Genetic Basis of Grain Size and Weight in Rice, Wheat, and Barley
Abstract
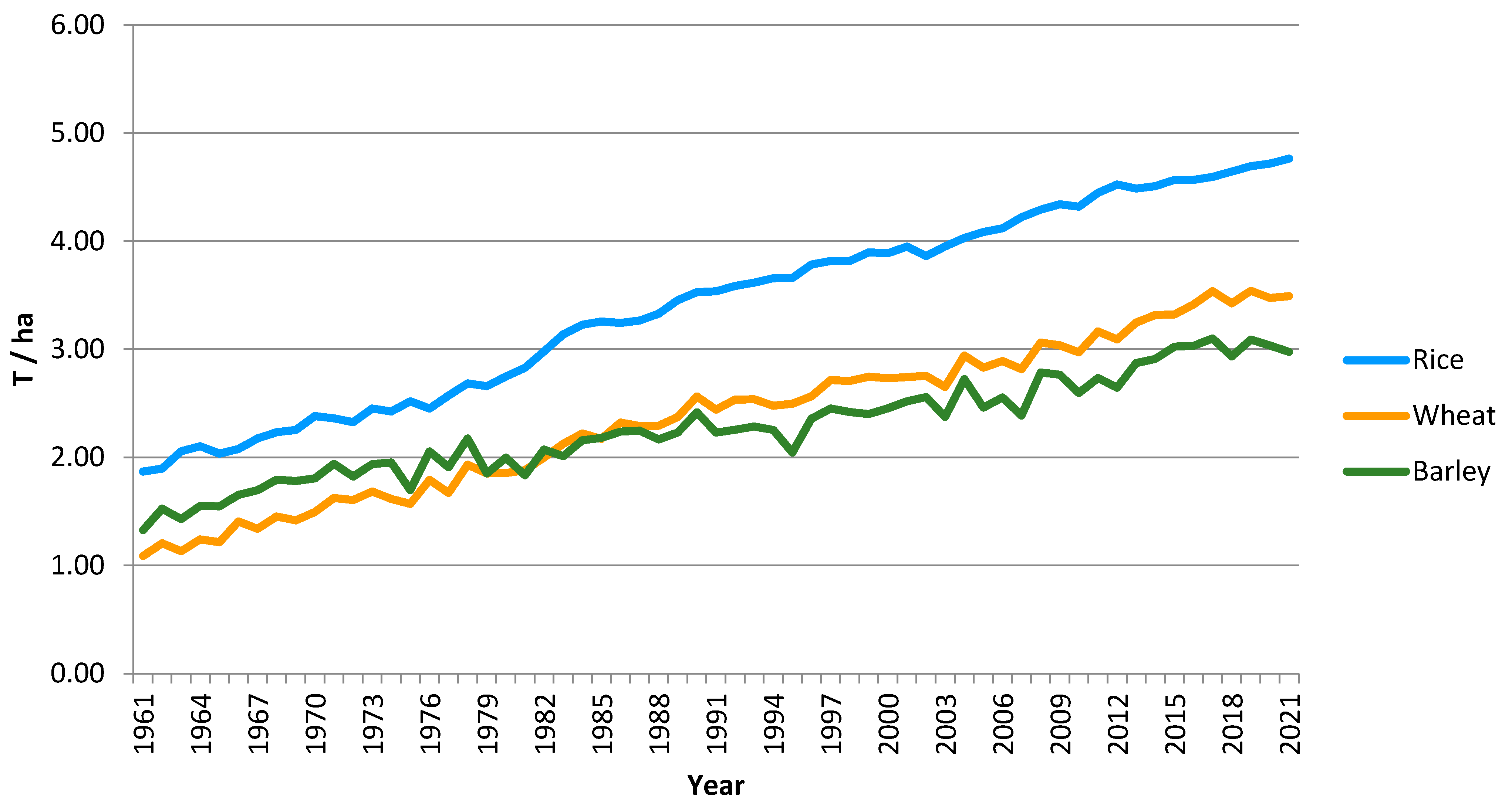
:1. Introduction
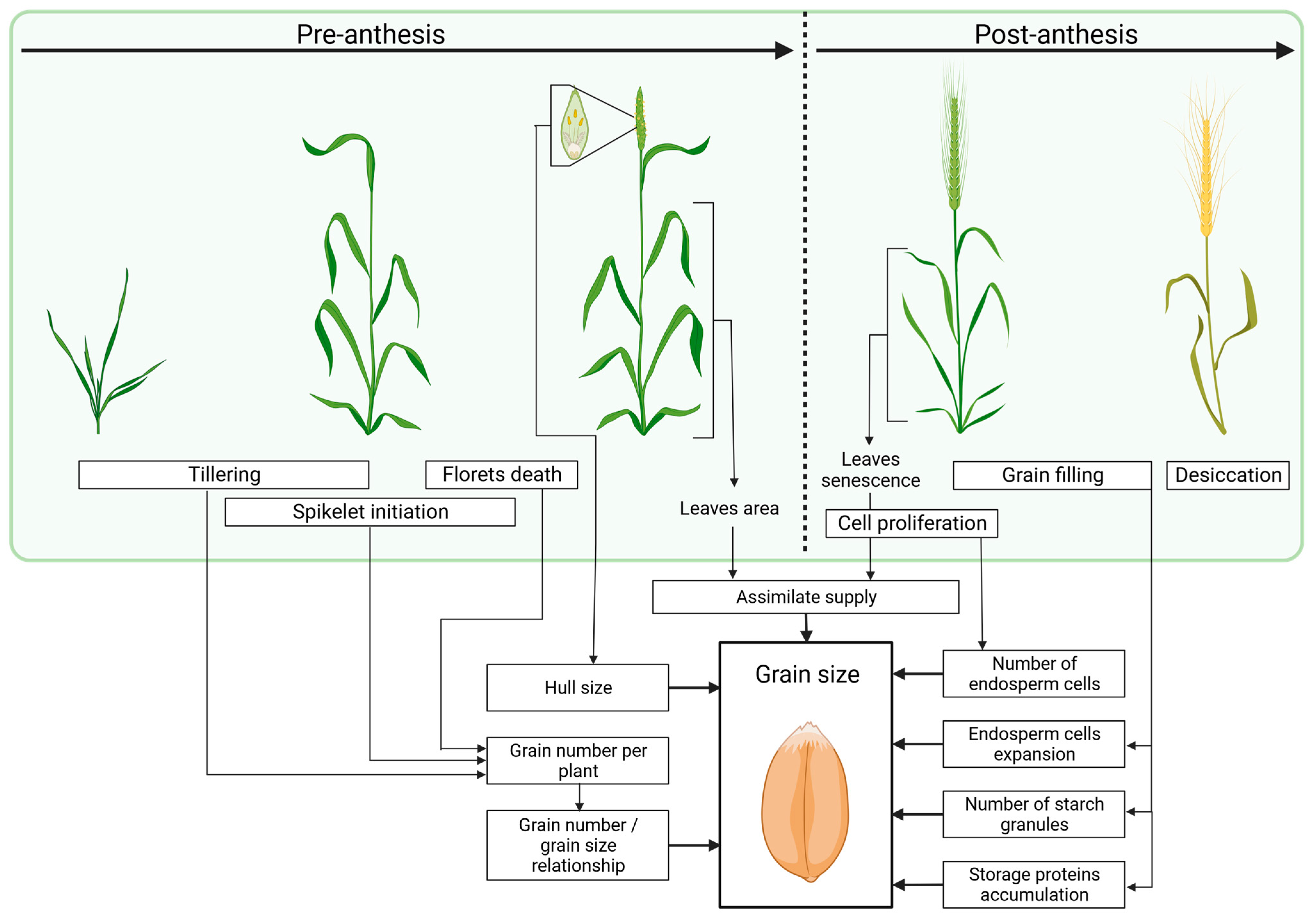
2. Factors Determining Grain Size and Weight during Plant Development
3. Genetic and Molecular Regulation of Grain Size
3.1. G Protein Signaling
| Gene or QTL Name | Gene ID 1 | Protein Category | Type of Regulation | Regulated Process | Affected Trait 2 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | ||||||
| Rice G Protein Alpha Subunit (RGA1) | Os05g0333200 | G protein α subunit | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [24] |
| Rice G Protein Beta Subunit (RGB1) | Os03g0669100 | G protein β subunit | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [25] |
| Grain Size 3 (GS3) | Os03g0407400 | G protein γ subunit | negative | cell proliferation | grain length | [28,29] |
| Dense And Erect Panicle 1 (DEP1) | Os09g0441900 | G protein γ subunit | positive | cell proliferation | grain length | [32,33] |
| GGC2 | Os08g0456600 | G protein γ subunit | positive | cell proliferation | grain length | [31] |
| RGG1 | Os03g0635100 | Type-B G protein γ subunit | negative | cell proliferation | grain size | [27] |
| RGG2 | Os02g0137800 | Type-A G protein γ subunit | negative | cell proliferation | grain size | [26] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| TaGS3 | TraesCS4A02G474000 | G protein γ subunit | negative | cell proliferation | grain size | [37,38] |
| TaDEP1 | FJ039902 | G protein γ subunit | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [39] |
| Barley | ||||||
| Brachytic1 (Brh1) | AF267485 | G protein α subunit | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [40] |
| HvDEP1 | FJ039903 | G protein γ subunit | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [41] |
3.2. Ubiquitin–Proteasome System
| Gene or QTL Name | Gene ID | Protein Category | Type of Regulation | Regulated Process | Affected Trait | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | ||||||
| Grain Width 2 (GW2) | Os02g0244100 | RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase | negative | cell proliferation | grain width | [47,50] |
| U-Box E3 Ubiquitin Ligase (TUD1) | Os03g0232600 | U-box domain-containing protein 75 | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [52] |
| Chang Li Geng 1 (CLG1) | Os05g47780 | RING E3 ligase | positive | cell proliferation | grain length | [53] |
| Wide And Thick Grain 1 (WTG1)/OsOTUB1 | Os08g0537800 | Otubain-like protease with deubiquitination activity | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [57,58] |
| Large Grain 1 (LG1) | Os02g0244300 | Ubiquitin-specific protease 15 | positive | cell proliferation | grain width | [60] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| Grain Width 2 (GW2) | TraesCS6A02G189300 | RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase | negative | cell proliferation | grain width | [48,49] |
| TaDA1 | TraesCSU01G007800 | ubiquitin receptor DA1 | negative | cell proliferation | grain size | [51] |
| TaSDIR1-4A | TraesCS4A02G096000 | RING finger E3 ligase | negative | ns 1 | grain size | [54] |
| ZnF-B | TraesCS4B02G042900 | zinc-finger RING-type E3 ligase | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [55] |
| Wide And Thick Grain 1 (WTG1) | TraesCS7A02G263900 | Otubain-like protease with deubiquitination activity | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [59] |
3.3. MAPK Signaling
| Gene or QTL Name | Gene ID | Protein Category | Type of Regulation | Regulated Process | Affected Trait | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | ||||||
| Small Grain 1 (SMG1) | Os02g0787300 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MKK4) | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [63] |
| Small Grain 2 (SMG2) | Os04g0559800 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 10 (MKK10) | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [66] |
| WRKY-type transcription factor WRKY53 | Os05g0343400 | Transcription factor WRKY53 | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [67] |
| Dwarf and Small Grain1 (DSG1)/OsMAPK6 | Os06g0154500 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [64,65] |
| Grain Size and Number 1 (GSN1)/LARGE8 | Os05g0115800 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase OsMKP1 | negative | cell proliferation | grain size | [68] |
| ROP GTPase (OsRac1) | Os01g0229400 | Rho-family GTPase | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [69] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| TaMPK3 | TraesCS4D02G198600 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase | negative | ns 1 | grain width | [70] |
3.4. Phytohormone Signaling
3.4.1. Auxin
3.4.2. Cytokinins
3.4.3. Gibberellins
3.4.4. Brassinosteroids
3.4.5. Ethylene
3.4.6. Jasmonate
| Gene or QTL Name | Gene ID | Protein Category | Type of Regulation | Regulated Process | Affected Trait | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auxin | ||||||
| Rice | ||||||
| Tillering And Small Grain 1 (TSG1)/FIB | Os01g0169800 | Tryptophan aminotransferase-related protein 2 | positive | cell proliferation/expansion | grain length | [72] |
| OsYUC11 | Os12g0189500 | Flavin-containing monooxygenase | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [73] |
| Thousand-Grain Weight (TGW6) | Os06g0623700 | IAA-glucose hydrolase | negative | cell expansion | grain size | [74] |
| Big Grain 1 (BG1) | Os03g0175800 | plasma membrane-associated protein | positive | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [77,78] |
| OsARF4 | Os01g0927600 | Auxin response factor 4 | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [82] |
| OsARF6 | Os02g0164900 | Auxin response factor 6 | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [80] |
| OsARF12 | Os04g0671900 | Auxin response factor 12 | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [81] |
| OsAUX3 | Os05g0447200 | Auxin transporter-like protein 2 | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [80] |
| qTGW3/OsGSK5 | Os03g0841800 | GSK3/SHAGGY-Like Kinase 41 | negative | ns 1 | grain length | [82] |
| Gnp4/LAX2 | Os04g0396500 | The RING-finger and wd40-associated ubiquitin-like protein | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [83] |
| OsIAA3 | Os01g0231000 | Auxin-responsive protein | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [83] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| Thousand-Grain Weight (TaTGW6) | TraesCS6A02G526800LC | IAA-glucose hydrolase | negative | cell expansion | grain size | [75,76] |
| Big Grain 1 (BG1) | TraesCSU02G223800 | plasma membrane-associated protein | positive | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [79] |
| Cytokinins | ||||||
| Rice | ||||||
| Big Grain3 (BG3)/OsPUP4 | Os01g0680200 | Purine permease | positive | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [87] |
| OsPUP7 | Os05g0556800 | Purine permease | positive | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [89,90] |
| AGO2 | Os04g0615700 | ARGONAUTE family protein | positive | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [88] |
| OsPIL15 | Os01g0286100 | bHLH transcription factor | negative | cell proliferation | grain size | [90] |
| OsSGL | Os02g0134200 | Putative DUF1645 protein family member | positive | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [91] |
| qGL3 (OsPPKL1) | Os03g0646900 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase | negative | ns | grain length | [92] |
| OsCKX2 | Os01g0197700 | Cytokinin dehydrogenase | negative | ns | grain size | [93] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| TaCKX2.2 | TraesCS3D02G143300 | Cytokinin dehydrogenase | negative | ns | grain size | [94] |
| TaCKX6-D1 | TraesCS3D02G143500 | Cytokinin dehydrogenase | negative | ns | grain size | [95,96] |
| Barley | ||||||
| HvCKX1 | Cytokinin dehydrogenase | negative | ns | grain size | [97] | |
| Gibberellins | ||||||
| Rice | ||||||
| BC12/GDD1 | Os09g0114500 | Kinesin-like protein | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [102] |
| GW6/OsGSR1 | Os06g0266800 | Gibberellic acid-stimulated transcript (GAST) family protein | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [103] |
| OsGARS9 | Os07g0592000 | Gibberellic acid-stimulated transcript (GAST) family protein | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [104] |
| GL10/OsMADS56 | Os10g0536100 | MADS-box transcription factor | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [105] |
| OsWRKY36 | Os04g0545000 | WRKY transcription factor | negative | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [106] |
| SLR1 | Os03g0707600 | DELLA protein | negative | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [106] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| Rth-B1 | TraesCS4B02G043100 | DELLA protein | negative | ns | grain size | [55] |
| Brassinosteroids | ||||||
| Rice | ||||||
| DWARF 2 (D2) | Os01g0197100 | Cytochrome P450 90D2 | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [108,113] |
| DWARF 11 (D11) | Os04g0469800 | Cytochrome P450 724B1 | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [109,110,111] |
