Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Punica granatum L. Polyphenols in Neurological Conditions
Abstract
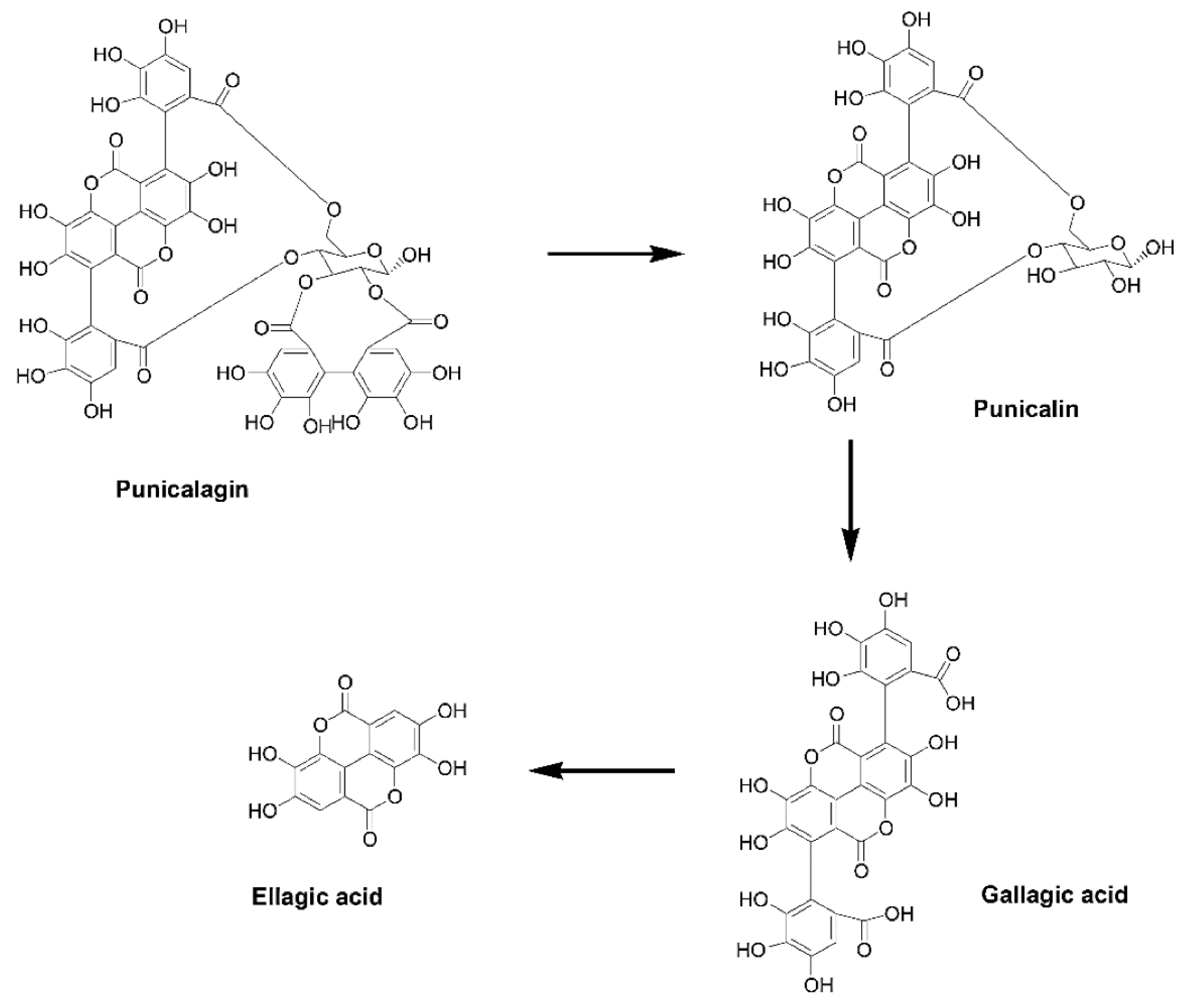
1. Pomegranate and Ellagitannins
2. Central Nervous System (CNS) as a Therapeutic Target for Pomegranate Polyphenols
2.1. Effect of ETs on Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression
2.2. Antinociceptive Action of Ellagitannins
2.3. Effects of ETs on Learning and Memory
3. Protective Mechanisms of Pomegranate Polyphenols in NDD
3.1. Amyloid Beta Deposition
3.2. Oxidative Stress
3.3. Inflammation
3.4. Neurogenesis
3.5. Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity
3.6. Neurotransmitter Interactions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Di Meo, F.; Valentino, A.; Petillo, O.; Peluso, G.; Filosa, S.; Crispi, S. Bioactive Polyphenols and Neuromodulation: Molecular Mechanisms in Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Guo, M.-S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, J.-M.; Tang, Y.; Ai, W.; Zhu, F.-D.; Law, B.Y.-K.; Chen, Q.; et al. Dietary Plant Polyphenols as the Potential Drugs in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Evidence, Advances, and Opportunities. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5288698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.; Gamage, E.; Travica, N.; Berk, M.; Jacka, F.N.; O’Neil, A.; Puri, B.K.; Carvalho, A.F.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Walder, K.; et al. Polyphenols as Adjunctive Treatments in Psychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders: Efficacy, Mechanisms of Action, and Factors Influencing Inter-Individual Response. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cory, H.; Passarelli, S.; Szeto, J.; Tamez, M.; Mattei, J. The Role of Polyphenols in Human Health and Food Systems: A Mini-Review. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Holvoet, S.; Mercenier, A. Dietary Polyphenols in the Prevention and Treatment of Allergic Diseases. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Duo, L.; Wang, J.; Gegen, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Tu, Y. A Unique Understanding of Traditional Medicine of Pomegranate, Punica Granatum L. And Its Current Research Status. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 271, 113877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgary, S.; Javanmard, S.; Zarfeshany, A. Potent Health Effects of Pomegranate. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014, 3, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdá, B.; Llorach, R.; Cerón, J.J.; Espín, J.C.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. Evaluation of the bioavailability and metabolism in the rat of punicalagin, an antioxidant polyphenol from pomegranate juice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2003, 42, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzulker, R.; Glazer, I.; Bar-Ilan, I.; Holland, D.; Aviram, M.; Amir, R. Antioxidant Activity, Polyphenol Content, and Related Compounds in Different Fruit Juices and Homogenates Prepared from 29 Different Pomegranate Accessions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9559–9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tian, L. Diverse phytochemicals and bioactivities in the ancient fruit and modern functional food pomegranate (Punica granatum). Molecules 2017, 22, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquadro, S.; Civra, A.; Cagliero, C.; Marengo, A.; Rittà, M.; Francese, R.; Sanna, C.; Bertea, C.; Sgorbini, B.; Lembo, D.; et al. Punica granatum Leaf Ethanolic Extract and Ellagic Acid as Inhibitors of Zika Virus Infection. Planta Med. 2020, 86, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.F.; Mei, Y.W.; Zhang, S.L.; Tao, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.H. Effect of Corilagin on anti-inflammation in HSV-1 encephalitis and HSV-1 infected microglias. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 635, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; García-Villalba, R.; González-Sarrías, A.; Selma, M.V.; Espín, J.C. Ellagic acid metabolism by human gut microbiota: Consistent observation of three urolithin phenotypes in intervention trials, independent of food source, age, and health status. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6535–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yisimayili, Z.; Abdulla, R.; Tian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Aisa, H.A.; Huang, C. A comprehensive study of pomegranate flowers polyphenols and metabolites in rat biological samples by high-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1604, 460472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espín, J.C.; Larrosa, M.