Biological Oxidation of Manganese Mediated by the Fungus Neoroussoella solani MnF107
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Identification of the Mn(II)-Oxidizing Fungus
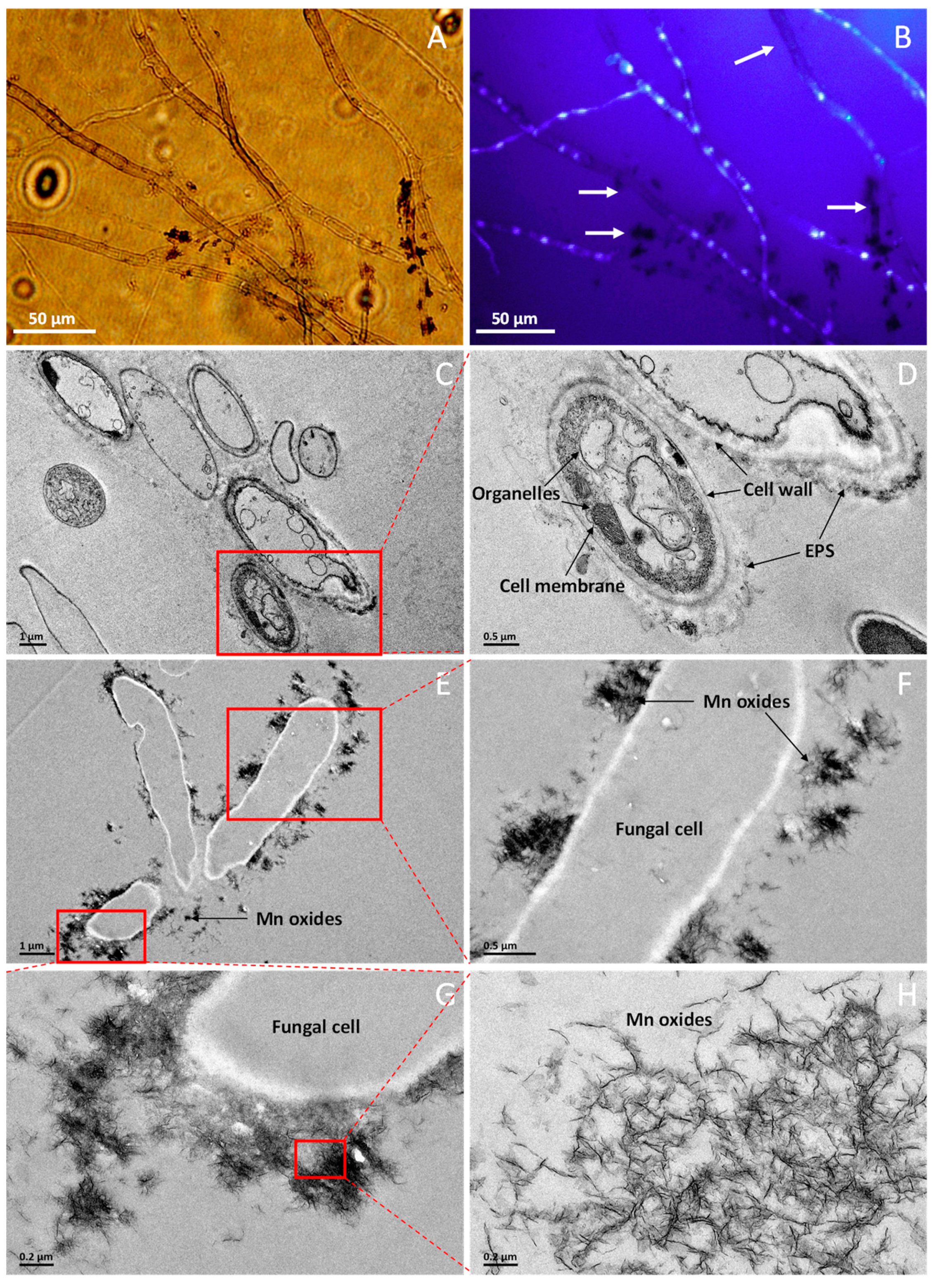
2.2. SEM, EDS, and TEM Characterizations of the Manganese Oxides
2.3. Composition and Structure Characterizations of Fungal Mn Oxides
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Identification of Manganese-Oxidizing Fungus
4.2. Light and Fluorescence Microscopy
4.3. Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
4.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.6. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) and Selected Area Diffraction (SAED)
4.7. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santelli, C.M.; Webb, S.M.; Dohnalkova, A.C.; Hansel, C.M. Diversity of Mn oxides produced by Mn (II)-oxidizing fungi. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 2762–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Sasaki, K.; Tanaka, K.; Ohnuki, T.; Hirajima, T. Structures factors of biogenic birnessite produced by fungus Paraconiothyrium sp. WL-2 strain affecting sorption of Co2+. Chem. Geol. 2012, 310, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.E. Manganese oxide minerals: Crystal structures and economic and environmental significance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, P.M.; Maynard, J.B.; Spiker, E.C.; Force, E.R. Isotope evidence for organic matter oxidation by manganese reduction in the formation of stratiform manganese carbonate ore. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2679–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunda, W.G.; Kieber, D.J. Oxidation of humic substances by manganese oxides yields low-molecular-weight organic substrates. Nature 1994, 367, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remucal, C.K.; Ginder-Vogel, M. A critical review of the reactivity of manganese oxides with organic contaminants. Environ. Sci. Proc. Impacts 2014, 26, 1247–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P. Review on manganese dioxide for catalytic oxidation of airborne formaldehyde. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Derry, L.A.; Lion, L.W. Pb scavenging from a freshwater lake by Mn oxides in heterogeneous surface coating materials. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, N.; Tani, Y.; Sakata, M.; Iwahori, K. Microbial manganese oxide formation and interaction with toxic metal ions. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2007, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, B.M.; Bargar, J.R.; Clement, B.G.; Dick, G.J.; Murray, K.J.; Parker, D.; Verity, R.; Webb, S.M. Biogenic manganese oxides: Properties and mechanisms of formation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 2004, 32, 287–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frierdich, A.J.; Catalano, J.G. Distribution and speciation of trace elements in iron and manganese oxide cave deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 91, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparatos, D. Sequestration of heavy metals from soil with Fe–Mn concretions and nodules. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lee, S.W.; Catalano, J.G.; Lezama-Pacheco, J.S.; Bargar, J.R.; Tebo, B.M.; Giammar, D.E. Adsorption of Uranium (VI) to manganese oxides: X-ray adsorption spectroscopy and surface complexation modeling. Envoron. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, O.W.; Rivera, N.A.; Gardner, T.G.; Andrews, M.Y.; Santelli, C.M.; Polizzotto, M.L. Morphology, structure, and metal binding mechanisms of biogenic manganese oxides in a superfund site treatment system. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2017, 19, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Santos, F.; Butler, K.; Herndon, E. A critical review on the multiple roles of manganese in stabilizing and destabilizing soil organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12136–12152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lin, H.; Ma, Q.; Bai, Y.; Qu, J. Manganese oxides in Phragmites rhizosphere accelerates ammonia oxidation in constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, S.; Jilani, G.; Mihoub, A.; Jamal, A.; Ahmad, I.; Chaudhary, A.N.; Saeed, M.F.; Alam, T. Bacterial redox cycling of manganese in calcareous soil enhances the nutrients bioavailability to wheat. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; He, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chai, H.; Yang, Y.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Wu, H. New insight into ammonium oxidation processes and mechanisms mediated by manganese oxide in constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; Feng, X.; Tan, W.; Liu, F. Oxidation behavior and kinetics of sulfide by synthesized manganese oxide mineral. J. Soil Sediment. 2011, 11, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, J.V.; Schulz-Vogt, H.N.; Dellwig, O.; Pollehne, F.; Schott, T.; Meeske, C.; Beier, S.; Jürgens, K. Biological manganese-dependent sulfide oxidation impacts elemental gradients in redox-stratified systems: Indications from the Black Sea water column. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, B.M.; Johnson, H.A.; McCarthy, J.K.; Templeton, A.S. Geomicrobiology of manganese (II) oxidation. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geszvain, K.; Butterfield, C.; Davis, R.E.; Madison, A.S.; Lee, S.W.; Parker, D.L.; Soldatva, A.; Spiro, T.G.; Luther, G.W.; Tebo, B.M. The molecular biogeochemistry of manganese (II) oxidation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nealson, K.H.; Tebo, B.M.; Rosson, R.A. Occurrence and mechanisms of microbial oxidation of manganese. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1988, 33, 279–318. [Google Scholar]
- Learman, D.R.; Voelker, B.M.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, A.I.; Hansel, C.M. Formation of manganese oxides by bacterially generated superoxide. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, G.J.; Podell, S.; Johnson, H.A.; Rivera-Espinoza, Y.; Bernier-Latmani, R.; McCarthy, J.K.; Torpey, J.W.; Clement, B.G.; Gaasterland, T.; Tebo, B.M. Genomic insights into Mn(II) oxidation by the marine alphaproteobacterium Aurantimonas sp. strain SI85-9A1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2646–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Gao, A.; Chen, H. Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of cultivable manganese bacteria in sediments from the Arctic Ocean. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 6364–6370. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharova, Y.R.; Parfenova, V.V.; Granina, L.Z.; Kravchenko, O.S.; Zemskaya, T.I. Distribution of iron- and manganese-oxidizing bacteria in the bottom sediments of Lake Baikal. Inland Water Biol. 2010, 3, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Wiens, M.; Divekar, M.; Grebenjuk, V.A.; Schroder, H.C.; Batel, R.; Muller, W.E.G. Isolation and characterization of a Mn(II)-oxidizing Bacillus strain from the demosponge Suberites domuncula. Mar. Drugs 2010, 9, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, D.N.; Pinto, A.; Anantharaman, K.; Ruberg, S.A.; Karmer, E.; Raskin, L.; Dick, G.J. Diverse manganese (II)-oxidizing bacteria are prevalent in drinking water systems. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 9, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Fu, C. Manganese-oxidizing microbes and biogenic manganese oxides: Characterization, Mn(II) oxidation mechanism and environmental relevance. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonin, M.I.; Illman, W.I.; Hartgerink, T. Oxidation of manganous salts of manganese by soil fungi. Can. J. Microbiol. 1972, 18, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wariishi, H.; Valli, K.; Gold, M.H. Manganese(II) oxidation by manganese peroxidase from the basidiomyces Phanerochaete chrysosporium kinetic mechanism and role of chelators. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 23688–23695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Torre, M.A.; Gomez-Alarcon, G. Manganese and iron oxidation by fungi isolated from building stone. Microbiol. Ecol. 1994, 27, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, I.A.; Huber, D.M.; Guest, C.A.; Schulze, D.G. Fungal manganese oxidation in a reduced soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, N.; Tani, Y.; Iwahori, K.; Soma, M. Enzymatic formation of manganese oxides by an Acremonium-like hyphomycete fungus, strain KR21-2. FEMS Microbiol. 