| BRD2 | Os10g0397400 | delta (24)-sterol reductase | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [112] |
| Slender Grain (SLG) | Os08g0562500 | BAHD acyltransferase-like protein | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [113] |
| Brassinosteroid Insensitive1 (OsBRI1) | Os01g0718300 | Leucin-rich-repeat receptor-like kinase | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [115] |
| OsBAK1 | Os03g0440900 | BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1-associated receptor kinase 1 | positive | cell proliferation | grain length | [116] |
| XIAO | Os04g0576900 | Leucine-rich repeat (LRR) receptor-like kinase | positive | cell proliferation | grain length | [147] |
| GSK3/Shaggy-like Kinase 2 (GSK2) | Os05g0207500 | Shaggy-related protein kinase GSK2 | negative | cell proliferation | grain size | [117] |
| Brassinazole Resistant 1 (BZR1) | Os07g0580500 | Transcription factor OsBZR1 | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [110] |
| Decreased Grain Size1 (DGS1) | Os03g0169800 | transmembrane protein | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [118] |
| Dwarf And Low Tillering (DLT) | Os06g0127800 | GRAS family protein 32 | negative | cell proliferation | grain width | [117,119] |
| Dwarf And Low Tillering 2 (DLT2) | Os03g0723000 | GRAS TF | negative | cell proliferation | grain width | [120] |
| Small Grain2 (SG2) | Os02g0450000 | Ribonuclease H-like domain protein | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [121] |
| Ovate Family Protein 1 (OsOFP1) | Os01g0226700 | Transcription repressor | negative | ns | grain width | [124] |
| Ovate Family Protein 3 (OsOFP3) | Os01g0732300 | Transcription repressor | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [125] |
| Ovate Family Protein 19 (OsOFP19) | Os05g0324600 | Transcription repressor | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [121] |
| Large1 | Os02g0517531 | MEI2-LIKE PROTEIN4 | negative | cell expansion | grain size | [126] |
| qGL3 (OsPPKL1) | Os03g0646900 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase | negative | cell proliferation | grain length | [130] |
| GW5 (qSW5/GW5) | Os05g0187500 | Calmodulin binding protein | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [131] |
| Grain Size 5 (GS5) | Os05g0158500 | Serine carboxypeptidase-like 26 | positive | cell proliferation | grain width | [132,133] |
| GW10 (ORF1) | Os10g0515400 | Cytochrome CYP89A2 | positive | ns | grain length | [136] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| TaD11 | TraesCS2A02G331800 | Cytochrome P450 | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [114] |
| Grain Size 5 (TaGS5) | TraesCS6A02G220200 | Serine carboxypeptidase-like 26 | positive | ns | grain size | [135] |
| Barley | ||||||
| GSK3/Shaggy-like Kinase1.1 (HvGSK1.1) | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0252610 | GSK3/SHAGGY-Like Kinase | negative | ns | grain size | [129] |
| Ethylene | ||||||
| Rice | ||||||
| OsFBK12 | Os03g0171600 | Kelch repeat-containing F-box family protein | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [139] |
| OsSPMS1 | Os06g0528600 | Aminopropyl transferase | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [141] |
| OsPAO5 | Os04g0671300 | Polyamine oxidase 5 | negative | cell proliferation | grain length | [140] |
| OsERF115 | Os08g0521600 | Ethylene response factor | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [142] |
| Jasmonate | ||||||
| Rice | ||||||
| OsTIFY11b | Os03g0181100 | TIFY family protein | positive | ns | grain size | [144] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| TGW1/KAT-2B | TraesCS6B01G432600 | keto-acyl thiolase 2B | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [146] |
3.5. Transcriptional Regulation
3.5.1. SPL Family Transcription Factors
3.5.2. GRF Transcription Factors
3.5.3. bHLH Family Transcription Factors
3.5.4. AP2/ERF Transcription Factors
3.5.5. MADS-Box Transcription Factors
3.5.6. Epigenetic Regulation
3.5.7. Other Transcriptional Regulators
| Gene or QTL Name | Gene ID | Protein Category | Type of Regulation | Regulated Process | Affected Trait | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | ||||||
| GLW7/OsSPL13 | Os07g0505200 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [148] |
| GW8/OsSPL16 | Os08g0531600 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [150] |
| OsSPL12 | Os06g0703500 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein | positive | cell expansion | grain width | [149] |
| OsSPL18 | Os09g0507100 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein | positive | cell proliferation | grain width | [154] |
| OsGRF1 | Os02g0776900 | Growth-regulating factor 1 | positive | ns 1 | grain size | [156] |
| GS2/OsGRF4 | Os02g0701300 | Growth-regulating factor 4 | positive | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [157,158,159] |
| OsGRF8 | Os11g0551900 | Growth-regulating factor 8 | positive | ns | grain length | [156] |
| OsGIF1 | Os03g0733600 | GRF-interacting factor 1 | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [158,159,160] |
| An-1 | Os04g0350700 | bHLH transcription factor | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [165] |
| PGL1 | Os03g0171300 | bHLH transcription factor | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [164] |
| OsBUL1 | Os02g0747900 | bHLH transcription factor | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [168,169] |
| Brassinosteroid Upregulated 1 (BU1) | Os06g0226500 | bHLH transcription factor | positive | ns | grain size | [167] |
| SMOS1 | Os05g0389000 | AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [84] |
| OsLG3 | Os03g0183000 | AP2 domain class transcription factor | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [171] |
| OsSNB | Os07g0235800 | AP2 transcription factor | negative | cell expansion | grain size | [172] |
| AFG1 | Os02g0682200 | MADS-box transcription factor 6 | positive | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [174] |
| Grain Weight 6a (GW6a)/OsgHAT1 | Os06g0650300 | GNAT-like histone acetyltransferase 1 | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [175] |
| PANDA | Os07g0175100 | Harbinger transposon derived protein | negative | ns | grain size | [176] |
| RAV6 | Os02g0683500 | B3 DNA-binding domain-containing protein | negative | ns | grain size | [177] |
| MISSEN | XLOC_057324 | Long noncoding RNA | negative | cell proliferation | grain size | [178] |
| OsGBP1 | Os06g0130600 | GAGA-binding factor | positive | ns | grain length | [179] |
| OsGBP3 | Os10g0115200 | GAGA-binding factor | negative | ns | grain length | [179] |
| HOS59 | Os06g0646600 | KNOX II transcription factor | negative | cell expansion | grain length | [180] |
| GL6 | Os06g0666100 | plant AT-rich sequence- and zinc-binding (PLATZ) protein | positive | cell proliferation | grain length | [181] |
| OsNF-YC10 | Os01g0346900 | NF-Y transcription factor | positive | cell proliferation | grain width | [182] |
| TH1/AFD1 | Os02g0811000 | ALOG domain associated protein | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [183,184] |
| OsFD2 | Os06g0720900 | basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor | negative | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [185] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| GLW7/TaSPL13 | TraesCS2A02G232400 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein | positive | cell expansion | grain size | [151] |
| GW8/OsSPL16 | TraesCS7A02G260500 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [152,153] |
| TaPGS1 | TraesCS1D02G094000 | bHLH transcription factor | positive | ns | grain size | [166] |
| TaGRF4-A1/TaGRF3-2A | TraesCS2A02G435100 | Growth-regulating factor | Positive | ns | grain size | [161,162,163] |
3.6. miRNAs
| Gene or QTL Name | Gene ID | Protein Category | Type of Regulation | Regulated Process | Affected Trait | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | ||||||
| miR167a | MI0000676 | miRNA | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [80] |
| miR156k | MI0001090 | miRNA | negative | cell proliferation | grain size | [154] |
| miR397a | MI0001049 | miRNA | positive | ns 1 | grain size | [186] |
| miR397b | MI0001050 | miRNA | positive | ns | grain size | [186] |
| miR530 | MI0003203 | miRNA | negative | cell proliferation/expansion | grain size | [187] |
3.7. Grain Filling and Sugar Transport Associated Regulators
| Gene or QTL Name | Gene ID | Protein Category | Type of Regulation | Regulated Process | Affected Trait | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | ||||||
| OsSWEET4 | Os02g0301100 | Bidirectional sugar transporter | positive | grain filling | grain size | [191] |
| OsSWEET11 | Os08g0535200 | Bidirectional sugar transporter | positive | grain filling | grain size | [192] |
| OsSWEET15 | Os02g0513100 | Bidirectional sugar transporter | positive | grain filling | grain size | [193] |
| OsSUT2 | Os12g0641400 | Sucrose transporter | positive | grain filling | grain size | [194] |
| Grain-Filling Rate1 (GRF1) | Os10g0508100 | membrane-localized protein | positive | grain filling | grain size | [196] |
| OsPK3 | Os04g0677500 | Pyruvate kinase | positive | grain filling | grain size | [197] |
