Epigenetic Dysregulation in MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epigenetic Regulation of MYCN Expression during Neural Crest Development
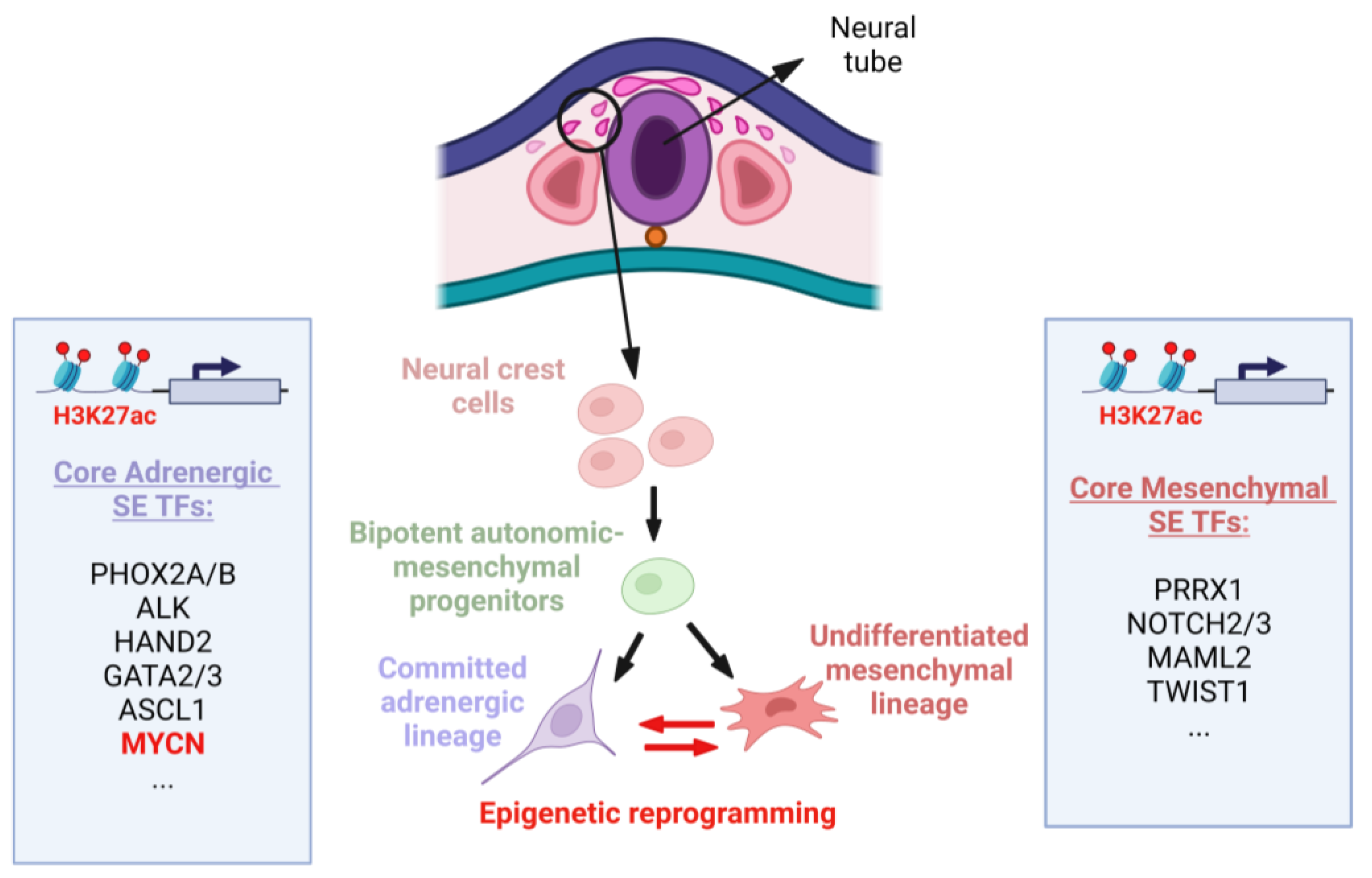
2.1. Neural Crest (NC) and NB Development
2.2. MYCN Levels during Neural Crest and MNA NB Development
2.3. Epigenetic Regulation of MYCN Expression during NC Development and Implications for MNA NB
3. Altered Epigenetic Mechanisms in MNA Neuroblastoma
3.1. DNA Methylation in MNA NB
3.2. Histone Modifications in MNA NB
3.2.1. Histone Acetylation
| Gene | Role | Methylation/Acetylation in MNA NB | Expression in MNA NB | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP300 | HAT | H3K27 acetylation | Increased | [69,70] |
| HDAC2 | HDAC | Deacetylates MIR183 promoter | Increased | [74] |
| HDAC5 | HDAC | Deacetylates CD9 | Increased | [75] |
| SIRT1 | HDAC | Deacetylation of tumor suppressors | Increased | [72] |
| HDAC1 | HDAC | Deacetylates NTRK1 promoter | Unknown | [73] |
| DOT1L | HMT | H3K79 methylation | Increased | [76] |
| EZH2 | Catalytic subunit of PRC2 complex | H3K27 trimethylation | Increased | [37,55] |
| KDM4B | Histone demethylase | H3K9me3/me2 demethylation | Increased | [77] |
| PRMT5 | HMT | H3R8 and H4R3 dimethylation | Increased | [78] |
| WDR5 | Histone H3K4 presenter | H3K4 trimethylation | Increased | [79] |
3.2.2. Histone Methylation
3.2.3. Histone Phosphorylation
3.3. Non-Coding RNAs and MNA NB
3.3.1. miRNAs
3.3.2. LncRNAs
3.3.3. circRNAs
| Non-Coding RNA | Expression in MNA NB | Associated Function | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ncRAN | Upregulated | Oncogenic | [137] |
| lncUSMycN | Co-amplified with MYCN | Oncogenic; upregulates MYCN mRNA expression via binding to NonO | [136] |
| SNHG1 | Upregulated | Oncogenic; downregulates miR338-3p, leading to PLK4 overexpression | [138] |
| lncNB1 | Upregulated | Upregulates E2F1 expression by binding RPL35, leading to transcription of DEPDC1B | [139] |
| NDM29 | Downregulated | Induces differentiation of MNA NB cells when overexpressed | [140] |
| T-UCRs (uc.347, uc.350, uc.279, uc.460, uc.379, uc.446 and uc.364) | Upregulated | Oncogenic; involved in proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation | [84] |
| MYCNOS-01 | Co-amplified with MYCN | Oncogenic; regulates MYCN protein expression | [141,142] |
| MYCNOS-02 | Co-amplified with MYCN | Oncogenic; interacts with G3BP1 and recruits CTCF to the MYCN promoter, thereby increasing MYCN expression. Suppresses differentiation and increases growth, invasion, and metastasis of NB cells | [141] |
| circ_0003287, circ_0008083, circ_0052767, circ_0000978, circ_0117720, chr2:15467874|15567918, circ_0008261 | Upregulated | Oncogenic | [41] |
| circARID1A | Upregulated | Oncogenic; promotes proliferation and survival of NB cells via direct interaction with KHSRP | [144] |
3.4. Super-Enhancers as Epigenetic Modifiers Regulating MYCN in NB
3.5. Bromodomains in MNA NB
3.6. Chromatin Remodeling Complexes in MNA NB
4. Epigenetic Therapies for MNA NB
4.1. HDAC and HAT Inhibitors in MNA NB
4.2. HMT Inhibitors in MNA NB
4.3. BET Inhibitors in MNA NB
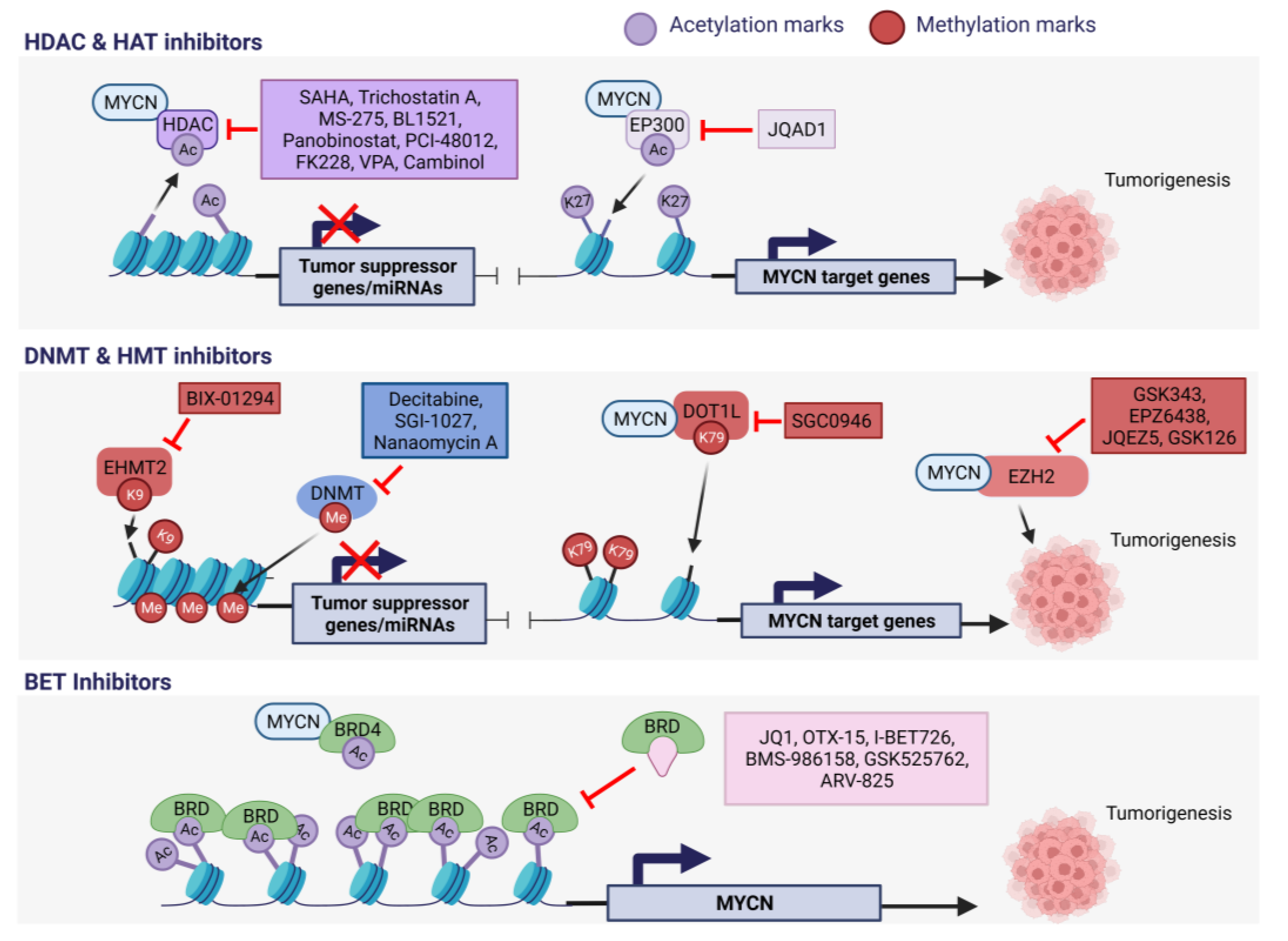
4.4. DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors in MNA NB
| Name | Drug Target in NB | Effect on MYCN in MNA NB | Clinical Status | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARV-825 | BRD4 inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical | [190] |
| BIX-01294 | EHMT2 (HMT) inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical | [178] |
| BL1521 | Pan-HDAC inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical | [166,191] |
| BMS-986158 | BRD4 inhibitor | Not specifically characterized | Pre-clinical and clinical Phase I:
| [169] |
| Cambinol | SIRT1 (HDAC) inhibitor | Not specifically characterized | Pre-clinical | [72] |
| Decitabine (5-Azacytidine) | DNMT 1 inhibitor | Not specifically characterized | Pre-clinical and clinical Phase I:
| [184,192] |
| Entinostat (MS-275) | HDAC I inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical | [167] |
| GSK343, Tazemetostat (EPZ6438), JQEZ5, GSK126 | EZH2 inhibitors | Downregulation (GSK343), others not specifically characterized | Pre-clinical and clinical Phase II (EPZ6439):
| [35,55,173,175,193] |
| I-BET726 (GSK726) | BRD4 inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical | [194] |
| JQ1/OTX-015 | BRD4 inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical | [159] |
| JQAD1 | EP300 (HAT) inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical | [69] |
| Molibresib (GSK525762, I-BET762) | BRD2/3/4 | Downregulation | Pre-clinical and clinical Phase I:
| [195] |
| Panobinostat | Pan-HDAC inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical and clinical Phase II:
| [159] |
| PCI-48012 | HDAC 8 inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical | [170] |
| Romidepsin (FK228) | HDAC I inhibitor | Not specifically characterized | Pre-clinical | [171] |
| SGC0946 | DOT1L (HMT) inhibitor | Unknown | Pre-clinical | [76] |
| SGI-1027, Nanaomycin A | DNMT1/3 inhibitors | Not specifically characterized | Pre-clinical | [185] |
| Trichostatin A | HDAC I/II inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical | [164] |
| Valproic acid (VPA) | HDAC I inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical and clinical Phase I:
| [196] |
| Vorinostat (SAHA) | HDAC I inhibitor | Downregulation | Pre-clinical and clinical Phase I:
Phase II:
| [165] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakagawara, A.; Li, Y.; Izumi, H.; Muramori, K.; Inada, H.; Nishi, M. Neuroblastoma. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 48, 214–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westermark, U.K.; Wilhelm, M.; Frenzel, A.; Henriksson, M.A. The MYCN Oncogene and Differentiation in Neuroblastoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2011, 21, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, S.S.; Clarke, S.; Veschi, V.; Thiele, C.J. Targeting MYCN in Pediatric and Adult Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 623679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, K.K.; Maris, J.M.; Schleiermacher, G.; Nakagawara, A.; Mackall, C.L.; Diller, L.; Weiss, W.A. Neuroblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.N.; Henderson, T.O. Late Effects and Survivorship Issues in Patients with Neuroblastoma. Children 2018, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo-Fernandez, R.; Watters, K.; Piskareva, O.; Stallings, R.L.; Bray, I. The Role of Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations in Neuroblastoma Disease Pathogenesis. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2013, 29, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatziapostolou, M.; Iliopoulos, D. Epigenetic Aberrations during Oncogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 1681–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, O.; Honarmand Tamizkar, K.; Hajiesmaeili, M.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Non-Coding RNAs Participate in the Pathogenesis of Neuroblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 617362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, L.; Linker, C.; Ruiz, P.; Guerrero, N.; Mayor, R. The Inductive Properties of Mesoderm Suggest That the Neural Crest Cells Are Specified by a BMP Gradient. Dev. Biol. 1998, 198, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, A.; Berliner, A.J.; Papanayotou, C.; Sirulnik, A.; Stern, C.D. Initiation of Neural Induction by FGF Signalling before Gastrulation. Nature 2000, 406, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Jeannet, J.P.; He, X.; Varmus, H.E.; Dawid, I.B. Regulation of Dorsal Fate in the Neuraxis by Wnt-1 and Wnt-3a. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13713–13718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarovina, K.; Schellenberger, J.; Schneider, C.; Rohrer, H. Progenitor Cell Maintenance and Neurogenesis in Sympathetic Ganglia Involves Notch Signaling. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2008, 37, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões-Costa, M.; Bronner, M.E. Establishing Neural Crest Identity: A Gene Regulatory Recipe. Development 2015, 142, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, A.J.; Dixon, J.; Dixon, M.J.; Trainor, P.A. Balancing Neural Crest Cell Intrinsic Processes with Those of the Microenvironment in Tcof1 Haploinsufficient Mice Enables Complete Enteric Nervous System Formation. Human Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1782–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, W.A.; Trainor, P.A. Chapter One—Neural Crest Cell Evolution: How and When Did a Neural Crest Cell Become a Neural Crest Cell. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Trainor, P.A., Ed.; Neural Crest and Placodes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 111, pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.-Y.; Say, E.H.M.; Zhou, X.-F. Isolation and Characterization of Neural Crest Progenitors from Adult Dorsal Root Ganglia. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 2053–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte, J.; Dyberg, C.; Pepich, A.; Johnsen, J.I. MYCN Function in Neuroblastoma Development. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 624079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzoni, M.; Bachetti, T.; Corrias, M.V.; Brignole, C.; Pastorino, F.; Calarco, E.; Bensa, V.; Giusto, E.; Ceccherini, I.; Perri, P. Recent Advances in the Developmental Origin of Neuroblastoma: An Overview. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pérez, M.V.; Henley, A.B.; Arsenian-Henriksson, M. The MYCN Protein in Health and Disease. Genes 2017, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomolonis, J.A.; Agarwal, S.; Shohet, J.M. Neuroblastoma Pathogenesis: Deregulation of Embryonic Neural Crest Development. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, J.I.; Dyberg, C.; Wickström, M. Neuroblastoma-A Neural Crest Derived Embryonal Malignancy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Guan, Z. Function of Oncogene Mycn in Adult Neurogenesis and Oligodendrogenesis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincentz, J.W.; VanDusen, N.J.; Fleming, A.B.; Rubart, M.; Firulli, B.A.; Howard, M.J.; Firulli, A.B. A Phox2- and Hand2-Dependent Hand1 Cis-Regulatory Element Reveals a Unique Gene Dosage Requirement for Hand2 during Sympathetic Neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.-X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.; Hu, R.; Dong, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhu, S.; Xia, Q.; Ding, H.-F.; Cui, H. Phox2B Correlates with MYCN and Is a Prognostic Marker for Neuroblastoma Development. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Weiss, W.A. Neuroblastoma and MYCN. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a014415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khudyakov, J.; Bronner-Fraser, M. Comprehensive Spatiotemporal Analysis of Early Chick Neural Crest Network Genes. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Kondoh, H. Regulation of the Neural Crest Cell Fate by N-Myc: Promotion of Ventral Migration and Neuronal Differentiation. Development 1997, 124, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravindan, N.; Subramanian, K.; Somasundaram, D.B.; Herman, T.S.; Aravindan, S. MicroRNAs in Neuroblastoma Tumorigenesis, Therapy Resistance, and Disease Evolution. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 1086–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, D.; Hagemann, S.; Bell, J.L.; Busch, B.; Lederer, M.; Bley, N.; Schulte, J.H.; Hüttelmaier, S. The MicroRNA Landscape of MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 647737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, B.C.; Kwon, M.; Kraemer, B.R.; Hickman, F.E.; Qiao, J.; Chung, D.H.; Carter, B.D. Expression of MYCN in Multipotent Sympathoadrenal Progenitors Induces Proliferation and Neural Differentiation, but Is Not Sufficient for Tumorigenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, M.; Mercurio, F.A.; Langella, E.; Piacenti, V.; Leone, M.; Adamo, M.F.A.; Saviano, M. Structural Insights on Tiny Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) Analogues of miRNA-34a: An in Silico and Experimental Integrated Approach. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 568575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaiah, M.J.; Pushpavalli, S.N.C.V.L.; Lavanya, A.; Bhadra, K.; Haritha, V.; Patel, N.; Tamboli, J.R.; Kamal, A.; Bhadra, U.; Pal-Bhadra, M. Novel Anthranilamide-Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Conjugates Modulate the Expression of P53-MYCN Associated Micro RNAs in Neuroblastoma Cells and Cause Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 5699–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-G.; He, J.-H.; Yu, L.; Hang, Z.-P.; Li, W.; Shun, W.-H.; Huang, G.X. microRNA-202 Suppresses MYCN Expression under the Control of E2F1 in the Neuroblastoma Cell Line LAN-5. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kobayashi, K.; Jakt, L.M.; Nishikawa, S.-I. Epigenetic Regulation of the Neuroblastoma Genes, Arid3b and Mycn. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tsubota, S.; Kishida, S.; Shimamura, T.; Ohira, M.; Yamashita, S.; Cao, D.; Kiyonari, S.; Ushijima, T.; Kadomatsu, K. PRC2-Mediated Transcriptomic Alterations at the Embryonic Stage Govern Tumorigenesis and Clinical Outcome in MYCN-Driven Neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5259–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubota, S.; Kadomatsu, K. Origin and Initiation Mechanisms of Neuroblastoma. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvetta, D.; Chayka, O.; Gherardi, S.; D’Acunto, C.W.; Cantilena, S.; Valli, E.; Piotrowska, I.; Perini, G.; Sala, A. Physical Interaction between MYCN Oncogene and Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) in Neuroblastoma: Functional And Therapeutic Implications. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 8332–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerosuo, L.; Neppala, P.; Hsin, J.; Mohlin, S.; Vieceli, F.M.; Török, Z.; Laine, A.; Westermarck, J.; Bronner, M.E. Enhanced Expression of MycN/CIP2A Drives Neural Crest toward a Neural Stem Cell-like Fate: Implications for Priming of Neuroblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7351–E7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansford, L.M.; Thomas, W.D.; Keating, J.M.; Burkhart, C.A.; Peaston, A.E.; Norris, M.D.; Haber, M.; Armati, P.J.; Weiss, W.A.; Marshall, G.M. Mechanisms of Embryonal Tumor Initiation: Distinct Roles for MycN Expression and MYCN Amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12664–12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, W.A.; Aldape, K.; Mohapatra, G.; Feuerstein, B.G.; Bishop, J.M. Targeted Expression of MYCN Causes Neuroblastoma in Transgenic Mice. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 2985–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Shi, T.; Feng, G. Comprehensive Characterization of Circular RNAs in Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820957622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonaci, M.; Wheeler, G.N. MicroRNAs in Neural Crest Development and Neurocristopathies. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corley, M.; Kroll, K.L. The Roles and Regulation of Polycomb Complexes in Neural Development. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 359, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braoudaki, M.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Zaravinos, A.; Lambrou, G.I. MYCN in Neuroblastoma: “Old Wine into New Wineskins”. Diseases 2021, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetahu, I.S.; Taschner-Mandl, S. Neuroblastoma and the Epigenome. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lázcoz, P.; Muñoz, J.; Nistal, M.; Pestaña, A.; Encío, I.; Castresana, J.S. Frequent Promoter Hypermethylation of RASSF1A and CASP8 in Neuroblastoma. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Djos, A.; Martinsson, T.; Kogner, P.; Carén, H. The RASSF Gene Family Members RASSF5, RASSF6 and RASSF7 Show Frequent DNA Methylation in Neuroblastoma. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrich, K.-O.; Bender, S.; Saadati, M.; Dreidax, D.; Gartlgruber, M.; Shao, C.; Herrmann, C.; Wiesenfarth, M.; Parzonka, M.; Wehrmann, L.; et al. Integrative Genome-Scale Analysis Identifies Epigenetic Mechanisms of Transcriptional Deregulation in Unfavorable Neuroblastomas. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5523–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teitz, T.; Inoue, M.; Valentine, M.B.; Zhu, K.; Rehg, J.E.; Zhao, W.; Finkelstein, D.; Wang, Y.