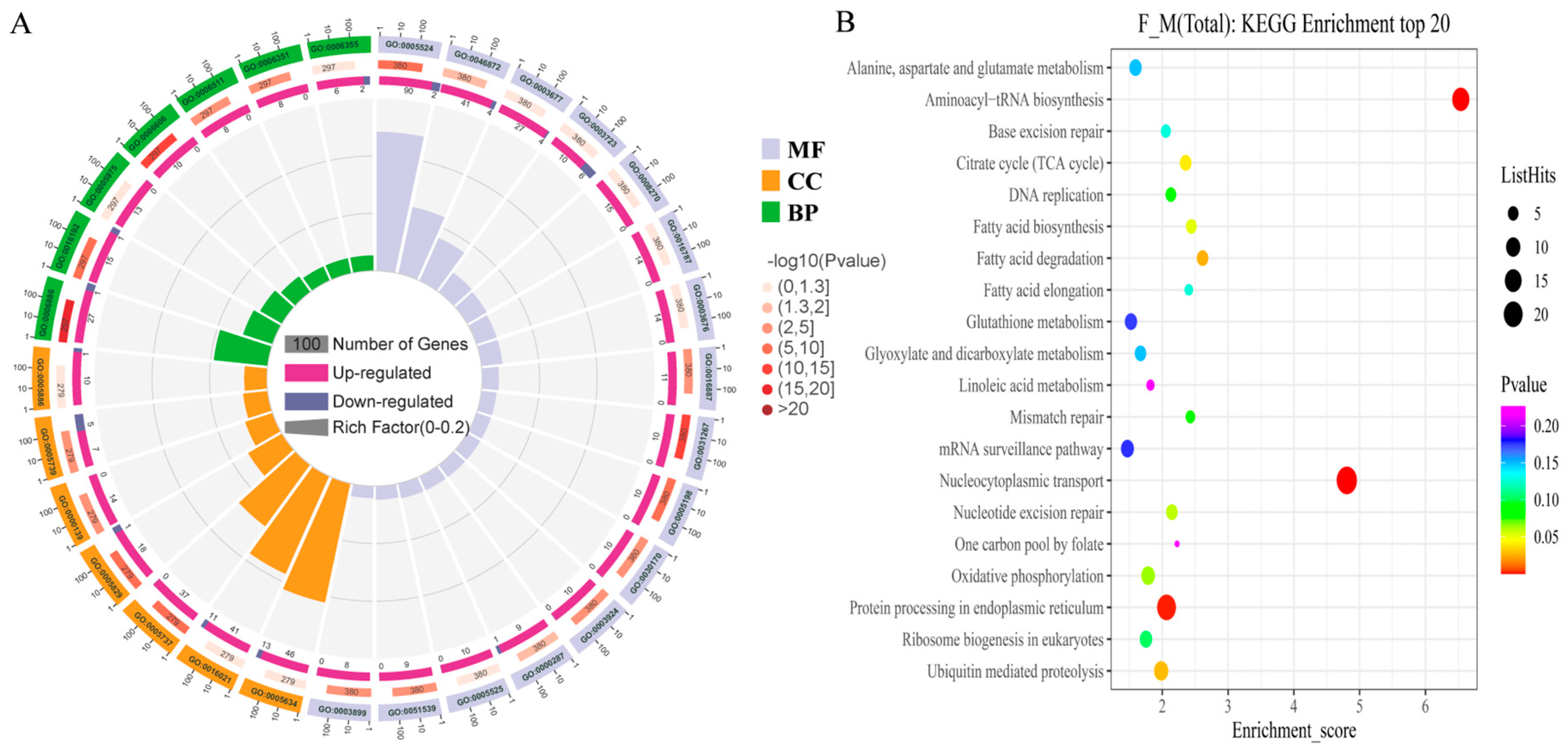
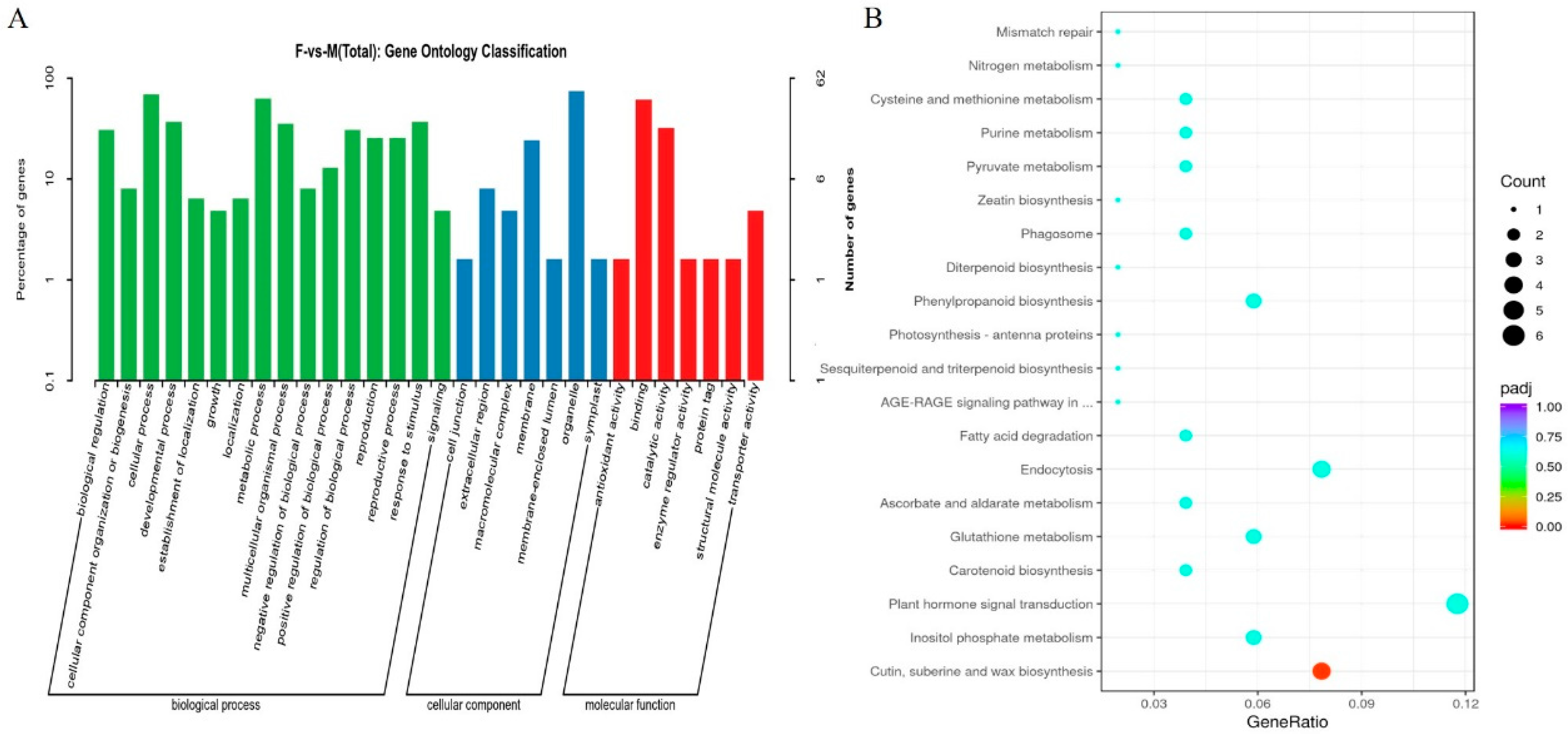
2.4. Differential Protein and Differential Gene Function Enrichment Analysis
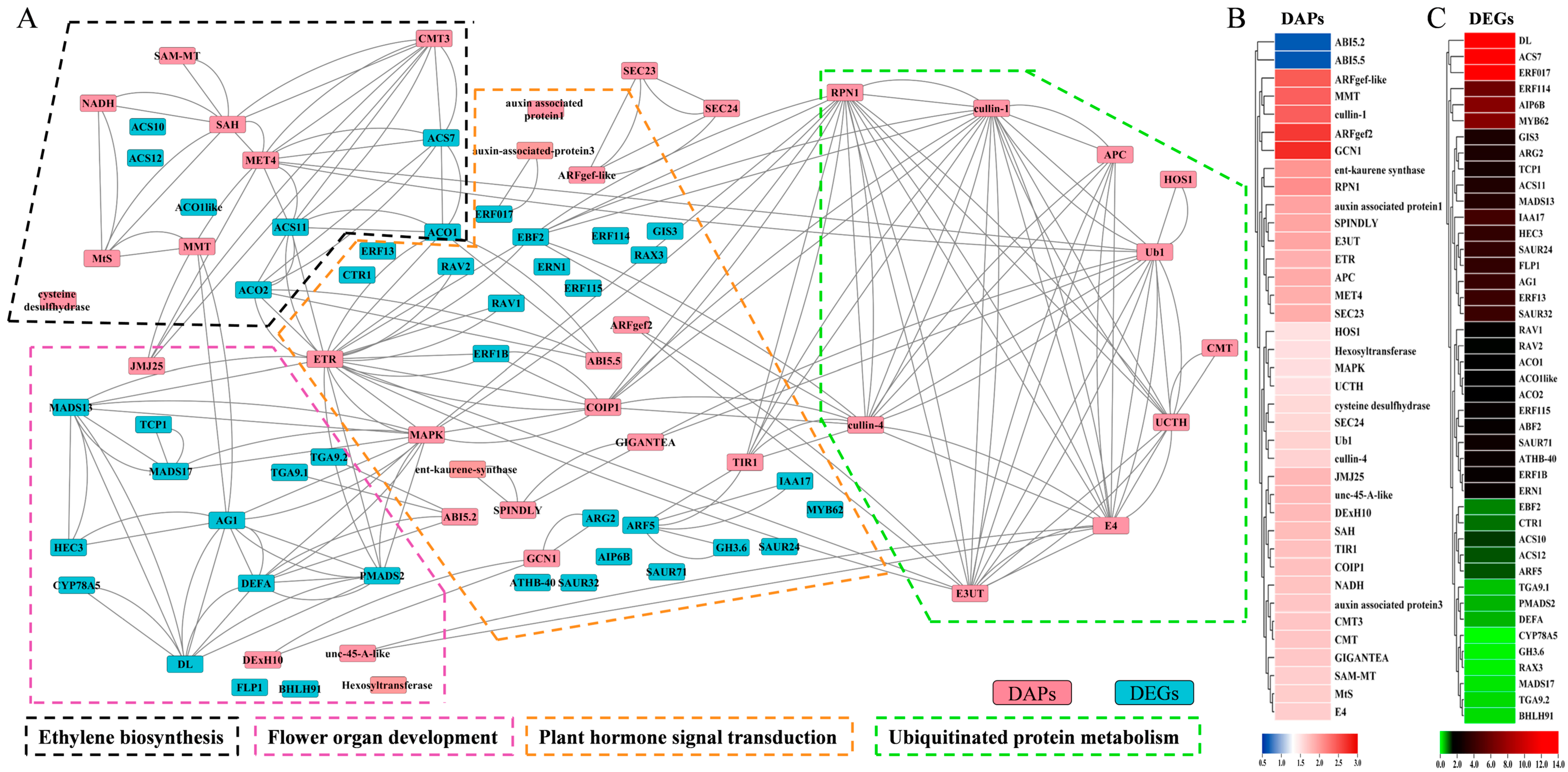
2.5. Differential Protein and Differential Gene Interaction Network Regulates Female Differentiation in Melon
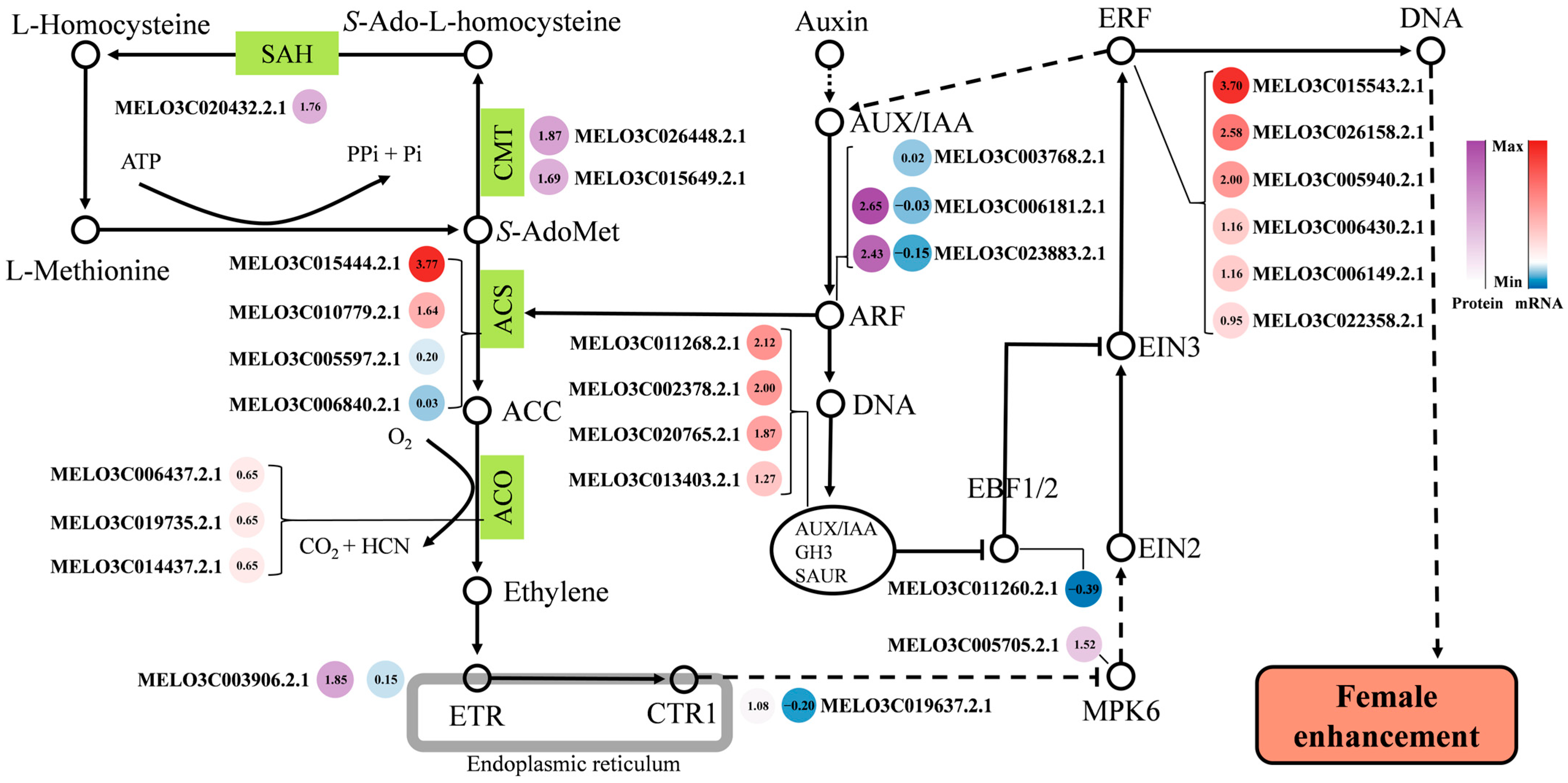
2.6. Ethylene-Mediated Study of Female Differentiation Regulatory Pathways in Melon
3. Discussion
3.1. Candidate Genes for Melon Female Development Revealed by Omics
3.2. A Regulatory Network Model for the Female Development of Melon
4. Materials and Methods
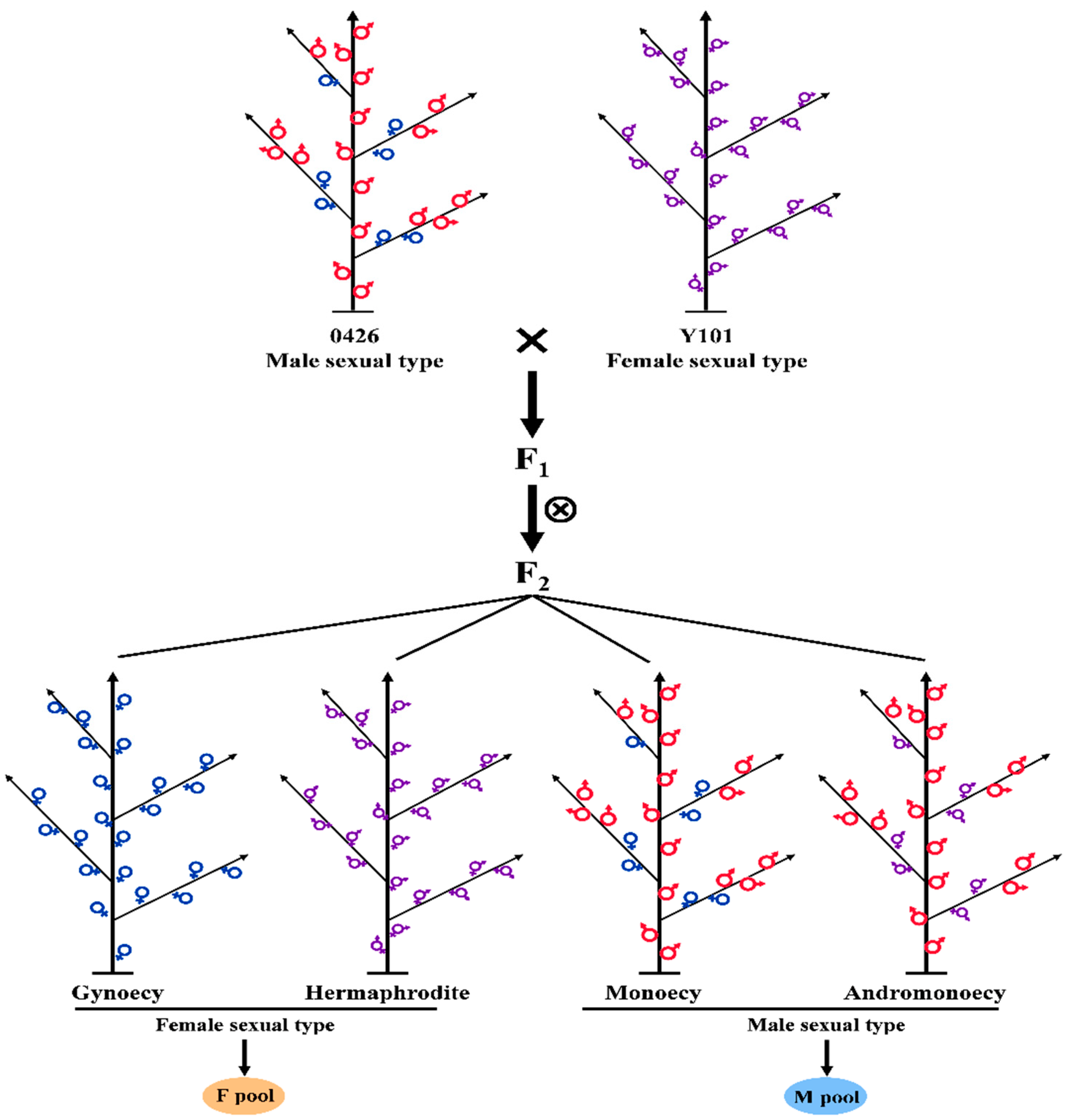
4.1. Plant Material and Flower Bud Collection
4.2. TMT Labeling Quantitative Proteome Sequencing and Analysis
4.3. F/M Mixed Pool RNA-Seq and Parametric Transcriptome Analysis
4.4. Functional Enrichment of DEGs and DAPs
4.5. Protein Interaction Network Analysis
4.6. qRT-PCR Analysis of Omics Data and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chibalina, M.V.; Filatov, D.A. Plant Y chromosome degeneration is retarded by haploid purifying selection. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devani, R.S.; Chirmade, T.; Sinha, S.; Bendahmane, A.; Dholakia, B.B.; Banerjee, A.K.; Banerjee, J. Flower bud proteome reveals modulation of sex-biased proteins potentially associated with sex expression and modification in dioecious Coccinia grandis. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Sheng, Y.; Niu, H.; Li, Z. Gene interactions regulating sex determination in Cucurbits. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, B.K.; Jha, S. Dynamics of sex expression and chromosome diversity in Cucurbitaceae: A story in the making. J. Genet. 