| DG1 | Os03g0229500 | MATE transporter | positive | grain filling | grain size | [198] |
| Barley | ||||||
| HvSWEET11b | HORVU.MOREX.r3.7HG0684580 | Bidirectional sugar transporter | positive | grain filling | grain size | [190] |
3.8. Other Regulators
| Gene or QTL Name | Gene ID | Protein Category | Type of Regulation | Regulated Process | Affected Trait | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | ||||||
| OsCYP704A3 | Os04g0573900 | Cytochrome CYP704A3 | negative | ns 1 | grain length | [199] |
| GIANT EMBRYO/BG2 | Os07g0603700 | Cytochrome CYP78A13 | negative | embryo development | grain length | [200,201] |
| Grain Length 7 (GL7/GW7/SLG7) | Os07g0603300 | TONNEAU1-recruiting motif protein | positive | cell proliferation | grain length | [203,204,205] |
| OsKinesin-13A/SRS3 | Os05g0154700 | Kinesin 13A | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [207,208] |
| OsIQD14 | Os08g0115200 | microtubule-associated protein | positive | cell expansion | grain length | [209] |
| OsAGSW1 | Os05g0323800 | ABC1-like kinase | positive | cell proliferation | grain size | [210] |
| FUWA | Os02g0234200 | NHL repeat-containing protein | negative | proliferation | grain width | [211] |
| TGW2 | Os02g0763000 | CELL NUMBER REGULATOR 1 (OsCNR1) | cell proliferation | grain size | [212] | |
| OsCOMT | Os08g0157500 | Flavone 3’-O-methyltransferase 1 | positive | ns | grain size | [213] |
| Wheat | ||||||
| TaCYP78A3 | KP768392 | Cytochrome CYP78A3 | positive | ns | grain size | [202] |
| TaGW7 | TraesCS2A01G176000 | TONNEAU1-recruiting motif protein | positive | cell proliferation | grain length | [206] |
4. Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, X.; Wu, B.; Xing, Y. Yield-related QTLs and their applications in rice genetic improvement. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2012, 54, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Ashikari, M.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Itoh, H.; Nishimura, A.; Swapan, D.; Ishiyama, K.; Saito, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Khush, G.S.; et al. A mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature 2002, 416, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Richards, D.E.; Hartley, N.M.; Murphy, G.P.; Devos, K.M.; Flintham, J.E.; Beales, J.; Fish, L.J.; Worland, A.J.; Pelica, F.; et al. ‘Green revolution’ genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators. Nature 1999, 400, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickelson, H.R.; Rasmusson, D.C. Genes for short stature in barley. Crop Sci. 1994, 34, 1180–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadolska-Orczyk, A.; Rajchel, I.K.; Orczyk, W.; Gasparis, S. Major genes determining yield-related traits in wheat and barley. TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. Theor. Und Angew. Genet. 2017, 130, 1081–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faostat 2021. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Gambín, B.L.; Borrás, L. Resource distribution and the trade-off between seed number and seed weight: A comparison across crop species. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2010, 156, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul-Victor, C.; Turnbull, L.A. The effect of growth conditions on the seed size/number trade-off. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadras, V.O. Evolutionary aspects of the trade-off between seed size and number in crops. Field Crops Res. 2007, 100, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Hong, Z. Genetic bases of rice grain shape: So many genes, so little known. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasiunas, G.; Barrangou, R.; Horvath, P.; Siksnys, V. Cas9-crRNA ribonucleoprotein complex mediates specific DNA cleavage for adaptive immunity in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2579–E2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramene. Available online: https://www.gramene.org/ (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Salse, J.r.m.; Bolot, S.p.; Throude, M.l.; Jouffe, V.; Piegu, B.t.; Quraishi, U.M.; Calcagno, T.; Cooke, R.; Delseny, M.; Feuillet, C. Identification and characterization of shared duplications between rice and wheat provide new insight into grass genome evolution. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsuda, T.; Pourkheirandish, M.; He, C.; Azhaguvel, P.; Kanamori, H.; Perovic, D.; Stein, N.; Graner, A.; Wicker, T.; Tagiri, A.; et al. Six-rowed barley originated from a mutation in a homeodomain-leucine zipper I-class homeobox gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, L.; Comadran, J.; Druka, A.; Marshall, D.F.; Thomas, W.T.; Macaulay, M.; MacKenzie, K.; Simpson, C.; Fuller, J.; Bonar, N.; et al. INTERMEDIUM-C, a modifier of lateral spikelet fertility in barley, is an ortholog of the maize domestication gene TEOSINTE BRANCHED 1. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreenivasulu, N.; Schnurbusch, T. A genetic playground for enhancing grain number in cereals. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, H.S.; Westgate, M.E. Reproductive development in grain crops during drought. In Advances in Agronomy; Donald, L.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; Volume 68, pp. 59–96. [Google Scholar]
- Jenner, C.; Ugalde, T.; Aspinall, D. The physiology of starch and protein deposition in the endosperm of wheat. Funct. Plant Biol. 1991, 18, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenbach, S.B.; DuPont, F.M.; Kothari, K.M.; Chan, R.; Johnson, E.L.; Lieu, D. Temperature, water and fertilizer influence the timing of key events during grain development in a US spring wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 37, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Rehman, A.; Wahid, A.; Siddique, K.H. Physiology of grain development in cereals. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Physiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 246–260. [Google Scholar]
- Stateczny, D.; Oppenheimer, J.; Bommert, P. G protein signaling in plants: Minus times minus equals plus. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 34, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S. Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling in plants: Conserved and novel mechanisms. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikari, M.; Wu, J.; Yano, M.; Sasaki, T.; Yoshimura, A. Rice gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant gene Dwarf 1 encodes the alpha-subunit of GTP-binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10284–10289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsunomiya, Y.; Samejima, C.; Takayanagi, Y.; Izawa, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Sawada, Y.; Fujisawa, Y.; Kato, H.; Iwasaki, Y. Suppression of the rice heterotrimeric G protein beta-subunit gene, RGB1, causes dwarfism and browning of internodes and lamina joint regions. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 67, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Yao, Y.; Du, X.; et al. Mutation of RGG2, which encodes a type B heterotrimeric G protein γ subunit, increases grain size and yield production in rice. Plant Biotech. J. 2019, 17, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Miao, J.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fan, F.; Xu, M.; et al. RGG1, Involved in the cytokinin regulatory pathway, controls grain size in rice. Rice 2020, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Xing, Y.; Mao, H.; Lu, T.; Han, B.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. Theor. Und Angew. Genet. 2006, 112, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Sun, S.; Yao, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, S.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19579–19584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Xing, Y. A causal C–A mutation in the second exon of GS3 highly associated with rice grain length and validated as a functional marker. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, L.; Mao, H.; Shao, L.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, Q. A G-protein pathway determines grain size in rice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Qian, Q.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; He, S.; Luo, D.; Xia, G.; Chu, C.; Li, J.; Fu, X. Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Yi, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Tang, S.; Gu, M.; Liang, G. Deletion in a quantitative trait gene qPE9-1 associated with panicle erectness improves plant architecture during rice domestication. Genetics 2009, 183, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Han, R.; Wu, K.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; et al. G-protein βγ subunits determine grain size through interaction with MADS-domain transcription factors in rice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, N.D.; Hamiditabar, Z.; Brunetti, S.C.; Gulick, P.J. Characterization of the heterotrimeric G protein gene families in Triticum aestivum and related species. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.