-D.; Johnson, M.D.; Calabrese, C.; et al. Th-MYCN Mice with Caspase-8 Deficiency Develop Advanced Neuroblastoma with Bone Marrow Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4086–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, A.; Rossouw, S.C.; Fatai, A.; Gamieldien, J.; Christoffels, A.; Bendou, H. Predicting Amplification of MYCN Using CpG Methylation Biomarkers in Neuroblastoma. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 4769–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decock, A.; Ongenaert, M.; Hoebeeck, J.; De Preter, K.; Van Peer, G.; Van Criekinge, W.; Ladenstein, R.; Schulte, J.H.; Noguera, R.; Stallings, R.L.; et al. Genome-Wide Promoter Methylation Analysis in Neuroblastoma Identifies Prognostic Methylation Biomarkers. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekusa, S.; Kawashima, H.; Sugito, K.; Yoshizawa, S.; Shinojima, Y.; Igarashi, J.; Ghosh, S.; Wang, X.; Fujiwara, K.; Ikeda, T.; et al. NR4A3, a Possibile Oncogenic Factor for Neuroblastoma Associated with CpGi Methylation within the Third Exon. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, K.; Watanabe, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Ohira, M.; Westermann, F.; Schwab, M.; Nakagawara, A.; Ushijima, T. Stronger Prognostic Power of the CpG Island Methylator Phenotype than Methylation of Individual Genes in Neuroblastomas. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 43, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hoebeeck, J.; Michels, E.; Pattyn, F.; Combaret, V.; Vermeulen, J.; Yigit, N.; Hoyoux, C.; Laureys, G.; Paepe, A.D.; Speleman, F.; et al. Aberrant Methylation of Candidate Tumor Suppressor Genes in Neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2009, 273, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Alexe, G.; Dharia, N.V.; Ross, L.; Iniguez, A.B.; Conway, A.S.; Wang, E.J.; Veschi, V.; Lam, N.; Qi, J.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 Screen Reveals a MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma Dependency on EZH2. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 128, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Ohira, M.; Kaneda, A.; Yagi, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Kitano, Y.; Takato, T.; Nakagawara, A.; Ushijima, T. CpG Island Methylator Phenotype Is a Strong Determinant of Poor Prognosis in Neuroblastomas. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalchungnunga, H.; Hao, W.; Maris, J.M.; Asgharzadeh, S.; Henrich, K.-O.; Westermann, F.; Tweddle, D.A.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Strathdee, G. Genome Wide DNA Methylation Analysis Identifies Novel Molecular Subgroups and Predicts Survival in Neuroblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 2006–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banelli, B.; Gelvi, I.; Di Vinci, A.; Scaruffi, P.; Casciano, I.; Allemanni, G.; Bonassi, S.; Tonini, G.P.; Romani, M. Distinct CpG Methylation Profiles Characterize Different Clinical Groups of Neuroblastic Tumors. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5619–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Casalà, C.; Gil-Guiñón, E.; Ordóñez, J.L.; Miguel-Queralt, S.; Rodríguez, E.; Galván, P.; Lavarino, C.; Munell, F.; de Alava, E.; Mora, J.; et al. The Calcium-Sensing Receptor Is Silenced by Genetic and Epigenetic Mechanisms in Unfavorable Neuroblastomas and Its Reactivation Induces ERK1/2-Dependent Apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Mühlethaler, A.; Bourloud, K.B.; Beck, M.N.; Gross, N. Hypermethylation-Mediated Regulation of CD44 Gene Expression in Human Neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003, 36, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.T.; Hesson, L.B.; Norris, M.D.; Marshall, G.M.; Haber, M.; Ashton, L.J. Prognostic Significance of Promoter DNA Methylation in Patients with Childhood Neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5690–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez, Y.; Grau, E.; Rodríguez-Cortez, V.C.; Hervás, D.; Vidal, E.; Noguera, R.; Hernández, M.; Segura, V.; Cañete, A.; Conesa, A.; et al. Two Independent Epigenetic Biomarkers Predict Survival in Neuroblastoma. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, F.; Carosio, R.; Ragusa, M.; Di Pietro, C.; Maugeri, M.; Barbagallo, D.; Sallustio, F.; Allemanni, G.; Pistillo, M.P.; Casciano, I.; et al. Epigenetic Dysregulation in Neuroblastoma: A Tale of miRNAs and DNA Methylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1859, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacenti, V.; Langella, E.; Autiero, I.; Nolan, J.C.; Piskareva, O.; Adamo, M.F.A.; Saviano, M.; Moccia, M. A Combined Experimental and Computational Study on Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) Analogues of Tumor Suppressive miRNA-34a. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 91, 103165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikram, F.; Ackermann, S.; Kahlert, Y.; Volland, R.; Roels, F.; Engesser, A.; Hertwig, F.; Kocak, H.; Hero, B.; Dreidax, D.; et al. Transcription Factor Activating Protein 2 Beta (TFAP2B) Mediates Noradrenergic Neuronal Differentiation in Neuroblastoma. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugito, K.; Kawashima, H.; Yoshizawa, S.; Uekusa, S.; Hoshi, R.; Furuya, T.; Kaneda, H.; Hosoda, T.; Konuma, N.; Masuko, T.; et al. Non-Promoter DNA Hypermethylation of Zygote Arrest 1 (ZAR1) in Neuroblastomas. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 48, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugito, K.; Kawashima, H.; Uekusa, S.; Yoshizawa, S.; Hoshi, R.; Furuya, T.; Kaneda, H.; Hosoda, T.; Masuko, T.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Identification of Aberrant Methylation Regions in Neuroblastoma by Screening of Tissue-Specific Differentially Methylated Regions. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoepfler, P.S.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, P.F.; Gafken, P.R.; McMahon, S.B.; Eisenman, R.N. Myc Influences Global Chromatin Structure. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2723–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, A.D.; Wang, T.; Wimalasena, V.K.; Zimmerman, M.W.; Li, D.; Dharia, N.V.; Mariani, L.; Shendy, N.A.M.; Nance, S.; Patel, A.G.; et al. EP300 Selectively Controls the Enhancer Landscape of MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 730–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; He, T.; Chen, K.; Cai, Y.; Gu, Y.; Pan, L.; Duan, P.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z. P300 Interacted With N-Myc and Regulated Its Protein Stability via Altering Its Post-Translational Modifications in Neuroblastoma. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2023, 22, 100504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.M.; Gherardi, S.; Xu, N.; Neiron, Z.; Trahair, T.; Scarlett, C.J.; Chang, D.K.; Liu, P.Y.; Jankowski, K.; Iraci, N.; et al. Transcriptional Upregulation of Histone Deacetylase 2 Promotes Myc-Induced Oncogenic Effects. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5957–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.M.; Liu, P.Y.; Gherardi, S.; Scarlett, C.J.; Bedalov, A.; Xu, N.; Iraci, N.; Valli, E.; Ling, D.; Thomas, W.; et al. SIRT1 Promotes N-Myc Oncogenesis through a Positive Feedback Loop Involving the Effects of MKP3 and ERK on N-Myc Protein Stability. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iraci, N.; Diolaiti, D.; Papa, A.; Porro, A.; Valli, E.; Gherardi, S.; Herold, S.; Eilers, M.; Bernardoni, R.; Valle, G.D.; et al. A SP1/MIZ1/MYCN Repression Complex Recruits HDAC1 at the TRKA and p75NTR Promoters and Affects Neuroblastoma Malignancy by Inhibiting the Cell Response to NGF. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodrini, M.; Oehme, I.; Schroeder, C.; Milde, T.; Schier, M.C.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Schulte, J.H.; Fischer, M.