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Tomás-Barberán, F. Biological Significance of Urolithins, the Gut Microbial Ellagic Acid-Derived Metabolites: The Evidence so Far. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2013, 2013, 270418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benchagra, L.; Berrougui, H.; Islam, M.O.; Ramchoun, M.; Boulbaroud, S.; Hajjaji, A.; Fulop, T.; Ferretti, G.; Khalil, A. Antioxidant effect of moroccan pomegranate (Punica granatum L. sefri variety) extracts rich in punicalagin against the oxidative stress process. Foods 2021, 10, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braidy, N.; Selvaraju, S.; Essa, M.M.; Vaishnav, R.; Al-Adawi, S.; Al-Asmi, A.; Al-Senawi, H.; Abd Alrahman Alobaidy, A.; Lakhtakia, R.; Guillemin, G.J. Neuroprotective effects of a variety of pomegranate juice extracts against MPTP-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress in human primary neurons. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdá, B.; Espín, J.C.; Parra, S.; Martínez, P.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. The potent in vitro antioxidant ellagitannins from pomegranate juice are metabolised into bioavailable but poor antioxidant hydroxy-6H-dibenzopyran-6-one derivatives by the colonic microflora of healthy humans. Eur. J. Nutr. 2004, 43, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, I.; Yayla, M.; Demirbağ, Ç.; Binnetoğlu, D. Pomegranate Peel Extract Reduces Cisplatin-Induced Toxicity and Oxidative Stress in Primary Neuron Culture. Clin. Exp. Health Sci. 2021, 11, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighenti, V.; Iseppi, R.; Pinzi, L.; Mincuzzi, A.; Ippolito, A.; Messi, P.; Sanzani, S.M.; Rastelli, G.; Pellati, F. Antifungal Activity and DNA Topoisomerase Inhibition of Hydrolysable Tannins from Punica granatum L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, I.; Bhardwaj, V.; Hariharan, S.; Kumar, M.N.V.R. Analytical Methods for Assay of Ellagic Acid and Its Solubility Studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarsini, K.I.; Khopde, S.M.; Kumar, S.S.; Mohan, H. Free Radical Studies of Ellagic Acid, a Natural Phenolic Antioxidant. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Ghosh, R.; Chen, X. Isolation of Ellagic Acid from Pomegranate Peel Extract by Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography Using Graphene Oxide Grafted Cotton Fiber Adsorbent. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, A.; Baghal, E.; Ghobadi, H.; Hashemidanesh, N.; Khodaparast, F.; Seydi, E. Mitochondrial, Lysosomal and DNA Damages Induced by Acrylamide Attenuate by Ellagic Acid in Human Lymphocyte. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.C.; Rosalen, P.L.; Lazarini, J.G.; Massarioli, A.P.; da Silva, C.F.; Nani, B.D.; Franchin, M.; de Alencar, S.M. Comprehensive Characterization of Bioactive Phenols from New Brazilian Superfruits by LC-ESI-QTOF-MS, and Their ROS and RNS Scavenging Effects and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Food Chem. 2019, 281, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-Z.; Fu, Z.-M.; Deng, G.; Guo, R.; Chen, D.-F. Free Radical Scavenging Potency of Ellagic Acid and Its Derivatives in Multiple H+/E- Processes. Phytochemistry 2020, 180, 112517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loren, D.J.; Seeram, N.P.; Schulman, R.N.; Holtzman, D.M. Maternal Dietary Supplementation with Pomegranate Juice Is Neuroprotective in an Animal Model of Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, C.; Raj, V.; Arya, J.; Balakrishnan, S. Evidence for the involvement of the monoaminergic system, but not the opioid system in the antidepressant-like activity of ellagic acid in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 682, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, C.; Raj, V.; Arya, J.; Balakrishnan, S. Involvement of the GABAergic system in the anxiolytic-like effect of the flavonoid ellagic acid in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. 2013, 710, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Wen, A.; Ding, Y. Ellagic acid protects mice against sleep deprivation-induced memory impairment and anxiety by inhibiting TLR4 and activating Nrf2. Aging 2020, 12, 10457–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasehi, M.; Mohammadi-Mahdiabadi-Hasani, M.H.; Zarrindast, M.R.; Zarrabian, S. Punicalagin effect on total sleep deprivation memory deficit in male Wistar rats. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 20, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveen, S.; Siddalingaswamy, M.; Singsit, D.; Khanum, F. Anti-depressive effect of polyphenols and omega-3 fatty acid from pomegranate peel and flax seed in mice exposed to chronic mild stress. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 67, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, W.; You, B.; Tang, W.; Gan, T.; Feng, C.; Li, C.; Yang, R. Serum Metabonomic Study on the Antidepressant-like Effects of Ellagic Acid in a Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Mouse Model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9546–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksandrova, S.; Tancheva, L.; Dragomanova, S.; Alova, L.; Stefanova, M.; Georgieva, A.; Simeonova, L.; Pavlova, E.; Kalfin, R. Preventive effect of ellagic acid on cognitive disorders in two mouse models of oxidative stress (influenza infection and scopolamine-induced dementia). In Proceedings of the 14th International Congress on Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins, Vienna, Austria, 3–7 August 2015; pp. 1607–1696. [Google Scholar]
- Tancheva, L.; Popatanasov, A.; Alova, L.; Dragomanova, S.; Miteva, S.; Stefanova, M.; Tsvetanova, E.; Kalfin, R. New mechanisms in preventive effect of ellagic acid on cognition in mice with Alzheimer’s disease type dementia. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 50, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Moneim, A.E. Evaluating the potential role of pomegranate peel in aluminum-induced oxidative stress and histopathological alterations in brain of female rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 150, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, D.; Chhillar, R. Antidepressant-like activity of ellagic acid in unstressed and acute immobilization-induced stressed mice. Pharm. Rep 2012, 64, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Anaya, N.; Azpilcueta-Morales, G.; Estrada-Camarena, E.; Ramírez Ortega, D.; Pérez de la Cruz, V.; González-Trujano, M.E.; López-Rubalcava, C. Pomegranate and Its Components, Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid, Promote Antidepressant, Antioxidant, and Free Radical-Scavenging Activity in Ovariectomized Rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 836681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Sustaita, B.; Estrada-Camarena, E.; González-Trujano, M.E.; López-Rubalcava, C. Estrogen receptors-β and serotonin mediate the antidepressant-like effect of an aqueous extract of pomegranate in ovariectomized rats. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 142, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Sustaita, B.; López-Rubalcava, C.; González-Trujano, M.E.; García-Viguera, C.; Estrada-Camarena, E. Aqueous Extract of Pomegranate Alone or in Combination with Citalopram Produces Antidepressant-Like Effects in an Animal Model of Menopause: Participation of Estrogen Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouachrif, A.; Khalki, H.; Chaib, S.; Mountassir, M.; Aboufatima, R.; Farouk, L.; Benharraf, A.; Chait, A. Comparative study of the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of two varieties of Punica granatum. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.T.; Naghizadeh, B.; Ghorbanzadeh, B.; Farbood, Y. Central and Peripheral Antinociceptive Effects of Ellagic Acid in Different Animal Models of Pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 707, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haranishi, Y.; Hara, K.; Terada, T. Analgesic potency of intrathecally administered punicalagin in rat neuropathic and inflammatory pain models. J. Nat. Med. 2022, 76, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Pareek, A.; Bhardwaj, Y.R.; Singh, N. Attenuating effect of standardized fruit extract of Punica granatum L. in rat model of tibial and sural nerve transection induced neuropathic pain. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropacki, S.A.; Patel, S.M.; Hartman, R.E. Pomegranate Supplementation Protects against Memory Dysfunction after Heart Surgery: A Pilot Study. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.X.; Li, X.; Deng, S.Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Deng, X.; Han, B.