-X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.-L.; Li, X.-J.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Q.-H.; Yang, Y.; Min, D.-H.; Zhang, X.-H. G-Protein β-subunit gene TaGB1-B enhances drought and salt resistance in wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.e.; Hu, W.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, G.; Liu, Z.; Cao, T.; et al. Cloning, characterization of TaGS3 and identification of allelic variation associated with kernel traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genet. 2019, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhi, L.; Liu, L.; Meng, D.; Su, Q.; Batool, A.; Ji, J.; Song, L.; Zhang, N.; Guo, L.; et al. Alternative splicing of TaGS3 differentially regulates grain weight and size in bread wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Qiu, J.-L.; Gao, C. Efficient and transgene-free genome editing in wheat through transient expression of CRISPR/Cas9 DNA or RNA. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braumann, I.; Dockter, C.; Beier, S.; Himmelbach, A.; Lok, F.; Lundqvist, U.; Skadhauge, B.; Stein, N.; Zakhrabekova, S.; Zhou, R.; et al. Mutations in the gene of the Gα subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein are the cause for the brachytic1 semi-dwarf phenotype in barley and applicable for practical breeding. Hereditas 2017, 155, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, T.; Holme, I.; Dockter, C.; Preuß, A.; Thomas, W.; Druka, A.; Waugh, R.; Hansson, M.; Braumann, I. HvDep1 Is a positive regulator of culm elongation and grain size in barley and impacts yield in an environment-dependent manner. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.J.; Amode, M.R.; Aneja, A.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D933–D941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D36–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalle, J.; Vierstra, R.D. The ubiquitin 26S proteasome proteolytic pathway. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 555–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadanandom, A.; Bailey, M.; Ewan, R.; Lee, J.; Nelis, S. The ubiquitin–proteasome system: Central modifier of plant signalling. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.-Q.; Xue, H.-W. The ubiquitin-proteasome system in plant responses to environments. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 2931–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.J.; Huang, W.; Shi, M.; Zhu, M.Z.; Lin, H.X. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Hao, C.; Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X. Identification and development of a functional marker of TaGW2 associated with grain weight in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Li, L.; Lv, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. TaGW2-6A allelic variation contributes to grain size possibly by regulating the expression of cytokinins and starch-related genes in wheat. Planta 2017, 246, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Huang, K.; Duan, P.; Li, N.; Xu, R.; Zeng, D.; Dong, G.; Zhang, B.; et al. The GW2-WG1-OsbZIP47 pathway controls grain size and weight in rice. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1266–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, H.; Hao, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Qin, L.; An, D.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. TaDA1, a conserved negative regulator of kernel size, has an additive effect with TaGW2 in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Biotech. J. 2020, 18, 1330–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Qian, Q.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.e.; Dong, G.; Gao, T.; Xie, Q.; Xue, Y. The U-Box E3 ubiquitin ligase TUD1 functions with a heterotrimeric G α subunit to regulate brassinosteroid-mediated growth in rice. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wu, K.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Guo, X.; Luo, W.; Sun, S.; Ouyang, Y.; Fu, X.; et al. The RING E3 ligase CLG1 targets GS3 for degradation via the endosome pathway to determine grain size in rice. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1699–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Mao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Yang, X.; Chang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. RING finger ubiquitin E3 ligase gene TaSDIR1-4A contributes to determination of grain size in common wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5377–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, J.; Cao, B.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Dong, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. Reducing brassinosteroid signalling enhances grain yield in semi-dwarf wheat. Nature 2023, 617, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijman, S.M.B.; Luna-Vargas, M.P.A.; Velds, A.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Dirac, A.M.G.; Sixma, T.K.; Bernards, R. A Genomic and functional inventory of deubiquitinating enzymes. Cell 2005, 123, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Wang, D.; Duan, P.; Zhang, B.; Xu, R.; Li, N.; Li, Y. WIDE AND THICK GRAIN 1, which encodes an otubain-like protease with deubiquitination activity, influences grain size and shape in rice. Plant J. 2017, 91, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, K.; Qian, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Pan, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Non-canonical regulation of SPL transcription factors by a human OTUB1-like deubiquitinase defines a new plant type rice associated with higher grain yield. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.J.; Hao, X.H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, H.; Wang, F. Reducing expression of TaOTUB1s decreases tiller number in wheat. Plant Signal. Behav. 2021, 16, 2018217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Ren, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Tian, P.; Pan, T.; Wang, Y.; Jing, R.; Liu, T.; et al. Ubiquitin specificprotease 15 has an important role in regulating grain width and size in rice. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, S. MAPK Cascades in plant disease resistance signaling. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in signaling plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Rao, Y.; Zeng, D.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, B.; Dong, G.; Qian, Q.; Li, Y. SMALL GRAIN 1, which encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4, influences grain size in rice. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 77, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hua, L.; Dong, S.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Fang, X.; Chen, F. OsMAPK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase, influences rice grain size and biomass production. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 84, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Duan, P.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Lyu, J.; Li, N.; et al. A mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase influences grain size and weight in rice. Plant J. 2018, 95, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Duan, P.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhuang, S.; Lyu, J.; et al. Control of grain size and weight by the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMAPK6 signaling pathway in rice. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; He, M.; Mei, E.; Zhang, B.; Tang, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, W.; et al. WRKY53 integrates classic brassinosteroid signaling and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway to regulate rice architecture and seed size. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 2753–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Chen, K.; Dong, N.-Q.; Shi, C.-L.; Ye, W.-W.; Gao, J.-P.; Shan, J.-X.; Lin, H.-X. GRAIN SIZE AND NUMBER1 negatively regulates the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMPK6 cascade to coordinate the trade-off between grain number per panicle and grain size in rice. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, R.; Xue, H.-W.; Yang, Z. The Rho-family GTPase OsRac1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating cell division. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16121–16126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, T.-F.; Li, Y.-T.; Zheng, L.; Lu, Z.-W.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.-P.; Sun, G.-Z.; et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase TaMPK3 suppresses ABA response by destabilising TaPYL4 receptor in wheat. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y. Essential roles of local auxin biosynthesis in plant development and in adaptation to environmental changes. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Chen, K.; Dong, N.-Q.; Ye, W.-W.; Shan, J.-X.; Lin, H.