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; et al. MYCN and HDAC2 Cooperate to Repress miR-183 Signaling in Neuroblastoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 6018–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, J.; Opitz, D.; Althoff, K.; Lodrini, M.; Hero, B.; Volland, R.; Beckers, A.; de Preter, K.; Decock, A.; Patil, N.; et al. MYCN and HDAC5 Transcriptionally Repress CD9 to Trigger Invasion and Metastasis in Neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66344–66359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.; Tee, A.E.L.; Milazzo, G.; Bell, J.L.; Poulos, R.C.; Atmadibrata, B.; Sun, Y.; Jing, D.; Ho, N.; Ling, D.; et al. The Histone Methyltransferase DOT1L Promotes Neuroblastoma by Regulating Gene Transcription. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; AlTahan, A.M.; Hu, D.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, P.-H.; Morton, C.L.; Qu, C.; Nathwani, A.C.; Shohet, J.M.; Fotsis, T.; et al. The Role of Histone Demethylase KDM4B in Myc Signaling in Neuroblastoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Szemes, M.; Vieira, G.C.; Melegh, Z.; Malik, S.; Heesom, K.J.; Von Wallwitz-Freitas, L.; Greenhough, A.; Brown, K.W.; Zheng, Y.G.; et al. Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 Is a Key Regulator of the MYCN Oncoprotein in Neuroblastoma Cells. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bell, J.L.; Carter, D.; Gherardi, S.; Poulos, R.C.; Milazzo, G.; Wong, J.W.H.; Al-Awar, R.; Tee, A.E.; Liu, P.Y.; et al. WDR5 Supports an N-Myc Transcriptional Complex That Drives a Protumorigenic Gene Expression Signature in Neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 5143–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeschert, I.; Poon, E.; Henssen, A.G.; Garcia, H.D.; Gatti, M.; Giansanti, C.; Jamin, Y.; Ade, C.P.; Gallant, P.; Schülein-Völk, C.; et al. Combined Inhibition of Aurora-A and ATR Kinase Results in Regression of MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, M.S.; Lee, E.; Schadt, E.E.; Sholler, G.S.; Zhu, J. Identification of Let-7 miRNA Activity as a Prognostic Biomarker of SHH Medulloblastoma. Cancers 2021, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shelton, S.D.; Oviedo, A.; Baker, A.L.; Bryant, C.P.; Omidvarnia, S.; Du, L. The PLAGL2/MYCN/miR-506-3p Interplay Regulates Neuroblastoma Cell Fate and Associates with Neuroblastoma Progression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buechner, J.; Einvik, C. N-Myc and Noncoding RNAs in Neuroblastoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestdagh, P.; Fredlund, E.; Pattyn, F.; Rihani, A.; Van Maerken, T.; Vermeulen, J.; Kumps, C.; Menten, B.; De Preter, K.; Schramm, A.; et al. An Integrative Genomics Screen Uncovers ncRNA T-UCR Functions in Neuroblastoma Tumours. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3583–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Stallings, R.L. Differential Patterns of microRNA Expression in Neuroblastoma Are Correlated with Prognosis, Differentiation, and Apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.-Y.; Gailhouste, L. Non-Genomic Control of Dynamic MYCN Gene Expression in Liver Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 618515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, K.; Liew, L.C.; Hagiwara, K.; Hironaka-Mitsuhashi, A.; Qin, X.; Furutani, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakagama, H.; Kojima, S.; Kato, T.; et al. MicroRNA-493-5p-mediated Repression of the MYCN Oncogene Inhibits Hepatic Cancer Cell Growth and Invasion. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Young, J.; Prabhala, H.; Pan, E.; Mestdagh, P.; Muth, D.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Reinhardt, F.; Onder, T.T.; Valastyan, S.; et al. miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-Activated microRNA, Regulates E-Cadherin and Cancer Metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Du, L.; Nagabayashi, G.; Seeger, R.C.; Gatti, R.A. ATM Is Down-Regulated by N-Myc-Regulated microRNA-421. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1506–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chava, S.; Reynolds, C.P.; Pathania, A.S.; Gorantla, S.; Poluektova, L.Y.; Coulter, D.W.; Gupta, S.C.; Pandey, M.K.; Challagundla, K.B. miR-15a-5p, miR-15b-5p, and miR-16-5p Inhibit Tumor Progression by Directly Targeting MYCN in Neuroblastoma. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechner, J.; Tømte, E.; Haug, B.H.; Henriksen, J.R.; Løkke, C.; Flægstad, T.; Einvik, C. Tumour-Suppressor microRNAs Let-7 and Mir-101 Target the Proto-Oncogene MYCN and Inhibit Cell Proliferation in MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, A.; Van Peer, G.; Carter, D.R.; Gartlgruber, M.; Herrmann, C.; Agarwal, S.; Helsmoortel, H.; Althoff, K.; Molenaar, J.J.; Cheung, B.B.; et al. MYCN-Driven Regulatory Mechanisms Controlling LIN28B in Neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 366, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenaar, J.J.; Domingo-Fernández, R.; Ebus, M.E.; Lindner, S.; Koster, J.; Drabek, K.; Mestdagh, P.; van Sluis, P.; Valentijn, L.J.; van Nes, J.; et al. LIN28B Induces Neuroblastoma and Enhances MYCN Levels via Let-7 Suppression. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienertova-Vasku, J.; Mazanek, P.; Hezova, R.; Curdova, A.; Nekvindova, J.; Kren, L.; Sterba, J.; Slaby, O. Extension of microRNA Expression Pattern Associated with High-Risk Neuroblastoma. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Hao, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Hua, Y.; Yang, L.; Yu, J.; Zhao, J.; Hou, L.; et al. MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-17-5p Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Non-MYCN Amplified Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastropasqua, F.; Marzano, F.; Valletti, A.; Aiello, I.; Di Tullio, G.; Morgano, A.; Liuni, S.; Ranieri, E.; Guerrini, L.; Gasparre, G.; et al. TRIM8 Restores P53 Tumour Suppressor Function by Blunting N-MYC Activity in Chemo-Resistant Tumours. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, C.Y.; Carter, D.R.; Liu, B.; Mayoh, C.; Beckers, A.; Lalwani, A.; Nagy, Z.; De Brouwer, S.; Decaesteker, B.; Hung, T.-T.; et al. Network Modeling of microRNA-mRNA Interactions in Neuroblastoma Tumorigenesis Identifies miR-204 as a Direct Inhibitor of MYCN. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3122–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomão, K.B.; Pezuk, J.A.; de Souza, G.R.; Chagas, P.; Pereira, T.C.; Valera, E.T.; Brassesco, M.S. MicroRNA Dysregulation Interplay with Childhood Abdominal Tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 783–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.T.; Tsanov, K.M.; Pearson, D.S.; Roels, F.; Spina, C.S.; Ebright, R.; Seligson, M.; de Soysa, Y.; Cahan, P.; Theiβen, J.; et al. Multiple Mechanisms Disrupt the Let-7 microRNA Family in Neuroblastoma. Nature 2016, 535, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennchen, M.; Stubbusch, J.; Abarchan-El Makhfi, I.; Kramer, M.; Deller, T.; Pierre-Eugene, C.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Delattre, O.; Ernsberger, U.; Schulte, J.B.; et al. Lin28B and Let-7 in the Control of Sympathetic Neurogenesis and Neuroblastoma Development. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 16531–16544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, I.Y.; Farazi, T.A.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Xu, H.; Tran, H.; Mihailovic, A.; Tuschl, T.; Cheung, N.-K.V. Deep MicroRNA Sequencing Reveals Downregulation of miR-29a in Neuroblastoma Central Nervous System Metastasis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shalom-Feuerstein, R.; Riley, J.; Zhang, S.-D.; Tucci, P.; Agostini, M.; Aberdam, D.; Knight, R.A.; Genchi, G.; Nicotera, P.; et al. miR-7 and miR-214 Are Specifically Expressed during Neuroblastoma Differentiation, Cortical Development and Embryonic Stem Cells Differentiation, and Control Neurite Outgrowth in Vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, B.; Alwin Prem Anand, A. Role of miRNA-9 in Brain Development. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, L.; Pearce, W.J. MicroRNAs in Brain Development and Cerebrovascular Pathophysiology. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 317, C3–C19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.C. The microRNA-17 ~ 92 Family as a Key Regulator of Neurogenesis and Potential Regenerative Therapeutics of Neurological Disorders. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kim, H.J.; Schafer, S.T.; Paquola, A.; Clemenson, G.D.; Toda, T.; Oh, J.; Pankonin, A.R.; Lee, B.S.; Johnston, S.T.; et al. Functional Implications of miR-19 in the Migration of Newborn Neurons in the Adult Brain. Neuron 2016, 91, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogilyansky, E.; Rigoutsos, I. The miR-17/92 Cluster: A Comprehensive Update on Its Genomics, Genetics, Functions and Increasingly Important and Numerous Roles in Health and Disease. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Aprea, J.; Nardelli, J.; Engel, H.; Selinger, C.; Mombereau, C.; Lemonnier, T.; Moutkine, I.; Schwendimann, L.; Dori, M.; et al. MicroRNAs Establish Robustness and Adaptability of a Critical Gene Network to Regulate Progenitor Fate Decisions during Cortical Neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, M.; Was, N.; Ziegenhals, T.; Wang, X.; Hafner, M.; Becker, M.; Fischer, U. The miR-26 Family Regulates Neural Differentiation-Associated microRNAs and mRNAs by Directly Targeting REST. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs257535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.-B.; Xu, L.; Lu, Y.; Sun, X.; Yue, S.; Xiong, X.-X.; Giffard, R.G. Astrocyte-Enriched miR-29a Targets PUMA and Reduces Neuronal Vulnerability to Forebrain Ischemia. Glia 2013, 61, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, C.E.L.; Tang, B.L. miR-34a in Neurophysiology and Neuropathology. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhari, A.; Yadav, S. MiR-34 and MiR-200: Regulator of Cell Fate Plasticity and Neural Development. NeuroMol. Med. 2019, 21, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, A.; Gentner, B.; Corno, D.; Di Tomaso, T.; Mestdagh, P.; Speleman, F.; Naldini, L.; Gritti, A. Dynamic Activity of miR-125b and miR-93 during Murine Neural Stem Cell Differentiation in Vitro and in the Subventricular Zone Neurogenic Niche. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Xu, L.; Deng, L.; Xue, L.; Meng, Q.; Wei, F.; Wang, J. RNA N6-Methyladenosine Modification Is Required for miR-98/MYCN Axis-Mediated Inhibition of Neuroblastoma Progression. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xylaki, M.; Paiva, I.; Al-Azzani, M.; Gerhardt, E.; Jain, G.; Islam, M.R.; Vasili, E.; Wassouf, Z.; Schulze-Hentrich, J.M.; Fischer, A.; et al. miR-101a-3p Impairs Synaptic Plasticity and Contributes to Synucleinopathy. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2023, 13, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, J.H.; Horn, S.; Otto, T.; Samans, B.; Heukamp, L.C.; Eilers, U.-C.; Krause, M.; Astrahantseff, K.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Buettner, R.; et al. MYCN Regulates Oncogenic MicroRNAs in Neuroblastoma. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Lu, H.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, J.C. miR-106b Regulates the Proliferation and Differentiation of Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells through Tp53inp1-Tp53-Cdkn1a Axis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristori, E.; Lopez-Ramirez, M.A.; Narayanan, A.; Hill-Teran, G.; Moro, A.; Calvo, C.-F.; Thomas, J.L.; Nicoli, S. A Dicer-miR-107 Interaction Regulates Biogenesis of Specific miRNAs Crucial for Neurogenesis. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Espinal, M.; de Luca, E.; Marzi, M.J.; Beckervordersandforth, R.; Armirotti, A.; Nicassio, F.; Fabel, K.; Kempermann, G.; De Pietri Tonelli, D. Synergic Functions of miRNAs Determine Neuronal Fate of Adult Neural Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, K.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H. MicroRNA-145 Overexpression Inhibits Neuroblastoma Tumorigenesis in Vitro and in Vivo. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhari, A.; Singh, T.; Yadav, S. Expression of miR-145 and Its Target Proteins Are Regulated by miR-29b in Differentiated Neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8978–8990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kloosterman, W.; Fekete, D.M. MicroRNA-183 Family Members Regulate Sensorineural Fates in the Inner Ear. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 3254–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Teng, Z.-Q.; Santistevan, N.J.; Szulwach, K.E.; Guo, W.; Jin, P.; Zhao, X. Epigenetic Regulation of miR-184 by MBD1 Governs Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, S.A.; Hald, Ø.H.; Fuchs, S.; Løkke, C.; Mikkola, I.; Flægstad, T.; Schulte, J.; Einvik, C. MicroRNA-193b-3p Represses Neuroblastoma Cell Growth via Downregulation of Cyclin D1, MCL-1 and MYCN. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18160–18179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beclin, C.; Follert, P.; Stappers, E.; Barral, S.; Coré, N.; de Chevigny, A.; Magnone, V.; Lebrigand, K.; Bissels, U.; Huylebroeck, D.; et al. miR-200 Family Controls Late Steps of Postnatal Forebrain Neurogenesis via Zeb2 Inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepko, T.; Pusch, M.; Müller, T.; Schulte, D.; Ehses, J.; Kiebler, M.; Hasler, J.; Huttner, H.B.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Vandendriessche, C.; et al. Choroid Plexus-derived miR-204 Regulates the Number of Quiescent Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Brain. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.; Fay, J.; Meehan, M.; Bryan, K.; Watters, K.M.; Murphy, D.M.; Stallings, R.L. MiRNA-335 Suppresses Neuroblastoma Cell Invasiveness by Direct Targeting of Multiple Genes from the Non-Canonical TGF-β Signalling Pathway. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Yan, C.; Tan, Z.; Liu, M.; Jiang, Y. Transcriptional Factor FoxM1-Activated microRNA-335-3p Maintains the Self-Renewal of Neural Stem Cells by Inhibiting P53 Signaling Pathway via Fmr1. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarbrick, A.; Woods, S.L.; Shaw, A.; Balakrishnan, A.; Phua, Y.; Nguyen, A.; Chanthery, Y.; Lim, L.; Ashton, L.J.; Judson, R.L.; et al. miR-380-5p Represses P53 to Control Cellular Survival and Is Associated with Poor Outcome in MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jia, J.; Liu, M.; Tan, Z.; Cui, Y. MiR-421 Binds to PINK1 and Enhances Neural Stem Cell Self-Renewal via HDAC3-Dependent FOXO3 Activation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 621187. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Ma, X.; Sung, D.; Li, M.; Kosti, A.; Lin, G.; Chen, Y.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Hsiao, T.-H.; Du, L. microRNA-449a Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Neuroblastoma through Inducing Cell Differentiation and Cell Cycle Arrest. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 538–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bao, J.; Kim, M.; Yuan, S.; Tang, C.; Zheng, H.; Mastick, G.S.; Xu, C.; Yan, W. Two miRNA Clusters, miR-34b/c and miR-449, Are Essential for Normal Brain Development, Motile Ciliogenesis, and Spermatogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2851–E2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, A.; París-Coderch, L.; Jubierre, L.; Martínez, A.; Zhou, X.; Piskareva, O.; Bray, I.; Vidal, I.; Almazán-Moga, A.; Molist, C.; et al. MicroRNA-497 Impairs the Growth of Chemoresistant Neuroblastoma Cells by Targeting Cell Cycle, Survival and Vascular Permeability Genes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9271–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.-J.; Ma, L.; Wang, R.-J.; Huang, S.-Q.; Gao, R.-R.; Liu, L.-H.; Shao, Z.-H.; et al. Novel Cerebellum-Enriched miR-592 May Play a Role in Neural Progenitor Cell Differentiation and Neuronal Maturation through Regulating Lrrc4c and Nfasc in Rat. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 1432–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megiorni, F.; Colaiacovo, M.; Cialfi, S.; McDowell, H.P.; Guffanti, A.; Camero, S.; Felsani, A.; Losty, P.D.; Pizer, B.; Shukla, R.; et al. A Sketch of Known and Novel MYCN-Associated miRNA Networks in Neuroblastoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.Y.; Erriquez, D.; Marshall, G.M.; Tee, A.E.; Polly, P.; Wong, M.; Liu, B.; Bell, J.L.; Zhang, X.D.; Milazzo, G.; et al. Effects of a Novel Long Noncoding RNA, lncUSMycN, on N-Myc Expression and Neuroblastoma Progression. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Ohira, M.; Li, Y.; Niizuma, H.; Oo, M.L.; Zhu, Y.; Ozaki, T.; Isogai, E.; Nakamura, Y.; Koda, T.; et al. High Expression of ncRAN, a Novel Non-Coding RNA Mapped to Chromosome 17q25.1, Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Neuroblastoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, F.