2004, 47, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, N.; Maruo, K.; Tani, Y.; Tsuno, H.; Seyama, H.; Soma, M.; Iwahori, K. Production of biogenic manganese oxides by anamorphic ascomyces fungi isolated from stream-bed pebbles. Geomicrobiol. J. 2006, 23, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, K.; Itoh, Y.; Ogino, T.; Kurosawa, K.; Sasaki, K. Phylogenetic analysis of manganese-oxidizing fungi isolated from manganese-rich aquatic environments in Hokkaido, Japan. Limnology 2006, 7, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyani, V.; Murase, J.; Ishibashi, E.; Asakawa, S.; Kimura, M. Phylogenetic position of Mn2+-oxidizing bacteria and fungi isolated from Mn nodules in rice field subsoils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2009, 45, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratovsky, I.; Gurr, S.J.; Hayward, M.A. The structure of manganese oxide formed by fungus Acremonium sp. strain KR21-2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 3291–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiner, C.A.; Purvine, S.O.; Zink, E.; Wu, S.; Paša-Tolić, L.; Chaput, D.L.; Santelli, C.M.; Hansel, C.M. Mechanisms of manganese(II) oxidation by filamentous ascomycete fungi vary with secretome composition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 610497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Dong, B.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Pei, X. An efficient manganese-oxidizing fungus Cladosporium halotolerans strain XM01: Mn(II) oxidization and Cd adsorption behavior. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Matsuda, M.; Hirajima, T.; Takano, K.; Konno, H. Immobilization of Mn (II) ions by Mn-oxidizing fungus Paraconiothyrium sp.-like strain at neutral pHs. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 2457–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, N.; Tani, Y.; Maruo, K.; Tuno, H. Manganese (IV) oxide production by Acremonium sp. KR21-1 and extracellular Mn(II) oxides activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6467–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ogasawara, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mizuno, N. Molybdenum-doped α-MnO2 as an efficient reusable heterogeneous catalyst for aerobic sulfide oxygenation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Castro, V.D.; Polzonetti, G. XPS study of MnO oxidation. J. Electron. Spectrosc. 1989, 48, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Banerjee, D. Interpretation of XPS Mn(2p) spectra of Mn oxyhydroxides and constrains on the mechanism of MnO2 precipitation. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perz, J.; Jeffries, T.W. Roles of manganese and organic acid chelators in regulating lignin degradation and biosynthesis of peroxidase by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, A.; Bovio, E.; Ranieri, L.; Varese, G.C.; Prigione, V. News from the sea: A new genus and seven new species in the Pleosporalean families Roussoellaceae and Thyridariaceae. Diversity 2020, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wang, B.; Hyde, K.D.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Raja, H.A.; Tanaka, K.; Abdel-Wahab, M.A.; Abdel-Aziz, F.A.; Doilom, M.; Phookamsak, R.; et al. Freshwater Dothideomycetes. Fungal Divers. 2020, 105, 319–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, E.A.; Felestrino, É.B.; Leão, V.A.; Guerra-Sá, R. Manganese (II) removal from aqueous solutions by Cladosporium halotolerans and Hypocrea jecorina. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 25, e00431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dong, H.; Hansel, C.M. Coupled Mn(II) and Cr(III) oxidation mediated by ascomycete fungi. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16236–16245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, D.; Garen, R.E.; Ghiorse, W.C. Formation of Metallogenium-like structures by a manganese-oxidizing fungus. Arch. Microbiol. 1989, 151, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zeiner, C.A.; Santelli, C.M.; Hansel, C.M. Fungal oxidative dissolution of the Mn(II)-bearing mineral rhodochrosite and the role of metabolites in manganese oxide formation. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, S.; Dove, P.M. An Overview of biomineralization processes and the problem of the vital effect. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 54, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, N.; Brunner, E.; Estroff, L.; Marin, F. The role of organic matrices in biomineralization. Discov. Mater. 