2015, 94, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, T.F.; Lebel-Hardenack, S.; Grant, S.R. Silver enhances stamen development in female white campion (Silene latifolia [Caryophyllaceae]). Am. J. Bot. 2002, 89, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, J.N.; Nayak, S.; Jha, S.; Joshi, R.K. Transcriptome profiling of the floral buds and discovery of genes related to sex-differentiation in the dioecious cucurbit Coccinia grandis (L.) Voigt. Gene 2017, 626, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Mo, N.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y. Transcriptomic Analysis Implies That GA Regulates Sex Expression via Ethylene-Dependent and Ethylene-Independent Pathways in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.S.; Shen, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, H.; Dou, X.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Song, J.; et al. Temperature and photoperiod changes affect cucumber sex expression by different epigenetic regulations. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawełkowicz, M.; Pryszcz, L.; Skarzyńska, A.; Wóycicki, R.K.; Posyniak, K.; Rymuszka, J.; Przybecki, Z.; Pląder, W. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals new molecular pathways for cucumber genes related to sex determination. Plant Reprod. 2019, 32, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Zhao, W.; Nie, L.; Niu, S.; Fang, S.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, K.; Zhang, Q. Transcriptome profiling reveals the occurrence mechanism of bisexual flowers in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Plant Sci. 2020, 301, 110694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Sheng, Y.; Luan, F.; Ma, H.; Liu, S. RNA-Seq Transcriptome profiling reveals differentially expressed genes involved in sex expression in melon. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gygi, S.P.; Rochon, Y.; Franza, B.R.; Aebersold, R. Correlation between protein and mRNA abundance in yeast. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Q.; Shi, Z.; Chambers, M.C.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Shaddox, K.F.; Kim, S.; et al. Proteogenomic characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2014, 513, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Gong, F.; Xiong, E.; Wang, W. Proteomics: A promising tool for research on sex-related differences in dioecious plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, B.B.; Langefeld, C.D.; Olivier, M.; Cox, L.A. Integrated Omics: Tools, Advances, and Future Approaches. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 62, R21–R45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girek, Z.; Prodanovic, S.; Zdravković, J.; Zivanovic, T.; Ugrinović, M.; Zdravkovic, M. The effect of growth regulators on sex expression in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2013, 165, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mas, J.; Benjak, A.; Sanseverino, W.; Bourgeois, M.; Mir, G.; Gonzalez, V.M.; Henaff, E.; Camara, F.; Cozzuto, L.; Lowy, E.; et al. The genome of melon (Cucumis melo L.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11872–11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezura, H.; Owino, W.O. Melon, an alternative model plant for elucidating fruit ripening. Plant Sci. 2008, 175, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Tan, F.Q.; Chung, C.H.; Slavkovic, F.; Devani, R.S.; Troadec, C.; Marcel, F.; Morin, H.; Camps, C.; Gomez Roldan, M.V.; et al. The control of carpel determinacy pathway leads to sex determination in cucurbits. Science 2022, 378, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Jamilena, M. To be a male or a female flower, a question of ethylene in cucurbits. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 59, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boualem, A.; Troadec, C.; Camps, C.; Lemhemdi, A.; Morin, H.; Sari, M.A.; Fraenkel-Zagouri, R.; Kovalski, I.; Dogimont, C.; Perl-Treves, R. A cucurbit androecy gene reveals how unisexual flowers develop and dioecy emerges. Science 2015, 350, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boualem, A.; Fergany, M.; Fernandez, R.; Troadec, C.; Bendahmane, A. A conserved mutation in an ethylene biosynthesis enzyme leads to andromonoecy in melons. Science 2008, 321, 836–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Troadec, C.; Boualem, A.; Rajab, M.; Fernandez, R.; Morin, H.; Pitrat, M.; Dogimont, C.; Bendahmane, A. A transposon-induced epigenetic change leads to sex determination in melon. Nature 2009, 461, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleblu, J.S.Y.; Haraghi, A.; Mania, B.; Camps, C.; Bendahmane, A.J.S.R. The gynoecious CmWIP1 transcription factor interacts with CmbZIP48 to inhibit carpel development. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ahammed, G.J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Wan, C.; Yang, Y. Transcriptomic insights into the blue light-induced female floral sex expression in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, R.; Luan, F.; Zhang, X.; Wei, C. Novel bisexual flower control gene regulates sex differentiation in melon (Cucumis melo L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15401–15414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñaranda, A.; Payan, M.C.; Garrido, D.; Gómez, P.; Jamilena, M. Production of fruits with attached flowers in zucchini squash is correlated with the arrest of maturation of female flowers. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Yan, C.D.; Zou, B.X.; Wang, C.J.; Xu, W.L.; Cui, C.S.; Qu, S.P. Morphological, transcriptomic and hormonal characterization of trimonoecious and subandroecious pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima) suggests important roles of