-L.; Ma, T.-S.; Zhang, Z.-D.Z.J.-J. LncRNA SNHG1 Contributes to Tumorigenesis and Mechanism by Targeting miR-338-3p to Regulate PLK4 in Human Neuroblastoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8971–8983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.Y.; Tee, A.E.; Milazzo, G.; Hannan, K.M.; Maag, J.; Mondal, S.; Atmadibrata, B.; Bartonicek, N.; Peng, H.; Ho, N.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA lncNB1 Promotes Tumorigenesis by Interacting with Ribosomal Protein RPL35. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloisio, S.; Garbati, P.; Viti, F.; Dante, S.; Barbieri, R.; Arnaldi, G.; Petrelli, A.; Gigoni, A.; Giannoni, P.; Quarto, R.; et al. Generation of a Functional Human Neural Network by NDM29 Overexpression in Neuroblastoma Cancer Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6097–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadie, N.; Saayman, S.; Lenox, A.; Ackley, A.; Clemson, M.; Burdach, J.; Hart, J.; Vogt, P.K.; Morris, K.V. MYCNOS Functions as an Antisense RNA Regulating MYCN. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.M.; Selfe, J.L.; Martins, A.S.; Walters, Z.S.; Shipley, J.M. The Long Non-Coding RNA MYCNOS-01 Regulates MYCN Protein Levels and Affects Growth of MYCN-Amplified Rhabdomyosarcoma and Neuroblastoma Cells. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Meng, F.; Lu, Q. Expression Profile Screening and Bioinformatics Analysis of circRNA, LncRNA, and mRNA in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Drug-Resistant Cells. Turk. J. Haematol. 2020, 37, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.; Danßmann, C.; Klironomos, F.; Winkler, A.; Fallmann, J.; Kruetzfeldt, L.-M.; Szymansky, A.; Naderi, J.; Bernhart, S.H.; Grunewald, L.; et al. Defining the Landscape of Circular RNAs in Neuroblastoma Unveils a Global Suppressive Function of MYCN. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, P.; Roberts, C.W.M. The SWI/SNF Complex in Cancer—Biology, Biomarkers and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Tao, T.; Abraham, B.J.; Durbin, A.D.; Zimmerman, M.W.; Kadoch, C.; Look, A.T. ARID1A Loss in Neuroblastoma Promotes the Adrenergic-to-Mesenchymal Transition by Regulating Enhancer-Mediated Gene Expression. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandapani, P. Super-Enhancers in Cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 199, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Groningen, T.; Koster, J.; Valentijn, L.J.; Zwijnenburg, D.A.; Akogul, N.; Hasselt, N.E.; Broekmans, M.; Haneveld, F.; Nowakowska, N.E.; Bras, J.; et al. Neuroblastoma Is Composed of Two Super-Enhancer-Associated Differentiation States. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, M.W.; Liu, Y.; He, S.; Durbin, A.D.; Abraham, B.J.; Easton, J.; Shao, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. C-MYC Drives a Subset of High-Risk Pediatric Neuroblastomas and Is Activated through Mechanisms Including Enhancer Hijacking and Focal Enhancer Amplification. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmsauer, K.; Valieva, M.E.; Ali, S.; Chamorro González, R.; Schöpflin, R.; Röefzaad, C.; Bei, Y.; Dorado Garcia, H.; Rodriguez-Fos, E.; Puiggròs, M.; et al. Enhancer Hijacking Determines Extrachromosomal Circular MYCN Amplicon Architecture in Neuroblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeid, R.; Lawlor, M.A.; Poon, E.; Reyes, J.M.; Fulciniti, M.; Lopez, M.A.; Scott, T.G.; Nabet, B.; Erb, M.A.; Winter, G.E.; et al. Enhancer Invasion Shapes MYCN Dependent Transcriptional Amplification in Neuroblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tan, T.K.; Durbin, A.D.; Zimmerman, M.W.; Abraham, B.J.; Tan, S.H.; Ngoc, P.C.T.; Weichert-Leahey, N.; Akahane, K.; Lawton, L.N.; et al. ASCL1 Is a MYCN- and LMO1-Dependent Member of the Adrenergic Neuroblastoma Core Regulatory Circuitry. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartlgruber, M.; Sharma, A.K.; Quintero, A.; Dreidax, D.; Jansky, S.; Park, Y.-G.; Kreth, S.; Meder, J.; Doncevic, D.; Saary, P.; et al. Super Enhancers Define Regulatory Subtypes and Cell Identity in Neuroblastoma. Nat. Cancer 2020, 2, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, M.W.; Durbin, A.D.; He, S.; Oppel, F.; Shi, H.; Tao, T.; Li, Z.; Berezovskaya, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Retinoic Acid Rewires the Adrenergic Core Regulatory Circuitry of Childhood Neuroblastoma. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe0834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-H.; Qu, Q.; Qi, T.-T.; Teng, X.-Q.; Zhu, H.-H.; Wang, J.-J.; Lu, Q.; Qu, J. Super-Enhancers: A New Frontier for Epigenetic Modifiers in Cancer Chemoresistance. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotekar, A.; Singh, A.K.; Devaiah, B.N. BRD4 and MYC: Power Couple in Transcription and Disease. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 4820–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdreich-Epstein, A.; Singh, A.R.; Joshi, S.; Vega, F.M.; Guo, P.; Xu, J.; Groshen, S.; Ye, W.; Millard, M.; Campan, M.; et al. Association of High Microvessel Avβ3 and Low PTEN with Poor Outcome in Stage 3 Neuroblastoma: Rationale for Using First in Class Dual PI3K/BRD4 Inhibitor, SF1126. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 52193–52210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Volegova, M.; Nasholm, N.; Das, S.; Kwiatkowski, N.; Abraham, B.J.; Zhang, T.; Gray, N.S.; Gustafson, C.; Krajewska, M.; et al. Synergistic Anti-Tumor Effect of Combining Selective CDK7 and BRD4 Inhibition in Neuroblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 773186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, J.; Liu, P.Y.; Atmadibrata, B.; Bradner, J.E.; Marshall, G.M.; Lock, R.B.; Liu, T. The Bromodomain Inhibitor JQ1 and the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Panobinostat Synergistically Reduce N-Myc Expression and Induce Anticancer Effects. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2534–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, R.; Hou, J.; Peng, W.; Wan, S.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhai, X.; Liang, P.; et al. SMARCE1 Promotes Neuroblastoma Tumorigenesis through Assisting MYCN-Mediated Transcriptional Activation. Oncogene 2022, 41, 4295–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laut, A.K.; Dorneburg, C.; Fürstberger, A.; Barth, T.F.E.; Kestler, H.A.; Debatin, K.-M.; Beltinger, C. CHD5 Inhibits Metastasis of Neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2022, 41, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, C.M.; Nyman, U.; Skotte, J.; Streubel, G.; Turner, S.; O’Connell, D.J.; Rraklli, V.; Dolan, M.J.; Chadderton, N.; Hansen, K.; et al. CHD5 Is Required for Neurogenesis and Has a Dual Role in Facilitating Gene Expression and Polycomb Gene Repression. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstic, A.; Konietzny, A.; Halasz, M.; Cain, P.; Oppermann, U.; Kolch, W.; Duffy, D.J. A Chemo-Genomic Approach Identifies Diverse Epigenetic Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 612518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Tee, A.E.L.; Porro, A.; Smith, S.A.; Dwarte, T.; Liu, P.Y.; Iraci, N.; Sekyere, E.; Haber, M.; Norris, M.D.; et al. Activation of Tissue Transglutaminase Transcription by Histone Deacetylase Inhibition as a Therapeutic Approach for Myc Oncogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18682–18687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, C.; Kozma, S.C.; Tauler, A.; Ambrosio, S. MYCN Concurrence with SAHA-Induced Cell Death in Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Cell Oncol. 2015, 38, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruijter, A.J.M.; Kemp, S.; Kramer, G.; Meinsma, R.J.; Kaufmann, J.O.; Caron, H.N.; van Kuilenburg, A.B.P. The Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor BL1521 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Neuroblastoma Cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaboin, J.; Wild, J.; Hamidi, H.; Khanna, C.; Kim, C.J.; Robey, R.; Bates, S.E.; Thiele, C.J. MS-27-275, an Inhibitor of Histone Deacetylase, Has Marked in Vitro and in Vivo Antitumor Activity against Pediatric Solid Tumors. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6108–6115. [Google Scholar]