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.Z.; et al. Urolithin A ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by targeting aryl hydrocarbon receptor. EBioMedicine 2021, 64, 103227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braidy, N.; Essa, M.M.; Poljak, A.; Selvaraju, S.; Al-Adawi, S.; Manivasagm, T.; Thenmozhi, A.J.; Ooi, L.; Sachdev, P.; Guillemin, G.J. Consumption of Pomegranates Improves Synaptic Function in a Transgenic Mice Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 64589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, R.E.; Shah, A.; Fagan, A.M.; Schwetye, K.E.; Parsadanian, M.; Schulman, R.N.; Finn, M.B.; Holtzman, D.M. Pomegranate juice decreases amyloid load and improves behavior in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 24, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morzelle, M.C.; Salgado, J.M.; Telles, M.; Mourelle, D.; Bachiega, P.; Buck, H.S.; Viel, T.A. Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate Peel Extract after Chronic Infusion with Amyloid-β Peptide in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookheimer, S.Y.; Renner, B.A.; Ekstrom, A.; Li, Z.; Henning, S.M.; Brown, J.A.; Jones, M.; Moody, T.; Small, G.W. Pomegranate juice augments memory and fMRI activity in middle-aged and older adults with mild memory complaints. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, E.F.; Hou, Y.; Palikaras, K.; Adriaanse, B.A.; Kerr, J.S.; Yang, B.; Lautrup, S.; Hasan-Olive, M.M.; Caponio, D.; Dan, X.; et al. Mitophagy Inhibits Amyloid-β and Tau Pathology and Reverses Cognitive Deficits in Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Huang, J.; Xu, B.; Ou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Ye, X.; Kong, X.; Long, D.; Sun, X.; et al. Urolithin a Attenuates Memory Impairment and Neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 Mice. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ares-Santos, S.; Granado, N.; Moratalla, R. The Role of Dopamine Receptors in the Neurotoxicity of Methamphetamine. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elfotuh, K.; Hamdan, A.M.E.; Abbas, A.N.; Alahmre, A.T.S.; Elewa, M.A.F.; Masoud, R.A.E.; Ali, A.A.; Othman, M.; Kamal, M.M.; Hassan, F.A.M.; et al. Evaluating the neuroprotective activities of vinpocetine, punicalagin, niacin and vitamin E against behavioural and motor disabilities of manganese-induced Parkinson’s disease in Sprague Dawley rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, H.; Tomiyama, M. What Mechanisms Are Responsible for the Reuptake of Levodopa-Derived Dopamine in Parkinsonian Striatum? Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancheva, L.P.; Lazarova, M.I.; Alexandrova, A.V.; Dragomanova, S.T.; Nicoletti, F.; Tzvetanova, E.R.; Hodzhev, Y.K.; Kalfin, R.E.; Miteva, S.A.; Mazzon, E.; et al. Neuroprotective mechanisms of three natural antioxidants on a rat model of parkinson’s disease: A comparative study. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, B.R.; Greenamyre, J.T. CHAPTER 1 Etiology and Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. In Oxidative Stress and Redox Signalling in Parkinson’s Disease; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, M.; Jourdes, M.; Kurpik, M.; Szulc, M.; Szaefer, H.; Chmielarz, P.; Kreiner, G.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Mikołajczak, P.Ł.; Teissedre, P.L.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of pomegranate juice against parkinson’s disease and presence of ellagitannins-derived metabolite—Urolithin A—In the brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, S.; Du, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, G.; Liu, R. Ellagic Acid Promotes Aβ42 Fibrillization and Inhibits Aβ42-Induced Neurotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batandier, C.; Poyot, T.; Marissal-Avry, N.; Couturier, K.; Canini, F.; Roussel, A.M.; Hininger-Favier, I. Acute emotional stress and high fat/high fructose diet modulate brain oxidative damage through NrF2 and uric acid in rats. Nutr. Res. 2020, 79, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Yan, C.; Frost, B.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Zeng, M.; Gao, H.; Kang, Y.; Liu, J. Pomegranate extract decreases oxidative stress and alleviates mitochondrial impairment by activating AMPK-Nrf2 in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kumar, M.; Bansal, N. Ellagic acid prevents 3-nitropropionic acid induced symptoms of Huntington’s disease. Naunyn Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busto, R.; Serna, J.; Perianes-Cachero, A.; Quintana-Portillo, R.