-X. Tillering and small grain 1 dominates the tryptophan aminotransferase family required for local auxin biosynthesis in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 581–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; E, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yun, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, B.; Chen, C. OsYUC11-mediated auxin biosynthesis is essential for endosperm development of rice. Plant Physiol. 2020, 185, 934–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, K.; Hirotsu, N.; Madoka, Y.; Murakami, N.; Hara, N.; Onodera, H.; Kashiwagi, T.; Ujiie, K.; Shimizu, B.; Onishi, A.; et al. Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.; Gao, F.; Liu, J.; Wen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Rasheed, A.; Xia, X.; He, Z.; Cao, S. TaTGW6-A1, an ortholog of rice TGW6, is associated with grain weight and yield in bread wheat. Mol. Breed. 2015, 36, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-J.; Zhang, H.-P.; Cao, J.-J.; Zhu, X.-F.; Wang, S.-X.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Z.Y.; Lu, J.; Chang, C.; Sun, G.-L.; et al. Characterization of an IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TaTGW6 associated with grain weight in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tong, H.; Xiao, Y.; Che, R.; Xu, F.; Hu, B.; Liang, C.; Chu, J.; Li, J.; Chu, C. Activation of Big Grain1 significantly improves grain size by regulating auxin transport in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11102–11107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.-F.; Cheng, M.-L.; Hsing, Y.-i.C.; Chen, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-W.; Hong, Y.-F.; Hsiao, Y.; Hsiao, A.-S.; Chen, P.-J.; Wong, L.-I.; et al. Rice big grain 1 promotes cell division to enhance organ development, stress tolerance and grain yield. Plant Biotech. J. 2020, 18, 1969–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, M.J.; Bowden, S.; Craze, M.; Wallington, E.J. Ectopic expression of TaBG1 increases seed size and alters nutritional characteristics of the grain in wheat but does not lead to increased yields. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Jiang, H.; Lin, Y.; Shang, L.; Wang, M.; Li, D.; Fu, X.; Geisler, M.; Qi, Y.; Gao, Z.; et al. A novel miR167a-OsARF6-OsAUX3 module regulates grain length and weight in rice. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1683–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Du, X.; Teotia, S.; Miao, C.; Sun, H.; Fan, G.; Tang, G.; Xue, H.; et al. The miR167-OsARF12 module regulates rice grain filling and grain size downstream of miR159. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, M.J.; He, H.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.H.; Jiang, L.; Sun, J.L.; Xin, X.; et al. A novel QTL qTGW3 encodes the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK5/OsSK41 that interacts with OsARF4 to negatively regulate grain size and weight in rice. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Tang, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Yao, G.; Li, G.; Guo, H.; Li, J.; et al. Gnp4/LAX2, a RAWUL protein, interferes with the OsIAA3–OsARF25 interaction to regulate grain length via the auxin signaling pathway in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 4723–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aya, K.; Hobo, T.; Sato-Izawa, K.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. A novel AP2-type transcription factor, SMALL ORGAN SIZE1, controls organ size downstream of an auxin signaling pathway. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankova, R. Cytokinin regulation of plant growth and stress responses. In Phytohormones: A Window to Metabolism, Signaling and Biotechnological Applications; Tran, L.-S.P., Pal, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 55–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Cytokinin signaling in plant development. Development 2018, 145, dev149344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Gao, S.; Liu, L.; Xu, F.; Che, R.; Wang, Y.; Tong, H.; Chu, C. Big grain3, encoding a purine permease, regulates grain size via modulating cytokinin transport in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Xiao, Y.; Niu, M.; Meng, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Qian, Y.; Sun, Z.; et al. ARGONAUTE2 enhances grain length and salt tolerance by activating BIG GRAIN3 to modulate cytokinin distribution in rice. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 2292–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Xiong, L. Characterization of a purine permease family gene OsPUP7 involved in growth and development control in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2013, 55, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Du, Y.; Li, F.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Peng, T.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, Q. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, OsPIL15, regulates grain size via directly targeting a purine permease gene OsPUP7 in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lu, X.; Xu, G.; Yin, X.; Cui, Y.; Huang, L.; Rocha, P.S.C.F.; Xia, X. OsSGL, a novel pleiotropic stress-related gene enhances grain length and yield in rice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Cao, S.; Yin, W.; Qian, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; et al. A cryptic inhibitor of cytokinin phosphorelay controls rice grain size. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Ng, C.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Tseng, T.H.; Li, W.H.; Ku, M.S. Down-regulation of cytokinin oxidase 2 expression increases tiller number and improves rice yield. Rice 2015, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, B.; Szala, K.; Przyborowski, M.; Bajguz, A.; Chmur, M.; Gasparis, S.; Orczyk, W.; Nadolska-Orczyk, A. TaCKX2.2 genes coordinate expression of other TaCKX family members, regulate phytohormone content and yield-related traits of wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Gao, L.-F.; Zhao, G.-Y.; Zhou, R.-H.; Zhang, B.-S.; Jia, J.-Z. TaCKX6-D1, the ortholog of rice OsCKX2, is associated with grain weight in hexaploid wheat. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chang, C.; Zhang, H.-P.; Wang, S.-X.; Sun, G.; Xiao, S.-H.; Ma, C.-X. Identification of a novel allele of TaCKX6a02 associated with grain size, filling rate and weight of common wheat. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewski, W.; Galuszka, P.; Gasparis, S.; Orczyk, W.; Nadolska-Orczyk, A. Silencing of the HvCKX1 gene decreases the cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase level in barley and leads to higher plant productivity. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 1839–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewski, W.; Orczyk, W.; Gasparis, S.; Nadolska-Orczyk, A. HvCKX2 gene silencing by biolistic or Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in barley leads to different phenotypes. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holubova, K.; Hensel, G.; Vojta, P.; Tarkowski, P.; Bergougnoux, V.; Galuszka, P. Modification of barley plant productivity through regulation of cytokinin content by reverse-genetics approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparis, S.; Przyborowski, M.; Kala, M.; Nadolska-Orczyk, A. Knockout of the HvCKX1 or HvCKX3 gene in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) by RNA-guided Cas9 nuclease affects the regulation of cytokinin metabolism and root morphology. Cells 2019, 8, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binenbaum, J.; Weinstain, R.; Shani, E. Gibberellin localization and transport in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Qian, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, J.; Du, C.; Luo, W.; Zou, G.; Chen, M.; et al. Mutation of rice BC12/GDD1, which encodes a kinesin-like protein that binds to a GA biosynthesis gene promoter, leads to dwarfism with impaired cell elongation. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.-L.; Dong, N.-Q.; Guo, T.; Ye, W.-W.; Shan, J.-X.; Lin, H.-X. A quantitative trait locus GW6 controls rice grain size and yield through the gibberellin pathway. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shi, S.; Tao, Q.; Tao, Y.; Miao, J.; Peng, X.; Li, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, G. OsGASR9 positively regulates grain size and yield in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Sci. 2019, 286, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Ma, S.; Xiao, Z.; Li, F.; Wei, X.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Ji, Z.; Fu, Y.; Pan, J.; et al. Natural variations in grain length 10 (GL10) regulate rice grain size. J. Genet. Genom. 2022, 49, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Lin, Q.; Zhou, C.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Miao, R.; Jing, R.; Mou, C.; Nguyen, T.; Zhu, X.; et al. Small grain and semi-dwarf 3, a WRKY transcription factor, negatively regulates plant height and grain size by stabilizing SLR1 expression in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2020, 104, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divi, U.K.; Krishna, P. Brassinosteroid: A biotechnological target for enhancing crop yield and stress tolerance. New Biotechnol. 