- Merck News Item. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20060914014021/http://www.merck.com/newsroom/press_releases/research_and_development/2006_0607.html (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Bartolucci, D.; Montemurro, L.; Raieli, S.; Lampis, S.; Pession, A.; Hrelia, P.; Tonelli, R. MYCN Impact on High-Risk Neuroblastoma: From Diagnosis and Prognosis to Targeted Treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettig, I.; Koeneke, E.; Trippel, F.; Mueller, W.C.; Burhenne, J.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Fabian, J.; Schober, A.; Fernekorn, U.; von Deimling, A.; et al. Selective Inhibition of HDAC8 Decreases Neuroblastoma Growth in Vitro and in Vivo and Enhances Retinoic Acid-Mediated Differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, S.V.; Togher, K.L.; O’Leary, E.; Solger, F.; Sullivan, A.M.; O’Keeffe, G.W. Romidepsin Induces Caspase-Dependent Cell Death in Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 653, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, J.; Lodrini, M.; Oehme, I.; Schier, M.C.; Thole, T.M.; Hielscher, T.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Opitz, L.; Capper, D.; von Deimling, A.; et al. GRHL1 Acts as Tumor Suppressor in Neuroblastoma and Is Negatively Regulated by MYCN and HDAC3. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2604–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownes, L.V.; Williams, A.P.; Marayati, R.; Stafman, L.L.; Markert, H.; Quinn, C.H.; Wadhwani, N.; Aye, J.M.; Stewart, J.E.; Yoon, K.J.; et al. EZH2 Inhibition Decreases Neuroblastoma Proliferation and in Vivo Tumor Growth. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Fosbrook, C.; Gibson, J.; Underwood, T.J.; Gray, J.C.; Walters, Z.S. Review: Targeting EZH2 in Neuroblastoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 119, 102600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellini, P.; Marrocco, B.; Borovika, D.; Polletta, L.; Carnevale, I.; Saladini, S.; Stazi, G.; Zwergel, C.; Trapencieris, P.; Ferretti, E.; et al. Pyrazole-Based Inhibitors of Enhancer of Zeste Homologue 2 Induce Apoptosis and Autophagy in Cancer Cells. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, N.; Béguelin, W.; Giulino-Roth, L. Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2) Inhibitors. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 1574–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seier, J.A.; Reinhardt, J.; Saraf, K.; Ng, S.S.; Layer, J.P.; Corvino, D.; Althoff, K.; Giordano, F.A.; Schramm, A.; Fischer, M.; et al. Druggable Epigenetic Suppression of Interferon-Induced Chemokine Expression Linked to MYCN Amplification in Neuroblastoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Salwen, H.R.; Chlenski, A.; Godley, L.A.; Raj, J.U.; Yang, Q. Histone Lysine Methyltransferase EHMT2 Is Involved in Proliferation, Apoptosis, Cell Invasion and DNA Methylation of Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Anticancer Drugs 2013, 24, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, J.A.; Conery, A.R.; Bryant, B.M.; Sandy, P.; Balasubramanian, S.; Mele, D.A.; Bergeron, L.; Sims, R.J. Targeting MYC Dependence in Cancer by Inhibiting BET Bromodomains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16669–16674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puissant, A.; Frumm, S.M.; Alexe, G.; Bassil, C.F.; Qi, J.; Chanthery, Y.H.; Nekritz, E.A.; Zeid, R.; Gustafson, W.C.; Greninger, P.; et al. Targeting MYCN in Neuroblastoma by BET Bromodomain Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Rellinger, E.J.; Kim, K.W.; Craig, B.T.; Romain, C.V.; Qiao, J.; Chung, D.H. Bet Inhibition Blocks Tumor Progression and Promotes Differentiation in Neuroblastoma. Surgery 2015, 158, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henssen, A.; Althoff, K.; Odersky, A.; Beckers, A.; Koche, R.; Speleman, F.; Schäfers, S.; Bell, E.; Nortmeyer, M.; Westermann, F.; et al. Targeting MYCN-Driven Transcription By BET-Bromodomain Inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2470–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piha-Paul, S.A.; Hann, C.L.; French, C.A.; Cousin, S.; Braña, I.; Cassier, P.A.; Moreno, V.; de Bono, J.S.; Harward, S.D.; Ferron-Brady, G.; et al. Phase 1 Study of Molibresib (GSK525762), a Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain Protein Inhibitor, in NUT Carcinoma and Other Solid Tumors. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2019, 4, pkz093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shang, L.; Wei, W.; Shen, Y.; Gu, Q.; Xie, X.; Dong, W.; Lin, Y.; Yue, Y.; et al. Decitabine and All-Trans Retinoic Acid Synergistically Exhibit Cytotoxicity against Elderly AML Patients via miR-34a/MYCN Axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penter, L.; Maier, B.; Frede, U.; Hackner, B.; Carell, T.; Hagemeier, C.; Truss, M. A Rapid Screening System Evaluates Novel Inhibitors of DNA Methylation and Suggests F-Box Proteins as Potential Therapeutic Targets for High-Risk Neuroblastoma. Targ. Oncol. 2015, 10, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Foley, N.; Bryan, K.; Watters, K.M.; Bray, I.; Murphy, D.M.; Buckley, P.G.; Stallings, R.L. MicroRNA Mediates DNA De-Methylation Events Triggered By Retinoic Acid During Neuroblastoma Cell Differentiation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7874–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iniguez, A.B.; Alexe, G.; Wang, E.J.; Roti, G.; Patel, S.; Chen, L.; Kitara, S.; Conway, A.; Robichaud, A.L.; Stolte, B.; et al. Resistance to Epigenetic-Targeted Therapy Engenders Tumor Cell Vulnerabilities Associated with Enhancer Remodeling. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 922–938.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čančer, M.; Drews, L.F.; Bengtsson, J.; Bolin, S.; Rosén, G.; Westermark, B.; Nelander, S.; Forsberg-Nilsson, K.; Uhrbom, L.; Weishaupt, H.; et al. BET and Aurora Kinase A Inhibitors Synergize against MYCN-Positive Human Glioblastoma Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R.E.; Lahti, J.M.; Adamson, P.C.; Zhu, K.; Finkelstein, D.; Ingle, A.M.; Reid, J.M.; Krailo, M.; Neuberg, D.; Blaney, S.M.; et al. Phase I Study of Decitabine with Doxorubicin and Cyclophosphamide in Children with Neuroblastoma and Other Solid Tumors: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lim, S.L.; Tao, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X.; et al. PROTAC Bromodomain Inhibitor ARV-825 Displays Anti-Tumor Activity in Neuroblastoma by Repressing Expression of MYCN or c-Myc. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 574525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, K.; de Ruijter, A.J.M.; van Bree, C.; Caron, H.N.; van Kuilenburg, A.B.P. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor BL1521 Induces a G1-Phase Arrest in Neuroblastoma Cells through Altered Expression of Cell Cycle Proteins. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpinelli, P.; Granata, F.; Augusti-Tocco, G.; Rossi, M.; Bartolucci, S. Antiproliferative Effects and DNA Hypomethylation by 5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidine in Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Anti-Cancer Drugs 1993, 4, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate-Eya, L.T.; Gierman, H.J.; Ebus, M.E.; Koster, J.; Caron, H.N.; Versteeg, R.; Dolman, M.E.M.; Molenaar, J.J. Enhancer of Zeste Homologue 2 Plays an Important Role in Neuroblastoma Cell Survival Independent of Its Histone Methyltransferase Activity. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyce, A.; Ganji, G.; Smitheman, K.N.; Chung, C.-W.; Korenchuk, S.; Bai, Y.; Barbash, O.; Le, B.; Craggs, P.D.; McCabe, M.T.; et al. BET Inhibition Silences Expression of MYCN and BCL2 and Induces Cytotoxicity in Neuroblastoma Tumor Models. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GlaxoSmithKline. A Phase I/II Open-Label, Dose Escalation Study to Investigate the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Clinical Activity of GSK525762 in Subjects with NUT Midline Carcinoma (NMC) and Other Cancers; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Tian, Y.; Chlenski, A.; Salwen, H.R.; Lu, Z.; Raj, J.U.; Yang, Q. Valproic Acid Shows Potent Antitumor Effect with Alteration of DNA Methylation in Neuroblastoma. Anticancer Drugs 2012, 23, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Epigenetic Mechanism | Role in Normal NC Development | Aberration in MNA NB | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-200b | NC induction/specification | Tumor suppressor; downregulated | [28,32,42] |