2021, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Pastén, P.A.; Gaillard, J.F.; Stair, P.C. Nanocrystalline todorokite-like manganese oxide produced by bacterial catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14284–14285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, J.; Ko, S.O. Characterization of the biogenic manganese oxides produced by Pseudomonas putida strain MnB1. Environ. Eng. Res. 2010, 15, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeon, S.; Lanson, B.; Miyata, N.; Tani, Y.; Manceau, A. Structure of nanocrystalline phyllomanganstes produced by freshwater fungi. Am. Mineral. 2010, 95, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkov, V.; Ren, Y.; Saratovsky, I.; Pasten, P.; Gurr, S.J.; Hayward, M.A.; Poeppelmeier, K.R.; Gaillard, J.F. Atomic-scale structure of biogenic materials by total X-ray diffraction: A study of bacterial and fungal MnOx. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Villalobos, M.; Toner, B.; Bargar, J.; Sposito, G. Characterization of the manganese oxide produced by Pseudomonas putida strain MnB1. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 2649–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.M.; Tebo, B.M.; Bargar, J.R. Structural characterization of biogenic Mn oxides produced in seawater by the marine Bacillus sp. strain SG-1. Am. Mineral. 2005, 90, 1342–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratovsky, I.; Wightman, P.G.; Pasten, P.A.; Gaillard, J.F.; Poeppelmeier, K.R. Manganese oxides: Parallels between abiotic and biotic structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11188–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Yu, L.; Sun, M.; Ye, F.; Zhong, Y.; Cheng, G.; Wang, H.; Mai, Y. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of novel 3D starfish-like δ-MnO2 nanosheets on carbon fiber paper for high-performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14910–14916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toupin, M.; Brousse, T.; Bélanger, D. Charge storage mechanism of MnO2 electrod used in aqueous electrochemical capacitor. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3184–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, J.M.; Hochella, M.F., Jr.; Knocke, W.R.; Cromer, T.F. Use of XPS to identify the oxidation state of Mn in solid surfaces of filtration media oxide samples from drinking water treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5881–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilton, E.S.; Post, J.E.; Heaney, P.J.; Ling, F.T.; Kerisit, S.N. XPS determination of Mn oxidation states in Mn (hydr) oxides. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 366, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, J.E.; Luther, G.W., III; Nealson, K.H. Chemical and biological reduction of Mn(III)-pyrophosphate complexes-potential importance of dissolved Mn(III) as an environmental oxidant. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 885–894. [Google Scholar]
- Klewicki, J.K.; Morgan, J.J. Kinetic behavior of Mn(III) complexes of pyrophosphate, EDTA, and citrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2916–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, H.; Wei, S. Identification of a manganese-oxidizing fungus isolated from marine sedimentand its Mn(II) oxidation characteristics. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2015, 21, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, S.; Wang, W.; Xiao, F. Biological Oxidation of Manganese Mediated by the Fungus Neoroussoella solani MnF107. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317093
Wei S, Wang W, Xiao F. Biological Oxidation of Manganese Mediated by the Fungus Neoroussoella solani MnF107. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):17093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317093
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Shiping, Wenxiu Wang, and Feirong Xiao. 2023. "Biological Oxidation of Manganese Mediated by the Fungus Neoroussoella solani MnF107" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 17093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317093
APA StyleWei, S., Wang, W., & Xiao, F. (2023). Biological Oxidation of Manganese Mediated by the Fungus Neoroussoella solani MnF107. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 17093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242317093