ethylene in sex expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, S.; Fujii, N.; Matsuura, S.; Mizusawa, H.; Takahashi, H. The M locus and ethylene-controlled sex determination in andromonoecious cucumber plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, D.; Devani, R.S.; Rodriguez-Granados, N.Y.; Abou-Choucha, F.; Troadec, C.; Morin, H.; Tan, F.Q.; Marcel, F.; Huang, H.Y.; Hanique, M.; et al. Ethylene produced in carpel primordia controls CmHB40 expression to inhibit stamen development. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Brumos, J.; Li, H.; Ji, Y.; Ke, M.; Gong, X.; Zeng, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; An, F.; et al. A small-molecule screen identifies l-kynurenine as a competitive inhibitor of TAA1/TAR activity in ethylene-directed auxin biosynthesis and root growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3944–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, L.; Stepanova, A.; Alonso, J. Molecular mechanisms of ethylene-auxin interaction. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1734–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlani, S.; Masiero, S.; Mizzotti, C. Fruit ripening: The role of hormones, cell wall modifications, and their relationship with pathogens. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 2993–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Niu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Ethylene responsive factor ERF110 mediates ethylene-regulated transcription of a sex determination-related orthologous gene in two Cucumis species. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2953–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Korasick, D.A.; Emenecker, R.J.; Morffy, N.; Wilkinson, E.G.; Powers, S.K.; Strader, L.C. Regulation of auxin response factor condensation and nucleo-cytoplasmic partitioning. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; Xie, Z.Z.; Hu, C.-G.; Zhang, J.Z. A Review of auxin response factors (ARFs) in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wen, H.; Chen, G.; Lin, W.-H.; Du, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lian, H.; Wang, G.; Cai, R.; et al. A positive feedback loop mediated by CsERF31 initiates female cucumber flower development. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, J.T. The inheritance of flower types in Cucumins and Citrullus. Hilgardia 1928, 3, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.F.; Grimball, P.C. Inheritance of new sex forms in Cucumis melo L. J. Hered. 1939, 30, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.L.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, R.; Ren, A.; Ma, H.Y.; Shu, L.B.; Shi, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, M.W. Integrated proteomics and metabolomics analysis provides insights into ganoderic acid biosynthesis in response to methyl jasmonate in Ganoderma lucidum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Zhu, X.; Ren, J.; Huang, S.; Xiao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Tan, Y. Quantitative proteomic analysis of cervical cancer based on TMT-labeled quantitative proteomics. J. Proteom. 2022, 252, 104453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, C.; Geng, X.; Zhang, J.; Sai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Du, Z.; Peng, C.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats based on tandem mass tag (TMT) quantitation technology. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Lin, Y. TMT-based quantitative proteomics analysis reveals the key proteins related with the differentiation process of goat intramuscular adipocytes. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, S.; Cai, L.; Hua, W. Transcriptomic analysis of differentially expressed genes in the oviduct of Rhacophorus omeimontis provides insights into foam nest construction. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pool | Total | Total Map | Unique Map | Multimap | Positive | Negative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 45,179,104 | 43,344,617 (95.94%) | 42,839,380 (94.82%) | 505,237 (1.12%) | 21,413,961 (47.4%) | 21,425,419 (47.42%) |
| M | 44,568,262 | 42,604,523 (95.59%) | 42,122,518 (94.51%) | 482,005 (1.08%) | 2,1056,584 (47.25%) | 2,1065,934 (47.27%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Yadav, V.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Intricate Gene Networks Involved in Female Development in Melon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316905
Wang Z, Yadav V, Chen X, Zhang S, Yuan X, Li H, Ma J, Zhang Y, Yang J, Zhang X, et al. Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Intricate Gene Networks Involved in Female Development in Melon. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):16905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316905
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhongyuan, Vivek Yadav, Xiaoyao Chen, Siyu Zhang, Xinhao Yuan, Hao Li, Jianxiang Ma, Yong Zhang, Jianqiang Yang, Xian Zhang, and et al. 2023. "Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Intricate Gene Networks Involved in Female Development in Melon" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 16905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316905
APA StyleWang, Z., Yadav, V., Chen, X., Zhang, S., Yuan, X., Li, H., Ma, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, X., & Wei, C. (2023). Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Intricate Gene Networks Involved in Female Development in Melon. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 16905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316905