| miR-17~92 | NC induction/specification | Oncogenic; upregulated | [28,29,42] |
| miR-20a | NC induction/specification | Oncogenic; upregulated | [28,29,42] |
| miR-204 | NC induction/specification, NCC EMT/migration | Tumor suppressor; downregulated | [28,42] |
| miR-34a | NCC EMT/migration | Tumor suppressor; downregulated | [28,29,31,32,42] |
| let-7 | NCC EMT/migration | Tumor suppressor; downregulated | [28,29,42] |
| Histone modifications of the MYCN gene | Shift from active H3K4me3 to repressive H3K27me3 mark for MYCN downregulation during neuronal differentiation/maturation | The active H3K4me3 mark is kept; MYCN expression is sustained | [34] |
| EZH2 | Controls the expression of genes crucial for neuronal differentiation/maturation via histone methylation, H3K27me3 is associated with gene repression | Recruitment of PRC2 by MYCN for EZH2-mediated epigenetic silencing | [35,37] |
| Gene | Role | Methylation Status in MNA NB | Expression in MNA NB | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCB1, CACNA1G, CD44, DUSP23, PRDM2, RBP1, CHD5, NTRK1, KRT19, PRPH, CNR1, QPCT, ASIC2, RGS5 | Involved in NB-relevant aberrant methylation | Hypermethylation | Decreased | [48] |
| CASP8 | Cell apoptosis | Hypermethylation | Decreased | [46,47,49,58] |
| CASR | Calcium-sensing receptor | Hypermethylation | Decreased | [59] |
| CD44 | Glycoprotein involved in cell–cell interactions, adhesion, and migration | Hypermethylation | Silenced | [54,60] |
| CXCR4, GAL, LRRN1, ODC1, TWIST1, WHSC1 DDX43, PRAME, TEX14, TMEM108, NEK2, NPY | Involved in biology of aggressive NB | Hypomethylation | Increased | [48] |
| DNAJC15, NTRK1, PYCARD | Candidate biomarker genes | Hypermethylation | Decreased | [61] |
| DUSP2, TP73, JAK2, MGMT, HPN, RB1, TDGF1 | Relevant roles in cancer biology | Hypermethylation | Increased/Decreased | [62] |
| MIR34B, MIR34C MIR124-2 | MiR-34b-3p, miR-34b-5p, miR-34c-5p, and miR-124-2-3p are tumor suppressors | Hypermethylation | Decreased | [31,63,64] |
| NR4A3 | Critical gene for neuronal development | Hypomethylation | Decreased | [52] |
| NXPH1, SOX2-OT, DLX5, TFAP2D, CAVIN3, VAX2, TERT, HHEX, KRT19, RNF207, MIRLET7BHG, CHRNE, DLX6-AS1, TMCO3 | 14 highly methylated genes in MNA NB | Hypermethylation | [50] | |
| PCDHB family | Cell–cell neural connection | Methylation | Unknown | [48] |
| RASSF family | Tumor suppressor proteins | Hypermethylation | Decreased/absent | [47] |
| TFAP2B | Transcription factor, expression associated with low-risk NB | Methylation | Decreased | [65] |
| ZAR1 | Ovary-specific maternal factor | Hypermethylation | Increased | [66] |
| ZNF206 | Transcription factor regulating embryonic stem cell gene expression and differentiation | Hypomethylation | Unknown | [67] |
| 291 genes | Candidate differentially methylated regions unique to NB subgroup associated with MNA | [57] |
| miRNA | Expression in MNA NB | Associated Function | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| let-7 | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Controls sympathetic neurogenesis; promotes neuronal differentiation | [29,99,100] |
| miR-7 | Upregulated | Oncogenic. Involved in cortical development and embryonic stem cell differentiation | [101,102] |
| miR-9 | Upregulated | Oncogenic. Regulates neurogenesis (neuronal migration and differentiation) | [88,103] |
| miR-15a-5p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Antiangiogenic in the brain | [90,104] |
| miR-15b-5p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor | [90] |
| miR-16-5p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Antiangiogenic in the brain | [90,104] |
| miR-17-5p | Upregulated | Oncogenic. Master regulator of neurogenesis in both developmental and adult brains | [29,105] |
| miR-19a-3p | Upregulated | Oncogenic. Enriched in NPCs and downregulated during neuronal development in the adult hippocampus | [29,106] |
| miR-19b-3p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Enriched in NPCs and downregulated during neuronal development in the adult hippocampus | [106,107] |
| miR-20a-5p | Upregulated | Oncogenic. Inhibits cyclin D1 level, involved in differentiation and proliferation of cortical progenitors | [29,108] |
| miR-26a | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Regulates neural differentiation | [92,109] |
| miR-29 (miR-29a-3p, miR-29b-3p, miR-29c) | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Inhibits apoptotic neural death by targeting the proapoptotic protein BCL2 | [49,101,110] |
| miR-34a | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Regulates neural stem/progenitor cell differentiation | [31,64,111] |
| miR-34c-5p | Upregulated/Downregulated | Oncogenic/Tumor suppressor. Regulates neural stem/progenitor cell differentiation | [29,31,64,112] |
| miR-93-5p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Maintenance/proliferation/differentiation of NSCs; downregulated in mature neurons | [29,113] |
| miR-98-5p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor | [114] |
| miR-101-3p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Involved in neuronal plasticity | [91,115] |
| miR-106a-5p | Upregulated | Oncogenic | [116] |
| miR-106b-5 | Upregulated | Oncogenic. Involved in NSC proliferation and differentiation | [96,117] |
| miR-107 | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Involved in differentiation of neuronal cells; interacts with dicer to control the biogenesis of miR-9 | [32,118] |
| miR-124-2-3p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Involved in neuronal identity; regulates adult neurogenesis | [63,119] |
| miR-145-5p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Crucial for fate determination of neurons | [120,121] |
| miR-183 | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Regulates sensory neurons | [74,122] |
| miR-184 | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Involved in neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation | [85,123] |
| miR-193b-3p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor | [124] |
| miR-200b-3p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Controls postnatal forebrain neurogenesis | [32,125] |
| miR-202 | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor | [33] |
| miR-204 | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Involved in adult somatic stem cell maintenance | [97,126] |
| miR-335-3p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Implicated in self-renewal of NSCs via inhibition of the p53 signaling pathway | [127,128] |
| miR-380-5p | Upregulated | Oncogenic | [129] |
| miR-421 | Upregulated | Oncogenic. Involved in NSC self-renewal via the PINK1/HDAC3/FOXO3 axis | [89,130] |
| miR-449 | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Essential for brain development; a key regulator of mitotic spindle orientation during neurogenesis | [131,132] |
| miR-488-5p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor | [29] |
| miR-497 | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor | [133] |
| miR-542-3p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Involved in neural development and astrogliogenesis differentiation | [29,134] |
| miR-542-5p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor. Involved in neural development and astrogliogenesis differentiation | [29,134] |
| miR-628-3p | Downregulated | Tumor suppressor | [135] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Epp, S.; Chuah, S.M.; Halasz, M. Epigenetic Dysregulation in MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317085
Epp S, Chuah SM, Halasz M. Epigenetic Dysregulation in MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):17085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317085
Chicago/Turabian StyleEpp, Soraya, Shin Mei Chuah, and Melinda Halasz. 2023. "Epigenetic Dysregulation in MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 17085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317085
APA StyleEpp, S., Chuah, S. M., & Halasz, M. (2023). Epigenetic Dysregulation in MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 17085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317085