2009, 26, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. The rice brassinosteroid-deficient dwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DIMINUTO/DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Ashikari, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Yano, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Fujisawa, Y.; et al. A novel cytochrome P450 Is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant, dwarf11, with reduced seed length. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, W.; Cui, X.; Chen, M.; Yin, C.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, J.; Lucas, W.J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D. Brassinosteroids promote development of rice pollen grains and seeds by triggering expression of carbon starved anther, a MYB domain protein. Plant J. 2015, 82, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Gu, P.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, C.; Tan, L. CLUSTERED PRIMARY BRANCH 1, a new allele of DWARF11, controls panicle architecture and seed size in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Zeng, D.; Yang, C.; Akhter, D.; Alamin, M.; Jin, X.; Shi, C. LTBSG1, a new allele of BRD2, regulates panicle and grain development in rice by brassinosteroid biosynthetic pathway. Genes 2018, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Roh, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Hu, J.; et al. SLG controls grain size and leaf angle by modulating brassinosteroid homeostasis in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 4241–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sun, H.; Dong, J.; Ma, C.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Hu, X.; Wu, M.; et al. The brassinosteroid biosynthesis gene TaD11-2A controls grain size and its elite haplotype improves wheat grain yields. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 2907–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morinaka, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Inukai, Y.; Agetsuma, M.; Kitano, H.; Ashikari, M.; Matsuoka, M. Morphological alteration caused by brassinosteroid insensitivity increases the biomass and grain production of rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Fan, S.; Huang, J.; Zhan, S.; Wang, S.; Gao, P.; Chen, W.; Tu, B.; Ma, B.; Wang, Y.; et al. 08SG2/OsBAK1 regulates grain size and number, and functions differently in Indica and Japonica backgrounds in rice. Rice 2017, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Liu, L.; Jin, Y.; Du, L.; Yin, Y.; Qian, Q.; Zhu, L.; Chu, C. DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2562–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Mou, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ji, J.; Yu, J.; Hao, Q.; Yang, C.; et al. Decreased grain size1, a C3HC4-type RING protein, influences grain size in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 105, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, M.; Wang, H.; Yin, W.; Meng, W.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Dong, N.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Rice DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING and the homeodomain protein OSH15 interact to regulate internode elongation via orchestrating brassinosteroid signaling and metabolism. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3754–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Liang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, Q.; et al. DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING 2 functions in brassinosteroid signaling and controls plant architecture and grain size in rice. Plant J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Dong, H.; Mou, C.; Wang, P.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wu, H.; Zhang, F.; Ma, T.; Miao, R.; et al. Ribonuclease H-like gene SMALL GRAIN2 regulates grain size in rice through brassinosteroid signaling pathway. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 1883–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.-S.; Li, Q.-F.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.-Q.; Pan, L.-X.; Ren, X.-Y.; Lu, J.; Gu, M.-H.; Liu, Q.-Q. GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yang, W.; Zhan, P.; Tan, Q.; Gou, Y.; Ma, S.; Luan, X.; Huang, C.; et al. GL9 from Oryza glumaepatula controls grain size and chalkiness in rice. Crop J. 2023, 11, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Tong, H.; Chu, C. Brassinosteroids regulate OFP1, a DLT interacting protein, to modulate plant architecture and grain morphology in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D.; Niu, M.; Tong, H.; Chu, C. GSK2 stabilizes OFP3 to suppress brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant J. 2020, 102, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Wang, D.; Duan, P.; Liu, Y.; Huang, K.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, L.; Dong, G.; Li, Y.; Xu, R.; et al. Control of grain size and weight by the GSK2-LARGE1/OML4 pathway in rice. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, T.; Nadler, S.; Schulze, E.; Fischer-Iglesias, C. Two homolog wheat glycogen synthase kinase 3/SHAGGY—Like kinases are involved in brassinosteroid signaling. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Xin, M.; Xu, R.; Chen, Z.; Cai, W.; Chai, L.; Xu, H.; Jia, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. A single amino acid substitution in STKc_GSK3 kinase conferring semispherical grains and its implications for the origin of Triticum sphaerococcum. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloc, Y.; Dmochowska-Boguta, M.; Zielezinski, A.; Nadolska-Orczyk, A.; Karlowski, W.M.; Orczyk, W. Silencing of HvGSK1.1—A GSK3/SHAGGY-Like Kinase enhances barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) growth in normal and in salt stress conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, P.; Tang, Z.; Bao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Tang, H.; et al. Rice qGL3/OsPPKL1 functions with the GSK3/SHAGGY-Like kinase OsGSK3 to modulate brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, X.; Wu, F.; Lin, Q.; Heng, Y.; Tian, P.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhou, K.; et al. GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signalling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Xing, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, L.; Sun, L.; Shao, D.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; et al. Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Genet 2011, 43, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q. Differential expression of GS5 regulates grain size in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2611–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Xu, J.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, B.; Geng, M.; Zhang, G.; Huang, K.; Huang, L.; Xu, R.; Ge, S.; et al. Natural variation in the promoter of GSE5 contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, T.; Hao, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X. TaGS5-3A, a grain size gene selected during wheat improvement for larger kernel and yield. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Wei, X.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Lin, S.; Li, F.; Bu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, H.; et al. GW10, a member of P450 subfamily regulates grain size and grain number in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 3941–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B.M. Ethylene signaling in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7710–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yin, C.-C.; Ma, B.; Chen, S.-Y.; Zhang, J.-S. Ethylene signaling in rice and Arabidopsis: New regulators and mechanisms. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 102–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Luo, W.; Li, W.; Chen, N.; Zhang, D.; Chong, K. The F-box protein OsFBK12 targets OsSAMS1 for degradation and affects pleiotropic phenotypes, including leaf senescence, in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Shao, G.; Jiao, G.; Sheng, Z.; Xie, L.; Hu, S.; Tang, S.; Wei, X.; Hu, P. Targeted mutagenesis of POLYAMINE OXIDASE 5 that negatively regulates mesocotyl elongation enables the generation of direct-seeding rice with improved grain yield. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, J.; Miao, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, D.; Gu, H.; Cui, H.; Shi, S.; et al. The spermine synthase OsSPMS1 regulates seed germination, grain size, and yield. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 1522–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ma, T.; Yuan, D.; Zhou, Y.; Long, Y.; Li, Z.; Dong, Z.; Duan, M.; Yu, D.; Jing, Y.; et al. The OsEIL1-OsERF115-target gene regulatory module controls grain size and weight in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1470–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasternack, C.; Strnad, M. Jasmonate signaling in plant stress responses and development—Active and inactive compounds. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakata, M.; Muramatsu, M.; Nakamura, H.; Hara, N.; Kishimoto, M.; Iida-Okada, K.; Kajikawa, M.; Imai-Toki, N.; Toki, S.; Nagamura, Y.; et al. Overexpression of TIFY genes promotes plant growth in rice through jasmonate signaling. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakata, M.; Kuroda, M.; Ohsumi, A.; Hirose, T.; Nakamura, H.; Muramatsu, M.; Ichikawa, H.; Yamakawa, H. Overexpression of a rice TIFY gene increases grain size through enhanced accumulation of carbohydrates in the stem. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wu, T.-T.; Zhang, G.-L.; Yin, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, S.; Chang, F.; Gou, J.-Y. Cloning of wheat keto-acyl thiolase 2B reveals a role of jasmonic acid in grain weight determination. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Bao, L.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. XIAO is involved in the control of organ size by contributing to the regulation of signaling and homeostasis of brassinosteroids and cell cycling in rice. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 70, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Gong, H.; Luo, J.; Hou, Q.; Zhou, T.; Lu, T.; Zhu, J.; Shangguan, Y.; et al. OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Yang, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-X.; Wang, J.-W.; Xue, H.-W. Rice SPL12 coevolved with GW5 to determine grain shape. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 2353–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, K.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Zeng, R.; Zhu, H.; Dong, G.; Qian, Q.; et al. Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Hua, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Li, W. CRISPR-induced miRNA156-recognition element mutations in TaSPL13 improve multiple agronomic traits in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Guo, L.; Ma, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H. Identification and functional characterization of squamosa promoter binding protein-like gene TaSPL16 in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, L.; Ren, Y.; Dong, Z.; Cui, D.; Chen, F. Genome-wide association study revealed that the TaGW8 gene was associated with kernel size in Chinese bread wheat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Qin, P.; Hu, L.; Zhan, S.; Wang, S.; Gao, P.; Li, J.; Jin, M.; Xu, Z.; Gao, Q.; et al. OsSPL18 controls grain weight and grain number in rice. J. Genet. Genom. 2019, 46, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidbakhshfard, M.A.; Proost, S.; Fujikura, U.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Growth-regulating factors (GRFs): A small transcription factor family with important functions in plant biology. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Z.; Ma, F.; Miao, X.; Shi, Z. OsmiR396/growth regulating factor modulate rice grain size through direct regulation of embryo-specific miR408. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Xu, J.; Yu, H.; Shi, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhang, D.; Kang, S.; et al. A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, P.; Ni, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y. Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Plants 2015, 2, 15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gao, F.; Xie, K.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y.; Zeng, J.; He, Z.; Ren, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, Q.; et al. The OsmiR396c-OsGRF4-OsGIF1 regulatory module determines grain size and yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 2134–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Zeng, J.; Ren, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, W.; Gao, F.; Cao, Y.; Luo, T.; Yuan, G.; Wu, X.; et al. OsGIF1 Positively regulates the sizes of stems, leaves, and grains in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tian, Y.; Wu, K.; Ye, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Hu, M.; Li, H.; Tong, Y.; et al. Modulating plant growth–metabolism coordination for sustainable agriculture. Nature 2018, 560, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avni, R.; Oren, L.; Shabtay, G.; Assili, S.; Pozniak, C.; Hale, I.; Ben-David, R.; Peleg, Z.; Distelfeld, A. Genome based meta-QTL analysis of grain weight in tetraploid wheat identifies rare alleles of GRF4 associated with larger grains. Genes 2018, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazhenov, M.S.; Chernook, A.G.; Bespalova, L.A.; Gritsay, T.I.; Polevikova, N.A.; Karlov, G.I.; Nazarova, L.A.; Divashuk, M.G. Alleles of the GRF3-2A gene in wheat and their agronomic value. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heang, D.; Sassa, H. Antagonistic actions of HLH/bHLH proteins are involved in grain length and weight in rice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, T.; Gu, B.; Huang, X.; Shangguan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. An-1 Encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein that regulates awn development, grain size, and grain number in rice. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3360–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fu, Y.; Lee, Y.-R.J.; Chern, M.; Li, M.; Cheng, M.; Dong, H.; Yuan, Z.; Gui, L.; Yin, J.; et al. The PGS1 basic helix-loop-helix protein regulates Fl3 to impact seed growth and grain yield in cereals. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Nakagawa, H.; Tomita, C.; Shimatani, Z.; Ohtake, M.; Nomura, T.; Jiang, C.J.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Kikuchi, S.; Sekimoto, H.; et al. BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; An, G.; Li, H.-Y. Rice leaf angle and grain size are affected by the OsBUL1 transcriptional activator complex. Plant Physiol. 2016, 173, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Li, H.Y. Oryza sativa BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1 LIKE1 induces the expression of a gene encoding a small leucine-rich-repeat protein to positively regulate lamina inclination and grain size in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Hou, X.-L.; Xing, G.-M.; Liu, J.-X.; Duan, A.-Q.; Xu, Z.-S.; Li, M.-Y.; Zhuang, J.; Xiong, A.-S. Advances in AP2/ERF super-family transcription factors in plant. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 750–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Miao, J.; Wang, W.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, G.; et al. OsLG3 contributing to rice grain length and yield was mined by Ho-LAMap. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Feng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Elesawi, I.E.; Xu, K.; Li, T.; Mei, H.; Liu, H.; Gao, N.; Chen, C.; et al. A novel rice grain size gene OsSNB was identified by genome-wide association study in natural population. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaczniak, C.; Immink, R.G.H.; Angenent, G.C.; Kaufmann, K. Developmental and evolutionary diversity of plant MADS-domain factors: Insights from recent studies. Development 2012, 139, 3081–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Xia, S.; Xu, Q.; Cui, Y.; Gong, M.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, L.; Jiao, G.; Gao, Z.; et al. ABNORMAL FLOWER AND GRAIN 1 encodes OsMADS6 and determines palea identity and affects rice grain yield and quality. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.J.; Kuroha, T.; Ayano, M.; Furuta, T.; Nagai, K.; Komeda, N.; Segami, S.; Miura, K.; Ogawa, D.; Kamura, T.; et al. Rare allele of a previously unidentified histone H4 acetyltransferase enhances grain weight, yield, and plant biomass in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Tao, S.; Li, X.; Gao, D.; Tang, M.; Liu, C.; Wu, D.; Bai, L.; He, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. The Harbinger transposon-derived gene PANDA epigenetically coordinates panicle number and grain size in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Cao, X.; Song, X. Epigenetic mutation of RAV6 affects leaf angle and seed size in rice. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2118–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-F.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Sun, Y.-M.; Yu, Y.; Lei, M.-Q.; Yang, Y.-W.; Lian, J.-P.; Feng, Y.-Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; et al. The parent-of-origin lncRNA MISSEN regulates rice endosperm development. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Cao, H.; Zhang, J.; Xie, K.; Wang, D.; Yu, S. Divergent functions of the GAGA-binding transcription factor family in rice. Plant J. 2018, 94, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Xue, T.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; et al. KNOX II transcription factor HOS59 functions in regulating rice grain size. Plant J. 2022, 110, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Hou, Q.; Si, L.; Huang, X.; Luo, J.; Lu, D.; Zhu, J.; Shangguan, Y.; Miao, J.; Xie, Y.; et al. The PLATZ transcription factor GL6 affects grain length and number in rice. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 2077–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Xiong, Y.; Xiao, P.; Wang, X.; Yao, J. OsNF-YC10, a seed preferentially expressed gene regulates grain width by affecting cell proliferation in rice. Plant Sci. 2019, 280, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Rao, Y.; Wu, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Leng, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhu, L.; et al. The pleiotropic ABNORMAL FLOWER AND DWARF1 affects plant height, floral development and grain yield in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Liu, L.; Fang, J.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, S.; Li, X. The rice TRIANGULAR HULL1 protein acts as a transcriptional repressor in regulating lateral development of spikelet. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Li, L.; Shi, W.; Tan, J.; Luo, X.; Zheng, S.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Zhuang, C.; Jiang, D. Florigen repression complexes involving rice CENTRORADIALIS2 regulate grain size. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 1260–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-C.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Liao, J.-Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Qu, L.-H.; Chen, F.; et al. Overexpression of microRNA OsmiR397 improves rice yield by increasing grain size and promoting panicle branching. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, X.H.; Li, Y.; Xie, L.; He, Y.; Li, W.; Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Xie, X. OsmiR530 acts downstream of OsPIL15 to regulate grain yield in rice. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-Q.; Hou, B.-H.; Lalonde, S.; Takanaga, H.; Hartung, M.L.; Qu, X.-Q.; Guo, W.-J.; Kim, J.-G.; Underwood, W.; Chaudhuri, B.; et al. Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 2010, 468, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breia, R.; Conde, A.; Badim, H.; Fortes, A.M.; Gerós, H.; Granell, A. Plant SWEETs: From sugar transport to plant–pathogen interaction and more unexpected physiological roles. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 836–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radchuk, V.; Belew, Z.M.; Gündel, A.; Mayer, S.; Hilo, A.; Hensel, G.; Sharma, R.; Neumann, K.; Ortleb, S.; Wagner, S.; et al. SWEET11b transports both sugar and cytokinin in developing barley grains. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 2186–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosso, D.; Luo, D.; Li, Q.-B.; Sasse, J.; Yang, J.; Gendrot, G.; Suzuki, M.; Koch, K.E.; McCarty, D.R.; Chourey, P.S.; et al. Seed filling in domesticated maize and rice depends on SWEET-mediated hexose transport. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, D.; Miao, Q.; Yang, J.; Xuan, Y.; Hu, Y. Essential role of sugar transporter OsSWEET11 during the early stage of rice grain filling. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Luo, D.; Yang, B.; Frommer, W.B.; Eom, J.S. SWEET11 and 15 as key players in seed filling in rice. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, J.-S.; Cho, J.-I.; Reinders, A.; Lee, S.-W.; Yoo, Y.; Tuan, P.Q.; Choi, S.-B.; Bang, G.; Park, Y.-I.; Cho, M.-H.; et al. Impaired function of the tonoplast-localized sucrose transporter in rice, OsSUT2, limits the transport of vacuolar reserve sucrose and affects plant growth. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; He, W.; Lu, B.; Lin, H.; et al. Control of rice grain-filling and yield by a gene with a potential signature of domestication. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Zeng, S.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Dang, X.; et al. Favorable alleles of GRAIN-FILLING RATE1 increase the grain-filling rate and yield of Rice1. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Tu, B.; Yang, W.; Yuan, H.; Li, J.; Guo, L.; Zheng, L.; Chen, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Mitochondria-associated pyruvate kinase complexes regulate grain filling in Rice1. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, P.; Zhang, G.; Hu, B.; Wu, J.; Chen, W.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Yuan, H.; Tu, B.; et al. Leaf-derived ABA regulates rice seed development via a transporter-mediated and temperature-sensitive mechanism. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Wu, T.; Ye, J.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, J.; Tang, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Wan, J. SNP-based analysis of genetic diversity reveals important alleles associated with seed size in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, N.; Hibara, K.; Heppard, E.P.; Vander Velden, K.A.; Luck, S.; Beatty, M.; Nagato, Y.; Sakai, H. GIANT EMBRYO encodes CYP78A13, required for proper size balance between embryo and endosperm in rice. Plant J. 2013, 75, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Fang, J.; Ou, S.; Gao, S.; Zhang, F.; Du, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Chu, J.; et al. Variations in CYP78A13 coding region influence grain size and yield in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Cheng, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Song, W.; Appels, R.; Zhao, H. Expression of TaCYP78A3, a gene encoding cytochrome P450 CYP78A3 protein in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), affects seed size. Plant J. 2015, 83, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Wu, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; et al. The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Miao, J.; Gu, H.; Peng, X.; Leburu, M.; Yuan, F.; Gu, H.; Gao, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Natural variations in SLG7 regulate grain shape in rice. Genetics 2015, 201, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, G.; Hu, J.; Jiang, L.; Yu, H.; Xu, J.; Fang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Xu, E.; Xu, J.; et al. Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Pan, Q.; Tian, B.; He, F.; Chen, Y.; Bai, G.; Akhunova, A.; Trick, H.N.; Akhunov, E. Gene editing of the wheat homologs of TONNEAU1-recruiting motif encoding gene affects grain shape and weight in wheat. Plant J. 2019, 100, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.Y.; Liu, L.T.; Li, T.; Yan, S.; Kuang, B.J.; Huang, S.J.; Yan, C.J.; Wang, T. OsKinesin-13A is an active microtubule depolymerase involved in glume length regulation via affecting cell elongation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, K.; Kurinami, S.; Oki, K.; Abe, Y.; Ando, T.; Kono, I.; Yano, M.; Kitano, H.; Iwasaki, Y. A novel kinesin 13 protein regulating rice seed length. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wendrich, J.R.; De Rybel, B.; Weijers, D.; Xue, H.-W. Rice microtubule-associated protein IQ67-DOMAIN14 regulates grain shape by modulating microtubule cytoskeleton dynamics. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shu, H.; Wang, Y.; Lai, J.; Du, J.; Yang, C. OsAGSW1, an ABC1-like kinase gene, is involved in the regulation of grain size and weight in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 5691–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, H.; Zheng, X.-M.; Jin, M.; Weng, J.-F.; Ma, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. An evolutionarily conserved gene, FUWA, plays a role in determining panicle architecture, grain shape and grain weight in rice. Plant J. 2015, 83, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Shang, L.; Zhang, B.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, A.; Liu, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. Natural variation in the promoter of TGW2 determines grain width and weight in rice. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, L.; Chen, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, E.; Miao, J.; Zuo, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; et al. OsCOMT, encoding a caffeic acid O-methyltransferase in melatonin biosynthesis, increases rice grain yield through dual regulation of leaf senescence and vascular development. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1122–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gasparis, S.; Miłoszewski, M.M. Genetic Basis of Grain Size and Weight in Rice, Wheat, and Barley. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316921
Gasparis S, Miłoszewski MM. Genetic Basis of Grain Size and Weight in Rice, Wheat, and Barley. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):16921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316921
Chicago/Turabian StyleGasparis, Sebastian, and Michał Miłosz Miłoszewski. 2023. "Genetic Basis of Grain Size and Weight in Rice, Wheat, and Barley" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 16921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316921
APA StyleGasparis, S., & Miłoszewski, M. M. (2023). Genetic Basis of Grain Size and Weight in Rice, Wheat, and Barley. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 16921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316921