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Canfrán-Duque, A.; Paino, C.L.; Lerma, M.; Casado, M.E.; Martín-Hidalgo, A.; et al. Ellagic acid protects from myelin-associated sphingolipid loss in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaidikar, L.; Byna, B.; Thakur, S.R. Neuroprotective effect of punicalagin against cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced oxidative brain injury in rats. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, 2869–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouayed, J.; Bohn, T. Exogenous antioxidants--Double-edged swords in cellular redox state: Health beneficial effects at physiologic doses versus deleterious effects at high doses. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2010, 3, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, K.; Wu, X.; Xin, C.; Zhou, M.; Lei, J.; Chen, J. Punicalagin alleviates brain injury and inflammatory responses, and regulates HO-1/Nrf-2/ARE signaling in rats after experimental intracerebral haemorrhage. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, F.; Zhou, B. Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of ellagic acid in liver and brain of rats treated by D-galactose. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Han, W. Punicalagin exerts beneficial functions in 6-hydroxydopamine-treated SH-SY5Y cells by attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammatory responses. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 5905–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkinezos, I.G.; Moraes, C.T. Reactive Oxygen Species and Mitochondrial Diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 12, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi, M.; Mohammadi Vadoud, S.A.; Haratian, A.; Talebi, M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Samarghandian, S. The Interplay between Oxidative Stress and Autophagy: Focus on the Development of Neurological Diseases. Behav. Brain Funct. 2022, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortalezas, S.; Tavares, L.; Pimpão, R.; Tyagi, M.; Pontes, V.; Alves, P.; McDougall, G.; Stewart, D.; Ferreira, R.; Santos, C. Antioxidant Properties and Neuroprotective Capacity of Strawberry Tree Fruit (Arbutus Unedo). Nutrients 2010, 2, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Devaraj, S.; Jialal, I. VITAMIN E, OXIDATIVE STRESS, and INFLAMMATION. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2005, 25, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K.; Packer, L. Antioxidant and Redox Regulation of Gene Transcription. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghadir, A.H.; Gabr, S.A.; Anwer, S.; Li, H. Associations between Vitamin E, Oxidative Stress Markers, Total Homocysteine Levels, and Physical Activity or Cognitive Capacity in Older Adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Targeting Oxidative Stress in Disease: Promise and Limitations of Antioxidant Therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelinek, M.; Jurajda, M.; Duris, K. Oxidative Stress in the Brain: Basic Concepts and Treatment Strategies in Stroke. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthaiyah, B.; Essa, M.M.; Chauhan, V.; Chauhan, A. Protective Effects of Walnut Extract against Amyloid Beta Peptide-Induced Cell Death and Oxidative Stress in PC12 Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 2096–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, E.A.; Vodhanel, J.; Abushaban, A. The Modulatory Effects of Ellagic Acid and Vitamin E Succinate on TCDD-Induced Oxidative Stress in Different Brain Regions of Rats after Subchronic Exposure. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2004, 18, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toney, A.M.; Albusharif, M.; Works, D.; Polenz, L.; Schlange, S.; Chaidez, V.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Chung, S. Differential Effects of Whole Red Raspberry Polyphenols and Their Gut Metabolite Urolithin A on Neuroinflammation in BV-2 Microglia. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, S.; Lati, Y.; Aviram, M.; Fuhrman, B. Pomegranate juice polyphenols induce a phenotypic switch in macrophage polarization favoring a M2 anti-inflammatory state. BioFactors 2015, 41, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardah, M.T.; Eid, N.; Kitada, T.; Haque, M.E. Ellagic acid prevents α-synuclein aggregation and protects sh-sy5y cells from aggregated α-synuclein-induced toxicity via suppression of apoptosis and activation of autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdar, B.S.; Erkmen, T.; Koçtürk, S. Combinations of Polyphenols Disaggregate Aβ1-42 by Passing through in Vitro Blood Brain Barrier Developed by Endothelium, Astrocyte, and Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2021, 81, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajide, O.A.; Kumar, A.; Velagapudi, R.; Okorji, U.P.; Fiebich, B.L. Punicalagin inhibits neuroinflammation in LPS-activated rat primary microglia. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yuan, C.; Wang, G.; Luo, J.; Ma, H.; Xu, L.; Mu, Y.; Li, Y.; Seeram, N.P.; Huang, X.; et al. Urolithins Attenuate LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation in BV2Microglia via MAPK, Akt, and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanović, I.; Šavikin, K.; Đedović, N.; Živković, J.; Saksida, T.; Momčilović, M.; Koprivica, I.; Vujičić, M.; Stanisavljević, S.; Miljković, Đ.; et al. Pomegranate peel extract ameliorates autoimmunity in animal models of multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velagapudi, R.; Baco, G.; Khela, S.; Okorji, U.; Olajide, O. Pomegranate inhibits neuroinflammation and amyloidogenesis in IL-1β-stimulated SK-N-SH cells. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.R.; Sui, H.C.; Zhu, B.T. Ellagic acid, a plant phenolic compound, activates cyclooxygenase-mediated prostaglandin production. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Sheng, S.; Li, J.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, F. Ellagic Acid Protects Dopamine Neurons via Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglia. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2963540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velagapudi, R.; Lepiarz, I.; El-Bakoush, A.; Katola, F.O.; Bhatia, H.; Fiebich, B.L.; Olajide, O.A. Induction of Autophagy and Activation of SIRT-1 Deacetylation Mechanisms Mediate Neuroprotection by the Pomegranate Metabolite Urolithin A in BV2 Microglia and Differentiated 3D Human Neural Progenitor Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1801237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toney, A.M.; Fox, D.; Chaidez, V.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Chung, S. Immunomodulatory Role of Urolithin A on Metabolic Diseases. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Chen, F.; Lei, J.; Li, Q.; Zhou, B. Activation of the miR-34a-Mediated SIRT1/mTOR Signaling Pathway by Urolithin A Attenuates d-Galactose-Induced Brain Aging in Mice. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Q.Y.; Cai, L.; Jing, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, D.X.; Chen, S.W.; Tian, H.L. Urolithin A alleviates blood-brain barrier disruption and attenuates neuronal apoptosis following traumatic brain injury in mice. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2007–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhuo, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, D.; Yu, S.; Lou, H. Urolithin A promotes mitophagy and suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells and MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Neuropharmacology 2022, 207, 108963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venusova, E.; Kolesarova, A.; Horky, P.; Slama, P. Physiological and immune functions of punicalagin. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms and Functional Implications of Adult Neurogenesis. Cell 2008, 132, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabopda, T.K.; Ngoupayo, J.; Liu, J.W.; Mitaine-Offer, A.-C.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Lacaille-Dubois, M.-A.; Luu, B. Induction of Neuronal Differentiation in Neurosphere Stem Cells by Ellagic Acid Derivatives. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbood, Y.; Sarkaki, A.; Dianat, M.; Khodadadi, A.; Haddad, M.K.; Mashhadizadeh, S. Ellagic Acid Prevents Cognitive and Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation Deficits and Brain Inflammation in Rat with Traumatic Brain Injury. Life Sci. 2015, 124, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carecho, R.; Carregosa, D.; Dos Santos, C.N. Low Molecular Weight (poly)Phenol Metabolites Across the Blood-Brain Barrier: The Underexplored Journey. Brain Plast 2021, 6, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teel, R.W. Distribution and metabolism of ellagic acid in the mouse following intraperitoneal administration. Cancer Lett. 1987, 34, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobowska, A.; Granica, S.; Filipek, A.; Melzig, M.F.; Moeslinger, T.; Zentek, J.; Kruk, A.; Piwowarski, J.P. Comparative studies of urolithins and their phase II metabolites on macrophage and neutrophil functions. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1957–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoi, K.; Saka, N.; Kaji, K.; Nozawa, R.; Kinae, N. Metabolic Fate of Luteolin and Its Functional Activity at Focal Site. BioFactors 2000, 12, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoi, K.; Nakayama, T. Glucuronidase Deconjugation in Inflammation. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 400, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Gálvez, M.A.; Giménez-Bastida, J.A.; González-Sarrías, A.; Espín, J.C. Tissue deconjugation of urolithin A glucuronide to free urolithin A in systemic inflammation. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3135–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Bodduluri, S.R.; Baby, B.V.; Hegde, B.; Kotla, N.G.; Hiwale, A.A.; Saiyed, T.; Patel, P.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; et al. Enhancement of the gut barrier integrity by a microbial metabolite through the Nrf2 pathway. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggia, R.; Turrini, F.; Roggeri, A.; Olivero, G.; Cisani, F.; Bonfiglio, T.; Summa, M.; Grilli, M.; Caviglioli, G.; Alfei, S.; et al. Neuroinflammation in aged brain: Impact of the oral administration of ellagic acid microdispersion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.z.; Zhu, G.f.; Zheng, C.q.; Li, J.j.; Sheng, S.; Li, D.d.; Wang, G.q.; Zhang, F. Ellagic acid protects dopamine neurons from rotenone-induced neurotoxicity via activation of Nrf2 signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9446–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Feng, J. Alzheimers Disease: Interactions between Cholinergic Functions and β- Amyloid. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2004, 1, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.A.; Sridhar, G.R.; Das, U.N. Elevated Butyrylcholinesterase and Acetylcholinesterase May Predict the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer’s Disease. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 69, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobini, E. Cholinesterase Inhibitors Stabilize Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2000, 25, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, M.N.; Farlow, M.R.; Relkin, N.; Beach, T.G. Do Cholinergic Therapies Have Disease-Modifying Effects in Alzheimer’s Disease? Alzheimer’s Dement. 2006, 2, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaSilva, N.A.; Nahar, P.P.; Ma, H.; Eid, A.; Wei, Z.; Meschwitz, S.; Zawia, N.H.; Slitt, A.L.; Seeram, N.P. Pomegranate ellagitannin-gut microbial-derived metabolites, urolithins, inhibit neuroinflammation in vitro. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Taweel, G.M.; Al-Mutary, M.G. Pomegranate juice reverses AlCl3-Induced neurotoxicity and improves learning and memory in female mice. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K. Cholinesterase Inhibitors as Alzheimer’s Therapeutics (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwajgier, D. Anticholinesterase Activity of Phenolic Acids and Their Derivatives. Z. Fur Naturforschung. C J. Biosci. 2013, 68, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, F.; Grosso, C.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B. Ellagic Acid and Derivatives FromCochlospermum AngolensisWelw. Extracts: HPLC-DAD-ESI/MSnProfiling, Quantification AndIn VitroAnti-Depressant, Anti-Cholinesterase and Anti-Oxidant Activities. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.M.; Jang, H.J.; Kang, M.G.; Song, S.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Noh, J.I.; Park, J.E.; Park, D.; Yee, S.T.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase-B inhibitory activities by ellagic acid derivatives isolated from Castanopsis cuspidata var. sieboldii. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzbahari, M.; Burgaz, E.V.; Ercetin, T.; Fallah, A.; Foroumadi, A.; Firoozpour, L.; Sahin, M.F.; Gazi, M.; Gulcan, H.O. Design, Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Urolithin Derivatives as Cholinesterase Inhibitor Agents. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2018, 15, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, Y.; Lee, R.; Henning, S.M.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Qing, T.; Hsu, M.; Nguyen, A.; Prabha, S.; et al. Pomegranate Metabolites Impact Tryptophan Metabolism in Humans and Mice. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, nzaa165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Cui, C. A red pomegranate fruit extract-based formula ameliorates anxiety/depression-like behaviors via enhancing serotonin (5-HT) synthesis in C57BL/6 male mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Taweel, G.M.; Al-Mutary, M.G. Pomegranate juice moderates anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in AlCl3-treated male mice. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 68, 126842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneberger, C.; Jüttner, R.; Rothe, T.; Grantyn, R. Postsynaptic Action of BDNF on GABAergic Synaptic Transmission in the Superficial Layers of the Mouse Superior Colliculus. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 88, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Condition | Experimental Model | Type of Extract |
|---|---|---|
| AD | APPsw/Tg2576 | pomegranate extract |
| APP/PS mice | ellagic acid | |
| scopolamine induced ICR mice | ellagic acid | |
| HT22 mice hippocampal neurons | punicalagin | |
| BBB model triculture-astrocyte, neuron, endothelial | punicalagin, ellagic acid | |
| PD | C57BL/6 mice rotenone induced | ellagic acid |
| Sprague-Dawley rat MnCl2-induced | punicalagin | |
| α-syn expressing SHSY5Y cells | ellagic acid | |
| MPTP-treated primary neurons | pomegranate juice extract | |
| 6-hydroxydopamine challenged SH-SY5Y cells | punicalagin | |
| MPTP-treated mice | urolithin | |
| Huntington’s disease | adult Wistar rats 3-nitropropionic acid treated | ellagic acid |
| MS | Lewis rats EAE | ellagic acid |
| rat C6 astroglia, human HOG oligodendrocytes | ellagic acid, urolithin A or B | |
| LPS-stimulated SIM-A9 microglia | urolithin A | |
| BV2 murine microglia | urolithin A | |
| C57BL/6 mice EAE | urolithin A | |
| D-galactose induced ageing | ICR mice; Sprague-Dawley rat | urolithin A; ellagic acid |
| ischemia/reperfusion | mouse neuroblastoma N2a cells | urolithin A |
| Wistar rats by middle cerebral artery occlusion | punicalagin | |
| Oxidative stress | PC12 cell induced by H2O2 | punicalagin |
| BV2 murine microglia; human SH-SY5Y neurons; induced by H2O2 | urolithins | |
| Wistar rates female induced by Al | pomegranate peel extract | |
| SWR/J mice female induced by Al | pomegranate juice | |
| rat primary neuron culture induced by cisplatin | pomegranate peel extract | |
| Wistar rats induced by Cu-nanoparticle exposure | pomegranate juice | |
| Sprague-Dawley rat microglia primary culture LPS challenged | punicalagin | |
| C57BL/6 mice hippocampal slice culture LPS challenged | punicalagin | |
| BV2 murine microglia LPS challenged | urolithins | |
| Wistar rats LPS challenged | ellagic acid | |
| SK-N-SH cells IL1b stimualted | freeze-dried pomegranate | |
| Depression/anxiety | Sleep deprivation C57BL/6J mice; Wistar rat | ellagic acid; punicalagin |
| chronic mild stress in C57BL/6 mice | pomegranate peel extract; ellagic acid | |
| Induced menopause in female Wistar rats | ellagic acid; punicalagin; pomegranate extract | |
| nociception | adult Wistar rats- radiant heat exposure | ellagic acid; pomegranate peel extract |
| Swiss mice-acetic acid stimulation | ellagic acid | |
| albino mice-formalin or acetic acid | pomegranate peel extract | |
| Wistar rats sciatic pain | punicalagin | |
| HSV-1 encephalitis | BV-2 microglia; Balb/c mice | corilagin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aleksandrova, S.; Alexova, R.; Dragomanova, S.; Kalfin, R.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C.; Mangano, K.; Tancheva, L. Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Punica granatum L. Polyphenols in Neurological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24031856
Aleksandrova S, Alexova R, Dragomanova S, Kalfin R, Nicoletti F, Fagone P, Petralia MC, Mangano K, Tancheva L. Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Punica granatum L. Polyphenols in Neurological Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24031856
Chicago/Turabian StyleAleksandrova, Simona, Ralitza Alexova, Stela Dragomanova, Reni Kalfin, Ferdinando Nicoletti, Paolo Fagone, Maria Cristina Petralia, Katia Mangano, and Lyubka Tancheva. 2023. "Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Punica granatum L. Polyphenols in Neurological Conditions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24031856
APA StyleAleksandrova, S., Alexova, R., Dragomanova, S., Kalfin, R., Nicoletti, F., Fagone, P., Petralia, M. C., Mangano, K., & Tancheva, L. (2023). Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Punica granatum L. Polyphenols in Neurological Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24031856











